Submitted:
07 January 2025
Posted:
08 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
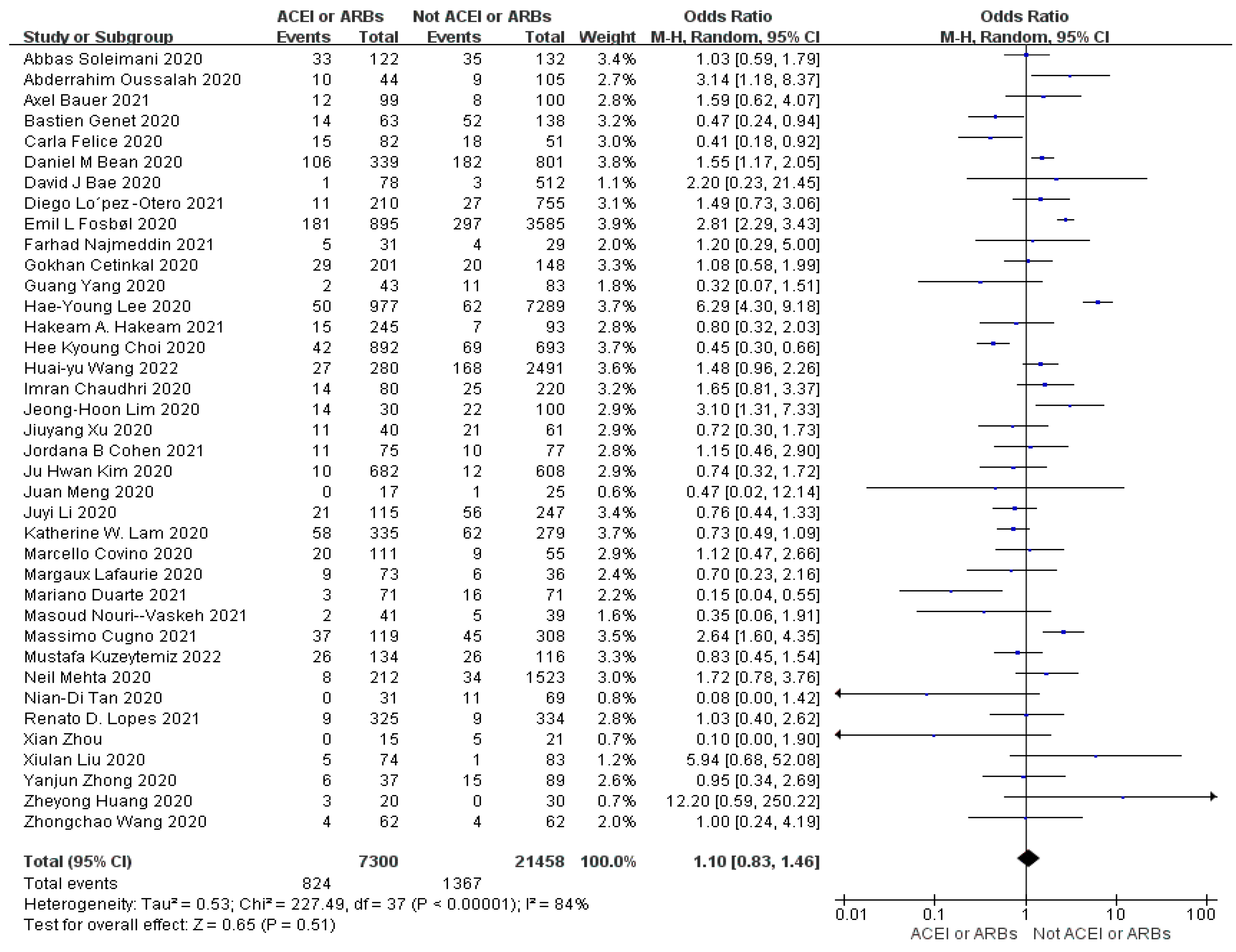
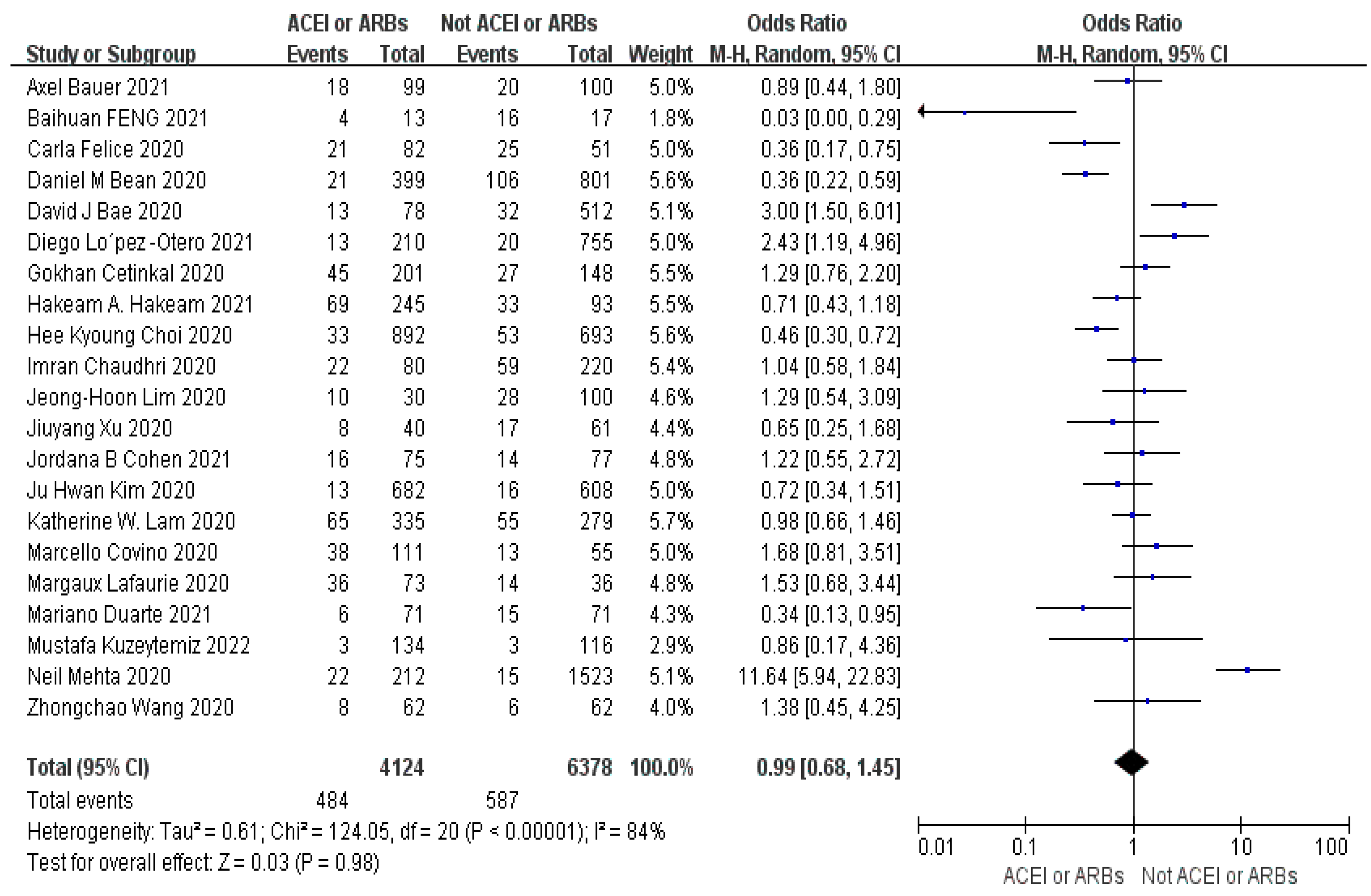
Objective: The primary objective of this study is to explore the potential link between the utilization of ACEIs or ARBs and its impact on mortality rates, disease severity, and healthcare resource utilization in individuals diagnosed with COVID-19. By conducting this research, we aim to establish a solid theoretical foundation for the safe and effective clinical administration of these medications. Method: we conducted a comprehensive search of various databases, including CNKI, PubMed, Springer, Web of Science, and Embase. We also traced the literature of the included studies to ensure a thorough analysis of the available evidence. After applying a set of predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, we ultimately included a total of 41 articles in our analysis. To determine the overall effect size for dichotomous variables, we used the Mantel-Haenszel odds ratio in random effect models. For continuous variables, we calculated the inverse variance SMD using random effect models. To assess the outcomes and heterogeneity, we considered p-values (p<0.05) and I2 values for all outcomes. We performed multivariate and univariate meta-regression analyses using the maximum likelihood approach with the CMA 3.0 software. Results: The results of our analysis indicated that the use of ACEIs or ARBs did not significantly influence mortality (OR=1.10, 95% CI 0.83-1.46, p=0.43, I2=84%), severity (OR=0.99, 95% CI 0.68-1.45, p=0.98, I2=84%) and healthcare resource utilization (SMD=0.03, 95% CI-0.06-0.12, p=0.54, I2=37%) in patients with COVID-19 compared to those not taking ACEIs or ARBs. The