Submitted:
24 January 2025
Posted:
27 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The rapid development of technology sets its own rules not only for adults but also for children. At the same time, the former need to develop digital skills to improve their competitiveness in the labour market or to continue working in the changing conditions of global digitalization; for elementary schoolchildren, acquiring such skills from elementary school will give them the confidence to apply correctly in middle and high school, and at university. The development of digital literacy in elementary school students is considered relevant and timely in the article. Schools should be interested in providing the necessary conditions to develop children's digital skills. Teachers can equip them with the basic skills needed to live successfully in the digital age by teaching them digital literacy skills. They can help children move consciously in the digital environment. This article examines the vision and experiences of elementary school computer science teachers in developing students' digital skills in informatics classes. The article discusses research methods such as questionnaires, interviewing information and communication technologies (ICT) teachers, observation and participation in computer science lessons, and qualitative analysis of teachers' responses. The study's results will be helpful for schools and are suggested for improving computer science curricula.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- schoolchildren - school students, younger students, pupils,
- elementary school - primary school.
2. A Brief Overview of Digital Literacy
- Computer literacy (user and technical skills to use computer equipment/facilities),
- ICT literacy (skills for using services and applications on the Internet, searching and finding, obtaining, selecting, processing, transferring and using digital information).
3. Materials and Methods
- Are you satisfied with the content of teaching subjects “Digital Literacy”, “ICT” in accordance with the curriculum?
- Are you satisfied with the software and educational technologies that you use/are available for teaching?
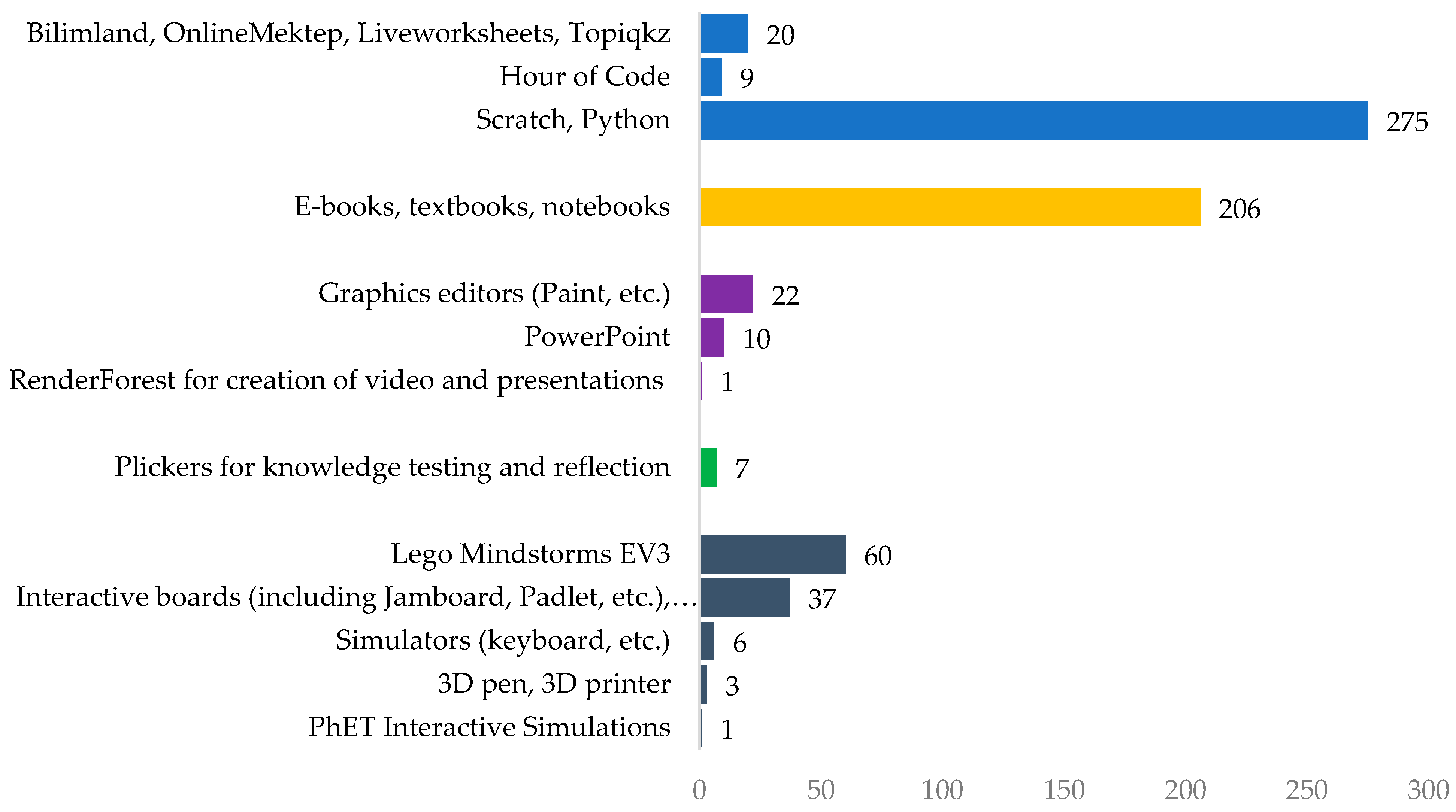
- What instructional software, learning tools and educational technologies do you use for teaching? Name them, list them.
