Submitted:
02 January 2025
Posted:
03 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
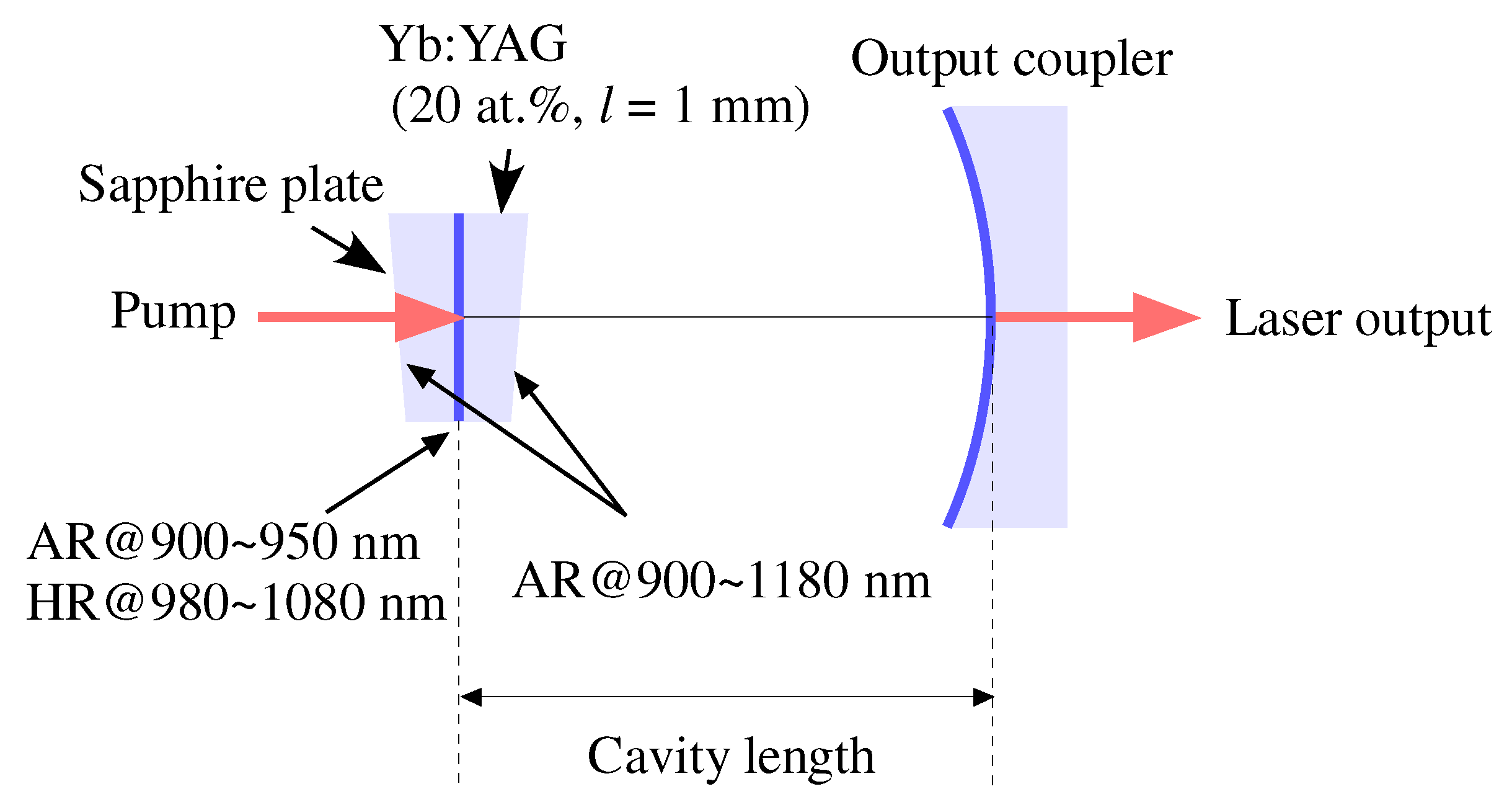
2.1. Experiment with the Hemispherical Short-Cavity Yb:YAG Laser
2.2. Quasi-Four-Level Laser Theory Including the Spatial Distribution of Pump and Laser Modes
3. Results
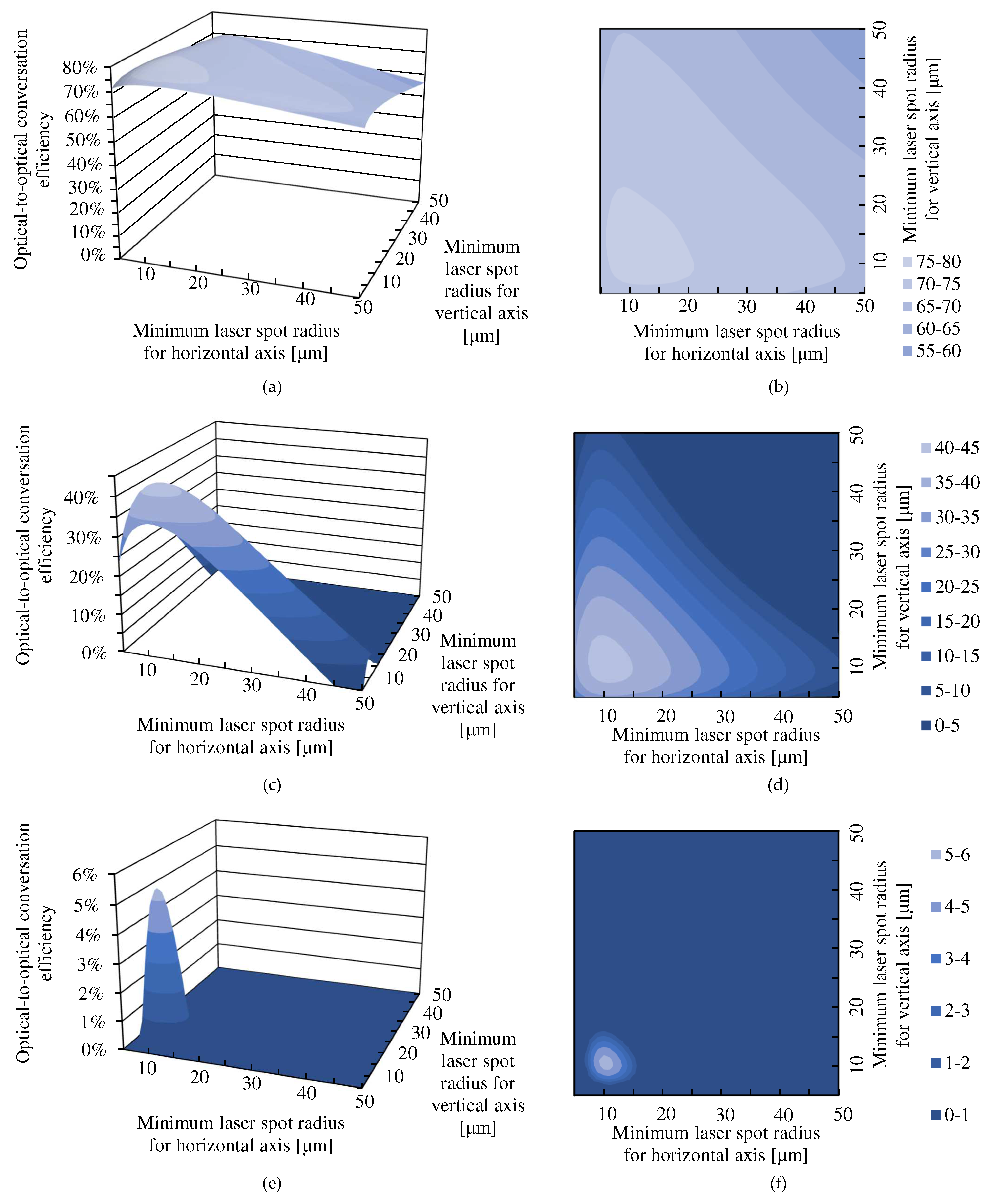
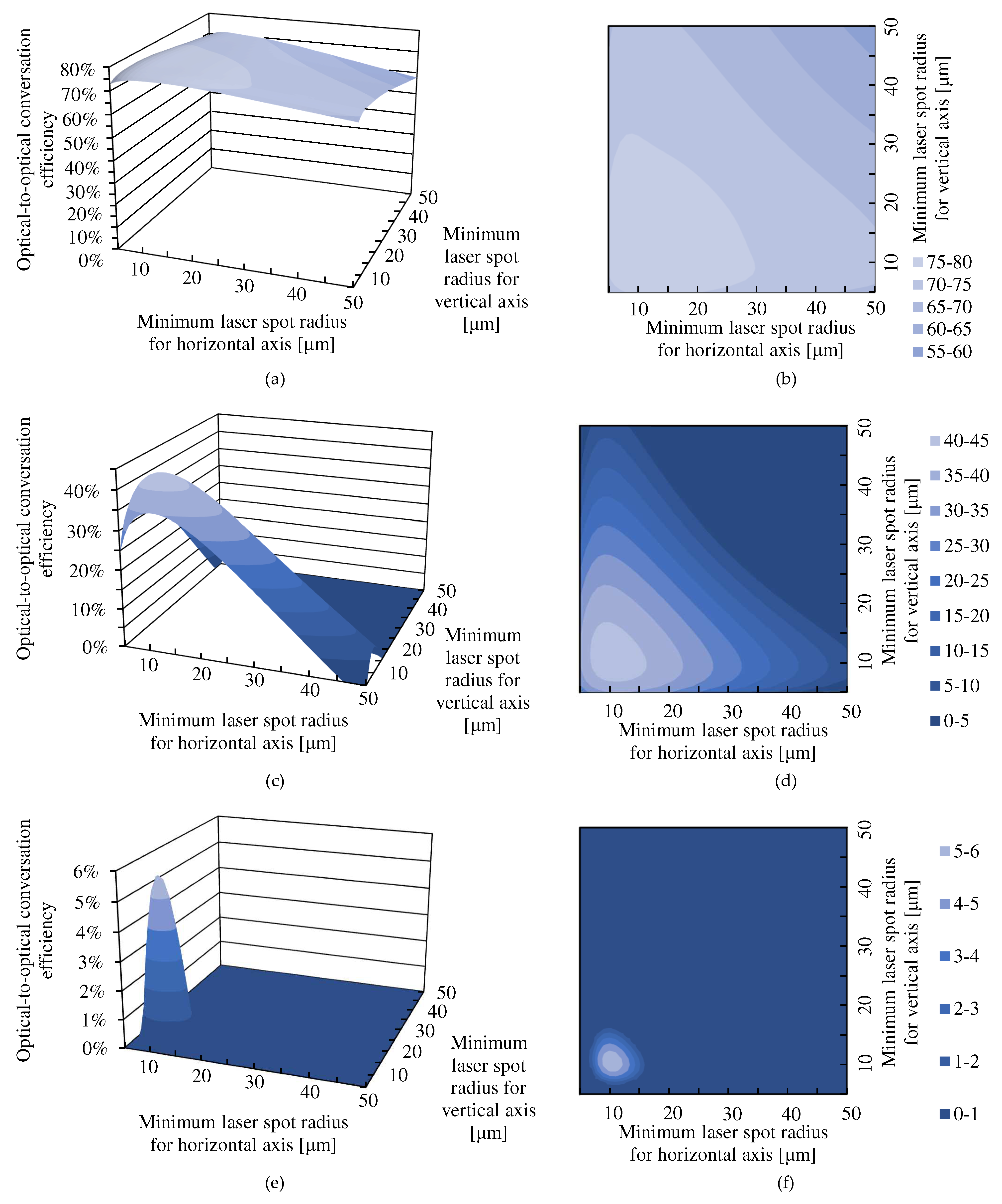
3.1. Theoretical Results for the Dependence of the Optical-to-Optical Conversion Efficiency on the Minimum Laser Spot Radii
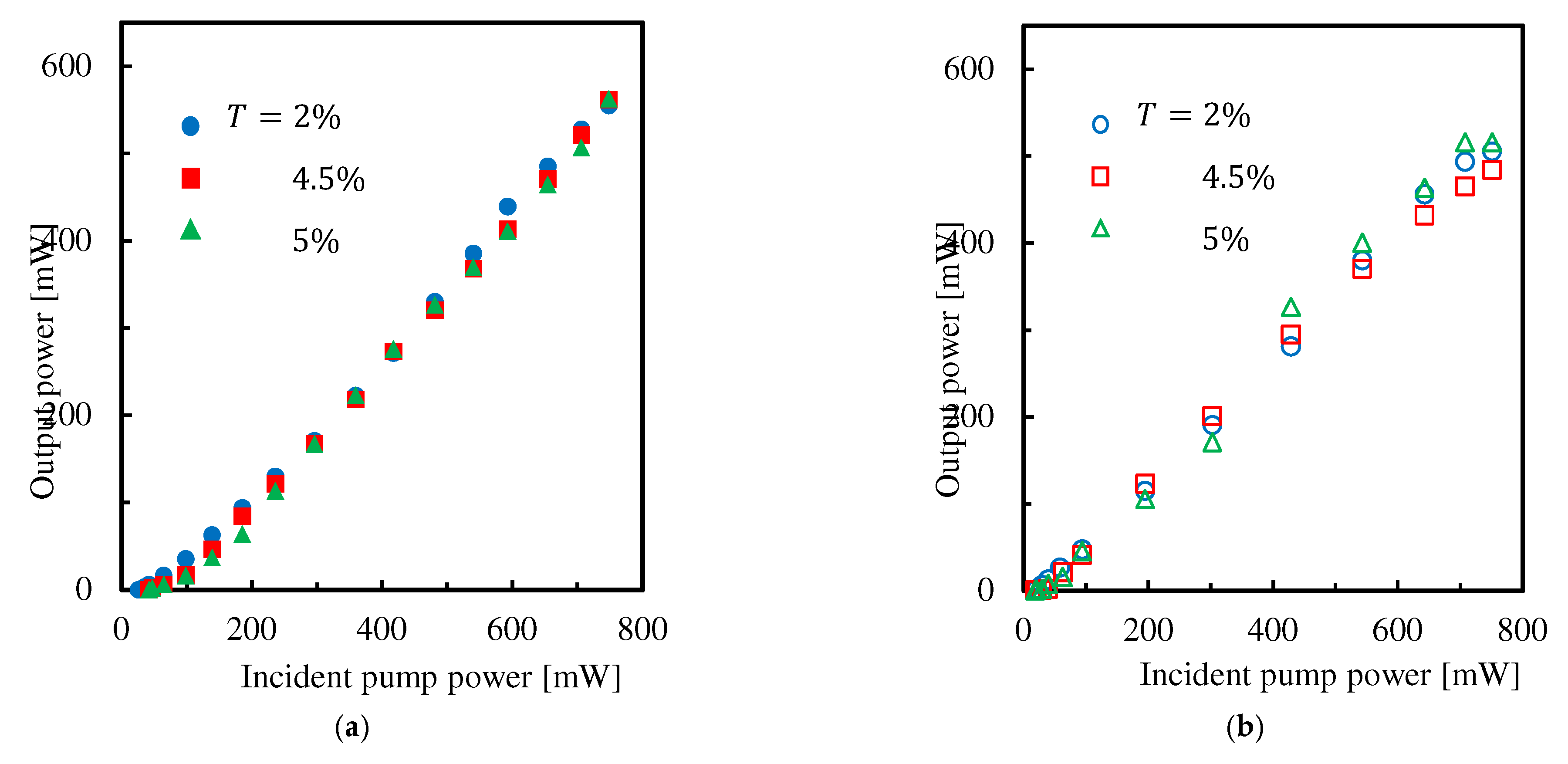
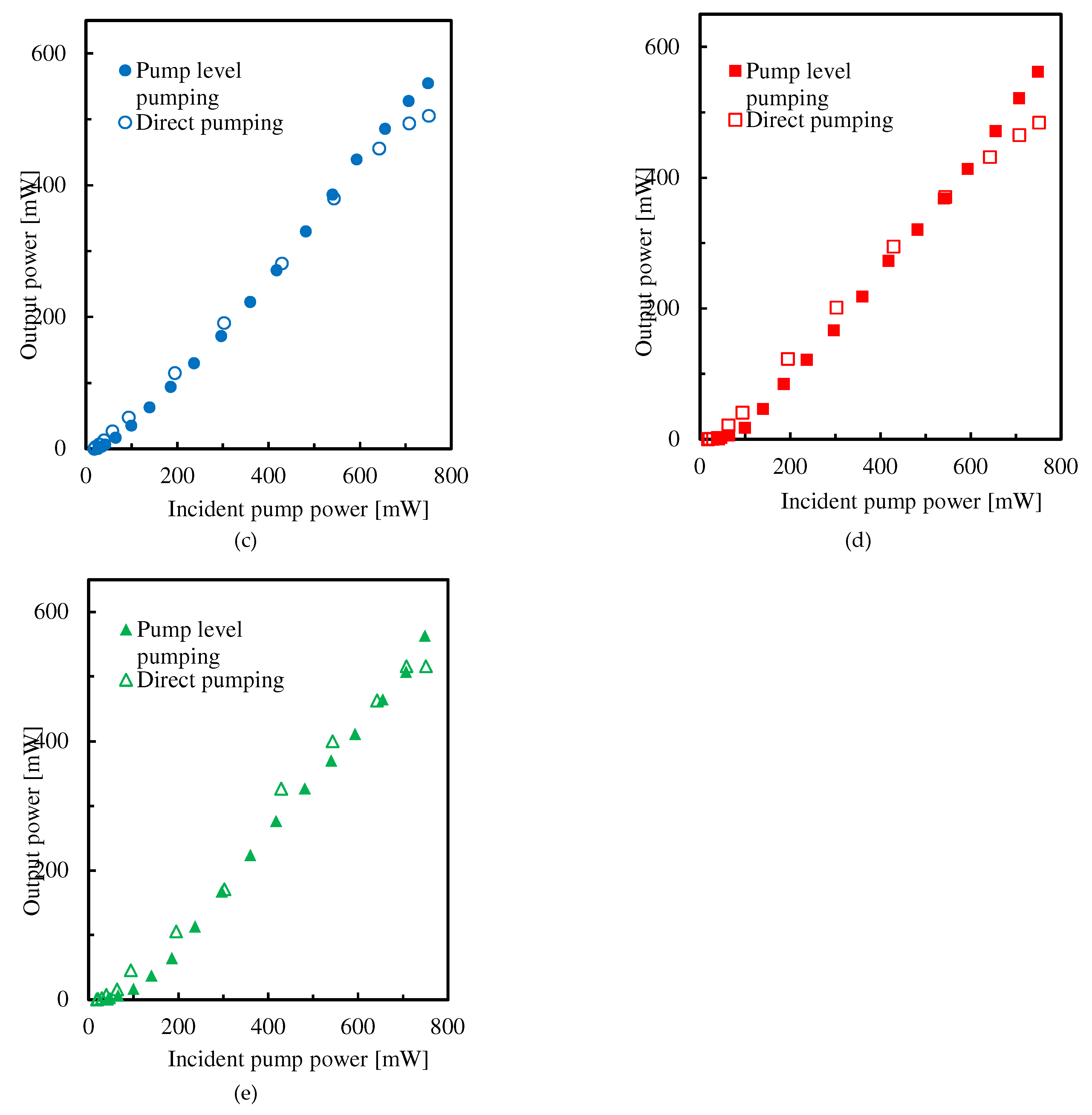
