Submitted:
18 March 2025
Posted:
18 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
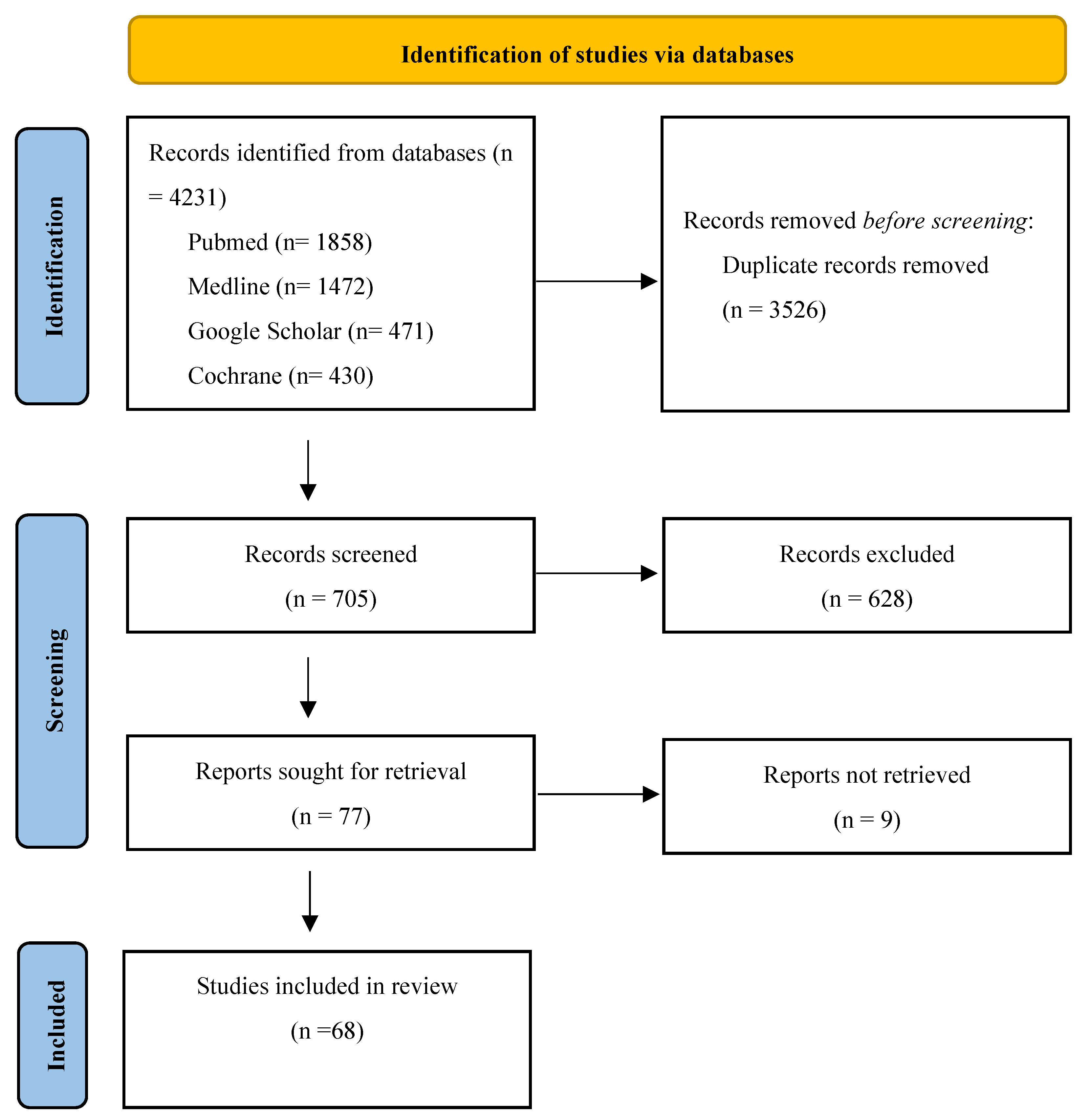
3. Results
3.1. Roots of IASLC Classification
3.2. Validation Studies
3.3. The “Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node” Component
| Répartition (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, year, country | Design | Patients (n) | HMLN - | HMLN + | HR DFS (p) | HR OS (p) |
| Wang et al.[44], 2021, China | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N2M0 (266) | 138 (52%) | 128 (48%) | NA | 1(0,993) |
| Sakao et al.[41], 2006, Japan | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-3N2M0 (53) | 39 (74%) | 14 (26%) | NA | 3,559 (0,0025) |
| Park et al.[43], 2019, South Korea | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N2M0 (339) | 197 (58%) | 142 (42%) | 1 (0,99) | 1,085 (0,429) |
| Marziali et al.[45], 2023, Italy | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N2M0 (68) | 37 (54%) | 31 (46%) | 3.2 (0,008) | 2 (0,002) |
| Zheng et al.[42], 2010, China | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N2M0 (549) | 303 (55,2%) | 246 (44,8%) | NA | 1,584 (<0,0001) |
| Liu et al.[46], 2024 China |
Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N2M0 (486) | 249 (53,2%) | 219 (46.8%) | 1.26 (0,115) | 1,45 (0.017) |
3.4. The “Carcinoma In Situ at Bronchial Margin” Component
3.5. The “Pleural Cytology” Component
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| UICC | Union Internationale Contre le Cancer |
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| IASLC | International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer |
| R(un) HMLN CIS BRM R1 cy+ PLC HR OS DFS LND |
Uncertain Resection Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node Carcinoma In-Situ at Bronchus Resection Margin Pleural lavage positive cytology Pleural lavage cytology Hazard ratio Overall Survival Disease Free Survival Lymph Node Dissection |
References
- Jett, J.R.; Schild, S.E.; Kesler, K.A.; Kalemkerian, G.P. Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd Ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e400S–e419S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; Crinò, L.; Dooms, C.; Douillard, J.Y.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Lim, E.; Rocco, G.; Senan, S.; Van Schil, P.; Veronesi, G.; et al. 2nd ESMO Consensus Conference on Lung Cancer: Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Consensus on Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Annals of Oncology 2014, 25, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Boffa, D.J.; Kim, A.W.; Tanoue, L.T. The Eighth Edition Lung Cancer Stage Classification. Chest 2017, 151, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- eUpdate – Early and Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Available online:. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/guidelines-by-topic/esmo-clinical-practice-guidelines-lung-and-chest-tumours/early-stage-and-locally-advanced-non-metastatic-non-small-cell-lung-cancer/eupdate-early-and-locally-advanced-non-small-cell-lung-cancer-nsclc-treatment-recommendations2 (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Donington, J.S.; Kim, Y.T.; Tong, B.; Moreira, A.L.; Bessich, J.; Weiss, K.D.; Colson, Y.L.; Wigle, D.; Osarogiagbon, R.U.; Zweig, J.; et al. Progress in the Management of Early-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in 2017. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2018, 13, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann Glob Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, Lucian. R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rami-Porta, R.; Wittekind, C.; Goldstraw, P. Complete Resection in Lung Cancer Surgery: Proposed Definition. Lung Cancer 2005, 49, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruke, T.; Suemasu, K.; Ishikawa, S. Lymph Node Mapping and Curability at Various Levels of Metastasis in Resected Lung Cancer. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 1978, 76, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rami Porta, R. Normativa Actualizada (1998) Sobre Diagnóstico y Estadifícación Del Carcinoma Broncogénico. Archivos de Bronconeumología 1998, 34, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountain, C.F. Surgical Therapy in Lung Cancer: Biologic, Physiologic, and Technical Determinants. Semin Oncol 1974, 1, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snijder, R.J.; Brutel de la Rivière, A.; Elbers, H.J.; van den Bosch, J.M. Survival in Resected Stage I Lung Cancer with Residual Tumor at the Bronchial Resection Margin. Ann Thorac Surg 1998, 65, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, G.; Doddoli, C.; Gasser, B.; Ducrocq, X.; Kessler, R.; Schumacher, C.; Jung, G.M.; Wihlm, J.M. Prognostic Implications of a Positive Bronchial Resection Margin. