1. Introduction
”FinTech refers to the integration of innovative digital technologies into the design, delivery, and management of financial products and services. It encompasses a wide range of applications, from digital payments and peer-to-peer lending to blockchain-based systems and robo-advisory platforms, that collectively aim to enhance efficiency, transparency, and accessibility in financial markets. This technological evolution challenges traditional financial intermediaries and regulatory frameworks by reshaping how financial transactions are conducted and monitored.” [
1]
Financial technology or “FinTech” challenges and sometime dismantles traditional paradigms with unprecedented agility. Developments such as decentralized blockchain infrastructure, autonomous trading algorithms, and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-infused risk assessment platforms have redefined the financial services ecosystem.
These shifts necessitate new approaches to project management that are both agile and deeply integrated with technological and stakeholder complexities. With the rise of Agentic AI, capable of independently analyzing, adapting, and acting based on dynamic conditions, such methodologies find themselves at the edge of a continuous transformation.
2. The Transformational Role of Agentic AI in FinTech Project Management
Agentic AI is defined by Nvidia as a system that “uses sophisticated reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously solve complex, multi-step problems.”[
2]. This capability is particularly beneficial in the fast-paced FinTech environment.
“Agentic AI” generally refers to artificial intelligence systems that exhibit agency characteristics commonly associated with autonomous decision-making, intentionality, and the capability to pursue set objectives without human intervention.
These AI systems are not merely tools but act as agents that can execute tasks, make decisions, and interact with their environment in an advanced, often human-like manner. According to Floridi and Sanders, agentic AI involves “interactive, autonomous, and adaptive” agents, where autonomy implies that “the system can change its state without direct response to interaction” [
3]. This notion is extended by Rahwan (2018), who points out that such systems not only operate independently but also can make decisions that “align with pre-defined goals, potentially modifying their strategies based on environmental feedback.” [
4]
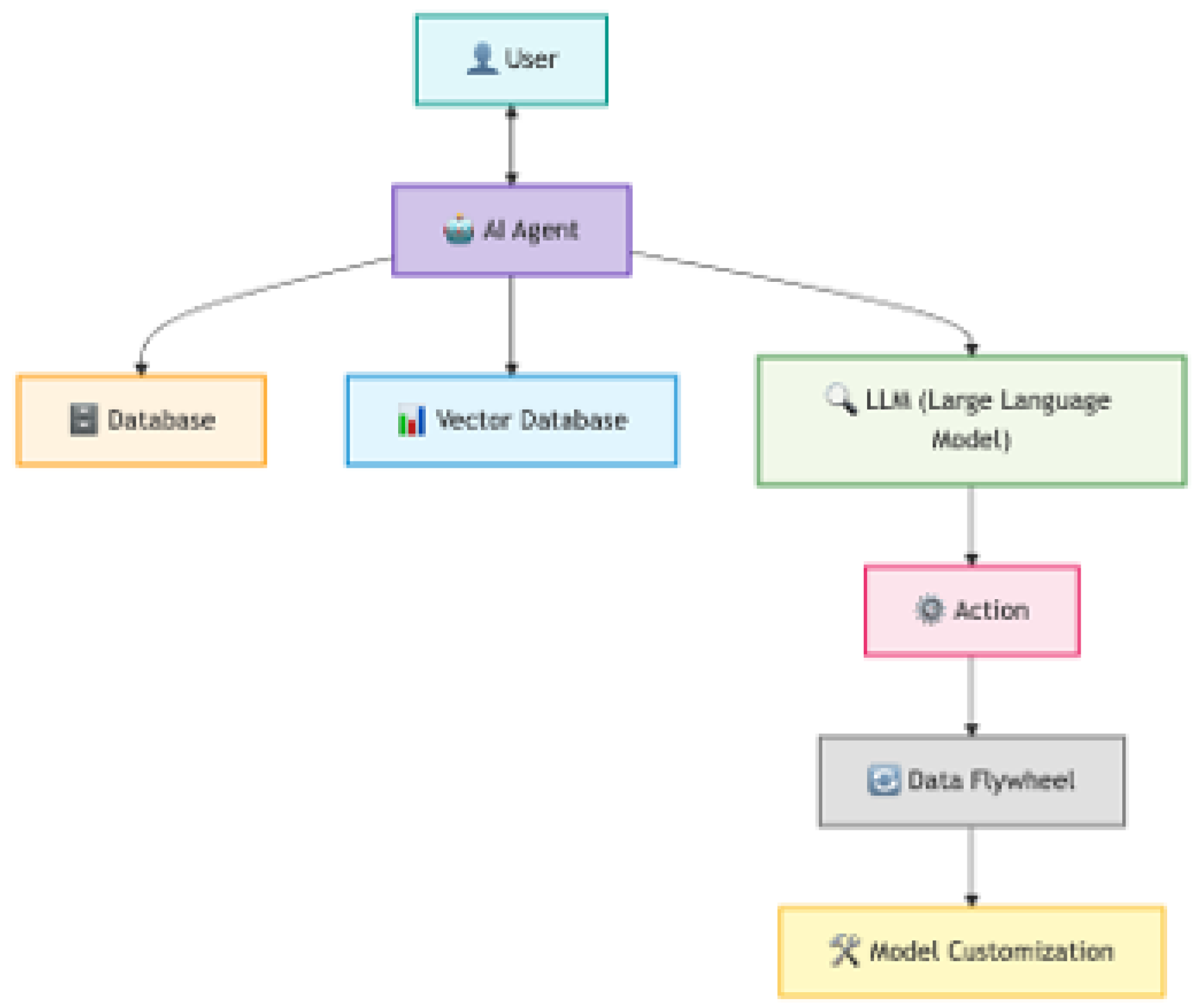
Figure 1.
Agentic AI definition. User (Light Blue): The starting point – the User engages directly with the AI Agent. AI Agent (Light Purple): Central hub processing inputs and orchestrating outputs. Database (Light Orange): Stores structured data for analysis. Vector Database (Light Blue): Handles unstructured data for deeper insights. LLM (Light Green): Core engine that analyzes input and generates actions. Action (Light Pink): The response generated by the LLM based on the input. Data Flywheel (Light Gray): Represents the feedback loop, enhancing the model over time.
Figure 1.
