Submitted:
29 March 2025
Posted:
31 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Research Objectives
- Identify the challenges faced by Iraqi universities in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Explore the opportunities for human resource development through these technologies.
- Provide detailed policy recommendations:
- ○
-
Securing Sustainable Funding:
- ▪
- Government: A commitment from the government to provide sustainable funding for the development of technological infrastructure and training programs for faculty and administrative staff.
- ▪
- International Organizations: Attracting funding from international organizations focused on developing education and technology in emerging countries.
- ○
-
Developing Strategic Partnerships:
- ▪
- With Technology Companies: Collaborations that offer practical training, knowledge transfer, and joint research and innovation projects.
- ▪
- With International Universities: Partnerships with renowned universities to facilitate the exchange of experiences, knowledge, and the development of academic programs.
- ▪
-
Enhancing Training Programs and Professional Development:Specialized Training Programs: Courses on modern technologies such as AI, IoT, and data analytics.
- ▪
- Workshops and Seminars: Activities to enhance understanding and appreciation of modern technologies, fostering a culture of innovation and openness to change.
1.3. Significance of the Study
2. Literature Review
2.1. Industry 4.0 Technologies in Education
2.2. Challenges in Adopting Industry 4.0 in Higher Education
2.3. Opportunities for Human Resource Development
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Challenges in Adopting Industry 4.0
- Technological Infrastructure: Many Iraqi universities suffer from a lack of technological infrastructure necessary to adopt Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Funding: Universities face difficulties in securing the necessary funding to upgrade infrastructure and develop training programs.
- Cultural Resistance: There is a degree of cultural resistance to change and technology, hindering the adoption process.
- Skills Gap: There is a lack of technical skills among faculty and administrative staff.
4.2. Opportunities for Human Resource Development
- Enhancing Technical Skills: Training programs can help develop the technical skills of university staff.
- Improving Administrative Efficiency: Automating administrative processes can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Enhancing Educational Innovation: AI and IoT technologies can improve education quality and provide interactive learning experiences.
- Boosting Scientific Research: Big data can enhance scientific research and data analysis more effectively.
5. Discussion
5.1. Addressing the Challenges
- Invest in Technological Infrastructure and Professional Development: This requires securing funding from the government and international organizations to upgrade infrastructure and provide specialized training programs for faculty and administrative staff.
- Promote a Culture of Innovation and Openness to Change: This can be achieved through workshops and seminars aimed at enhancing understanding and appreciation of the benefits of modern technologies.
- Develop Partnerships with Industry and International Institutions: These partnerships can offer opportunities for practical training, knowledge transfer, and collaborative research and innovation projects.
5.2. Leveraging the Opportunities
- Enhance Education and Research Quality: This can be achieved through the adoption of AI-supported personalized learning technologies and the creation of interactive learning environments using virtual and augmented reality.
- Improve Administrative Processes and Reduce Costs: Automating routine tasks and utilizing data analytics can enhance administrative efficiency.
- Create a More Dynamic and Responsive Educational Environment: Smart classrooms equipped with IoT technologies can create engaging and interactive learning experiences, enhancing student participation.
6. Opportunities for Human Resource Development
6.1. Enhancing Technical Skills
6.2. Fostering Innovation and Research
6.3. Improving Administrative Efficiency
6.4. Enhancing Student Learning Experiences
7. Conclusions
Funding
Availability of Data and Material:
Acknowledgements
Appendices
Appendix A: Survey Questionnaire
- Section 1: Demographics
- Age: __
- Gender: __
- Position: __ (e.g., faculty, administrative staff)
- Department: __
- Years of Experience: __
- Yes
- No
- How would you rate the current technological infrastructure at your university?
- ○
- Poor
- ○
- Fair
- ○
- Good
- ○
- Very Good
- ○
- Excellent
- 8.
- Are there sufficient funds allocated for the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in your university?
- Yes
- No
- 9.
- What are the main sources of funding for technological advancements at your university?
- ○
- Government
- ○
- Private Sector
- ○
- International Organizations
- ○
- Other: __
- 10.
- How receptive are faculty and staff to the adoption of new technologies? - Very Resistant - Somewhat Resistant - Neutral - Somewhat Receptive - Very Receptive
- 11.
- Do you feel that there is a significant gap in the technical skills required to implement Industry 4.0 technologies?
- 12.
