Submitted:
06 January 2025
Posted:
07 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
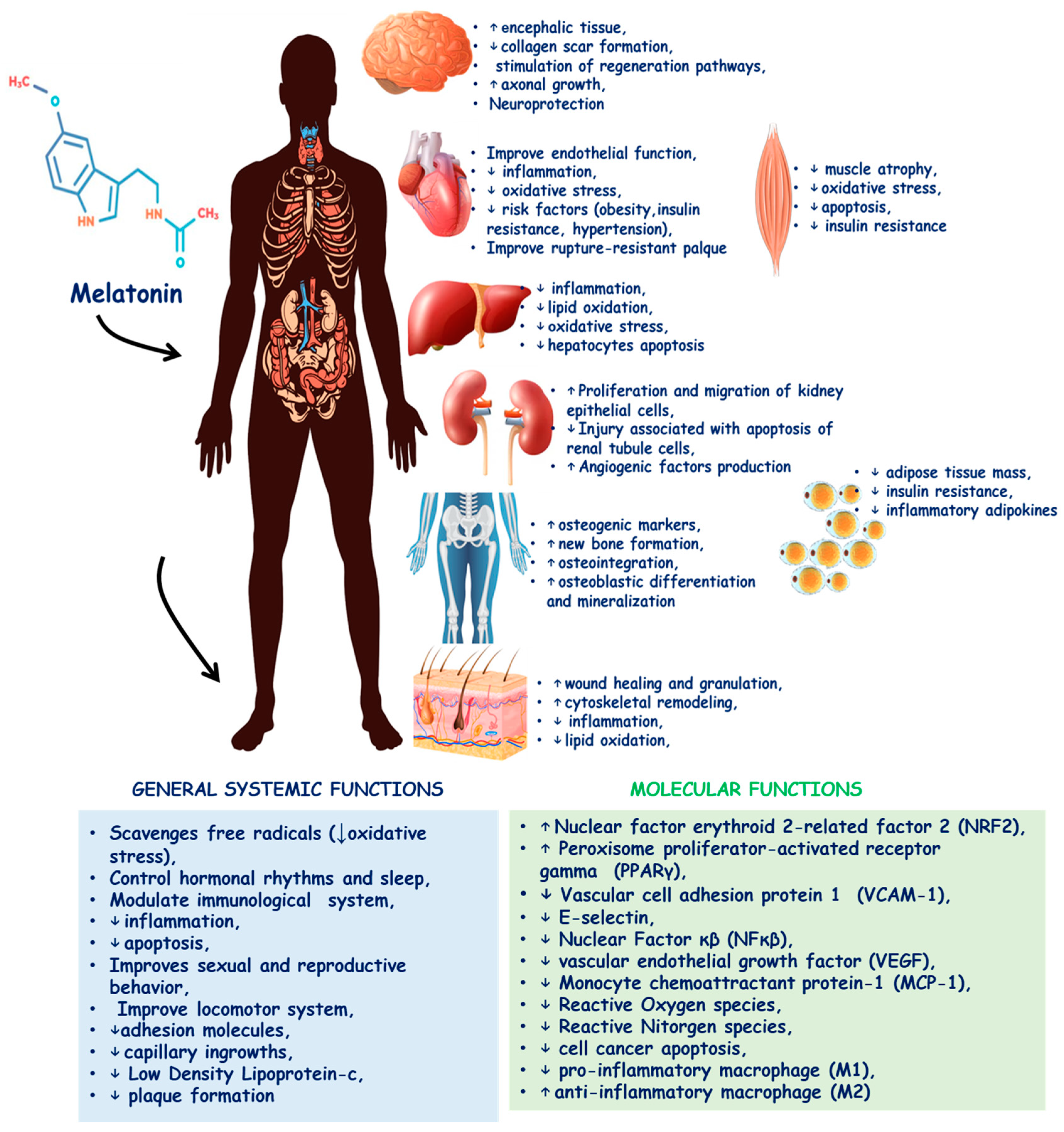
1. Introduction
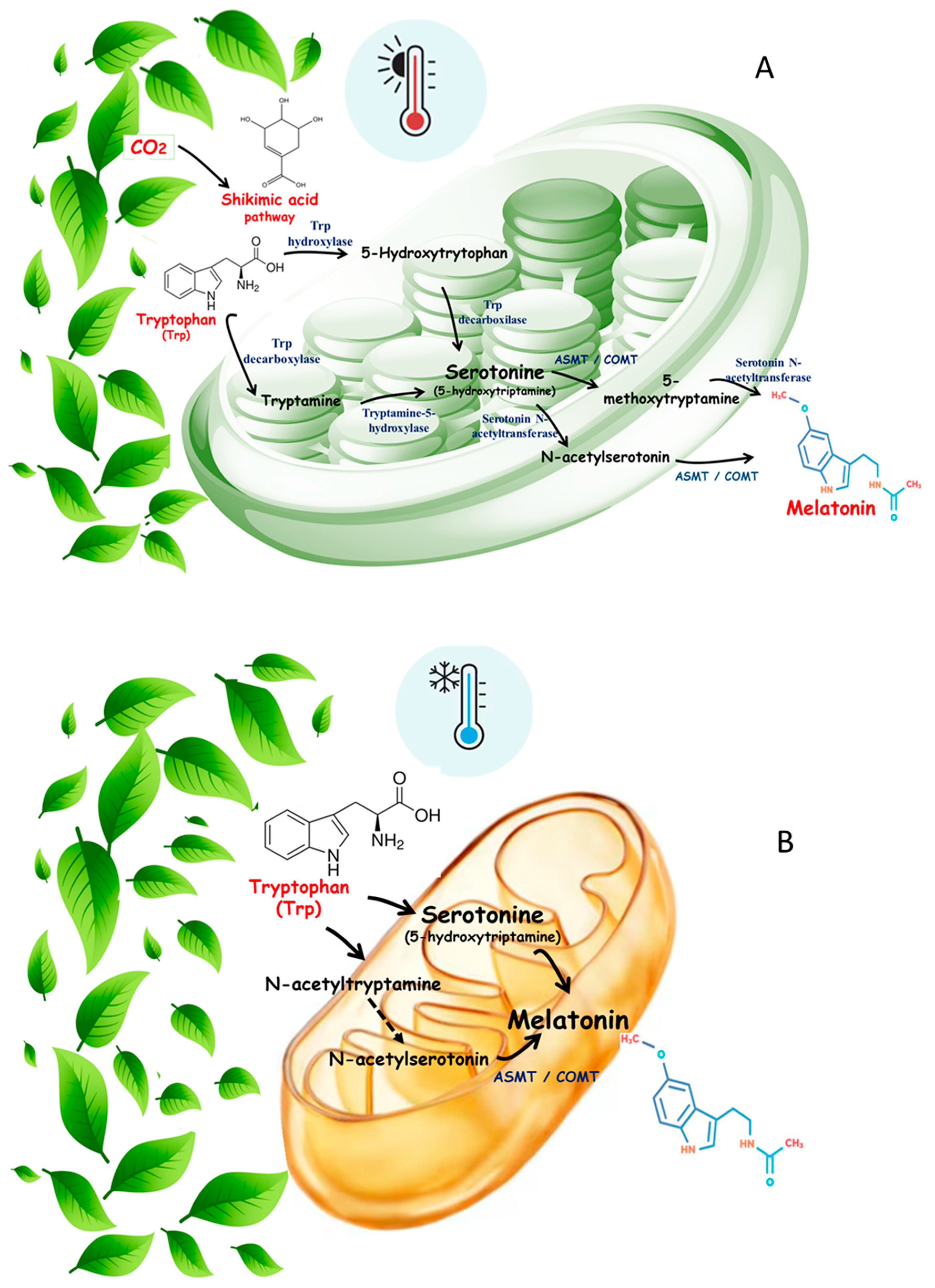
2. Summary of Melatonin Biosynthesis in Plants
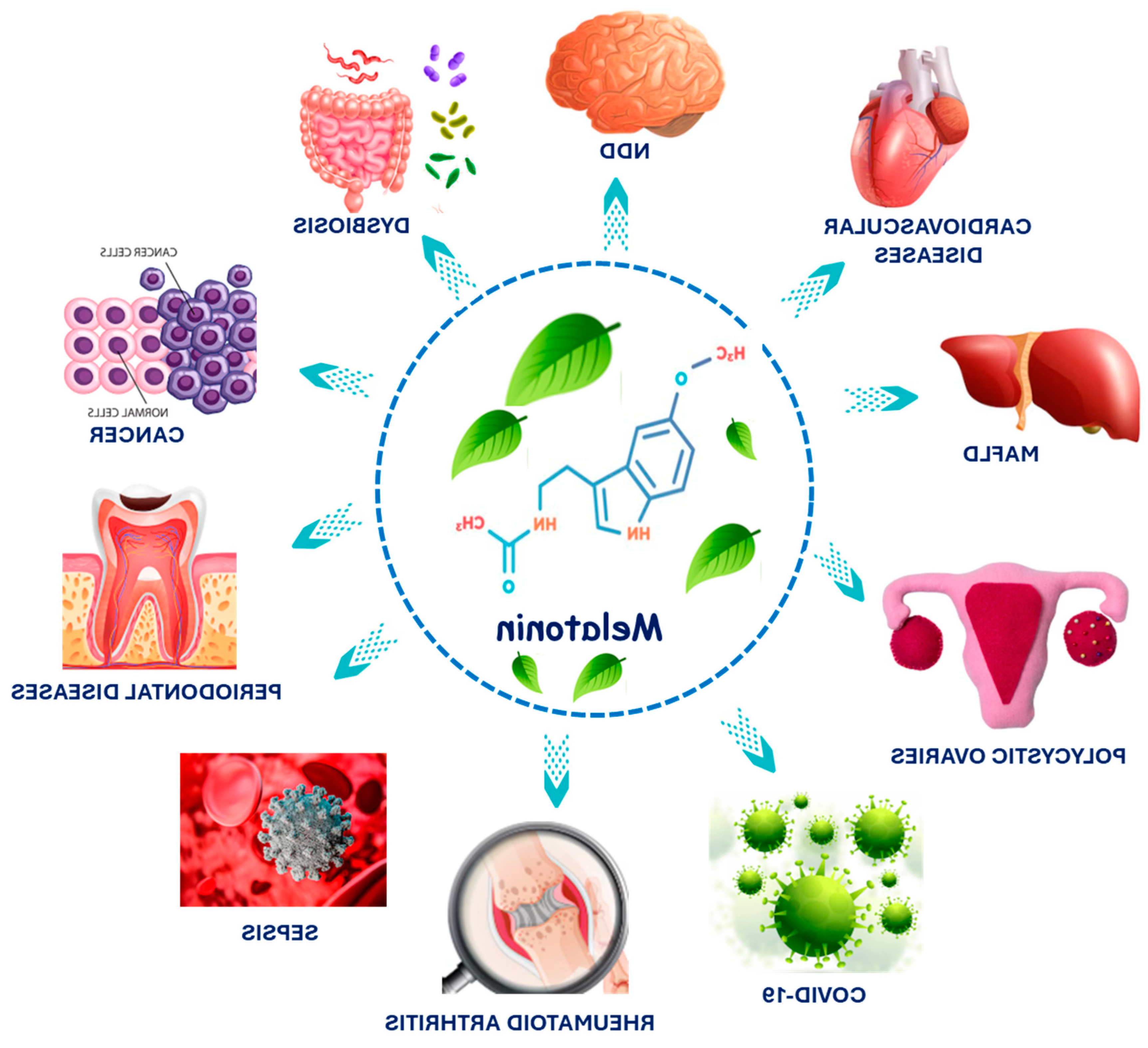
3. Melatonin in Cardiovascular Diseases and MAFLD
4. Effects of Melatonin on Rheumatoid Arthritis
5. Effects of Melatonin on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [101] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial | 84 women with polycystic ovary syndrome were randomized into 4 groups: placebo group (26,200 ± 5.72y, 20♀), melatonin+magnesium group (28.22 ± 6.38y, 22♀), melatonin group (25.57 ± 4.99y, 21♀) and magnesium group (25.57 ± 4.88y, 21♀) | 2 tablets a day of 3 mg melatonin each + 250-mg magnesium oxide tablet | 8 weeks | ↓Weight, BMI, WC in the melatonin and melatonin+magnesium groups. ↓TNF-α in the melatonin and melatonin+magnesium groups. ↓Hirsutism in the melatonin+magnesium group. ↑TAC in the melatonin+magnesium group |
| [102] | Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Iran) | 58 patients with polycystic ovary syndrome were randomized into 2 groups: placebo (26.0±3.3y, 29♀) or melatonin (26.5±3.5y, 29 ♀) | 2 capsules of 5mg of melatonin each a day | 12 weeks | ↓PSQI, BDI index, BAI index, serum insulin, HOMA-IR, LDL-c in the melatonin group. ↑PPAR-γ and LDL Receptor gene expression in the melatonin group |
| [103] | Randomized, controlled, double-blind trial (Italy) | 526 women with PCOS were randomized into 3 groups: control group (32 ± 3.6y, 195♀), group A (31.2 ± 2.1y, 165♀), and group B (31.5 ± 2.8y, 166♀) | 3 mg of melatonin + 4000 mg myo-inositol + 400 mcg folic acid daily | From the first day of the cycle to 14 days after embryo transfer | ↑Oocyte and embryo quality with melatonin+myo-inositol supplementation |
6. Effects of Melatonin on Dermatitis
