Submitted:
22 April 2025
Posted:
23 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Calculation of the Simulated Spectrum
2.2. Datasource
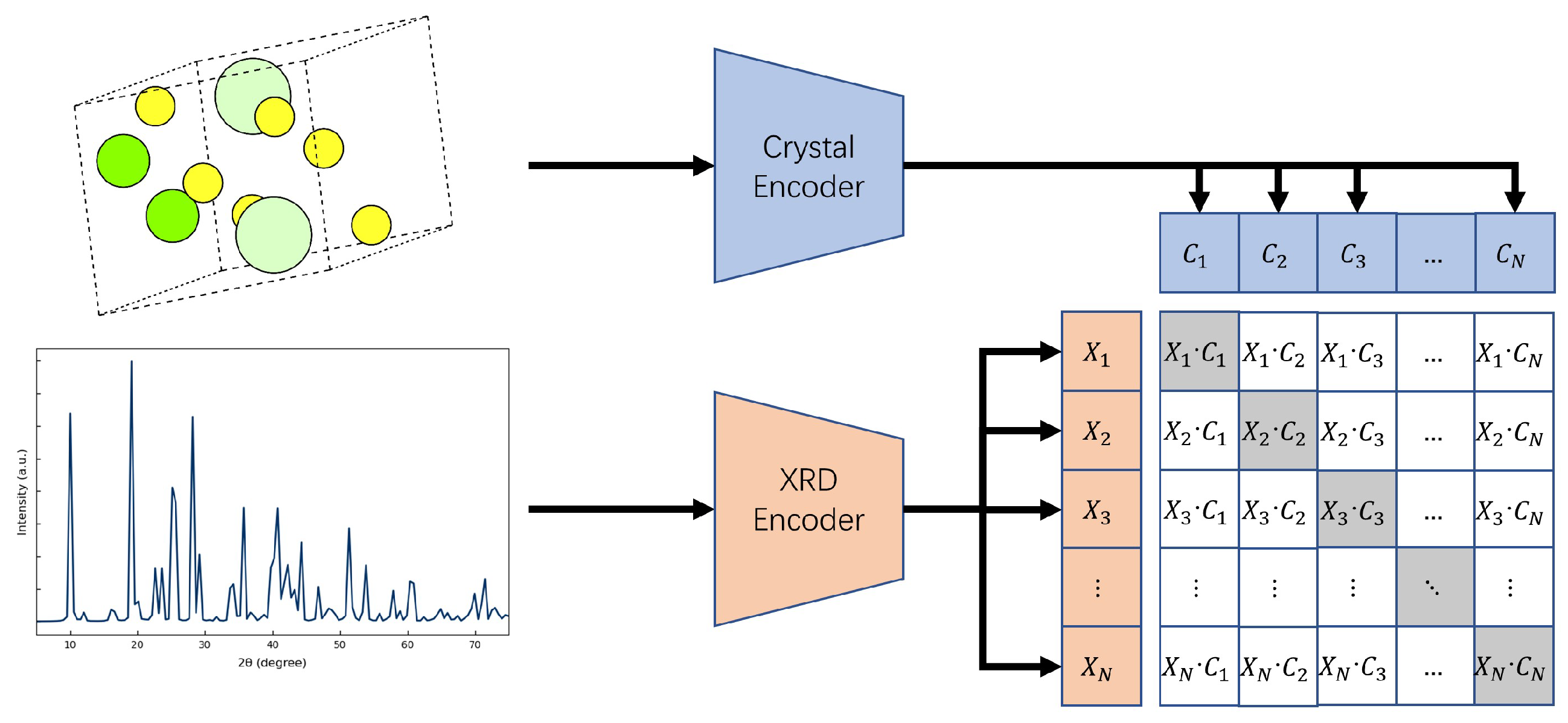
2.3. Crystal Structure Encoder
2.4. Diffraction Pattern Encoder
2.5. Loss Function
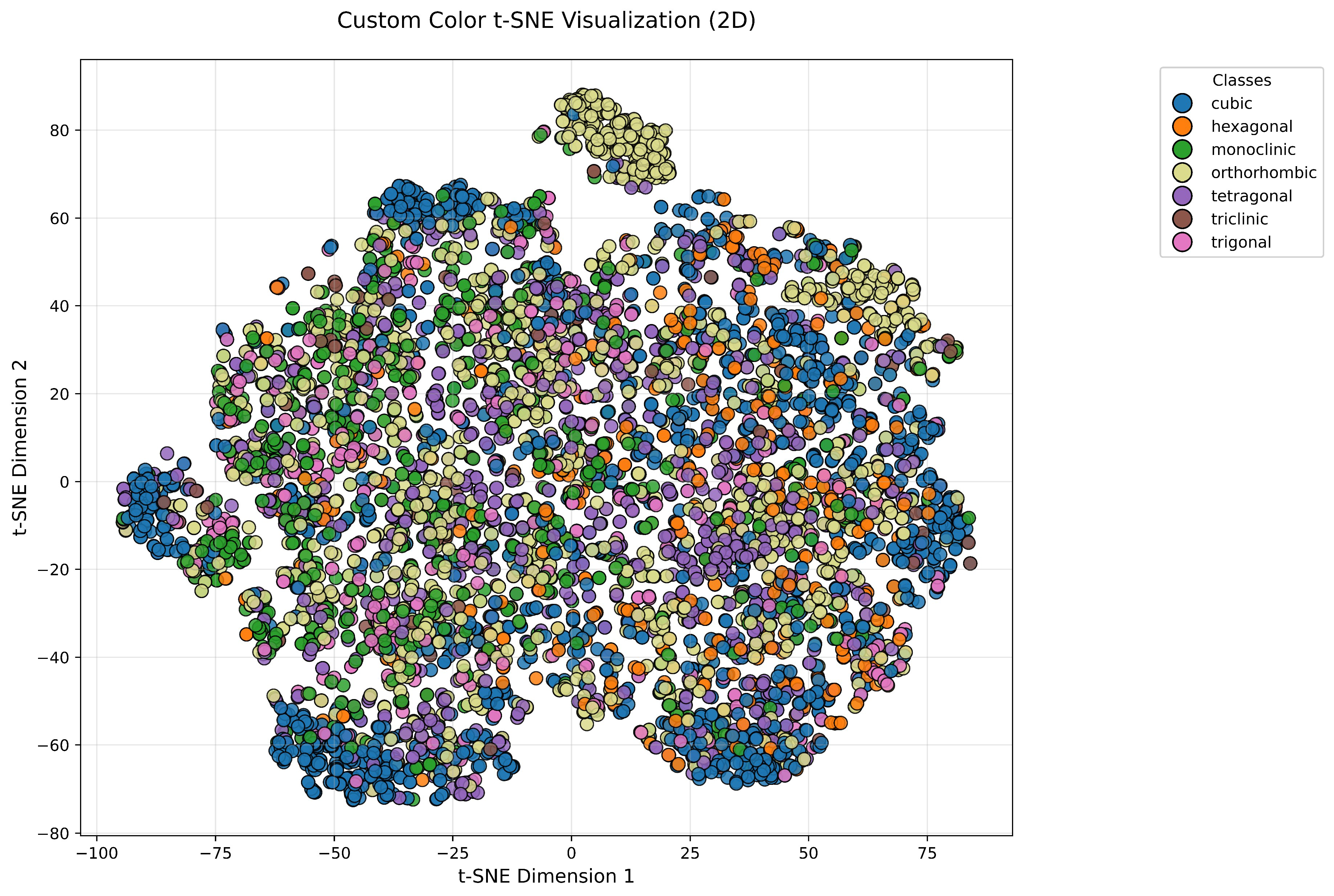
