1. Introduction
Congenital syphilis is a multisystemic infection caused by Treponema pallidum, acquired through vertical transmission either transplacentally or during passage through the birth canal. In 2022, reported national incidences of congenital syphilis within European Union member states ranged from 0 to 42.4 cases per 100,000 live births, with the highest rate observed in Bulgaria. Although the incidence has fluctuated, a general upward trend has emerged in recent years [
1]. In Italy, during the five-year period from 2018 to 2022, the incidence varied between 0.2 and 1.6 cases per 100,000 live births [
1].
In pregnant women with untreated early syphilis, vertical transmission to the fetus occurs in the majority of cases (70–100%), commonly after the 28th week of gestation. Prompt maternal treatment prior to this gestational milestone typically prevents fetal involvement. Although many infected newborns are asymptomatic at birth, complications such as prematurity, low birth weight, and even stillbirth—occurring in up to one-third of cases—are frequently observed [
1,
2,
3].
Congenital syphilis often presents differently than in adults. Infected neonates experience direct spirochetemia with rapid dissemination of T. pallidum to multiple organ systems [
2]. Clinical findings at birth vary widely but commonly include hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal abnormalities (osteochondritis and periostitis), jaundice, lymphadenopathy, nasal discharge (luetic coryza), skin rashes, anemia, and thrombocytopenia [
2].
Typical skin manifestations consist of diffuse, red-to-brown maculopapular lesions frequently involving the back, buttocks, posterior thighs, and characteristically the palms and soles. Over time, these lesions may progress to desquamation and crusting. A bullous variant, known as syphilitic pemphigus, is a rare and under-recognized form of congenital syphilis [
2,
4].
This review describes a newly diagnosed case of syphilitic pemphigus at an Italian hospital and presents a comprehensive review of the available literature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
A comprehensive systematic search was conducted in Medline (PubMed), Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials from their respective inceptions up to November 2024. The search strategy incorporated relevant Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and keywords, including “pemphigus syphiliticus” and “bullous lesions and congenital syphilis.” These terms guided the identification of articles that addressed the primary objectives of this review, specifically the demographic and clinical features of congenital pemphigus syphiliticus, diagnostic approaches, therapeutic interventions, and patient outcomes.
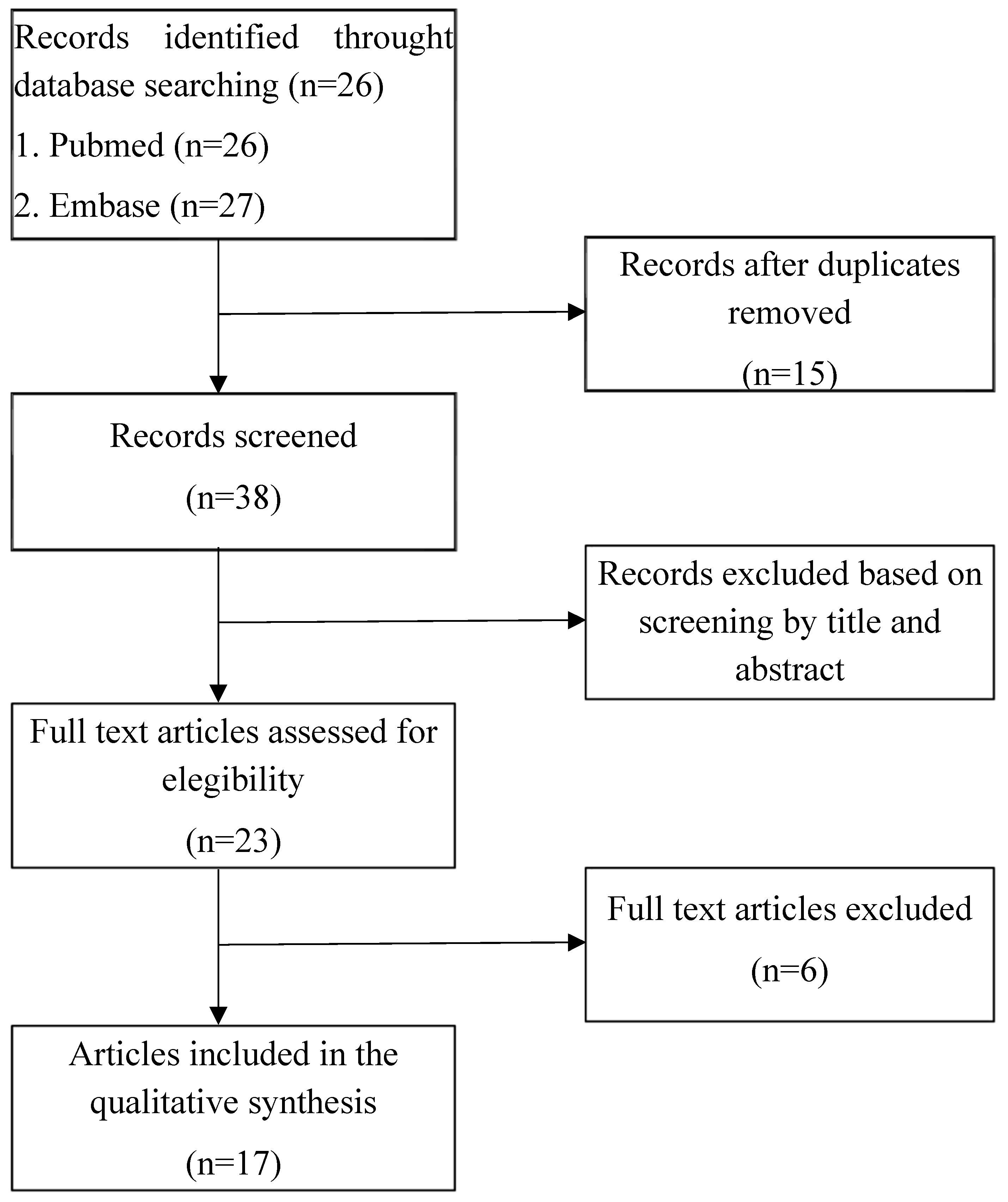