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2000, 17, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistuba, I.I.; Gazdar, A.F. LUNG CANCER PRENEOPLASIA. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2006, 1, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhr, J.; Berghäuser, K.H.; Morr, H.; Dobroschke, J.; Ebner, H.J. Tumor Cells in Intraoperative Pleural Lavage. An Indicator for the Poor Prognosis of Bronchogenic Carcinoma. Cancer 1990, 65, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Asamura, H.; Suemasu, K.; Goya, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Naruke, T.; Yamagishi, K.; Uei, Y. Prognostic Significance of Pleural Lavage Cytology Immediately after Thoracotomy in Patients with Lung Cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1993, 106, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Higashiyama, M.; Doi, O.; Kodama, K.; Yokouchi, H.; Tateishi, R.; Horai, T.; Ashimura, J.; Nagumo, S.; Naruse, Y. Pleural Lavage Cytology Immediately after Thoracotomy and before Closure of the Thoracic Cavity for Lung Cancer without Pleural Effusion and Dissemination: Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 1997, 4, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagan, R.T.; Bernatz, P.E.; Payne, W.S.; Pairolero, P.C.; Williams, D.E.; Goellner, J.R.; Piehler, J.M. Pleural Lavage after Pulmonary Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1984, 88, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Nishio, W.; Uchino, K.; Tsuboshima, K.; Tsubota, N. Pleural Lavage Cytology in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Lessons from 1000 Consecutive Resections. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2003, 126, 1911–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, M.; Ohshima, S.; Kotake, Y.; Morino, H.; Kikui, M.; Yasumitsu, T. Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytolopgy in Lung Cancer Patients. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 1991, 51, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, R.; Mulè, V.; Angiò, L.; Monaco, F.; Smedile, F.; Fabiano, G.; Mondello, B.; Monaco, M. [Intraoperative pleural lavage for restaging of bronchogenic carcinoma]. Minerva Chir 2003, 58, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vicidomini, G.; Santini, M.; Fiorello, A.; Parascandolo, V.; Calabrò, B.; Pastore, V. Intraoperative Pleural Lavage: Is It a Valid Prognostic Factor in Lung Cancer? The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2005, 79, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresler, C.M.; Fratelli, C.; Babb, J. Prognostic Value of Positive Pleural Lavage in Patients with Lung Cancer Resection. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 1999, 67, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquet, M.; Badoual, C.; Le Pimpec Barthes, F.; Lhote, F.-M.; Souilamas, R.; Hubsch, J.-P.; Danel, C. Visceral Pleura Invasion and Pleural Lavage Tumor Cytology by Lung Cancer: A Prospective Appraisal. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2003, 75, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Ali, A.; Theodorou, P.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ladas, G.; Goldstraw, P. Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology Is an Independent Prognostic Indicator for Staging Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2004, 127, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoulas, C.; Lazopoulos, G.; Karaiskos, T.; Tomos, P.; Konstantinou, M.; Papamichalis, G.; Politi, D.; Lioulias, A. Prognostic Significance of Pleural Lavage Cytology after Resection for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 2001, 20, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliasso, M.; Migliaretti, G.; Ardissone, F. Assessing the Prognostic Impact of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Proposed Definitions of Complete, Uncertain, and Incomplete Resection in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Surgery. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.G.; Chansky, K.; Schil, P.V.; Nicholson, A.G.; Boubia, S.; Brambilla, E.; Donington, J.; Galateau-Sallé, F.; Hoffmann, H.; Infante, M.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Analysis of Resection Margin Status and Proposals for Residual Tumor Descriptors for Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2020, 15, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osarogiagbon, R.U.; Faris, N.R.; Stevens, W.; Fehnel, C.; Houston-Harris, C.; Ojeabulu, P.; Akinbobola, O.; Lee, Y.