Submitted:
10 February 2025
Posted:
10 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
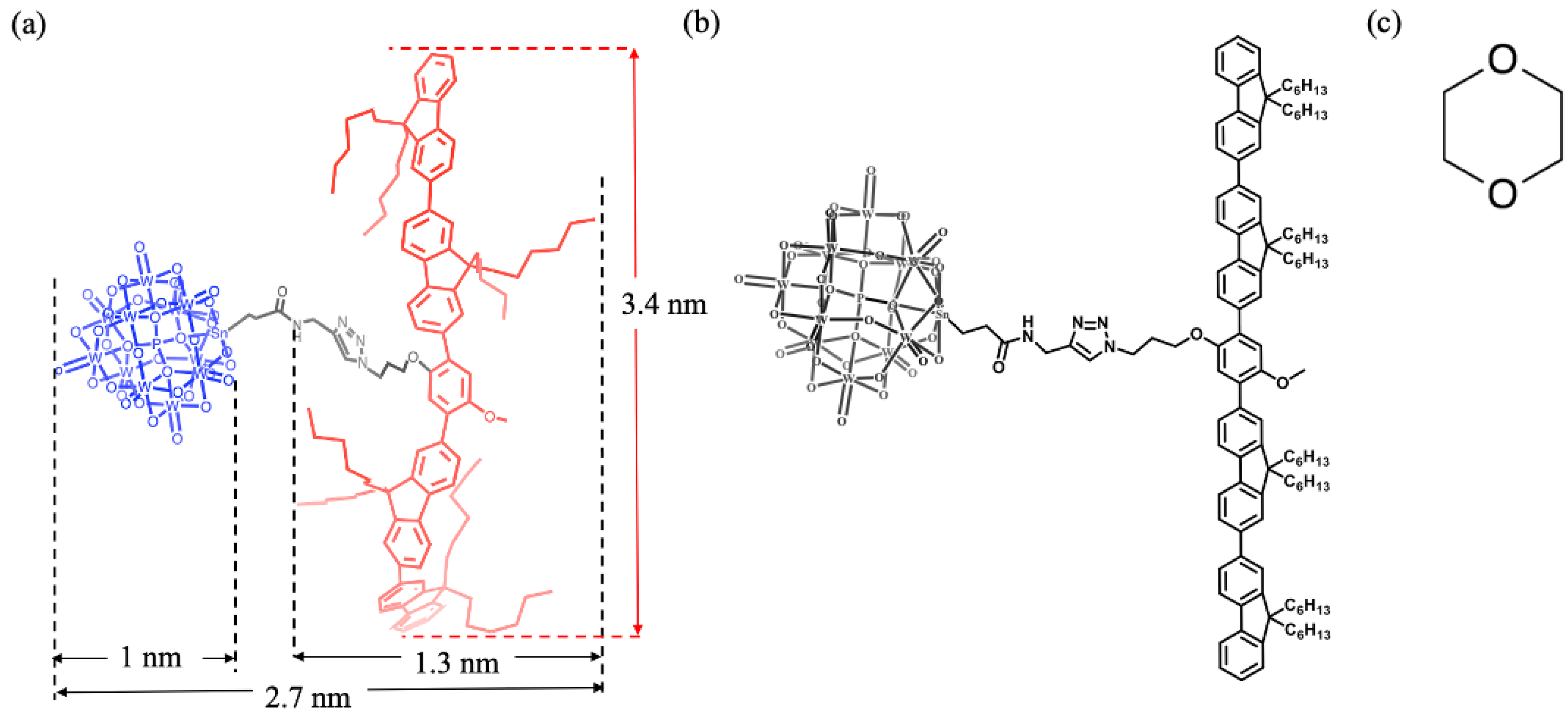
2.1. The Material Synthesis
