Submitted:
26 March 2025
Posted:
28 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Brief Description of the Analysed Groups
The FMSF Methodology
Statistical Analysis
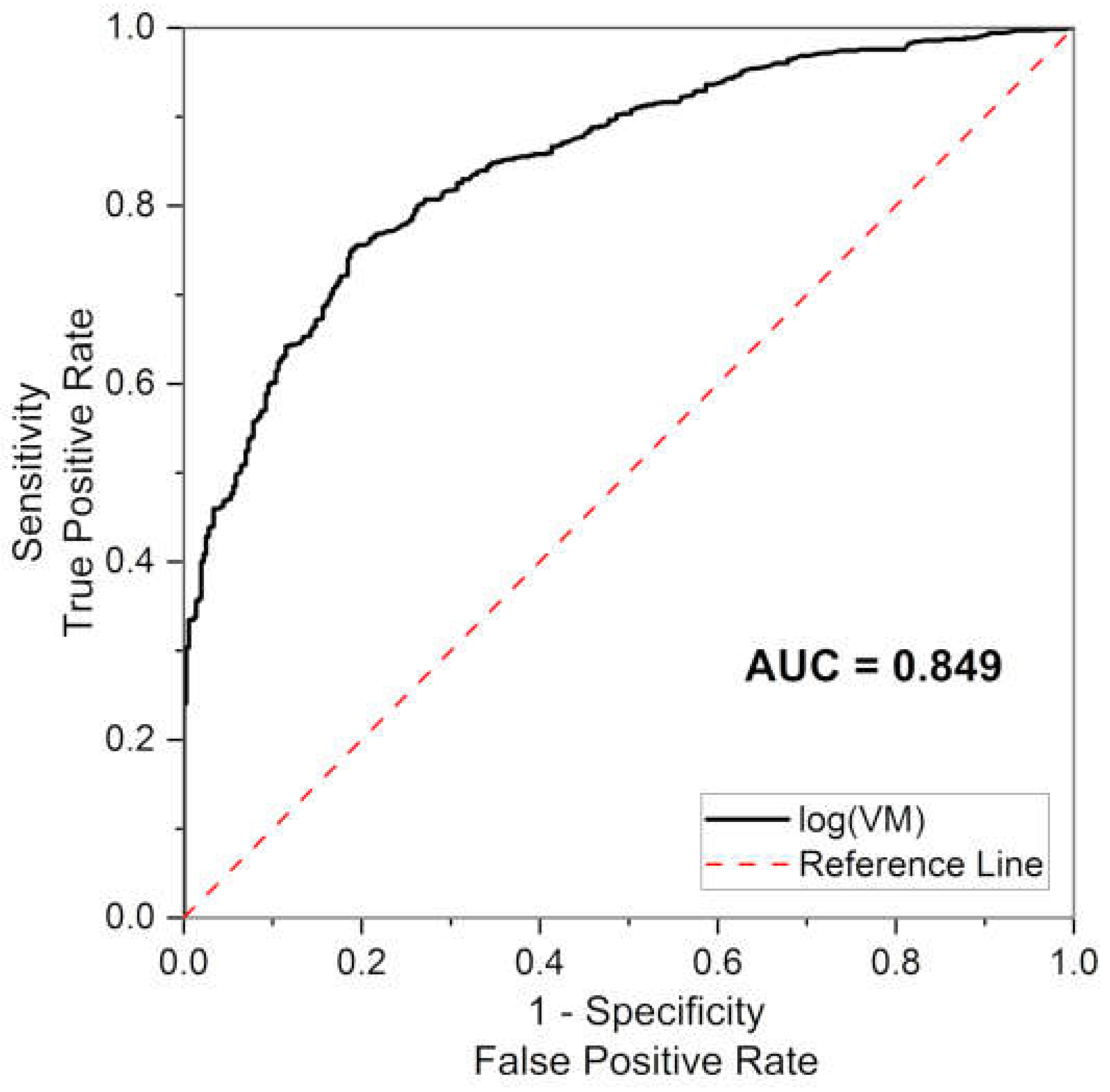
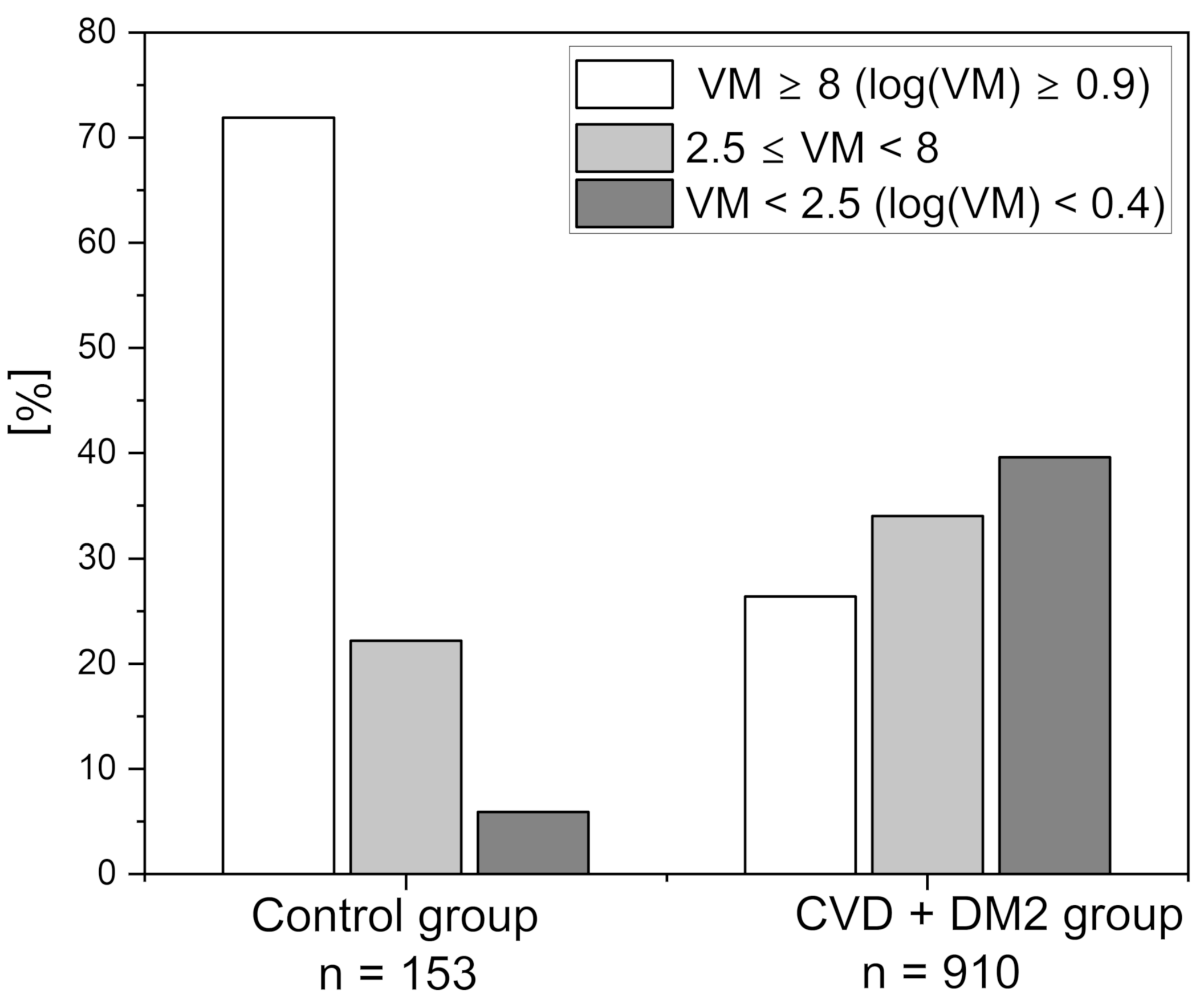
3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nilsson, H.; Aalkjaer, C. Vasomotion: Mechanisms and Physiological Importance. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalkjær, C.; Boedtkjer, D.; Matchkov, V. Vasomotion – What Is Currently Thought? Acta Physiol. 2011, 202, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.-S.; Lee, M.-G. Rescue Effect of Exercise on Impaired Arteriolar Myogenic Response with Advancing Age. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 26, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, I.; Larsson, M.; Strömberg, T.; Iredahl, F. Vasomotion Analysis of Speed Resolved Perfusion, Oxygen Saturation, Red Blood Cell Tissue Fraction, and Vessel Diameter: Novel Microvascular Perspectives. Ski. Res. Technol. 2022, 28, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Son, S.-M.; Choi, S.-Y.; Koo, B.; Rah, C.-S.; Nam, J.H.; Ju, M.J.; Lee, J.S.; You, R.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, J.; Bae, J.-W.; Kim, C.H.; Choi, W.; Kim, H.S.; Xu, W.-X.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Yun, H.-Y. Vasomotion in Human Arteries and Their Regulations Based on Ion Channel Regulations: 10 Years Study. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 2076–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Carpi, A.; Galetta, F.; Franzoni, F.; Santoro, G. The Investigation of Skin Blood Flowmotion: A New Approach to Study the Microcirculatory Impairment in Vascular Diseases? