1. Introduction
The eCommerce industry's spectacular growth is driven by the requirement for online retail platforms to function effectively at large volumes and an increasingly digital consumer base. eCommerce systems need versatile, scalable, and cost-effective cloud computing solutions since they manage various tasks, including order processing, inventory control, payment processing, and real-time user interactions. Because of this reliance on cloud infrastructure, it is now more crucial than ever to allocate resources effectively to meet changing demands, especially during periods of high demand like sales, promotions, or holidays when the strain on cloud resources may suddenly increase. But because they frequently rely on static or manual provisioning, existing cloud resource allocation techniques are unable to optimize for such dynamic and changeable workloads, which frequently results in problems like over-provisioning and under-provisioning. In order to guarantee performance during peak loads, cloud service providers over-provision, which avoids performance bottlenecks but results in needless operating costs because of resource waste. On the other hand, under-provisioning restricts the usage of resources, increasing the possibility of subpar performance, slower response times, and even revenue loss as a result of a less than ideal user experience. The stakes are high when juggling these trade-offs in a cutthroat sector like eCommerce: cost effectiveness has a direct impact on revenue, but a smooth user experience is crucial for attracting and keeping customers. In order to optimize resource allocation in real-time and enable more effective and responsive administration of cloud resources, cloud service providers are progressively investigating dynamic, AI-driven solutions.
With the use of sophisticated machine learning algorithms that allow for dynamic, predictive, and automatic resource management, artificial intelligence (AI) presents promising solutions to the problems associated with cloud resource allocation. This study looks at how artificial intelligence (AI) methods, particularly genetic algorithms (GA), neural networks (NN), and reinforcement learning (RL), might be used to improve resource allocation tactics in the eCommerce industry. The development of intelligent agents that can learn from and adjust to changing surroundings using historical data and real-time feedback is made possible by reinforcement learning. RL agents can automatically scale resources up or down to maintain optimal performance and cost efficiency through a reward-based mechanism. On the other hand, neural networks are ideal for workload prediction because they can proactively manage resources by analyzing past demand patterns to predict times of high traffic. By gradually changing resource allocation configurations, genetic algorithms add another layer of optimization and produce effective configurations that meet the various workload requirements of the eCommerce sector.
An intelligent, flexible cloud architecture that can adapt to the particular requirements of eCommerce apps is made possible by the integration of various AI-driven methodologies. This study compares the efficiency of AI-driven allocation to conventional techniques by modeling a variety of real-world eCommerce scenarios, such as unanticipated changes in user behavior or abrupt traffic increases during flash deals. The findings show that AI-based resource allocation greatly increases resource utilization, lowers operating costs, and improves performance stability—all of which contribute to a more scalable and resilient cloud environment for eCommerce.
Essentially, this study shows that by integrating AI into cloud resource management, eCommerce companies may improve customer experiences while being cost-effective in a cutthroat market. The results have wider ramifications for industries that rely on the cloud, where operational success is driven by comparable requirements for scalability and performance. To further improve the efficacy and resilience of AI-powered resource allocation in eCommerce, future research will concentrate on solving the practical usability of these AI models in live cloud environments, tackling issues like latency and data security.
2. Problem Statement
In the eCommerce sector, managing erratic, frequently highly fluctuating demand requires a scalable, dependable, and effective cloud infrastructure. These dynamic workloads cannot be adequately handled by traditional cloud resource allocation techniques, which are often focused on static provisioning or manual modifications. While under-provisioning results in performance bottlenecks that affect user experience and may result in revenue loss, over-provisioning wastes resources and raises operating costs. Intelligent, flexible resource allocation systems that can strike a balance between cost and performance are therefore desperately needed, especially during times of high demand. By using artificial intelligence (AI) approaches to create a dynamic resource allocation model tailored to the eCommerce sector, this study seeks to address these issues. This method aims to automate and optimize cloud resource allocation based on historical and real-time data by combining genetic algorithms (GA), neural networks (NN), and reinforcement learning (RL). The goal is to develop an AI-powered system that can proactively scale resources in response to anticipated demand, lowering expenses and enhancing system functionality.