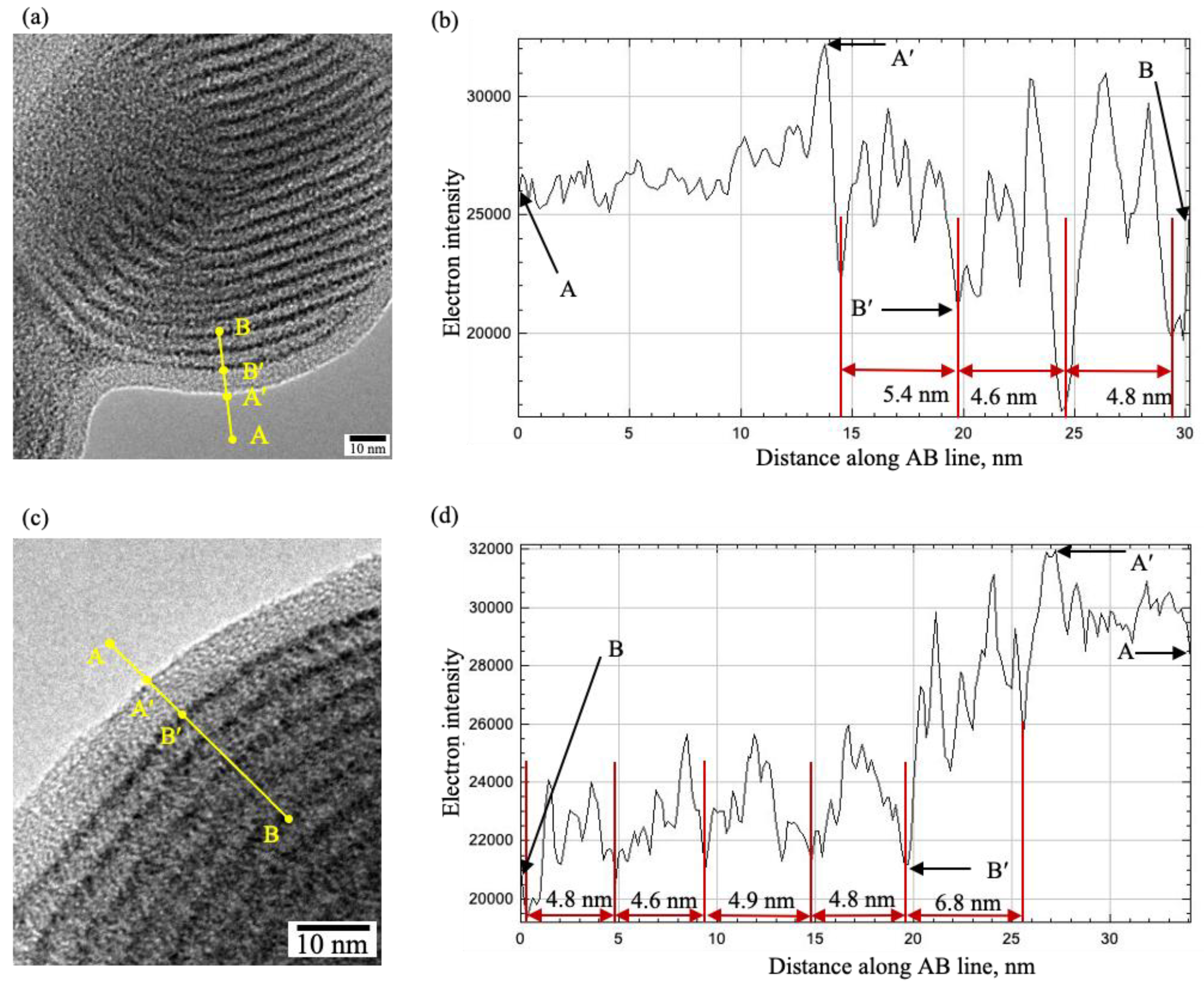
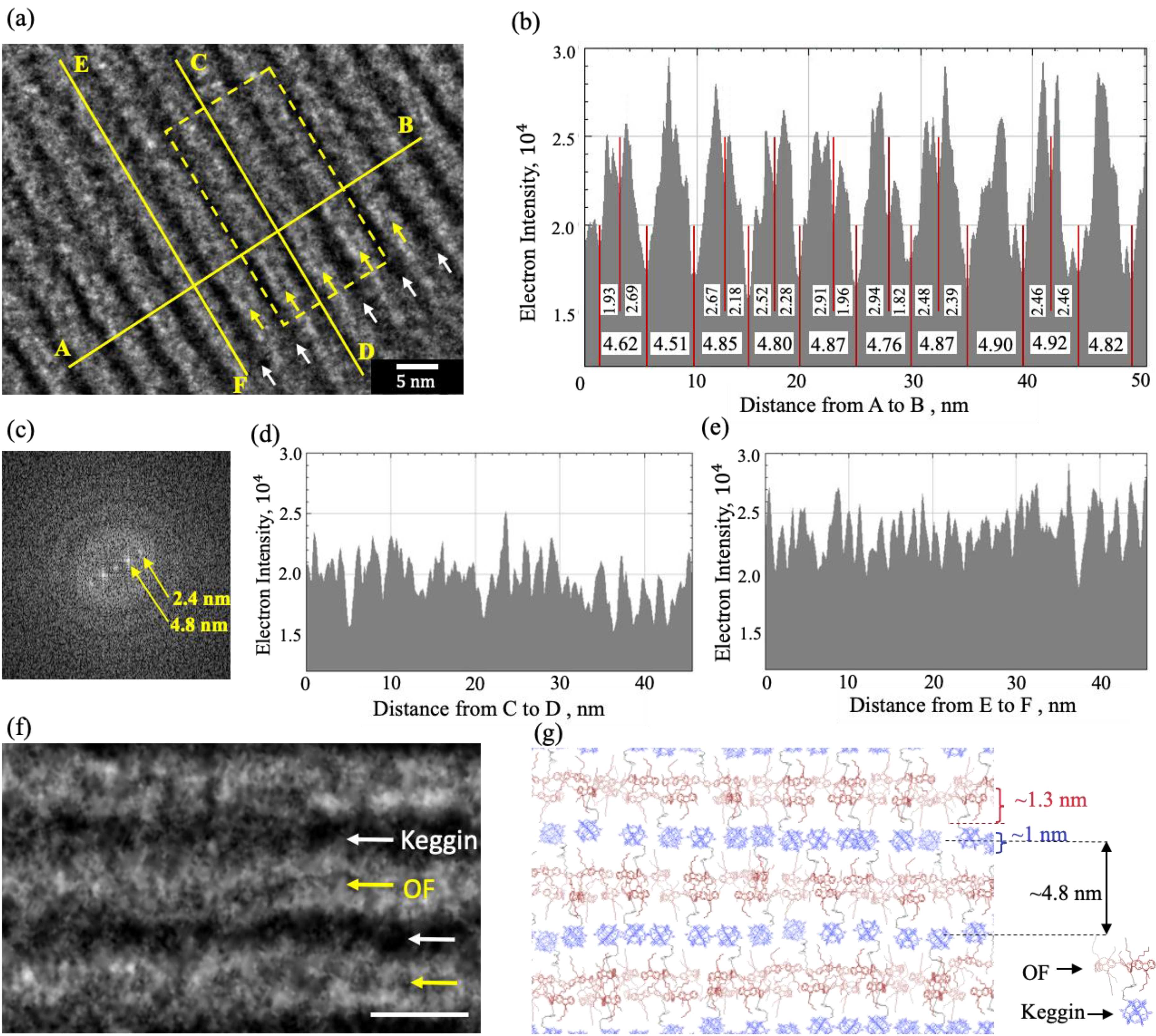
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy.
