Submitted:
28 March 2025
Posted:
31 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Multimodal Data Integration: We propose a novel multimodal fall detection framework that integrates both skeleton and sensor data. This approach combines the strengths of both data modalities, addressing the limitations of unimodal systems and improving robustness, computational efficiency, and adaptability to different environments.
- Dual-Stream Architecture: The framework uses a Graph-based Spatial-Temporal Convolutional and Attention Neural Network (GSTCAN) to capture spatial and temporal relationships from skeleton and motion data. For sensor data, the system employs a Bi-LSTM integrated with CA. The Bi-LSTM captures long-range temporal dependencies, while the CA mechanism refines feature representations. This integration enhances feature extraction by capturing both spatial and temporal information and improving the model’s sensitivity to important features.
- Feature Fusion for Improved Classification: The features extracted from the GSTCAN for skeleton and motion data, as well as Bi-LSTM-CA branches for sensor data, are fused and passed through a fully connected layer for classification. This fusion allows the system to leverage complementary information from both streams, improving the overall understanding of human motion and increasing fall detection accuracy.
- State-of-the-Art Performance: The proposed system was rigorously evaluated on the Fall Up dataset, achieving a classification accuracy of 99.09%, significantly outperforming existing methods. This demonstrates the system’s robust performance and its potential for real-time fall detection and continuous healthcare monitoring.
2. Related Work
2.1. Inertial Sensor-Based Fall Detection Systems
2.2. Video-Based Fall Detection System
2.3. Using Multimodal Features Fall Detection System
3. Datasets
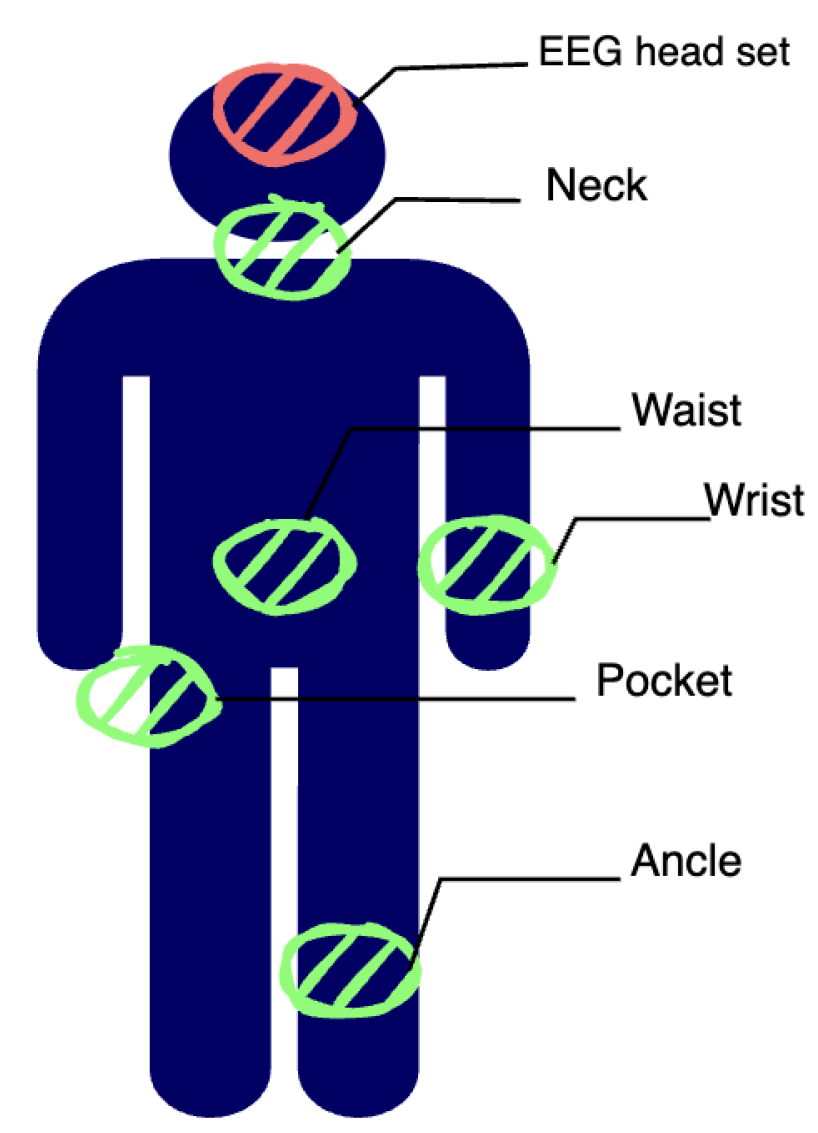
3.1. Fall UP Dataset
3.2. UR-Fall Dataset
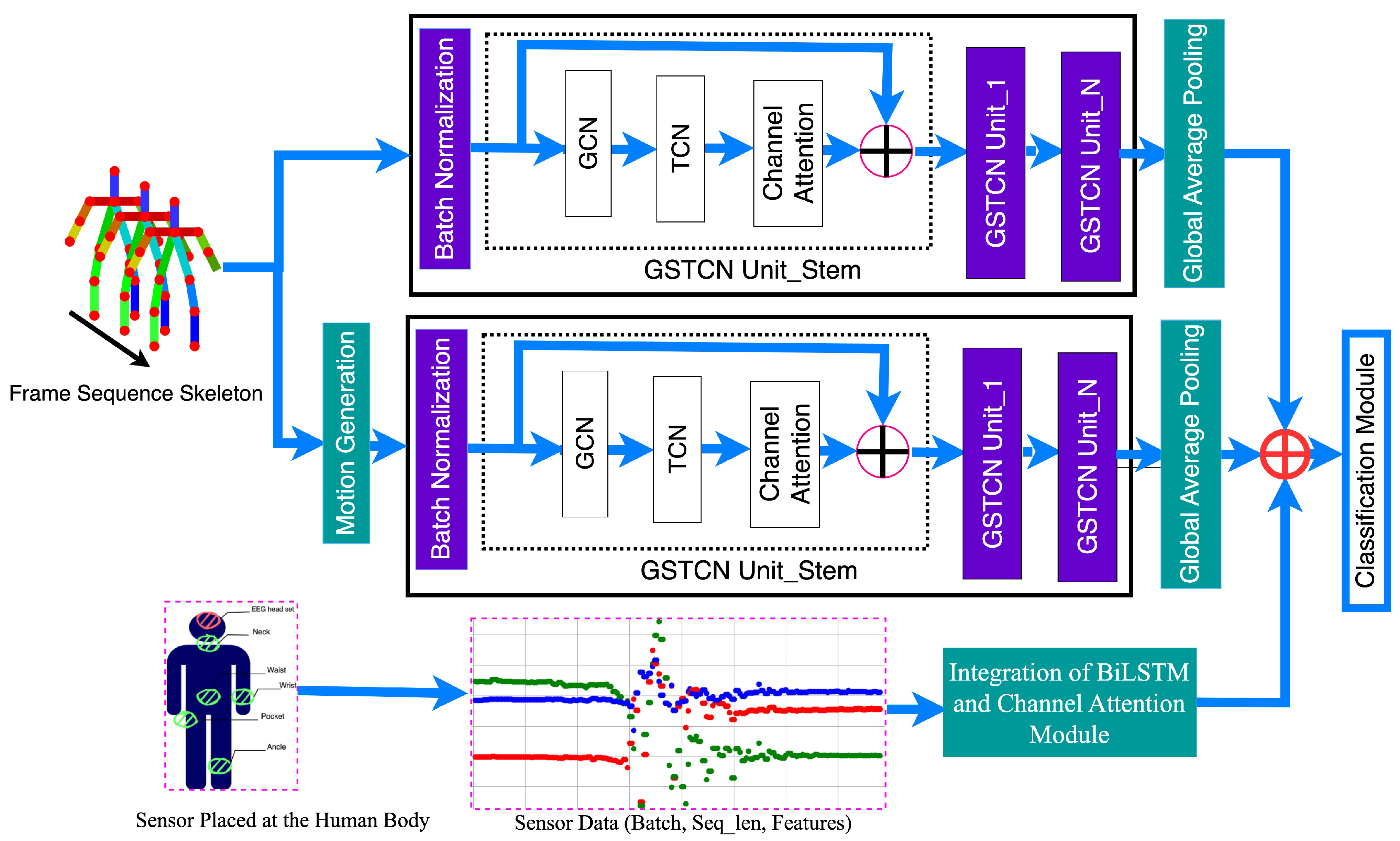
4. Proposed Methodology
4.1. Stream-1 Skeleton-Based GCN
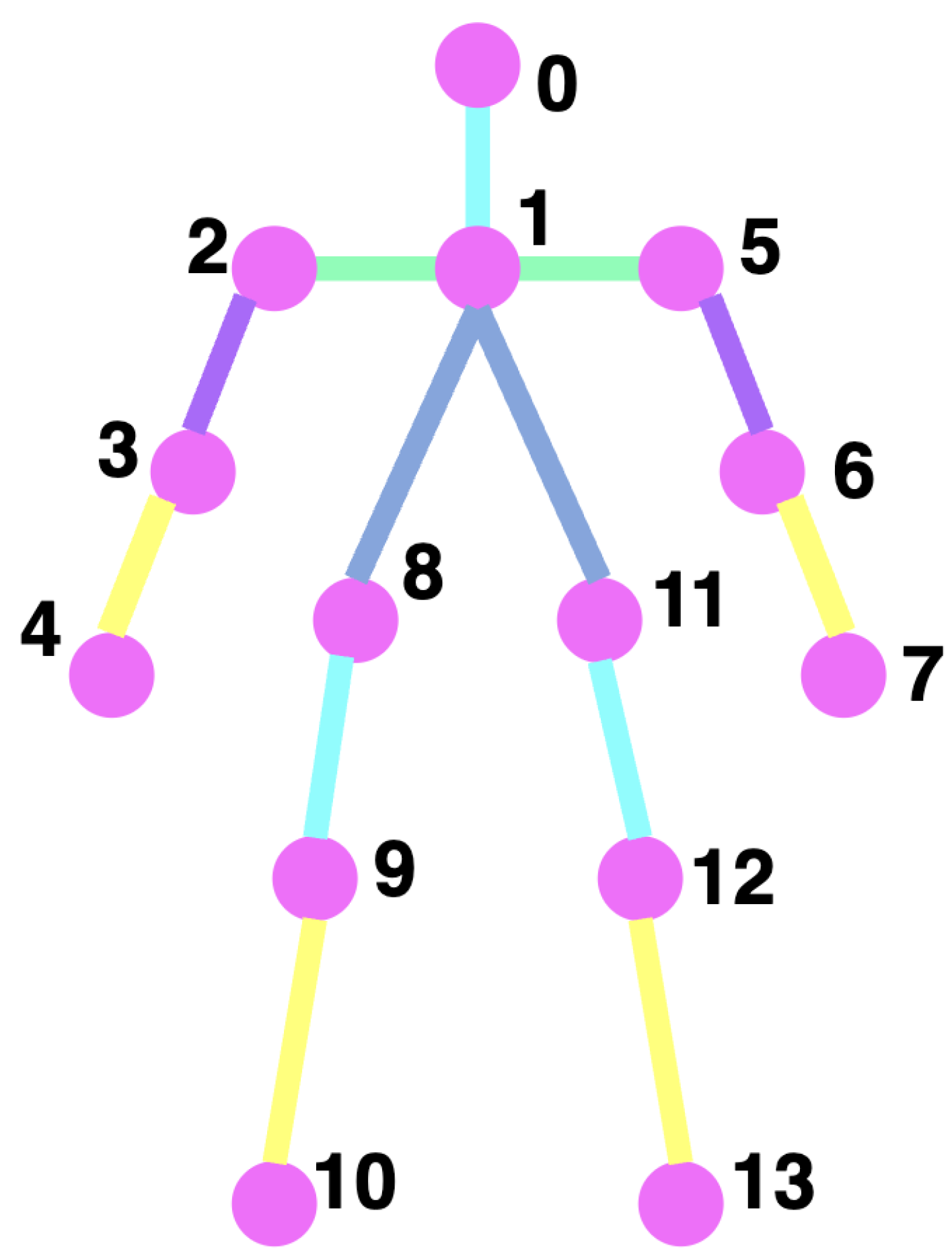
4.2. Data Extraction Using Alphapose
4.2.1. Motion Calculation and Graph Construction
4.2.2. Graph Convolutional Network (GCN)
4.3. Skeleton Feature Using GSTCAN
4.4. Motion Feature Using GSTCAN
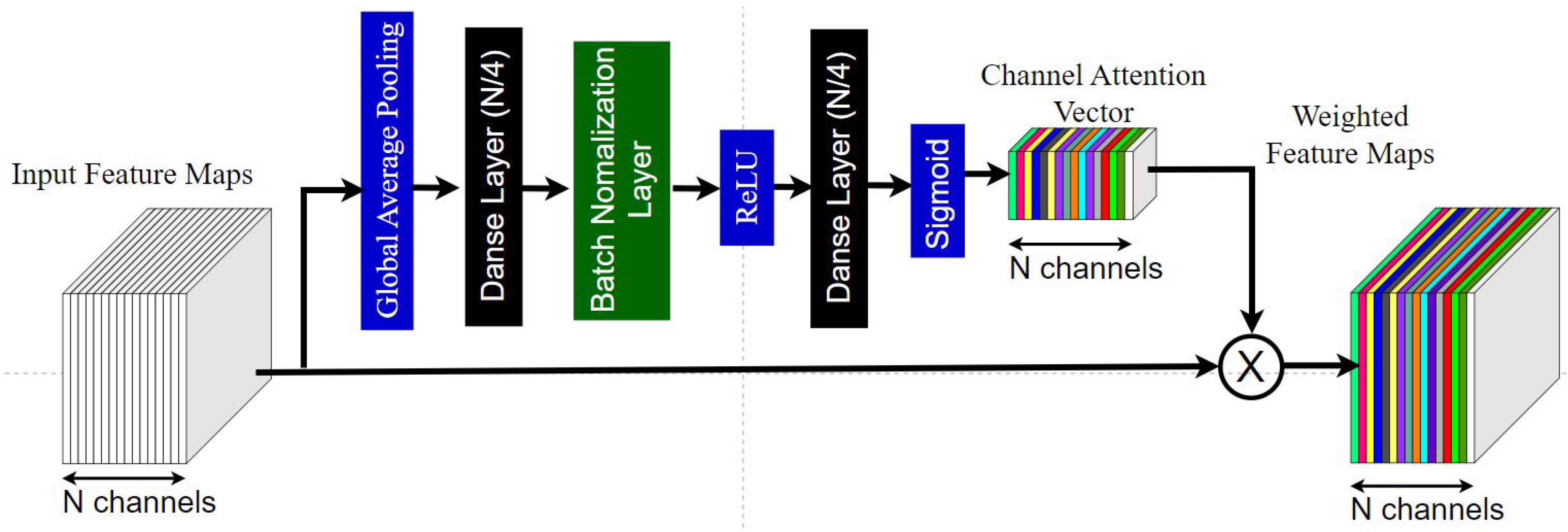
