1. The Symmetry of P/2n and Prime Numbers Conjectures
We have
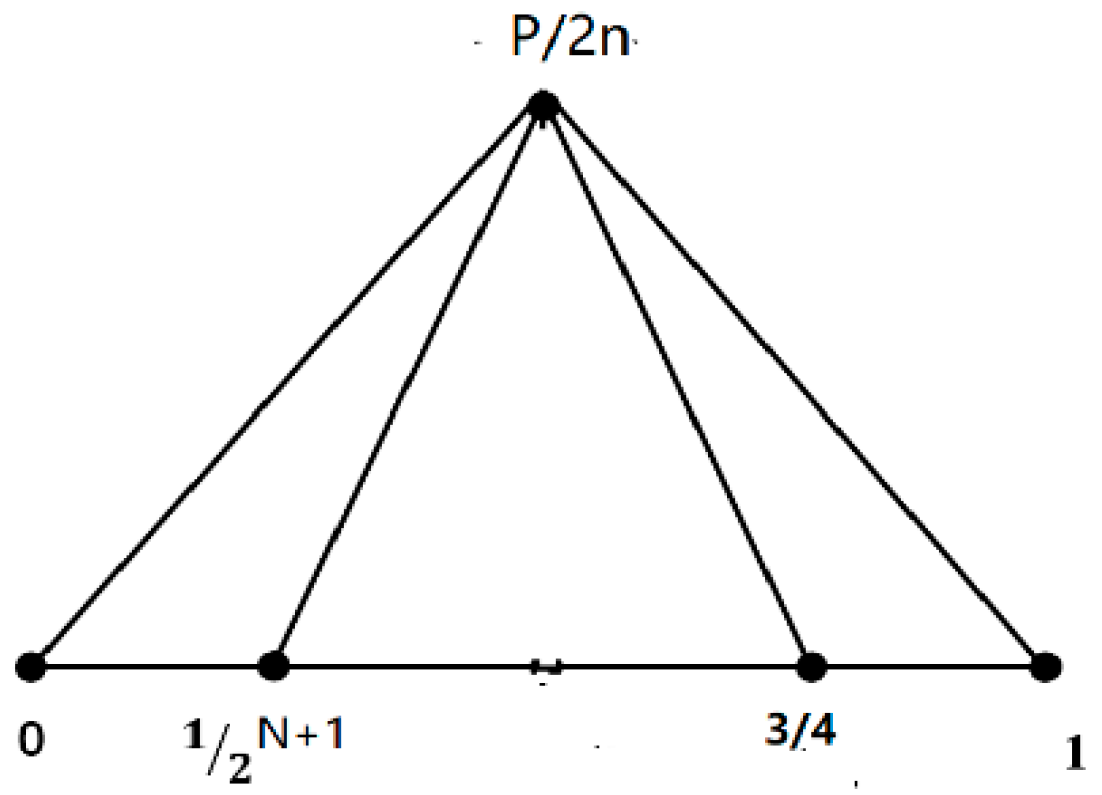
Figure 1.
P/2n number structure with points [ 0 1/2N+1 3/4 1].
Figure 1.
P/2n number structure with points [ 0 1/2N+1 3/4 1].
All natural numbers
All natural numbers excepted 0
All prime numbers
and
And We have
p0∈ ~(0, n]
And based on Bertrand -Chebyshev Theorem:when , there are at least a prime
number between n and 2n.
pn∈ ~[n, 2n)
So we have:
So
This is the proof of Goldbach conjecture.
and
This is the proof of Twin Primes Conjecture
And we also have
And
This is the proof of Polignac’s conjecture.
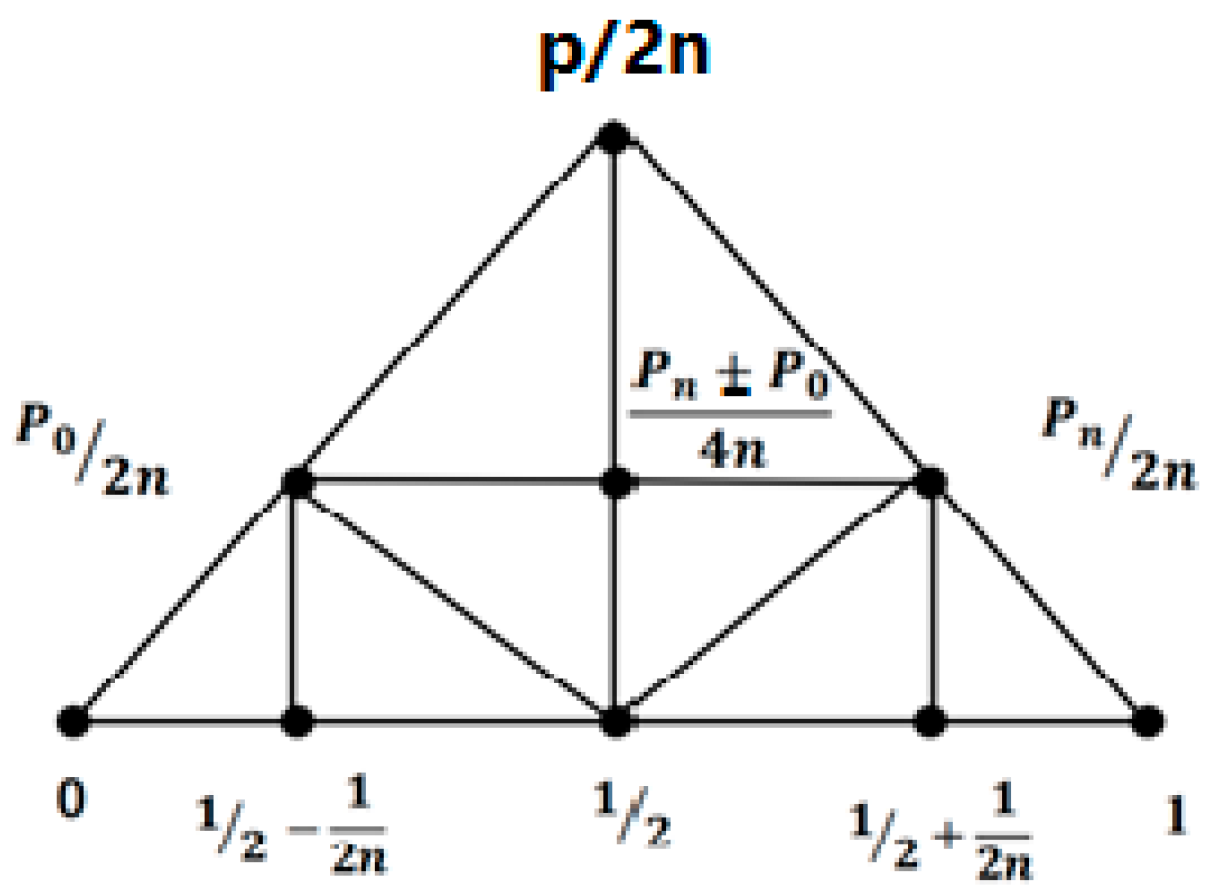
So we get a symmetry
structure of P/2n asFigure 2
Figure 2.
a symmetry structure of P/2n about line-1/2.