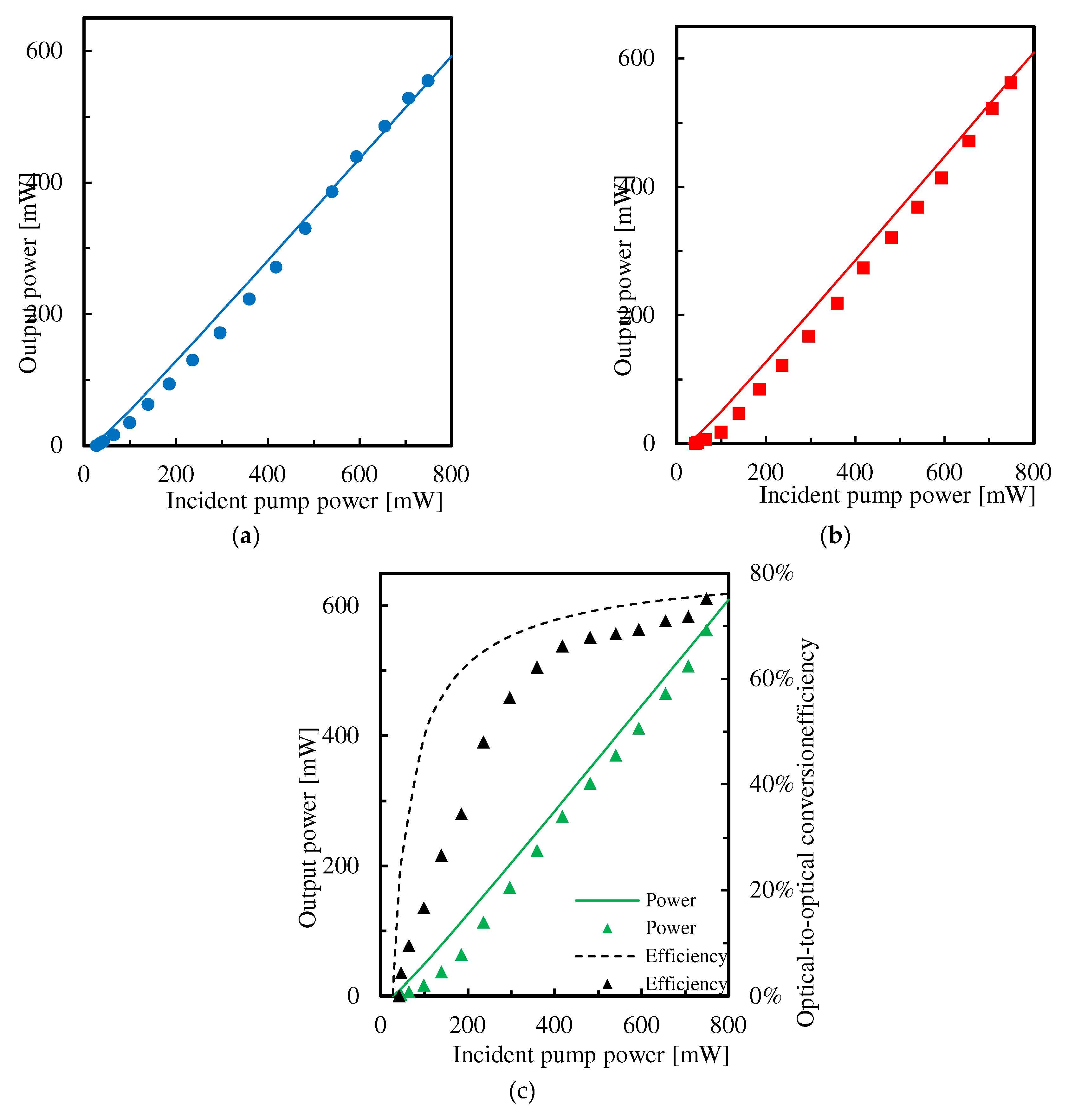
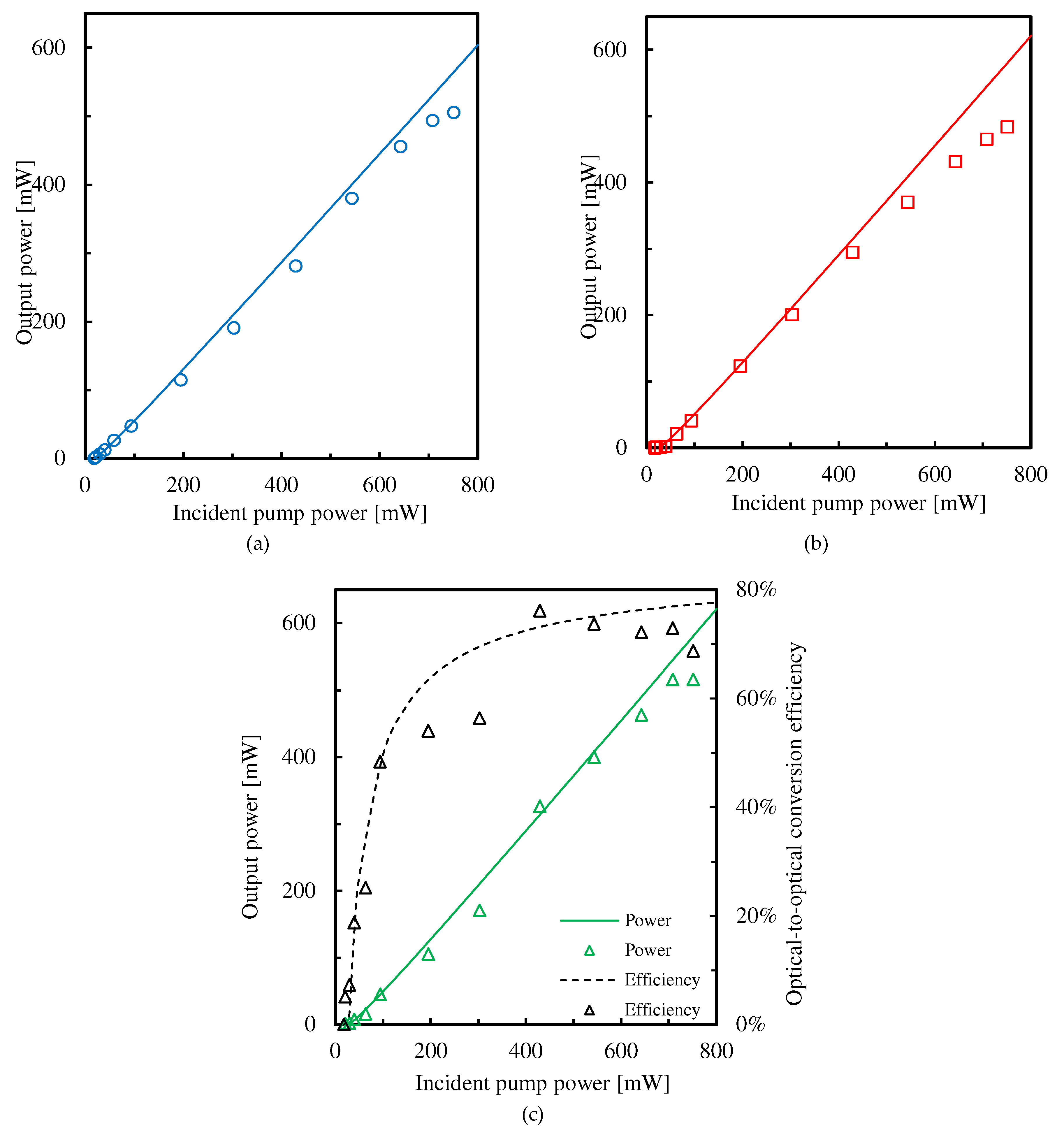
3.2. Experimental Results for Input-Output Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, L.F.; Geusic; J.E.; Van Uitert, L.G. COHERENT OSCILLATIONS FROM Tm3+, Ho3+, Yb3+ and Er3+ IONS IN YTTRIUM ALUMINUM GARNET. Appli. Phys. Lett. 1965, 7, 127–129. [CrossRef]
- Reinberg, A.R.; Riseberg, L.A.; Brown, R.M.; Wacker, R.W.; Holton, W.C. GaAs: Si LED Pumped Yb-Doped YAG Laser. Appli. Phys. Lett. 1971, 19, 11–13. [CrossRef]
