Submitted:
02 May 2025
Posted:
06 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Sleep Deprivation
2.3. Subcellular Fractioning
2.4. Immunoprecipitation
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. F-actin and G-Actin Fractionation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
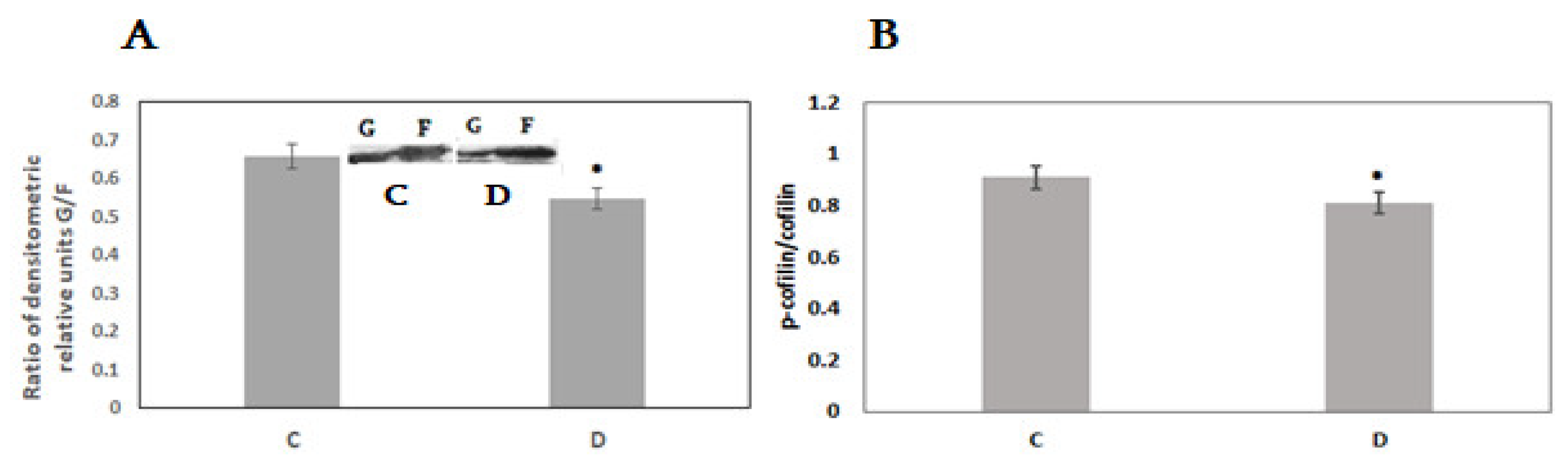
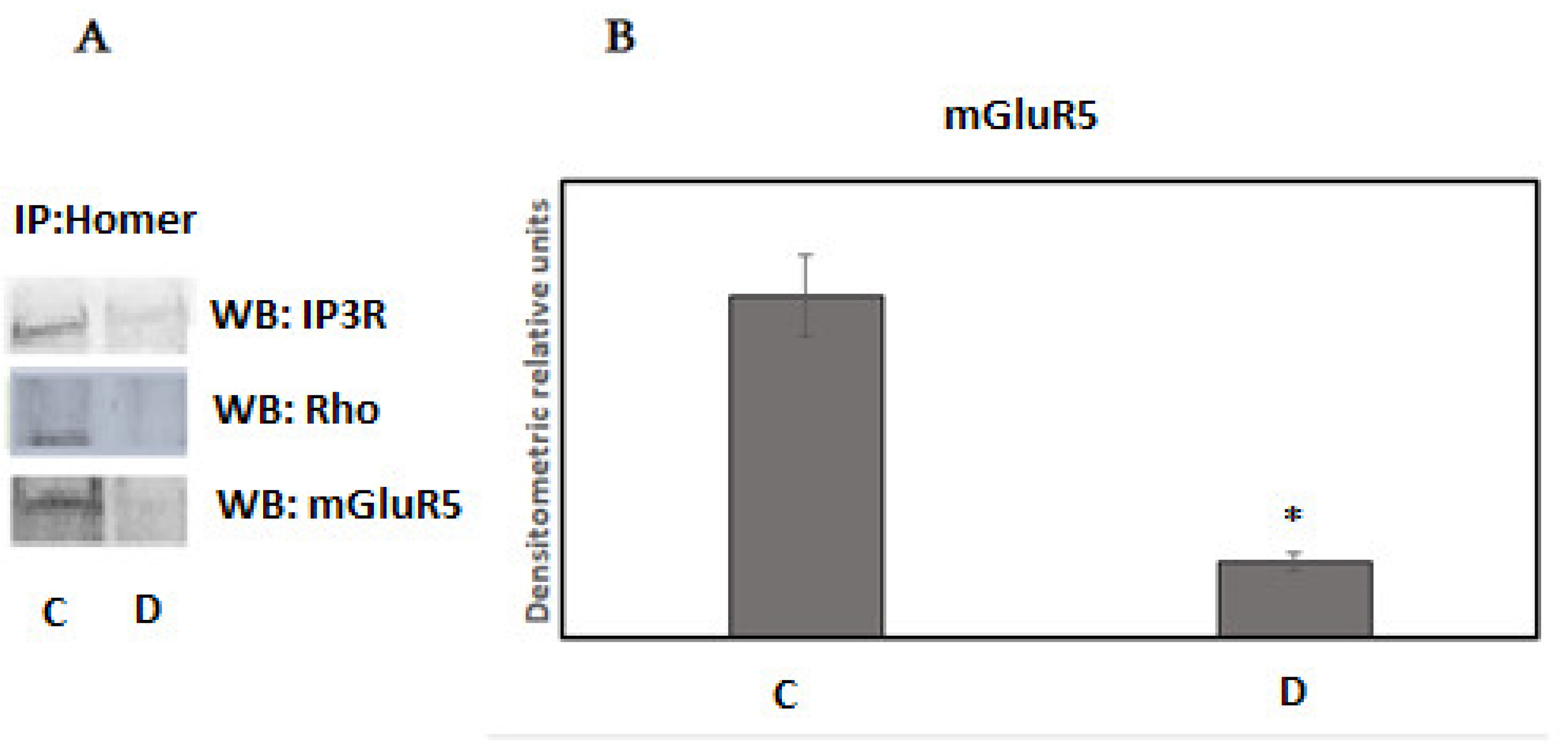
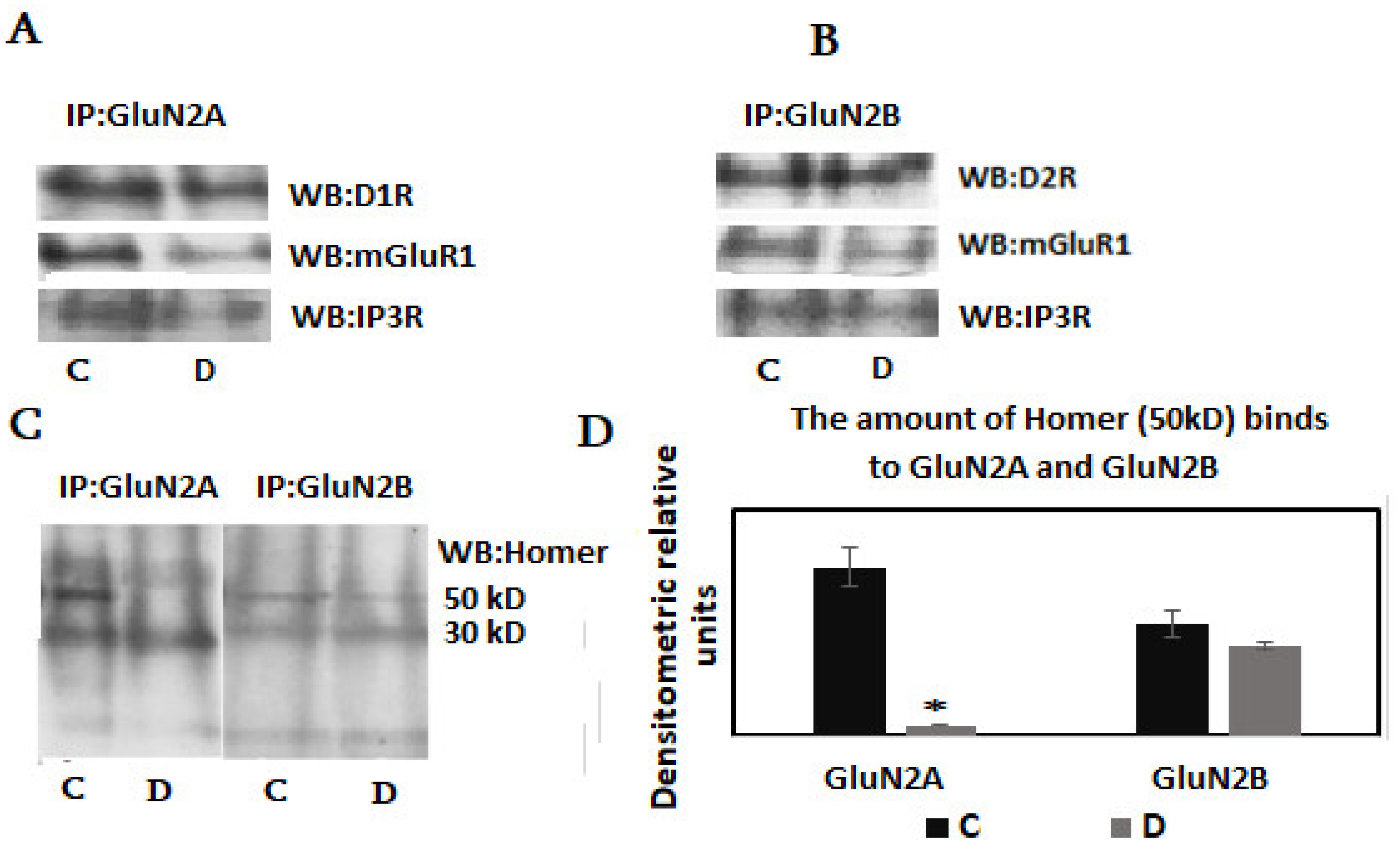
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SD | Sleep Deprivation |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-D-Aspartate |
| AMPA | α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| mGluR1/5 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 |
| IP3R | Inositol trisphosphate receptor |
| DA | Dopamine |
| D1R | Dopamine1 receptor |
| D2R | Dopamine2 receptor |
| PSD | Postsynaptic density |
| GRIP | Glutamate receptor-interacting protein |
| LTD | Long-term depression |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| GluN2A | GluN2A subunit of NMDA glutamate receptor |
| GluN2B | GluN2B subunit of NMDA glutamate receptor |
| GluN1(NR1) | GluN1 subunit of NMDA glutamate receptor |
References
- Shepherd, J.D. Memory, plasticity and sleep - A role for calcium permeable AMPA receptors? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanté, F.; Toledo-Salas, J.-C.; Ondrejcak, T.; Rowan, M.J.; Ulrich, D. Removal of Synaptic Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors during Sleep. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3953–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngomba, R.T.; Lüttjohann, A.; Dexter, A.; Ray, S.; van Luijtelaar, G. The Metabotropic Glutamate 5 Receptor in Sleep and Wakefulness: Focus on the Cortico-Thalamo-Cortical Oscillations. Cells 2023, 12, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holter, K.M.; Pierce, B.E.; Gould, R.W. Metabotropic glutamate receptor function and regulation of sleep-wake cycles. 2023; 93–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.M.; Mitchell, T.R.; Galloway, M.P.; Prevost, K.E.; Fang, J.; Moore, G.J.; Uhde, T.W. Region-specific alteration in brain glutamate: Possible relationship to risk-taking behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 99, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S.C.; Sousek, A.; Hefti, K.; Saberi-Moghadam, S.; Buck, A.; Ametamey, S.M.; Scheidegger, M.; Franken, P.; Henning, A.; Seifritz, E.; et al. Cerebral mGluR5 availability contributes to elevated sleep need and behavioral adjustment after sleep deprivation. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, W. Multiple Dopamine Functions at Different Time Courses. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 259–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, J.I.; Yang, K.; Levine, A.T.; Tsetsenis, T.; Jenson, D.; Cao, F.; Garcia, I.; Arenkiel, B.R.; Zhou, F.