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruning, R.S.; Kenney, W.L.; Alexander, L.M. Altered Skin Flowmotion in Hypertensive Humans. Microvasc. Res. 2015, 97, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, I.V.; Kosyakova, N.I.; Tankanag, A.V.; Chemeris, N.K. Oscillations of Skin Microvascular Blood Flow in Patients with Asthma. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizeva, I.; Makovik, I.; Dunaev, A.; Krupatkin, A.; Meglinski, I. Analysis of Skin Blood Microflow Oscillations in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebicki, J.; Katarzynska, J.; Cholewinski, T.; Sieron, L.; Marcinek, A. Flowmotion Monitored by Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF): A Tool for Characterization of Microcirculatory Status. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovska, A.; Bracic, M.; Kvernmo, H.D. Wavelet Analysis of Oscillations in the Peripheral Blood Circulation Measured by Laser Doppler Technique. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 46, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.; Roustit, M.; Cracowski, J.L. Skin Microvascular Endothelial Function as a Biomarker in Cardiovascular Diseases? Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cracowski, J.-L.; Roustit, M. Current Methods to Assess Human Cutaneous Blood Flow: An Updated Focus on Laser-Based-Techniques. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cracowski, J.-L.; Roustit, M. Human Skin Microcirculation. In Comprehensive Physiology; Prakash, Y.S., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Chapter 3; Volume 10, pp. 1105–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, E.; Marczyk, B.; Chukwu, O.; Chlopicki, S.; Sacha, T. Endothelial Function in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Is