Agentic AI definition. User (Light Blue): The starting point – the User engages directly with the AI Agent. AI Agent (Light Purple): Central hub processing inputs and orchestrating outputs. Database (Light Orange): Stores structured data for analysis. Vector Database (Light Blue): Handles unstructured data for deeper insights. LLM (Light Green): Core engine that analyzes input and generates actions. Action (Light Pink): The response generated by the LLM based on the input. Data Flywheel (Light Gray): Represents the feedback loop, enhancing the model over time.
Agentic AI can analyze large datasets and provide insights that enhance decision-making processes. As noted, it allows for teams of “specialized AI agents” to work together, which can lead to more informed financial strategies.
Agentic AI transcends traditional AI capabilities by autonomously perceiving, planning, and executing actions within the project ecosystem. These self-governing systems promise radical efficiency improvements across FinTech domains.
2.1. Autonomous Task Management and Operational Efficiency
AI agents can autonomously undertake routine compliance audits usimg LLMs, significantly reducing human oversight requirements by defining grounded processes.
In FinTech project management, agentic AI systems optimize workflows by automating repetitive tasks such as manual data entry, compliance checks, and transaction processing. This increases efficiency but also form a risk perspective reduces the potential for human error.
The 2020 research conducted by the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance and the World Economic Forum emphasized the expanding role of AI in finance. The survey respondents included 151 institutions across 33 countries, comprising both FinTechs (54% of respondents) and incumbent financial institutions (46%), representing various sectors within the financial services industry. Participants were primarily senior management in areas such as deposits and lending, payments, insurance, investment management, capital markets, and professional services. Firms headquartered in regions such as Europe, Asia Pacific (including China), the US, and the UK were highly represented.[
5]
Some of the notable respondent companies or institutions mentioned in the document include IBM, Fidelity, Julius Bär, ING, S&P Global, Societe Generale, Quantifeed, Kabbage, ForwardLane, PrepayWay, DTCC (Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation)
It is also noted that many participants preferred to remain confidential, and their names were withheld.
Table 1.
Sample-wide adoption statistics of AI in main business domains.
Table 1.
Sample-wide adoption statistics of AI in main business domains.
| Values |
Risk Management |
Process Re-engineering |
New Revenue Potential |
Customer Service |
Client
Acquisition |
| Sum of Not Implemented but Planning to Implement Within Two Years (%) |
18 |
21 |
15 |
15 |
15 |
| Sum of Currently Implementing (%) |
21 |
26 |
28 |
24 |
23 |
| Sum of Implemented (%) |
56 |
47 |
52 |
50 |
46 |
AI is projected to become a critical driving force in the financial services sector shortly, with 77% of respondents predicting that AI will have a significant or extremely significant impact on their businesses within the next two years. Currently, AI holds greater strategic importance for FinTech companies, but traditional financial institutions are expected to bridge this gap within the same timeframe,
Agentic AI, characterized by its autonomy and ability to make decisions based on complex data inputs, has the potential to redefine project management in FinTech. The survey highlights that AI adoption is becoming mainstream within financial industry, with results in enhancing efficiency, automating processes, and opening new monetisation opportunities.
On the Other hand, The Stanford AI Index Report 2024 [
6] thighlights emergence of benchmarks like AgentBench and MLAgentBench demonstrates the growing focus on evaluating AI agents’ performance in specific tasks relevant to FinTech, such as risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer service automation.
Agentic AI analyzes vast amounts of data quickly, providing reliable synthesis for decision-making processes in project management. BlackRock’s platform Aladdin is known for using advanced machine learning to detect market trends, assess investment risks, and enhance advisory Servicies with Alladin Wealth.
Despite the described benefits, the report also puts accent on the need for thorough evaluations of AI systems to ensure their reliability and transparency. As agentic AI systems become more prevalent in FinTech, addressing concerns related to data privacy, security, and ethical considerations will be essential.
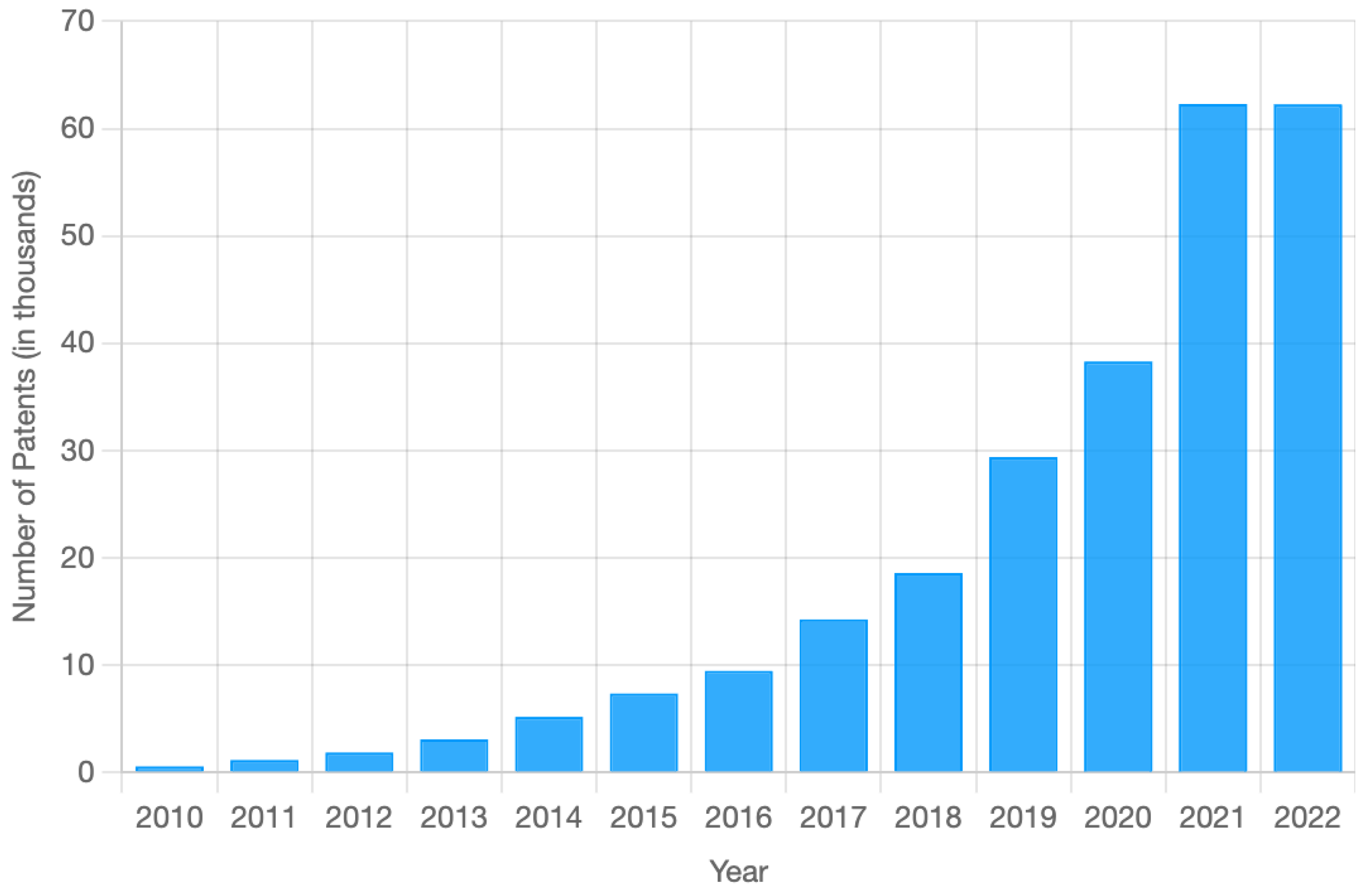
Figure 2.