Case Context: Take ShopEase, a global eCommerce site that sees high user traffic and erratic demand patterns, especially during major sales occasions like Cyber Monday or Black Friday. User traffic increases significantly during these occasions, frequently surpassing daily average traffic by several orders of magnitude. Cloud resources are heavily taxed by these demand spikes, necessitating quick scaling of CPU, memory, and storage capacity to preserve efficiency and avoid service interruptions.
Challenge: ShopEase presently uses a conventional resource allocation strategy that involves human modifications during peak times and static provisioning for routine demand. Nevertheless, this approach has not been effective in fulfilling the platform's requirements. Under-provisioning has impacted sales and frustrated users by causing page load failures and application slowdowns during periods of high traffic. ShopEase has periodically over-provisioned in anticipation of strong demand, which raised cloud costs because idle resources occurred during periods of lower-than-expected traffic.
3. Literature Survey
| Paper Title |
Description |
| The State-of-The-Art Review on Resource Allocation Problem Using Artificial Intelligence Methods on Various Computing Paradigms |
Widely used to automate provisioning, optimize resource scheduling, and forecast resource demands. Regression models, clustering algorithms, and reinforcement learning (RL) are some of the methods. These techniques anticipate workload trends and react to urgent demands, allowing for dynamic allocation. |
|
Orchestrating Efficiency: AI-Driven Cloud Resource Optimization forEnhanced Performance and Cost Reduction
|
The author investigates how AI methods can be incorporated into cloud resource management. It emphasizes techniques like anomaly detection, reinforcement learning for dynamic allocation, and machine learning for workload prediction. Real-world applications in e-commerce, SaaS, and streaming services are presented with issues like over-provisioning and adaptability. The study highlights AI's revolutionary potential in increasing productivity, cutting expenses, and resolving environmental issues. Future directions include improving system explainability and integrating edge computing. |
| Optimizing cloud resource allocation using advanced AI techniques: A comparative study of reinforcement learning and genetic algorithms in multi-cloud environments |
This paper offers a thorough comparison of Genetic Algorithms (GA) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) for allocating cloud resources in multi-cloud settings. While RL's flexibility and ability to learn continuously make it perfect for workloads that are dynamic and fluctuating, GA's effectiveness in convergent to optimal solutions provides a notable edge in stable conditions that demand quick optimization. The results highlight the context-dependent nature of each technique's effectiveness, with GA doing better in more stable environments and RL performing better in volatile ones. |
| Enhancing Cloud Scalability with AI-Driven Resource Management |
The author investigates how to enhance cloud scalability and resource management through the application of sophisticated machine learning methods. In order to improve operational efficiency, reduce expenses, and maximize resource usage, it assesses methods including Reinforcement Learning (RL), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM), Autoencoders, and Neural Architecture Search (NAS). The findings show how AI may be used to handle the increasing difficulties of cloud resource management by highlighting notable gains in cost reduction, service effectiveness, and demand forecasting accuracy. |
|
How Machine Learning Enhances Cloud ResourceAllocation
|
This study investigates how decision-making can be automated using machine learning (ML), which improves performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in cloud resource distribution. ML methods that improve resource allocation based on real-time data include clustering algorithms, reinforcement learning, and predictive demand modeling. Businesses can prevent over- or under-provisioning by integrating machine learning (ML) into cloud infrastructures, guaranteeing that resources are accessible when needed. ML will become more and more crucial as cloud computing develops in order to achieve effective, economical resource management in a variety of sectors, such as banking, healthcare, and e-commerce. |
| Integration of Cloud Computing with Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Telecom Sector—A Case Study |
The authors examine how these technologies enhance user experiences and allow for more intelligent service delivery by increasing network flexibility and operational efficiency. The case study specifically focuses on how the MGA-MENA Company in the Middle East has used cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) to manage network operations, cut expenses, and improve service delivery. Self-healing networks, traffic optimization, and effective resource allocation have all been made possible by AI-powered machine learning techniques, which have ultimately led to a telecom infrastructure that is more flexible and responsive to consumer needs. |
4. Current Methodology
Traditional forecasting techniques and manual tracking were the mainstays of eCommerce inventory management. Retailers used historical sales data to forecast demand for certain products and kept set stock levels. To forecast demand trends, they employed simple algorithms, frequently linear regression models. These algorithms, however, found it difficult to adjust to abrupt changes in customer behavior, such as those brought on by promotions, seasonal trends, or unexpected viral demand. This resulted in problems like overstocking or understocking, which had an impact on consumer happiness and operational effectiveness.