Not Related to Cardiovascular Risk Assessed by the Systematic Coronary Risk Estimation 2 Algorithm. Polish Arch. Intern. Med. 2024, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvernmo, H.D.; Stefanovska, A.; Kirkebøen, K.A.; Kvernebo, K. Oscillations in the Human Cutaneous Blood Perfusion Signal Modified by Endothelium-Dependent and Endothelium-Independent Vasodilators. Microvasc. Res. 1999, 57, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvandal, P.; Landsverk, S.A.; Bernjak, A.; Stefanovska, A.; Kvernmo, H.D.; Kirkebøen, K.A. Low-Frequency Oscillations of the Laser Doppler Perfusion Signal in Human Skin. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 72, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderström, T.; Stefanovska, A.; Veber, M.; Svensson, H. Involvement of Sympathetic Nerve Activity in Skin Blood Flow Oscillations in Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H1638–H1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalkjaer, C.; Nilsson, H. Vasomotion: Cellular Background for the Oscillator and for the Synchronization of Smooth Muscle Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cracowski, J.-L.; Minson, C.T.; Salvat-Melis, M.; Halliwill, J.R. Methodological Issues in the Assessment of Skin Microvascular Endothelial Function in Humans. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.M.; Indu, T.; Michael, S., G.; and Medow, M.S. Noninvasive Measure of Microvascular Nitric Oxide Function in Humans Using Very Low-Frequency Cutaneous Laser Doppler Flow Spectra. Microcirculation 2007, 14, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, G.J.; Mallette, M.M.; Martin, Z.T.; Del Pozzi, A.T. Effect of Sympathetic Nerve Blockade on Low-Frequency Oscillations of Forearm and Leg