multivariate meta-regression analysis model explained 63%, 31%, and 100% of the sources of heterogeneity for the three outcome indicators. Conclusions: The use of ACEIs and ARBs is not significantly correlated with mortality, severity and healthcare resource utilization in patients with COVID-19, indicating safe clinical use of the medications.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusions and Exclusions Criteria
2.3. Literature Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
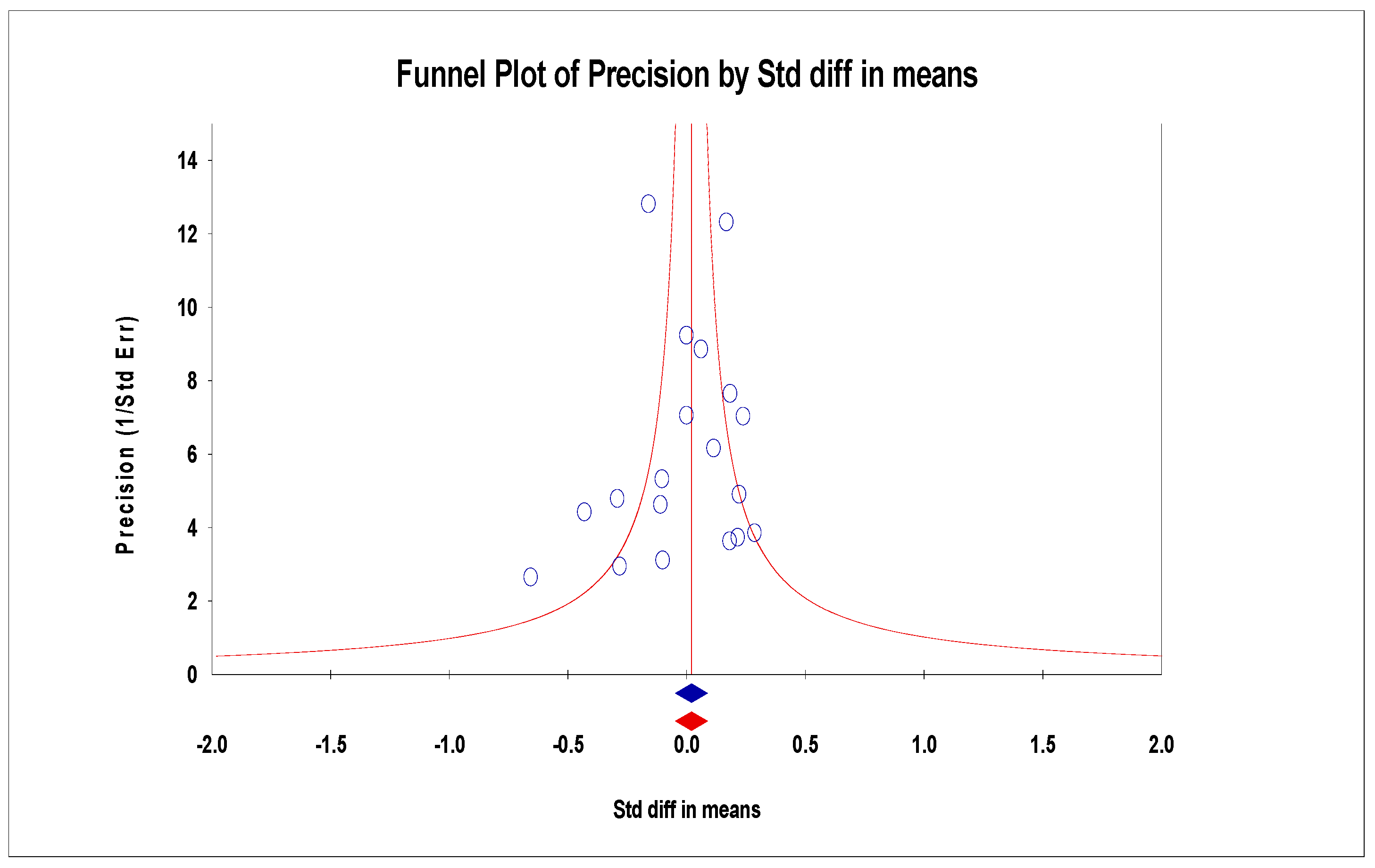
2.6. Publication Bias of Assessment
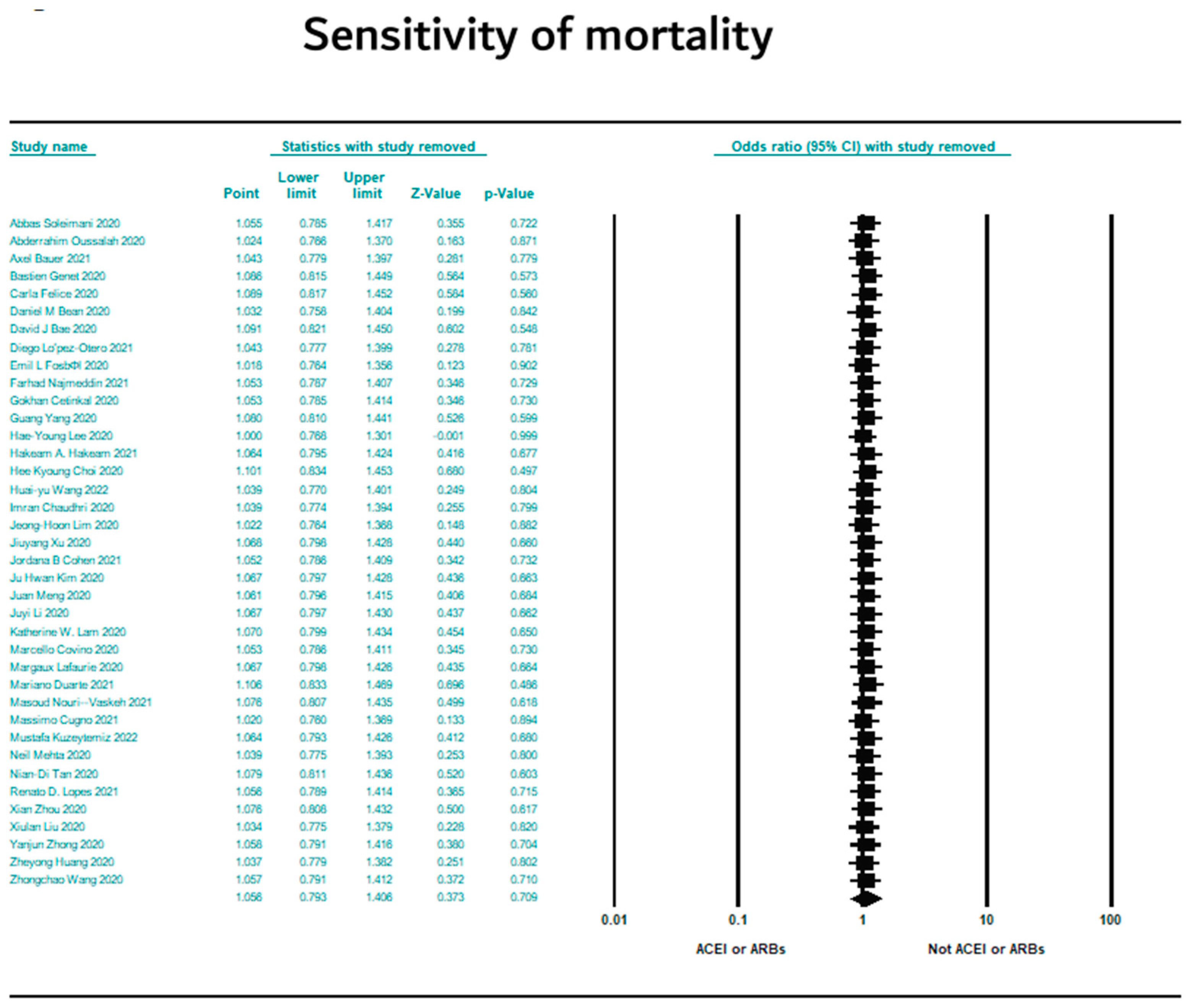
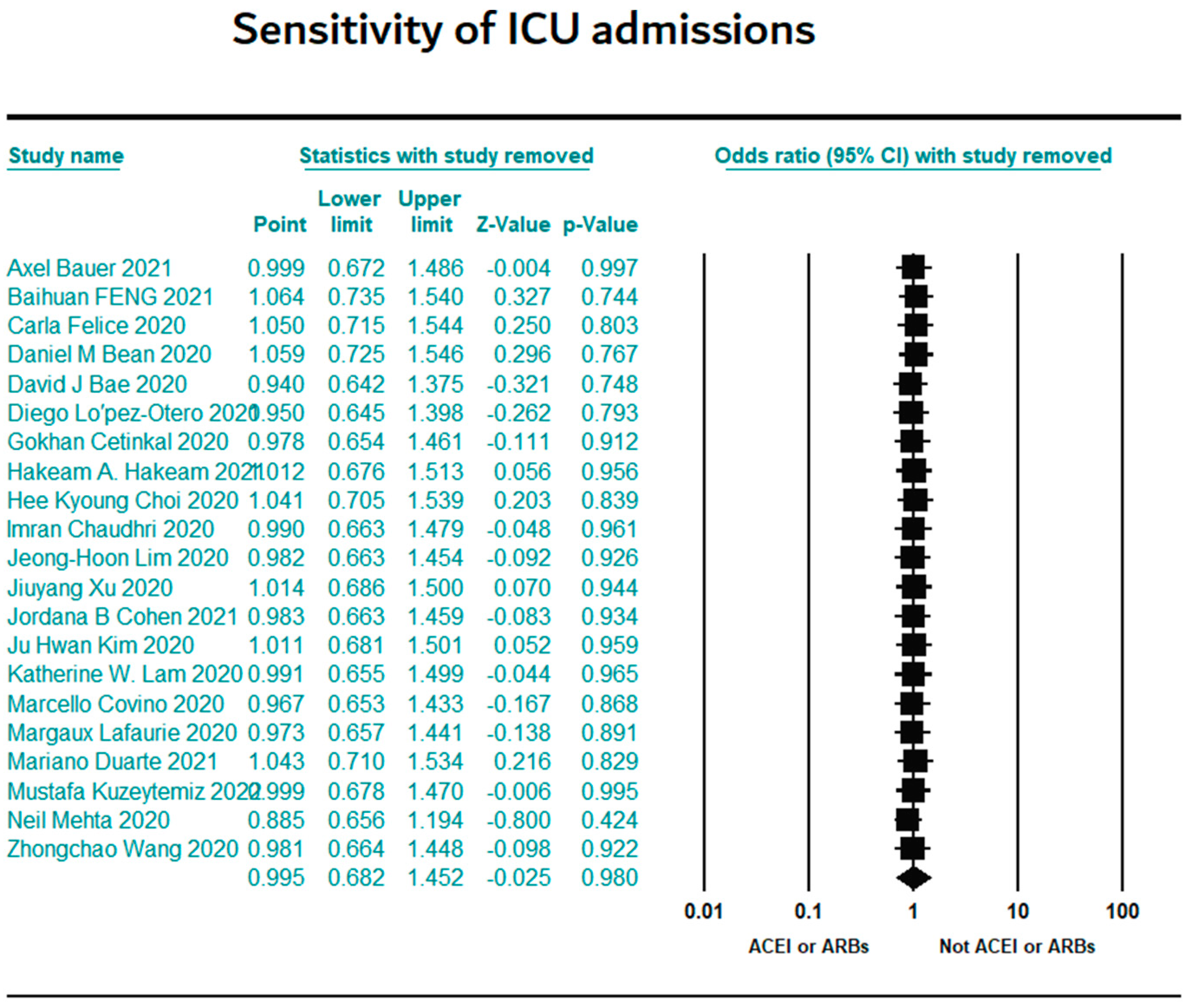
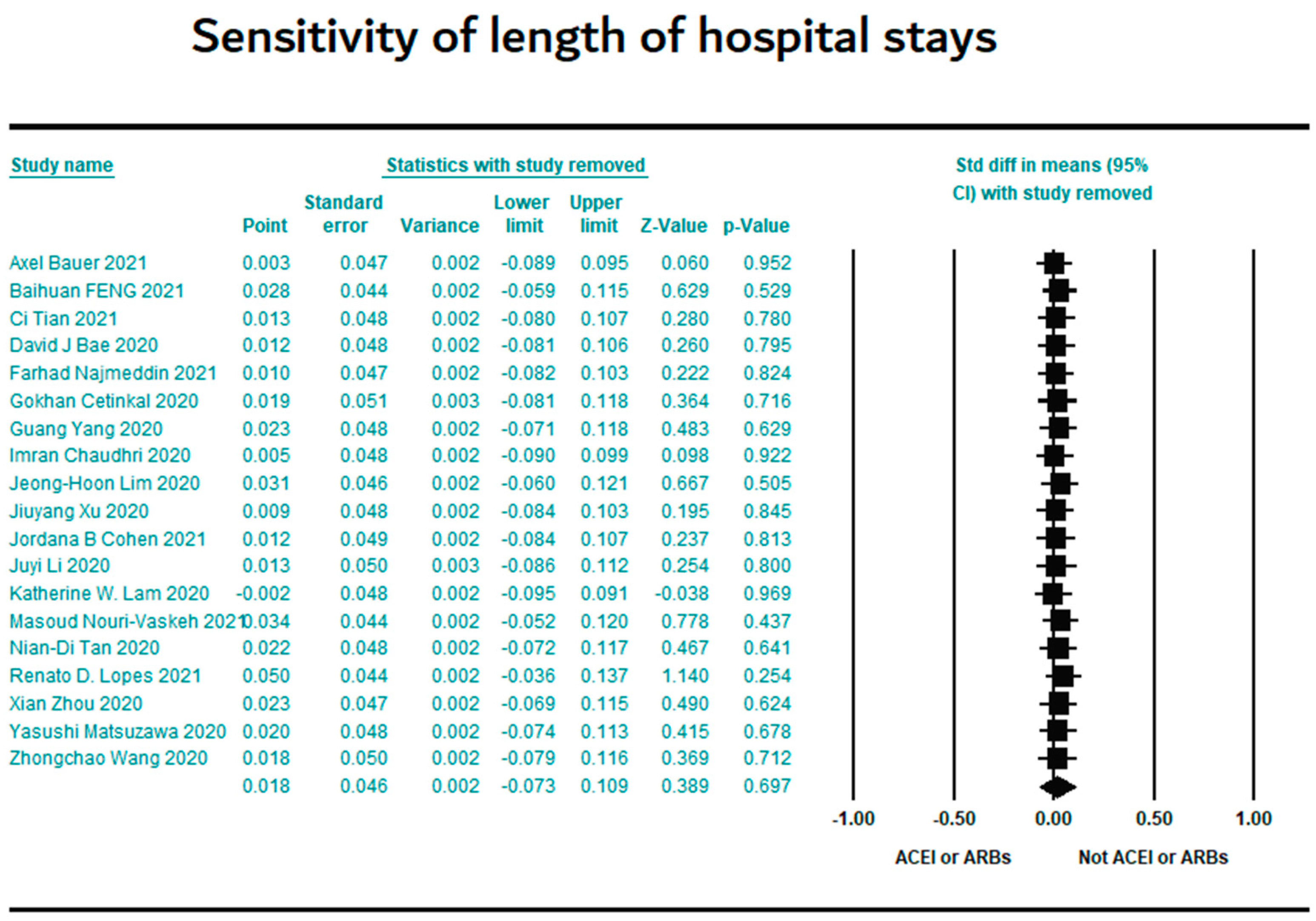
2.7. Sensitivity Analysis
2.8. Statement
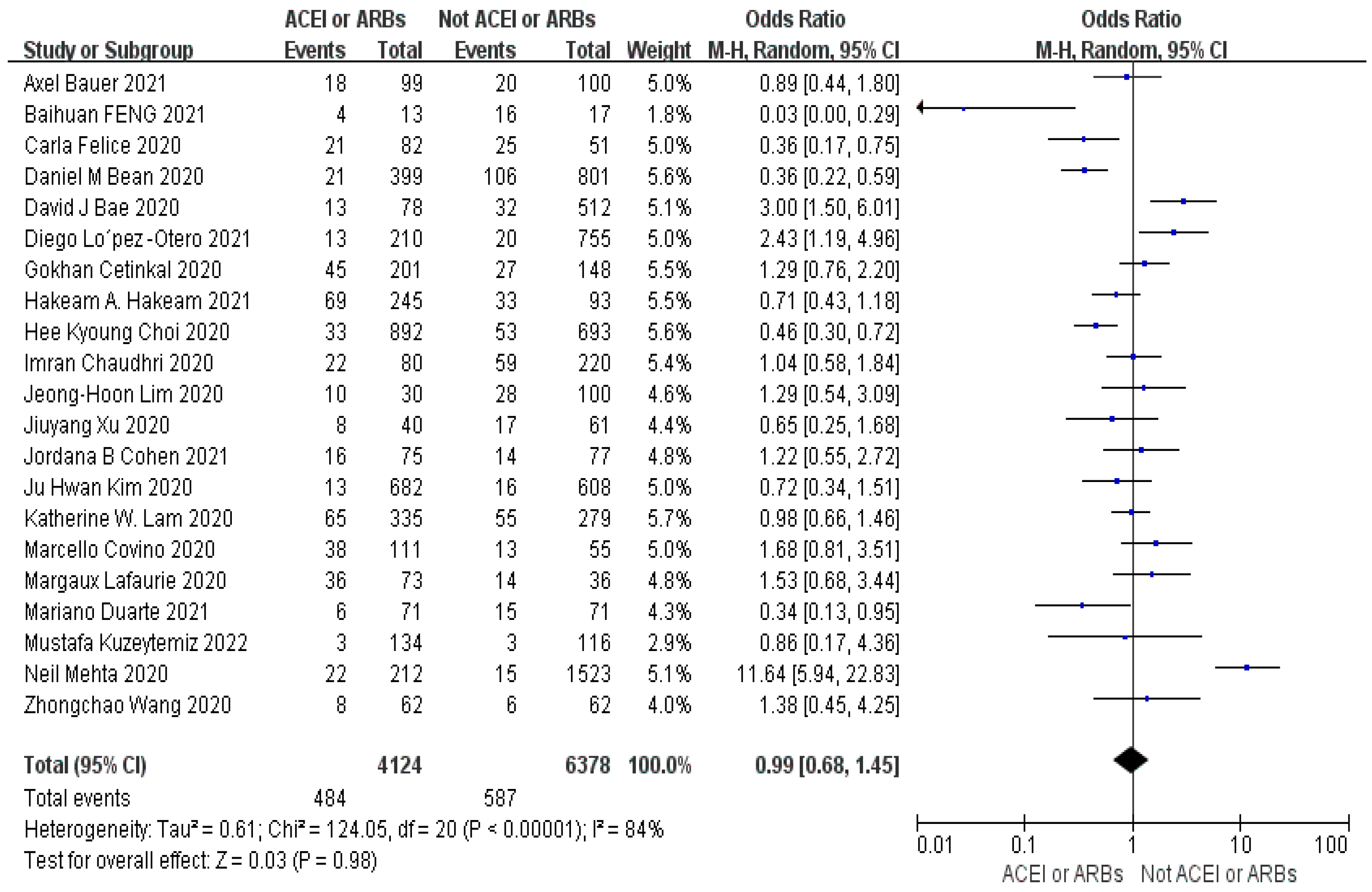
3. Results
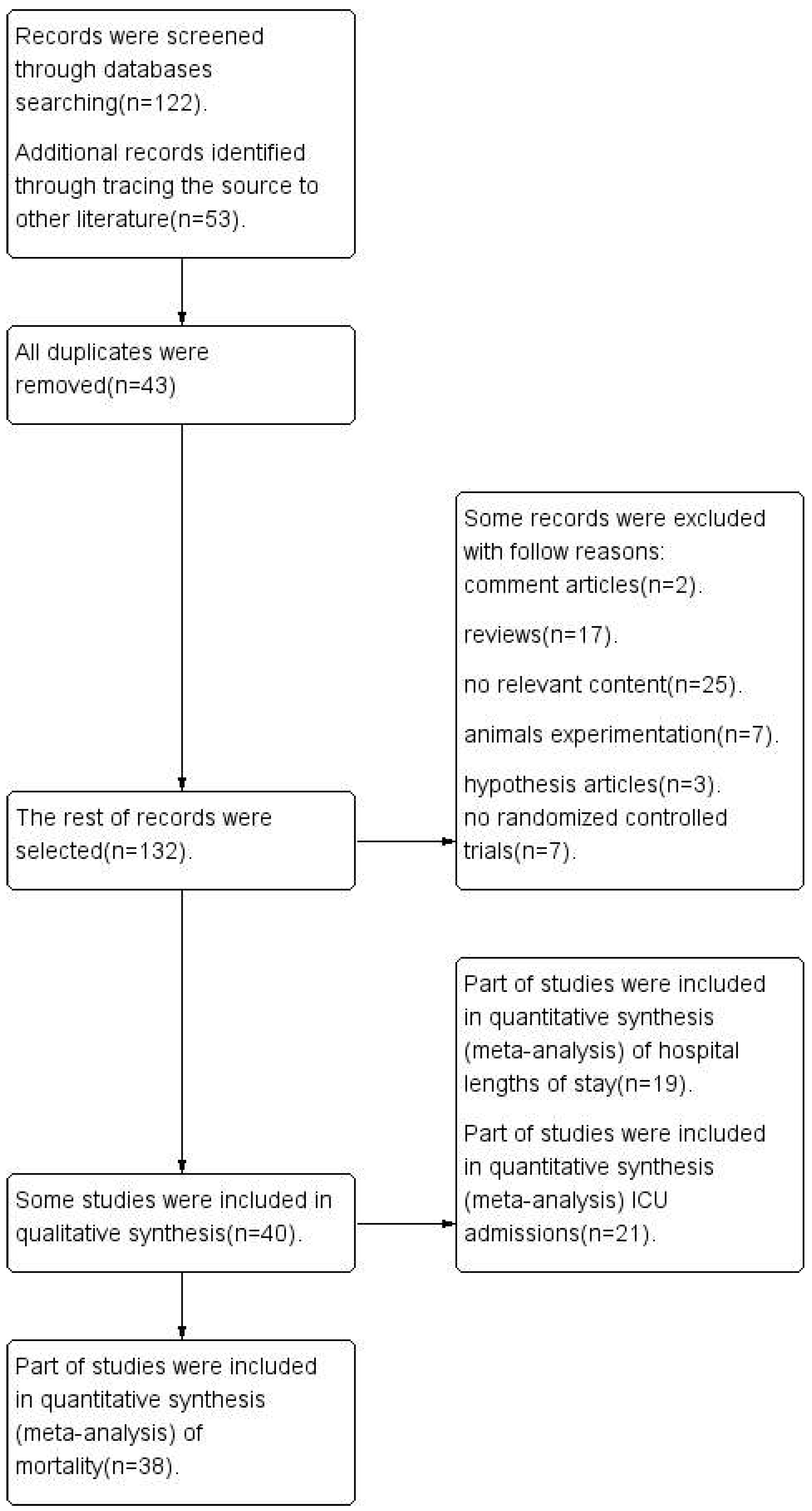
3.1. Articles Search Results
3.2. Basic Characteristics of the Included Studies
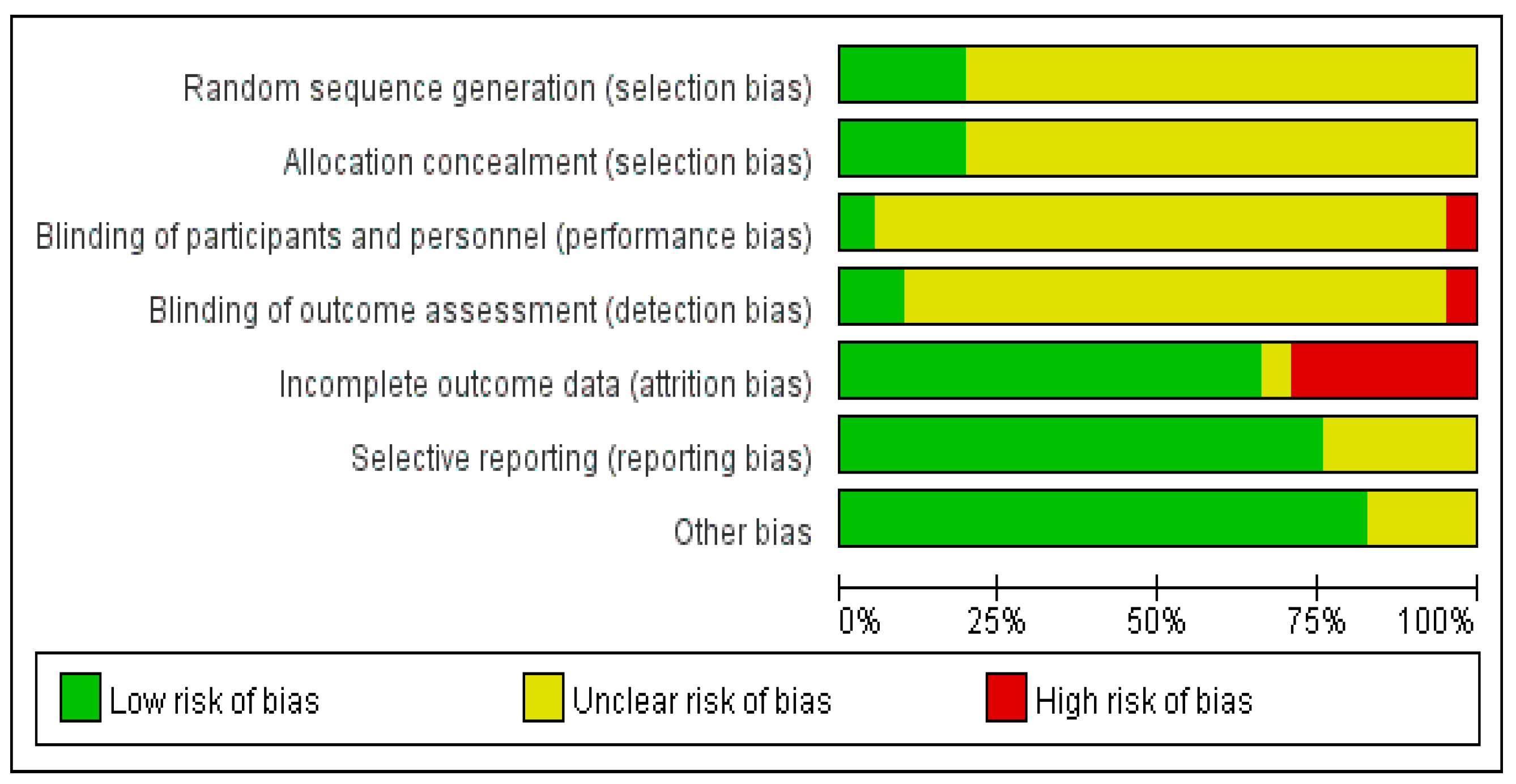
3.3. Quality Evaluation of the Included Literature
3.4. Meta-Analysis Outcomes
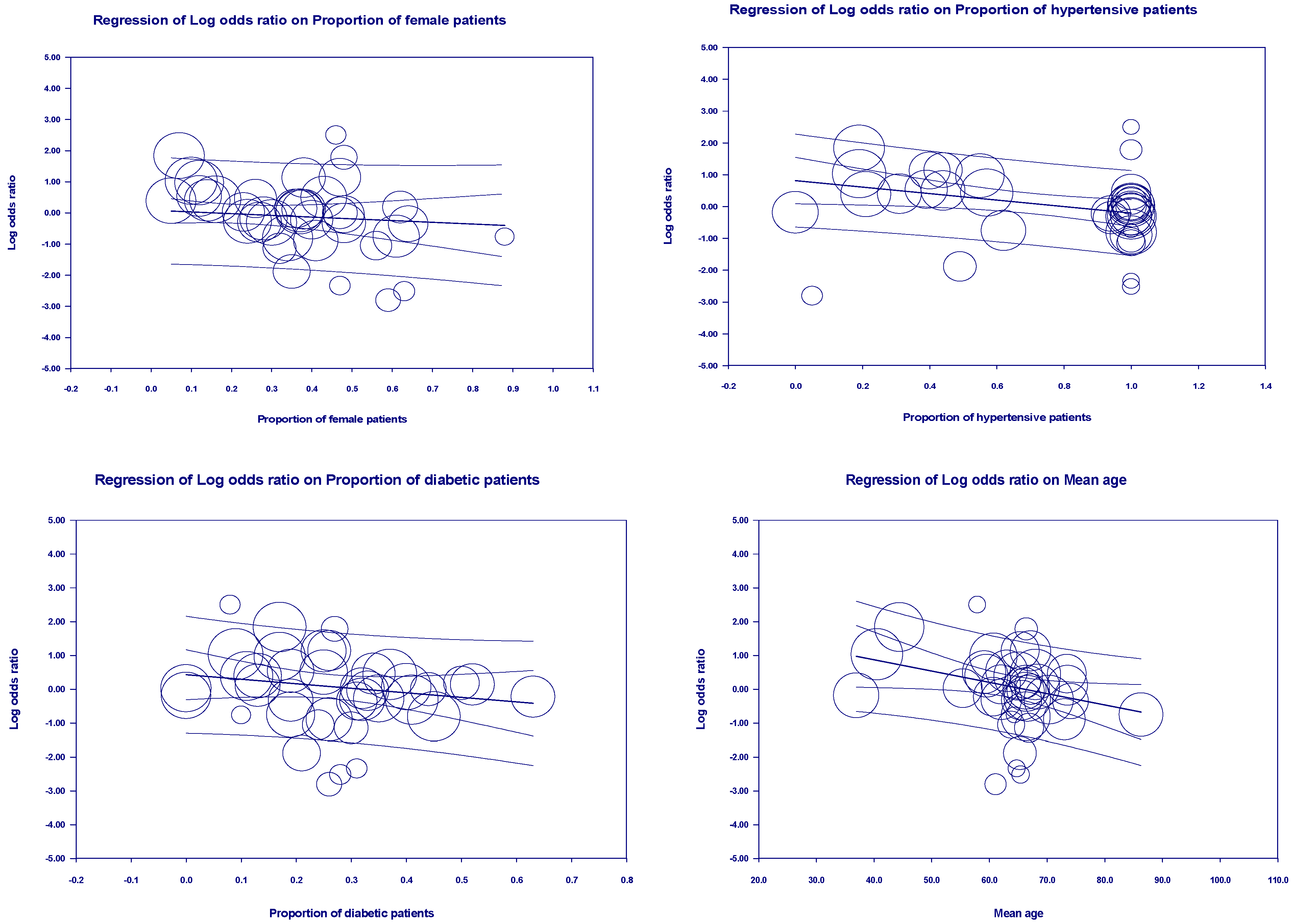
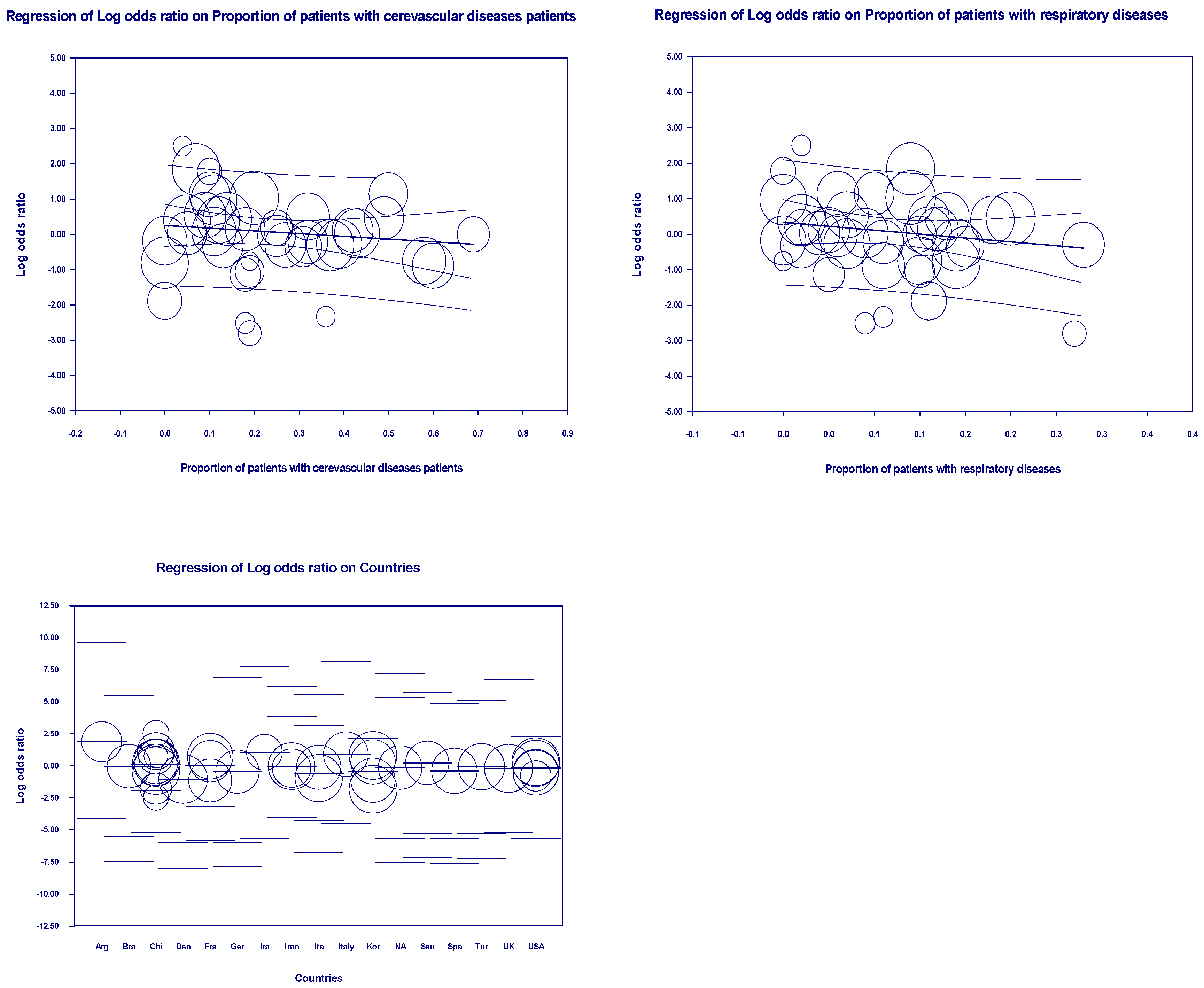
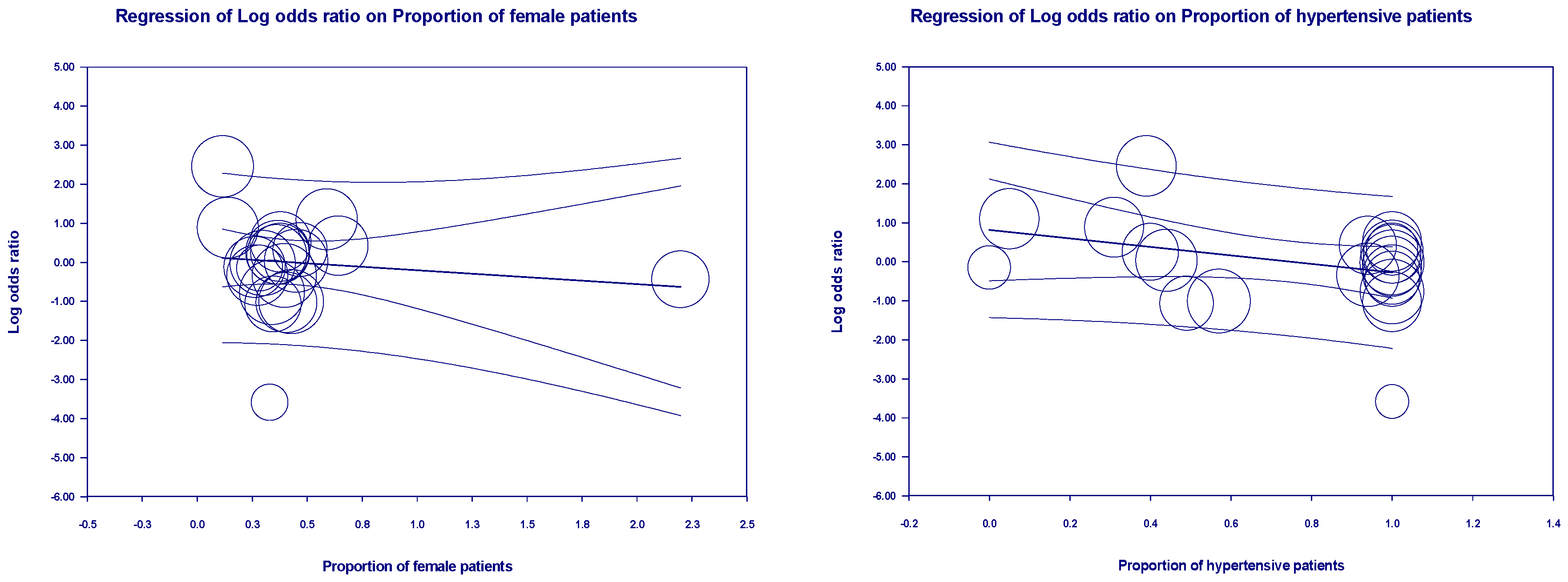
3.5. Meta-Regression Outcomes
3.6. Publication Bias
3.7. Sensitivity Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Ethics approval
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, P.G.; Termini, L.; Durigon, E.L.; Lepique, A.P.; Sposito, A.C.; Boccardo, E. Diacerein: A potential multi-target therapeutic drug for COVID-19. Med Hypotheses 2020, 144, 109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnah, A.A.; Al-Amri, S.S.; Hassan, A.M.; Almasoud, A.S.; Mousa, M.; Almahboub, S.A.; Alhabbab, R.Y.; Mirza, A.A.; Hindawi, S.I.; Alharbi, N.K.; et al. Seroprevalence of MERS-CoV in healthy adults in western Saudi Arabia, 2011-2016. J Infect Public Health 2020, 13, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group; Sterne, J. A.C.; Murthy, S.; Diaz, J.V.; Slutsky, A.S.; Villar, J.; Angus, D.C.; Annane, D.