Submitted:
14 March 2025
Posted:
17 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Potential Mechanisms Involved in Forest Bathing for Health
Evidence That Exposure to Forest Monoterpenes Can Impact Physiological Processes
2. What Are the Volatile Organic Compound Molecules in Northern Temperate Forests?
2.1. Isoprene
2.2. Monoterpenes
3. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
4. Therapeutic Effects
4.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Asthma and Other Respiratory Problems
4.2. Anxiolytic Effects
5. Discussion
5.1. Pharmacokinetics
5.2. Mode of Administration
5.3. Possible Therapeutic Mechanisms of Action
5.3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
5.3.2. Anxiolytic Mechanisms
6. Future Directions
6.1. Determining Relevant Metabolites
6.2. Inflammation
6.3. Possibilities of Synergies
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | tuberculosis |
References
- Bostock, J.; Riley, H. T., The Natural History of Pliny. Henry G. Bohn; Project Gutenberg: https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/60688/pg60688-images.html: London, 1865; Vol. V.
- Li, Q. , Effects of forest environment (Shinrin-yoku/Forest bathing) on health promotion and disease prevention -the Establishment of "Forest Medicine". Environ Health Prev Med 2022, 27, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victorson, D. , Cultivating Reciprocity Between People and Planet: Habit-Stacking Planetary Health Prescriptions Into Existing Nature RX Encounters During Integrative Health Visits. Glob Adv Integr Med Health 2024, 13, 27536130241245429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, M. P.; Alcock, I.; Grellier, J.; Wheeler, B. W.; Hartig, T.; Warber, S. L.; Bone, A.; Depledge, M. H.; Fleming, L. E. , Spending at least 120 minutes a week in nature is associated with good health and wellbeing. Sci Rep 2019, 91, 7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, M. H.; Chang, M. C.; Lee, S. J. , The effects of forest therapy on depression and anxiety in patients with chronic stroke. Int J Neurosci 2017, 1273, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S. C.; Park, S. J.; Park, C. W.; Yoon, W. S.; Choung, J. T.; Yoo, Y. , Clinical and immunological effects of a forest trip in children with asthma and atopic dermatitis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2015, 141, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Donelli, D.; Antonelli, M.; Baraldi, R.; Corli, A.; Finelli, F.; Gardini, F.; Margheritini, G.; Meneguzzo, F.; Neri, L.; Lazzerini, D.; Ardissino, D.; Piacentini, G.; Zabini, F.; Cogo, A. , Exposure to forest air monoterpenes with pulmonary function tests in adolescents with asthma: A cohort study. Forests 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T. M.; Hwang, J. S.; Lin, S. T.; Wu, C.; Tsai, M. J.; Su, T. C. , Forest Bathing Is Better than Walking in Urban Park: Comparison of Cardiac and Vascular Function between Urban and Forest Parks. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G. X.; Cao, Y. B.; Lan, X. G.; He, Z. H.; Chen, Z. M.; Wang, Y. Z.; Hu, X. L.; Lv, Y. D.; Wang, G. F.; Yan, J. , Therapeutic effect of forest bathing on human hypertension in the elderly. J Cardiol 2012, 606, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B. J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Kasetani, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. , The physiological effects of Shinrin-yoku (taking in the forest atmosphere or forest bathing): evidence from field experiments in 24 forests across Japan. Environ Health Prev Med 2010, 151, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, A. L.; Ellsworth-Kopkowski, A.; Prather, J. G.; Passel, C.; Rogers, H. H.; Hansen, M. M. , Shinrin-Yoku (Forest Bathing): A Scoping Review of the Global Research on the Effects of Spending Time in Nature. Glob Adv Integr Med Health 2024, 13, 27536130241231258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, R. J.; Hart, J. L.; Bhatnagar, A. , Greenspaces And Cardiovascular Health. Circ Res 2024, 1349, 1179–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Babak, A.; Motamedi, N.; Mousavi, S. Z.; Ghasemi Darestani, N. , Effects of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction on Blood Pressure, Mental Health, and Quality of Life in Hypertensive Adult Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study. J Tehran Heart Cent 2022, 173, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, T.; Mittal, D.; Mohanty, K.; Faiq, M. A.; Bhat, M. A.; Yadav, R. K.; Sihota, R.; Sidhu, T.; Velpandian, T.; Kalaivani, M.; Pandey, R. M.; Gao, Y.; Sabel, B. A.; Dada, R. , Mindfulness Meditation Reduces Intraocular Pressure, Lowers Stress Biomarkers and Modulates Gene Expression in Glaucoma: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Glaucoma 2018, 2712, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, S. G.; Gomez, A. F. , Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Anxiety and Depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am 2017, 404, 739–749. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Myazaki, Y. , Pysiological effects of visual stimulation with forest imagery. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2018, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, H.; Tang, L. , Determination of D-limonene in mice plasma and tissues by aa new GC-MS/MS method: Comparison of the pharmokinetics and tissue distribution by oral and ihalation administration in mice. Biomed Chromatogr 2019, 337, e453. [Google Scholar]