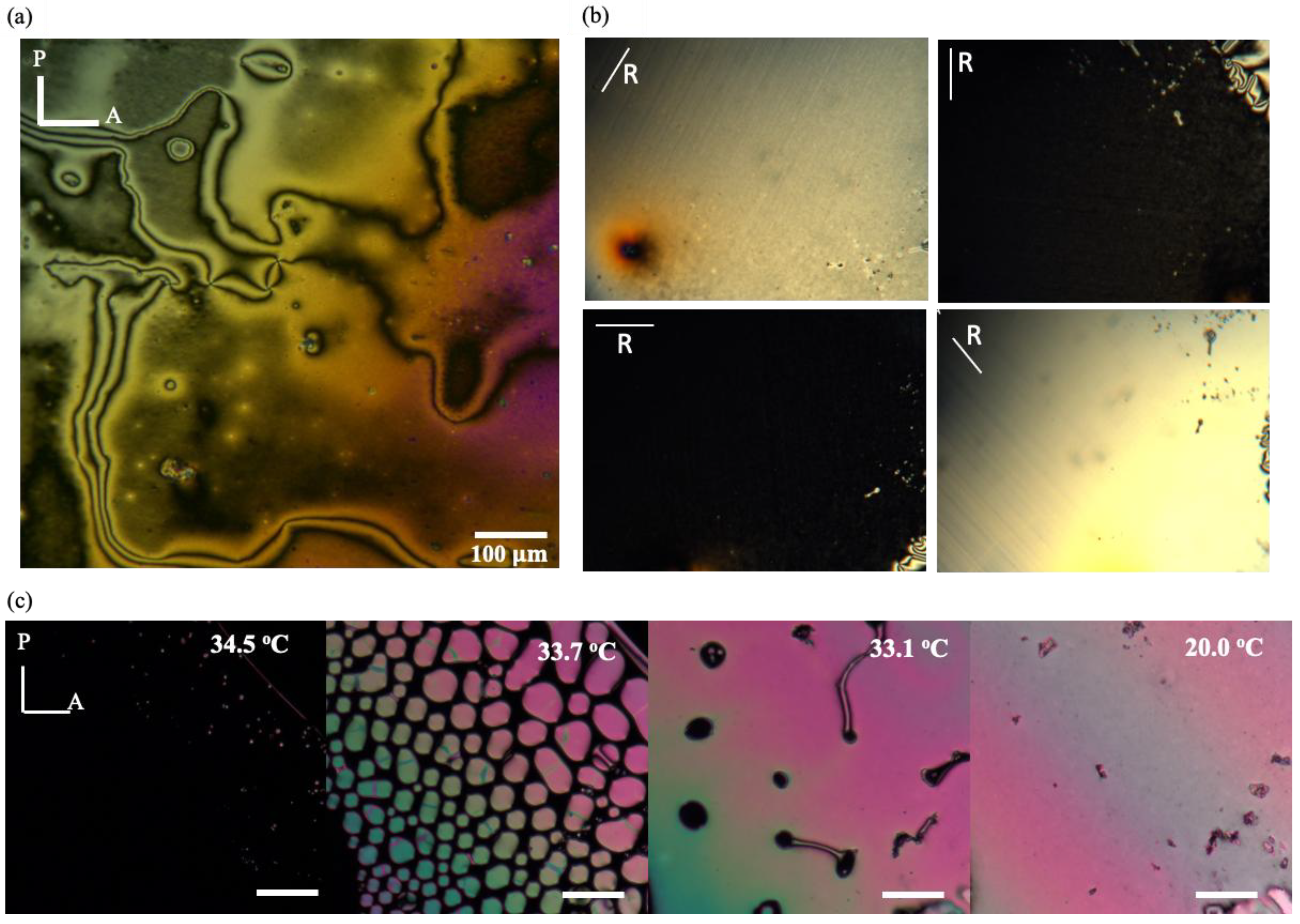
2.3. Polarized Optical Microscopy Study of High Concentrated KTOF4.
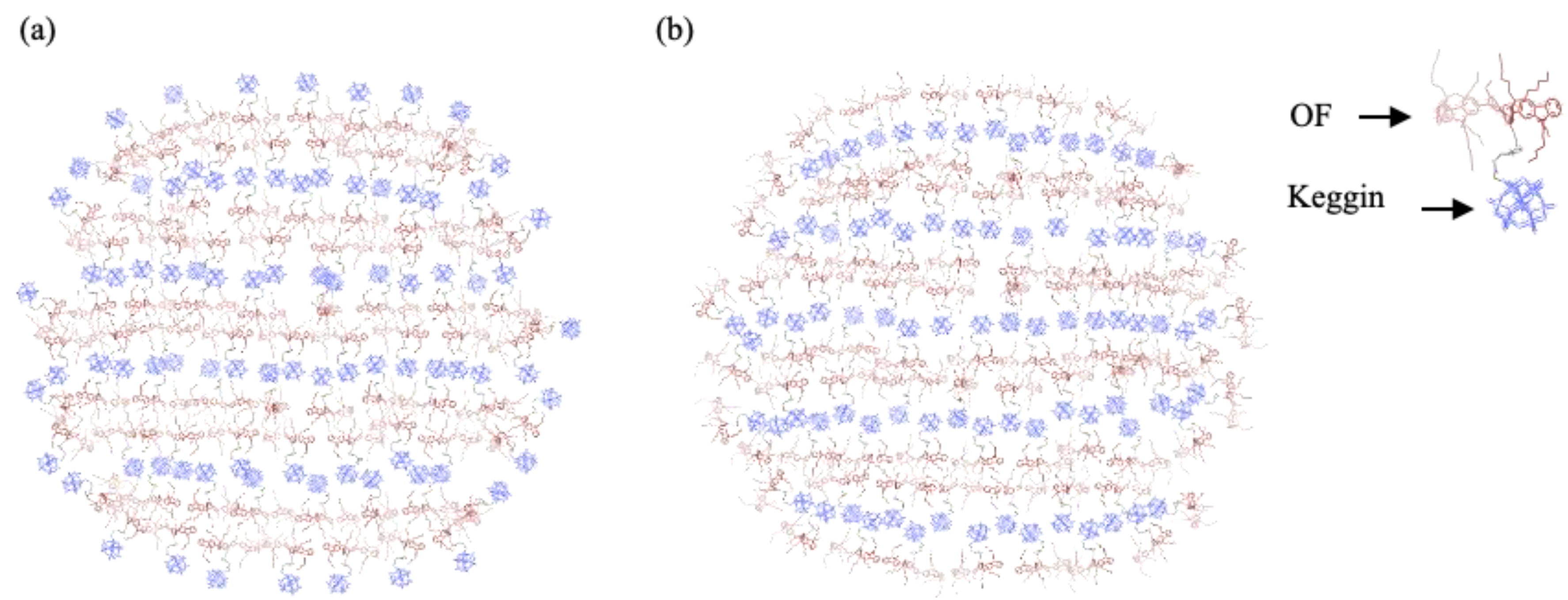
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walde, P.; Ichikawa, S. Enzymes inside lipid vesicles: preparation, reactivity and applications. Biomolecular engineering 2001, 18, 143–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percec, V.; Wilson, D.A.; Leowanawat, P.; Wilson, C.J.; Hughes, A.D.; Kaucher, M.S.; Hammer, D.A.; Levine, D.H.; Kim, A.J.; Bates, F.S. Self-assembly of Janus dendrimers into uniform dendrimersomes and other complex architectures. Science 2010, 328, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-S.; Park, S.W.; Hammond, P.T. Hydrogen-bonding layer-by-layer-assembled biodegradable polymeric micelles as drug delivery vehicles from surfaces. ACS nano 2008, 2, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, L.; Teply, B.A.; Mann, N.; Wang, A.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Precise engineering of targeted nanoparticles by using self-assembled biointegrated block copolymers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Szoka, F.C. Chemical approaches to triggerable lipid vesicles for drug and gene delivery. Accounts of chemical research 2003, 36, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet, X.; Boyd, B.J.; Drummond, C.J. Advances in drug delivery and medical imaging using colloidal lyotropic liquid crystalline dispersions. Journal of colloid and interface science 2013, 393, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulik-Krzywicki, T.; Dedieu, J.; Roux, D.; Degert, C.; Laversanne, R. Freeze− Fracture Electron Microscopy of Sheared Lamellar Phase. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4668–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T. Self-assembly of phase-segregated liquid crystal structures. Science 2002, 295, 2414–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhong, Z.; Hao, J. Self-assembly of onion-like vesicles induced by charge and rheological properties in anionic–nonionic surfactant solutions. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7812–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Amphiphilic building blocks for self-assembly: from amphiphiles to supra-amphiphiles. Accounts of chemical research 2012, 45, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miravet, J.F.; Escuder, B.; Segarra-Maset, M.D.; Tena-Solsona, M.; Hamley, I.W.; Dehsorkhi, A.; Castelletto, V. Self-assembly of a peptide amphiphile: transition from nanotape fibrils to micelles. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3558–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A.; Magazù, S.; Calandra, P. Amphiphiles self-assembly: basic concepts and future perspectives of supramolecular approaches. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics 2015, 2015, 151683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liu, T.; Qian, K.; Wei, B.; Hu, Y.; Gao, M.; Sun, X.; Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Bera, M.K. Continuous Curvature Change into Controllable and Responsive Onion-like Vesicles by Rigid Sphere–Rod Amphiphiles. ACS nano 2020, 14, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillissen, M.A.; Koenigs, M.M.; Spiering, J.J.; Vekemans, J.A.; Palmans, A.R.; Voets, I.K.; Meijer, E. Triple helix formation in amphiphilic discotics: demystifying solvent effects in supramolecular self-assembly. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percec, V.; Dulcey, A.E.; Balagurusamy, V.S.; Miura, Y.; Smidrkal, J.; Peterca, M.; Nummelin, S.; Edlund, U.; Hudson, S.D.; Heiney, P.A. Self-assembly of amphiphilic dendritic dipeptides into helical pores. Nature 2004, 430, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Sun, T.; Hao, A. Vesicles from supramolecular amphiphiles. RSC advances 2013, 3, 24776–24793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Kumar, S. Liquid-crystal nanoscience: an emerging avenue of soft self-assembly. Chemical Society Reviews 2011, 40, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Mizoshita, N. Self-assembly and phase segregation in functional liquid crystals. Current opinion in solid state and materials science 2002, 6, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltenhagen, P.; Kleman, M.; Lavrentovich, O. Freeze-fracture observations in the Lα phase of a swollen surfactant in the vicinity of the L3 and the L1 phase transitions. Journal de Physique II 1994, 4, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Cai, C. Self-assembly of copolymer micelles: higher-level assembly for constructing hierarchical structure. Chemical reviews 2020, 120, 4111–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ray, A.; Pramanik, N. Self-assembly of surfactants: An overview on general aspects of amphiphiles. Biophysical Chemistry 2020, 265, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. In Handbook of Liquid Crystals—Volume II: Advanced Aspects and Applications; Springer, 2024; pp. 203–243. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Wang, J.; Cao, F.; Lee, R.J.; Zhai, G. Lyotropic liquid crystal systems in drug delivery. Drug discovery today 2010, 15, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, V.P.; Dyawanapelly, S.; Dawre, S.; Ferreira-Faria, I.; Bezbaruah, R.; Gogoi, N.R.; Kolimi, P.; Dave, D.J.