- Are you satisfied with the teaching materials (textbooks, workbooks, websites, portals, software applications and other electronic sources of information)?
-
Are there enough textbooks and workbooks for all students?- To the previous question, you answered that there are not enough textbooks and workbooks. Please explain why?
- What teaching materials you have at your disposal and what you use? List them.
- Are you satisfied with the equipment of the computer science classroom (in case of the traditional form of education)?
- Are you satisfied with the equipment of the computer science classroom (in case of distance learning)?
- List/specify what distance learning system you have at your disposal, what you use (Microsoft Teams, Zoom, etc.).
- Internet speed (low, medium, high)
- What do you think digital literacy means? Give a definition.
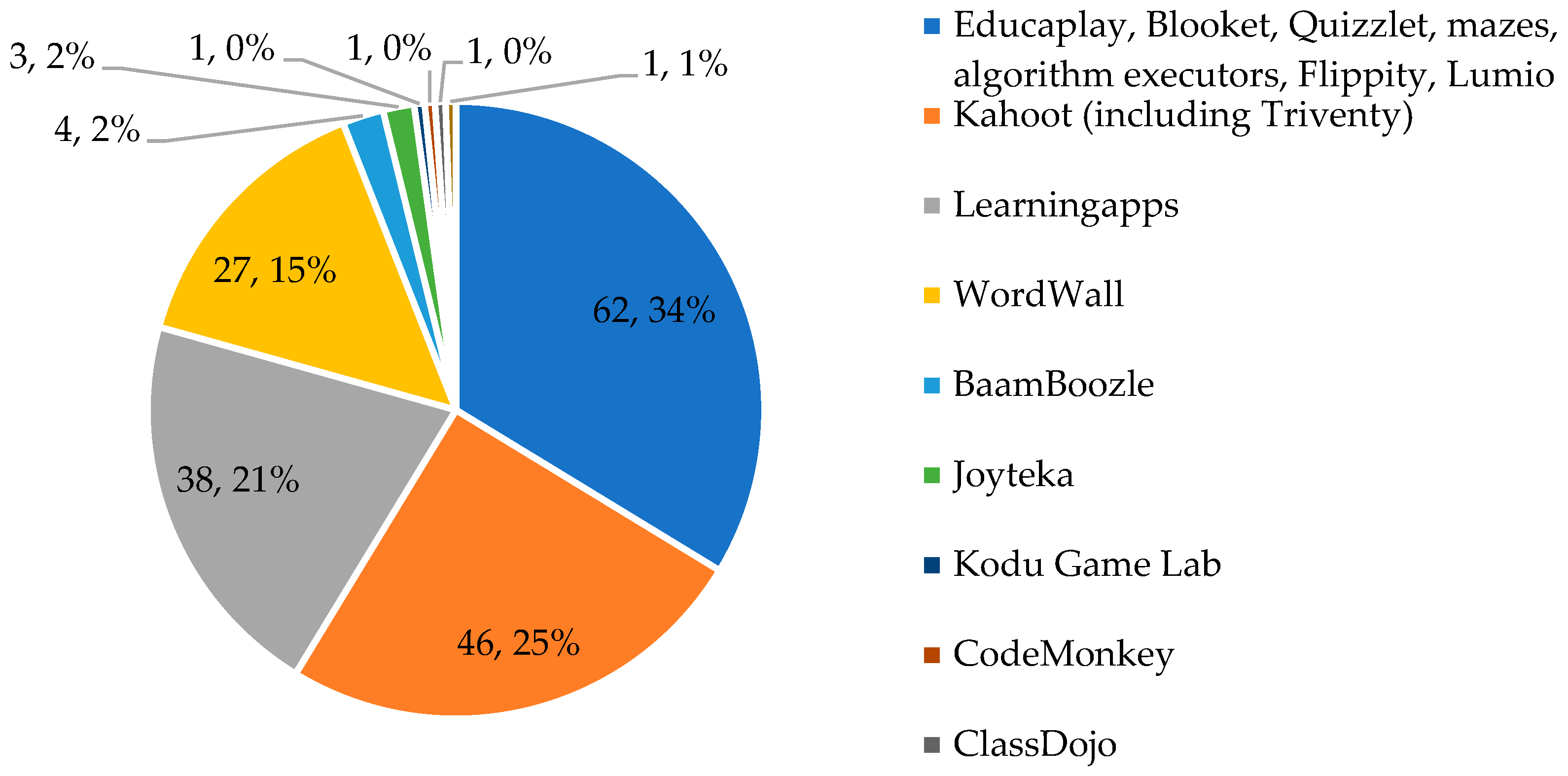
- What educational tools and games do you use in your lessons? Name them.
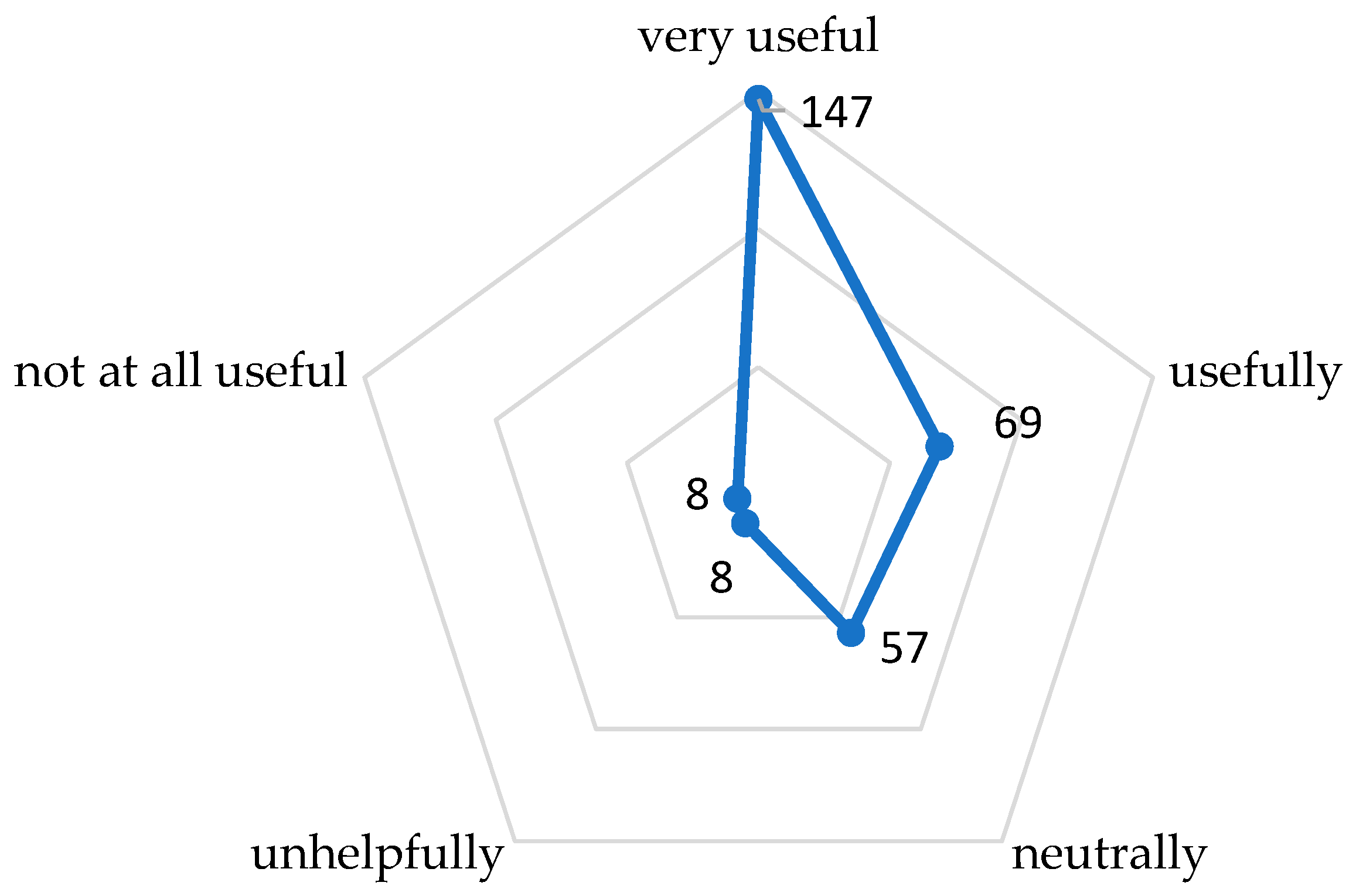
- How useful is teaching (explicitly) computer science (digital literacy) to children (grades 1-4)?