- Sumitomo, K.; Akutsu, H.; Fukuyama, S.; Minoshima, A.; Kukita, S.; Yamamura, Y.; Sato, Y.; Hayasaka, T.; Osanai, S.; Funakoshi, H.; Hasebe, N.; Nakamura, M. , Conifer-Derived Monoterpenes and Forest Walking. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo) 2015, 41, A0042. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Perdue, E. M.; Paviostathis, S. G.; Auraujo, R. , Physicochemical properties of selected monoterpenes. Environ. Int. 1998, 243, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Juurlink, B. H. , The impaired glutathione system and its up-regulation by sulforaphane in vascular smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 2001, 1910, 1819–25. [Google Scholar]
- Satou, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Kasuya, H.; Masuo, Y.; Koike, K. , Mouse brain concentrations of alpha-pinene, limonene, Linalool, and 1,8, cineole following inhalation. Flavour Fragrance J. 2017, 32, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.; Kim, J.-W.; Park, M.-J.; Kim, S. R.; Lee, S.-S.; Jeung, E.-B. , Anti-inflammatory effects of natural volatile organic compounds from Pinus koraiensis and Larix kaempferi in mouse model. J. Biomed. Res. 2019, 335, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Lee, J. H.; Kim, J. W.; Park, M. J.; Lee, S. S.; Jeung, E. B. , Alleviation effects of natural volatile organic compounds from Pinus densiflora and Chamaecyparis obtusa on systemic and pulmonary inflammation. Biomed Rep 2018, 95, 405–414. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M. J.; Kell, D. B.; Pretorius, E. , The role of lipopolysaccharide-induced cell signalling in chronic inflammation. Chronic Stress 2022, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Laothawornkitkul, J.; Taylor, J. E.; Paul, N. D.; Hewitt, C. N. , Biogenic volatile compounds in the Earth System. New Phytologist 2009, 1831, 27–51. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta Navarro, J. C.; Smolander, S.; Struthers, H.; Zorita, E.; Ekman, A. M.; Kaplan, J. O.; Guenther, A.; Arneth, A.; Riipinen, I. , Global emissions of terpenoid VOCs from terrestrial vegetation in the last millennium. J Geophys Res Atmos 2014, 11911, 6867–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki, M.; Aalto, J.; Hellen, H.; Pihlatie, M.; Back, J. , Interannual and Seasonal Dynamics of Volatile Organic Compound Fluxes From the Boreal Forest Floor. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Geron, C.; Rasmussen, R.; Arnts, R. R.; Guenther, A. , A review and synthesis of monoterpenes speciation from forests in the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1761–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Runyon, J. B.; Gray, C. A.; Jenkins, M. J. , Volatiles of High-Elevation Five-Needle Pines: Chemical Signatures through Ratios and Insight into Insect and Pathogen Resistance. J Chem Ecol 2020, 463, 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Borsdorf, H.; Bentele, M.; Müller, M.; Rebmann, C.; Mayer, T. , Comparison of seasonal and diurnal concentration profiles of BVOCs in coniferous and deciduous forests. Atmosphere 2023, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Calogirou, A.; Larsen, B. R.; Kotzias, D. , Gas-phase terpene oxidation products: a review. Atmos. Envirn. 1999, 33, 1423–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, K. H.; Jacob, D. J. , A new model mechanism for atmospheric oxidation of isoprene: global effects on oxidants, nitrogen oxides, organic products, and secondary organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferracci, V.; Bolas, C. G.; Freshwater, R. A.; Staniaszek, Z.; King, T.; Jaars, K.; Otu-Larbi, F.; Beale, J.; Malhi, Y.; Waine, T. W.; Jones, R. L.; Ashworth, K.; Harris, N. R. P. , Continuous isoprene measurments in a UK Temperate Forest for a whole growing season: Effects of drought stress during the 2018 heatwave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, S. M.; Copolovici, L.; Niinemtes, Ü. , Seasonal variation in vertical volatile compounds air concentration within a remote hemiboreal mixed forest. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3909–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Sukul, P.; Richter, A.; Junghanss, C.; Schubert, J. K.; Miekisch, W. , Origin of breath isoprene in humans is revealed via multi-omic investigations. Commun Biol 2023, 61, 999. [Google Scholar]
- Cailleux, A.; Cogny, M.; Allain, P. , Blood isoprene concentrations in humans and in some animal species. Biochem Med Metab Biol 1992, 472, 157–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lun, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J. , Biogenic volatile organic compounds emissions, atmospheric chemistry, and environmental implications: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 3033–3058. [Google Scholar]
- Hakola, H.; Tarvainen, V.; Laurila, T.; Hiltunen, V.; Hellén, H.; Keronen, P. , Seasonal variation of VOC concentrations above a boreal coniferous forest. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Riba, M. L.; Tathy, J. P.; Tsiropouos, N.; Monsarat, B.; Torres, L. , Diurnal variation in the concentration of a-pinene and b-pinene in the Landes Forest (France). Atmos. Environ. 1987, 211, 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Staudt, M.; Lhoutellier, L. , Monoterpene and sesquiterpene emissions from Quercus coccifera exhibit interacting response to light and temperature. Biogeosci. 2011, 8, 2757–2771. [Google Scholar]