Figure 2.
a symmetry structure of P/2n about line-1/2.
2. A Concise Proof of The Fermat’ Last Theorem
he Fermat’ Last Theorem:
has no solution.
The equivalent proposition of this conjecture is
has no solution.
And We can get the figures as
Figure 3.
Figure 3.
D1/2+1/2 with points 1/2-1/2n and 1/2-1/2n
Figure 3.
D1/2+1/2 with points 1/2-1/2n and 1/2-1/2n
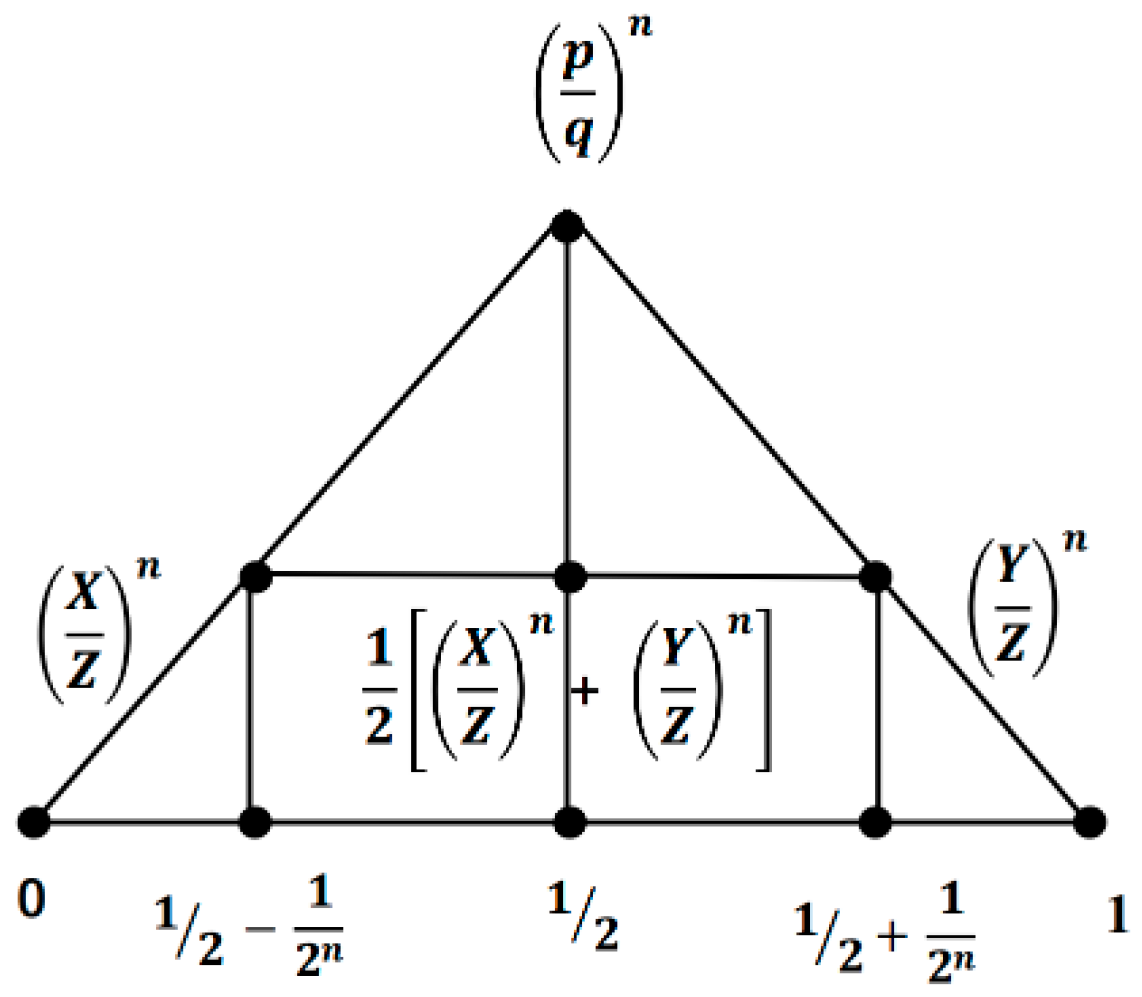
Figure 4.
a symmetry structure of about line-1/2.
Figure 4.
a symmetry structure of about line-1/2.