One of the biggest challenges in eCommerce was delivering a personalized consumer experience. Retailers frequently used simple segmentation and focused marketing techniques based on past purchases or general customer demographics. These approaches lacked the accuracy and flexibility needed to accommodate each customer's unique preferences. Other than the occasional discount or a simple product recommendation, the experience was frequently generic. Traditionally, rule-based search engines and product recommendations used collaborative filtering or simple keyword matching. But they were much less advanced than contemporary AI-based recommendation systems, and they frequently failed to forecast user preferences with any degree of accuracy. Many clients were forced to sort through pointless products due to the lack of customisation, which resulted in a less than ideal browsing experience and possibly reduced conversion rates.
Scaling eCommerce systems was one of the most challenging tasks. It became more difficult to sustain optimal efficiency without AI techniques as the number of clients and transactions increased. It was necessary to manually scale the infrastructure, which frequently resulted to performance snags during busy periods like product launches or sales events.
Prior to the incorporation of AI methods, eCommerce systems encountered considerable difficulties in supply chain optimization, infrastructure scaling, inventory management, and user experience personalization. It was challenging to manage the dynamic and unpredictable nature of eCommerce due to the dependence on human procedures, rule-based systems, and static models. However, as AI technologies began to offer creative solutions that made it possible for real-time data processing, individualized client interactions, and effective resource management, the landscape started to shift. An important turning point in the development of eCommerce was the shift to AI-driven mechanisms, which enabled platforms to scale and more accurately and efficiently satisfy client expectations.
5. Proposed Mechanism
This section is not mandatory but may be added if there are patents resulting from the work reported in this manuscript. One of the top eCommerce platforms, ShopEase, took delight in providing millions of customers with a flawless purchasing experience. Every Black Friday, though, the staff prepared for the mayhem. Their static resource allocation system frequently malfunctioned, resulting in either over-provisioning (which caused idle resources to drive up prices) or under-provisioning (which caused slowdowns and page failures).
For instance, traffic increased 200% more than anticipated during the most recent Black Friday sale, which resulted in a large loss of revenue due to irate consumers who were unable to finish their orders. As a result of unused infrastructure, the team overcompensated by allocating an excessive amount of resources on subsequent sales, which depleted their operating budget. To deal with such erratic traffic patterns, ShopEase required a more intelligent, flexible strategy.
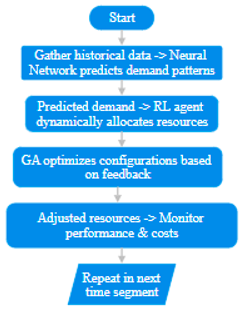
We suggest an AI-driven dynamic resource allocation method for ShopEase that makes use of reinforcement learning (RL), neural networks (NN), and genetic algorithms (GA) in order to get beyond the inefficiencies of static provisioning and manual changes. Without requiring continual human involvement, this intelligent system would forecast future demand and modify resource allocation in real-time, guaranteeing peak performance and cost effectiveness. There are three primary parts to the suggested mechanism:
5.1. Predicting Workload with Neural Networks
A neural network model based on historical data, such as traffic patterns, sales trends, and promotional schedules, was incorporated by the team. The NN anticipated a precise demand curve as Black Friday drew near by examining years' worth of previous sale events. For example, the NN expected that traffic would surge 400% more than usual at 9 PM, when it would peak. With this knowledge in hand, ShopEase planned ahead and made sure they had the capacity to manage the spike without going overboard during the slower pre-sale hours.
Input: Past workload information (such as sales and traffic trends).
Output: Forecasted demand over the next several periods.
5.2. Reinforcement Learning (RL) for Real-Time Resource Adjustment
The RL agent took over as the sale started. Real-time parameters such as CPU, memory, and incoming traffic were monitored by the RL agent, which dynamically modified resources to meet demand. The RL agent ensured seamless performance for shoppers by increasing CPU and RAM allocations by 50% in a matter of seconds at 9 PM, when traffic peaked as expected. On the other hand, the RL agent reduced cloud expenses by scaling back resources at 2 AM, when traffic drastically slowed. With large awards for effective resource use during peak hours and penalties for over-provisioning or allowing the system to lag, the reward system encouraged the RL agent to keep things in balance.