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [105] | Randomized, double-blind, controlled, clinical trial (Denmark) | 48 patients diagnosed with breast cancer undergoing radiotherapy were randomized between the groups: placebo (64± 10y, 22♀) and melatonin group (62± 9y, 26♀) | Application of 1g of cream containing 25 mg/g of melatonin twice a day on the irradiated area of the skin during radiotherapy | from the first day of radiation to the last fraction of radiation |
There was no significant difference in quality of life between groups after treatment. ↓BS score in the melatonin group |
| [106] | Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial (Iran) | 70 children diagnosed with atopic dermatitis were randomized between the groups: placebo (8.4±2.2y, 17♀ and 18♂) and melatonin (8.9±2.1y, 19♀ and 16♂) | Supplementation with 2 tablets of 3mg of melatonin a day | 6 weeks | ↓ sleep latency, ↑total sleep time in the melatonin group. There was no significant difference in pruritus, CRP, weight and BMI scores |
| [107] | Randomized clinical trial used a double-blind, placebo-controlled | 48 pacientes com dermatite atópica foram randomizados em dois grupos: placebo (7.3±3.5y, 10♀ e 14♂) e melatonina (13± 54y, 13♀ e 11♂) | 3mg/dia de melatonina oralmente | 4 weeks | ↓ SCORAD index; ↓ sleep latency in the melatonin-treated group |
| [108] | Phase II, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study | 47 patients undergoing conservative surgery for breast cancer were randomized between the groups: placebo (55y, 21♀) and melatonin (54y, 26♀) | Cream containing 50g melatonin, applied on the irradiated breast twice a day | 5 weeks | ↓ presence of dermatitis in the group treated with melatonin |
7. Effects of Melatonin on Sepsis
8. Effects of Melatonin on COVID-19
9. Effects of Melatonin on Cancer
10. Effects of Melatonin on Dysbiosis
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.A.; Nasser, M.A.; Abdelhamid, A.N.; Ali, I.A.; Saudy, H.S.; Hassan, K.M.J.J.o.S.S.; Nutrition, P. Melatonin as a key factor for regulating and relieving abiotic stresses in harmony with phytohormones in horticultural plants—a review. 2024, 24, 54–73.