The global increase in AI patents awarded from 2010 to 2022.
Figure 2.
The global increase in AI patents awarded from 2010 to 2022.
Notably, the rise was moderate in the early part of the decade, with a 56.1% growth from 2010 to 2014. The acceleration of AI Patents became particularly pronounced in recent years, with a 62.7% increase from 2021 to 2022 alone, with little governance in AI on the other side.
In project management contexts, Agentic AI can enable decision-making autonomy, ensuring projects are aligned with real-time risk assessments, data analytics, and performance metrics.
AI-enabled project management systems assist in optimizing resource allocation by leveraging real-time data to improve forecasting accuracy and project timelines. This aligns with the document’s insights on financial institutions utilizing AI-enabled data analytics, which is the most common use case in the industry so far.
2.2. Project Management Methodologies in FinTech Software Development
The integration of Agentic AI within FinTech project management frameworks presents a notable advancement across multiple methodologies.
Agile benefits from AI-enhanced sprint planning and automated backlog prioritization, leading to measurable improvements in deployment speed and quality. Similarly, Scrum’s iterative and incremental value creation is further enriched by the potential of AI “team members” and SWARMS, which dynamically adjust priorities and mitigate bottlenecks in real time. Kanban’s visual workflow management also gains from predictive analytics, allowing for proactive resource allocation and risk management.
Even the traditionally Waterfall methodology, prevalent in compliance environments such as banking or capital markets trading, evolves into a more responsive system when infused with AI-driven predictive insights and continuous monitoring.
2.2.1. Agile Methodology
The Agile framework is a dominant force in FinTech project management due to its iterative nature. The FinTech industry appreciates Agile increased efficacy, utilizing workflows by test-driven development (TDD) and DevOps practices.
By embedding predictive analytics into iterative cycles, they achieved a documented improvement in deployment speed and a notable reduction in post-release failures. The burgeoning role of Agentic AI further strengthens Agile.
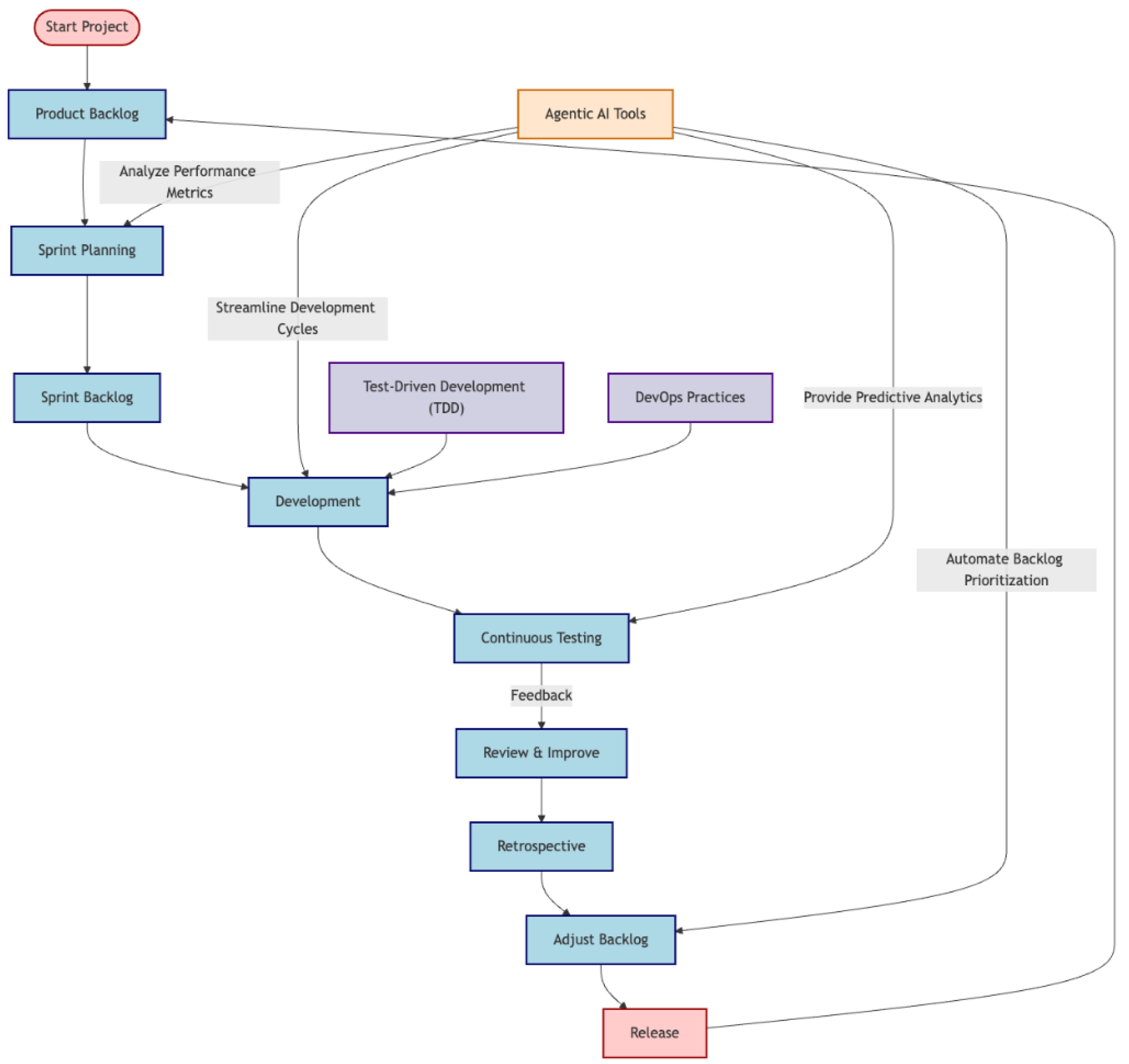
Figure 3.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech Agile Methodology. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red borders for clarity. Process Nodes: Standard Agile phases like “Product Backlog” and “Retrospective” are in light blue with dark blue borders. AI Components: AI-related features are emphasized in light orange, representing their growing importance. Complementary Methods: Test-Driven Development (TDD) and DevOps are in light purple, showing their role as enhancements.