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Berwanger, O.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; et al. Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis. JAMA 2020, 324, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Gupta, V. SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics: how far do we stand from a remedy? Pharmacol Rep. 2021, 73, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard |WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data,https://covid19.who.int/.
- Xu, Y.; Rong, J.; Zhang, Z. The emerging role of angiotensinogen in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y. Recombinant human ACE2: potential therapeutics of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its complication. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2020, 41, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.; Arnold, A.C. Angiotensin-(1-7): Translational Avenues in Cardiovascular Control. Am J Hypertens 2019, 32, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikmet, F.; Méar, L.; Edvinsson, Å.; Micke, P.; Uhlén, M.; Lindskog, C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Mol Syst Biol 2020, 16, e9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Bansal, V.; Feschotte, C. A single-cell RNA expression map of human coronavirus entry factors. bioRxiv 2020, 32, 108175. [Google Scholar]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Labandeira, C.M.; Valenzuela, R.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Quijano, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. Drugs Modulating Renin-Angiotensin System in COVID-19 Treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Liang, W.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.R.; Chen, Z.S.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, R.C.; Tang, C.L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Respir J 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Wan, X.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res 2018, 27, 1785–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.J.; Tehrani, D.M.; Rabadia, S.V.; Frost, M.; Parikh, R.V.; Calfon-Press, M.; Aksoy, O.; Umar, S.; Ardehali, R.; Rabbani, A.; et al. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Use Among Outpatients Diagnosed With COVID-19. Am J Cardiol 2020, 132, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Schreinlechner, M.; Sappler, N.; Dolejsi, T.; Tilg, H.; Aulinger, B.A.; Weiss, G.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Adolf, C.; Wolf, D.; et al. Discontinuation versus continuation of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors in COVID-19 (ACEI-COVID): a prospective, parallel group, randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Respir Med 2021, 9, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, D.M.; Kraljevic, Z.; Searle, T.; Bendayan, R.; Kevin, O.; Pickles, A.; Folarin, A.; Roguski, L.; Noor, K.; Shek, A.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers are not associated with severe COVID-19 infection in a multi-site UK acute hospital trust. Eur J Heart Fail 2020, 22, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkal, G.; Kocas, B.B.; Ser, O.S.; Kilci, H.; Yildiz, S.S.; Ozcan, S.N.; Verdi, Y.; Altinay, M.; Kilickesmez, K. The Association between Chronic Use of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and in-Hospital Adverse Events among COVID-19 Patients with Hypertension. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul 2020, 54, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhri, I.; Koraishy, F.M.; Bolotova, O.; Yoo, J.; Marcos, L.A.; Taub, E.; Sahib, H.; Bloom, M.; Ahmad, S.; Skopicki, H.; et al. Outcomes Associated with the Use of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Kidney360 2020, 1, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi HK (College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea), Koo H (College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea), Seok H (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Jeon JH (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Choi WS (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Kim DJ (Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Republic of Korea), Park DW (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Han E (College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea). ARB/ACEI use and severe COVID-19: A nationwide case-control study, 2020, (unpublish work).Choi HK (College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea), Koo H (College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea), Seok H (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Jeon JH (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Choi WS (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Kim DJ (Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Republic of Korea), Park DW (Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Republic of Korea), Han E (College of Pharmacy, Yonsei Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea). ARB/ACEI use and severe COVID-19: A nationwide case-control study, 2020, (unpublish work).