-M.; De Biasi, M.; et al. Dopamine Regulates Aversive Contextual Learning and Associated In Vivo Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eban-Rothschild, A.; Rothschild, G.; Giardino, W.J.; Jones, J.R.; de Lecea, L. VTA dopaminergic neurons regulate ethologically relevant sleep–wake behaviors. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1356–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, E.; Miyasaka, A.; Sakurai, K.; Cherasse, Y.; Li, Y.; Sakurai, T. Rapid eye movement sleep is initiated by basolateral amygdala dopamine signaling in mice. Science 2022, 375, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Effects of sleep deprivation on typical neurotransmitters. E3S Web of Conferences 2024, 553, 05041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Feng, S.; Freda, S.N.; Kumari, P.; Dumrongprechachan, V.; Kozorovitskiy, Y. Dopamine pathways mediating affective state transitions after sleep loss. Neuron 2024, 112, 141–154.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethus, I.; Tse, D.; Morris, R.G.M. Dopamine and Memory: Modulation of the Persistence of Memory for Novel Hippocampal NMDA Receptor-Dependent Paired Associates. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Duszkiewicz, A.J.; Sonneborn, A.; Spooner, P.A.; Yamasaki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Smith, C.C.; Fernández, G.; Deisseroth, K.; Greene, R.W.; et al. Locus coeruleus and dopaminergic consolidation of everyday memory. Nature 2016, 537, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidolin, D.; Tortorella, C.; Marcoli, M.; Cervetto, C.; De Caro, R.; Maura, G.; Agnati, L.F. Modulation of Neuron and Astrocyte Dopamine Receptors via Receptor–Receptor Interactions. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diering, G.H.; Huganir, R.L. The AMPA Receptor Code of Synaptic Plasticity. Neuron 2018, 100, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakeman, P.R.; Lanahan, A.A.; O'Brien, R.; Roche, K.; Barnes, C.A.; Huganir, R.L.; Worley, P.F. Homer: a protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature 1997, 386, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S. C.; Monroe, S. K.; Diering, G. H. Homer1a and mGluR1/5 Signaling in Homeostatic Sleep Drive and Output. Yale J Biol Med 2019, 92, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Clifton, N.E.; Trent, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Hall, J. Regulation and Function of Activity-Dependent Homer in Synaptic Plasticity. Complex Psychiatry 2019, 5, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diering, G.H.; Nirujogi, R.S.; Roth, R.H.; Worley, P.F.; Pandey, A.; Huganir, R.L. Homer1a drives homeostatic scaling-down of excitatory