p,
q is relatively prime and
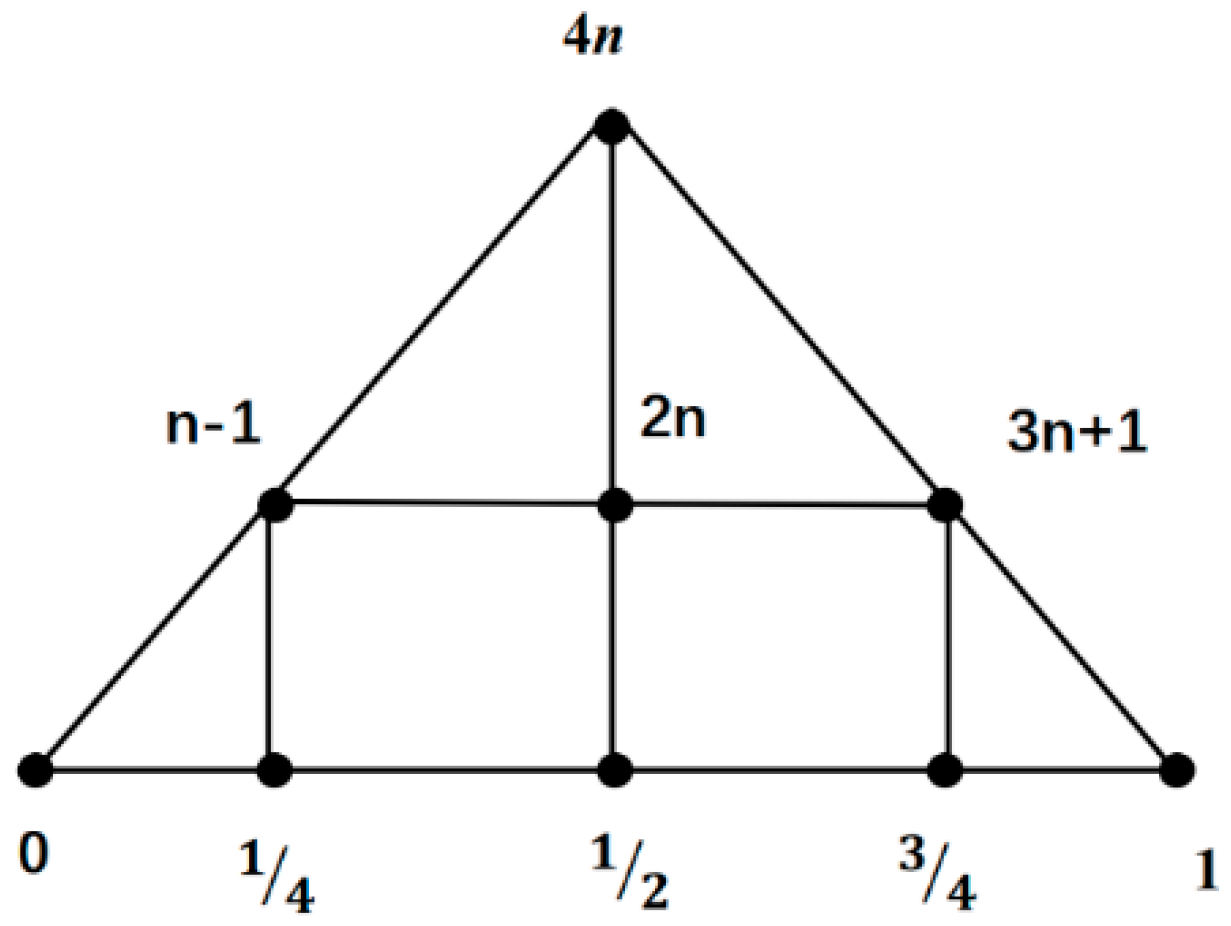
3. a concise proof of Collatz Conjecture
Collatz Conjecture:
Figure 5.
a symmetry structure of about line-1/2.
Figure 5.
a symmetry structure of about line-1/2.
4. The symmetry of L1/2±ε (0 1/2 1) and Riemann Hypothesis
The trivial zero-points of Riemann Zeta-Function is
-2n (n~1,2,3,…….)
Riemann Hypothesis:
all the Non-trivial zero-point of Zeta-Function
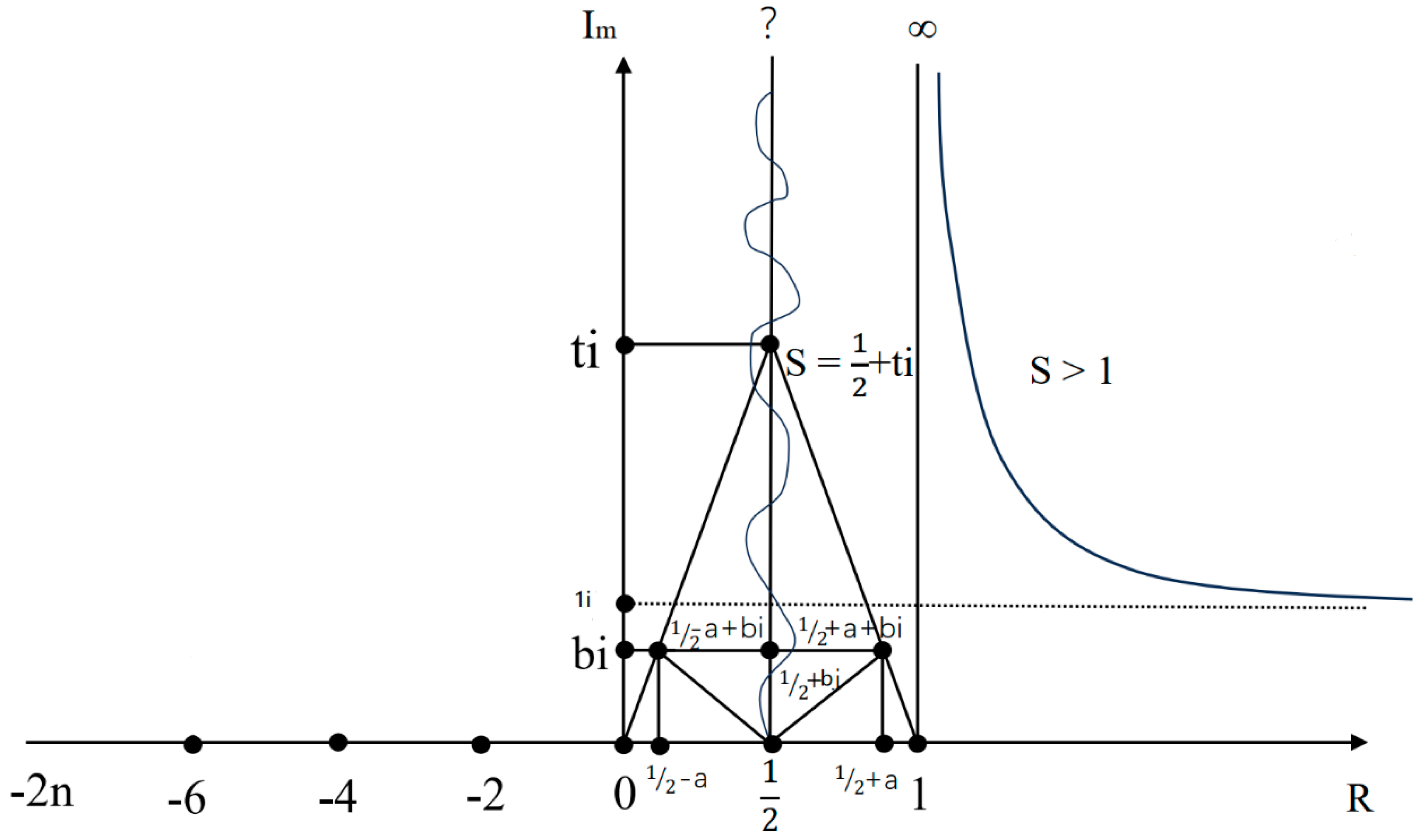
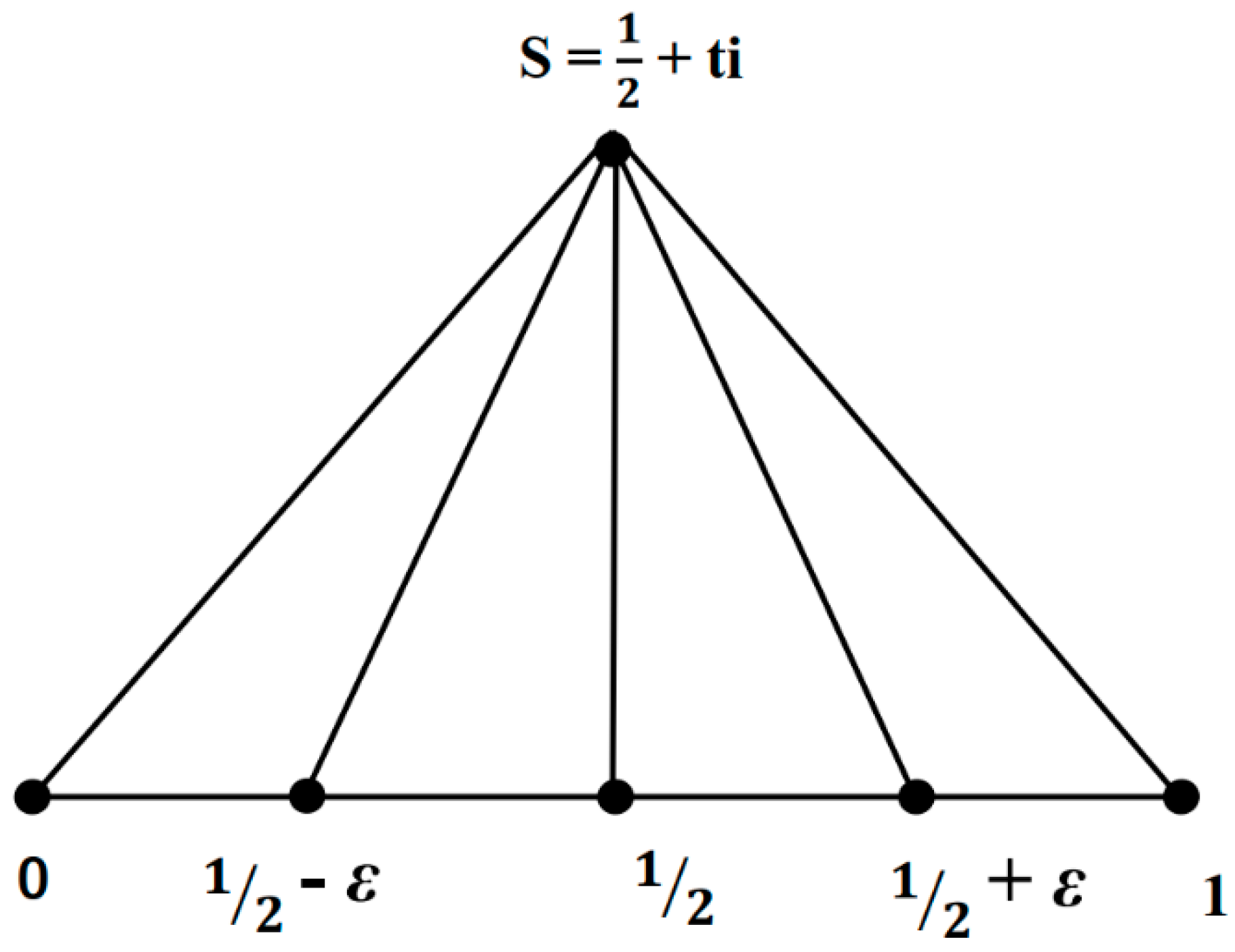
Figure 6.