Figure 3.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech Agile Methodology. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red borders for clarity. Process Nodes: Standard Agile phases like “Product Backlog” and “Retrospective” are in light blue with dark blue borders. AI Components: AI-related features are emphasized in light orange, representing their growing importance. Complementary Methods: Test-Driven Development (TDD) and DevOps are in light purple, showing their role as enhancements.
AI-driven sprint planning tools analyze performance metrics and autonomously suggest backlog prioritization, which has significantly narrowed development cycles in pilot studies. Emerging AI tools have the capability to reduce the overall time required for planning and executing development tasks and an automated backlog prioritization can streamline the process, thereby cutting down the time spent on each development cycle, increasing overall the effectiveness and sustainability of any given project.
2.2.2. Scrum Framework
Scrum, a subset of Agile, excels at incremental value creation through sprint-based planning. Integrating Agentic AI has the potential to revolutionize Scrum further, with AI “team members” autonomously addressing low-priority, resource-intensive backlog items in parallel with human teams.
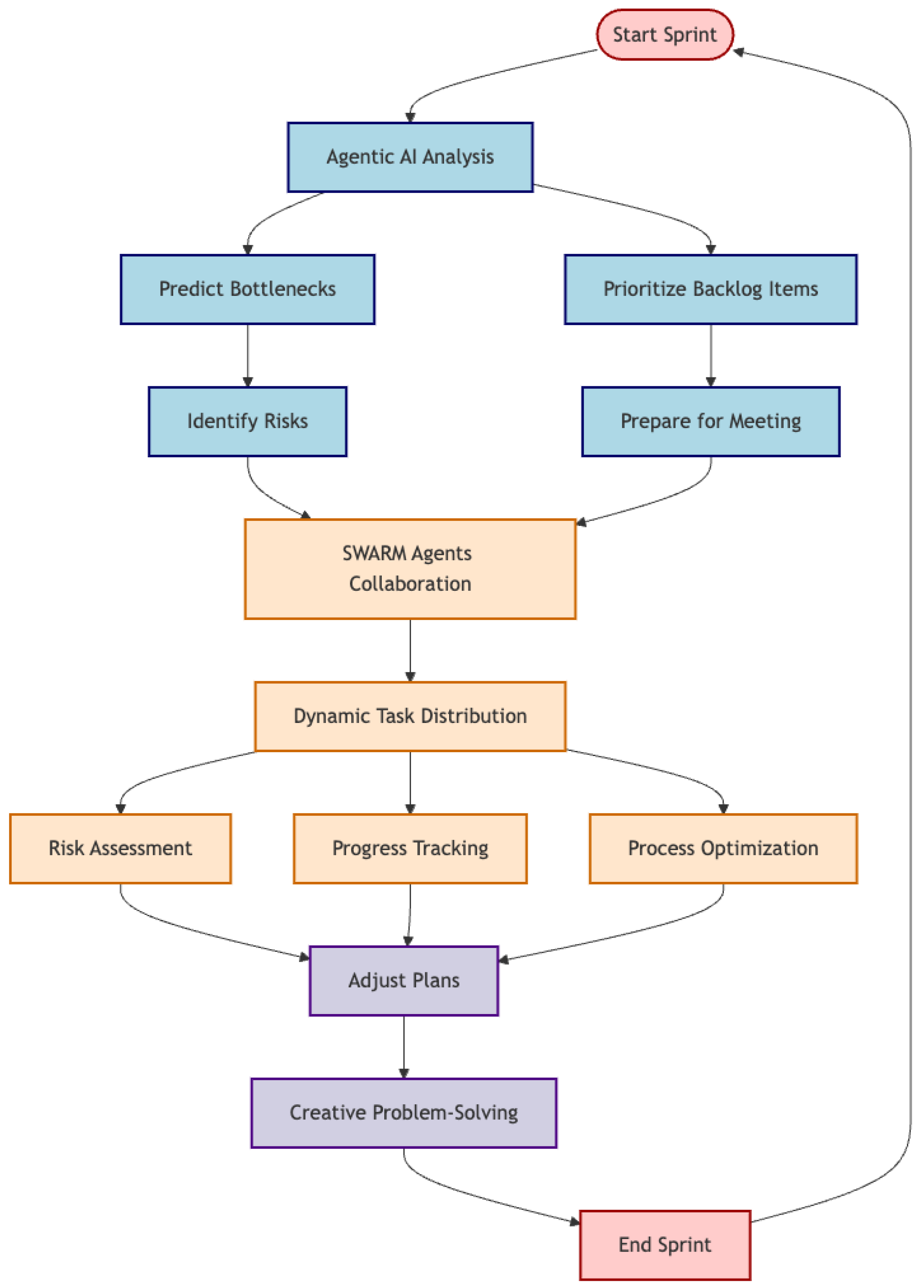
Figure 4.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech SCRUM Flowchart. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red borders for clarity. Process Nodes: Standard Agile phases like “Product Backlog” and “Retrospective” are in light blue with dark blue borders. AI Components: AI-related features are emphasized in light orange, representing their growing importance. Complementary Methods: Test-Driven Development (TDD) and DevOps are in light purple, showing their role as enhancements.