synapses during sleep. Science 2017, 355, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Callaghan, V.S.; Couvy-Duchesne, B.; Strike, L.T.; McMahon, K.L.; Byrne, E.M.; Wright, M.J. A meta-analysis of the relationship between subjective sleep and depressive symptoms in adolescence. Sleep Med. 2021, 79, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noya, S.B.; Colameo, D.; Brüning, F.; Spinnler, A.; Mircsof, D.; Opitz, L.; Mann, M.; Tyagarajan, S.K.; Robles, M.S.; Brown, S.A. The forebrain synaptic transcriptome is organized by clocks but its proteome is driven by sleep. Science 2019, 366, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyássy, P.; Todorov-Völgyi, K.; Tóth, V.; Györffy, B.A.; Puska, G.; Simor, A.; Juhász, G.; Drahos, L.; Kékesi, K.A. The Effect of Sleep Deprivation and Subsequent Recovery Period on the Synaptic Proteome of Rat Cerebral Cortex. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1301–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baucum, A.J. Proteomic Analysis of Postsynaptic Protein Complexes Underlying Neuronal Plasticity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardoni, F.; Di Luca, M. Protein-protein interactions at the NMDA receptor complex: From synaptic retention to synaptonuclear protein messengers. Neuropharmacology 2021, 190, 108551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautz, J.D.; Tsegay, K.B.; Zhu, Z.; Gniffke, E.P.; Welsh, J.P.; Smith, S.E. Synaptic protein interaction networks encode experience by assuming stimulus-specific and brain-region-specific states. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110076–110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavito, V.; Fabene, P.F.; Grassi-Zucconi, G.; Pifferi, F.; Lamberty, Y.; Bentivoglio, M.; Bertini, G. Experimental sleep deprivation as a tool to test memory deficits in rodents. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Incontro, S.; Nicoll, R.A.; Roche, K.W. PSD-95 stabilizes NMDA receptors by inducing the degradation of STEP 61. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 201609702–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western blot protocol. 2020. Available online: https://www.abcam.com/protocols/general-western-blot-protocol (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Bhambhvani, H.P.; Mueller, T.M.; Simmons, M.S.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. Actin polymerization is reduced in the anterior cingulate cortex of elderly patients with schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, 1278–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.-Y.; Wu, L.-L.; Li, X.-N.; Yuan, Y.-L.; Zhao, W.-W.; Qi, J.-X.