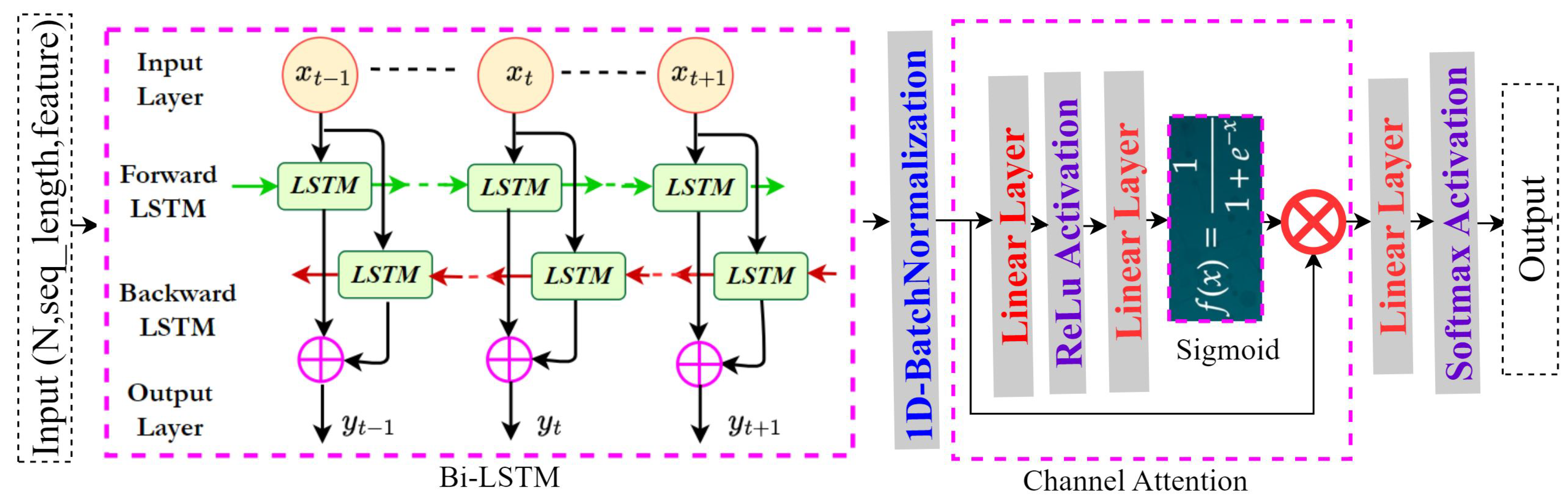
4.5. Stream-2: Sensor Stream Methodology - Bi-LSTM Integration with Channel Attention (CA) Model
4.5.1. Bi-LSTM and Channel Attention Integration
4.5.2. Model Derivation
4.6. Multimodal Feature Fusion and Classification
5. Experimental Evaluation
5.1. Environmental Setting
5.2. Ablation Study
5.2.1. Ablation Study with UP-Fall Dataset
5.2.2. Ablation Study with UR-Fall Dataset
5.3. Performance Result of the Proposed Model with UP-Fall Dataset
5.4. State of the Art Comparison for UP-FAll Dataset
5.5. Performance Result of the Proposed Model with UR-FAll Dataset
5.6. State of the Art Comparison for the UR-FALL Multimodal Dataset
5.7. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Health, L.; Welfare. Fall Accidents. [Accessed: 08 January 2025].