- Lacovara, P.; Choi, H.K.; Wang, C.A.; Aggarwal, R.L.; Fan, T.Y. Room-temperature diode-pumped Yb:YAG laser. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 1089–1091. [CrossRef]
- Taira, T. Yb solid state lasers. Jpn. J. Opt. 1999, 28, 435–442.
- Pavel, N.; Saikawa, J.; Taira, T. Radial-Pumped Microchip High-Power Composite Yb:YAG laser: Design and Power Charac-teristics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, 146–152. [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Tokita, S.; Kawanaka, J.; Fujita, M.; Izawa, Y. Quantum-defect-limited operation of diode-pumped Yb:YAG laser at low temperature. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, L496–L498. [CrossRef]
- Ripin, D.J.; Ochoa, J.R.; Aggarwal, R.L.; Fan, T.Y. 165-W cryogenically cooled Yb:YAG laser. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 2154–2156. [CrossRef]
- Giesen, A.; Hügel, H.; Voss, A.; Wittig, K.; Brauch, U.; Opower, H. Scalable concept for Diode-Pumped High-Power Solid-state Lasers. Appl. Phys. B 1994, 58, 365–372. [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Kränkel, C.; Petermann, K.; Huber, G. Broadly tunable high-power Yb:Lu_2O_3 thin disk laser with 80% slope efficiency. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7075–7082. [CrossRef]
- Stolzenburg, C.; Voss, A.; Graf, T.; Larionov, M.; Giesen, A. Advanced pulsed thin disk laser sources. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6871, 68710H. [CrossRef]
- Hanna, D.C.; Percival, R.M.; Peryy, I.R.; Smart, R.G.; Suni, P.J.M.; Townsend, J.E.; Tropper, A.C. Contiuous-wave oscillation of a monomode ytterbium-doped fiber laser. Electron. Lett. 1988, 24, 1111–1113.
- Armitage, J.R.; Wyatt, R.; Ainslie, B.J.; Craig-Ryan, S.P. Efficient 980-nm Operation of a Yb3+-Doped Silica Fiber Laser. Advanced Solid State Lasers 1989 (OSA Proceedings Series 1989), paper JJ2. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Sahu, J.K.; Payne, D.N.; Nilsson, J. Ytterbium-doped large-core fiber laser with 1.36 kW continuous-wave output power. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 6088–6092. [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, S.; Ueda, T.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. Highly Efficient Continuous-Wave Laser Oscillation in Microchip Yb:YAG Laser at Room Temperature. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, L132–L134. [CrossRef]
- Takama, M.; Matsubara, S.; Ueda, T.; Inoue, M.; Tanaka, M.; Otani, K.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. Highly efficient nanosecond-pulse Yb:YAG laser. Smart Process. Technol. 2007, 2, 281–283.
- Kawato, S.; Kadoya, H.; Sugiki, F.; Kobayashi, R.; Kanetake, T.; Nakajima, N.; Kataoka, S. Laser efficiency improvement on hemispherical short cavity lasers by high intensity pumping. In Proceedings of the EMN Angkor Meeting & CC Physical Chemistry, Ankor, Cambodia, 12–13 March 2018; p. A14.