3. Results and Discussion
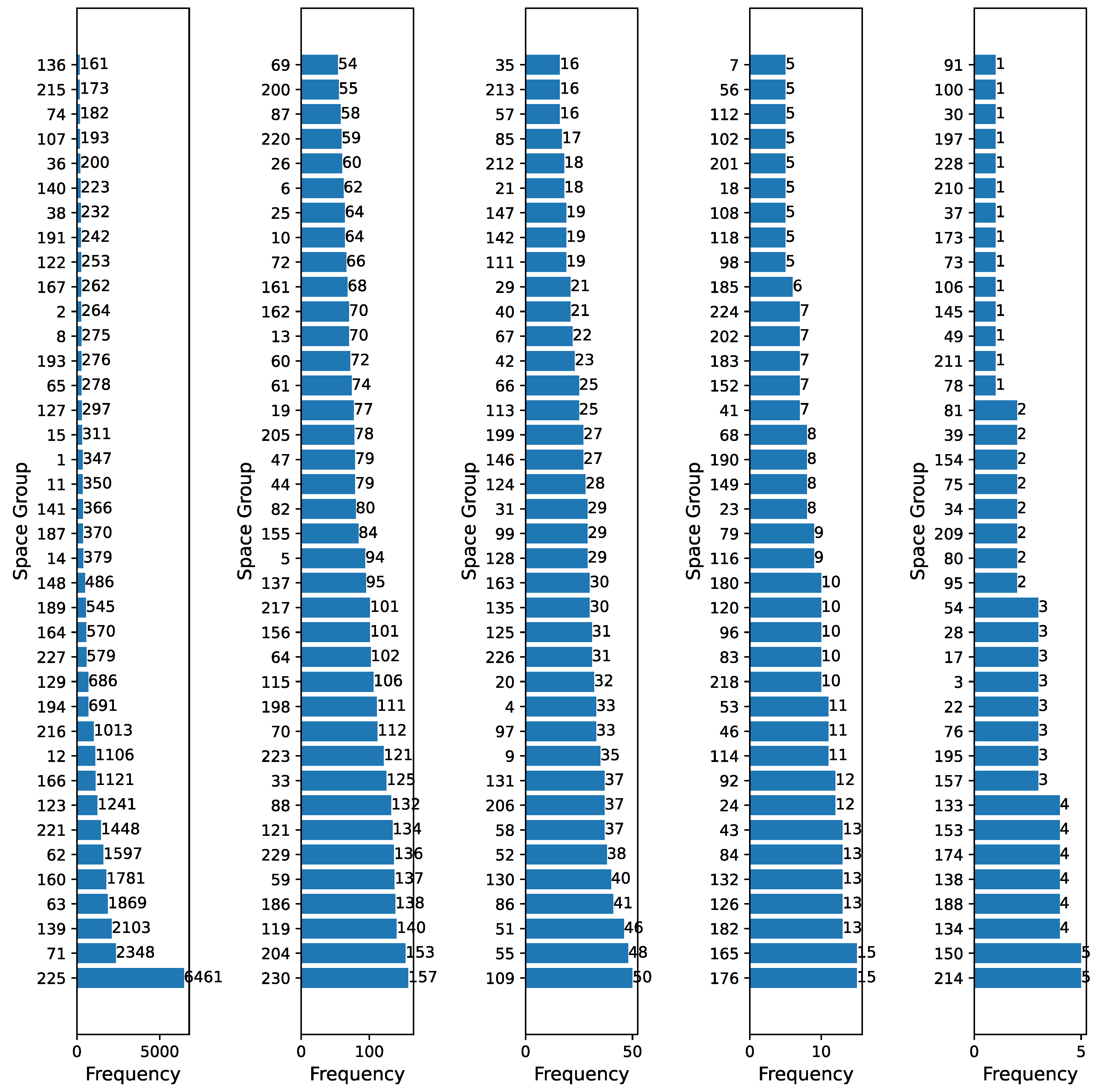
| Space Group | Frequency | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| 225 | 808 | 95.92% |
| 3, 24, 34, 37, 39 | 1 (each) | 96.00% |
| 41, 48, 50, 95, 97 | ||
| 112, 116, 120, 132, 138 | ||
| 143, 157, 159, 180, 192 | ||
| 195, 197, 202, 203, 214 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, W.; Zhang, H.; Du, Y.; Meng, Q.; Chen, W.; Zheng, N.; Shao, B.; Liu, T.Y. SE (3) equivariant graph neural networks with complete local frames. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2022, pp. 5583–5608.