- Hakola, H.; Hellén, H.; Tarvainen, V.; Bãck, J.; Patokoski, P. , Annual variations of atmospheric VOC concentrations in a boreal forest. Boreal Environ. Res. 2009, 14, 722–730. [Google Scholar]
- Petersson, G. , High ambient concentrations of monoterpenes in a Scandanavian pine forest. Atmos. Environ. 1988, 22, 2617–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, G.-Y.; Park, G.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Bae, J.-S.; Park, H.-Y.; Seo, Y.-G.; Yang, S.-I.; Lee, J.-K.; S-H. , J.; Lee, W.-J., Comparison of major monoterpene concentrations in the ambient air of South Korea forests. J. Korean For. Soc. 2010, 995, 698–705. [Google Scholar]
- Hakola, H.; Hellén, H.; Hemmilä, M.; Rinne, J.; Kulmala, M. , In situ measurement of volatile organic compounds in a boreal forest. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 11665–11678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Shen, W. , Protective effects of D-Limonene against transient cerebral ischemia in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Ther Med 2018, 151, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Eddin, L. B.; Azimullah, S.; Jha, N. K.; Nagoor Meeran, M. F.; Beiram, R.; Ojha, S. , Limonene, a Monoterpene, Mitigates Rotenone-Induced Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration by Modulating Neuroinflammation, Hippo Signaling and Apoptosis in Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 246. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah, M.; Mahmood, T.; Ahsan, F.; Bano, S.; Zaidi, S. M. H.; Khan, M. M. U. , Cardioprotective Potential of d-limonene against Isoproterenol induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Cell Biochem Biophys 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Victor Antony Santiago, J.; Jayachitra, J.; Shenbagam, M.; Nalini, N. , Dietary d-limonene alleviates insulin resistance and oxidative stress-induced liver injury in high-fat diet and L-NAME-treated rats. Eur J Nutr 2012, 511, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Razazi, A.; Kakanezhadi, A.; Raisi, A.; Pedram, B.; Dezfoulian, O.; Davoodi, F. , D-limonene inhibits peritoneal adhesion formation in rats via anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and antioxidative effects. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 322, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Kathem, S. H.; Nasrawi, Y. S.; Mutlag, S. H.; Nauli, S. M. , Limonene Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect on LPS-Induced Jejunal Injury in Mice by Inhibiting NF-kappaB/AP-1 Pathway. Biomolecules 2024, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Oesch, F.; Fabian, E.; Landsiedel, R. , Xenobiotica-metabolizing enzymes in the lung of experimental animals, man and in human lung models. Arch Toxicol 2019, 9312, 3419–3489. [Google Scholar]
- Heuberger, E.; Ilmberger, J.; Hartter, E.; Buchbauer, G. , Physiological and behavioral effects of 1,8-cineole and (+)-Linalool: Comparison of inhalation and massage aromatherapy. Natural `prod. Comm. 2008; 3, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Emond, C.; Krishnan, K. , A physiological pharmacokinetic model based on tissue lipid content for simulating inhalation pharmacokinetics of highly lipophilic volatile organic chemicals. Toxicol Mech Methods 2006, 168, 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- de Alvarenga, J. F. R.; Genaro, B.; Costa, B. L.; Purgatto, E.; Manach, C.; Fiamoncini, J. , Monoterpenes: current knowledge on food source, metabolism, and health effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2023, 6310, 1352–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L. K.; Espenship, M. F.; Newman, C. A.; Blount, B. C.; De Jesus, V. R. , Quantification of Seven Terpenes in Human Serum by Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 2020, 5421, 13861–13867. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.-W.; Wang, C.; Lin, C.-Y., Biomonitoring serum levels of three monoterpenes and their association with liver function tests in US adults: NHANES 2013-2014. Research Square 2024, 2024, https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4152134/v1.
- Falk-Filipsson, A.; Lof, A.; M. , H.; Hjelm, E. W.; Wang, Z., D-Limonene exposure to humans by inhalation: Uptake, distribution, elimination, and effects on the pulmonary function. J. Tox.Environ. Health 1993, 38, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlert, C.; van Rensen, I.; Marz, R.; Schindler, G.; Graefe, E. U.; Veit, M. , Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of natural volatile terpenes in animals and humans. Planta Med 2000, 666, 495–505. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, L.; Goen, T. , R-Limonene metabolism in humans and metabolite kinetics after oral administration. Arch Toxicol 2017, 913, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Crowell, P. L.; Lin, S.; Vedejs, E.; Gould, M. N. , Identification of metabolites of the antitumor agent d-limonene capable of inhibiting protein isoprenylation and cell growth. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1992, 313, 205–12. [Google Scholar]