- Kolupaev, Y.E.; Yemets, A.; Yastreb, T.O.; Blume, Y. Functional interaction of melatonin with gasotransmitters and ROS in plant adaptation to abiotic stresses. Frontiers in plant science 2024, 15, 1505874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.A.; Shahid, R.; Ren, M.-X.; Altaf, M.M.; Jahan, M.S.; Khan, L.U.J.J.o.S.S.; Nutrition, P. Melatonin mitigates nickel toxicity by improving nutrient uptake fluxes, root architecture system, photosynthesis, and antioxidant potential in tomato seedling. 2021, 21, 1842–1855.
- Esmaeili, S.; Sharifi, M.; Ghanati, F.; Soltani, B.M.; Samari, E.; Sagharyan, M.J.S.R. Exogenous melatonin induces phenolic compounds production in Linum album cells by altering nitric oxide and salicylic acid. 2023, 13, 4158.
- Cano, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Arnao, M.B.J.C.R.i.P.S. Role of exogenous melatonin in plant biotechnology: Physiological and applied aspects. 2024, 43, 395–404.
- Li, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kohtz, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Kong, X.; Xue, H.; Jia, P.; Bai, N.J.F.C.R. Exogenous melatonin improves peanut field productivity and quality at reduced nitrogen application. 2024, 319, 109650.
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Melatonin in plants: what we know and what we don’t. Food Quality and Safety 2021, 5, fyab009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, A.; Muneer, S. Role of Circadian Rhythms in Major Plant Metabolic and Signaling Pathways. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 836244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Huang, Y.; Bie, Z.; Ahmed, W.; Reiter, R.J.; Niu, M.; Hameed, S. Melatonin: Current Status and Future Perspectives in Plant Science. Frontiers in Plant Science 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murch, S.J.; Erland, L.A.E. A Systematic Review of Melatonin in Plants: An Example of Evolution of Literature. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Looi, L.J.; Zhang, Z. The potential of melatonin and its crosstalk with other hormones in the fight against stress. Frontiers in plant science 2024, 15, 1492036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-López, A.I.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Lardone, P.J.; Bejarano, I.; Aspiazu-Hinostroza, K.; Ponce-España, E.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Melatonin, an Antitumor Necrosis Factor Therapy. Journal of pineal research 2025, 77, e70025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shneider, A.; Kudriavtsev, A.; Vakhrusheva, A. Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic? Int Rev Immunol 2020, 39, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasey, C.; McBride, J.; Penta, K. Circadian Rhythm Dysregulation and Restoration: The Role of Melatonin. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunata, M.; Parlakpinar, H.; Acet, H.A. Melatonin: A review of its potential functions and effects on neurological diseases. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2020, 176, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, W.H. Melatonin and Cancer Hallmarks. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Mostafa, S.; Lu, Z.; Jin, B.J.F.i.p.s. Melatonin-mediated abiotic stress tolerance in plants. 2022, 13, 847175.
- Yawoot, N.; Govitrapong, P.; Tocharus, C.; Tocharus, J. Ischemic stroke, obesity, and the anti-inflammatory role of melatonin. Biofactors 2021, 47, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R. Aging, Melatonin, and the Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Networks. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimus, D.M.; Popescu, M.R.; Voiculescu, S.E.; Panaitescu, A.M.; Pavel, B.; Zagrean, L.; Zagrean, A.M. Melatonin's Impact on Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Reprogramming in Homeostasis and Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, D.P.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Brown, G.M. Melatonin as a Chronobiotic and Cytoprotector in Non-communicable Diseases: More than an Antioxidant. Sub-cellular biochemistry 2024, 107, 217–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamieniak, M.; Kośmider, K.; Miziak, B.; Czuczwar, S.J. The Oxidative Stress in Epilepsy-Focus on Melatonin. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertollo, A.G.; Dalazen, J.B.; Cassol, J.V.; Hellmann, M.B.; Mota, T.L.; Ignácio, Z.M.; Bagatini, M.D. Melatonin's Impact on Cytokine Storm and Modulation of Purinergic Receptors for COVID-19 Prognosis: A Mental Health Perspective. Journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 2024, 74, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Sharma, R.; Romero, A.; Simko, F.; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A.; Cardinali, D.P. Melatonin stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques: an association that should be clinically exploited. Frontiers in medicine 2024, 11, 1487971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Sharma, R.N.; Manucha, W.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Almieda Chuffa, L.G.; Loh, D.; Luchetti, F.; Balduini, W.; Govitrapong, P. Dysfunctional mitochondria in age-related neurodegeneration: Utility of melatonin as an antioxidant treatment. Ageing research reviews 2024, 101, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G. Melatonin, BAG-1 and cortisol circadian interactions in tumor pathogenesis and patterned immune responses. Exploration of targeted anti-tumor therapy 2023, 4, 962–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, M.J.; Denburg, N.L. Melatonin in Alzheimer's Disease: Literature Review and Therapeutic Trials. Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2024, 101, S193–s204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvani, F.; Cammarota, M.; Vacondio, F.; Rivara, S.; Boscia, F. Protective Activity of Melatonin Combinations and Melatonin-Based Hybrid Molecules in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Journal of pineal research 2024, 76, e70008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Ni, L.; Di, X.; Ma, B.; Niu, S.; Liu, C.; Reiter, R.J.J.L.s. COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment. 2020, 250, 117583.
- Borges, L.; Gennari-Felipe, M.; Dias, B.B.; Hatanaka, E.J.F.i.N. Melatonin, zinc, and vitamin C: Potential adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 patients. 2022, 8, 1325.
- Calvo, J.R.; Maldonado, M.D. Immunoregulatory properties of melatonin in the humoral immune system: A narrative review. Immunology letters 2024, 269, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridzadeh, A.; Tabashiri, A.; Miri, H.H.; Mahmoudi, M. The role of melatonin as an adjuvant in the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; et al. Melatonin ameliorates cognitive deficits through improving mitophagy in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Pineal Res 2021, 71, e12774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, M.W.; DeParis, S.; Oppezzo, M.; Mah, C.; Roche, M.; Frehlich, L.; Fredericson, M. Nutritional Supplements for Healthy Aging: A Critical Analysis Review. American journal of lifestyle medicine 2024, 15598276241244725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Xiang, L.; Su, Z. Harnessing the benefits of physical exercise-induced melatonin: a potential promising approach to combat Alzheimer's disease by targeting beta-amyloid (Aβ). Hormones (Athens, Greece), 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lloret, S.; Cardinali, D.P. Melatonin as a Chronobiotic and Cytoprotective Agent in Parkinson's Disease. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 650597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Upadhyay, K.K.; Vohra, A.; Shirsath, K.; Devkar, R. Melatonin induces Nrf2-HO-1 reprogramming and corrections in hepatic core clock oscillations in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Faseb j 2021, 35, e21803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Elkin, K.; Yip, J.; Guan, L.; Han, W.; Ding, Y. From circadian clocks to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert review of gastroenterology & hepatology 2019, 13, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.J.; Huang, C.C.; Liu, S.C.; Tang, C.H. Reconsidering the Role of Melatonin in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikyo, N. Circadian Regulation of Macrophages and Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.F.; Skare, T.L. Melatonin supplementation improves rheumatological disease activity: A systematic review. Clinical nutrition ESPEN 2023, 55, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarlis, C.; Anagnostouli, M. The role of melatonin in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol Sci 2020, 41, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojaverrostami, S.; Asghari, N.; Khamisabadi, M.; Heidari Khoei, H. The role of melatonin in polycystic ovary syndrome: A review. Int J Reprod Biomed 2019, 17, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaei, S.; Hasani, M.; Malekahmadi, M.; Daneshzad, E.; Kadkhodazadeh, K.; Heshmati, J. Effect of melatonin supplementation on cardiometabolic risk factors, oxidative stress and hormonal profile in PCOS patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Journal of ovarian research 2024, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, A.K.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Hałubiec, P.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Jaworek, J. Melatonin as an Antioxidant and Immunomodulator in Atopic Dermatitis-A New Look on an Old Story: A Review. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, G.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Ricci, L.; Di Serio, T.; Vardaro, E.; Laneri, S. Clinical Studies Using Topical Melatonin. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, D.P.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Possible Application of Melatonin in Long COVID. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; An, S.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Lin, X.; Gao, Y. Melatonin suppresses ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in the mouse model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Int Immunopharmacol 2022, 112, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Ma, H.; Na, M.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, H.; Deng, X. Roles of melatonin in the field of reproductive medicine. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 144, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón, J.; Besseau, L.; Fuentès, M.; Sauzet, S.; Magnanou, E.; Boeuf, G. Structural and functional evolution of the pineal melatonin system in vertebrates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2009, 1163, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivko, O.M.; Trofimova, S.V.; Trofimov, A.V.; Sharkovich, Z.; Mogilev, V.A. [Peptidergic regulation of expression of cellular aging marker proteins in buccal epithelium.]. Advances in gerontology = Uspekhi gerontologii 2024, 37, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gubin, D.; Malishevskaya, T.; Weinert, D.; Zakharova, E.; Astakhov, S.; Cornelissen, G. Circadian Disruption in Glaucoma: Causes, Consequences, and Countermeasures. Frontiers in bioscience (Landmark edition) 2024, 29, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehela, Y.; Killiny, N. Diaphorina citri Genome Possesses a Complete Melatonin Biosynthesis Pathway Differentially Expressed under the Influence of the Phytopathogenic Bacterium, Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus. Insects 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kang, K.; Lee, K.; Back, K. Characterization of tryptamine 5-hydroxylase and serotonin synthesis in rice plants. Plant Cell Rep 2007, 26, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf, M.A.; Sharma, N.; Srivastava, D.; Mandal, S.; Adavi, S.; Jena, R.; Bairwa, R.K.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Kumar, A.; Dey, A.; et al. Deciphering the melatonin-mediated response and signalling in the regulation of heavy metal stress in plants. Planta 2023, 257, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehaman, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Ferdose, A.; Per, T.S.; Hanief, M.; Jan, A.T.; Asgher, M.J.F. Melatonin in plant defense against abiotic stress. 2021, 12, 1404.