Action Space: Boost, preserve, or cut back on resources.
Rewards: High rewards are given for keeping utilization within predetermined ranges, while excessive expenses and subpar performance are penalized.
5.3. Genetic Algorithms (GA) for Configuration Optimization
In the background, resource allocation tactics were continuously refined by genetic algorithms. GA adjusted ShopEase's resource settings for a range of workloads, including flash sales, periods with high search traffic, and checkout-dominant periods, by modeling alternative configurations and choosing the best-performing ones. For instance, GA suggested the best combination of processing and storage power during a flash sale in the middle of the sale, allowing ShopEase to handle a spike in product searches without overtaxing servers.
.# Simplified example of RL-based dynamic scaling
class ShopEaseEnvironment:
def __init__(self):
self.state = [0.5, 0.5] # Initial CPU and memory utilization
def step(self, action):
# Simulate demand fluctuation
demand_factor = np.random.uniform(0.8, 1.2)
self.state = [min(max(self.state[0] * demand_factor, 0), 1),
min(max(self.state[1] * demand_factor, 0), 1)]
# Adjust based on action
if action == "increase":
self.state = [s + 0.1 for s in self.state]
elif action == "decrease":
self.state = [s - 0.1 for s in self.state]
return self.state
env = ShopEaseEnvironment()
print(env.step("increase"))
Following the "increase" operation, the ShopEaseEnvironment is currently in the state [0.629, 0.629]. This shows the revised CPU and memory utilization levels following a 0.1 resource increase and demand fluctuation simulation. To guarantee practical resource use, the values are kept normalized (bounded between 0 and 1).
6. Results and Discussion
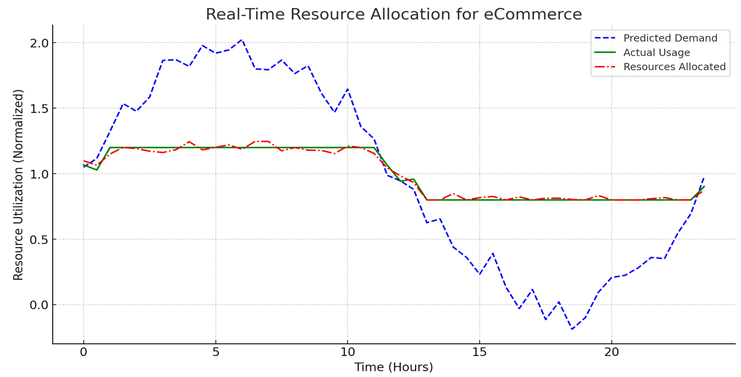
Key patterns in anticipated demand, actual usage, and resource allocation are displayed in the graph, which depicts the real-time dynamic resource allocation for an eCommerce platform such as ShopEase. Based on neural network analysis of past data and traffic patterns, the expected demand—shown by the blue dashed line—reflects variations in workload over a 24-hour period. The platform's actual resource utilization is shown by the green solid line, which records variances in real time brought on by erratic user behavior. Lastly, the AI-driven system's modifications to dynamic resource allocation are shown by the red dashed line. This successfully manages the platform's fluctuating workload demands by ensuring an ideal balance between cost-effectiveness and performance.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Simulate data for real-time resource allocation (time vs resource utilization)
np.random.seed(42)
time = np.arange(0, 24, 0.5) # Time in hours (half-hour intervals)
predicted_demand = np.sin(2 * np.pi * time / 24) + 1 + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, len(time))
# Simulated demand
actual_usage = np.clip(predicted_demand + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, len(time)), 0.8, 1.2)
# Actual usage with noise
resources_allocated = np.clip(actual_usage + np.random.uniform(-0.05, 0.05, len(time)), 0.8, 1.5)
# Adjustments by AI
# Create a table for the data
data = pd.DataFrame({
"Time (Hours)": time,
"Predicted Demand": predicted_demand.round(2),
"Actual Usage": actual_usage.round(2),
"Resources Allocated": resources_allocated.round(2)
})
# Plot the data
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(time, predicted_demand, label="Predicted Demand", linestyle="--", color="blue")
plt.plot(time, actual_usage, label="Actual Usage", linestyle="-", color="green")
plt.plot(time, resources_allocated, label="Resources Allocated", linestyle="-.", color="red")
plt.xlabel("Time (Hours)")
plt.ylabel("Resource Utilization (Normalized)")
plt.title("Real-Time Resource Allocation for eCommerce")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# Display the first few rows of the table
data.head()
By avoiding under-provisioning during periods of high traffic and over-provisioning during periods of low activity, this simulation demonstrates how AI-driven algorithms dynamically distribute resources to successfully handle demand changes.