Two independent reviewers (EC and NDC) screened all retrieved citations. When information in the abstracts was insufficient to determine eligibility, the full texts were examined to ensure that articles met the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any disagreements between the reviewers were resolved through discussion and consensus, thus maintaining a consistent and transparent selection process (
Figure 1). Additionally, the clinical data from the authors’ newly documented case were integrated into the overall dataset, further enhancing the robustness of the pooled analysis and providing a richer understanding of this rare condition.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics of the subjects included are reported. Categorical variables are summarized using absolute and relative frequencies while for numerical ones, mean and standard deviation both with median and interquartile range are reported. As each study contributed to the overall design with only one subject (case report), estimates were performed without pooling the results. All the analyses were performed using SAS 9.4 and R.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Patients and Infection
From 1950 through December 2024, a total of 19 patients with congenital syphilis were diagnosed and reported in the literature across multiple countries, with 18 cases providing sufficient clinical detail for inclusion in this review [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. These cases span a wide geographic range and reflect the ongoing global prevalence of syphilis over several decades, with a noted increase in reporting in recent years. Key demographic, clinical, radiological, and laboratory findings are summarized in
Table 1; a more comprehensive dataset is provided in the Supplementary Appendix.
Gender distribution was balanced, with 9 female (52.9%) and 8 (47.1%) male patients. The most common initial presentation was a bullous eruption affecting the palms and/or soles (the so-called “palmoplantar” pattern), observed in 11 patients (64.7%). The second most common pattern was diffuse involvement, noted in 6 patients (35.4%), typically affecting acral areas as well as other body sites. These lesions most frequently appeared at birth (n=15, 83.3%), only 1 at 25 days, 1 at 60 days and 1 at 3 months. Moreover, 9 (52.94%) times were observed in preterm infants. The predominant associated cutaneous manifestations included erythema (n=14, 77.8%), desquamation (n=13, 72.2%), and erosions (n=10, 55.6%).
Early congenital syphilis frequently presented with hepatosplenomegaly (n=13, 72.2%), respiratory distress (n=6, 33.3%), and luetic coryza (n=4, 22.2%), these findings often cohexist with pemphigus syphiliticus. Additionally, osteitis, periostitis, and metaphyseal destruction were reported in 38.9% (n=7) of patients. Laboratory abnormalities commonly included thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and anemia, with respective frequencies of 41.2%, 16.7%, and 22.2%.