Figure 4.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech SCRUM Flowchart. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red borders for clarity. Process Nodes: Standard Agile phases like “Product Backlog” and “Retrospective” are in light blue with dark blue borders. AI Components: AI-related features are emphasized in light orange, representing their growing importance. Complementary Methods: Test-Driven Development (TDD) and DevOps are in light purple, showing their role as enhancements.
Agentic AI might analyze past sprints to predict potential bottlenecks or prioritize backlog items before a meeting even starts, allowing teams to focus more on creative problem-solving rather than on routine planning.
One exciting development is the idea of SWARMS—multiple lightweight, specialized AI agents collaborating in real time. Rather than having one central system, these SWARMS could distribute tasks like risk assessment, progress tracking, and process optimization across several agents. These agents would work together, adjusting plans dynamically as a sprint develops, much like how a swarm of bees coordinates to build and protect their hive.
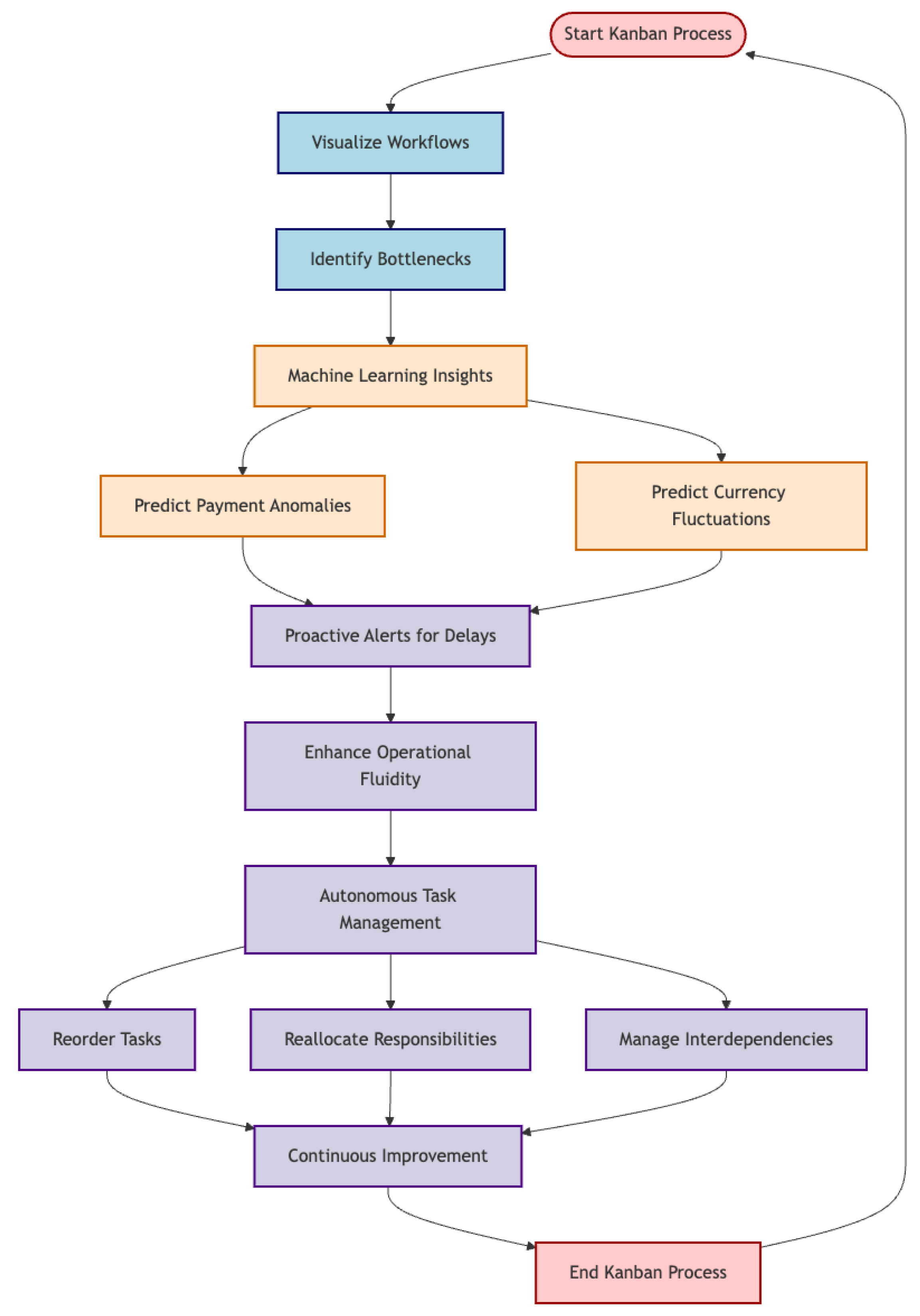
2.2.3. Kanban
Kanban thrives on visualizing workflows, resolving bottlenecks, and enabling real-time adaptability. A Kanban dashboard layered with machine learning models could be capable of predicting payment anomalies and currency fluctuation patterns.
Figure 5.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech KANBAN Flowchart. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red border boxes represent the initiation and completion tasks of the Kanban process. Process Nodes: In light blue with dark blue borders represent the core workflow steps like visualizing tasks and identifying bottlenecks. AI Components: AI-related features are highlighted in light orange, predictive capabilities such as forecasting payment anomalies and currency fluctuations, which support proactive decision-making. Complementary Methods: Shown in light purple, representing enhancements to the process, including real-time adaptability and autonomous management features that improve overall operational efficiency.
Figure 5.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech KANBAN Flowchart. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red border boxes represent the initiation and completion tasks of the Kanban process. Process Nodes: In light blue with dark blue borders represent the core workflow steps like visualizing tasks and identifying bottlenecks. AI Components: AI-related features are highlighted in light orange, predictive capabilities such as forecasting payment anomalies and currency fluctuations, which support proactive decision-making. Complementary Methods: Shown in light purple, representing enhancements to the process, including real-time adaptability and autonomous management features that improve overall operational efficiency.
These insights reduce decision latency, enhancing operational fluidity as teams can receive proactive alerts when tasks are likely to become delayed or when additional resources may be needed.
With Agentic AI, Kanban boards become proactive actors themselves—reordering tasks, reallocating responsibilities, and autonomously managing interdependencies.