- Cohen, J.B.; Hanff, T.C.; William, P.; Sweitzer, N.; Rosado-Santander, N.R.; Medina, C.; Rodriguez-Mori, J.E.; Renna, N.; Chang, T.I.; Corrales-Medina, V.; et al. Continuation versus discontinuation of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: a prospective, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Respir Med 2021, 9, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covino, M.; De Matteis, G.; Burzo, M.L.; Santoro, M.; Fuorlo, M.; Sabia, L.; Sandroni, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F.; Gambassi, G.; Gemelli Against COVID-19 Group. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers and prognosis of hypertensive patients hospitalised with COVID-19. Intern Med J 2020, 50, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugno, M.; Gualtierotti, R.; Casazza, G.; Tafuri, F.; Ghigliazza, G.; Torri, A.; Costantino, G.; Montano, N.; Peyvandi, F. Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 on Renin Angiotensin System Inhibitor Long-Term Treatment: An Observational Study Showing that Things Are Not Always as They Seem. Adv Ther 2021, 38, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Pelorosso, F.; Nicolosi, L.N.; Salgado, M.V.; Vetulli, H.; Aquieri, A.; Azzato, F.; Castro, M.; Coyle, J.; Davolos, I.; et al. Telmisartan for treatment of Covid-19 patients: An open multicenter randomized clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, C.; Nardin, C.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Grossi, U.; Bernardi, E.; Scaldaferri, L.; Romagnoli, M.; Tonon, L.; Cavasin, P.; Novello, S.; et al. Use of RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Clinical Deterioration in COVID-19: Results From an Italian Cohort of 133 Hypertensives. Am J Hypertens 2020, 33, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosbøl, E.L.; Butt, J.H.; Østergaard, L.; Andersson, C.; Selmer, C.; Kragholm, K.; Schou, M.; Phelps, M.; Gislason, G.H.; Gerds, T.A.; et al. Association of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Use With COVID-19 Diagnosis and Mortality. JAMA 2020, 324, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genet, B.; Vidal, J.S.; Cohen, A.; Boully, C.; Beunardeau, M.; Marine Harlé, L.; Gonçalves, A.; Boudali, Y.; Hernandorena, I.; Bailly, H.; et al. COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality and Use of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers in Geriatrics Patients. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2020, 21, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeam, H.A.; Alsemari, M.; Duhailib, Z.A.; Ghonem, L.; Alharbi, S.A.; Almutairy, E.; Sheraim, N.M.B.; Alsalhi, M.; Alhijji, A.; AlQahtani, S.; et al. Association of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Blockers With Severity of COVID-19: A Multicenter, Prospective Study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 2021, 26, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, J.; Yao, Y.; Jin, X.; Luo, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, C.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; et al. The effect of RAS blockers on the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. Ann Transl Med 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Baek, Y.H.; Lee, H.; Choe, Y.J.; Shin, H.J.; Shin, J.Y. Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 following the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers among patients with hypertension in Korea: a nationwide study. Epidemiol Health 2021, 43, e2021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzeytemiz, M.; Tenekecioglu, E. Effect of renin-angiotensin system blocker on COVID-19 in young patients with hypertension. J Investig Med 2022, 70, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaurie, M.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Delobel, P.; Charpentier, S.; Sommet, A.; Moulis, G. Outcome of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and exposure to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers in France: results of the ACE-CoV study. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2021, 35, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.W.; Chow, K.W.; Vo, J.; Hou, W.; Li, H.; Richman, P.S.; Mallipattu, S.K.; Skopicki, H.A.; Singer, A.J.; Duong, T.Q. Continued In-Hospital Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Use in Hypertensive COVID-19 Patients Is Associated With Positive Clinical Outcome. J Infect Dis 2020, 222, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Kalra, A.; Nowacki, A.S.; Anjewierden, S.; Han, Z.; Bhat, P.; Carmona-Rubio, A.E.; Jacob, M.; Procop, G.W.; Harrington, S.; et al. Association of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors on COVID-19-Related Outcome. JAMA Cardiol 2020, 5, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, A. Association of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors With Severity or Risk of Death in Patients With Hypertension Hospitalized for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol 2020, 5, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.Y.; Jeon, S.; Noh, H.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Chang, H.H.; et al. Adverse impact of renin-angiotensin system blockade on the clinical course in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 20250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Yan, S.; Bai, X.; Li, J.; Liu, D. Efficacy of ACEIs/ARBs vs CCBs on the progression of COVID-19 patients with hypertension in Wuhan: A hospital-based retrospective cohort study. J Med Virol 2021, 93, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; Macedo, A.V.S.; de Barros ESilva, P.G.M.; Moll-Bernardes, R.J.; Dos Santos, T.M.; Mazza, L.; Feldman, A.; D'Andréa Saba Arruda, G.; de Albuquerque, D.C.; Camiletti, A.S.; et al. Effect of Discontinuing vs Continuing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on Days Alive and Out of the Hospital in Patients Admitted With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otero, D.; López-Pais, J.; Cacho-Antonio, C.E.; Antúnez-Muiños, P.J.; González-Ferrero, T.; Pérez-Poza, M.; Otero-García, Ó.; Díaz-Fernández, B.; Bastos-Fernández, M.; Bouzas-Cruz, N.; Sanmartín-Pena, X.C.; et al. Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers on COVID-19 in a western population. CARDIOVID registry. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 2021, 74, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Ou, M.; Bi, J.; Yang, R.; Di, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020, 9, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmeddin, F.; Solhjoo, M.; Ashraf, H.; Salehi, M.; Rasooli, F.; Ghoghaei, M.; Soleimani, A.; Bahreini, M. Effects of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitors on Early Outcomes of Hypertensive COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Triple-Blind Clinical Trial. Am J Hypertens 2021, 34, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri-Vaskeh, M.; Kalami, N.; Zand, R.; Soroureddin, Z.; Varshochi, M.; Ansarin, K.; Rezaee, H.; Taghizadieh, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Ahangari Maleki, M.; et al. Comparison of losartan and amlodipine effects on the outcomes of patient with COVID-19 and primary hypertension: A randomised clinical trial. Int J Clin Pract 2021, 75, e14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussalah, A.; Gleye, S.; Clerc Urmes, I.; Laugel, E.; Callet, J.; Barbé, F.; Orlowski, S.; Malaplate, C.; Aimone-Gastin, I.; Caillierez, B.M.; et al. Long-term ACE Inhibitor/ARB Use Is Associated With Severe Renal Dysfunction and Acute Kidney Injury in Patients With Severe COVID-19: Results From a Referral Center Cohort in the Northeast of France. Clin Infect Dis 2020, 71, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, A.; Kazemian, S.; Karbalai Saleh, S.; Aminorroaya, A.; Shajari, Z.; Hadadi, A.; Talebpour, M.; Sadeghian, H.; Payandemehr, P.; Sotoodehnia, M.; et al. Effects of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) on In-Hospital Outcomes of Patients With Hypertension and Confirmed or Clinically Suspected COVID-19. Am J Hypertens 2020, 33, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.D.; Qiu, Y.; Xing, X.B.; Ghosh, S.; Chen, M.H.; Mao, R. Associations Between Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Use, Gastrointestinal Symptoms, and Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Peng, S.; Ye, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Zeng, R.; Yao, Y.; He, F.; Li, J.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor is associated with the reduced risk of all-cause mortality in COVID-19 among patients with/without hypertension. Front Med 2022, 16, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Huan, J.; Wu, Y.; Xia, C.; Li, Z.; Qi, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. A Retrospective Study from 2 Centers in China on the Effects of Continued Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in Patients with Hypertension and COVID-19. Med Sci Monit 2020, 26, e926651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, C.; Fan, G.; Liu, Z.; Shang, L.; Zhou, F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, L.; Xie, K.; et al. Use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers in context of COVID-19 outbreak: a retrospective analysis. Front Med 2020, 14, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Peng, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, J.; Yang, R.; Han, J.; Huang, Y.; He, S. Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers and ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) Inhibitors on Virus Infection, Inflammatory Status, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19 and Hypertension: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Hypertension 2020, 76, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, J.; Park, J.; Kang, C.K.; Won, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Chung, K.H.; Joh, J.S.; Bang, J.H. ; et al. Different therapeutic associations of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors with coronavirus disease 2019 compared with usual pneumonia. Korean J Intern Med 2021, 36, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, G.; Hu, C.; Wu, C.; Xu, M.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Yu, B.; et al. Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors use on mortality in severe COVID-19 patients with hypertension: a retrospective observational study. J Int Med Res 2020, 48, 300060520979151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, T. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients with hypertension on renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Clin Exp Hypertens 2020, 42, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Yu, F.; Zou, Q.; Xie, G.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Lou, B.; et al. Effects of angiotensin II receptor blocker usage on viral load, antibody dynamics, and transcriptional characteristics among COVID-19 patients with hypertension. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2021, 22, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Kimura, K.; Konishi, M.; Kirigaya, J.; Fukui, K.; Tsukahara, K.; Shimizu, H.; Iwabuchi, K.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors and the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 in Kanagawa, Japan: a retrospective cohort study. Hypertens Res 2020, 43, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Li, N.; Bai, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, S.; Ge, Q.G.; Shen, N.; Ma, Q.B. Angiotensin converting enzymes inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers should be continued in COVID-19 patients with hypertension. World J Clin Cases 2021, 9, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirbasli, M. The effects of antihypertensive medications on severity and outcomes of COVID19. J Hum Hypertens 2022, 36, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wösten-van Asperen, R.M.; Lutter, R.; Specht, P.A.; Moll, G.N.; van Woensel, J.B.; van der Loos, C.M.; van Goor, H.; Kamilic, J.; Florquin, S.; Bos, A.P. Acute respiratory distress syndrome leads to reduced ratio of ACE/ACE2 activities and is prevented by angiotensin-(1-7) or an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. J Pathol 2011, 225, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Liu, Z. ACE2 exhibits protective effects against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting the LPS-TLR4 pathway. Exp Mol Pathol 2020, 113, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Zaizafoun, M.; Stock, E.; Ghamande, S.; Arroliga, A.C.; White, H.D. Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and statins on viral pneumonia. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2018, 31, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, E.; Palma, A.C.; Ulaf, R.G.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Bernardes, A.F.; Nunes, T.A.; Agrela, M.V.; Bombassaro, B.; Monfort-Pires, M.; Camargo, R.L.; et al. Safety and Outcomes Associated with the Pharmacological Inhibition of the Kinin-Kallikrein System in Severe COVID-19. Viruses 2021, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
