Submitted:
28 March 2025
Posted:
31 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant samples
2.2. Identification of imp and idpA homologues
2.3. Cloning and PCR amplification of imp and idpA genes
2.4. Sequencing of imp and idpA genes
2.5. Genetic diversity
2.6. Phylogenetic analysis of X-disease phytoplasmas
3. Results
3.1. Identification of imp and idpA ORFs in X-disease genomes
3.2. PCR amplifications and sequencing
3.3. Sequences homology and predicted protein structure
3.3. Genetic diversity
3.4. Phylogeny based on 16S rRNA, idpA and imp genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maejima, K.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Exploring the phytoplasmas, plant pathogenic bacteria. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2014, 80, 210-221. [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, Y. Phytoplasma Taxonomy: Nomenclature, Classification, and Identification. Biology 2022, 11, 1119. [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Beanland, L. Insect vectors of phytoplasmas. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 91-111. [CrossRef]
- Bertaccini, A.; Arocha-Rosete, Y.; Contaldo, N.; Duduk, B.; Fiore, N.; Montano, H. G.; Kube, M.; Kuo, C.H.; Martini, M.; Oshima, K.; Qualigno, F.; Schenider, B.; Wei, W.; Zamorano, A. Revision of the ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ species description guidelines. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 2022, 72(4). [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, D.E.; Lee, I.M.; Schaff, D.A.; Harrison, N.A.; Chang, C.J.; Davis, R.E.; Kingsbury, D.T. Genomic diversity and differentiation among phytoplasma strains in 16S rRNA groups I (aster yellows and related phytoplasmas) and III (X-disease and related phytoplasmas). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1996, 46, 64-75. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Lee, I.M.; Shao, J.; Suo, X.; Davis, R.E. Construction of an interactive online phytoplasma classification tool, iPhyClassifier, and its application in analysis of the peach X-disease phytoplasma group (16SrIII). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2582-2593. [CrossRef]
- Liefting, L.W.; Andersen, M.T.; Beever, R.E.; Gardner, R.C.; Forster, R.L. Sequence heterogeneity in the two 16S rRNA genes of Phormium yellow leaf phytoplasma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3133-3139. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Davis, R.E. Criteria for phytoplasma 16Sr group/subgroup delineation and the need of a platform for proper registration of new groups and subgroups. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2121–2123. [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.T.; Kung, H.J.; Huang, W.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Kuo, C.H. Species boundaries and molecular markers for the classification of 16SrI phytoplasmas inferred by genome analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1531. [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, G.; Malembic-Maher, S.; Salar, P.; Bonnet, P.; Maixner, M.; Marcone, C.; Boudon-Padieu, E.; Foissac, X. Multilocus sequence typing confirms the close genetic interrelatedness of three distinct flavescence dorée phytoplasma strain clusters and group 16SrV phytoplasmas infecting grapevine and alder in Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4001–4010. [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Zhao, Y.; Dally, E.L.; Lee, I.M.; Jomantiene, R.; Douglas, S.M. 'Candidatus Phytoplasma pruni', a novel taxon associated with X-disease of stone fruits, Prunus spp.: multilocus characterization based on 16S rRNA, secY, and ribosomal protein genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 766-776. [CrossRef]
- Abeysinghe, S.; Abeysinghe, P.D.; Kanatiwela-de Silva, C.; Udagama, P.; Warawichanee, K.; Aljafar, N.; Dickinson, M. Refinement of the taxonomic structure of 16SrXI and 16SrXIV phytoplasmas of gramineous plants using multilocus sequence typing. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2001–2010. [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S.; Kamagata, Y. A multiplex-PCR method for strain identification and detailed phylogenetic analysis of AY-group phytoplasmas. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 299–305. [CrossRef]
- Toth, R.; Ilic, A.M.; Huettel, B.; Duduk, B.; Kube, M. Divergence within the Taxon 'Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris' Confirmed by Comparative Genome Analysis of Carrot Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1016. [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, P.; Chuvochina, M.; Oren, A.; Parks, D.H.; Soo, R.M. Prokaryotic taxonomy and nomenclature in the age of big sequence data. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1879–1892. [CrossRef]
- Galdeano, E.; Guzmán, F.; Fernández, F.; Conci, L. Genetic diversity of 16SrIII group phytoplasmas in Argentina. Predominance of subgroups 16SrIII-J and B and two new subgroups 16SrIII-W and X. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 137, 753–764. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, E.; Luna-Rodríguez, M.; Olivier, C.Y.; Dumonceaux, T.J. The underestimated diversity of phytoplasmas in Latin America. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 492–513. [CrossRef]
- Montano, H.G.; Bertaccini, A.; Fiore, N. Phytoplasma-Associated Diseases in South America: Thirty Years of Research. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1311. [CrossRef]
- Amaral Mello, A.P.O.; Eckstein, B.; Flôres, D.; Kreyci, P.F.; Bedendo, I.P. Identification by computer-simulated RFLP of phytoplasmas associated with eggplant giant calyx representative of two subgroups, a lineage of 16SrIII-J and the new subgroup 16SrIII-U. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1454–1461 . [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, F.; Zamorano, A.; Pino, A.M.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, A.; Fiore, N. Identification of phytoplasma belonging to X-disease group in cherry in Chile. Bull. Insectol. 2011, 64 (Suppl.), S235–S236.