Skin Blood Flow in Healthy Humans. Microcirculation 2017, 24, e12388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Schalkwijk, C.; Kroon, A.; Schram, M.T.; Stehouwer, C.; Houben, A. Different Measures of Hyperglycemia Are Negatively Associated With Skin Microvascular Flowmotion: The Maastricht Study. Microcirculation 2024, 31, e12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarzynska, J.; Lipinski, Z.; Cholewinski, T.; Piotrowski, L.; Dworzynski, W.; Urbaniak, M.; Borkowska, A.; Cypryk, K.; Purgal, R.; Marcinek, A.; Gebicki, J. Non-Invasive Evaluation of Microcirculation and Metabolic Regulation Using Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF): Technical Aspects and Methodology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.; Tarnawska, M.; Dudziak, M.; Dorniak, K.; Roustit, M.; Cracowski, J.L. Reproducibility of Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence to Assess Microvascular Function. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 113, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnawska, M.; Dorniak, K.; Kaszubowski, M.; Dudziak, M.; Hellmann, M. A Pilot Study with Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence: A Novel Device to Assess Microvascular Endothelial Function in Coronary Artery Disease. Cardiol. J. 2018, 25, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinek, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Sieron, L.; Skokowski, R.; Zielinski, J.; Gebicki, J. Non-Invasive Assessment of Vascular Circulation Based on Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF). Biology. 2023, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinek, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Gebicki, J. A New Approach to Vascular Screening: Identification of Impaired Vascular Function Using the FMSF Technique. Sensors. 