Riemann Hypothesis: all the non-trivial Zero points of Riemann zeta-function are on the 1/2 axis.
Figure 6.
Riemann Hypothesis: all the non-trivial Zero points of Riemann zeta-function are on the 1/2 axis.
We can get a symmetry structure including all numbers about the
line-1/2 as
Figure 6
As the
Figure 7 If we
have zero points of
as
And is the first zero point on line-1/2
We can get a zero point as
It is contrary to that is the first zero point on line-1/2
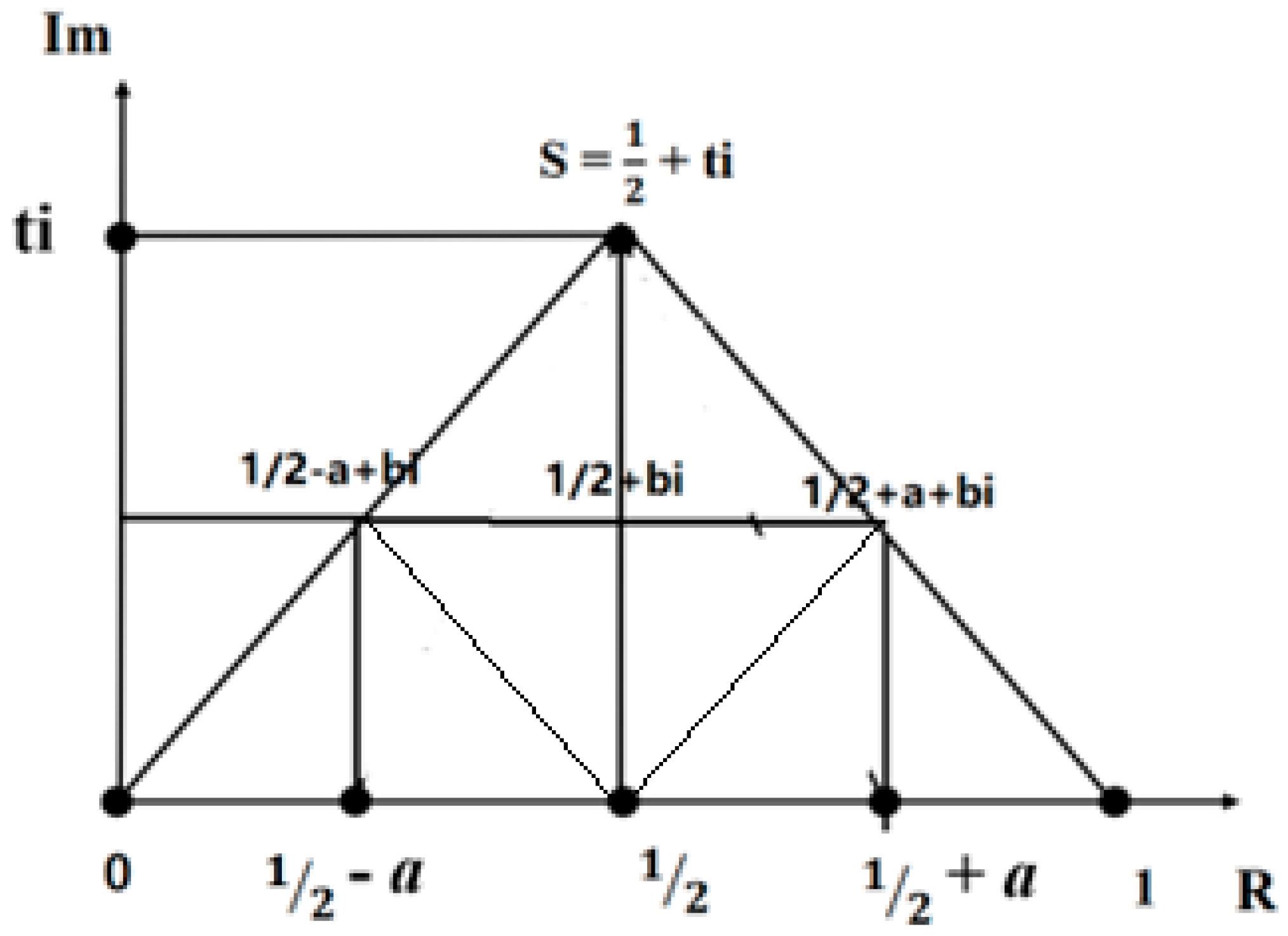
Figure 7.