- NCGG. What makes it easier to fall? [Accessed: 08 January 2025].
- Semwal, V.B.; Katiyar, S.A.; Chakraborty, R.; Nandi, G.C. Biologically-inspired push recovery capable bipedal locomotion modeling through hybrid automata. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2015, 70, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Falls. [Accessed: 08 January 2025].
- Naja, S.; Makhlouf, M.; Chehab, M.A.H. An ageing world of the 21st century: a literature review. Int J Community Med Public Health 2017, 4, 4363–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, L.; Marani, R.; Petitti, A.; Milella, A.; D’Orazio, T.; Cicirelli, G. Image-Based Mobility Assessment in Elderly People from Low-Cost Systems of Cameras: A Skeletal Dataset for Experimental Evaluations. In Proceedings of the Ad-Hoc, Mobile, and Wireless Networks; Grieco, L.A.; Boggia, G.; Piro, G.; Jararweh, Y.; Campolo, C., Eds. Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 125–130.
- Azmat, U.; Jalal, A. Smartphone inertial sensors for human locomotion activity recognition based on template matching and codebook generation. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Communication Technologies (ComTech). IEEE; 2021; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Horn, B.K. Video-based fall detection for seniors with human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th international conference on Universal Village (UV). IEEE; 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmughapriya, M.; Gunasundari, S.; Bharathy, S. Loitering detection in home surveillance system. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology-Signal and Information Processing (ICETET-SIP-22). IEEE; 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, F.; Jalal, A. Semantic segmentation based crowd tracking and anomaly detection via neuro-fuzzy classifier in smart surveillance system. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 2023, 48, 2173–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.V.; Nguyen, H.; Huynh, S.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, B.T. Fall detection using multimodal data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling. Springer; 2022; pp. 392–403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Bazarevsky, V.; Vakunov, A.; Tkachenka, A.; Sung, G.; Chang, C.L.; Grundmann, M. Mediapipe hands: On-device real-time hand tracking. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10214 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Villaseñor, L.; Ponce, H.; Brieva, J.; Moya-Albor, E.; Núñez-Martínez, J.; Peñafort-Asturiano, C. UP-fall detection dataset: A multimodal approach. Sensors 2019, 19, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadi, Y.; Javeed, M.; Alarfaj, M.; Shloul, T.; Alsuhibany, S.; Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D.S. MS-DLD: Multi-sensors based daily locomotion detection via kinematic-static energy and body-specific HMMs. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 23964–23979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Joint distance maps based action recognition with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.M.; Tran, L.V.; Dao, S.V.T. A feature selection approach for fall detection using various machine learning classifiers. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 115895–115908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Huang, G.; Yu, M.; Guo, Y. Fall prediction based on key points of human bones. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2020, 540, 123205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubashir, M.; Shao, L.; Seed, L. A survey on fall detection: Principles and approaches. Neurocomputing 2013, 100, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucerquia, A.; López, J.D.; Vargas-Bonilla, J.F. Real-life/real-time elderly fall detection with a triaxial accelerometer. Sensors 2018, 18, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucerquia, A.; López, J.D.; Vargas-Bonilla, J.F. SisFall: A fall and movement dataset. Sensors 2017, 17, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Mane, P.; Dsilva, M.; Zare, A.; Shingala, P.; Ambawade, D. A novel machine learning based wearable belt for fall detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON). IEEE; 2020; pp. 502–505. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, F.; Hussain, F.; Ehatisham-ul Haq, M.; Azam, M.A. Activity-Aware Fall Detection and Recognition Based on Wearable Sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal 2019, 19, 4528–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fula, V.; Moreno, P. Wrist-based fall detection: towards generalization across datasets. Sensors 2024, 24, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casilari, E.; Santoyo-Ramón, J.A.; Cano-García, J.M. Umafall: A multisensor dataset for the research on automatic fall detection. Procedia Computer Science 2017, 110, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.; Moreno, P. Online Fall Detection Using Wrist Devices. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Villaseñor, L.; Ponce, H.; Brieva, J.; Moya-Albor, E.; Núñez-Martínez, J.; Peñafort-Asturiano, C. UP-Fall Detection Dataset: A Multimodal Approach. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maray, N.; Ngu, A.H.; Ni, J.; Debnath, M.; Wang, L. Transfer Learning on Small Datasets for Improved Fall Detection. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Shin, J.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Rahim, M.A. BenSignNet: Bengali Sign Language Alphabet Recognition Using Concatenated Segmentation and Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Jang, S.W.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, J. Multi-Stream General and Graph-Based Deep Neural Networks for Skeleton-Based Sign Language Recognition. Electronics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, Abu Saleh Musa, S.J.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Rahim, M.A.; Okuyama, Y. Rotation, Translation And Scale Invariant Sign Word Recognition Using Deep Learning. Computer Systems Science and Engineering 2023, 44, 2521–2536. [CrossRef]
- Juang, L.H.; Wu, M.N. Fall down detection under smart home system. Journal of medical systems 2015, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Zhao, H.; Min, W.; Cui, H.; Zhou, X.; Zuo, K.; Liu, R. A Two-Stream Approach to Fall Detection With MobileVGG. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 17556–17566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, T. Fall detection for elderly person care using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th international congress on image and signal processing, biomedical engineering and informatics (CISP-BMEI). IEEE; 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Wu, Y.; Feng, L.; Song, J. Deep Learning for Fall Detection: Three-Dimensional CNN Combined With LSTM on Video Kinematic Data. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2019, 23, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, T.; Muhammad, G. Human Fall Detection Using 3D Multi-Stream Convolutional Neural Networks with Fusion. Diagnostics 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiyue.; Wei. An Improved Feature-Based Method for Fall Detection. Tehnicki vjesnik - Technical Gazette, 2019.
- Tsai, T.H.; Hsu, C.W. Implementation of Fall Detection System Based on 3D Skeleton for Deep Learning Technique. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 153049–153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, Y. Lightweight Fall Detection Algorithm Based on AlphaPose Optimization Model and ST-GCN. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2022, 2022, 9962666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, S.; Kolawole, S.S.; Naz, A.; Gong, L.; Ahmed, S.W.; Prasad, P.S.; Yu, M.; Wingate, J.; Ardakani, S.P. Computer Vision Based Transfer Learning-Aided Transformer Model for Fall Detection and Prediction. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 28798–28809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inturi, A.R.; Manikandan, V.M.; Kumar, M.N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Synergistic Integration of Skeletal Kinematic Features for Vision-Based Fall Detection. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Saha, A.; Kumar, P.; Pal, G. Fall detection approach based on combined two-channel body activity classification for innovative indoor environment. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2022, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, Y.M.; Portela, L.; Ferreira, J.; Barros, P.; De Araújo Fagundes, O.A.; Fernandes, B.J.T. A Framework for Anomaly Identification Applied on Fall Detection. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 77264–77274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahan, S.; Hassan, G.M.; Mian, A. SDFA: Structure-Aware Discriminative Feature Aggregation for Efficient Human Fall Detection in Video. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2023, 19, 8713–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, R.; Miah, A.S.M.; Hirooka, K.; Tomioka, Y.; Shin, J. Dynamic Fall Detection Using Graph-Based Spatial Temporal Convolution and Attention Network. Electronics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahyati, D.; Hawari, R. Fall Detection on Multimodal Dataset using Convolutional Neural Netwok and Long Short Term Memory. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems (ICACSIS); 2020; pp. 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Nooruddin, S.; Karray, F. Multimodal Human Activity Recognition for Smart Healthcare Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC); 2022; pp. 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Alshouiliy, K.; Agrawal, D.P. Dimensionality reduction for human activity recognition using google colab. Information 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwolek, B.; Kepski, M. Human fall detection on embedded platform using depth maps and wireless accelerometer. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine 2014, 117, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igual, R.; Medrano, C.; Plaza, I. Challenges, issues and trends in fall detection systems. Biomedical engineering online 2013, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Conly, C.; Athitsos, V. Athitsos, V. A survey on vision-based fall detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 8th ACM international conference on PErvasive technologies related to assistive environments, 2015, pp.