2024, 24, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinek, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Gebicki, J. Simultaneous Assessment of Mitochondrial and Vascular Function Using the Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence Technique. Front. Physiol. 2025, 16, 1509159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, W.C.; Gordon, G.R.; Braun, A.P. Cellular and Ionic Mechanisms of Arterial Vasomotion. In Smooth Muscle Spontaneous Activity: Physiological and Pathological Modulation; Hashitani, H., Lang, R.J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2019; Volume 1124, pp. 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Bi, T.; Du, G.; Yan, L.; Hou, H. Dynamic Non-Invasive Detection of NADH Based on Blood Flow-Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF) Method. Open J. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1437–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Xie, H.; Ruan, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Shi, H.; Jia, J.-M. Ca2+ Oscillation in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Control Myogenic Spontaneous Vasomotion and Counteract Post-Ischemic No-Reflow. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, C.E.; Shore, A.C. The Role of Perfusion in the Oxygen Extraction Capability of Skin and Skeletal Muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H1277–H1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.; Gilbert-Kawai, E.; Wythe, S.; Meale, P.; Mythen, M.; Levett, D.; Mitchell, K.; Grocott, M.; Clough, G.; Martin, D.; Group, for the X. E. 2 R. Sustained Vasomotor Control of Skin Microcirculation in Sherpas versus Altitude-Naive Lowlanders: Experimental Evidence from Xtreme Everest 2. Exp. Physiol. 