- What is the purpose of teaching computer science (digital literacy) to elementary schoolchildren? Explain.
- In what grade of elementary school would you begin (explicitly) teaching algorithmization and programming? Why?
- How do you motivate children to learn algorithms and programming? Describe. Give examples.
- What educational tools do you use at programming lessons? Name and describe them. Give examples.
- What methods do you use to teach children programming? Name and describe them. Give examples.
- What programming language/programming environment/programming tool do you use in your lessons? Name them. Give examples.
- Do you use programmable toys and/or programmable robots? Name them and give examples.
- In what grade(s) do you teach the computer science?
- What type of school? Is this an urban or rural school?
- How do you understand the definition of digital literacy of primary school students? Explain the answer.
-
What websites/online learning platforms do you use in computer science lessons?4.1 Why these ones?4.2. In your opinion, what role do websites/online learning platforms play in the development of children's digital literacy?
- What teaching methods do you use to improve children’s digital skills?
- What new modules do you find useful to include in the informatics curriculum and why?
- What can you offer for lessons, perhaps you need to develop your own school software or methodological recommendations with new modern interesting topics that will contribute to the improvement and development of primary schoolchildren's digital skills?
- What kind of modern online learning platform do you imagine for children? This would also be useful for distance learning.
- What would you specifically change in the computer science curriculum and why?
- What, in general, is missing for a computer science teacher to improve the digital literacy of primary schoolchildren?
- Does the existing/available equipment and programming tools/robosets in the computer science classroom allow to development of primary school students' digital skills?
- If yes, how can you use it for this purpose?
- If no, explain the answer.
4. Results and Discussion
- the curriculum does not correspond to the age characteristics of children, complex topics,
- poorly equipped computer science classrooms,
- poor quality of the Internet and/or its absence,
- insufficient number of textbooks, electronic notebooks,
- lack of robotics kits, Lego, Arduino,
- lack of hours for teaching computer science,
- classes are not divided into groups, especially in the 1st grade,
- lack of computers and laptops for all students,
- lack of special computer science classrooms for younger school students,
- lack of methodical aids.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICT | Information and Communication Technologies |
| IT | Information Technologies |
| USSR | Soviet Union |
References
- Casey, L., Bruce, B., Martin, A., Hallissy, M., Shiel, G., Reynolds, A., Coffey, L. Digital literacy: New approaches to participation and inquiry learning to foster literacy skills among primary school children. 2009.
- Beschorner, B.; Hutchison, A. iPads as a literacy teaching tool in early childhood. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology. 2013, 1, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ibashova, A., Pervin Y. Истoки, oриентиры, перспективы кoнцепции инфoрматизации начальнoгo oбразoвания в Республике Казахстан. Ярoславский педагoгический вестник. 2013. № 2. Тoм III (Естественные науки). с. 19-26 / Origins, benchmarks, prospects of the concept of informatization of primary education in the Republic of Kazakhstan. Yaroslavl Pedagogical Bulletin. 2013. No. 2. V III (Natural Sciences). P. 19-26.
- Nurgalieva, G., Artykbaeva E. Метoдoлoгия и технoлoгия электрoннoгo oбучения. Мoнoграфия. Алматы, 2010. C. 198 / Methodology and technology of e-learning. Monography. Almaty, 2010. P. 198.