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial, temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2018, Vol.
- Zheng, H.; Liu, Y. Lightweight fall detection algorithm based on AlphaPose optimization model and ST-GCN. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskes, O.; Noumeir, R. Vision-based fall detection using st-gcn. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 28224–28236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.; Miah, A.S.M.; Suzuki, T.; Shin, J. Gradual Variation-Based Dual-Stream Deep Learning for Spatial Feature Enhancement With Dimensionality Reduction in Early Alzheimer’s Disease Detection. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 31701–31717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.S.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.; Xiu, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Lu, C. AlphaPose: Whole-Body Regional Multi-Person Pose Estimation and Tracking in Real-Time. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Shin, J. Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition using Multi-Branch Attention Based Graph and General Deep Learning Model. IEEE Access 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Nishimura, S.; Shin, J. Sign Language Recognition Using Graph and General Deep Neural Network Based on Large Scale Dataset. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 34553–34569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Miah, A.S.M.; Suzuki, K.; Hirooka, K.; Hasan, M.A.M. Dynamic Korean Sign Language Recognition Using Pose Estimation Based and Attention-Based Neural Network. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 143501–143513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Miah, A.S.M.; Suzuki, K.; Okuyama, Y.; Shin, J. Stacked CNN-based multichannel attention networks for Alzheimer disease detection. Scientific Reports 2025, 15, 5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Shin, J.; Okuyama, Y.; Tomioka, Y. Multistage Spatial Attention-Based Neural Network for Hand Gesture Recognition. Computers 2023, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Okuyama, Y.; Tomioka, Y.; Shin, J. Spatial–temporal attention with graph and general neural network-based sign language recognition. Pattern Analysis and Applications 2024, 27, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, S.Z.; Amin, M.G. Radar-Based Human-Motion Recognition With Deep Learning: Promising Applications for Indoor Monitoring. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2019, 36, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Kernec, J.; Fioranelli, F.; Ding, C.; Zhao, H.; Sun, L.; Hong, H.; Lorandel, J.; Romain, O. Radar Signal Processing for Sensing in Assisted Living: The Challenges Associated With Real-Time Implementation of Emerging Algorithms. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2019, 36, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Miah, A.S.M.; Shin, J. A deep bidirectional LSTM model enhanced by transfer-learning-based feature extraction for dynamic human activity recognition. Applied Sciences 2024, 14, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Schmidhuber, J. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Networks 2005, 18, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, A.; Mohamed, A.r.; Hinton, G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing. Ieee; 2013; pp. 6645–6649. [Google Scholar]
- Hafeez, S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Alazeb, A.; Mudawi, N.A.; Kim, W. Multi-Sensor-Based Action Monitoring and Recognition via Hybrid Descriptors and Logistic Regression. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 48145–48157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssfi Alaoui, A.; Tabii, Y.; Oulad Haj Thami, R.; Daoudi, M.; Berretti, S.; Pala, P. Fall detection of elderly people using the manifold of positive semidefinite matrices. Journal of Imaging 2021, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Han, G. Vision-based fall detection with multi-task hourglass convolutional auto-encoder. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 44493–44502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Ye, M. Vision-based fall event detection in complex background using attention guided bi-directional LSTM. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161337–161348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.H.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Bao, X.Y.; Mao, K.M. Fall detection based on dual-channel feature integration. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 103443–103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class No | Class Description | Class No | Class Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Falling forward using knees | 7 | Standing |