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Vora, L.K. Lyotropic liquid crystalline phases: drug delivery and biomedical applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2023, 647, 123546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammady, S.Z.; Pouzot, M.; Mezzenga, R. Oleoylethanolamide-based lyotropic liquid crystals as vehicles for delivery of amino acids in aqueous environment. Biophysical journal 2009, 96, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzenga, R.; Seddon, J.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Schröder-Turk, G.E.; Sagalowicz, L. Nature-Inspired design and application of lipidic lyotropic liquid crystals. Advanced materials 2019, 31, 1900818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Fernández, G.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Fernández-Ferreiro, A.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Lipidic lyotropic liquid crystals: Insights on biomedical applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2023, 313, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.; Le, T.; Drummond, C.J. Lyotropic liquid crystal engineering–ordered nanostructured small molecule amphiphile self-assembly materials by design. Chemical Society Reviews 2012, 41, 1297–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Moghaddam, M.J.; Sagnella, S.M.; Conn, C.E.; Danon, S.J.; Waddington, L.J.; Drummond, C.J. Lyotropic liquid crystalline self-assembly material behavior and nanoparticulate dispersions of a phytanyl pro-drug analogue of capecitabine− A chemotherapy agent. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2011, 3, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Van‘t Hag, L.; Gras, S.L.; Conn, C.E.; Drummond, C.J. Lyotropic liquid crystal engineering moving beyond binary compositional space–ordered nanostructured amphiphile self-assembly materials by design. Chemical society reviews 2017, 46, 2705–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentovich, O.D. Hierarchy of defect structures in space filling by flexible smectic-A layers. Sov Phys JETP 1986, 64, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Kurik, M.; Lavrentovich, O. Monopole structures and shape of drops of smectic C. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz 1983, 85, 11–526. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C. Liquid-crystalline structures in solutions of a polypeptide. Transactions of the Faraday Society 1956, 52, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jun-Yan Suen, J.; Prince, E.; Larin, E.M.; Klinkova, A.; Thérien-Aubin, H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B.; Helmy, A.S.