a symmetry structure about line1/2+/-a at the zero piont s=1/2+ti.
Figure 7.
a symmetry structure about line1/2+/-a at the zero piont s=1/2+ti.
As the
Figure 8.
If we have zero points of
as
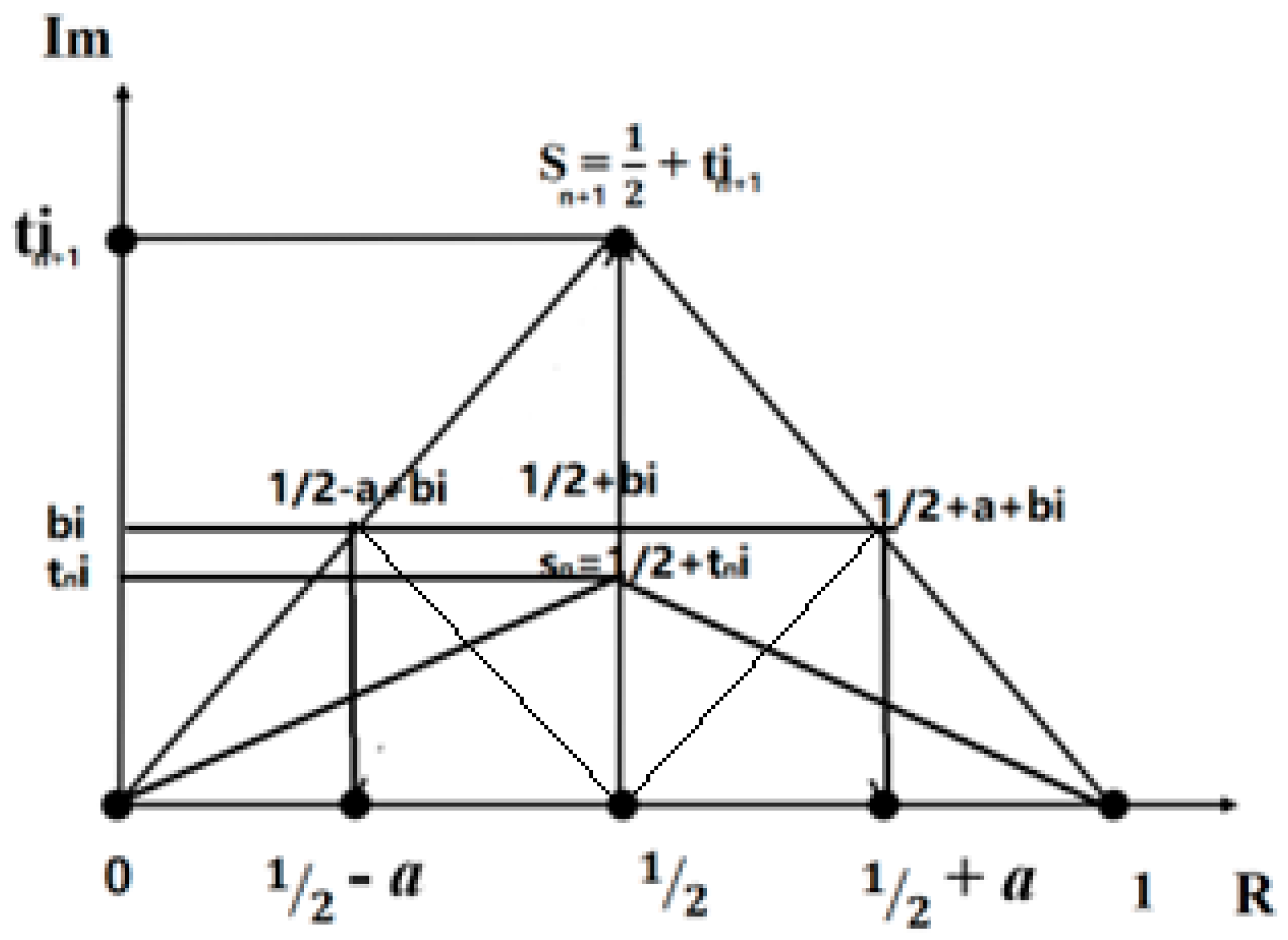
Figure 8.
a symmetry structure about line1/2+/-a at the zero point sn=1/2+tni and sn+1=1/2+tn+1i.
Figure 8.
a symmetry structure about line1/2+/-a at the zero point sn=1/2+tni and sn+1=1/2+tn+1i.