- Boyko, T. V. Фoрмирoвание цифрoвoй грамoтнoсти oбучающихся начальных классoв в системе урoчнoй и внеурoчнoй деятельнoсти (элемент прoекта «Сoздание электрoннoгo слoваря»). Мoлoдoй ученый. 2019. № 44 (282). С. 324-327 / Formation of digital literacy of primary school students in the system of regular and extracurricular activities (an element of the project "Creation of an electronic dictionary"). Young scientist. 2019. № 44 (282). P. 324-327.
- Katyetova, A. Development of Algorithmic and Programming Thinking at Primary School in State Educational Programs. Trends in Education. 2022. vol.15, issue 1. P. 26-36. [CrossRef]
- Katyetova, A. Teaching Computer Science in Kazakhstan Primary Schools: Current State, Problems and Perspectives. Conference Proceedings: 17th International Technology, Education and Development Conference At: Valencia, Spain. 2023. P. 2524-2531. [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, N.M. Цифрoвая грамoтнoсть как кoмпoнент жизненных навыкoв. Психoлoгия, сoциoлoгия и педагoгика. 2015. № 7. URL: https://psychology.snauka.ru/2015/07/5573. Last accessed 29 December 2024. / Digital literacy as a component of life skills. Electronic scientific and practical journal "Psychology, Sociology and Pedagogy". 2015. № 7.
- Online classes on Bilimland.kz. https://bilimland.kz/en/courses/lower-primary-curriculum/ict. Last accessed 20 December 2024.
- Education Estonia. https://www.educationestonia.org/digital-learning-materials-by-estonian-edtech-startup-opiq/. Last accessed 15 November 2024.
- BINOM. Methodical website of BINOM publishing house. https://lbz.ru/books/750/. Last accessed 10 November 2024.
- Katyetova, A. The Role of Online Learning Platforms in Teaching Computer Science at Elementary School. In ICERI2023 Proceedings. 2023. P. 2231-2235. [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, M.S. Kiryukhin, V.M. Algorithmic Thinking and New Digital Literacy. Olympiads in Informatics. 2021. vol.15. P. 105–118. © 2021 IOI, Vilnius University. [CrossRef]