- Jindal, P.; Kant, K.; Kaur, N.; Gupta, S.; Ali, A.; Naeem, M.J.E.; Botany, E. Melatonin: Discovery, biosynthesis, phytohormones crosstalk, and roles in agricultural crops under abiotic stress conditions. 2024, 105942.
- Yan, M.; Li, M.; Ding, Z.; Qiao, F.; Jiang, X.J.H. Plant Hormone Signals Mediate Melatonin Synthesis to Enhance Osmotic Stress Tolerance in Watermelon Cells. 2023, 9, 927. 9.
- Arnao, M.B.; Giraldo-Acosta, M.; Castejón-Castillejo, A.; Losada-Lorán, M.; Sánchez-Herrerías, P.; El Mihyaoui, A.; Cano, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.J.M. Melatonin from microorganisms, algae, and plants as possible alternatives to synthetic melatonin. 2023, 13, 72. 13.
- Kang, K.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Molecular cloning of rice serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate gene in plant melatonin biosynthesis. Journal of Pineal Research 2013, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Sharopov, F.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Kobylinska, A.; Jonge, L.d.; Tadio, K.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Posmyk, M.M.; Martorell, M.; Martins, N.J.C. Melatonin in medicinal and food plants: occurrence, bioavailability, and health potential for humans. 2019; 8, 681. [Google Scholar]
- Padumanonda, T.; Johns, J.; Sangkasat, A.; Tiyaworanant, S. Determination of melatonin content in traditional Thai herbal remedies used as sleeping aids. Daru : journal of Faculty of Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2014, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B.J.N. Dietary sources and bioactivities of melatonin. 2017, 9, 367.
- Aguilera, Y.; Herrera, T.; Benítez, V.; Arribas, S.M.; López de Pablo, A.L.; Esteban, R.M.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A. Estimation of scavenging capacity of melatonin and other antioxidants: contribution and evaluation in germinated seeds. Food chemistry 2015, 170, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A. Melatonin as a multifunctional modulator: emerging insights into its role in health, reproductive efficiency, and productive performance in livestock. Frontiers in physiology 2024, 15, 1501334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, A.; Migitaka, H.; Iigo, M.; Itoh, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohtani-Kaneko, R.; Hara, M.; Suzuki, T.; Reiter, R.J. Identification of melatonin in plants and its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochemistry and molecular biology international 1995, 35, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oladi, E.; Mohamadi, M.; Shamspur, T.; Mostafavi, A. "Expression of Concern to Spectrofluorimetric Determination of Melatonin in Kernels of Four Different Pistacia Varieties after Ultrasound-Assisted Solid-Liquid Extraction" [Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 132 (2014) 326-329]. Spectrochimica acta. Part A, Molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy 2019, 217, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J.; Park, W.; Monis, K.; Qi, W.J.L.S. High levels of melatonin in the seeds of edible plants: possible function in germ tissue protection. 2000, 67, 3023–3029.
- Tauil, R.B.; Golono, P.T.; de Lima, E.P.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Guiguer, E.L.; Bechara, M.D.; Nicolau, C.C.T.; Yanaguizawa Junior, J.L.; Fiorini, A.M.R.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; et al. Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: The Influence of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunctions, and the Role of Polyphenols. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, E.P.; Tanaka, M.; Lamas, C.B.; Quesada, K.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Araújo, A.C.; Guiguer, E.L.; Catharin, V.; de Castro, M.V.M.; Junior, E.B.; et al. Vascular Impairment, Muscle Atrophy, and Cognitive Decline: Critical Age-Related Conditions. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, E.P.; Moretti, R.C., Jr.; Torres Pomini, K.; Laurindo, L.F.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A.; Castro, M.V.M.; Baldi, E., Jr.; Ferraz, B.F.R.; de Souza Bastos Mazuqueli Pereira, E.; et al. Glycolipid Metabolic Disorders, Metainflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Unraveling Pathways. Biology 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cól, J.P.; de Lima, E.P.; Pompeu, F.M.; Cressoni Araújo, A.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Bechara, M.D.; Laurindo, L.F.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Barbalho, S.M. Underlying Mechanisms behind the Brain-Gut-Liver Axis and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Rossi, J.L.; Barbalho, S.M.; Reverete de Araujo, R.; Bechara, M.D.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: Going beyond traditional risk factors. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews 2022, 38, e3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tang, Y.Y.; Zhou, L. Melatonin as an adjunctive therapy in cardiovascular disease management. Science progress 2024, 107, 368504241299993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, M.; Cheraghpour, M.; Jafarirad, S.; Alavinejad, P.; Asadi, F.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Yari, Z. The effect of melatonin on treatment of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized double blind clinical trial. Complement Ther Med 2020, 52, 102452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, J.; Laing, A.; Middleton, B.; Schwedhelm, E.; Marx, N.; Federici, M.; Kastner, M.; Skene, D.J.; Böger, R. Effect of oral melatonin treatment on insulin resistance and diurnal blood pressure variability in night shift workers. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Pharmacological research 2024, 199, 107011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Gonzalez, M.; Axler, M.R.; Kaseman, K.E.; Lobene, A.J.; Farquhar, W.B.; Witman, M.A.; Kirkman, D.L.; Lennon, S.L. Melatonin supplementation reduces nighttime blood pressure but does not affect blood pressure reactivity in normotensive adults on a high-sodium diet. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2023, 325, R465–r473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpooya, M.; Mazdeh, M.; Rahmani, E.; Khazaie, M.; Ahmadimoghaddam, D. Melatonin supplementation may benefit patients with acute ischemic stroke not eligible for reperfusion therapies: Results of a pilot study. J Clin Neurosci 2022, 106, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseini, S.G.; Heshmat-Ghahdarijani, K.; Khosrawi, S.; Garakyaraghi, M.; Shafie, D.; Mansourian, M.; Roohafza, H.; Azizi, E.; Sadeghi, M. Melatonin supplementation improves N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels and quality of life in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Results from MeHR trial, a randomized clinical trial. Clin Cardiol 2022, 45, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.G.; Heshmat-Ghahdarijani, K.; Khosrawi, S.; Garakyaraghi, M.; Shafie, D.; Roohafza, H.; Mansourian, M.; Azizi, E.; Gheisari, Y.; Sadeghi, M. Effect of melatonin supplementation on endothelial function in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A randomized, double-blinded clinical trial. Clin Cardiol 2021, 44, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwaich, K.H.; Al-Amran, F.G.; Al-Sheibani, B.I.; Al-Aubaidy, H.A. Melatonin effects on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Impact on the outcome in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. Int J Cardiol 2016, 221, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Rodriguez, A.; Abreu-Gonzalez, P.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.J.; Kaski, J.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Jimenez-Sosa, A. A unicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study of Melatonin as an Adjunct in patients with acute myocaRdial Infarction undergoing primary Angioplasty The Melatonin Adjunct in the acute myocaRdial Infarction treated with Angioplasty (MARIA) trial: study design and rationale. Contemp Clin Trials 2007, 28, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Wang, D.; Momeni, M.R. Chronobiological disruptions: unravelling the interplay of shift work, circadian rhythms, and vascular health in the context of stroke risk. Clinical and experimental medicine 2024, 25, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, S.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Pourbarkhordar, V.; Hayes, A.W.; Karimi, G. Melatonin regulates mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy: Cardiovascular protection. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2024, 28, e70074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherifard, A.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Koosha, F.; Sheibani, M.; Karimi-Behnagh, A.; Reiter, R.J.; Mehrzadi, S. Melatonin and bone-related diseases: an updated mechanistic overview of current evidence and future prospects. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 2023, 34, 1677–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.M.; Joo, S.S. Melatonin Can Modulate Neurodegenerative Diseases by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munmun, F.; Witt-Enderby, P.A. Melatonin effects on bone: Implications for use as a therapy for managing bone loss. Journal of pineal research 2021, 71, e12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, A.; Szklarczyk, J.; Barańska, I.; Majda, A.; Jaworek, J. Association between levels of serotonin, melatonin, cortisol and the clinical condition of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology international 2023, 43, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Jeong, H.; Choi, S.E.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, S.S. Impact of obesity on clinical outcomes and treatment continuation in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving non-TNF-targeted therapies. Therapeutic advances in musculoskeletal disease 2024, 16, 1759720x241308027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurindo, L.F.; de Maio, M.C.; Barbalho, S.M.; Guiguer, E.L.; Araújo, A.C.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Flato, U.A.P.; Júnior, E.B.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Dos Santos Haber, J.F.; et al. Organokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Critical Review. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Pang, C.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L. Analysis of how melatonin-upregulated clock genes PER2 and CRY2 alleviate rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. European journal of pharmacology 2025, 986, 177136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.M.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, H.T.; Wu, Y.S.; Yang, S.F.; Tang, C.H. Melatonin Regulates Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts-Related Inflammation: Implications for Pathological Skeletal Muscle Treatment. Journal of pineal research 2024, 76, e13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghhi, F.; Ghaznavi, H.; Sheervalilou, R.; Razavi, M.; Sepidarkish, M. Effects of metformin and curcumin in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A factorial clinical trial. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2024, 135, 156160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellberg, A.; Salamon, D.; Ujvari, D.; Rydén, M.; Hirschberg, A.L. Weight Changes Are Linked to Adipose Tissue Genes in Overweight Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, F.M.V.; Pestana, R.M.C.; Ferreira, C.N.; Silva, I.F.O.; Candido, A.L.; Oliveira, F.R.; Reis, F.M.; Gomes, K.B. GDF-15 levels in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome treated with metformin: a combined clinical and in silico pathway analysis. Archives of endocrinology and metabolism 2024, 68, e230416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, T.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.; Shao, J.; Guan, W.; Zhang, S. Exploring melatonin's multifaceted role in female reproductive health: From follicular development to lactation and its therapeutic potential in obstetric syndromes. Journal of advanced research 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postolache, T.T.; Al Tinawi, Q.M.; Gragnoli, C. The melatonin receptor genes are linked and associated with the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome. Journal of ovarian research 2024, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, R.; Alizadeh, M.; Asghari Jafarabadi, M.; Heidari, L.; Nikbakht, R.; Babaahmadi Rezaei, H.; Karandish, M. Effects of Melatonin and/or Magnesium Supplementation on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biol Trace Elem Res 2022, 200, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, A.; Foroozanfard, F.; Kavossian, E.; Aghadavod, E.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Reiter, R.J.; Eftekhar, T.; Asemi, Z. Effects of melatonin administration on mental health parameters, metabolic and genetic profiles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Affect Disord 2019, 250, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacchiarotti, A.; Carlomagno, G.; Antonini, G.; Pacchiarotti, A. Effect of myo-inositol and melatonin versus myo-inositol, in a randomized controlled trial, for improving in vitro fertilization of patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol 2016, 32, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simoni, E.; Candelora, M.; Belleggia, S.; Rizzetto, G.; Molinelli, E.; Capodaglio, I.; Ferretti, G.; Bacchetti, T.; Offidani, A.; Simonetti, O. Role of antioxidants supplementation in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a critical narrative review. Frontiers in nutrition 2024, 11, 1393673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetner, D.; Kamby, C.; Gülen, S.; Christophersen, C.; Paulsen, C.B.; Piga, E.; Hoffmeyer, B.; Mahmood, F.; Rosenberg, J. Quality-of-life outcomes following topical melatonin application against acute radiation dermatitis in patients with early breast cancer: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Pineal Res 2023, 74, e12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi Ardakani, A.; Farrehi, M.; Sharif, M.R.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Mirhosseini, N.; Kheirkhah, D.; Moosavi, S.G.A.; Behnejad, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Asemi, Z. The effects of melatonin administration on disease severity and sleep quality in children with atopic dermatitis: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2018, 29, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Lin, M.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, P.L.; Dai, Y.S.; Chu, K.H.; Sun, C.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, L.C.; Yu, H.H.; et al. Melatonin Supplementation for Children With Atopic Dermatitis and Sleep Disturbance: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr 2016, 170, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, M.A.; Elkayam, R.; Gelernter, I.; Pfeffer, R.M. Melatonin for Prevention of Breast Radiation Dermatitis: A Phase II, Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Isr Med Assoc J 2016, 18, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mansilla-Roselló, A.; Hernández-Magdalena, J.; Domínguez-Bastante, M.; Olmedo-Martín, C.; Comino-Pardo, A.; Escames, G.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. A phase II, single-center, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial to explore the efficacy and safety of intravenous melatonin in surgical patients with severe sepsis admitted to the intensive care unit. Journal of pineal research 2023, 74, e12845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wagenberg, L.; Witteveen, E.; Wieske, L.; Horn, J. Causes of Mortality in ICU-Acquired Weakness. Journal of intensive care medicine 2020, 35, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulli, I.; Carcione, A.M.; D'Amico, F.; Quartarone, G.; Chimenz, R.; Gitto, E. Corticosteroids in Pediatric Septic Shock: A Narrative Review. Journal of personalized medicine 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottari, G.; Ranieri, V.M.; Ince, C.; Pesenti, A.; Aucella, F.; Scandroglio, A.M.; Ronco, C.; Vincent, J.L. Use of extracorporeal blood purification therapies in sepsis: the current paradigm, available evidence, and future perspectives. Critical care (London, England) 2024, 28, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, A.; Shokoohmand, F.; Abdoli, E.; Mohammadi, Y.; Mehrpooya, M. A pilot study on the melatonin treatment in patients with early septic shock: results of a single-center randomized controlled trial. Ir J Med Sci 2022, 191, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, H.F.; Allen, L.; Colin, P.J.; Galt, S.P.; Webster, N.R. Dose assessment of melatonin in sepsis (DAMSEL2) study: Pharmacokinetics of two doses of oral melatonin in patients with sepsis. J Pineal Res 2022, 73, e12830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisa-Alvarez, A.; Soto, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Camarena-Alejo, G.; Franco-Granillo, J.; Martínez-Rodríguez, E.A.; Gamboa Ávila, R.; Manzano Pech, L.; Pérez-Torres, I. Usefulness of Antioxidants as Adjuvant Therapy for Septic Shock: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Medicina (Kaunas) 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.; Wen, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Ni, S.; Le, W.; Wei, L.; Qi, D.; Wang, S.; et al. Classification of Coronavirus Spike Proteins by Deep-Learning-Based Raman Spectroscopy and its Interpretative Analysis. J Appl Spectrosc 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, W.; Yin, L.