- What types of training programs would be beneficial for enhancing technical skills?
- ○
- Workshops
- ○
- Online Courses
- ○
- Certification Programs
- ○
- Industry Partnerships
- ○
- Other: __
Appendix B: Interview Guide
- Briefly introduce the purpose of the interview.
- Ensure confidentiality and anonymity.
Appendix C: Data Analysis Methods
- Descriptive Statistics: Used to summarize the basic features of the data collected through surveys.
- Inferential Statistics: Employed to make inferences about the population based on the sample data, including hypothesis testing and regression analysis.
- Transcription: Interviews were transcribed verbatim to capture detailed responses.
- Coding: Thematic coding was applied using NVivo software to identify recurring themes and patterns in the interview data.
- Content Analysis: A systematic analysis was conducted to interpret the contextual meaning of the qualitative data.
Appendix D: Additional Tables and Figures
| Question |
Response Options | Frequency | Percentage |
|
Technological Infrastructure |
Yes | 30 | 60% |
| No | 20 | 40% | |
| Financial Constraints |
Yes | 15 | 30% |
| No | 35 | 70% | |
|
Receptivity to Technology |
Very Resistant |
5 | 10% |
| Somewhat Resistant | 10 | 20% | |
| Neutral | 15 | 30% | |
| Somewhat Receptive | 10 | 20% | |
| Very Receptive | 10 | 20% |
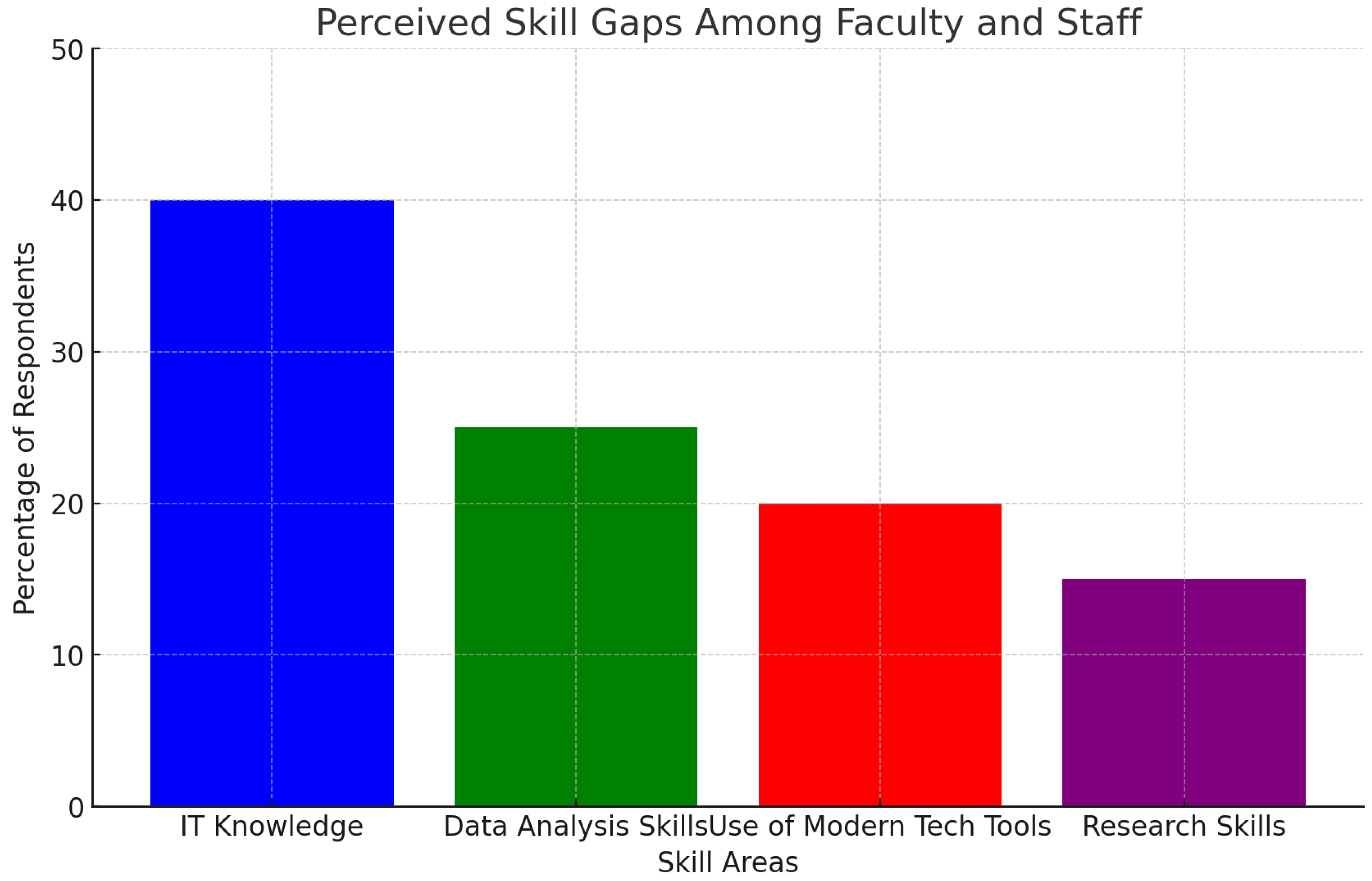
| Training Program | Frequency | Percentage |
| Workshops | 25 | 50% |
| Online Courses | 15 | 30% |
| Certification Programs | 5 | 10% |
| Industry Partnerships | 5 | 10% |
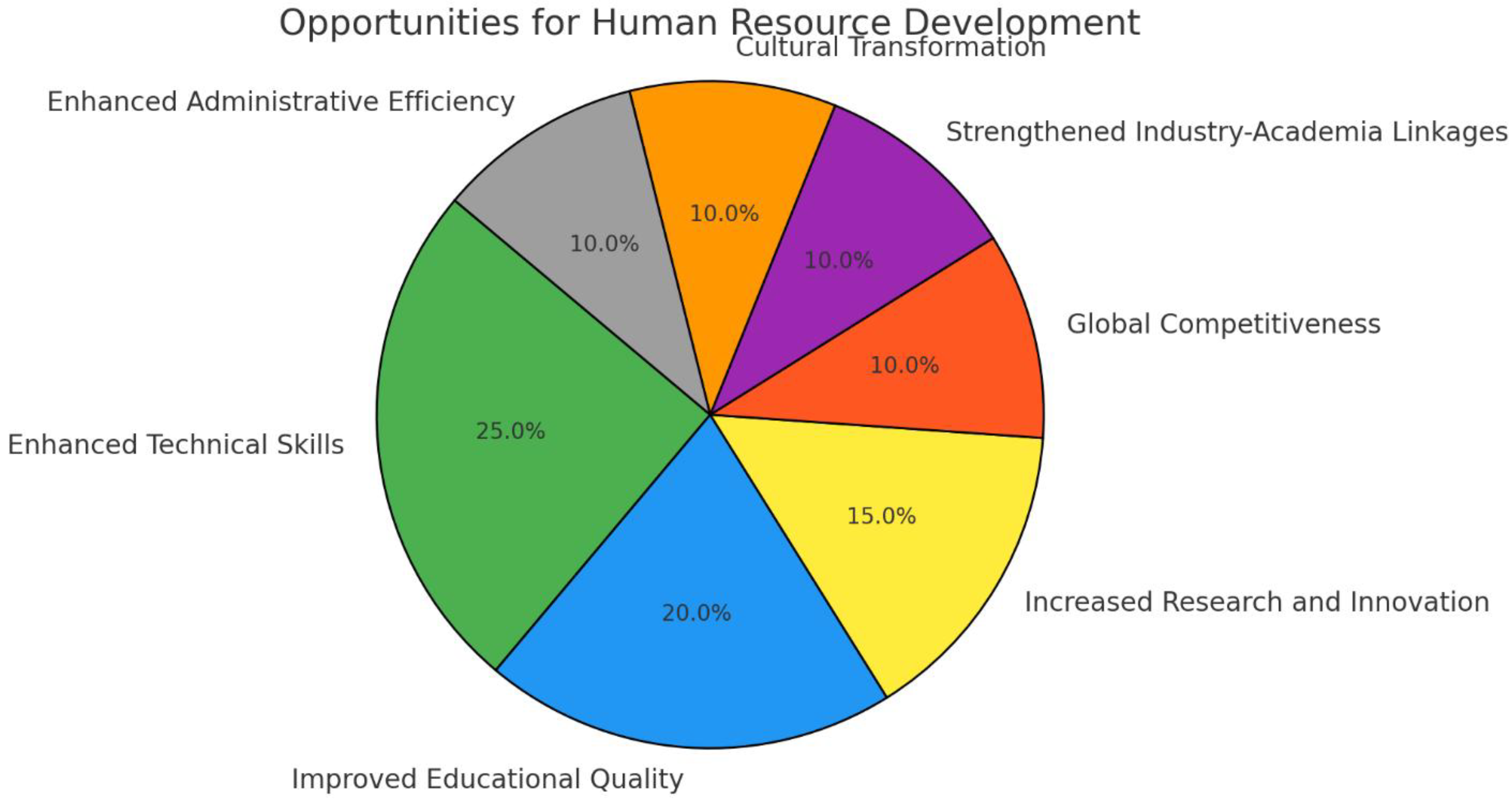
- Enhanced Technical Skills
- ○
- Training programs focused on Industry 4.0 technologies such as AI, IoT, big data, and robotics.