- Crowell, P. L.; Elson, C. E.; Bailey, H. H.; Elegbede, A.; Haag, J. D.; Gould, M. N. , Human metabolism of the experimental cancer therapeutic agent d-limonene. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1994, 351, 31–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, T.; Shindo, M.; Miyazawa, M. , Species differences in the metabolism of (+)- and (-)-limonenes and their metabolites, carveols and carvones, by cytochrome P450 enzymes in liver microsomes of mice, rats, Guinea pigs, rabbits, dogs, monkeys, and humans. Dru Metab. Pharmacokin. 2002, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A. T.; Massiah, M. A.; Bozak, R. E.; Hicks, R. J.; Talalay, P. , Potency of Michael reaction acceptors as inducers of enzymes that protect against carcinogenesis depends on their reactivity with sulfhydryl groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 986, 3404–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S. T.; Chen, C.; Chen, R. X.; Li, R.; Chen, W. L.; Jiang, G. H.; Du, L. L. , Michael acceptor molecules in natural products and their mechanism of action. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 1033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, A. A.; Hagberg, M. T.; Lof, A. E.; Wigaeus-Hjelm, E. M.; Wang, Z. P. , Uptake, distribution and elimination of alpha-pinene in man after exposure by inhalation. Scand J Work Environ Health 1990, 165, 372–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waidyanatha, S.; Hackett, M.; Black, S. R.; Stout, M. D.; Fennell, T. R.; Silinski, M. R.; Watson, S. L.; Licause, J.; Robinson, V. G.; Sparrow, B.; Fernando, R. A.; Cooper, S.; Rider, C. V. , Toxicokinetic evaluation of the common indoor air pollutant, alpha-pinene, and its potential reactive metabolite, alpha-pinene oxide, following inhalation exposure in rodents. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2021, 418, 115496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, L.; Goen, T. , Human metabolism of alpha-pinene and metabolite kinetics after oral administration. Arch Toxicol 2017, 912, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Xie, Z.; Lorkiewicz, P.; Srivastava, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Conklin, D. J. , Endothelial-dependent relaxation of alpha-pinene and two metabolites, myrtenol and verbenol, in isolated murine blood vessels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2023, 3256, H1446–H1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, A.; Lof, A.; Hagberg, M.; Hjelm, E. W.; Wang, Z. , Human exposure to 3-carene by inhalation: toxicokinetics, effects on pulmonary function and occurrence of irritative and CNS symptoms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1991, 1102, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.; Belov, V. N.; Goen, T. , Human metabolism of Delta3-carene and renal elimination of Delta3-caren-10-carboxylic acid (chaminic acid) after oral administration. Arch Toxicol 2015, 893, 381–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duisken, M.; Benz, D.; Peiffer, T. H.; Blomeke, B.; Hollender, J. , Metabolism of Delta(3)-carene by human cytochrome p450 enzymes: identification and characterization of two new metabolites. Curr Drug Metab 2005, 66, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jāger, K.; Našel, C.; Binder, R.; Stimpfl, T.; Vycudilik, W.; Buchbauer, G. , Pharmaokinetic studies of the frangrance compound 1,8-cineole in humans during inhalation. Chem. Senses 1996, 21, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, S. M.; Heuberger, E.; Oedendorfer, K.; Kitzer, S.; Jaganjac, L.; Stappen, I.; Reznicek, G. , Quantitification of 1,8-cineole in himan blood and plasma and the impact of liner choice in heaf-space chromatography. Ciurr. Bioactive Compounds 2015, 11, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, K.; Rychlik, M. , Quantification of 1,8-cineole and of its metabolites in humans using stable isotope dilution assays. Mol Nutr Food Res 2010, 5410, 1515–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, F.; Horst, K.; Röhrig, W.; Rychlik, M.; Buettner, A. , Tracing metabolite profiles in human milk: studies on the odorant 1,8-cineole transferred into breast milk after oral intake. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, F.; Buettner, A. , Characterisation of the metabolites of 1,8-cineole transferred into human milk: concentrations and ratio of enantiomers. Metabolites 2013, 31, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, R. , Endothelium. The MacMillan Co.,: New York, 1954; p 157.
- Huertas, A.; Guignabert, C.; Barbera, J. A.; Bartsch, P.; Bhattacharya, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bonsignore, M. R.; Dewachter, L.; Dinh-Xuan, A. T.; Dorfmuller, P.; Gladwin, M. T.; Humbert, M.; Kotsimbos, T.; Vassilakopoulos, T.; Sanchez, O.; Savale, L.; Testa, U.; Wilkins, M. R. , Pulmonary vascular endothelium: the orchestra conductor in respiratory diseases: Highlights from basic research to therapy. Eur Respir J 2018, 514. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, X.; Xie, L.; Patterson, C. , Emerging Roles of Vascular Endothelium in Metabolic Homeostasis. Circ Res 2018, 1234, 477–494. [Google Scholar]