And is the No. n zero point on line-1/2
is the No. n+1 zero point on line-1/2
We can get a zero point between
as
It is contrary to that are the adjacent zero points on line-1/2
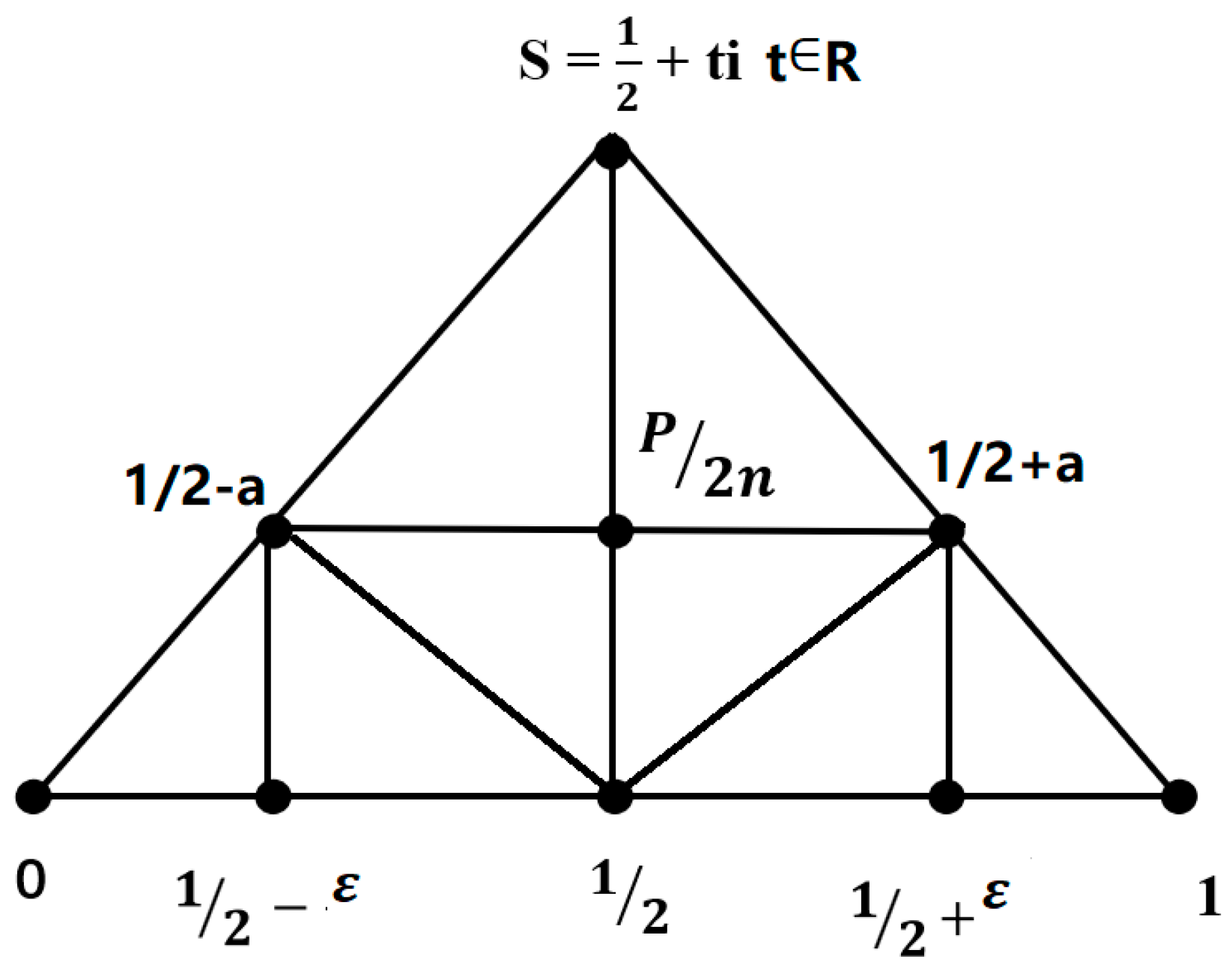
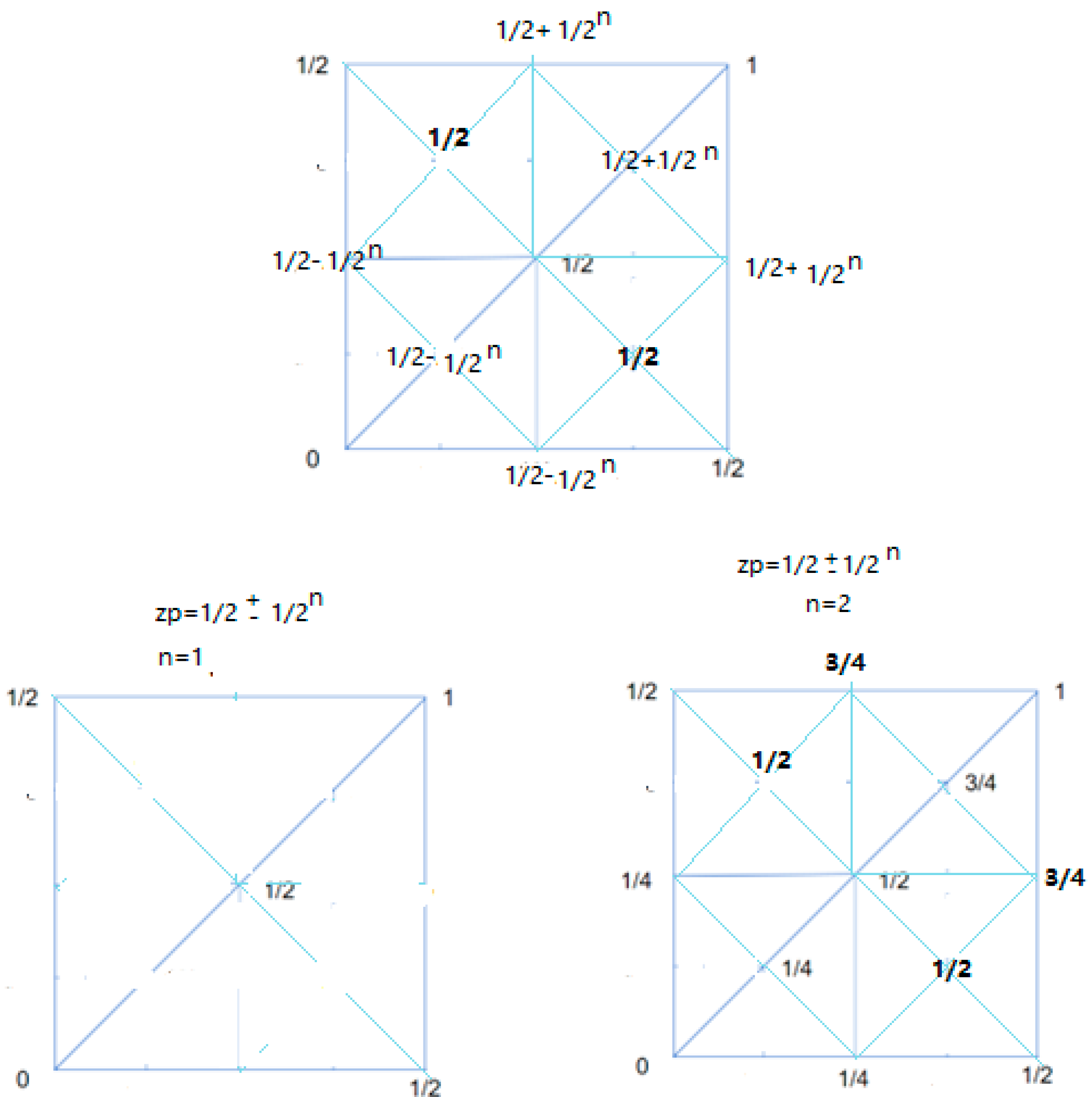
So on complex plane, We can have the symmetry
structure about the line-1/2 with zp=1/2±a
show as on
Figure 9.