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; et al. Colloidal cholesteric liquid crystal in spherical confinement. Nature communications 2016, 7, 12520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Prince, E.; Cho, S.; Salari, A.; Mosaddeghian Golestani, Y.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Kumacheva, E. Periodic assembly of nanoparticle arrays in disclinations of cholesteric liquid crystals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114, 2137–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurik, M.; Lavrentovich, O. Topological defects of cholesteric liquid crystals for volumes with spherical shape. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals 1982, 72, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun-Gyu, L.; Sundas, M.; Soo-Young, P. Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Droplets for Biosensors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2016, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; Seč, D.; Almeida, P.L.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Žumer, S.; Godinho, M.H. Liquid crystal necklaces: cholesteric drops threaded by thin cellulose fibres. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 7928–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, A.R.; Bernardino, N.R.; Silvestre, N.M.; Telo da Gama, M.M. Effect of curvature on cholesteric liquid crystals in toroidal geometries. Physical Review E 2017, 95, 012702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seč, D.; Porenta, T.; Ravnik, M.; Žumer, S. Geometrical frustration of chiral ordering in cholesteric droplets. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11982–11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, T.; Fernandez-Nieves, A. Drops and shells of liquid crystal. Colloid and Polymer Science 2011, 289, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bukusoglu, E.; Martínez-González, J.A.; Rahimi, M.; Roberts, T.F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Abbott, N.L.; De Pablo, J.J. Structural transitions in cholesteric liquid crystal droplets. ACS nano 2016, 10, 6484–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micoine, K.; Hasenknopf, B.; Thorimbert, S.; Lacôte, E.; Malacria, M. A general strategy for ligation of organic and biological molecules to Dawson and Keggin polyoxotungstates. Organic letters 2007, 9, 3981–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Sakurai, T.; Matsuda, W.; Seki, S.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, K.-Y.; Yan, X.-Y. Topologically directed assemblies of semiconducting sphere–rod conjugates. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2017, 139, 18616–18622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Feng, X.; Zhang, R.; Shan, W.; Su, Z.; Mao, J.