- Augustin, H. G.; Koh, G. Y. , A systems view of the vascular endothelium in health and disease. Cell 2024, 18718, 4833–4858. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, R.; Nakamura, H.; Bhatti, S. A.; Ngatu, N. R.; Muzembo, B. A.; Dumavibhat, N.; Eitoku, M.; Sawamura, M.; Suganuma, N. , Limonene inhalation reduces allergic airway inflammation in Dermatophagoides farinae-treated mice. Inhal Toxicol 2012, 246, 373–81. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, T.; Marc, M.; Zabiegala, B. , Chemical Composition of Atmospheric Air in Nemoral Scots Pine Forests and Submountainous Beech Forests: The Potential Region for the Introduction of Forest Therapy. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, Y.; Iihoshi, M.; Nazunin, J. T.; Abe, D.; Fukuba, Y. , Dynamic Characteristics of Ventilatory and Gas Exchange during Sinusoidal Walking in Humans. PLoS One 2017, 121, e0168517. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, H. S. R.; de Carvalho, F. O.; dos Santos, D. M.; da Silva, E. A. P.; Silva, E. R.; Shanmugam, S.; Heimfarth, L.; Nunes, P. S.; de Oliveira e Silva, A. M.; de Souza Araújo, A. A.; de Albuquerque, R. L. C.; dos Santos, M. R. V. , Inhaled D-limonene minimizes acute lung injury and reduces oxidative stress induced by smoke in rats. Phytomed. Plus 2022, 23, 100308. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Narke, D.; Kurade, M.; Frey, K. M.; Rajalingam, S.; Siddiquee, A.; Mustafa, S. J.; Ledent, C.; Ponnoth, D. S. , Limonene-induced activation of A(2A) adenosine receptors reduces airway inflammation and reactivity in a mouse model of asthma. Purinergic Signal 2020, 163, 415–426. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S. Y.; Chung, C. K.; Seo, J. H.; Rah, S. Y.; Kim, H. M.; Jeong, H. J. , The therapeutic efficacy of alpha-pinene in an experimental mouse model of allergic rhinitis. Int Immunopharmacol 2014, 231, 273–82. [Google Scholar]
- Christman, J. W.; Blackwell, T. S.; Juurlink, B. H. , Redox regulation of nuclear factor kappa B: therapeutic potential for attenuating inflammatory responses. Brain Pathol 2000, 101, 153–62. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X. X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. , NF kappa B in biology and targetted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Therap. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, G. A. , Measurement of respiratory volume for virus retention studies in mice. Appl Microbiol 1972, 245, 812–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bejeshk, M. A.; Aminizadeh, A. H.; Jafari, E.; Motamed, S.; Zangiabadi, I.; Ghasemi, A.; Fathi, M.; Nexhadi, A.; Akhgarandouz, F.; Bejeshk, F.; Mohamedi, L.; Mohamedi, F.; Rajizadeh, M. A. , Myrtenol ameliorates recognition memories’ impairment and anxiety-like behaviors induced by asthma mitigating hippocampal inflammation and oxidative stress in rats. Neuroimmunomod. 2023, 30, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.; Ahn, C.; Park, M. J.; Na, H.; Jeung, E. B. , 3-carene supresses inflammatory cytokine interleukin-4, interleukin-5 and interleukin-13 in a murine model of asthma. J Physiol Pharmacol 2024, 752, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Hov, Ø.; Schjoldager, J.; Wathne, M. , Measurement and modeling of the concentrations of terpenes in coniferous forest air. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 10679–10688. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, V. P.; Gomes, A. S.; Lima, F. J.; Brito, T. S.; Soares, P. M.; Pinho, J. P.; Silva, C. S.; Santos, A. A.; Souza, M. H.; Magalhaes, P. J. , Inhaled 1,8-cineole reduces inflammatory parameters in airways of ovalbumin-challenged Guinea pigs. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2011, 1081, 34–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther, A.; Zimmerman, P.; Wildermuth, M. , Natural volatile compound emission rate estimates for US woodland landscapes. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Hakola, H.; Laurila, T.; Rinne, J.; Puhto, K. , The ambient concentrations of biogenic hydrocarbons at a northern European, boreal site. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy-Feitosa, E.; Okuro, R. T.; Pinho Ribeiro, V.; Lanzetti, M.; Barroso, M. V.; Zin, W. A.; Porto, L. C.; Brito-Gitirana, L.; Valenca, S. S. , Eucalyptol attenuates cigarette smoke-induced acute lung inflammation and oxidative stress in the mouse. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2016, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Rao, R.; Li, W. , Protective effects of 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol) on respiratory system: A systemic review and meta-analysis from animal studies. Pharmacon. Mag. 2020, 37, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, H.; Dethlefsen, U. , Patients with asthma benefit from concomitant therapy with cineole: a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. J Asthma 2012, 498, 849–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juergens, L. J.; Racké, K.; Tuleta, I.; Stoeber, M.; Juergens, U. W. , Anti-inflammatory effects of 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol) improve glucocorticoid effects in vitro: A novel approach of steroid-sparing dd-on therapy for COPD and asthma. Synergy 2017, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juergens, L. J.; Worth, H.; Juergens, U. R. , New Perspectives for mucolytic, anti-inflammatory and adjunctive therapy with 1,8-Cineole in COPD and asthma: Review on the new therapeutic approach. Adv Ther 2020, 375, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, D.; Meneguzzo, F.; Antonelli, M.; Aedissino, D.; Niccoli, G.; Gronchi, G.; Baraldi, R.; Neri, L.; Zabini, F. , Effects of plant-emitted monoterpenes on anxiety symptoms: A propensity-matched obsevational cohort study. J. Environ. Res. Oublic Health 2023, 20, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-C.; Dinh, T.-V.; Oh, H.-K.; Son, Y.-S.; Ahn, J.-W.; Song, K.-Y.; Choi, I.-Y.; Park, C.-R.; Szulejko, J. E.; Kim, J.-H. , The potential benefits of therapeutic treatment using gaseous terpenes at ambient low levels. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Našel, C.; Naše, B.; Samec, P.; Schindler, E.; Buchbauer, G. , Functional imaging effects of fragrances on the human brain after prolonged inhalation. Chem. Senses 1994, 19, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, N. G.; De Sousa, D. P.; Pimenta, F. C.; Alves, M. F.; De Souza, F. S.; Macedo, R. O.; Cardoso, R. B.; de Morais, L. C.; Melo Diniz Mde, F.; de Almeida, R. N. , Anxiolytic-like activity and GC-MS analysis of (R)-(+)-limonene fragrance, a natural compound found in foods and plants. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2013, 1033, 450–4. [Google Scholar]