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, X. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2: The gradual boom of lateral flow immunoassay. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 1090281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkız, H. The Biological Functions and Clinical Significance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Corcern. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 849217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Minniti, G.; Miola, V.F.B.; Haber, J.; Bueno, P.; de Argollo Haber, L.S.; Girio, R.S.J.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Dall'Antonia, C.T.; Rodrigues, V.D.; et al. Organokines in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, J.; Bi, X.; Xiong, W.; Feng, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Innovative public strategies in response to COVID-19: A review of practices from China. Health care science 2024, 3, 383–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Mohd Nassir, C.M.N.; Che Ramli, M.D.; Jaffer, U.; Abdul Hamid, H.; Mehat, M.Z.; Mohamad Ghazali, M.; Kottakal Cheriya, E.N. Neurological Sequelae of Post-COVID-19 Fatigue: A Narrative Review of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV-Mediated Cerebrovascular Complications. Current issues in molecular biology 2024, 46, 13565–13582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, E.; Divani, A.A.; Viñan-Garces, A.E.; Olivella-Gomez, J.; Quintero-Altare, A.; Pérez, S.; Reyes, L.F.; Sasso, N.; Biller, J. Tackling persistent neurological symptoms in patients following acute COVID-19 infection: an update of the literature. Expert review of neurotherapeutics 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; Nonaka, F.; Tsuji, Y.; Tamai, M.; Kawakami, A. The COVID-19 Pandemic Heightens Interest in Cytokine Storm Disease and Advances in Machine Learning Diagnosis, Telemedicine, and Primordial Prevention of Rheumatic Diseases. European journal of rheumatology 2024, 11, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosi, M.L.M.; Lima, M.D.M.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Cardoso, A.M. Possible role of purinergic signaling in COVID-19. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2021, 476, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruvito, L.; Sananez, I.; Seery, V.; Russo, C.; Geffner, J. Purinergic signaling pathway in severe COVID-19. Current opinion in pharmacology 2023, 70, 102379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehia, A.; Abulseoud, O.A. Melatonin: a ferroptosis inhibitor with potential therapeutic efficacy for the post-COVID-19 trajectory of accelerated brain aging and neurodegeneration. Molecular neurodegeneration 2024, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempesis, I.G.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Reiter, R.J.; Spandidos, D.A. A mid-pandemic night's dream: Melatonin, from harbinger of anti-inflammation to mitochondrial savior in acute and long COVID-19 (Review). International journal of molecular medicine 2024, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, T.; Al-Abdallat, H.; Hamamreh, R.; Alomari, O.; Hos, B.H.; Reiter, R.J. Assessing the antiviral potential of melatonin: A comprehensive systematic review. Reviews in medical virology 2024, 34, e2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwosu, N. Cancer: A Disease of Modern Times? Cureus 2024, 16, e74666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurindo, L.F.; Pomini, K.T.; de Lima, E.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Rodrigues, V.D.; da Silva Camarinha Oliveira, J.; Araújo, A.C.; Guiguer, E.L.; Rici, R.E.G.; Maria, D.A.; et al. Isoorientin: Unveiling the hidden flavonoid's promise in combating cancer development and progression - A comprehensive review. Life sciences 2025, 360, 123280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Torres Pomini, K.; Lima, E.P.; da Silva Camarinha Oliveira, J.; Boaro, B.L.; Cressoni Araújo, A.; Landgraf Guiguer, E.; Rici, R.E.G.; Maria, D.A.; Haber, J.; et al. Fantastic Frogs and Where to Use Them: Unveiling the Hidden Cinobufagin's Promise in Combating Lung Cancer Development and Progression Through a Systematic Review of Preclinical Evidence. Cancers 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurindo, L.F.; de Lima, E.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Rodrigues, V.D.; Chagas, E.F.B.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Araújo, A.C.; Guiguer, E.L.; Pomini, K.T.; Rici, R.E.G.; et al. The therapeutic potential of bee venom-derived Apamin and Melittin conjugates in cancer treatment: A systematic review. Pharmacological research 2024, 209, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A.; Kavalakatt, J.; Sunkara, C.; Johnson, O.; Zinzuwadia, S.S.; Collignon, T.E.; Banerjee, S.; Barbalho, S.M. Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.): A comprehensive and critical review on cancer prevention and intervention. Food chemistry 2024, 457, 140142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Huang, X.; Long, J.; Guo, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lin, P.; Xie, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, A.Y.; et al. Advances in traditional Chinese herbal medicine and their pharmacodynamic mechanisms in cancer immunoregulation: a narrative review. Translational cancer research 2024, 13, 1166–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collignon, T.E.; Webber, K.; Piasecki, J.; Rahman, A.S.W.; Mondal, A.; Barbalho, S.M.; Bishayee, A. Avocado (Persea americana Mill) and its phytoconstituents: potential for cancer prevention and intervention. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2024, 64, 13072–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurjus, A.; El Masri, J.; Ghazi, M.; El Ayoubi, L.M.; Soueid, L.; Gerges Geagea, A.; Jurjus, R. Mechanism of Action of Melatonin as a Potential Adjuvant Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheibani, M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Fatemi, I.; Naeini, A.J.; Mehrzadi, S. Practical application of melatonin for pancreas disorders: protective roles against inflammation, malignancy, and dysfunctions. Pharmacological reports : PR, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharypoor, A.; Ajdari, A.; Seirafianpour, F.; Pakbaz, Y.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Mehrzadi, S. Signaling pathways in skin cancers and the protective functions of melatonin. Biochimie 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; De Almeida Chuffa, L.G.; Simão, V.A.; Martín Giménez, V.M.; De Las Heras, N.; Spandidos, D.A.; Manucha, W. Melatonin and vitamin D as potential synergistic adjuvants for cancer therapy (Review). International journal of oncology 2024, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiyian, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Rasooli Manesh, S.M.; Asemi, R.; Sharifi, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Mansournia, M.A.; Asemi, Z. Programmed cell death and melatonin: A comprehensive review. Functional & integrative genomics 2024, 24, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hao, B.; Zhang, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Lin, S.; Zheng, T.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Yue, L.; Abay, B.; et al. Melatonin enhances radiofrequency-induced NK antitumor immunity, causing cancer metabolism reprogramming and inhibition of multiple pulmonary tumor development. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2021, 6, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaely, F.; Mahmoudzadeh, A.; Cheki, M.; Shirazi, A. The radioprotective effect of melatonin against radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in radiology. Journal of cancer research and therapeutics 2020, 16, S59–s63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartini, D.; Taher, A.; Panigoro, S.S.; Setiabudy, R.; Jusman, S.W.; Haryana, S.M.; Abdullah, M.; Rustamadji, P.; Purwanto, D.J.; Sutandyo, N.; et al. Effect of melatonin supplementation in combination with neoadjuvant chemotherapy to miR-210 and CD44 expression and clinical response improvement in locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute 2020, 32, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookprasert, A.; Johns, N.P.; Phunmanee, A.; Pongthai, P.; Cheawchanwattana, A.; Johns, J.; Konsil, J.; Plaimee, P.; Porasuphatana, S.; Jitpimolmard, S. Melatonin in patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anticancer research 2014, 34, 7327–7337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schernhammer, E.S.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Gantman, K.; Savoie, J.; Scheib, R.; Parker, L.M.; Chen, W.Y. A randomized controlled trial of oral melatonin supplementation and breast cancer biomarkers. Cancer causes & control : CCC 2012, 23, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N. The role of fecal microbiota transplantation in type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment. Frontiers in endocrinology 2024, 15, 1469165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, R.; Albarqi, S.A.; Albalawi, W.; Alatwi, H.E.; Alatawy, M.; Bedaiwi, R.I.; Almotairi, R.; Husain, E.; Zubair, M.; Alanazi, G.; et al. Emerging Role of Gut Microbiota in Breast Cancer Development and Its Implications in Treatment. Metabolites 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, A.; Migliorini, F.; Jeyaraman, N.; Vaishya, R.; Balaji, S.; Ramasubramanian, S.; Maffulli, N.; Jeyaraman, M. Molecular Mimicry Between Gut Microbiome and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Concepts. Medical sciences (Basel, Switzerland) 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, N.; Garashchenko, N.; Kolesnikov, S.; Darenskaya, M.; Kolesnikova, L. Gut Microbiome Interactions with Oxidative Stress: Mechanisms and Consequences for Health. Pathophysiology : the official journal of the International Society for Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hung, I.; Liu, C.; Ren, W.; Ge, L.; Wang, H. Melatonergic Signaling Sustains Food Allergy Through FcεRI Recycling. Research (Washington, D.C.) 2024, 7, 0418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wen, Y.; Tong, Q.; Peng, Y.; Yu, D.; Rao, Y.; Zeng, Y. Gut microbiota-melatonin signaling axis in acute pancreatitis: Revealing the impact of gut health on pancreatic inflammation and disease severity in a case-control study. Medicine 2024, 103, e38689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Kurth, S.; Pugin, B.; Bokulich, N.A. Microbial melatonin metabolism in the human intestine as a therapeutic target for dysbiosis and rhythm disorders. NPJ biofilms and microbiomes 2024, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Taghizadieh, M.; Mehdizadehfar, E.; Hasani, A.; Khalili Fard, J.; Feizi, H.; Hamishehkar, H.; Ansarin, M.; Yekani, M.; Memar, M.Y. Gut microbiota in neurological diseases: Melatonin plays an important regulatory role. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2024, 174, 116487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFort, K.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Song, B.J. Melatonin Prevents Alcohol- and Metabolic Dysfunction- Associated Steatotic Liver Disease by Mitigating Gut Dysbiosis, Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, and Endotoxemia. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonmatí-Carrión, M.; Rol, M.A. Melatonin as a Mediator of the Gut Microbiota-Host Interaction: Implications for Health and Disease. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Lang, J.; Zhang, Q. Effect of melatonin on gut microbiome and metabolomics in diabetic cognitive impairment. Frontiers in pharmacology 2024, 15, 1489834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kang, W.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Yang, P.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Medina, A.; Liu, D.; et al. Melatonin Ameliorates Cadmium-Induced Liver Fibrosis Via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Journal of pineal research 2024, 76, e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, T.; Richard, M.L.; Sokol, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Melatonin alleviates heat stress-induced spermatogenesis dysfunction in male dairy goats by regulating arachidonic acid metabolism mediated by remodeling the gut microbiota. Microbiome 2024, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Bai, Y.; Yang, F. Melatonin in animal husbandry: functions and applications. Frontiers in veterinary science 2024, 11, 1444578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Gao, J.W.; Zhang, Q.P.; Xu, X.M.; Zhao, R.Y.; Li, H.H.; Wei, B. Melatonin supplementation protects against traumatic colon injury by regulating SERPINA3N protein expression. iMeta 2023, 2, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Dietary Melatonin on Antioxidant Capacity, Immune Defense, and Intestinal Microbiota in Red Swamp Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Marine biotechnology (New York, N.Y.) 2024, 26, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y. The Effect Mechanism of N6-adenosine Methylation (m6A) in Melatonin Regulated LPS-induced Colon Inflammation. International journal of biological sciences 2024, 20, 2491–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, A.; Karnik, R.; Desai, M.; Vyas, H.; Kulshrestha, S.; Upadhyay, K.K.; Koringa, P.; Devkar, R. Melatonin-mediated corrective changes in gut microbiota of experimentally chronodisrupted C57BL/6J mice. Chronobiology international 2024, 41, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Niu, P.; Chen, T. Melatonin mitigates manganese-induced neural damage via modulation of gut microbiota-metabolism in mice. The Science of the total environment 2024, 923, 171474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yong, J.Y.; He, Y.; Yu, L.; Luo, G.N.; Chen, J.; Ge, Y.M.; Yang, Y.J.; Ding, W.J.; Hu, Y.M. Melatonin restores DNFB-induced dysbiosis of skin microbiota in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis. Life sciences 2024, 342, 122513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, S.; Guan, W.; et al. Melatonin alleviates high temperature exposure induced fetal growth restriction via the gut-placenta-fetus axis in pregnant mice. Journal of advanced research 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, C.N.; Xia, X.; Heng, C.W.; Tan, Y.S.; Lee, D.P.S.; Fam, J.; Kim, J.E. The impact of 5-hydroxytryptophan supplementation on sleep quality and gut microbiota composition in older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2024, 43, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Plant Source | Part of the Plant | Melatonin (ng/g Or pg/g Of Dry Weight) | Reference | Edible Part |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Almond | Seeds | 39 ng/g | [61] |  |
| Black pepper | Leaves | 1093 ng/g | [61,62] |  |
| Coffee arabica | Beans | 6800 ng/g | [61,63] |  |
| Curcuma longa | Roots | 120 ng/g | [63] |  |
| Grape | Skin | 0.9 ng.g−1 | [1] |  |
| Lentils | Seeds | 15–25 pg/g | [64] |  |
| Oats | Grain | 25–45 pg/g | [65] |  |
| Rice | Bran | 80–150 pg/g | [66] |  |
| Pistachio | Seeds | 233,000 ng/g | [63,67] |  |
| Soybeans | Seeds | 10–50 pg/g | [65] |  |
| Sunflower | Seeds | 29 | [68] |  |
| Walnuts | Nuts | 3,000–4,000 ng/g | [65] |  |
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Risk Factors | |||||
| [76] | Double-blind, randomized, multicenterplacebo-controlled study | 24 rotating night shift workers | 2 mg of sustained-release melatonin versus placebo | 12 weeks of treatment | The treatment improved sleep quality but did not significantly affect insulin resistance and blood pressure in rotating night-shift subjects |
| [77] | Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover design | 22 participants (11 men/11 women, 26.5 ± 3.1 y | Subjects in a high-sodium diet (6,900 mg Na/d) received 10 mg/day of melatonin or placebo | 10 days | Melatonin did not change 24-h Mean arterial pressure but reduced nighttime peripheral and central blood pressure on the high-sodium diet compared to placebo |
| [78] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled single-center clinical trial | 65 patients with acute ischemic stroke and not eligible for reperfusion therapy were divided into groups: placebo (67.33 ± 12.81y, 22♂ and 11♀) and melatonin (64.22 ± 10.26y, 20♂ and 12♀) | Supplementation with 20mg of melatonin orally daily | 5 days | ↓Mean of NIHSS and mRS in the melatonin group There was no significant difference in the functional independence criteria |