Figure 9.
symmetry structure about the line-1/2 with zp=1/2±a.
Figure 9.
symmetry structure about the line-1/2 with zp=1/2±a.
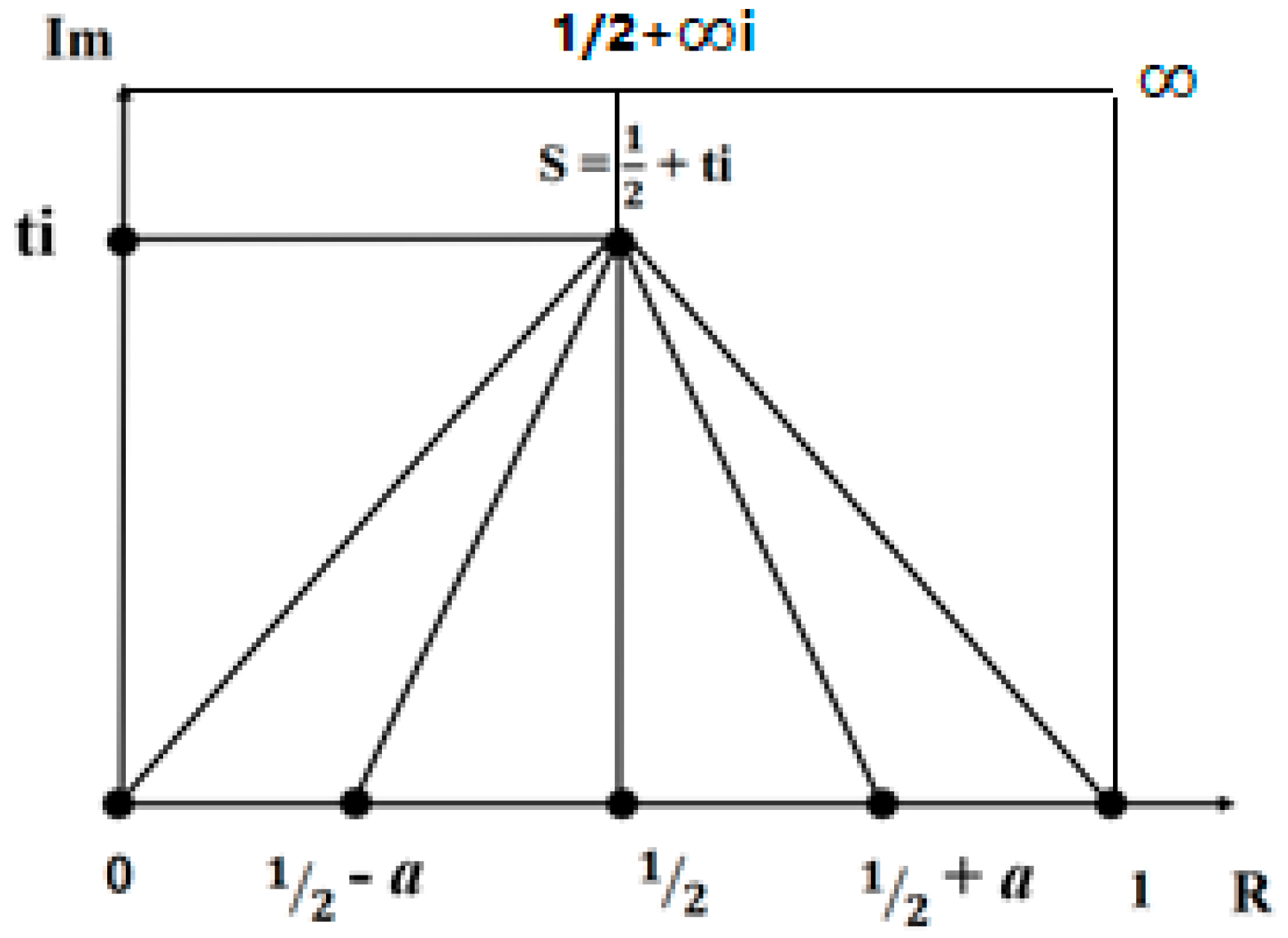
This is mean that there are no zero points on
line-1/2±.
Hardy and Littlewood give a proof that there are
infinite zero points on line-1/2 (Hardy and Littlewood. 1914 )
So we give a proof that all the non-trivial Zero
points of Riemann zeta-function are on the Line-1/2. This is the proof of
Riemann Hypothesis.
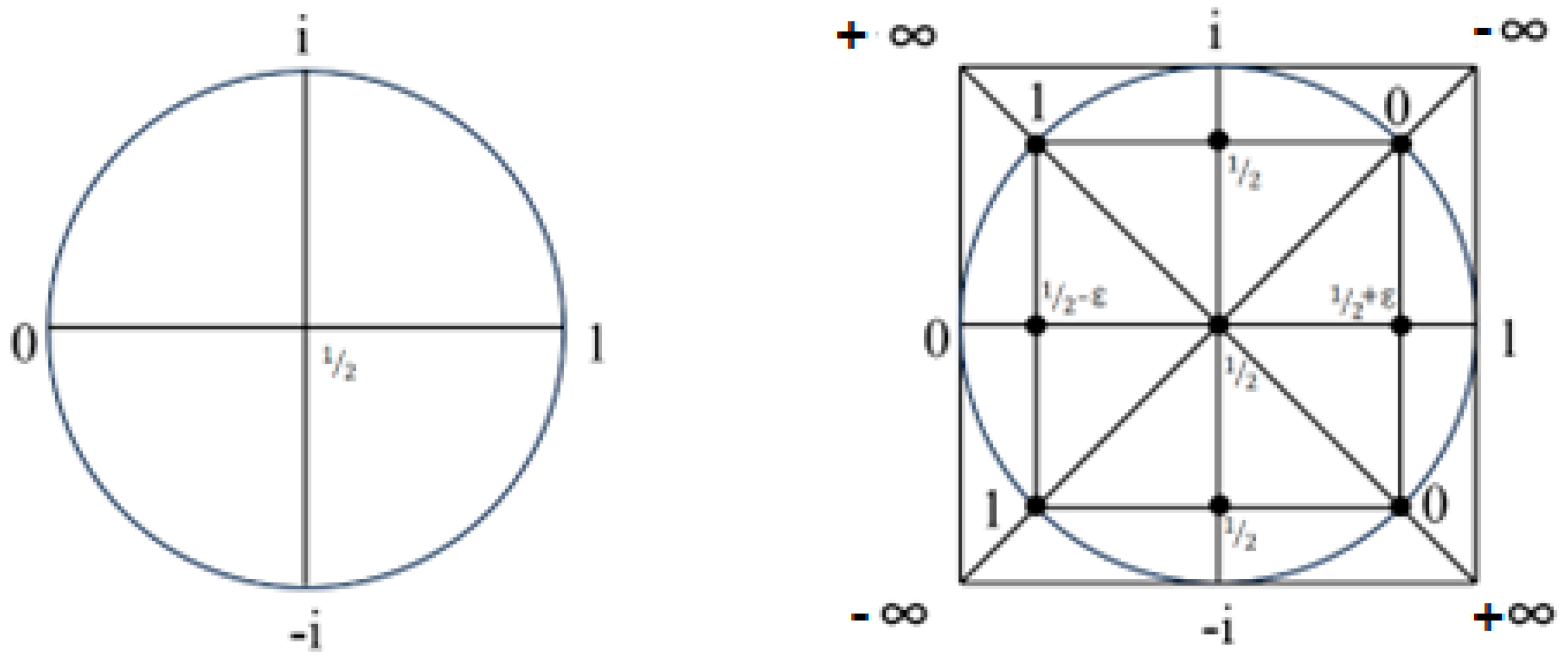
5. The Symmetry Number Structure about Line-1/2 including all numbers
In fact, we have a symmetry number structure about
line-1/2 as
Figure 10:
Figure 10.