- Witkin, J. M.; Barrett, J. E. , ANXIOLYTICS: Origins, drug discovery, and mechanisms. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2024, 245, 173858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Seo, S.; Lamichhane, S.; Seo, J.; Hong, J. T.; Cha, H. J.; Yun, J. , Limonene has anti-anxiety activity via adenosine A2A receptor-mediated regulation of dopaminergic and GABAergic neuronal function in the striatum. Phytomedicine 2021, 83, 153474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, R.-R. M. , Anti-anxiety effect of alpha-pinene in comparison with Diazepam in adult male rats. J. Kasham Un. Med. Sci. 2020, 24, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, M. R.; Salvadori, M. G.; de Almeida, A. A.; de Sousa, D. P.; Jordan, J.; Satyal, P.; de Freitas, R. M.; de Almeida, R. N. , Anxiolytic-like effects and mechanism of (-)-myrtenol: a monoterpene alcohol. Neurosci Lett 2014, 579, 119–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Yang, H.; Yoon, M.; Gadhe, C. G.; Pae, A. N.; Cho, S.; Lee, C. J. , 3-Carene, a Phytoncide from Pine Tree Has a Sleep-enhancing Effect by Targeting the GABA(A)-benzodiazepine Receptors. Exp Neurobiol 2019, 285, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceremuga, T. E.; McClellan, C. B.; Green, X. C.; Heber, B. E.; Jolly, M. L.; Malone, T. B.; Schaaf, J. L.; Isaacs, A. P. , Investigation of the Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects of Eucalyptol (1,8-Cineole), a Compound From Eucalyptus, in the Adult Male Sprague-Dawley Rat. AANA J 2017, 854, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Dougnon, G.; Ito, M. , Inhalation Administration of the Bicyclic Ethers 1,8- and 1,4-cineole Prevent Anxiety and Depressive-Like Behaviours in Mice. Molecules 2020, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. Y.; Seo, H. J.; Min, S. S.; Park, M.; Seol, G. H. , The effect of 1,8-cineole inhalation on preoperative anxiety: a randomized clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014, 2014, 820126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffen, S.; Wyllie, S. G.; Markham, J. , Determination of octanol-water partition coefficients for terpenoids using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 864, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcorn, J. , The xenobiotic elimination system: An overview. Nova Publishers: Broccoli: Cultivation, Nutritional Properties and Effects on Health, 2016; p 342.
- Prescott, J. A.; Mitchell, J. P.; Cook, S. J. , Inhibitory feed-back control of NF-kB signalling in health and disease. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2619–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bshesh, K.; Zhao, B.; Spight, D.; Biaggioni, I.; Feokistov, I.; Denenberg, A.; Wong, H. R.; Shanley, T. P. , The A2A receptor mediates an endogenous regulatory pathway of cytokine expression in THP-1 cells. J Leukoc Biol 2002, 725, 1027–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Fng, W.; Cai, L.; Wang, Z.; Kou, B.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Z.; Wei, M.; Zhang, S. , A2AR regulate inflammation through PKA/NF-kB signaling pathways in invertebral disc degeneration. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Sands, W. A.; Martin, A. F.; Strong, E. W.; Palmer, T. M. , Specific inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent inflammatory responses by cell type-specific mechanisms upon A2A adenosine receptor gene transfer. Mol Pharmacol 2004, 665, 1147–59. [Google Scholar]
- Koroskenyi, K.; Kiss, B.; Szondy, Z. , Adenosine A2A receptor signaling attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine formation of mouse macrophages by inducing the expression of DUSP1. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, (7 Pt A), 1461–71. [Google Scholar]
- Quintans, J. S. S.; Shanmugam, S.; Heimfarth, L.; Araujo, A. A. S.; Almeida, J.; Picot, L.; Quintans-Junior, L. J. , Monoterpenes modulating cytokines - A review. Food Chem Toxicol 2019, 123, 233–257. [Google Scholar]
- Salminen, A.; Lehtonen, M.; Suuronen, T.; Kaarniranta, K.; Huuskonen, J. , Terpenoids: natural inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling with anti-inflammatory and anticancer potential. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008, 6519, 2979–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yarom, M.; Tang, X. W.; Wu, E.; Carlson, R. G.; Vander Velde, D.; Lee, X.; Wu, J. , Identification of inosine as an endogenous modulator for the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABAA receptors. J Biomed Sci 1998, 54, 274–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, M.; Bright, D. P.; Fagotti, J.; Dorovykh, V.; Cerna, B.; Smart, T. G. , Forty Years Searching for Neurosteroid Binding Sites on GABA(A) Receptors. Neuroscience 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bakas, T.; van Nieuwenhuijzen, P. S.; Devenish, S. O.; McGregor, I. S.; Arnold, J. C.; Chebib, M. , The direct actions of cannabidiol and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol at GABA(A) receptors. Pharmacol Res 2017, 119, 358–370. [Google Scholar]