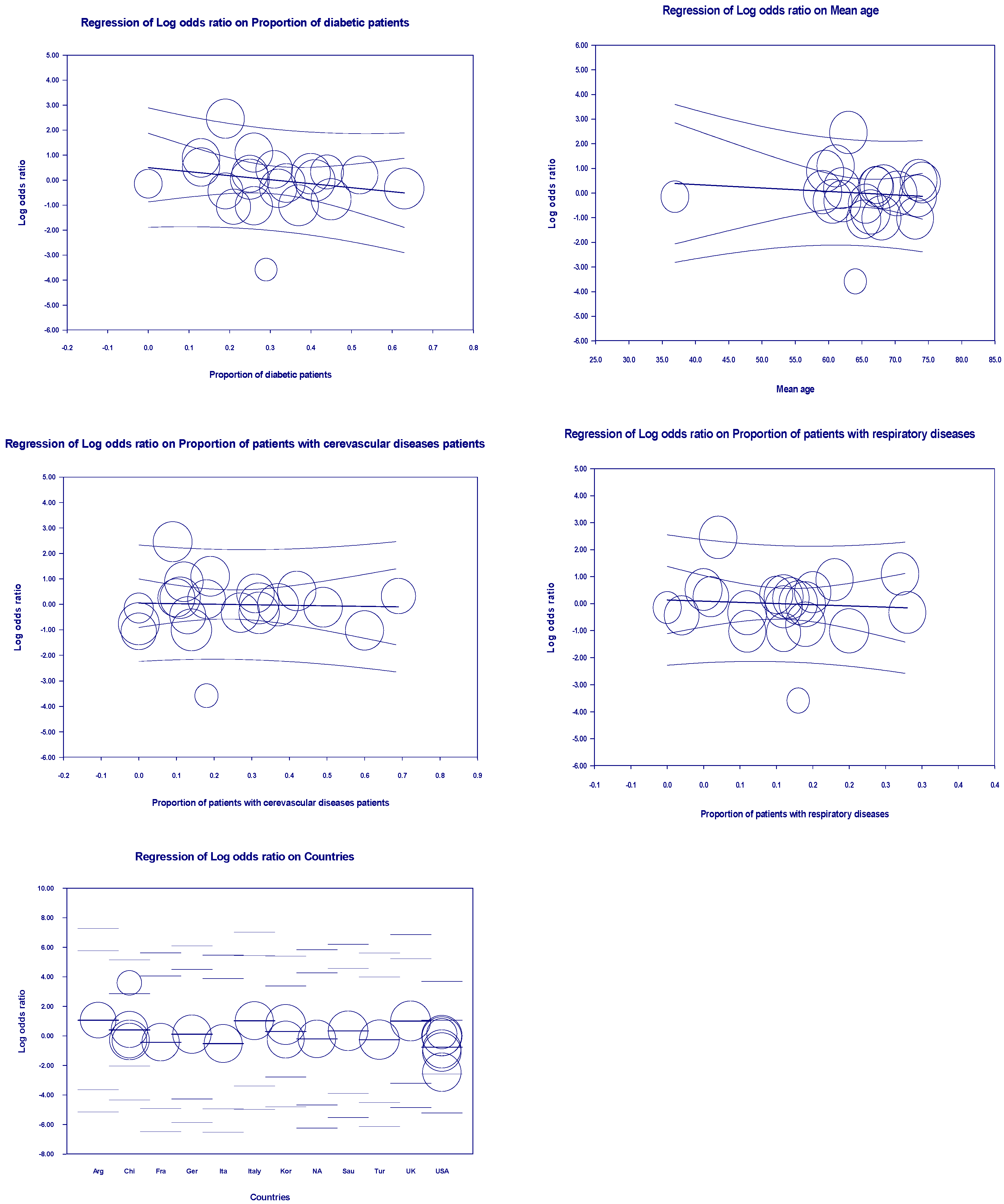
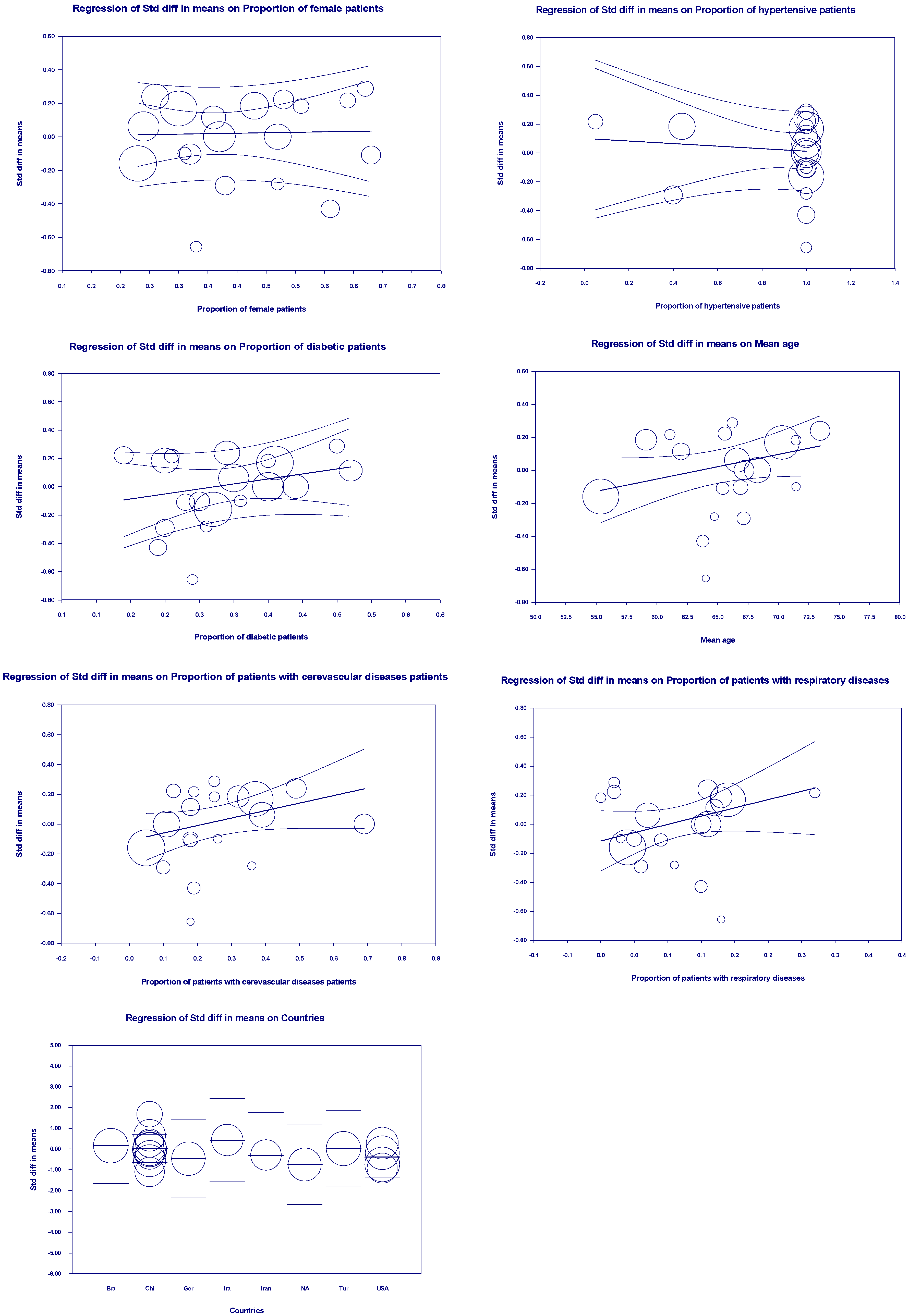
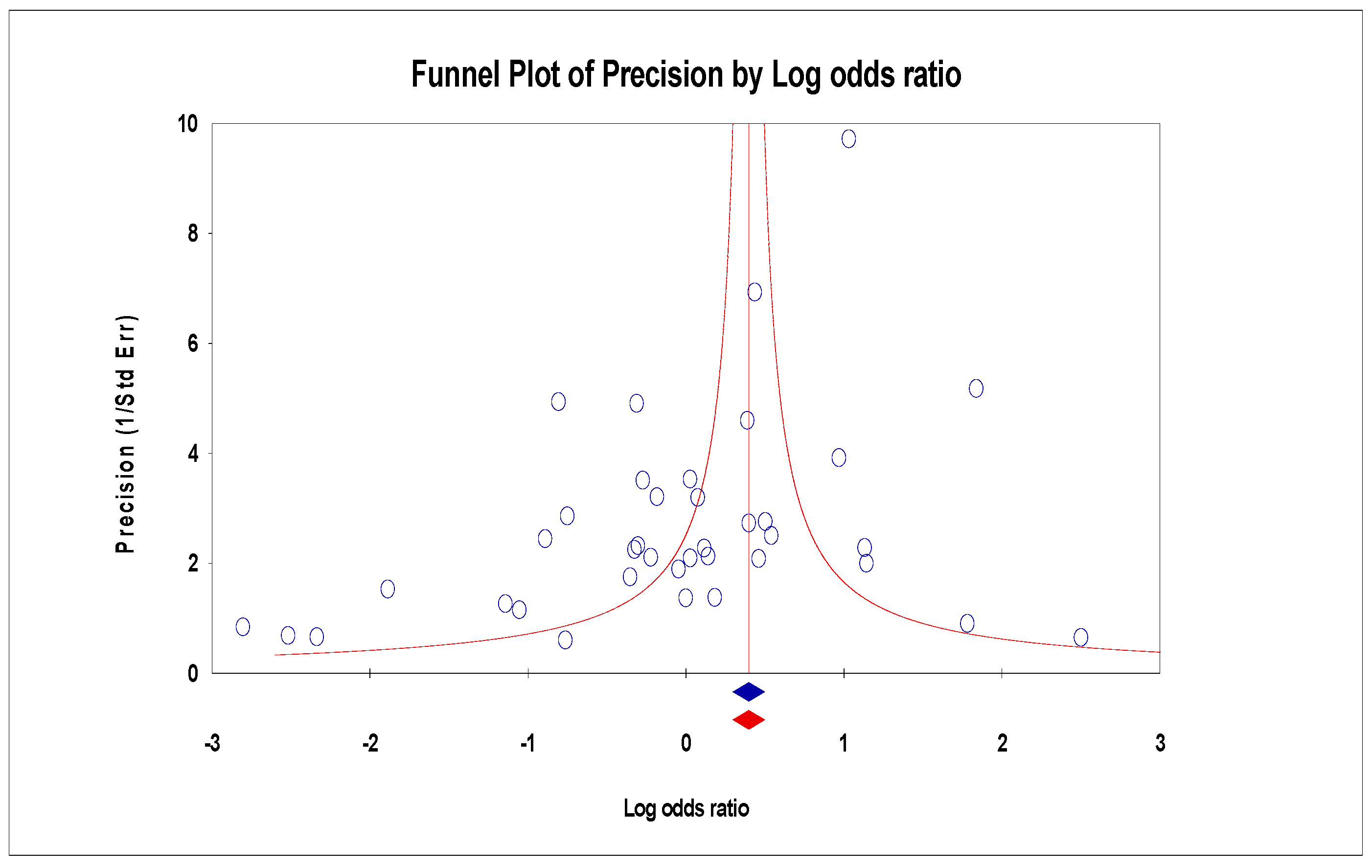
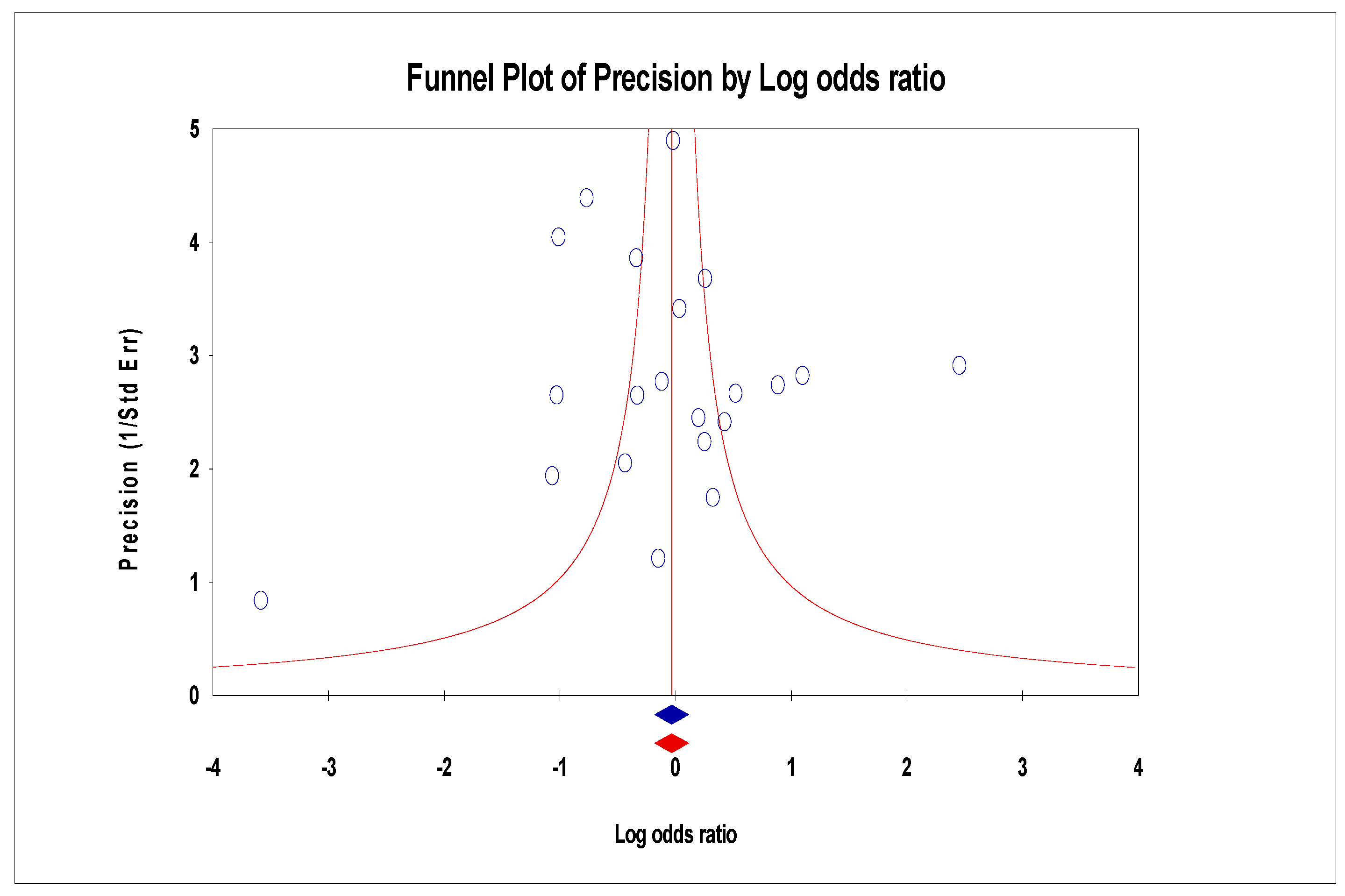
| First author | Contries | Yp | Mean age | Pf | Ph | Pd | Pc | Pr | Control group | Experimental group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Cm | Cl,mean,d | Ci | No. | Em | El,mean,d | Ei | |||||||||
| Abbas Soleimani | Iran | 2020 | 66.39 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 132 | 35 | NA | NA | 122 | 33 | NA | NA |
| Abderrahim Oussalah | France | 2020 | 65.34 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 105 | 9 | NA | NA | 44 | 10 | NA | NA |
| Axel Bauer | Austria and Germany | 2021 | 73.44 | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.16 | 100 | 8 | 10.35 | 20 | 99 | 12 | 12.32 | 18 |
| Baihuan FENG | China | 2021 | 64.03 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 17 | NA | 49.29 | NA | 13 | NA | 18.73 | NA |
| Bastien Genet | France | 2020 | 86.28 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 138 | 52 | NA | NA | 63 | 14 | NA | NA |
| Carla Felice | Italy | 2020 | 73.02 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 0.26 | 0.60 | 0.11 | 51 | 18 | NA | 25 | 82 | 15 | NA | 21 |
| Ci Tian | China | 2021 | 71.46 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 27 | NA | 13.07 | 15 | 27 | NA | 14.29 | NA |
| Daniel M Bean | UK | 2020 | 67.97 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 801 | 182 | NA | 106 | 399 | 106 | NA | 21 |
| David J Bae | USA | 2020 | 45.98 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 512 | 3 | 7.08 | 13 | 78 | 1 | 8.71 | 7.2 |
| Diego Lo´pez -Otero | Spain | 2021 | 59.50 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 755 | 27 | NA | 20 | 210 | 11 | NA | 13 |
| Emil L Fosbøl | Denmark | 2020 | 40.52 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 3585 | 297 | NA | NA | 895 | 181 | NA | NA |
| Farhad Najmeddin | Iran | 2021 | 66.21 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 29 | 4 | 3.64 | NA | 31 | 5 | 4.71 | 4 |
| Gokhan Cetinkal | Turkey | 2020 | 68.28 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 148 | 20 | 8.70 | 27 | 201 | 29 | 8.70 | 45 |
| Guang Yang | China | 2020 | 66.90 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 83 | 11 | 29.70 | NA | 43 | 2 | 28.40 | NA |
| Hae-Young Lee | Repunlic of | 2020 | 44.40 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 7289 | 62 | NA | NA | 977 | 50 | NA | NA |
| Hakeam A. Hakeam | Saudi Arabia | 2021 | 60.61 | 0.40 | 0.94 | 0.63 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 93 | 7 | NA | 33 | 245 | 15 | NA | 69 |
| Hee Kyoung Choi | Repunlic of korea | 2020 | 66.31 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 693 | 69 | NA | 53 | 892 | 42 | NA | 33 |
| Huai-yu Wang | China | 2022 | 65.00 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 2491 | 168 | NA | NA | 280 | 27 | NA | NA |
| Imran Chaudhri | USA | 2020 | 59.11 | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 220 | 25 | 7.00 | 59 | 80 | 14 | 9.00 | 22 |
| Jeong-Hoon Lim | Repunlic of korea | 2020 | 67.14 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 100 | 22 | 24.90 | 28 | 30 | 14 | 20.30 | 10 |
| Jiuyang Xu | China | 2020 | 65.60 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 61 | 21 | 11.12 | 17 | 40 | 11 | 12.29 | 8 |
| Jordana B Cohen | 7 countries | 2021 | 62.00 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 77 | 10 | 6.06 | 14 | 75 | 11 | 6.71 | 16 |
| Ju Hwan Kim | Repunlic of | 2020 | 62.09 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 608 | 12 | NA | 16 | 682 | 10 | NA | 13 |
| Juan Meng | China | 2020 | 64.30 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 25 | 1 | NA | NA | 17 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Juyi Li | China | 2020 | 66.60 | 0.24 | 1.00 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 247 | 56 | 19.00 | 56 | 115 | 21 | 19.70 | NA |
| Katherine W. Lam | USA | 2020 | 70.30 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 279 | 62 | 6.70 | 55 | 335 | 58 | 7.70 | 65 |
| Marcello Covino | Italy | 2020 | 73.55 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 55 | 9 | NA | 13 | 111 | 20 | NA | 38 |
| Margaux Lafaurie | France | 2020 | 74.09 | 0.64 | 0.94 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 36 | 6 | NA | 14 | 73 | 9 | NA | 36 |
| Mariano Duarte | Argentina | 2021 | 65.30 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 71 | 16 | 15.00 | 15 | 71 | 3 | 9.00 | 6 |
| Masoud Nouri- Vaskeh | Iran | 2021 | 63.79 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 39 | 5 | 7.30 | NA | 41 | 2 | 4.57 | NA |
| Massimo Cugno | Italy | 2021 | 60.70 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 308 | 45 | NA | NA | 119 | 37 | NA | NA |
| Mustafa Kuzeytemiz | USA | 2022 | 36.92 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 116 | 26 | NA | 3 | 134 | 26 | NA | 3 |
| Neil Mehta | USA | 2020 | 63.00 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1523 | 34 | NA | 15 | 212 | 8 | NA | 22 |
| Nian-Di Tan | China | 2020 | 65.42 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 69 | 11 | 34.24 | NA | 31 | 0 | 32.64 | NA |
| Renato D. Lopes | Brazil | 2021 | 55.39 | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 334 | 9 | 7.80 | NA | 325 | 9 | 6.70 | NA |
| Xian Zhou | China | 2020 | 64.74 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.11 | 21 | 5 | 11.70 | NA | 15 | 2 | 10.10 | NA |
| Xiulan Liu | China | 2020 | 66.39 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 83 | 1 | NA | NA | 74 | 5 | NA | NA |
| Yanjun Zhong | China | 2020 | 66.31 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 89 | 15 | NA | NA | 37 | 6 | NA | NA |
| Zheyong Huang | China | 2020 | 57.90 | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 30 | 0 | NA | NA | 20 | 3 | NA | NA |
| Zhongchao Wang | China | 2020 | 67.18 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.44 | 0.69 | 0.15 | 62 | NA | 17.00 | 6 | 62 | 4 | 17.00 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