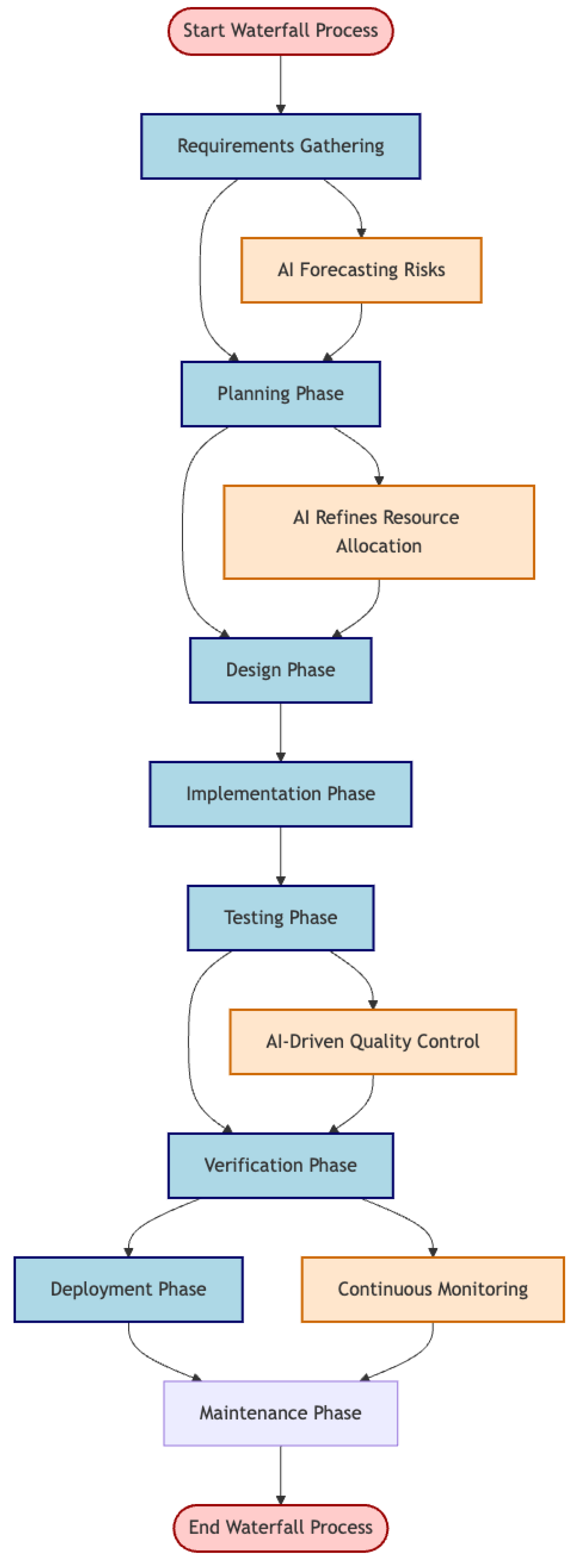
2.2.4. Waterfall Methodology
Legacy compliance-heavy operations often tether toward the Waterfall methodology for its linear and heavily documented approach.
The infusion of Agentic AI into Waterfall project management transforms a static, linear process into one that is more responsive and predictive.
This evolution is particularly relevamt in FinTech environments where regulatory constanta, rapid iteration based on predictive insights, and high quality standards are necessary for successful project outcomes. During the dependency collection and planning stages, AI systems can utilize historical data to estimate any potential risks and refine resource allocation, thereby establishing more realistic project timelines.
This data-driven approach not only enhances the precision of initial planning but also supports a more robust risk management during the testing and verification phases, continuous AI-driven monitoring can facilitate quality control by swiftly identifying anomalies and defects.
Figure 6.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech Waterfall Flowchart. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red borders the initiation and completion point of the Waterfall methodology. Process Nodes: In light blue with dark blue border “boxes” represent the sequential phases of the Waterfall process, including “Requirements Gathering,” “Planning Phase,” “Design Phase,” “Implementation Phase,” “Testing Phase,” “Verification Phase,” “Deployment Phase,” and “Maintenance Phase.” AI Components: AI-integrations are highlighted in light orange, such as “AI Forecasting Risks” during requirements gathering and “AI Refines Resource Allocation” during planning, alongside “AI-Driven Quality Control” and “Continuous Monitoring” during testing and deployment. Complementary Methods: Shown in light purple, representing a Maintenance Phase, assuring that deployed systems remain functional, relevant, and compliant over time while addressing user needs and unexpected challenges.
Figure 6.
Use of Agentic AI Tools in FinTech Waterfall Flowchart. Start/End Nodes: Highlighted in light red with dark red borders the initiation and completion point of the Waterfall methodology. Process Nodes: In light blue with dark blue border “boxes” represent the sequential phases of the Waterfall process, including “Requirements Gathering,” “Planning Phase,” “Design Phase,” “Implementation Phase,” “Testing Phase,” “Verification Phase,” “Deployment Phase,” and “Maintenance Phase.” AI Components: AI-integrations are highlighted in light orange, such as “AI Forecasting Risks” during requirements gathering and “AI Refines Resource Allocation” during planning, alongside “AI-Driven Quality Control” and “Continuous Monitoring” during testing and deployment. Complementary Methods: Shown in light purple, representing a Maintenance Phase, assuring that deployed systems remain functional, relevant, and compliant over time while addressing user needs and unexpected challenges.
Such automatic feedback loops reduce the time to resolution and enhance the reliability of the final deliverable. By integrating these intelligent processes into the inherently sequential structure of the Waterfall model, Agentic AI introduces a degree of dynamism that traditionally is absent from this methodology framework.
2. New Advanced Tools in Software Development and FinTech Project Management
In FinTech innovation, the deployment of advanced technological tools enable the capacity to increase efficiency of software development and streamline financial services.
GitHub Copilot stands out as an example of AI application that is much more than basic code suggestion functionalities, enabling real-time collaborative coding, intelligently adapting to the dynamic requirements of projects, helping developers to increase efficiency and adaptability in software development.
It assists developers by generating code snippets and suggesting contextually relevant code, has shown in a study involving over 2,000 developers, GitHub Copilot was found to be extremely easy to use by 43% of the participants, and 51% rated it as extremely useful [
9].
Table 2.
GitHub Copilot Adoption - Survey on Perceived Productivity.
Table 2.