- Hajagos-Tóth, J.; Hódi, A.; Seres, A. B.; Gáspár, R. , Effects of d- and l-limonene on the pregrnant rat myometrium in vivo. Coat. Med. J. 2015, 56, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H. M.; Lee, J. H.; Yaoyao, J.; Jun, H. J.; Lee, S. J. , Limonene, a natural cyclic terpene, is an agonistic ligand for adenosine A(2A) receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011, 4041, 345–8. [Google Scholar]
- Felger, J. C. , Imaging the Role of Inflammation in Mood and Anxiety-related Disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol 2018, 165, 533–558. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelzangs, N.; Beekman, A. T.; de Jonge, P.; Penninx, B. W. , Anxiety disorders and inflammation in a large adult cohort. Transl Psychiatry 2013, 34, e249. [Google Scholar]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Kappelmann, N.; Ye, Z.; Lamers, F.; Moser, S.; Jones, P. B.; Burgess, S.; Penninx, B.; Khandaker, G. M. , Association of inflammation with depression and anxiety: evidence for symptom-specificity and potential causality from UK Biobank and NESDA cohorts. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 2612, 7393–7402. [Google Scholar]
- Kunnumakkara, A. B.; Shabnam, B.; Girisa, S.; Harsha, C.; Banik, K.; Devi, T. B.; Choudhury, R.; Sahu, H.; Parama, D.; Sailo, B. L.; Thakur, K. K.; Gupta, S. C.; Aggarwal, B. B. , Inflammation, NF-kappaB, and Chronic Diseases: How are They Linked? Crit Rev Immunol 2020, 401, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rusnak, F.; Reiter, T. , Sensing electrons: protein phosphatase redox regulation. Trends Biochem Sci 2000, 2511, 527–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, T. , Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell 1995, 802, 225–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghinejad, L.; Noyan, H.; Juurlink, B. H. J. , Cellular Redox: Aging and Diet. In Broccoli: Cultivation, Nutritional Properties and Effects on Health, Juurlink, B. H. J., Ed. Nova Publishers: New York, 2016; pp 87-110.
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. , An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 2522. [Google Scholar]
- Chiurchiu, V.; Maccarrone, M. , Chronic inflammatory disorders and their redox control: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011, 159, 2605–41. [Google Scholar]
- Juurlink, B. H. J. , The Nrf2 Signalling System. In Broccoli: Cultivation, Nutritional Properties and Effects on Health, Juurlink, B. H. J., Ed. Nova Publishers: New York, 2016; Vol. 1, pp 111-119.
- Ma, Q. , Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar]
- Talalay, P.; Fahey, J. W.; Holtzclaw, W. D.; Prestera, T.; Zhang, Y. , Chemoprotection against cancer by phase 2 enzyme induction. Toxicol Lett 1995, 82-83, 173–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J. W.; Shapiro, T. A. , In Memoriam. Inimitable Paul Talalay (1923-2019). Trends Pharmacol. 2019, 40, 359–361. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T. L. , Paul Talalaty: The Catalyst. In Broccoli: Cultivation, Nutritional `properties and Effects on Health, Juurlink, B. H. J., Ed. Nova Publishers: New York, 2016; Vol. 1, pp 1-8.
- Wild, A. C.; Mulcahy, R. T. , Regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunit gene expression: insights into transcriptional control of antioxidant defenses. Free Radic Res 2000, 324, 281–301. [Google Scholar]
- Juurlink, B. H. , Therapeutic potential of dietary phase 2 enzyme inducers in ameliorating diseases that have an underlying inflammatory component. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2001, 793, 266–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A. A.; Avila, J. G.; Schultke, E.; Kamencic, H.; Skihar, V.; Obayan, A.; Juurlink, B. H. , Amelioration of experimental allergic encephalitis (EAE) through phase 2 enzyme induction. Biomed Sci Instrum 2002, 38, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Noyan Ashraf, M. H.; Facci, M.; Wang, R.; Paterson, P. G.; Ferrie, A.; Juurlink, B. H. , Dietary approach to attenuate oxidative stress, hypertension, and inflammation in the cardiovascular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 10118, 7094–9. [Google Scholar]
- Noyan-Ashraf, M. H.; Sadeghinejad, Z.; Juurlink, B. H. , Dietary approach to decrease aging-related CNS inflammation. Nutr Neurosci 2005, 82, 101–10. [Google Scholar]
- Noyan-Ashraf, M. H.; Wu, L.; Wang, R.; Juurlink, B. H. , Dietary approaches to positively influence fetal determinants of adult health. FASEB J 2006, 202, 371–3. [Google Scholar]
- Noyan-Ashraf, M. H.; Sadeghinejad, Z.; Davies, G. F.; Ross, A. R.; Saucier, D.; Harkness, T. A.; Juurlink, B. H. , Phase 2 protein inducers in the diet promote healthier aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2008, 6311, 1168–76. [Google Scholar]
- Senanayake, G. V.; Banigesh, A.; Wu, L.; Lee, P.; Juurlink, B. H. , The dietary phase 2 protein inducer sulforaphane can normalize the kidney epigenome and improve blood pressure in hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 2012, 252, 229–35. [Google Scholar]