2018, 103, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, D.; Thanaj, M.; Davies, T.; Gilbert-Kawai, E.; Mitchell, K.; Levett, D.Z.H.; Mythen, M.G.; Martin, D.S.; Grocott, M.P.; Chipperfield, A.J.; Clough, G.F. Enhanced Flow-Motion Complexity of Skin Microvascular Perfusion in Sherpas and Lowlanders during Ascent to High Altitude. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, P.; Faini, A.; Castiglioni, P.; Brunacci, F.; Montaguti, L.; Severi, F.; Gautier, S.; Pretolani, E.; Benetos, A.; Parati, G. Increase in Slow-Wave Vasomotion by Hypoxia and Ischemia in Lowlanders and Highlanders. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikosiński, J.; Mikosiński, P.; Kwapisz, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Gebicki, J. Conclusions from an Observational Study of Patients with Vascular Diseases Using the FMSF Technique. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katarzynska, J.; Borkowska, A.; Czajkowski, P.; Los, A.; Szczerbinski, L.; Milewska-Kranc, A.; Marcinek, A.; Kretowski, A.; Cypryk, K.; Gebicki, J. Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence Technique Reveals Remarkable Effect of Age on Microcirculation and Metabolic Regulation in Type 1 Diabetes. Microvasc. Res. 2019, 124, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarzynska, J.; Borkowska, A.; Los, A.; Marcinek, A.; Cypryk, K.; Gebicki, J. Flow-Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF) Technique for Studying Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 693–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaj, O.; Zieliński, J.; Kusy, K.; Kantanista, A.; Wieliński, D.; Guzik, P. The Effect of Exercise on the Skin Content