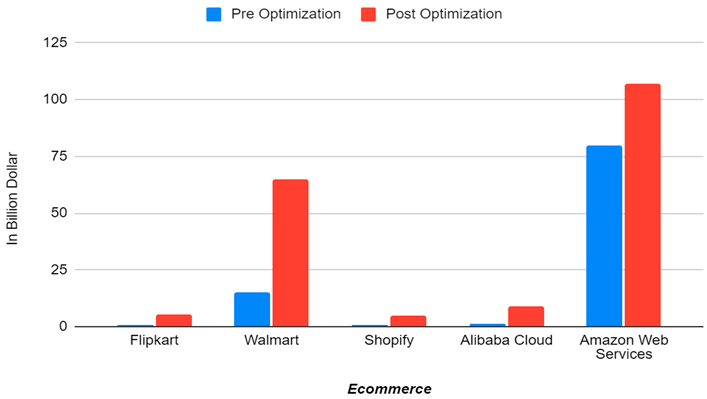
The graph unequivocally shows that the revenue of eCommerce businesses is significantly impacted by AI optimization for cloud resource allocation. When compared to the blue bars (pre-optimization), the rise in red bars (post-optimization) indicates:
Decreased downtime.
Increased capacity to scale.
Improved use of resources.
Increased client satisfaction during periods of high traffic.
The tendency is obvious for Walmart and Amazon Web Services, where the post-optimization findings imply transformative growth. Notable advancements were also made by smaller competitors like Flipkart and Shopify, demonstrating the broad advantages of implementing AI methods in cloud operations.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
References
- Author 1, Joloudari, Javad Hassannataj. Title of the article. The State-of-The-Art Review on Resource Allocation Problem Using Artificial Intelligence Methods on Various Computing Paradigms. ArXiv.org, 2022, arxiv.org/abs/2203.12315.
- Author 1, Srinivasa, Angajala. Orchestrating Efficiency: AI-Driven Cloud Resource Optimization for Enhanced Performance and Cost Reduction. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews, vol. 4, no. 12, 9 Dec. 2023, pp. 2007–2009. [CrossRef]
- Author 1, Pranav Murthy. Optimizing Cloud Resource Allocation Using Advanced AI Techniques: A Comparative Study of Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithms in Multi-Cloud Environments. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, vol. 7, no. 2, 30 Aug. 2020, pp. 359–369. [CrossRef]
- Author 1, A. Choudhury, Amit; Author 2, Yuvaraj Madheswaran. Enhancing Cloud Scalability with AI-Driven Resource Management International Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Management, vol. 11, no. 5, Oct. 2024, pp. 32–39. [CrossRef]
- Author 1 Choudhury, Kenny. How Machine Learning Enhances Cloud Resource Allocation EasyChair Preprint, no. 15444, Nov. 2024, pp. 1–8, https://easychair.org/publications/preprint/GCpjN/open.
- Author 1, El Khatib, Mounir M, Integration of Cloud Computing with Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Telecom Sector—a Case Study IBusiness, vol. 11, no. 01, 2019, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Author 1, Ashawa, Moses, Improving Cloud Efficiency through Optimized Resource Allocation Technique for Load Balancing Using LSTM Machine Learning Algorithm Journal of Cloud Computing, vol. 11, no. 1, 3 Dec. 2022, journalofcloudcomputing.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13677-022-00362-x. [CrossRef]
- Author 1, Bhowmick, Dipasree, Assessment of Reservoir Performance of a Well in South-Eastern Part of Bangladesh Using Type Curve Analysis Oil & Gas Research, vol. 04, no. 03, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Author 1, Goswami, Pratik, AI Based Energy Efficient Routing Protocol for Intelligent Transportation System IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 2, Feb. 2022, pp. 1670–1679. [CrossRef]
- Author 1, Kaipu, Sandeep AI-Powered Dynamic Optimization of Cloud Resource Allocation European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 9(9), 100–106. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