- Rappussi, M.C.C.; Eckstein, B.; Flôres, D.; Haas, I.C.R.; Amorim, L.; Bedendo, I.P. Cauliflower stunt associated with a phytoplasma of subgroup 16SrIII-J and the spatial pattern of disease. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 829–840. [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.; Uset, A.; Baumgratz, G.; Conci, L. Detection and identification of a 16SrIII-J phytoplasma affecting cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) in Argentina. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2018, 13, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.D.; Guzmán, F.A.; Baffoni, P.; Reinoso, L.; Kiehr, M.; Delhey, R.; Conci, L.R. Phytoplasmas of subgroup 16SrIII-J associated with Beta vulgaris in Argentina. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2020, 45, 143–147. [CrossRef]
- Arneodo, J.D.; Galdeano, E.; Orrego, A.; Stauffer, A.; Nome, S.F.; Conci, L.R. Identification of two phytoplasmas detected in China-trees with decline symptoms in Paraguay. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2005, 34, 583–585. [CrossRef]
- Flôres, D.; Haas, I.C.; Canale, M.C.; Bedendo, I.P. Molecular identification of a 16SrIII-B phytoplasma associated with cassava witches’ broom disease. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 137, 237–242. [CrossRef]
- Galdeano, E.; Torres, L.E.; Meneguzzi, N.; Guzmán, F.; Gomez, G.G.; Docampo, D.M.; Conci, L.R. Molecular characterization of 16S ribosomal DNA and phylogenetic analysis of two X-disease group phytoplasmas affecting China-tree (Melia azedarach L.) and garlic (Allium sativum L.) in Argentina. J. Phytopathol. 2004, 152, 174–181. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.D.; Carloni, E.; Alessio, F.; Bongiorno, V.; Conci, L.R. First report of a 16SrIII-X phytoplasma associated with Lactuca sativa witches’ broom in Argentina. New Dis. Rep. 2022, 46, e12103. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.; Mejía, J.F.; Llano, G.; Loke, J.; Calari, A.; Duduk, B.; Bertaccini, A. Characterization of a phytoplasma associated with frogskin disease in cassava. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 1139–1145. [CrossRef]
- Konnerth, A., Krczal, G., & Boonrod, K. (2016). Immunodominant membrane proteins of phytoplasmas. Microbiol., 162(8), 1267-1273. [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Jung, H.Y.; Suzuki, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Arashida, R.; Lee, J.T.; Miyata, S.; Ugaki, M.; Namba, S. Positive selection acting on a surface membrane protein of the plant-pathogenic phytoplasmas. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3424–3428. [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Ishii, Y.; Hoshi, A.; Maejima, K.; Jung, H.Y.; Yamaji, Y.; Namba, S. Cloning of immunodominant membrane protein genes of phytoplasmas and their in planta expression. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 293, 92–101. [CrossRef]
- Galetto, L.; Siampour, M.; Marzachì, C. Preparation of phytoplasma membrane recombinant proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 938, 351–369. [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15.
- Deng, S.; Hiruki, C. Amplification of 16S rRNA genes from culturable and unculturable Mollicutes. J. Microbiol. Methods 1991, 14, 53–61. [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.M.; Hammond, R.W.; Davis, R.E.; Gundersen, D.E. Universal amplification and analysis of pathogen 16S rDNA for classification and identification of MLOs. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 834–842. [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420-423. [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; p. 174.