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Ward, N.; Wang, J. Molecular Mechanisms of AMPA Receptor Trafficking in the Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimune, A.; Isaac, J.T.; Molnar, E.; Noel, J.; Nash, S.; Tagaya, M.; Collingridge, G.L.; Nakanishi, S.; Henley, J.M. NSF Binding to GluR2 Regulates Synaptic Transmission. Neuron 1998, 21, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D. Excitation control: balancing PSD-95 function at the synapse. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 1, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovic, J. AMPA receptors in the synapse: Very little space and even less time. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.-I.; Nagai, T.; Miyawaki, A.; Hayashi, Y. Rapid and persistent modulation of actin dynamics regulates postsynaptic reorganization underlying bidirectional plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, J.N.; Harris, K.M. Balancing Structure and Function at Hippocampal Dendritic Spines. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malenka, R.C. AMPA Receptor Trafficking and Synaptic Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Hayashi, Y. Structural plasticity of dendritic spines. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J.; Yasuda, R.; Raghavachari, S. Mechanisms of CaMKII action in long-term potentiation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havekes, R.; Park, A.J.; Tudor, J.C.; Luczak, V.G.; Hansen, R.T.; Ferri, S.L.; Bruinenberg, V.M.; Poplawski, S.G.; Day, J.P.; Aton, S.J.; et al. Sleep deprivation causes memory deficits by negatively impacting neuronal connectivity in hippocampal area CA1. eLife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.; Espinoza, S.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Dopamine receptors – IUPHAR Review 13. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 172, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H. D.; Schain, M.; Deng, H. P.; Mandeville, J. B.; Rosen, B. R.; Sander, C. Y. Differential D 1 and D 2 receptor internalization and recycling induced by amphetamine in vivo. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Romero-Fernandez, W.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Ciruela, F.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. On the Existence of a Possible A2A–D2–β-Arrestin2 Complex: A2A Agonist Modulation of D2 Agonist-Induced β-Arrestin2 Recruitment. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perroy, J.; Raynaud, F.; Homburger, V.; Rousset, M.-C.; Telley, L.; Bockaert, J.; Fagni, L. Direct Interaction Enables Cross-talk between Ionotropic and Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6799–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. Insights on the Functional Interaction between Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI) and ErbB Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, B.; Born, J. About Sleep's Role in Memory. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 681–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, C. Sleep and synaptic changes. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, T.E.; Goda, Y. The role of AMPA receptors in postsynaptic mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, C.; Tononi, G. The why and how of sleep-dependent synaptic down-selection. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 125, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarcio, F.; Tononi, G.; Cirelli, C. Effects of non-rapid eye movement sleep on the cortical synaptic expression of GluA1-containing AMPA receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 60, 3961–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovskiy, V.V.; Cirelli, C.; Pfister-Genskow, M.; Faraguna, U.; Tononi, G. Molecular and electrophysiological evidence for net synaptic potentiation in wake and depression in sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Faraguna, U.; Cirelli, C.; Tononi, G.; Gao, X.-B. Direct Evidence for Wake-Related Increases and Sleep-Related Decreases in Synaptic Strength in Rodent Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8671–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Bjorness, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Rybalchenko, V.; Suzuki, A.; Bridges, C.; Harrington, A.J.; Cowan, C.W.; Takahashi, J.S.; Konopka, G.; Greene, R.W.; et al. An essential role for MEF2C in the cortical response to loss of sleep in mice. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, K. E.; Kulkarni, A.; Pandey, R.; Dehnad, M.; Konopka, G.; Greene, R. W. Sleep need driven oscillation of glutamate synaptic phenotype. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Zablah, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gugustea, R.; Jia, Z. LIM-Kinases in Synaptic Plasticity, Memory, and Brain Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.B.; Starck, S.R.; Roberts, R.W.; Schuman, E.M. Dopaminergic Stimulation of Local Protein Synthesis Enhances Surface Expression of GluR1 and Synaptic Transmission in Hippocampal Neurons. Neuron 2005, 45, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, M.A.; Ito, H.T.; Cressy, P.; Kempf, C.; Woo, J.C.; Schuman, E.M. Miniature Neurotransmission Stabilizes Synaptic Function via Tonic Suppression of Local Dendritic Protein Synthesis. Cell 2006, 125, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, J.F.; Alberts, B.M.; Krogan, N.J. Discovery and significance of protein-protein interactions in health and disease. Cell 2024, 187, 6501–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Chu, X.-P.; Mao, L.-M.; Wang, M.; Lan, H.-X.; Li, M.-H.; Zhang, G.