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Huang, J.; Yan, X.Y.; Liu, T. Breaking parallel orientation of rods via a dendritic architecture toward diverse supramolecular structures. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2019, 58, 11879–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Kim, Y.K.; Zhang, C.; Borshch, V.; Zhou, S.; Park, H.S.; Jákli, A.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Tamba, M.G.; Kohlmeier, A. Direct observation of liquid crystals using cryo-TEM: Specimen preparation and low-dose imaging. Microscopy research and technique 2014, 77, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierski, J.; Raszewski, Z.; Kojdecki, M.; Kruszelnicki-Nowinowski, E.; Perkowski, P.; Piecek, W.; Miszczyk, E.; Zieliński, J.; Morawiak, P.; Ogrodnik, K. Determination of ordinary and extraordinary refractive indices of nematic liquid crystals by using wedge cells. Opto-Electronics Review 2010, 18, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowiorski, K.; Kędzierski, J.; Raszewski, Z.; Kojdecki, M.; Herman, J.; Miszczyk, E.; Piecek, W. Application of modified interference wedge method in measurements of indices of refraction and birefringence of nematic liquid crystals. Acta Physica Polonica A 2013, 124, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T.K. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Advanced electron microscopy of nanophased synthetic polymers and soft complexes for energy and medicine applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sadashiva, B.; Lavrentovich, O.; Jákli, A. Cryo-TEM studies of two smectic phases of an asymmetric bent-core material. Liquid Crystals 2013, 40, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repula, A.; Grelet, E. Elementary edge and screw dislocations visualized at the lattice periodicity level in the smectic phase of colloidal rods. Physical review letters 2018, 121, 097801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershan, P.S. Dislocation effects in smectic-A liquid crystals. Journal of Applied Physics 1974, 45, 1590–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhdeir, N.M.; Rey, A.D. Edge dislocation core structure in lamellar smectic-A liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelidis, I.; Blanc, C.; Kléman, M. Optical and confocal microscopy observations of screw dislocations in smectic-A liquid crystals. Physical Review E—Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics 2006, 74, 051710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gennes, P.G. An analogy between superconductors and smectics A. Solid State Communications 1972, 10, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleman, M.; Williams, C.E. Interaction between