of the Reduced Form of NAD and Its Response to Transient Ischemia and Reperfusion in Highly Trained Athletes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaj, O.; Kusy, K.; Kantanista, A.; Korman, P.; Wieliński, D.; Zieliński, J. The Effect of a 7-Week Training Period on Changes in Skin NADH Fluorescence in Highly Trained Athletes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudzik, M.; Cender, A.; Mordaka, R.; Zieliński, J.; Katarzyńska, J.; Marcinek, A.; Gebicki, J. Chronic Fatigue Associated with Post-COVID Syndrome versus Transient Fatigue Caused by High-Intensity Exercise: Are They Comparable in Terms of Vascular Effects? Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Walczak-Jedrzejowska, R.; Adamczewska, D.; Byczkiewicz, P.; Marchlewska, K.; Katarzynska, J.; Gebicki, J. A New Approach to the Assessment of Erectile Dysfunction Based on Vasomotion Monitored by the Flow-Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF) Technique—A Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jewell, U.R.; Kvietikova, I.; Scheid, A.; Bauer, C.; Wenger, R.H.; Gassmann, M. Induction of HIF–1α in Response to Hypoxia Is Instantaneous. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinek, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Cypryk, K.; Los-Stegienta, A.; Slowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Walczak-Jedrzejowska, R.; Zielinski, J.; Gebicki, J. Assessment of Microvascular Function Based on Flowmotion Monitored by the Flow-Mediated Skin Fluorescence Technique. Biosensors. 2024, 14, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Carpi, A.; Di Maria, C.; Galetta, F.; Santoro, G. Spectral Analysis of Laser Doppler Skin Blood Flow Oscillations in Human Essential Arterial Hypertension. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 72, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