- ○
- Workshops and certification programs to develop specialized skills.
- ○
- Collaboration with industry partners for hands-on training and real-world applications.
- 2.
- Improved Educational Quality
- Implementation of smart classrooms equipped with advanced technological tools.
- Use of data analytics to personalize learning experiences and improve student outcomes.
- Adoption of e-learning platforms to provide flexible and accessible education.
- 3.
- Increased Research and Innovation
- Encouraging faculty and students to engage in research projects utilizing Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Establishing innovation labs and centers of excellence to foster creativity and experimentation.
- Securing grants and funding for research initiatives related to Industry 4.0.
- 4.
- Global Competitiveness
- Aligning educational programs with global standards to enhance the employability of graduates.
- Participating in international collaborations and exchange programs.
- Adopting best practices from leading educational institutions worldwide.
- 5.
- Strengthened Industry-Academia Linkages
- Developing partnerships with local and international industries to ensure curriculum relevance.
- Facilitating internships, co-op programs, and joint research initiatives.
- Establishing advisory boards with industry experts to guide educational strategies.
- 6.
- Cultural Transformation
- Promoting a culture of continuous learning and adaptability among faculty and staff.
- Encouraging the acceptance and integration of new technologies in everyday practices.
- Providing support and resources to overcome resistance to change.
- 7.
- Enhanced Administrative Efficiency
- Using digital tools for administrative tasks to improve efficiency and reduce paperwork.
- Implementing data-driven decision-making processes.
- Streamlining communication and collaboration through digital platforms.
- Green: Enhanced Technical Skills
- Blue: Improved Educational Quality
- Yellow: Increased Research and Innovation
- Red: Global Competitiveness
- Purple: Strengthened Industry-Academia Linkages
- Orange: Cultural Transformation
- Gray: Enhanced Administrative Efficiency
References
- Ashton, K. (2009). That ‘Internet of Things’ Thing. RFID Journal.
- Brynjolfsson, E., & McAfee, A. (2014). The Second Machine Age: Work, Progress, and Prosperity in a Time of Brilliant Technologies. W.W. Norton & Company.
- Chen, H., Chiang, R. H. L., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business Intelligence and Analytics: From Big Data to Big Impact. MIS Quarterly, 36(4), 1165-1188. [CrossRef]
- Heeks, R. (2002). Information Systems and Developing Countries: Failure, Success, and Local Improvisations. The Information Society, 18(2), 101-112. [CrossRef]
- Kagermann, H., Wahlster, W. and Helbig, J. (2013) Securing the Future of German Manufacturing Industry: Recommendations for Implementing the Strategic Initiative Industrie 4.0. Final Report of the Industrie 4.0 Working Group, Acatech— National Academy of Science and Engineering, 678 p.
- Joon-Kyung Kim, Sang Dal Shim, Jun-Il Kim (1995). The Role of the Government in Promoting Industrialization and Human Capital Accumulation in Korea, The National Bureau of Economic Research, (p. 181 - 200).
- Siciliano, B., & Khatib, O. (2016). Springer Handbook of Robotics. Springer.
- Bruno Siciliano, Oussama Khatib: Springer Handbook of Robotics. Springer Handbooks, Springer 2016, ISBN 978-3-319-32550-7.
- Almela, T. (2023). Impact of the Industry 4.0 on Higher Education. In: Al-Maadeed, M.A.S.A., Bouras, A., Al-Salem, M., Younan, N. (eds) The Sustainable University of the Future. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