| [79] | Placebo-controlled double-blinded randomized clinical trial (Finland) | 92 heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction were randomized between the d groups: placebo (58.5y, 40♂ and 6♀) and melatonin (63.5y, 40♂ and 6♀) | 10 mg of melatonin (tablets) daily | 24 weeks | ↓NT-Pro BNP Improved quality of life by MLHFQ There was no difference in echocardiographic parameters |
| [80] | Randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial | 92 heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction were randomized between the groups: placebo (59.1±11.5y, 40♂ and 6♀) and melatonin (62.7±10.3y, 40♂ and 6♀) | 10mg/day of melatonin orally | 24 weeks | ↑FMD There was no difference in blood pressure, total antioxidant capacity, and MDA levels |
| [81] | Double-blind placebo-controlled study | 45 patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting were distributed into three groups: placebo (47-60y, 12♂ and 3♀), low-dose melatonin (45-65y, 12♂ and 3♀) and high-dose melatonin (45-64y, 11♂ and 4♀) | 10 or 20 mg melatonin capsules daily | From the fifth day before surgery | ↑Ejection fraction, ↓heart rate, ↓CTnI, ↓IL-1β, ↓iNOS and ↓caspase-3 in both melatonin-treated groups |
| [82] | Single-center, randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (phase 2) (Spain) | 272 patients presenting within 6 h of onset of AMI symptoms were randomized between placebo and melatonin groups | 11.61 mg intravenous melatonin (approximately 166 μg/kg) | 30 min before percutaneous revascularization and remaining doses in the subsequent 120 min | ↓area of Infarction |
| MAFLD | |||||
| [75] | Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial (Iran) | 45 patients with MAFLD were randomized into 2 groups: placebo (44 ± 9.62y, 17♂ and 7♀) and melatonin (37.71± 11.31y, 14♂e 7♀) | 6 mg melatonin daily | 12 weeks | ↓ Weight, ↓waist circumference, ↓blood pressure, ↓leptin levels, ↓alanine aminotransferase, and ↓liver fat in the melatonin group |
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [94] | Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | 64 participants diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis were randomized between the melatonin (49,31 ± 10.82y, 24 ♀ and 8♂) and placebo (49.44 ± 12.71y, 27♀ and 5♂) groups | Oral supplementation with 6 mg/ day of melatonin (2 tablets containing 3mg of melatonin) 1 hour before bedtime | 12 weeks | ↓MDA and ↓LDL-c |
| [95] | Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | 75 participants diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis were randomized between the melatonin (65.11±2.1y, 25♀ and 12♂) and placebo (60.0±1.8y, 28♀ and 10♂) groups | Oral supplementation with 10 mg/ day of melatonin (melatonina de liberação imediata, 8,5 mg/day, and | 6 months | No significant outcomes |
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [109] | Phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial | 29 subjects with severe sepsis (with an infectious systemic inflammatory syndrome, organ dysfunction, hypoperfusion, and/ or hypotension (needing surgery). | Patients received 60 mg of melatonin | 5 days | Melatonin decreased redox status compared to the placebo. Procalcitonin showed better effects in the melatonin subjects (neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio reduced significantly, improving the evolution of the condition. |
| [113] | Prospective, double-blind, randomized clinical trial | 40 patients with septic shock were randomized between groups: placebo (53.95 ± 13.17y, 14♂ and 6♀) and melatonin (55.75 ± 11.45y, 13♂ and 7♀) | 50 mg/day melatonin orally | 5 days | ↓ significant in required vasopressor dose ↓Number of deaths, ↓severity of organ dysfunctions, ↓mean SOFA score, ↓use of ventilatory support and ↓need for renal replacement therapy all without statistically significant difference |
| [114] | Cohort study | 10 patients with sepsis due to community-acquired pneumonia were divided into two cohorts: cohort 1- melatonin 50mg (54-70y, 5♂ and 0♀) melatonin and cohort 2- 20mg (45-83y, 4♂ and 1♀) | 20 or 50mg of solution containing 1mg/mL of melatonin orally in a single dose | 24 hours | ↑Maximum concentration of melatonin in the group treated with 50mg Maximum concentration of 6-OHMS similar between the two groups |
| [115] | Controlled, randomized, triple-blind clinical trial | 97 patients diagnosed with septic shock were randomized between groups: vitamin C (22–95y, 6♂ and 6♀), vitamin E (22-91y, 12♂ and 6♀), NAC (18-95y, 11♂ and 9♀), melatonin (46-95y, 10♂ and 10♀) and control (51-89y, 10♂e 11♀) | 50 mg of melatonin in capsules daily | 5 days | ↓SOFA score, ↓LPO, ↓PCT in melatonin-treated group |
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [130] | Single-center, double-blind, randomized clinical trial | 44 hospitalized patients with confirmed mild-to-moderate COVID-19 divided into intervention (50,75±14,43y, 10♀ and 14♂) and control (52,95±14,07y, 12♀ and 8♂) groups | 3 mg of melatonina 3 times daily | 14 days | ↓ Time of hospital discharge, ↓respiratory symptoms, ↓fatigue |
| [131] | 3 arm, parallel, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | 96 non-hospitalized patients that tested positive for COVID-19 divided into placebo (54y, 24♀ and 10♂), Vitamin C (50y, 19♀ and 13♂) and melatonin (52y, 21♀ and 11♂) groups | 10 mg of melatonin once a day at bedtime orally | 14 days | ↑ Symptoms improvement, ↑quality-of-life scores |
| [132] | Single-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial | 158 patients with severe COVID-19 divided into melatonin (56,8±7,5y, 24♀ and 58♂) and control (55,7±8,0y, 20♀ and 56♂) groups | 10 mg/day of melatonin, 20-30 minutes before bedtime orally | 14 days | ↓Thrombosis, ↓sepsis, ↓mortality rate |
| [133] | Open-label, randomized controlled clinical trial | 96 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 divided into melatonin (51,06±15,86y, 23♀ and 25♂) and control (54.77±15.34y, 30♀ and 18♂) groups | 3 mg/day of melatonin orally 1 hour before bedtime | 10 days | ↑Sleep quality, ↑oxygen blood saturation |
| References | Study | Population | Intervention | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [146] | Non-randomized and open-label study | Patients >18 y with biopsy-proven of lung cancer | 5 mg/day orally melatonin 1 week after radiofrequency (RFA) ablation treatment. | 12 months | ↓ lung injury nodules and the probability of malignant transformation or enlargement of nodules in other areas. Enhancement of local RFA ablation-stimulated natural killer (NK) cells and re-programmed tumor metabolism |
| [147] | Non-randomized and open-label study | Volunteers of 25-35 y without a history of radiation exposure | 100g of melatonin at 9 am; blood samples collected 5–10 min before and at 1 and 2 h after melatonin administration. Sample was irradiated with a dose of 10 mGy |
- | Melatonin significantly reduced the induction of γH2AX foci after irradiation with X-ray when ingested 2 or 1 h before it. Melatonin before exposure to irradiation can benefit a patient set to undergo computed tomography |
| [148] | Double blinded, parallel, randomized controlled trial | Fifty patients with Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) | 25 patients received a melatonin (20mg) and NC (cisplatin, taxane, and 5-fluorouracil), and 25 received neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone | 3 cycles (each cycle with an interval of 3 weeks) | Melatonin decreased miR-210, CD44, and miR-210 compared to the placebo. These effects were followed by a decrease in residual tumor percentage (not significant) compared to placebo |
| [149] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study | 151 patients with advanced NSCLC; 18-70y | 10 or 20 mg of melatonin or placebo (associated with traditional therapy) | 7 months | Subjects in the melatonin group: had better health-related quality of life and a smaller amount of DNA damage |
| [150] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled study | 97 postmenopausal women with a history of stages 0-III breast cancer | 3 mg of melatonin (n = 48) or placebo/day | 4 months | Postmenopausal women with a history of breast cancer did not show modifications in the levels of hormones (IGF-1, estradiol, or IGFBP-3) after having melatonin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