- Friedrich, W.; Knipping, P.; Laue, M. Interferenzerscheinungen bei roentgenstrahlen. Annalen der Physik 1913, 346, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W.H.; Bragg, W.L. The reflection of X-rays by crystals. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character 1913, 88, 428–438. [Google Scholar]
- Debye, P.; Scherrer, P. Interferenzen an regellos orientierten Teilchen im Röntgenlicht. I. Nachrichten von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen, Mathematisch-Physikalische Klasse 1916, 1916, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: the genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. Applied Crystallography 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. Applied Crystallography 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.B.; Chung, J.; Jung, J.; Sohn, K.; Singh, S.P.; Pyo, M.; Shin, N.; Sohn, K.S. Classification of crystal structure using a convolutional neural network. IUCrJ 2017, 4, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo, F.; Ren, Z.; Sun, S.; Settens, C.; Liu, Z.; Hartono, N.T.P.; Ramasamy, S.; DeCost, B.L.; Tian, S.I.; Romano, G.; et al. Fast and interpretable classification of small X-ray diffraction datasets using data augmentation and deep neural networks. npj Computational Materials 2019, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinge, S.J.; Levin, I. The problem with determining atomic structure at the nanoscale. science 2007, 316, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.; Snyder, R.L.; et al. Introduction to X-ray powder diffractometry; Vol. 138, Wiley Online Library, 1996.
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’keeffe, M.; Peskov, M.A.; Ramsden, S.J.; Yaghi, O.M. The reticular chemistry structure resource (RCSR) database of, and symbols for, crystal nets. Accounts of chemical research 2008, 41, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Cao, B.; Hu, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.Y. CGWGAN: crystal generative framework based on Wyckoff generative adversarial network. Journal of Materials Informatics 2024, 4, N. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davel, C.; Bassiri-Gharb, N.; Correa-Baena, J.P. Machine Learning in X-ray Scattering for Materials Discovery and Characterization 2024.
- Prasianakis, N.I. AI-enhanced X-ray diffraction analysis: towards real-time mineral phase identification and quantification. IUCrJ 2024, 11, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdu, V.A.; Gyorgy, R. X-ray diffraction data analysis by machine learning methods—a review. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guan, Z.; Yao, S.; Qin, H.; Nguyen, M.H.; Yager, K.; Yu, D. Deep learning for analysing synchrotron data streams. In Proceedings of the 2016 New York Scientific Data Summit (NYSDS). IEEE, 2016, pp. 1–5.
- Czyzewski, A.; Krawiec, F.; Brzezinski, D.; Porebski, P.J.; Minor, W. Detecting anomalies in X-ray diffraction images using convolutional neural networks. Expert systems with applications 2021, 174, 114740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sharma, R. See deeper: Identifying crystal structure from x-ray diffraction patterns. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW). IEEE, 2020, pp. 49–54.