3.2. Diagnosis, Treatment of Infection, and Outcomes
Diagnosis was established through a combination of clinical evaluation, radiologic assessment, and laboratory investigations. Nontreponemal tests, including the Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) and the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test, were the most frequently performed serologic procedures, conducted in 88.9% of mothers and 100% of newborns. Treponemal tests, such as the Treponema pallidum Hemagglutination Assay (TPHA) or Treponema pallidum Particle Agglutination Assay (TPPA), were performed in 64.7% (n=11) of maternal and neonatal cases, respectively. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was undertaken in 47.1% (n=8) of newborns, with VDRL being the most commonly reported CSF test (58.8%, n=10). Additional assays, including the Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption (FTA-ABS) test and ELISA for IgM antibodies, were also frequently employed.
Penicillin G represented the most commonly prescribed treatment (87.5%), followed by intramuscular penicillin (12.5%). In some instances, empirical antibiotic therapy was initiated before confirmation of the diagnosis. Penicillin dosing regimens varied considerably among the reported cases, ranging from 100,000 U/kg IV for 14 days to 2,000,000 U/kg/day IV for 10 days. Overall, most patients achieved complete remission (83.3%). However, one patient (x%) developed neurosensory deafness as a complication, and three patients (16.67%) unfortunately died, with respiratory insufficiency and multiorgan failure cited as the leading causes of mortality. A detailed summary of these data is provided in
Table 2.
3.3. Our Case
We present the case of a female newborn delivered at 35+3 weeks of gestational age (GA) by urgent cesarean section due to nonreassuring fetal heart tracings. At birth, the infant’s weight was appropriate for GA (2,270 g). The amniotic fluid was Grade III meconium-stained, and the Apgar scores were 1 at both one and five minutes. Initial examination revealed hepatosplenomegaly, mild axial hypotonia, and reduced mobility of the right wrist and hand with a weak grasp, although archaic reflexes were normal, and lymph nodes were not palpable.
Within the first hour of life, the newborn developed respiratory distress requiring escalating respiratory support, initially via high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) and subsequently non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) with an FiO2 up to 40%. At six hours of life, due to further clinical deterioration, the infant was nasotracheally intubated and administered surfactant. Blood tests indicated hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia, necessitating platelet and packed red blood cell transfusions.
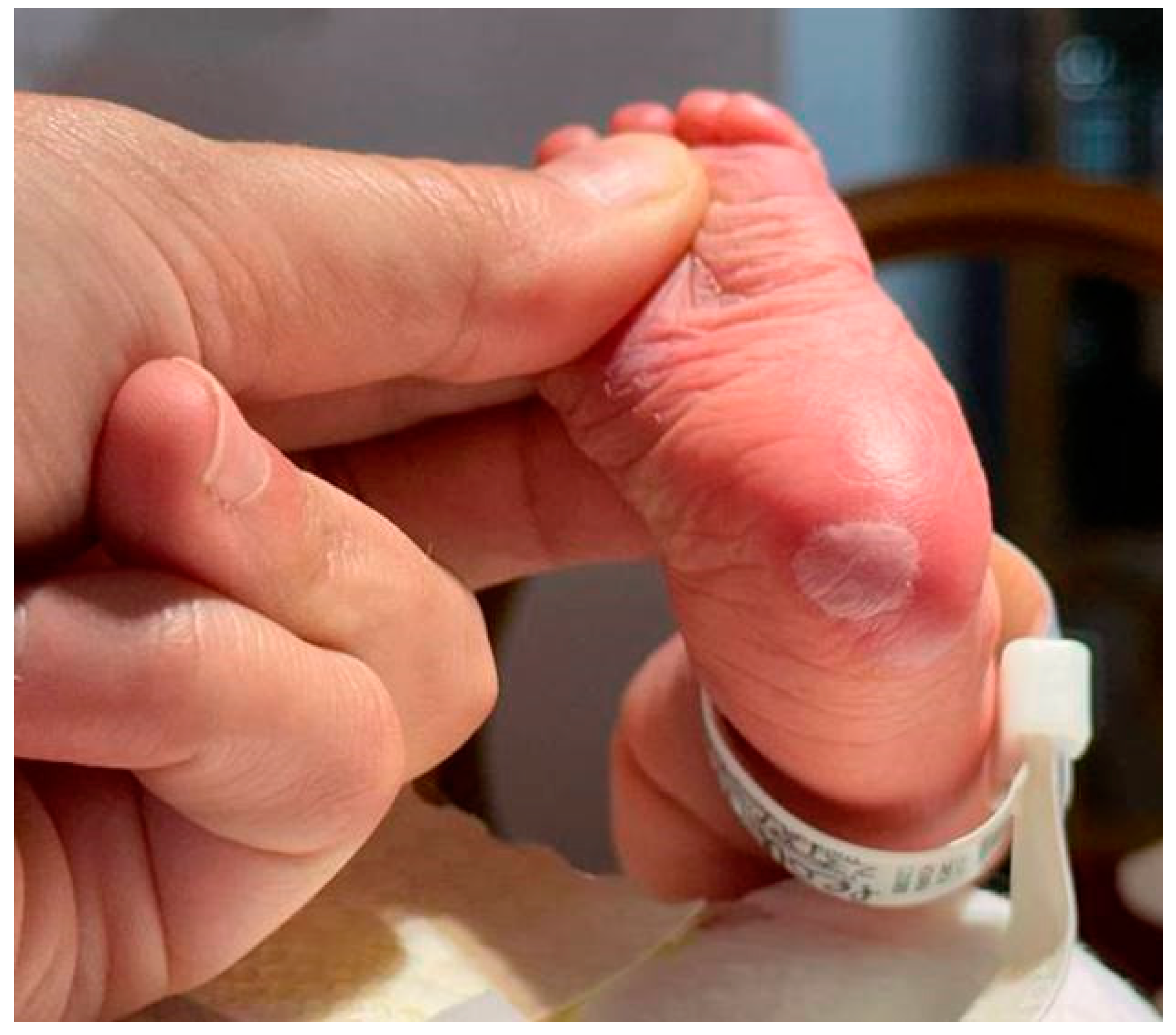