parallel edge dislocation lines in a smectic A liquid crystal. Journal de Physique Lettres 1974, 35, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleman, M. Defects in liquid crystals. Reports on Progress in Physics 1989, 52, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allain, M.; Kleman, M. Thermodynamic defects, instabilities and mobility processes in the lamellar phase of a non-ionic surfactant. Journal de Physique 1987, 48, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleman, M. Surfactant-Water Systems with Small Layer Rigidity Phase Stability, Defects Models and Defects Mobility in Polyoxyethylene Surfactant with Water. Liquid Crystals 1988, 3, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Sluckin, T. Core structure of a screw disclination in smectic-A liquid crystals. Physical Review E 1993, 48, R3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleman, M.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Soft Matter Physics: An Introduction; Springer: New York, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrentovich, O.D. Topological defects in dispersed liquid crystals, or words and worlds around liquid crystal drops. Liquid crystals 1998, 24, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovik, G.E.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Topological dynamics of defects: boojums in nematic drops. Zh Eksp Teor Fiz 1983, 85, 1997–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Kim, D.S.; Yoon, D.K. Surface-induced orientation of liquid crystal phases. Giant 2024, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentovich, O. Defects in liquid crystals: surface and interfacial anchoring effects. In Patterns of symmetry breaking; Springer, 2003; pp. 161–195. [Google Scholar]
- Faetti, S. Anchoring at the interface between a nematic liquid crystal and an isotropic substrate. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals 1990, 179, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
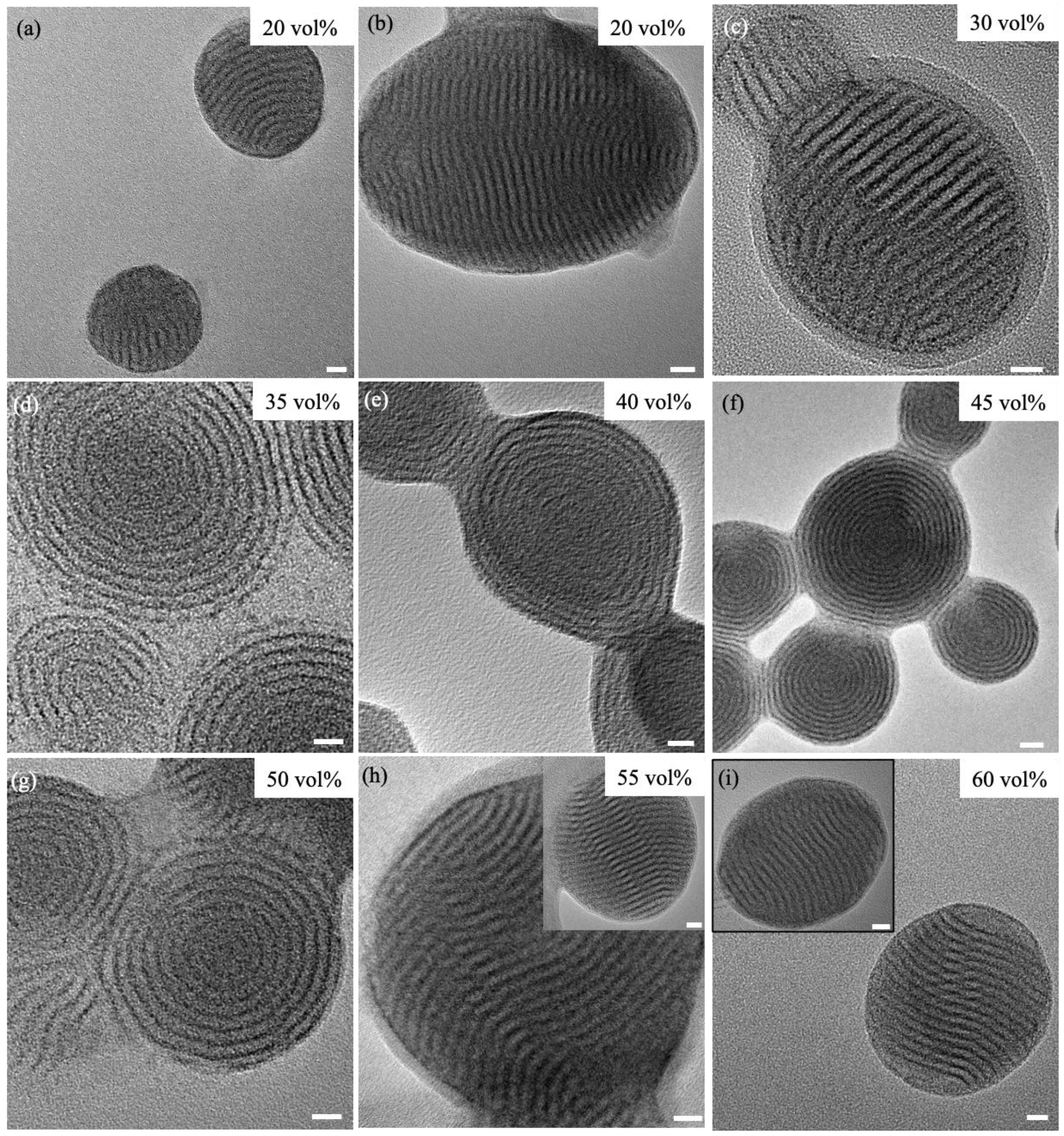
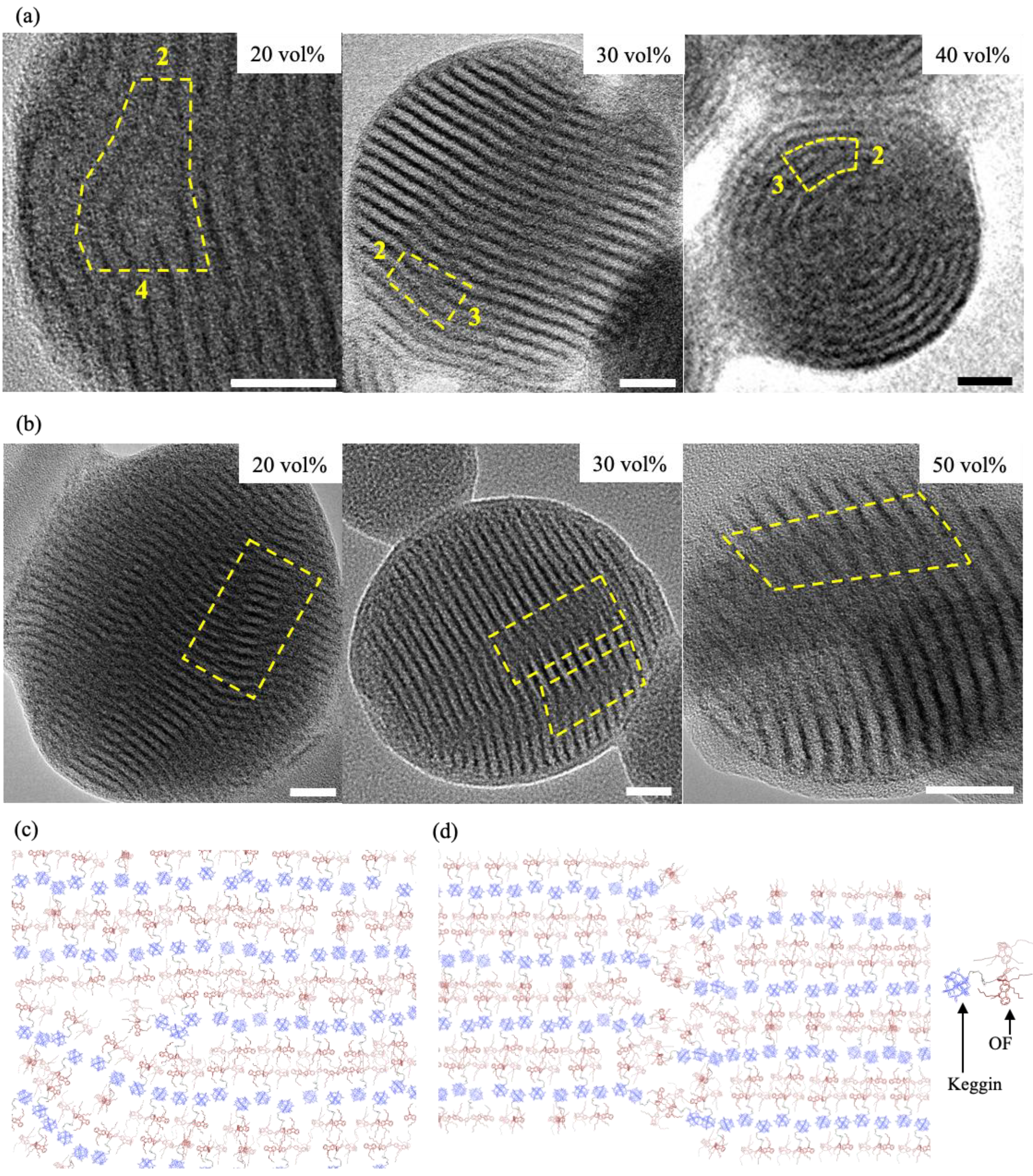
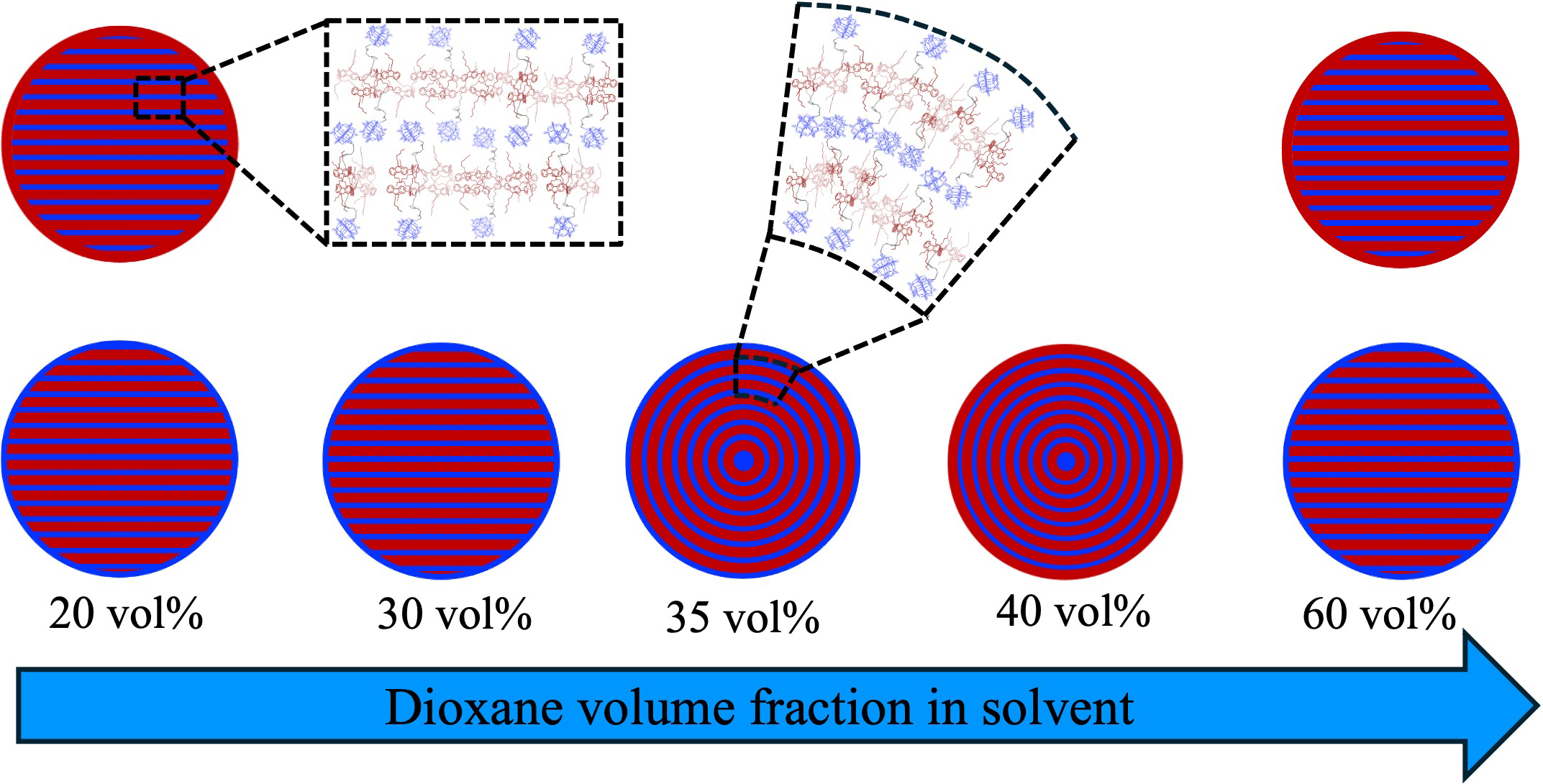
| Dioxane vol% | Concentric layers | Flat layers | Surface composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | Not observed | Frequently observed | Keggin/OF |
| 30 | Not observed | Frequently observed | Keggin |
| 35 | Frequently observed | Not observed | Keggin |
| 40 | Frequently observed | Not observed | OF |
| 45 | Frequently observed | Not observed | OF |
| 50 | Frequently observed | Observed (but rare) | OF |
| 55 | Not observed | Frequently observed | Keggin/OF |
| 60 | Not observed | Frequently observed | Keggin/OF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