-C.; Parelkar, N.K.; Fibuch, E.E.; Haines, M.; et al. Modulation of D2R-NR2B Interactions in Response to Cocaine. Neuron 2006, 52, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.J.; Xue, S.; Pei, L.; Vukusic, B.; Chéry, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Niznik, H.B.; Yu, X.-M.; Liu, F. Dual Regulation of NMDA Receptor Functions by Direct Protein-Protein Interactions with the Dopamine D1 Receptor. Cell 2002, 111, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, L.; Lee, F.J.S.; Moszczynska, A.; Vukusic, B.; Liu, F. Regulation of Dopamine D1 Receptor Function by Physical Interaction with the NMDA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladepeche, L.; Dupuis, J.P.; Bouchet, D.; Doudnikoff, E.; Yang, L.; Campagne, Y.; Bézard, E.; Hosy, E.; Groc, L. Single-molecule imaging of the functional crosstalk between surface NMDA and dopamine D1 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 18005–18010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, S.-H.; Liu, J.; Lee, F.J.; Frankland, P.W.; Liu, F. Uncoupling the D1-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Complex Promotes NMDA-Dependent Long-Term Potentiation and Working Memory. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénac, N.; Saraceno, G.E.; Butler, C.; Kuga, N.; Nishimura, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Su, P.; Sasaki, T.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Galland, R.; et al. Non-canonical interplay between glutamatergic NMDA and dopamine receptors shapes synaptogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.K.Y.; Zhai, D.; Su, P.; Jiang, A.; Boychuk, J.; Liu, F. The receptor-receptor interaction between mGluR1 receptor and NMDA receptor: a potential therapeutic target for protection against ischemic stroke. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 14423–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, K.; Dore, K.; Tang, K.; Irvine, M.; Fang, G.; Burnell, E.S.; Malinow, R.; Jane, D.E.; Monaghan, D.T. The NMDA Receptor Intracellular C-Terminal Domains Reciprocally Interact with Allosteric Modulators. Biochemical Pharmacology 2019, 159, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit-Pedrol, M.; Groc, L. Regulation of membrane NMDA receptors by dynamics and protein interactions. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillman, M.; Lautz, J.D.; Johnson, R.S.; MacCoss, M.J.; Smith, S.E.P. Activity dependent dissociation of the Homer1 interactome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, T.-X.; Hallett, P.J.; Watanabe, M.; Grant, S.G.N.; Isacson, O.; Yao, W.-D. PSD-95 Uncouples Dopamine–Glutamate Interaction in the D1/PSD-95/NMDA Receptor Complex. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2948–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