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 676–679. [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [CrossRef]
- Villamor, D.E.V.; Eastwell, K.C. Multilocus characterization, gene expression analysis of putative immunodominant protein coding regions, and development of recombinase polymerase amplification assay for detection of 'Candidatus Phytoplasma pruni' in Prunus avium. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 983–992. [CrossRef]
- Siampour, M.; Izadpanah, K.; Galetto, L.; Salehi, M.; Marzachi, C. Molecular characterization, phylogenetic comparison and serological relationship of the Imp protein of several 'Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia' strains. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 452–45. [CrossRef]
- Blomquist, C.L.; Barbara, D.J.; Davies, D.L.; Clark, M.F.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. An immunodominant membrane protein gene from the Western X-disease phytoplasma is distinct from those of other phytoplasmas. Microbiology 2001, 147, 571–580. [CrossRef]
- Neriya, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Maejima, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Komatsu, K.; Minato, N.; Miura, C.; Kakizawa, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Cloning, expression analysis, and sequence diversity of genes encoding two different immunodominant membrane proteins in poinsettia branch-inducing phytoplasma (PoiBI). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 324, 38–47. [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Quaglino, F.; Bertaccini, A. Multilocus genetic characterization of phytoplasmas. In Phytoplasmas: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria-III: Genomics, Host Pathogen Interactions and Diagnosis; Bertaccini, A., Oshima, K., Kube, M., Rao, G.P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 161–200. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Shan, H.L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.H.; Li, W.F.; Huang, Y.K. Multilocus sequence typing reveals two distinct populations of "Candidatus Phytoplasma sacchari" in China. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2023, 48, 199–206. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Cheng, H.P.; Lin, C.P.; Liao, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Lin, S.J.; Wang, H.C. Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of phytoplasma immunodominant membrane protein. IUCrJ 2024, 11, 384–394. [CrossRef]
- Bohunická, M.; Valentová, L.; Suchá, J.; Nečas, T.; Eichmeier, A.; Kiss, T.; Cmejla, R. Identification of 17 'Candidatus Phytoplasma pyri' genotypes based on the diversity of the imp gene sequence. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 971–977. [CrossRef]
- Pusz-Bochenska, K.; Perez-Lopez, E.; Wist, T.J.; Bennypaul, H.; Sanderson, D.; Green, M.; Dumonceaux, T.J. Multilocus sequence typing of diverse phytoplasmas using hybridization probe-based sequence capture provides high resolution strain differentiation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 959562. 10.3389/fmicb.2022.959562.
- Fernández, F.D.; Guzmán, F.A.; Conci, L.R. Draft genome sequence of Cicuta witches' broom phytoplasma, subgroup 16SrIII-J: A subgroup with phytopathological relevance in South America. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2024, 49, 558–565. [CrossRef]
- Filippin, L.; Trivellone, V.; Galetto, L.; Marzachì, C.; Elicio, V.; Angelini, E. Development of an anti-Imp serological assay for the detection of "flavescence dorée" phytoplasmas in grapevine, insect vectors and host plants. Phytopathog. Mollicutes 2019, 9, 75–76. 10.5958/2249-4677.2019.00038.0.
- Tan, C.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Li, J.R.; Chien, Y.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Chou, L.; Yang, J.Y. Accelerating complete phytoplasma genome assembly by immunoprecipitation-based enrichment and MinION-based DNA sequencing for comparative analyses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 766221. 10.3389/fmicb.2021.766221.