- Kawato, S. Influence of High-Intensity Pumping on Gain Medium Temperature Increase and Laser Mode Tunability in a Hemispherical Short Cavity. Photonics 2023, 10, 1239. [CrossRef]
- Newman, R. Excitation of the Nd3+ Fluorescence in CaWO4 by Recombination Radiation in GaAs. J. Appl. Phys. 1963 34, 437. [CrossRef]
- Fan, T. Y.; Byer, R. L. Diode Laser-Pumped Solid-State Lasers. IEEE J Quantum. Electron. 1988, 24, 895–912. [CrossRef]
- Loiko, P.; Serres, J.M.; Mateos, X.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.; Jambunathan, V.; Navratil, P.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Microchip Yb:CaLnAlO_4 lasers with up to 91% slope efficiency. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2431–2434. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Griebner, U.; Petrov, V.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Efficient continuous-wave and Q-switched operation of a diode-pumped Yb:Klu(WO4)2Yb:Klu(WO4)2 laser with self-Raman conversion. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 2427–2429. [CrossRef]
- Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. Design of End-Pumped Thin Rod Yb:YAG Laser Amplifiers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 2705–2710. [CrossRef]
- Kubodera, K.; Otsuka, K. Single-transverse-mode LiNdP4O12 slab waveguide laser. J. Appl. Phys. 1979, 50, 653–659. [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.Y.; Byer, R.L. Medeling and CW Operation of a Quasi-Three-Level 946 nm Nd:YAG Laser. IEEE J. Quantum. Electron. 1987, 23, 605–612. [CrossRef]
- Risk, W.P. Modeling of longitudinally pumped solid-state lasers exhibiting reabsorption losses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1988, B5, 1412–1423. [CrossRef]
- Taira, T.; Tuloch, M.W.; Byer, L.R. Modeling of quasi-three-level lases and operation of cw Yb:YAG lasers. Appl. Opt. 1997, 20, 1867–1874. [CrossRef]
- Sumida, S.D.; Fan, Y.T. Effect of radiation trapping on fluorescence lifetime and emission cross section measurements in solid-state laser media. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1343–1345. [CrossRef]
- Krupke, F.W. Ytteribium Solid-State Lasers—The First Decate. IEEE J. Quantum. Electron. 2000, 6, 1287–1296. [CrossRef]
- Koechner, W. Section 2.6. Yb:YAG. Solid State Laser Engineering, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 97–101.
- Findlay, D.; Clay, R.A. The Measument of internal losses in 4-level lasers. Phys. Lett. 1966, 20, 277–278. [CrossRef]
- Koechner, W. Sections 5.1.3. Resonator Configurations—5.1.4. Stability of Laser Resonators Solid State Laser Engineering, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 217–222.
- Yariv, A.; Yeh, P. Section 4.4. Mode Stability Criteria. Photonics, Optical Electronics in Mordern Communications, 6th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 176–177.
- Oezisik, M.N. Heat Conduction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 10.
- Whitaker, S. Elementary Heat Transfer Analysis, Pergamon Unified Engineering Series, Pergamon Press Inc.; New York, NY, USA, 1976; p. 4.
- Russbueldt, P.; Mans, T.; Rotarius, G.; Weitenberg, J.; Hoffmann, H.D.; Poprawe, R. 400W Yb:YAG Innoslab fs-Amplifier. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 12230–12245. [CrossRef]
- Sueda, K.; Takahashi, H.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. High-efficiency laser-diodes-pumped microthickness Yb:Y3Al5O12 slab laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 151110. [CrossRef]
- Chenais, S.; Balembois, F.; Druon, F.; Lucas-Leclin, G.; Georges, P. Thermal lensing in diode-pumped ytterbium Lasers-Part I: Theoretical analysis and wavefront measurements. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2004, 40, 1217–1234. [CrossRef]
- Chénais, S.; Druon, F.; Forget, S.; Balembois, F.; Georges, P. On thermal effects in solid-state lasers: The case of ytterbium-doped materials. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2006, 30, 89–126. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Shirakawa, A.; Ueda, K.; Kaminskii, A. Effect of ytterbium concentration on cw Yb:YAG microchip laser performance at ambient temperature—Part I: Experiments. Appl. Phys. B 2007, 89, 359–365. [CrossRef]
- Pirri, A.; Toci, G.; Alderighi, A.; Vannini, M. Effects of the excitation density on the laser output of two different doped Yb:YAG ceramics. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 17262–17272. [CrossRef]
- Brauch, U.; Röcker, C.; Graf, T.; Ahmed, M.A. High-power, high-brightness solid-state laser architectures and their characteristics. Appl. Phys. B 2022, 128, 58. [CrossRef]
- Shang, P.; Bai, L.; Wang, S.; Cai, D.; Li, B. Research progress on thermal effect of LD pumped solid state laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108640. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