- Chakraborty, A.; Sharma, R. A deep crystal structure identification system for X-ray diffraction patterns. The Visual Computer 2022, 38, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massuyeau, F.; Broux, T.; Coulet, F.; Demessence, A.; Mesbah, A.; Gautier, R. Perovskite or Not Perovskite? A Deep-Learning Approach to Automatically Identify New Hybrid Perovskites from X-ray Diffraction Patterns. Advanced Materials 2022, 34, 2203879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishitsuka, K.; Ojima, H.; Mogi, T.; Kajiwara, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Asanuma, H. Characterization of hydrothermal alteration along geothermal wells using unsupervised machine-learning analysis of X-ray powder diffraction data. Earth Science Informatics 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Vecsei, P.M.; Choo, K.; Chang, J.; Neupert, T. Neural network based classification of crystal symmetries from x-ray diffraction patterns. Physical Review B 2019, 99, 245120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Hino, H.; Hawai, T.; Saito, K.; Kotsugi, M.; Ono, K. Symmetry prediction and knowledge discovery from X-ray diffraction patterns using an interpretable machine learning approach. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 21790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venderley, J.; Mallayya, K.; Matty, M.; Krogstad, M.; Ruff, J.; Pleiss, G.; Kishore, V.; Mandrus, D.; Phelan, D.; Poudel, L.; et al. Harnessing interpretable and unsupervised machine learning to address big data from modern X-ray diffraction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2022, 119, e2109665119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utimula, K.; Hunkao, R.; Yano, M.; Kimoto, H.; Hongo, K.; Kawaguchi, S.; Suwanna, S.; Maezono, R. Machine-Learning Clustering Technique Applied to Powder X-Ray Diffraction Patterns to Distinguish Compositions of ThMn12-Type Alloys. Advanced Theory and Simulations 2020, 3, 2000039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utimula, K.; Yano, M.; Kimoto, H.; Hongo, K.; Nakano, K.; Maezono, R. Feature space of XRD patterns constructed by an autoencoder. Advanced Theory and Simulations 2023, 6, 2200613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, T.; Du, B.; Hu, S.; Xiong, J.; Pan, D. Kolmogorov–Arnold Network Made Learning Physics Laws Simple. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2024, 15, 12393–12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Xu, F.; Yao, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, S.; He, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. End-to-End Crystal Structure Prediction from Powder X-Ray Diffraction. Advanced Science 2025, 12, 2410722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Goldfeder, J.; Lan, L.; Ray, A.; Yang, A.H.; Chen, B.; Billinge, S.J.L.; Lipson, H. Towards end-to-end structure determination from x-ray diffraction data using deep learning. npj Computational Materials 2024, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, C.; Fitterer, A.; Buchsbaum, C.; Habermehl, S.; Chierotti, M.R.; Nervi, C.; Schmidt, M.U. Ambiguous structure determination from powder data: four different structural models of 4, 11-difluoroquinacridone with similar X-ray powder patterns, fit to the PDF, SSNMR and DFT-D. IUCrJ 2022, 9, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parackal, A.S.; Goodall, R.E.; Faber, F.A.; Armiento, R. Identifying crystal structures beyond known prototypes from x-ray powder diffraction spectra. Physical Review Materials 2024, 8, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PmLR, 2021, pp. 8748–8763.
- Drautz, R. Atomic cluster expansion for accurate and transferable interatomic potentials. Physical Review B 2019, 99, 014104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batatia, I.; Kovacs, D.P.; Simm, G.; Ortner, C.; Csányi, G. MACE: Higher order equivariant message passing neural networks for fast and accurate force fields. Advances in neural information processing systems 2022, 35, 11423–11436. [Google Scholar]
- Fredericks, S.; Parrish, K.; Sayre, D.; Zhu, Q. PyXtal: A Python library for crystal structure generation and symmetry analysis. Computer Physics Communications 2021, 261, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmer, J.; Schoenholz, S.S.; Riley, P.F.; Vinyals, O.; Dahl, G.E. Neural message passing for quantum chemistry. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2017, pp. 1263–1272.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp. 770–778.
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PmLR, 2020, pp. 1597–1607.