-S.; Ray, M.A.; Smeltzer, M.P. Beyond Margin Status: Population-Based Validation of the Proposed IASLC Residual Tumor Classification Re-Categorization. J Thorac Oncol 2020, 15, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.K.; Lee, G.D.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, D.K.; Park, S.-I.; Kim, H.R. A Validation Study of the Recommended Change in Residual Tumor Descriptors Proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer for Patients With pN2 NSCLC. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2021, 16, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, J.-S.; Yang, F. Investigation of the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Uncertain Resection: A Population-Based Study. Lung Cancer 2022, 171, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; She, Y.; Tang, H.; Deng, J.; Jiang, G.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C. Prognostic Evaluation of the Proposed Residual Tumor Classification in a Chinese Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Population. J Surg Oncol 2022, 125, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadomatsu, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Ueno, H.; Goto, M.; Ozeki, N.; Fukumoto, K.; Fukui, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F. Prognostic Value of Uncertain Resection for Overall Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2022, 114, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, G.; Kang, D.; Yun, J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Shin, S.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, Y.S.; et al. Validation of the IASLC Residual Tumor Classification in Patients With Stage III-N2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Followed By Surgery. Annals of Surgery 2023, 277, e1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Fu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Han, H.; Li, H.; Ye, T.; Hu, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Residual Tumor Descriptors Proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer May Not Be Applicable to Stage I and Ground-Glass Opacity-Featured Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2023, 12, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, J.; Deng, J.; She, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wu, C.; Hou, L.; Jiang, L.; et al. Prognostic Significance of the Proposed Residual Tumor Classification in Patients With NSCLC After Sleeve Lobectomy. JTO Clin Res Rep 2023, 4, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergé, R.; Rouch, A.; Rabinel, P.; Renaud, C.; Cazaux, M.; Brouchet, L. Evaluation of Uncertain Resection for Localized Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Crucial Prognosis of Suboptimal Lymph Node Assessment. Ann Thorac Surg 2025, S0003-4975(25)00170-5. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, L.-C.; Chang, J.-F.; Lin, K.-H.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Hsu, P.-K.; Huang, C.-S.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Hsu, H.-S. The Role of Extensive Lymph Node Dissection in the New Grading System for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 2024, 50, 108540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.L.; Ocampo, P.S.S.; Xia, Y.; Zhong, H.; Russell, P.A.; Minami, Y.; Cooper, W.A.; Yoshida, A.; Bubendorf, L.; Papotti, M.; et al. A Grading System for Invasive Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: A Proposal From the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Pathology Committee. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2020, 15, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakao, Y.; Miyamoto, H.; Yamazaki, A.; Oh, T.; Fukai, R.; Shiomi, K.; Saito, Y. Prognostic Significance of Metastasis to the Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2006, 81, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Hu, X.; Jiang, G.; Gao, W.; Jiang, S.; Xie, H.; Ding, J.; Chen, C. Define Relative Incomplete Resection by Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers: Rationale Based on Prognosis Analysis. Lung Cancer 2011, 72, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Byun, G.E.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, D.J.; Paik, H.C.; Chung, K.Y. Clinical Implications of Uncertain Resection in Scenarios of Metastasis of the Highest or Most Distant Mediastinal Lymph Node Station Following Surgical Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 138, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.D.; Liu, G.W.; Li, X.; Sui, X.Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, J. Propensity-Matched Analysis of Clinical Relevance of the Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis. Ann Thorac Surg 2021, 111, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, V.; Frasca, L.; Ambrogi, V.; Patirelis, A.; Longo, F.; Crucitti, P. Prognostic Significance of Uncertain Resection for Metastasis in the Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node after Surgery for Clinical N0 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Surg 2023, 10, 1115696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Cao, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, J. Prognostic Significance of the Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Stage III-N2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Watanabe, S.; Kawachi, R.; Suzuki, K.; Asamura, H. The Impact of Residual Tumor Morphology on Prognosis, Recurrence, and Fistula Formation after Lung Cancer Resection. J Thorac Oncol 2008, 3, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, N.; Beattie, E.J.; Cliffton, E.E.; Melamed, M.R. Radiologically Occult Lung Cancer: Report of 26 Cases. Surgical Clinics of North America 1974, 54, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soorae, A.S.; Stevenson, H.M. Survival with Residual Tumor on the Bronchial Margin after Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1979, 78, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.R.; Hodson, M.E.; Lennox, S.C. Implications of Histologically Reported Residual Tumour on the Bronchial Margin after Resection for Bronchial Carcinoma. Thorax 1982, 37, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, L.; Harjula, A.; Suomalainen, R.J.; Mattila, P.; Mattila, S. Residual Carcinoma in Bronchial Resection Line. Ann Chir Gynaecol 1986, 75, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, R.I.; Kaplan, D.K.; Sharpe, D.A.; Muehrcke, D.D.; Donnelly, R.J. Carcinoma of the Bronchus with Unsuspected Microscopic Resection-Line Involvement. Cancer 1988, 62, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasse, Y.; Bucher, H.C.; Wong, E.; Griffith, L.; Walter, S.; Ginsberg, R.J.; Guyatt, G.H. “Incomplete Resection” in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Need for a New Definition. Canadian Lung Oncology Group. Ann Thorac Surg 1998, 65, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffini, E.; Bongiovanni, M.; Cavallo, A.; Filosso, P.L.; Giobbe, R.; Mancuso, M.; Molinatti, M.; Oliaro, A. The Significance of Associated Pre-Invasive Lesions in Patients Resected for Primary Lung Neoplasms. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2004, 26, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaud, S.; Bongiovanni, M.; Pache, J.-C.; Fioretta, G.; Robert, J.H. Survival According to the Site of Bronchial Microscopic Residual Disease after Lung Resection for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009, 137, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.; de Castro, P.L.; Astudillo, J.; Fernández-Llamazares, J.; Bronchogenic Carcinoma Cooperative Group of the Spanish Society of Pneumology and Thoracic Surgery Bronchial Stump Infiltration after Lung Cancer Surgery. Retrospective Study of a Series of 2994 Patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2009, 9, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.D.; Kim, D.K.; Jang, S.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, S.-I. Significance of R1-Resection at the Bronchial Margin after Surgery for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 2017, 51, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aokage, K.; Yoshida, J.; Ishii, G.; Enatsu, S.; Hishida, T.; Nishimura, M.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Nagai, K. The Impact on Survival of Positive Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology in Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2010, 139, 1246–1252.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Okumura, N.; Kokado, Y.; Miyoshi, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Kameyama, K. Clinical Relevance of Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2007, 83, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, M.; Oda, K.; Okami, J.; Maeda, J.; Kodama, K.; Takenaka, A.; Nakayama, T.; Yoneda, G. Prognostic Value of Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology for Lung Cancer without Carcinomatous Pleuritis: Importance in Patients with Early Stage Disease during Long-Term Follow-Up. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 2009, 35, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawachi, R.; Nakazato, Y.; Masui, K.; Takei, H.; Koshi-ishi, Y.; Goya, T. Clinical Significance of Pleural Lavage Cytology for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Is Surgical Resection Valid for Patients with Positive Pleural Lavage Cytology? Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 2009, 9, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Suzuki, K.; Mochizuki, T.; Ohde, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakamura, H.; Toyoda, F. Prognostic Significance and Possibility in Guiding Adjuvant Therapy of the Pleural Lavage Cytology in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2009, 8, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Ohta, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Ikeda, N.; Kanou, T.; Tomita, E.; Nakagawa, K.; Yasumitsu, T.; Ohno, Y. Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology after Lung Resection as an Independent Prognostic Factor for Staging Lung Cancer. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2009, 137, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameyama, K.; Okumura, N.; Miyaoka, E.; Asamura, H.; Yoshino, I.; Tada, H.; Fujii, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Mori, M.; et al. Prognostic Value of Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology for Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Influence of Positive Pleural Lavage Cytology Results on T Classification. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2014, 148, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Miwa, K.; Adachi, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Haruki, T.; Horie, Y. Prognostic Significance of Pleural Lavage Cytology after Thoracotomy and before Closure of the Chest in Lung Cancer. Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 2009, 9, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, T.; Uramoto, H.; Kuwata, T.; Takenaka, M.; Chikaishi, Y.; Oka, S.; Nagata, Y.; Shigematsu, Y.; Shimokawa, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Intrapleural Chemotherapy Improves the Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Positive Pleural Lavage Cytology. Surg Today 2013, 43, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, M.; Yokoi, K.; Ito, S.; Niwa, H.; Takao, M.; Kondo, R.; Arimura, T.; Saito, Y. The Value of Pleural Lavage Cytology Examined during Surgery for Primary Lung Cancer. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 2012, 41, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, N.; Shiono, S.; Abiko, M.; Abe, M.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, I.; Uematsu, M.; Ogata, S.; Sato, T.; Tamura, G. Positive Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology Is a Predictive Marker of Disease Recurrence in Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma. Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 2014, 18, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, F.; Ferrari, E.; Maineri, P.; Dozin, B.; Ratto, G.B. Pleural Lavage Cytology Predicts Recurrence and Survival, Even in Early Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Surg Today 2015, 45, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HOKKA, D.; UCHINO, K.; TANE, K.; OGAWA, H.; TANE, S.; TANAKA, Y.; TAUCHI, S.; NISHIO, W.; YOSHIMURA, M.; MANIWA, Y. Pleural Lavage Cytology as an Independent Prognostic Factor in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Stage I Disease and Adenocarcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol 2015, 3, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Hoshi, R.; Ishikawa, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Uehara, H.; Mun, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Okumura, S. Prognosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Positive Pleural Lavage Cytology. Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 2015, 20, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, K.; Nishino, M.; Sesumi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sato, K.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Suda, K.; Shimizu, S.; Sato, T.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Pleural Lavage Cytology in Patients with Primary Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2016, 102, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Isaka, M.; Terada, Y.; Konno, H.; Mizuno, T.; Tone, K.; Kawata, T.; Nakajima, T.; Funai, K.; Ohde, Y. Intraoperative Rapid Diagnosis of Pleural Lavage Cytology in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2024, 72, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Isaka, M.; Ono, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Terada, Y.; Yasuura, Y.; Kayata, H.; Konno, H.; Kojima, H.; Mizuno, T.; et al. Impact of Positive Pleural Lavage Cytology for Each Stage of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2021, 111, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, K.; Sakurada, A.; Hoshi, F.; Abe, J.; Hasumi, T.