GitHub Copilot Adoption - Survey on Perceived Productivity.
| Category |
Statement |
Percentage (%) |
| Perceived Productivity |
I am more productive |
88 |
| Satisfaction and Well-being |
Less frustrated when coding |
59 |
| Satisfaction and Well-being |
More fulfilled with my job |
60 |
| Satisfaction and Well-being |
Focus on more satisfying work |
74 |
| Efficiency and Flow |
Faster completion |
88 |
| Efficiency and Flow |
Faster with repetitive tasks |
96 |
| Efficiency and Flow |
More in the flow |
73 |
| Efficiency and Flow |
Less time searching |
77 |
| Efficiency and Flow |
Less mental effort on repetitive tasks |
87 |
The quick adoption rate, with 81.4% of developers installing the Copilot IDE extension on the same day they received a license, underlines its ease of integration and immediate impact on productivity. The tool also led to a 15% increase in the pull request merge rate..
Further research highlighted the system’s impact on developer satisfaction, with the majority reporting significant reductions in mental effort during repetitive tasks. This enhancement in job satisfaction and the decrease in cognitive load could contribute to long-term benefits for developers and organizations by reducing burnout and promoting a more engaging work environment.
The use of AI-powered predictive analytics is upgrading also DevOps processes. Tools can incorporate regression algorithms to analyze operational anomalies, thereby preempting potential incidents, facilitated by tools such as BigPanda, witch can enhance monitoring and management of IT systems. These tools use big data to identify patterns that can predict potential issues, allowing teams to proactively address them before they escalate. This not only speeds up delivery but also ensures releases with significant fever bugs [
10].
These examples show the transformative impact that advanced AI tools are having on the FinTech sector, shaping a new era of enhanced automation and innovation.
Deploying risk-sensitive AI agents, a Trading Company can preemptively flag and resolve anomalies in high-frequency trading algorithms. Agentic systems have tha capability to continuously monitor risk factors and autonomously reroute trades, a capability unmatched at this time by conventional tools. Integrated AI agents within collaboration platforms like Slack or Jira can autonomously schedule sprints, review tasks dynamically, and even draft preliminary user stories, greatly reducing overhead interaction costs.
Jira Service Management utilizes an AI-powered virtual agent that operates in Slack, bringing together humans, processes, data, agents, and AI into one conversational interface. The virtual agent automates common support interactions, leveraging Atlassian Intelligence to generate AI answers from the linked (grounded) knowledge base to handle requests. This setup not only speeds up response times but also allows ticket management within Jira from Slack interactions, optimizing both platforms for better user experience and efficiency [
11].
The HelpDesk+ app enhances Jira Service Management by integrating two-way Slack support, converting conversations into Jira tickets and syncs replies in real-time. This app also uses AI to recommend articles from the grounded knowledge base, enabling quick tocket responses and reducing the overall volume of support requests. This integration allows support agents to spend less time switching between systems and more time focusing on other issues, improving overall productivity.
Platforms like Celoxis and Asana are integrating AI to transform project management, as Celoxis’ AI tool, Lex, employs predictive analytics and natural language processing to help project managers plan and execute projects more effectively, enabling real-time data integration and decision-making support. Asana – with a larger adoption rate - incorporates AI for project management tasks, enhance decision-making, and improve collaboration across teams [
13]
The 2024 State of AI at Work report by Asana’s Work Innovation Lab and Anthropic reveals that over half of knowledge workers now use generative AI tools weekly, marking a significant increase in AI adoption over the past nine months. “Workers who see AI as a teammate rather than a tool are 33% more likely to report productivity gains” [
15] highlights the value of integrating AI collaboratively in advanced software and project management workflows. However, organizations remain largely unprepared for this shift, with low AI literacy among workers and only 31% having a formal AI strategy.
This aligns with the previous mentioned ”A Global AI in Financial Services Survey”, World Economic Forum insights on financial institutions utilizing AI-enabled data analytics, which is the most common use case in the industry.
3. Labor Market Impact of Agentic Ai in FinTech Project Management
The World Economic Forum & Accenture white paper titled “Jobs of Tomorrow: Large Language Models and Jobs” addresses the transformative role large language models (LLMs) are expected to play in reshaping the labor market and the future of work [
7].
This analysis is relevant in understanding the implications of integrating agentic artificial intelligence (AI) into industries like FinTech project management by examining over 19,000 tasks across 867 occupations. The report offers a structured perspective on how LLMs influence job workflows, create new opportunities, and change established roles. The paper outlines that 23% of global jobs are projected to undergo change in the next five years as industries adopt AI-driven technologies. At the core of this transformation is the capacity of LLMs to dramatically automate routine and repetitive tasks, such as data entry, document verification, and clerical work. Jobs like Credit Authorizers, Management Analysts and Statistical Assistants work-fields with high exposure to repetitive workflows are prime candidates for automation.
However, the role of LLMs goes beyond displacement, as they can significantly enhance the potential of more complex and abstract jobs. For example, roles that require deep reasoning, human creativity, and collaborative problem-solving, such as those in scientific analysis or software development, are likely to be augmented.
Historically, technological innovation has led to disruptions but has brought up new roles and industry opportunities. In this sense, FinTech and other high-exposure industries stand to benefit with the rise of emerging job categories necessitated by LLM adoption. For example, entirely new professions, such as AI Prompt Engineers, Data Curators, Interaction Designers, and Ethics/Governance Specialists, demonstrate the evolving needs of an AI-driven organizational structure.
That said, the labor market shifts brought about by LLMs are not uniform. The financial services sector, which encompasses FinTech project management, is among the most exposed to these technologies, with an estimated 70% of working hours at risk of being impacted.
For roles that involve customer-facing interactions, such as client management or fraud detection, AI tools offer augmentation rather than pure replacement, automating tedious processes while enabling human experts to engage in higher-value problem-solving tasks.
The rapid adoption of LLMs does raise grounded concerns about employment security, socioeconomic disparities, and workforce readiness and relevance of current educational programs. The challenge for businesses and governments lies in ensuring that these transformations benefit society at large instead of exacerbating inequalities. The report higlights the need for workforce development initiatives, including reskilling programs and lifelong learning systems, to prepare employees for the “jobs of tomorrow”.
Companies are called upon aligning their internal workforce planning and upskilling strategies to responsibly manage transitions, increase efficiency and maximize the benefits of generative AI technologies.