Dermatologic examination revealed petechiae over the trunk at the proximal regions of the upper and lower limbs, two plantar bullous lesions measuring approximately 0.5 to 1.5 cm, and a small de-epithelialized lenticular area on the back of the left hand (Fig. 1). Given the presence of hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, and acral bullous lesions, both maternal and neonatal RPR and TPHA tests were obtained. The neonate’s RPR was positive at 1:1, and maternal RPR was also positive at 1:1. Neonatal TPHA titer was 1:2560, mirroring the maternal titer of 1:2560. The newborn tested negative for IgM antibodies, while the mother tested positive. HIV, HCV, and HBV serologies were negative in both. Blood cultures ruled out bacterial infection, including staphylococcal involvement. Although the mother’s first-trimester screening was normal, she did not attend the recommended clinical and serological follow-up in the third trimester.
A diagnosis of congenital pemphigus syphiliticus was established. Treatment with aqueous crystalline penicillin G at 100,000 units/kg/day IV was initiated, given as 50,000 units/kg per dose every 12 hours for the first seven days of life, then every eight hours thereafter for a total of ten days.
Five hours after the first penicillin dose, the infant developed fever (skin temperature 38°C) and hypotension resistant to fluid boluses, necessitating a norepinephrine infusion. This therapy was discontinued on the fourth day after hemodynamic stabilization, likely representing a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.
Neurological evaluation, including cerebrospinal fluid analysis, was normal. Upper limb radiographs showed areas of rarefaction consistent with luetic metaphysitis. Abdominal and cardiac ultrasound, as well as otolaryngological and ophthalmological examinations, revealed no abnormalities. The ulcerated skin lesions resolved by the seventh day of treatment. The infant was discharged in stable condition following the complete course of antibiotic therapy.
Figure 1.
a-b) Single plantar erythematous bullous lesion present since birth.
Figure 1.
a-b) Single plantar erythematous bullous lesion present since birth.
4. Discussion
Congenital syphilis is a preventable infection that, if untreated, can lead to severe acute and long-term complications. Approximately one-third of affected fetuses experience miscarriages or stillbirths, and during the perinatal period, morbidity and mortality rates are estimated at 33.6–40% and 6.5–10%, respectively [
22,
23,
24]. Notably, up to two-thirds of newborns with congenital syphilis may be asymptomatic at birth, with low birth weight often the only initial clinical sign. Although cutaneous manifestations in congenital syphilis are typically nonspecific—most commonly a diffuse erythematous, desquamative rash—less frequently reported bullous and erosive lesions can serve as critical diagnostic clues [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Such findings significantly narrow the differential diagnosis to a select group of conditions, including acral peeling syndrome, congenital epidermolysis bullosa, bullous impetigo/staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, neonatal pemphigus, pemphigus syphiliticus, and erythema multiforme [
4,
5].