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, Y.; Okada, Y. Clinicopathological Features of Intraoperative Pleural Lavage Cytology for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2020, 68, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Otsuki, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Funai, K. Pleural Lavage Cytology after Lung Resection in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and the Feasibility of 20 mL Saline Solution. Asian J Surg 2019, 42, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-M.; Ling, Z.-G.; Wu, Y.-B.; Cai, S.-Q.; Tang, Z.-M.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y.-Q. Prognostic Value of Pleural Lavage Cytology in Patients with Lung Cancer Resection: An Updated Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0157518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recuero Díaz, J.L.; Gatius Caldero, S.; Rosado Rodríguez, J.; Caamaño Villaverde, V.; Gómez de Antonio, D.; Tejerina, E.; Sánchez Moreno, L.; Martino González, M.; Moldes Rodríguez, M.; Abdulkader Nallib, I.; et al. Impact of Pleural Lavage Cytology Positivity on Early Recurrence After Surgery for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Arch Bronconeumol. [CrossRef]
- Vallières, E.; Houtte, P.V.; Travis, W.D.; Rami-Porta, R.; Goldstraw, P. Carcinoma In Situ at the Bronchial Resection Margin: A Review. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2011, 6, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, A.R.; Sosin, D.M.; Wells, C.K. The Will Rogers Phenomenon. New England Journal of Medicine 1985, 312, 1604–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquet, M. Curage : Ô Désespoir, ô Will Rogers et Okies ! Revue des Maladies Respiratoires 2005, 22, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsias, T.; Okiror, L.; Veres, L.; King, J.; Harrison-Phipps, K.; Routledge, T.; Pilling, J.; Bille, A. New N1/N2 Classification and Lobe Specific Lymphatic Drainage: Impact on Survival in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Surgery. Lung Cancer 2021, 151, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlachtenberger, G.; Doerr, F.; Menghesha, H.; Heldwein, M.B.; Hagmeyer, L.; Michel, M.; Schaefer, S.C.; Wahlers, T.; Hekmat, K. Postoperative Long-Term Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Skip-N2 Metastases. Surgical Oncology 2021, 38, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xu, J.; Qiao, R.; Zhong, H.; Han, B.; Zhong, R. Patterns of Recurrence and Survival Rate After Complete Resection of Pathological Stage N2 Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 675354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatis, G.; Müller, S.; Weinreich, G.; Schwarz, B.; Eberhardt, W.; Pöttgen, C.; Aigner, C. Significantly Favourable Outcome for Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Stage IIIA/IIIB and Single-Station Persistent N2 (Skip or Additionally N1) Disease after Multimodality Treatment. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2022, 61, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Uchino, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Okuda, Y.; Tane, K.; Tauchi, S.; Nishio, W.; Maniwa, Y.; Yoshimura, M. Efficacy of Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients with Positive Pleural Lavage Cytology Findings. Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 2015, 21, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, Y.S.; Cho, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Kang, D.; Yun, J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Shin, S.; Cho, J.H.; et al. Reclassifying the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Residual Tumor Classification According to the Extent of Nodal Dissection for NSCLC: One Size Does Not Fit All. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2022, 17, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, S.W.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Rong, Y.; Liu, J.F. [The impact of uncertainty resection on the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2024, 62, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, F.; Wen, Z.; Deng, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Segment Location and Ground Glass Opacity Ratio Reliably Predict Node-Negative Status in Lung Cancer. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2020, 109, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, G.E.; Allen, M.S.; Decker, P.A.; Ballman, K.; Malthaner, R.A.; Inculet, Richard. ; Jones, D.R.; McKenna, R.J.; Landreneau, R.J.; Rusch, V.W.; et al. Randomized Trial of Mediastinal Lymph Node Sampling Versus Complete Lymphadenectomy During Pulmonary Resection in the Patient with N0 or N1 (Less Than Hilar) Non-Small Cell Carcinoma: Results of the ACOSOG Z0030 Trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011, 141, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, S.C. Less Is More… (More or Less…). The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2011, 141, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, G.E. Lymph Node Assessment in Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Lymph Node Dissection or Sampling? Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2020, 68, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, V.; Frasca, L.; Longo, F.; Vega, R.; Crucitti, P. The Wide Range of Uses of Indocyanine Green in Thoracic Surgery: State of Art. Journal of Surgery 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gregor, A.; Ujiie, H.; Yasufuku, K. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Lung Cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2020, 68, 1061–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pechoux, C.; Pourel, N.; Barlesi, F.; Lerouge, D.; Antoni, D.; Lamezec, B.; Nestle, U.; Boisselier, P.; Dansin, E.; Paumier, A.; et al. Postoperative Radiotherapy versus No Postoperative Radiotherapy in Patients with Completely Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Proven Mediastinal N2 Involvement (Lung ART): An Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2022, 23, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez De Dios, N.; Navarro-Martin, A.; Cigarral, C.; Chicas-Sett, R.; García, R.; Garcia, V.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Gonzalo, S.; Murcia-Mejía, M.; Robaina, R.; et al. GOECP/SEOR Radiotheraphy Guidelines for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2022, 13, 237–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, G.; Choy, H.; Bradley, J.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Bogart, J.; Curran, W.J.; Gore, E.; Langer, C.; Louie, A.V.; Lutz, S.; et al. Adjuvant Radiation Therapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Executive Summary of an American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline. Practical Radiation Oncology 2015, 5, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris, M.G.; Gaspar, L.E.; Chaft, J.E.; Kennedy, E.B.; Azzoli, C.G.; Ellis, P.M.; Lin, S.H.; Pass, H.I.; Seth, R.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. Adjuvant Systemic Therapy and Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Stage I to IIIA Completely Resected Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology/Cancer Care Ontario Clinical Practice Guideline Update. JCO 2017, 35, 2960–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, S.; Yuan, L.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Z. The High-Risk Features and Effect of Postoperative Radiotherapy on Survival for Patients with Surgically Treated Stage IIIA-N2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2023, 21, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-C.; Hou, R.-P.; Xia, W.-Y.; Zeng, W.-Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.-M.; Lv, C.-X.; Luo, Q.-Q.; Zhao, H.; Yu, W.; et al. Prognostic Index for Estimating the Survival Benefit of Postoperative Radiotherapy in Pathologic N2 Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Real-World Validation Study. Lung Cancer 2021, 156, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-C.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.-W.; Feng, W.; Fu, X.-L. A Decision Support Framework for Postoperative Radiotherapy in Patients with Pathological N2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Radiother Oncol 2022, 173, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.-Q.; Feng, W.; Xie, L.; Zhang, C.-C.; Yu, W.; Cai, X.-W.; Fu, X.-L. Postoperative Radiotherapy for Resected Stage IIIA-N2 Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Population-Based Time-Trend Study. Lung 2019, 197, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, H.; Xiu, W.; Tian, X.; Gong, Y. Uncertain Resection of Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node Positive among pN2 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Survival Analysis of Postoperative Radiotherapy and Driver Gene Mutations. Jpn J Radiol 2023, 41, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; E, H.; Li, C.; Wu, H.; Zhao, D.; Hu, Y.; et al. The Additional Radiotherapy to Adjuvant Chemotherapy Improves the Prognosis of Stage III-N2 with