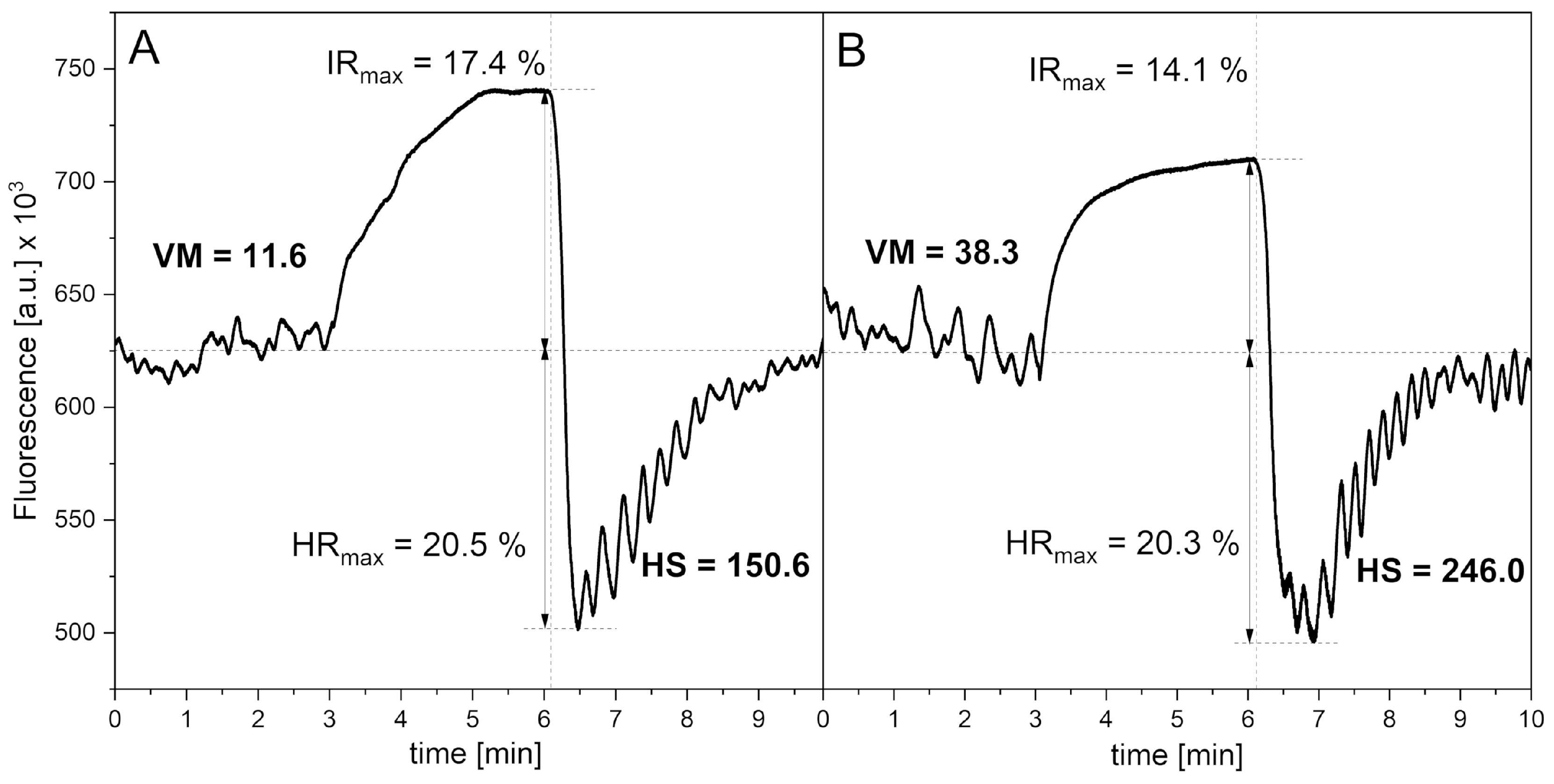
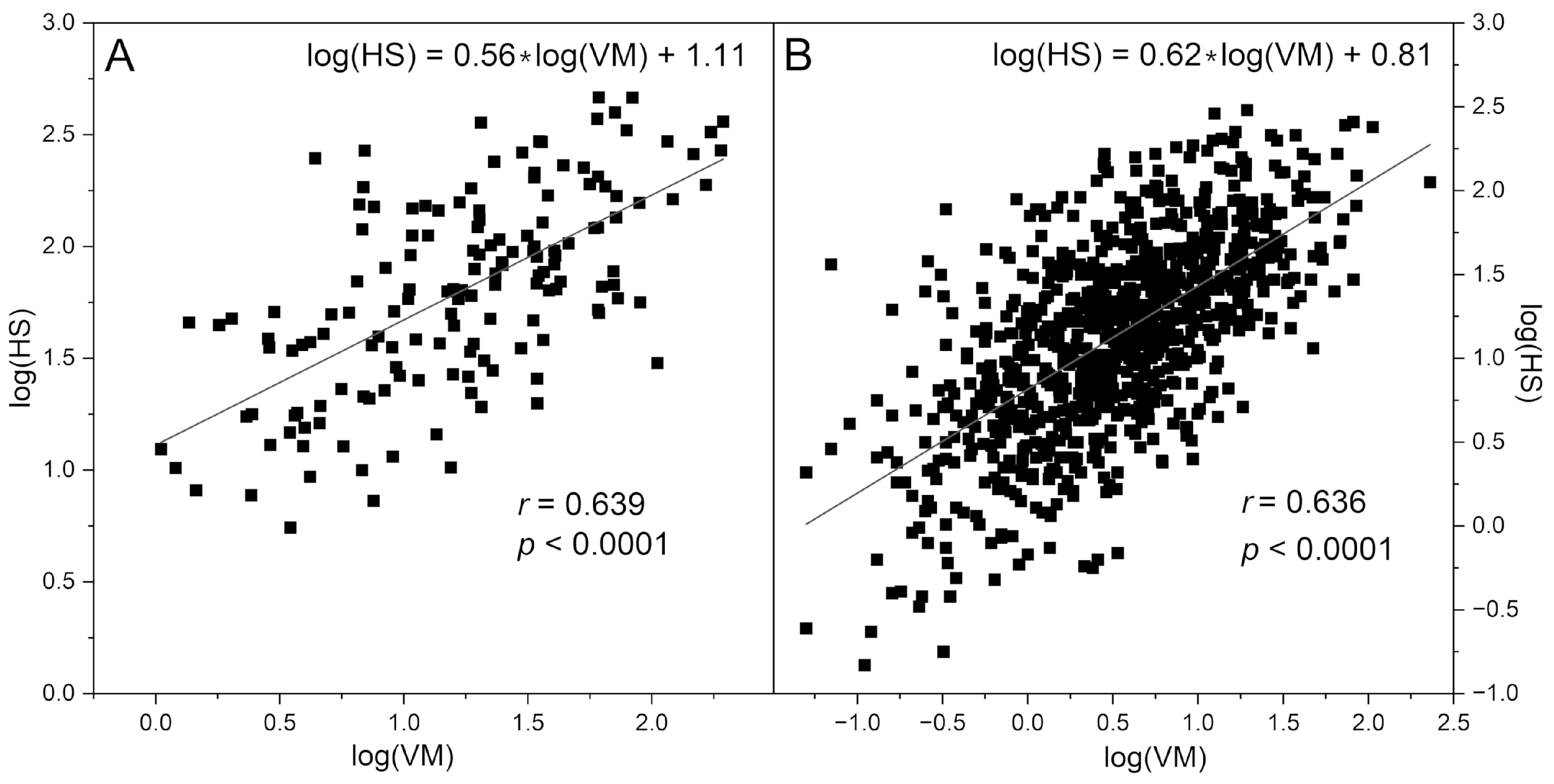
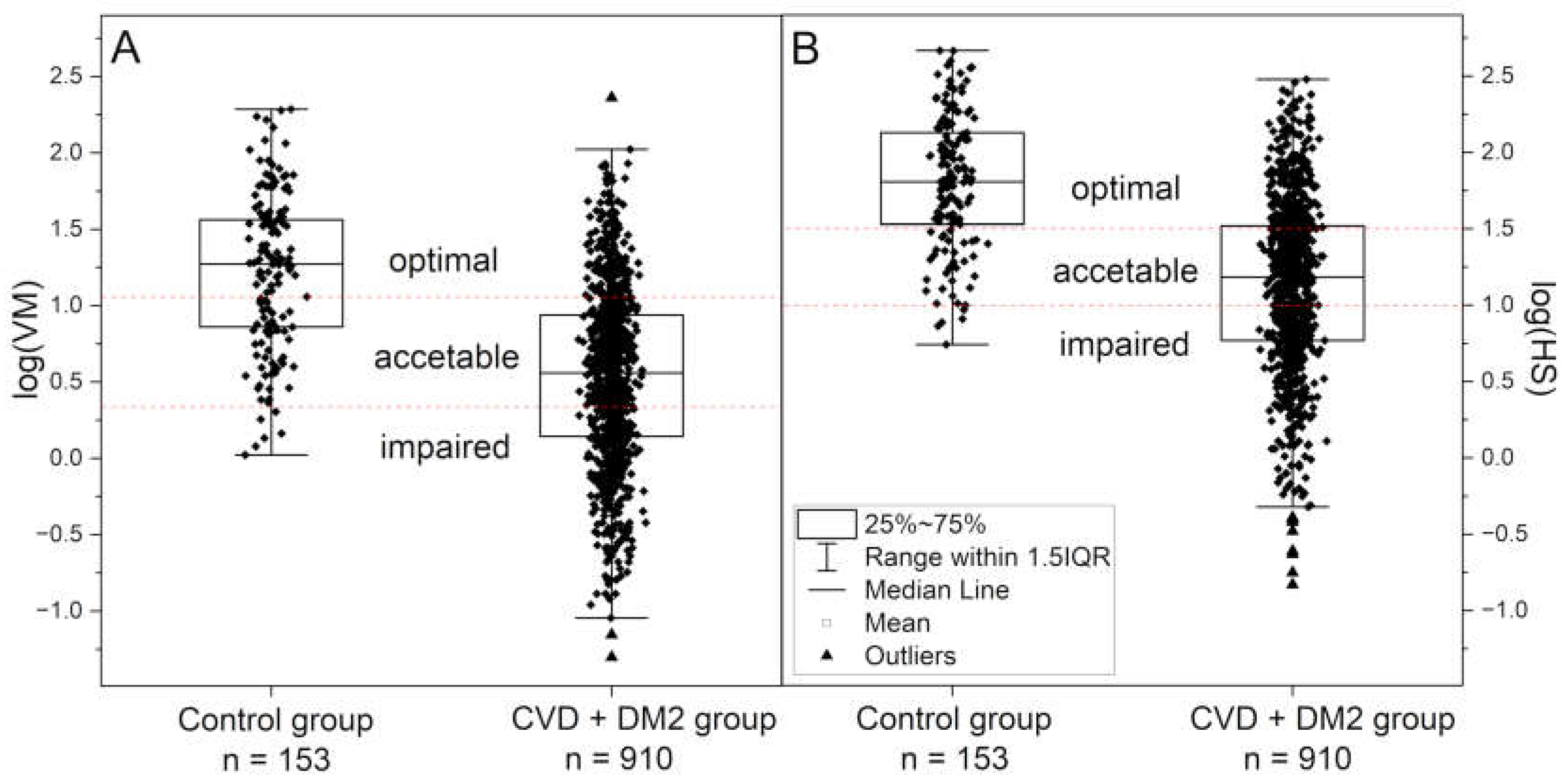
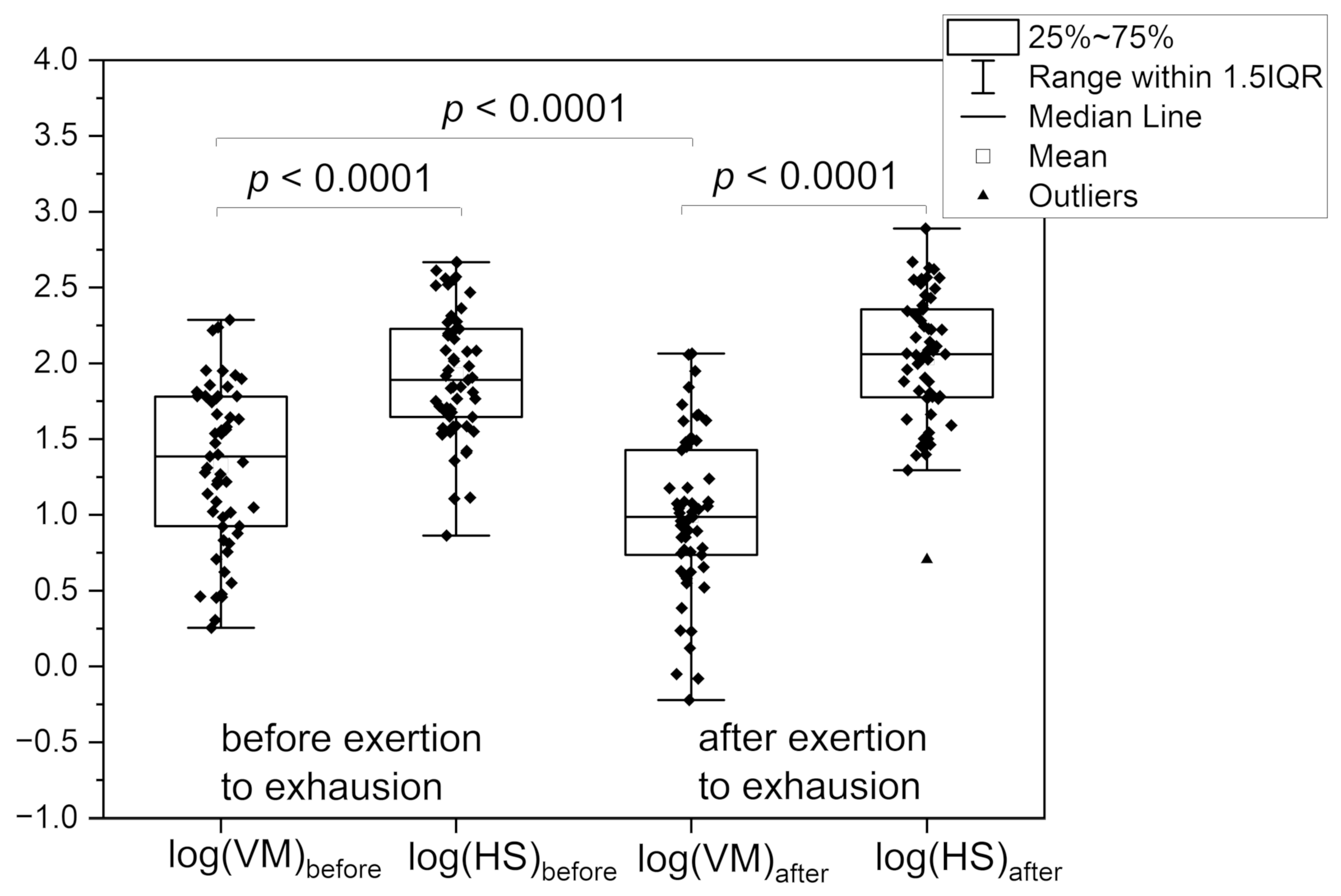
| Control group | CVD+DM2 group | Athletes group | IHT group | |||
| before exertion to exhausion | after exertion to exhausion | before intermittent hypoxia treatment | after intermittent hypoxia treatment | |||
| N | 153 | 910 AH (508) CVD (475) DM2 (273) |
56 | 9 | ||
| Female/ Male | 34 / 119 | 519 / 391 | 10 / 46 | 4 / 5 | ||
| Age [years] | 32.6 ± 11.7 | 67.6 ± 12.5 | 25.7 ± 4.8 | 26.2 ± 10.4 | ||
| BMI [kg/m2] | 24.3 ± 4.0 | 28.9 ± 5.8 | 22.4 ± 2.4 | 20.6 ± 1.7 | ||
|
DBP [mm Hg] |
77.1 ± 10.3 | 74.9 ± 10.7 | 71.3 ± 7.7 | 72.9 ± 8.1 | 69.2 ± 7.8 | 72.2 ± 7.3 |
|
SBP [mm Hg] |
130.4 ± 13.9 | 137.5 ± 18.1 | 129.7 ± 12.2 | 158.4 ± 19.8 | 118.3 ± 12.3 | 112.9 ± 7.8 |
| IRmax [%] | 16.3 ± 5.8 | 11.4 ± 5.6 | 18.6 ± 5.2 | 13.1 ± 5.4 | 20.1 ± 8.5 | 19.5 ± 4.1 |
| HRmax [%] | 19.8 ± 4.6 | 16.5 ± 5.1 | 20.6 ± 4.7 | 19.9 ± 4.8 | 18.5 ± 5.4 | 19.9 ± 5.6 |
| log(VM) | 1.23 ± 0.50 | 0.53 ± 0.58 | 1.32 ± 0.53 | 0.99 ± 0.52 | 1.06 ± 0.39 | 1.34 ± 0.34 |
| log(HS) | 1.80 ± 0.44 | 1.14 ± 0.56 | 1.91 ± 0.41 | 2.04 ± 0.43 | 1.89 ± 0.20 | 1.95 ± 0.22 |
| Control group | CVD+DM2 group | |||||
| slope [a.u./year] |
r (Pearson coefficient) |
p-value | slope [a.u./year] |
r (Pearson coefficient) |
p-value | |
| log(VM) vs age | -0.017 ± 0.003 | -0.385 | <0.0001 | -0.012 ± 0.002 | -0.264 | <0.0001 |
| log(HS) vs age | -0.012 ± 0.003 | -0.311 | <0.0001 | -0.013 ± 0.002 | -0.280 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.f |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