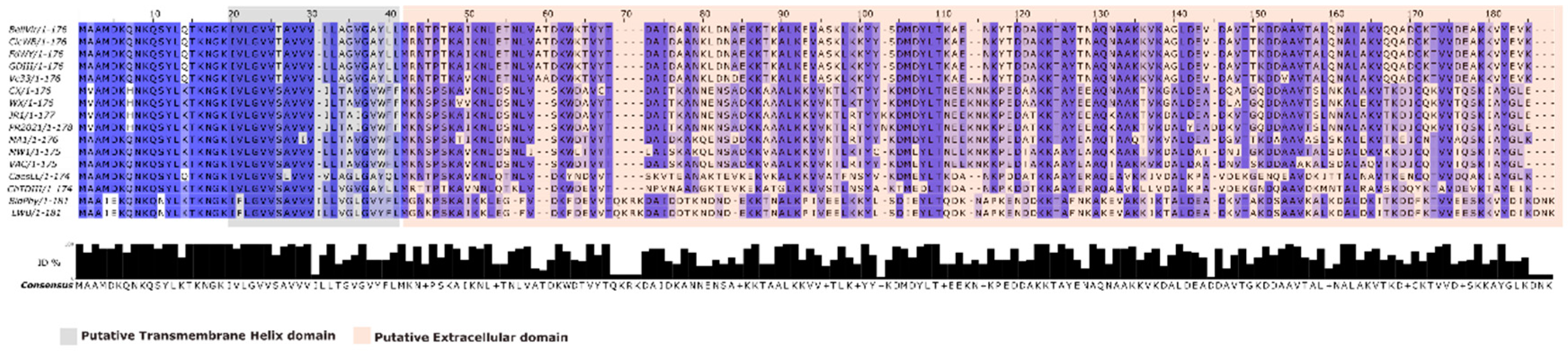
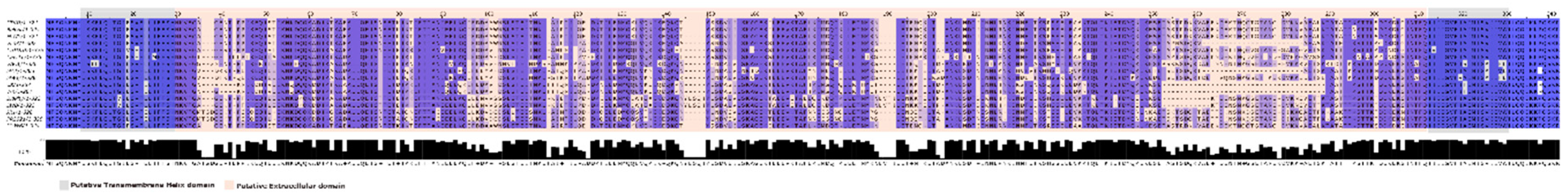
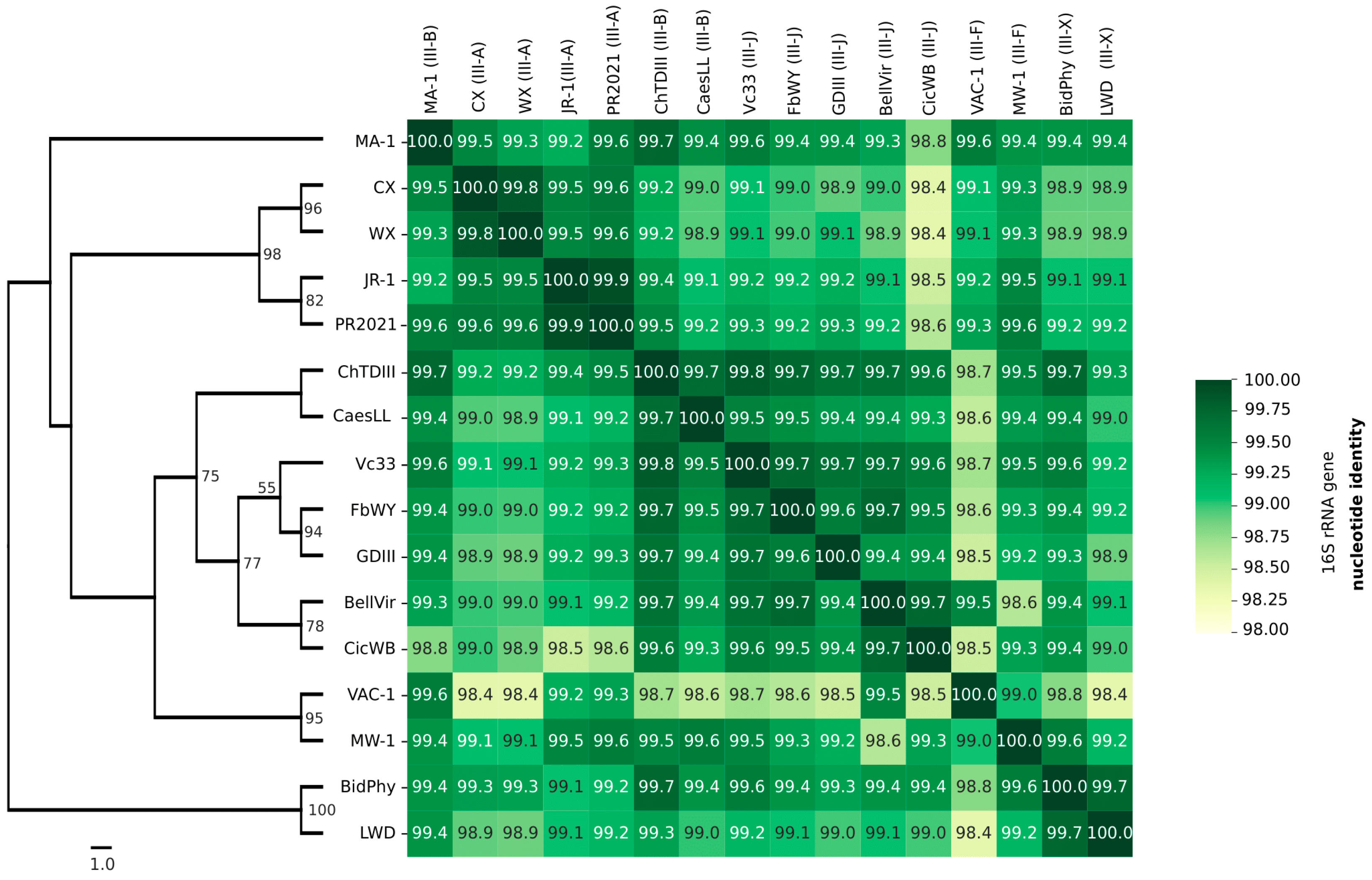
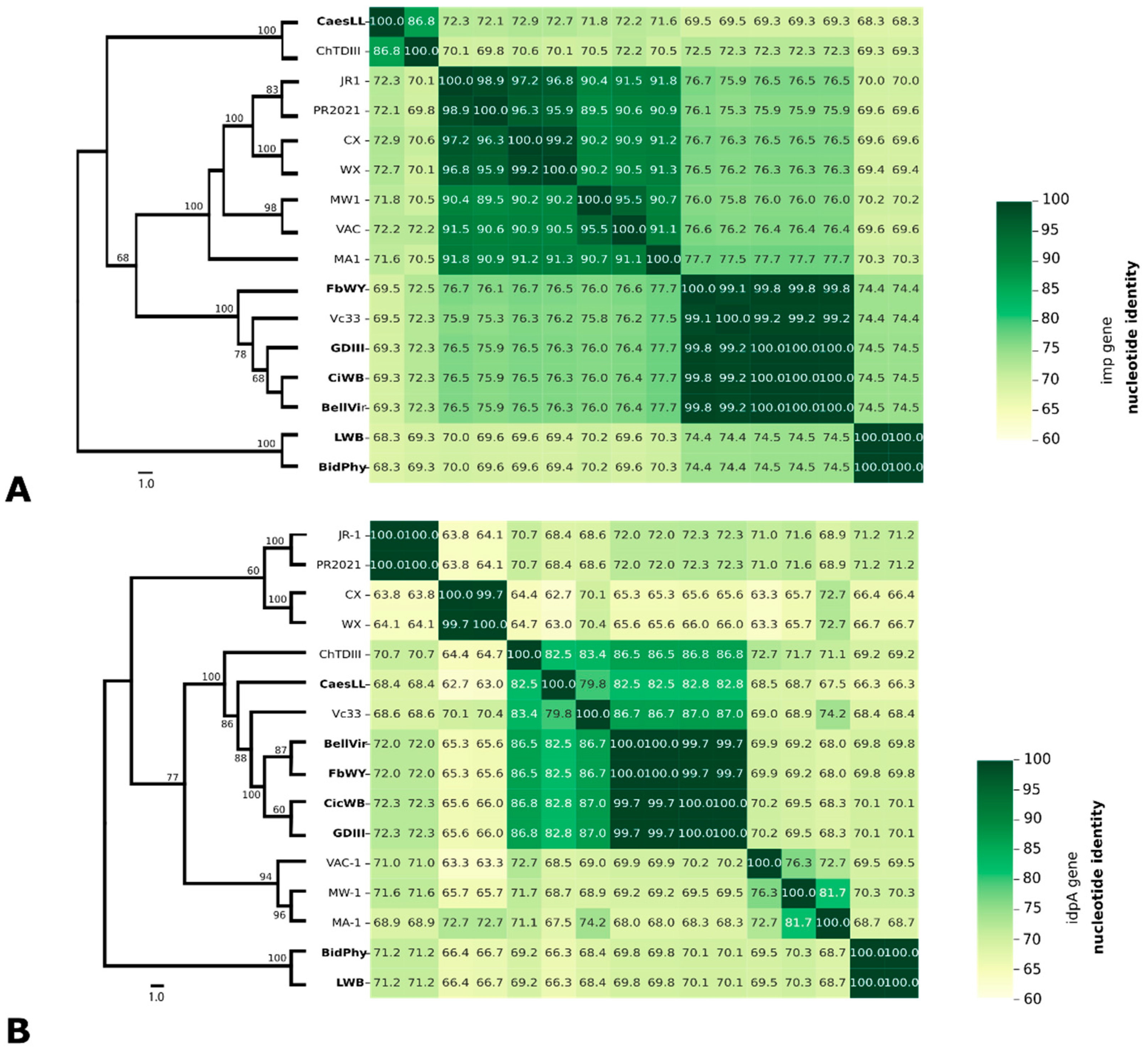
| Phytoplasma strain | 16SrIII* | Host |
imp PCR (+) |
idpA PCR (+) |
#Accession (imp/idpA) |
| Bellis virescence (BellVir) | III-J | Bellis perennis | 2/2 | 2/2 | MG435348.1/MG435349.1 |
| Garlic Decline (GDIII) | III-J | Allium sativum | 2/2 | 2/2 | PQ429243.1/PQ429237.1 |
| Fodder Beet Wilting- Yellowing (FbWY) | III-J | Beta vulgaris var. rapacea | 2/2 | 2/2 | PQ429242.1/PQ429236.1 |
| Sugar Beet Wilting-Yellowing (SugBeetWY) | III-J | Beta vulgaris var. altissima | 0/3 | 0/3 | - |
| Cicuta Witches Broom (CicWB) | III-J | Conium maculatum | 2/2 | 2/2 | PQ429241.1/PQ429238.1 |
| China tree decline (ChTDIII) | III-B | Melia azedarach | 3/3 | 3/3 | NWN45603.1/NWN45596.1 |