Distinguishing these entities demands thorough clinical evaluation, detailed maternal and neonatal histories, appropriate serological tests, and radiographic imaging. Pemphigus syphiliticus is distinguished by flaccid bullae and erosions, often with minimal or absent peripheral erythema. In this review, we identified three distinct clinical phenotypes of pemphigus syphiliticus: a confined palmoplantar pattern, an acral distribution, and a more diffuse rash associated with severe bullous and erosive lesions. Recognizing these variants is crucial for guiding early diagnosis and ensuring timely, appropriate intervention.
Early detection and management of congenital syphilis are contingent upon identifying active infection in pregnant women. Routine screening with a nontreponemal test (RPR or VDRL) is recommended during the first and third trimesters. Neonates born to mothers with suspected or confirmed syphilis should also be tested. A neonatal nontreponemal titer fourfold higher than the maternal titer is highly indicative of congenital syphilis [
14]. Treponemal IgG antibodies can persist in the neonate due to passive transfer from the mother and remain for up to 18 months, rendering them less useful for initial diagnosis. In contrast, the detection of IgM antibodies, which are not transferred from the mother, can support the diagnosis; however, a negative IgM test at birth does not rule out congenital syphilis [
26].
The management of congenital syphilis follows CDC guidelines [
3], which stratify treatment intensity based on diagnostic certainty. Confirmed or highly probable congenital syphilis, as well as possible congenital syphilis, typically warrants intravenous aqueous crystalline penicillin G therapy (100,000–150,000 units/kg/day for 10 days). Procaine penicillin G or, in certain circumstances, benzathine penicillin G may be considered in possible or less likely congenital syphilis.
Our findings suggest that the extent of cutaneous involvement may not correlate directly with patient prognosis. Instead, severe pulmonary involvement emerged as a leading cause of mortality in the cases examined. Among the three fatal cases reported in the literature, two did not receive intravenous penicillin G (instead receiving intramuscular forms), and in the third case, treatment details were not documented. These observations highlight the importance of both the appropriateness and the route of therapy.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we present a newly described case of congenital syphilis and provide a comprehensive review of the existing literature. This work underscores the significance of recognizing pemphigus syphiliticus as an early, albeit rare, marker of the disease. Dermatologists, pediatricians, and other frontline clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for congenital syphilis when encountering neonatal bullous lesions, ensuring early diagnosis and prompt treatment to prevent potentially fatal sequelae.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, E.C. and E.E.; methodology, E.C and E.E.; software, C.A..; validation, E.C.., E.E., E.B., V. B. and P.S.; formal analysis, N.D.C; investigation, E.C., E.E. and N.D.C.; resources, P.S; data curation, C.A.; E.C. writing—original draft preparation, E.C. and P.S.; writing—review and editing, C.A..; visualization, P.S.; supervision, C.A., P.S; project administration, P.S.
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
References
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Congenital syphilis. In: ECDC. Annual epidemiological report for 2022. Stockholm: ECDC; 2024.
- Leslie, S.W.; Vaidya, R. Congenital and Maternal Syphilis. [Updated 2024 Aug 17]. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537087/.
- https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/congenital-syphilis.htm.