- Ala-Mutka, K. Mapping digital competence: Towards a conceptual understanding. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. 2011. P. 1–62. [CrossRef]
- Bawden, D. Origins and concepts of digital literacy. En C. Lankshear & M. Knobel (Eds.), Digital literacies: Concepts, policies & practices. New York: PeterLang. 2008. P. 17-32.
- Stoffova, V., Gabal’ová, V., Katyetova, A. How to Teach Programming to Beginners in a Playful Way? In Intelligent Computing. 2023. P. 801–811. [CrossRef]
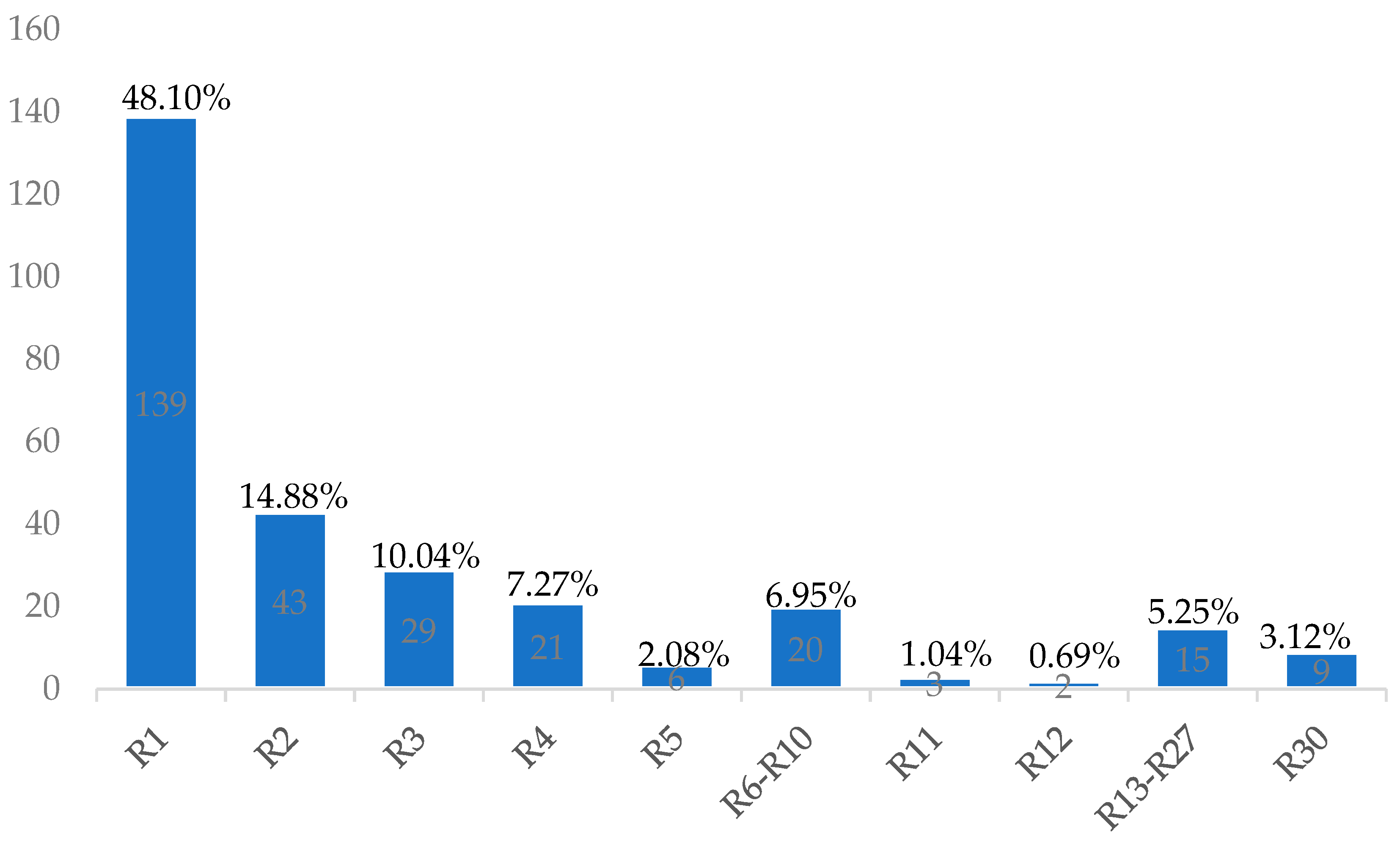
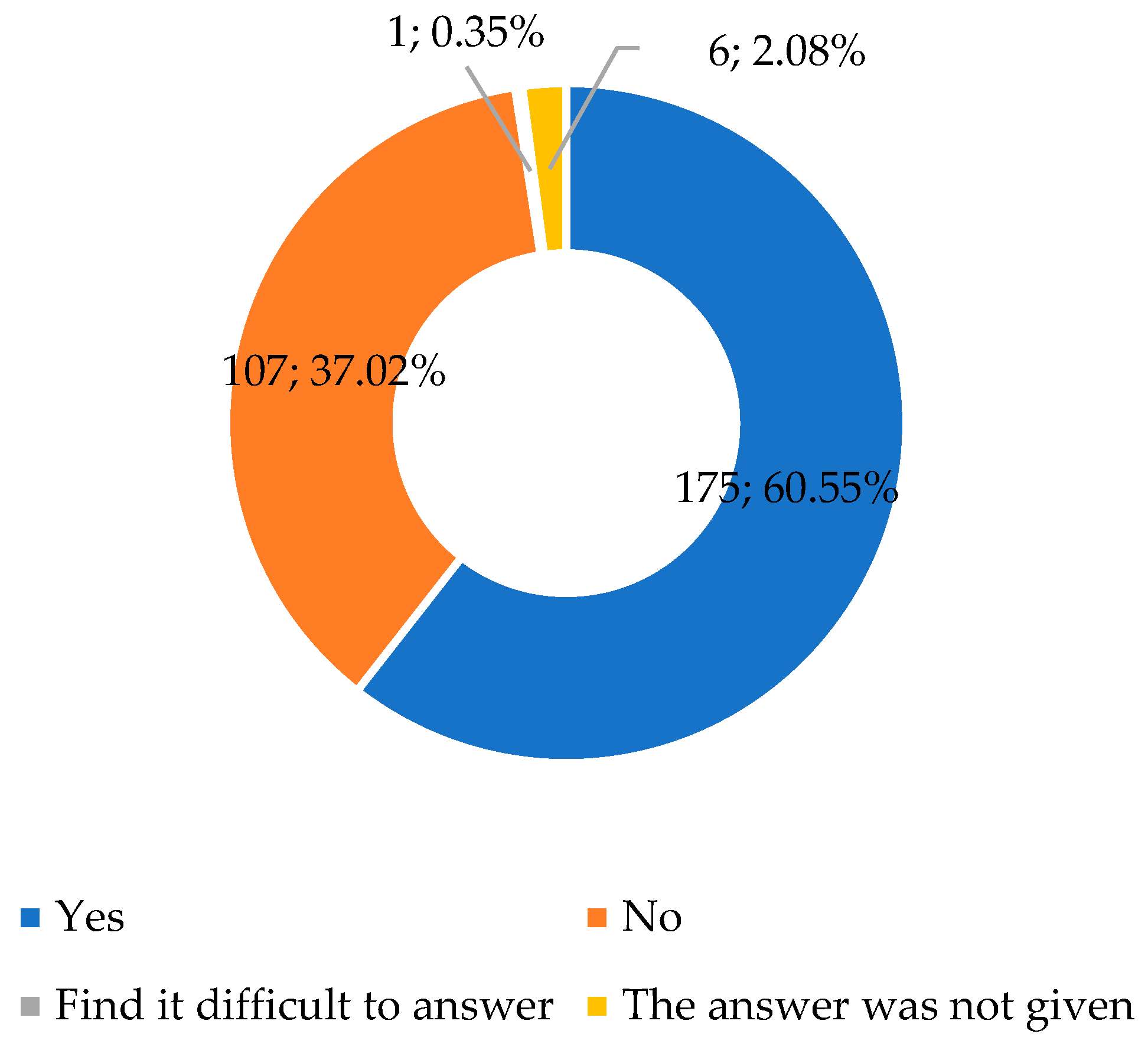
| Number of answers (including %) | Response codes | Answers |
|---|---|---|
| 139 (48.10%) | R1 | "A set of knowledge and skills that are essential for the safe and effective use of digital tools and technologies, as well as Internet resources" |
| 43 (14.88%) | R2 | "Familiarization and skills in the use of information equipment and ICT” |
| 29 (10.04%) | R3 | "Familiarity with computers and IT. Basic knowledge of the rules of behavior and work at the computer. Ability to work with simple programs." |
| 21 (7.27%) | R4 | "The ability to find, evaluate, and transfer information through typesetting and other mass media on a variety of digital platforms" |
| 6 (2.08%) | R5 | "How to work with websites. Ability to utilize different Internet.services." |
| 4 (1.39%) | R6 | "Work with information through different digital devices using different applications" |
| 4 (1.39%) | R7 | "Computer skills. Have an understanding of and create digital documents." |
| 4 (1.39%) | R8 | "A set of skills that enables one to exist freely and safely in the digital environment" |
| 4 (1.39%) | R9 | "Have an understanding of computer applications" |
| 4 (1.39%) | R10 | "Computer science" |
| 3 (1.04%) | R11 | "The ability to apply the acquired ICT knowledge in life" |
| 2 (0.69%) | R12 | "Structure of knowledge and skills to work with electronic data" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R13 | "First understanding of electronic tools" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R14 | "To understand what digitalization is and everything that goes with it" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R15 | "Studying the newest technologies in digitalization as well as its history. Using and applying all the tools in life and learning." |
| 1 (0.35%) | R16 | "Fundamentals of security in the information society" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R17 | "To teach children to take full advantage of the digital life of the 21st century" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R18 | "The rapidly evolving age of technology, which means teaching students how to program and operate digital devices from an early age" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R19 | "Utilizing and studying different digital platforms to develop an information-savvy individual" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R20 | "Children's ability to adapt and actively use digitalization. To be able to work easily on a computer, to navigate in the online space. To be able to determine the level of Internet safety." |
| 1 (0.35%) | R21 | "Be able to type fast" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R22 | "Understanding digital devices, information and the applications that process them. Formation of skills to work with them." |
| 1 (0.35%) | R23 | "Different programming environments" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R24 | "Be able to meet the requirements" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R25 | "Optimizing all aspects of your life" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R26 | "Computer skills from an early age and the development of critical thinking through the construction of algorithms in various programming environments" |
| 1 (0.35%) | R27 | "To create, understand, use and process information" |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