| Caesalpinia little leaf (CaesLL) | III-B | Caesalpinia gilliesii | 2/2 | 2/2 | PQ429239.1/PQ429233.1 |
| Argentinean Peach Yellows (ArPY) | III-B | Prunus persica | 0/3 | 0/3 | - |
| Lettuce Witches’ Broom (LWB) | III-X | Lactuca sativa | 2/2 | 2/2 | PQ871563/ PQ429235.1 |
| Bidens Phyllody (BidPhy) | III-X | Bidens subalternans | 1/3 | 1/3 | PQ429240.1/PQ429234.1 |
| Heterosperma Phyllody (HetPhy) | III-X | Heterosperma ovatifolium | 0/3 | 0/3 | - |
|
Phytoplasma [strain] |
16SrIII* | Host | Location | GenBank accession |
|
Ca. Phytoplasma pruni [WX] |
III-S | Prunus avium | USA | AF533231.1 |
|
Ca. Phytoplasma pruni [CX] |
III-A | Prunus domestica | USA | LHCF00000000.1 |
|
Ca. Phytoplasma pruni [PR2021] |
III-A | Euphorbia pulcherrima | Taiwan | CP119306.1 |
| Poinsettia branch-inducing [JR1] |
III-A | Euphorbia pulcherrima | USA | AKIK00000000.1 |
| Clover Phyllody [MA1] |
III-B | Chrysanthemum leuchantemum | Italy | AKIM00000000.1 |
| Vaccinium Witches’ Broom [VAC1] |
III-F | Vaccinium myrtillus | Italy | AKIN00000000.1 |
| Milkweed Yellows [MW1] |
III-F | Asclepias syriaca | USA | AKIL00000000.1 |
|
Ca. Phytoplasma sp [Vc33] |
III-J | Catharanthus roseus | Chile | LLKK00000000.1 |
| Chinaberry tree decline [ChTDIII] |
III-B | Melia azedarach | Argentina | JABUOH000000000.1 |
| Normalized dN-dS >0 | |||||||||
| Dataset | Nº | S | P | dN-dS | p-value | TM | HD | #codons | % |
| imp | 16 | 258 | 0.18272 | 3,474 | 0.01 | 10 | 70 | 157 | 50.955 |
| idpA | 16 | 268 | 0.10407 | -3,090 | 0.002 | 11 | 104 | 253 | 45.454 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