- Pañgan, E.A.C.; Asetre-Luna, I.; Uy, M.E.V.; Esguerra, A.K.M. Pemphigus syphiliticus with Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in a newborn. Pediatr Dermatol 2024, 41, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires Figueiredo, L.; Botelho Brito, T.; Labrusco, M.; Brigham Figueiredo, M.; Lopo Tuna, M. A Rare But Pathognomonic Sign of Congenital Syphilis. J Pediatr 2023, 262, 113622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petric, U.B.; Ordonez, J.; Thomas, C. Perianal plaques, acral bullae, and desquamation in a neonate. Pediatr Dermatol 2023, 40, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeh, O.; Duffy, R.F.; Feingold, A.; Manders, S.M. Congenital bullous syphilis in a newborn: A novel approach to diagnosis using immunohistochemical staining on a blister roof. Pediatr Dermatol 2024, 41, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Barrueco, A.; Grasa, C.D.; Grandioso-Vas, D.; Del Rosal, T.; Sánchez-Holgado, M.; Sánchez-García, L.; López-Ortego, P.; Falces-Romero, I.; García-Rodríguez, J.; Quiles-Melero, I. Treponema pallidum causing congenital syphilis with severe multisystem involvement. J Travel Med 2023, 30, taac152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnapura Lakshminarayana, S.; Devadas, S.; Bharath, K.; Kariyappa, M.; Byadarahalli Keshavamurthy, B.; Bagewadi, S.M.; Veeranna Sajjan, S.; Vineet, D.; Mohammed, T. Early congenital syphilis: missed opportunities in a mother owing to many problems during pregnancy - a case report. Paediatr Int Child Health 2022, 42, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callista, B.; Triastuti, I.; Gge Doddy Kurnia, I. Congenital syphilis present with pemphigus syphilitics and atelectatic congenital pneumonia: a case report. Intisari Sains Medis 2021, 12, 998–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, S. Congenital pemphigus syphiliticus: a characteristic feature of a forgotten disease. BMJ Case Rep 2021, 14, e246310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, J.; Naseem, J.A.; Neupane, N.; Parameswaran, N.; Chandrashekar, L. An unusual presentation of early congenital syphilis with annular configuration of blisters resembling "string-of-pearls". Pediatr Dermatol 2019, 36, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.H.; Jagati, A.J.; Santoshodev, P.; Chaudhary, R. G. Early congenital syphilis: Resurgence of an entity nearing elimination. Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology 2019, 20, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.A.; Chambers, C.J.; Silverstein, M. A rare presentation of congenital syphilis: Pemphigus syphiliticus in a newborn infant with extensive desquamation of the extremities. Pediatr Dermatol 2018, 35, e110–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Congenital pemphigus syphiliticus. Int J Infect Dis 2016, 49, 149–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.C. Early congenital syphilis presenting with vesicobullous eruptions beyond palmoplantar regions. Acta Derm Venereol 2014, 94, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strowd, L.C.; Ali, S.; Yospovitch, G. Acral blisters in a neonate. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012, 31, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, B.J.; Hoon, Y.B.; KIMJH. Early congenital syphilis presenting with skin eruption alone: a case report. Korean J Pediatr. 2011, 54, 512–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, S.R.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, M.S.; Jo, H.S. Congenital syphilis presenting with a generalized bullous and pustular eruption in a premature newborn. Ann Dermatol. 2011, 23 (Suppl 1), S127–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pelegay, J.; Sánchez-Salas, M.P.; Ventura-Faci, P.; Grasa-Jordán, M.P.; Carapeto, F.J. Pénfigo sifilítico: ¿pasado, presente o futuro? [The past, present, and future of pemphigus syphiliticus]. Actas Dermosifiliogr 2008, 99, 664–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.; Santos, G.A. A propósito de um caso de pênfigo sifilítico [Case of pemphigus syphiliticus]. J Pediatr (Rio J). 1950, 16, 111–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, P.S.; Cantey, J.B.; Zeray, F.; Leos, N.K.; Michelow, I.C.; Sheffield, J.S.; Wendel, G.D.; Sánchez, P.J. The Mortality of Congenital Syphilis. J Pediatr 2023, 263, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uku, A.; Albujasim, Z.; Dwivedi, T.; Ladipo, Z.; Konje, J.C. Syphilis in pregnancy: The impact of "the Great Imitator". Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2021, 259, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.R.; Brooks, L.C.; Davis, D.W.; Torrone, E.A.; Weinstock, H.S. Congenital syphilis: trends in mortality and morbidity in the United States, 1999 through 2013. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2016, 214, 381.e1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Tsai, C.N.; Wong, W.R.; Hong, H.S.; Chuang, Y.H. Early congenital syphilis and erythema multiforme-like bullous targetoid lesions in a 1-day-old newborn: detection of Treponema pallidum genomic DNA from the targetoid plaque using nested polymerase chain reaction. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006, 55, S11–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, R.; Luck, S. Syphilis is on the increase: the implications for child health. Arch Dis Child 2008, 93, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).