- Black, A. M.; Armstrong, E. A.; Scott, O.; Juurlink, B. J. H.; Yager, J. Y. , Broccoli sprout supplementation during pregnancy prevents brain injury in the newborn rat following placental insufficiency. Behav Brain Res 2015, 291, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A. T.; Copple, I. M. , Advances and challenges in therapeutic targeting of Nrf2. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 44, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K. J. S.; Vani, M. G.; Wang, S. Y. , Limonene protects human skin keratinocytes against UVB-induced photodamage and photoaging by activating the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant defense system. Environ Toxicol 2022, 3712, 2897–2909. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Q.; Pang, M.; Wu, Y.; Feng, X.; Tao, X.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, W. , Activation of the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway mediates the neuroprotective effect of Perillyl alcohol against cerebral hypoxic-ischemic damage in neonatal rats. Redox Rep 2024, 291, 2394714. [Google Scholar]
- Alvi, A. M.; Al Kury, L. T.; Alattar, A.; Ullah, I.; Muhammad, A. J.; Alshaman, R.; Shah, F. A.; Khan, A. U.; Feng, J.; Li, S. , Carveol Attenuates Seizure Severity and Neuroinflammation in Pentylenetetrazole-Kindled Epileptic Rats by Regulating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021, 2021, 9966663. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z. U.; Al Kury, L. T.; Alattar, A.; Tan, Z.; Alshaman, R.; Malik, I.; Badshah, H.; Uddin, Z.; Khan Khalil, A. A.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, S.; Ali, A.; Shah, F. A.; Li, J. B.; Li, S. , Carveol a Naturally-Derived Potent and Emerging Nrf2 Activator Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 621538. [Google Scholar]
- Porres-Martinez, M.; Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Carretero, M. E.; Gomez-Serranillos, M. P. , In vitro neuroprotective potential of the monoterpenes alpha-pinene and 1,8-cineole against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 2016, 71, 191–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bejeshk, M. A.; Najafipour, H.; Khaksari, M.; Nematollahi, M. H.; Rajizadeh, M. A.; Dehesh, T.; Bagheri, F.; Sepehri, G. , Myrtenol-loaded niosomes can prevent lung ischemia-reperfusion injury model in rats by balancing the Nrf2/Keap1 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Jin, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, M.; Ma, X.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gao, W. , 1,8-Cineole Alleviates OGD/R-Induced Oxidative Damage and Restores Mitochondrial Function by Promoting the Nrf2 Pathway. Biol Pharm Bull 2023, 4610, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Kamencic, H.; Lyon, A.; Paterson, P. G.; Juurlink, B. H. , Monochlorobimane fluorometric method to measure tissue glutathione. Anal Biochem 2000, 2861, 35–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vari, R.; D'Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Carotenuto, S.; Scazzocchio, B.; Santangelo, C.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. , Protocatechuic acid induces antioxidant/detoxifying enzyme expression through JNK-mediated Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. J Nutr Biochem 2011, 225, 409–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A. T.; Holtzclaw, W. D.; Cole, R. N.; Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Talalay, P. , Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 9918, 11908–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Ma, Q.; Li, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhen, D.; Liu, M.; Wei, C. , Combination of 1,8-cineole and beta-caryophyllene synergistically reverses cardiac hypertrophy in isoprenaline-induced mice and H9c2 cells. Bioorg Chem 2022, 124, 105823. [Google Scholar]
- Kardos, P.; Khaletskaya, O.; Kropova, O. , Efficacy and safety of cineole (Soledum) in the treatment of patients with acute bronchitis: Results of an open-label randomized clinical phase III study) Clin. Phytosci. 2021, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Terpene | Parent Compound | Metabolite | Metabolite |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isoprene 63.12 daltons |
 |
||
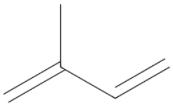
| Monoterpene D-Limonene 136.238 daltons |
 |
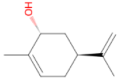 Carveol 152.237 daltons |
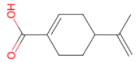 Perillic acid 166.22 daltons |
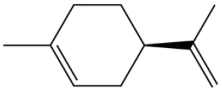
| Monoterpene a-Pinene 136.238 daltons |
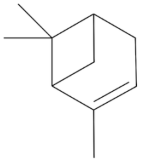 |
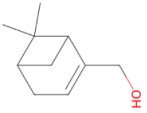 Myrtenol 152.237 daltons |
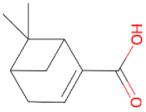 Myrtenic acid 166.220 daltons |
| Monoterpene D3-Carene 136.238 daltons |
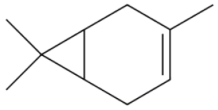 |
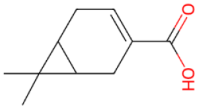 D3-caren-10-carboxylic acid 180.247 daltons |
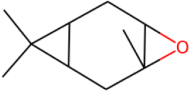 D3-Carene epoxide D3-Carene epoxide152.237 daltons |
| Monoterpene 1,8-Cineol 154.252 daltons |
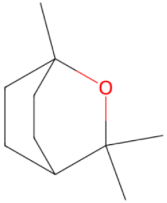 |
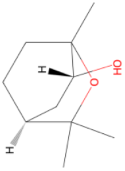 2-hydroxy1,8-cineole |
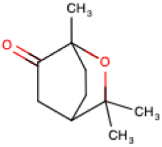 2-oxo-1,8-cineole |
| Sesquiterpene b-Caryophyllene 204.357 daltons |
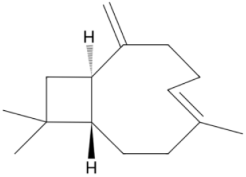 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