| 2 | Falling forward using hands | 8 | Sitting |
| 3 | Falling backward | 9 | Picking up an object |
| 4 | Falling sideward | 10 | Jumping |
| 5 | Falling sitting in an empty chair | 11 | Laying |
| 6 | Walking |
| Ablation | Stream-1 Skeleton | Stream-2 Sensor | Result with UR-FALL (10 fold mean) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes or No Stream-1 | No of GSTCN Skeleton | Yes or No Stream-2 | Model Name | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score | |
| 1 | No | - | Yes | Only CNN | 97.78 | 93.79 | 92.92 | 93.02 |
| 2 | No | - | Yes | Bi-LSTM with CNN | 99.04 | 96.92 | 97.24 | 96.91 |
| 3 | No | - | Yes | Bi-LSTM with Channel Attention | 99.07 | 96.63 | 97.21 | 96.75 |
| 4 | Yes | 3 | No | - | 91.57 | - | - | - |
| 5 | Yes | 4 | No | - | 91.56 | - | - | - |
| 6 | Yes | 6 | No | - | 91.86 | - | - | - |
| 7 | Yes | 9 | No | - | 91.67 | - | - | - |
| 8 | Yes | 3 | Yes | Bi-LSTM with Channel Attention | 98.53 | - | - | - |
| 8 | Yes | 9 | Yes | Bi-LSTM with Channel Attention | 98.66 | - | - | - |
| 9 | Yes | 6 | Yes | Bi-LSTM with Channel Attention | 99.09 | 97.06 | 97.18 | 96.99 |
| Ablation | Stream-1 | Stream-2 | Result with UR-FALL (10 fold mean) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Num of GSTCN | BiLSTM-CNN | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 99.14 | 99.06 | 99.041 | 99.04 |
| 2 | 4 | 1 | 99.15 | 99.19 | 98.81 | 98.99 |
| 3 | 5 | 1 | 99.24 | 99.12 | 99.19 | 99.15 |
| 4 | 6 | 1 | 99.16 | 99.20 | 98.48 | 98.82 |
| 5 | 9 | 1 | 99.32 | 99.23 | 99.19 | 99.21 |
| Fold | Accuracy [%] | Precision [%] | Recall [%] | F1-Score [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k = 1 | 99.35 | 98.65 | 98.29 | 98.45 |
| 2 | 99.44 | 98.25 | 98.15 | 98.14 |
| 3 | 99.45 | 97.48 | 98.28 | 97.84 |
| 4 | 99.58 | 98.90 | 98.67 | 98.76 |
| 5 | 98.2 | 94.62 | 95.16 | 94.86 |
| 6 | 98.96 | 95.97 | 97.20 | 96.31 |
| 7 | 98.75 | 96.46 | 96.25 | 96.15 |
| 8 | 98.42 | 95.79 | 95.44 | 95.43 |
| 9 | 99.38 | 97.69 | 97.27 | 97.38 |
| 10 | 99.33 | 96.83 | 97.08 | 96.67 |
| Average | 99.09 | 97.064 | 97.18 | 96.99 |
| Author | Data Modality | Method Name | Accuracy [%] | Precision [%] | Recall [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Martínez et al. [13] | Multi-Sensor | SVM (IMU)+EEG System | 90.77 | - | - |
| Ghadi et al. [14] | Multi-Sensor | MS-DLD System | 88.75 | - | - |
| Le et al. [16] | Multi-Sensor | Naive Bayes Classifier | 88.61 | - | - |
| Li et al. [15] | Skelton | JDM | 88.10 | - | - |
| Hafeez et al. [69] | Skeleton+Multi-Sensor | Logistic Regression (LR) | 91.51 | 90.00 | 91.00 |
| Our Proposed System | Sensor+Skeleton | Two-Stream DNN | 99.09 | 97.06 | 97.18 |
| Fold | Accuracy [%] | Precision [%] | Recall [%] | F1-Score [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 99.31 | 99.53 | 98.70 | 99.11 |
| 3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 4 | 99.68 | 99.80 | 99.23 | 99.51 |
| 5 | 96.69 | 96.68 | 96.71 | 96.68 |
| 6 | 99.68 | 99.17 | 99.80 | 99.48 |
| 7 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 8 | 99.42 | 98.65 | 99.63 | 99.13 |
| 9 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 10 | 98.38 | 98.47 | 97.83 | 98.14 |
| Average | 99.32 | 99.23 | 99.19 | 99.21 |
| Author | Data Modality | Method Name | Accuracy [%] | Precision [%] | Recall [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kwolek [49] | Depth | SVM | 94.28 | - | - |
| Youssfi [70] | Skeleton | SVM | 96.55 | - | - |
| Cai [71] | - | HCAE | 90.50 | - | - |
| Chen et al. [72] | RGB | Bi-LsTM | 96.70 | - | - |
| Zheng [53] | Skeleton | 97.28 | 97.15 | 97.43 | |
| Wang [73] | Keypoints | - | 97.33 | 97.78 | 97.78 |
| Our Proposed System | Sensor+Skeleton | Two-Stream DNN | 99.32 | 99.23 | 99.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).