Highest Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2023, 149, 13311–13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, T.S.; Mohamed, N.; Gill, P.K.; Khan, S. A Comparative Analysis of Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery and Thoracotomy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Terms of Their Oncological Efficacy in Resection: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e25443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altorki, N.; Wang, X.; Damman, B.; Mentlick, J.; Landreneau, R.; Wigle, D.; Jones, D.R.; Conti, M.; Ashrafi, A.S.; Liberman, M.; et al. Lobectomy, Segmentectomy, or Wedge Resection for Peripheral Clinical T1aN0 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Post Hoc Analysis of CALGB 140503 (Alliance). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2024, 167, 338–347.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Ostrowski, M.; Hoffmann, H.; Rami-Porta, R.; Osarogiagbon, R.U.; Donnington, J.; Infante, M.; Marino, M.; Marom, E.M.; Nakajima, J.; et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the Classification of Residual Tumor After Resection for the Forthcoming (Ninth) Edition of the TNM Classification of Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2024, S1556-0864(24)00129-1. [CrossRef]
| Répartition (%) | Reason for reclassification (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, year, country | Design | Patients (n) | R0 | R(un) | R1+2 | Insufficient LND | HMLN + | CIS BRM | Cy+ | HR OS (p) |
| Gagliasso et al.[28], 2017, Italy | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N0-2M0 (1277) | 1003 (78,5%) | 185 (14,5%) | 89 (7%) |
107 (56,6%) | 76 (41%) |
5 (2,6%) |
NA | 1,69 (0,0001) |
| Edwards et al.[29], 2019, mainly Japan | Retrospective, International database | pT1-4N0-3M0 (14712) | 6070 (41%) | 8185 (56%) | 457 (3%) | 7824 (95,7%) | 312 (3,8%) | 11 (0,01%) |
34 (0,5%) |
N+ 1.27 (< 0.001) |
| Osarogiagbon et al.[30], 2019, USA | Retrospective, Population-based | Resected NSCLC (3361) | 1119 (33%) | 2044 (61%) | 198 (6%) | 2004 (98%) |
119 (5,8%) | 0 (0%) |
3 (0,1%) |
1,36 (<0,0001) |
| Yun et al.[31], 2021, South Korea | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pN2 NSLC(1039) | 432 (41,6%) | 212 (20,4%) | 395 (38%) | 21 (10,2%) |
185 (89,8%) | 6 (from R1) |
NA | 1.06 (0.595) |
| Wang et al.[32], 2022, China | Retrospective, Single Instutition | pT1-4N0-2M0 (2782) | 1897 (68%) | 885 (32%) | 0 (0%) | 717 (81%) |
168 (19%) | 0 | 0 | 1.302 (0,003) |
| Ren et al.[33], 2022, China | Retrospective, Single Instutition | Resected NSCLC (5293) | 3819 (72,1%) | 1371 (25,9%) | 103 (1,9%) | 929 (67,7%) |
511 (37,2%) | 2 | 11 | 1,41 (0,001) |
| Kadomatsu et al.[34], 2022, Japan | Retrospective, Single Instutition | Resected NSCLC (355) | 197 (55,5%) | 158 (44,5%) | 0 (0%) | 137 (87%) |
8 (5%) | 3 (2%) |
10 (6%) |
N+ 2,657 (0,007) |
| Lee et al.[35], 2023, South Korea | Retrospective, Single Instutition | Stage III-N2 (910) | 302 (33,2%) | 329 (36,2%) | 279 (30,7%) | 278 (84,5%) | 104 (31,6%) | 0 | NA | 1,18 (p for trend 0,002) |
| Wen et al.[36] 2023, China | Retrospective, Single Instutition | Resected NSCLC (5200) | 3228 (62%) | 1727 (33%) | 145 (5%) | 1179 (68,3%) | 663 (38,3%) | 3 (0,2%) | NA | 1,4 (<0,001) |
| Chen et al.[37], 2023 China | Retrospective, Single Instutition | Sleeve lobectomy (682) | 489 (71,7%) | 110 (16,1%) | 83 (12,2%) | 28 (25%) | 82 (74%) | 14 (12%) | 0 | 1,59 (0,023) |
| Vergé et al.[38], 2025 France |
Retrospective, Single Instutition | Resected cN0M0 (1108) | 732 (66.1%) | 291 (26.2%) | 85 (7.7%) | 251 (86.3%) | 40 (13,7%) | 2 (0.6%) | NA | 1.26 (<0.001) |
| Liu et al[39], 2024 Taiwan |
Retrospective, Single Instutition | Resected adenocarcinomas (1258) | 429 (33.9%) | 829 (65.9) | 0 (excluded) | 829 (100%) | NA | NA | NA | 1.57 (0.001) |
| Author, year | Patients (n) | CIS (n) | SCC (n) | CIS % of Population | Local Recurrence (n) | 5-year survival CIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Martini et al.[48], 1974 | 26 | 2 | 2 | 7.6 | 0 | NA |
| Soorae et al.[49], 1979 | 434 | 10 | 10 | 2.3 | NA | 70 |
| Law et al.[50], 1982 | 1000 | 9 | 9 | 0.9 | NA | 66.7 |
| Heikkila et al.[51], 1986 | 1069 | 5 | NA | 0.46 | NA | NA |
| Whyte et al.[52], 1988 | 560 | 2 | 2 | 0.36 | NA | NA |
| Lacasse et al.[53], 1998 | 399 | 3 | NA | 0.8 | NA | NA |
| Ruffini et al.[54], 2004 | 1090 | 5 | 5 | 0.45 | NA | NA |
| Kawaguchi et al.[47], 2008 | 4493 | 9 | 9 | 0.2 | 1 | 63 |
| Collaud et al.[55], 2009 | 584 | 3 | 3 | 0.5 | 2 | 100 |
| Fernandez et al.[56],2009 | 2994 | 52 | 45 | 1.7 | NA | NA |
| Total | 15,738 | 138 | 114 | 0.9 | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