symmetry structure about the line-1/2 with zp=1/2±ε.
Figure 10.
symmetry structure about the line-1/2 with zp=1/2±ε.
We called it L
1/2±ε 【0 1/2 1
】 and
analytic continuation to
we can get
Figure 11.
Figure 11.
The Symmetry of L1/2±ε 【0 1/2 1】 with
Figure 11.
The Symmetry of L1/2±ε 【0 1/2 1】 with
All
natural numbers
All
natural numbers excepted 0
We
can get a matrix (
)
The tr(A)=1/2*n
Figure 12.
The Symmetry of S∞+i.
Figure 12.
The Symmetry of S∞+i.
all the natural numbers.
All natural numbers excepted 0
All odd prime number
And we find that
0 (Euler’s Formula)
all the natural numbers.
All odd prime number
And
It is like the Euler’s Polyhedron Formula
We can get
Figure 12. This is a symmetry number structure about line-1/2 including all numbers.
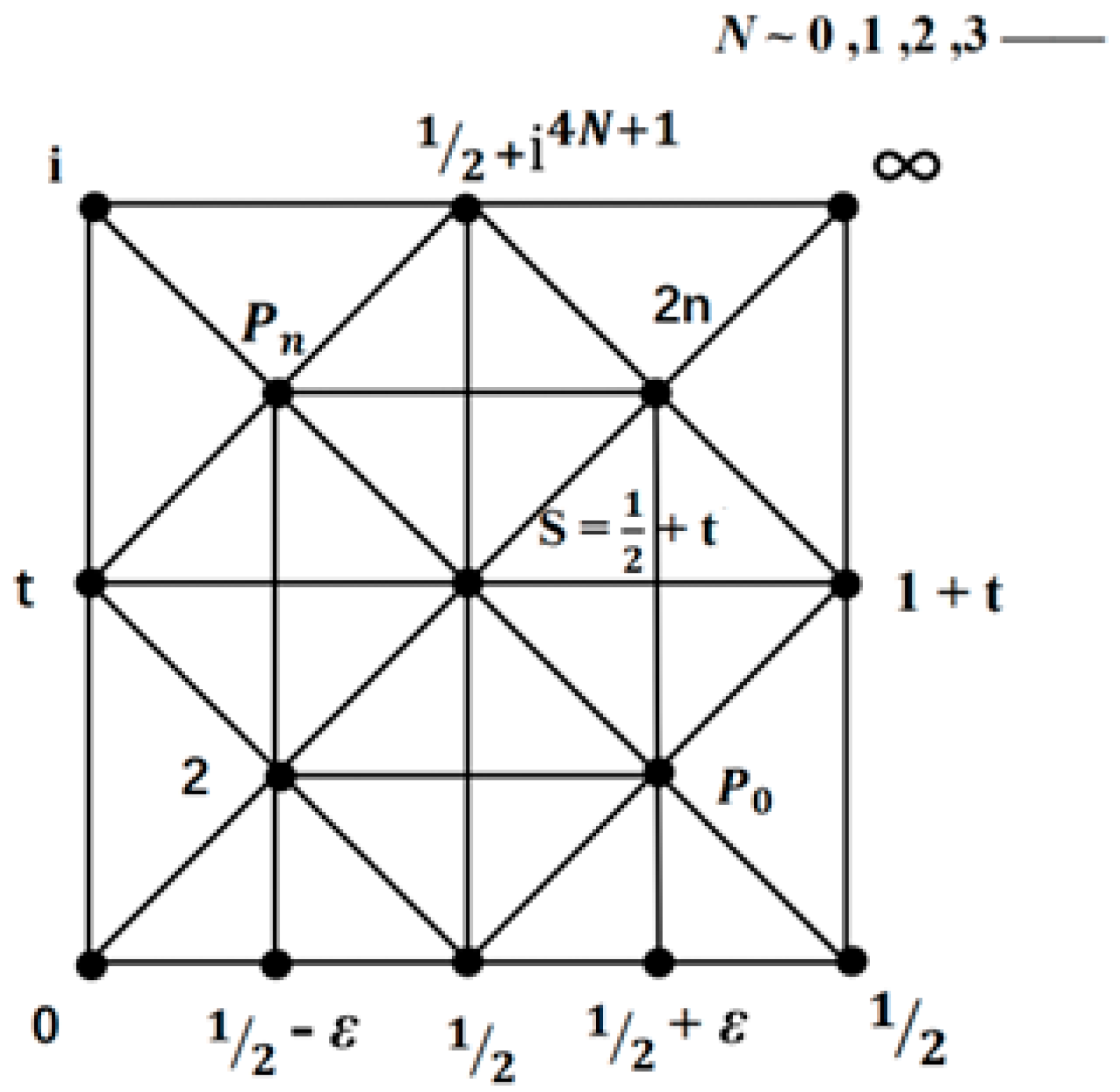
And we can get a symmetry number structure about line-1/2 as
Figure 13. We should call it
Reimann dynamic space.
Figure 13.
Reimann dynamic space.
Figure 13.
Reimann dynamic space.
All natural numbers
All natural numbers excepted 0
All prime numbers
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Competing Interests statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).