- Su, T.; Cui, Y.; Lian, Z.; Hu, M.; Li, M.; Lu, W.; Ren, W. Physics-Based Feature Makes Machine Learning Cognizing Crystal Properties Simple. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2021, 12, 8521–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
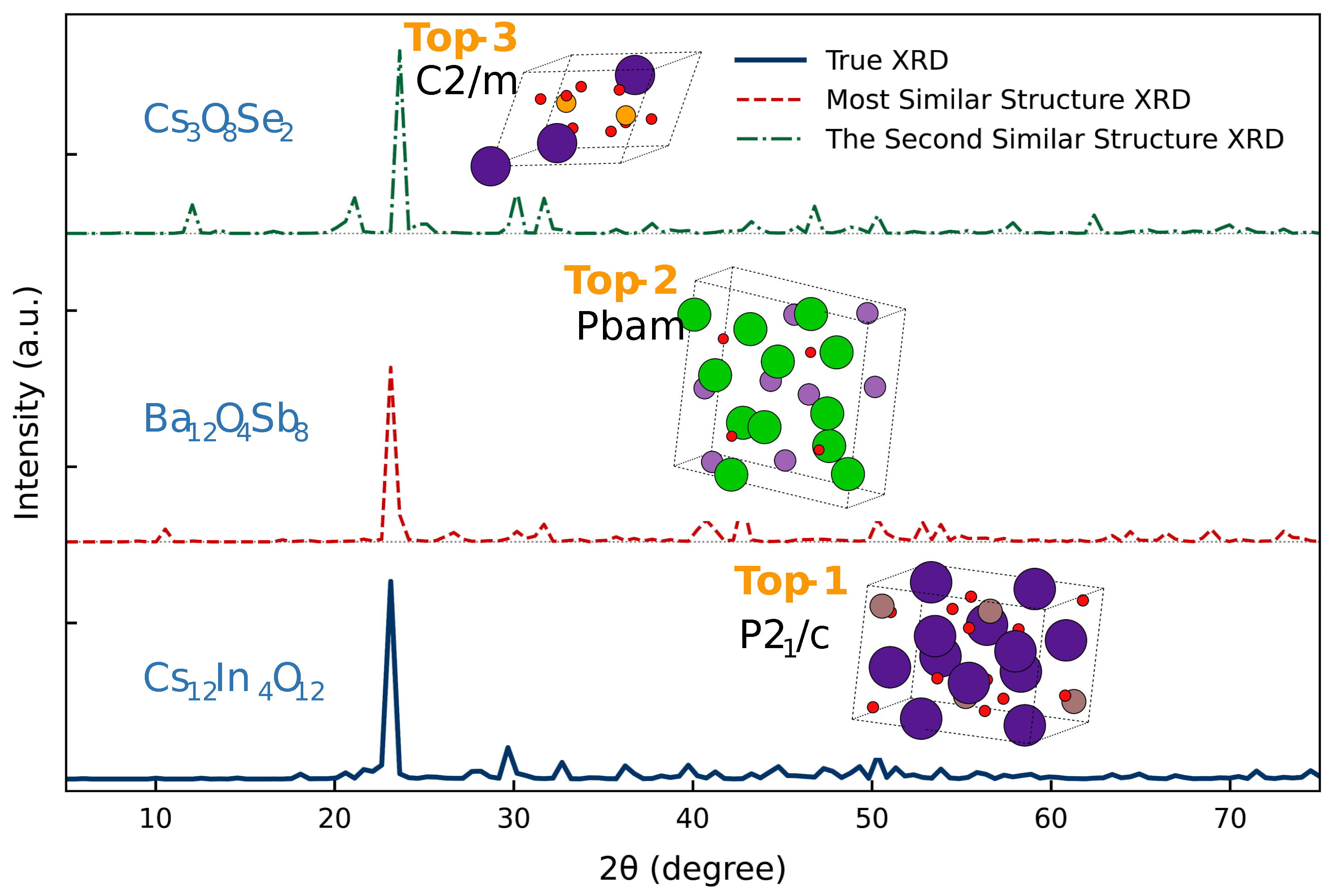
| Model | Top-1 (%) | Top-3 (%) | Top-5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Name | 95.96 | 99.95 | 99.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