Table 3.
Jobs with Highest potential for automation (World Economic Forum).
Table 3.
Jobs with Highest potential for automation (World Economic Forum).
| Occupations |
Exposure % |
Augmentation |
Lower Potential |
Non-language Tasks |
| Credit Authorizers, Checkers and Clerks |
81 |
7 |
12 |
|
| Management Analysts |
70 |
7 |
24 |
|
| Telemarketers |
68 |
18 |
13 |
|
| Statistical Assistants |
61 |
1 |
34 |
7 |
| Tellers |
93 |
4 |
37 |
|
| Forensic Science Technicians |
60 |
1 |
4 |
37 |
| Receptionists and Information Clerks |
58 |
11 |
31 |
|
| Brokerage Clerks |
58 |
16 |
17 |
10 |
| Production, Planning and Expediting Clerks |
57 |
15 |
18 |
10 |
| File Clerks |
56 |
7 |
11 |
26 |
| Word Processors and Typists |
55 |
5 |
40 |
|
| Bookkeeping, Accounting and Auditing Clerks |
55 |
23 |
22 |
|
| Legal Secretaries and Administrative Assistants |
54 |
23 |
12 |
11 |
| Loan Interviewers and Clerks |
54 |
27 |
13 |
7 |
| Bill and Account Collectors |
53 |
9 |
21 |
17 |
The study highlights that LLMs can impact roughly 80% of the workforce, with tasks being completed up to 15% faster at similar quality—rising to 47-56% with specialized software. In FinTech project management, agentic AI can optimize task assignments by analyzing project workflows and reallocating labor-intensive efforts to AI agents, particularly in repetitive tasks like where, AI Agents or SWARMS can automate most processes while augmenting human capabilties, ensuring quality and scalability [
7].
Adoption challenges for AI in FinTech project management may reflect constraints seen in broader applications, such as trust in model output, ethical concerns, and dependency on user adaptation
3. Conclusions
The integration of Agentic AI in FinTech project management is on a growing trend as most industries, leading to improved financial solutions and efficient project outcomes. As the Nvidia CEO, Jensen Huang, states, this new era of AI will enable “complex problem-solving” that can transform the financial landscape.
Integrating agentic AI into advanced FinTech project management can significantly enhance operational efficiency, sustianability, decision-making, and can improve project outcomes while addressing the challenges of transparency and regulation.
The insights from the Stanford AI Index Report underscore the importance of ongoing research and development in this area. Large language models offer an opportunity to redefine current professional roles, particularly in innovative-heavy sectors like FinTech.
However, we will need to address challenges in workforce displacement and disruption by ensuring a balance between job automation and task augmentation in sync with a new workforce policy. It is time for upskilling and proactive measures, agentic AI can not only optimize business operations but also fuel long-term productivity, industry innovation, and robust job growth in increasingly dynamic markets.
Agentic AI systems are set to redefine the operational frameworks within FinTech projects. These systems will integrate deeply into existing project management paradigms, facilitating a symbiotic relationship that transforms traditional workflows. The resultant shift will likely enhance the efficiency and adaptability of project management practices, allowing for a more fluid and responsive approach to managing complex FinTech projects.
Secondly, the capacity to hyper-customize user interfaces (Hyper UX) based on user data, these analytics will grow user engagement by tailoring experiences to individuals needs. This level of personalization is expected to enhance user satisfaction and engagement metrics, positioning predictive analytics as a critical tool in the development of user-centric FinTech applications.
The increasing complexity of global regulatory environments requires a dynamic approach to compliance - in this usecases AI Agents will play a crucial role in ensuring that FinTech projects remain compliant across different jurisdictions. Using crawlers and large grounded data sets, they can quickly adapt to regulatory changes, safeguarding projects against potential legal and operational risks associated with non-compliance.
Combining agentic adaptability, predictive intelligence, and user-focused design innovations will constitute the cornerstones of FinTech’s future mode of operations.
Stakeholders who understand and will implement these evolving dynamics stand poised not merely to survive but are statistically determined to thrive in a complex and competitive landscape of Agentic AI Advanced FinTech Project Management.
References
- Gomber P, Koch J-A, Siering M. Digital Finance and FinTech: Current Research and Future Research Directions. Journal of Business Economics 2017; 87(5): 537-580. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11573-017-0852-x.
- Nvidia. What is Agentic AI? Available from: https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/what-is-agentic-ai/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Floridi L, Sanders JW. On the Morality of Artificial Agents. Minds and Machines 2004; 14(3): 349-379.
- Rahwan I. Society-in-the-loop: Programming the Algorithmic Social Contract. Ethics and Information Technology 2018; 20(1): 5-14.
- Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance. Transforming Paradigms. Available from: https://www.jbs.cam.ac.uk/faculty-research/centres/alternative-finance/publications/transforming-paradigms/ (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Stanford AI Index. 2024 Report. Available from: https://aiindex.stanford.edu/report/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- World Economic Forum. Jobs of Tomorrow: Generative AI. Available from: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Jobs_of_Tomorrow_Generative_AI_2023.pdf (accessed on 05 February 2025).
- Cornell University. GPTs are GPTs: An Early Look at the Labor Market Impact Potential of Large Language Models. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00001 (accessed on 02 January 2025).
- GitHub. Quantifying GitHub Copilot’s Impact in the Enterprise with Accenture. Available from: https://github.blog/news-insights/research/research-quantifying-github-copilots-impact-in-the-enterprise-with-accenture/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- DZone. Predictive Analytics in DevOps Applications and Benefits. Available from: https://dzone.com/articles/predictive-analytics-in-devops-applications-and-be (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- IEEE. Artificial Intelligence in FinTech: Emerging Trends and Use Cases. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10638924 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Atlassian. Jira Service Management Features. Available from: https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira/service-management/features/itsm/ai (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Atlassian Marketplace. HelpDesk: AI-Powered Slack Support. Available from: https://marketplace.atlassian.com/apps/1224706/helpdesk-ai-powered-slack-support?tab=overview&hosting=cloud (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Celoxis. Best AI Project Management Tools. Available from: https://www.celoxis.com/article/best-ai-project-management-tools (accessed on 07 February 2025).
- Asana. AI in Project Management. Available from: https://asana.com/product/ai/project-management (accessed on 01 December 2024).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).