1. Background
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) was designed as a brief cognitive screening test for identifying milder forms of cognitive impairment in the elderly population [
1]. It has been extensively studied in Brazil and elsewhere, affirming its utility in assessing cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease (PD) [
2,
3,
4]. Despite its broad application, the MoCA faces challenges, including potential item biases and overall test structure. Originally developed in English, it has been adapted into several languages, including Brazilian Portuguese [
5]
The effectiveness of MoCA in identifying cognitive impairment may vary, particularly in populations with lower education levels. This could lead to incorrect diagnoses or missed cases. Data from a normative study conducted in São Paulo, for example, has revealed that MoCA effectiveness in detecting cognitive impairment among Brazilian seniors varies significantly with age and education [
6]. It was found that MoCA scores differ across cognitively normal individuals, those with “cognitive impairment no dementia” (CIND), and dementia patients, necessitating the adjustment of MoCA scores based on educational levels. The study notably pointed out the MoCA's limited effectiveness in detecting CIND in individuals with low educational levels despite its utility in diagnosing dementia in more educated groups.
The need to vary cutoff scores according to educational levels in different populations presents a significant challenge in validating cognitive assessment tools like MoCA. This variability complicates the efficiency of screening processes and increases the likelihood of human error. Research conducted in various countries highlights this issue, with recommendations for a range of cutoff scores tailored to different education and age groups [
6,
7,
8]. This lack of universally applicable cutoff scores underscores the limitations of a one-size-fits-all approach and emphasizes the need for population-specific norms and scoring guidelines.
Central to this challenge is item bias, where certain test item characteristics, not directly related to the cognitive construct being measured, affect responses differently among groups [
9]. Conventional scoring methods, which often treat all test items uniformly and may adjust scores for educational background, do not adequately tackle the influence of these factors on individual test items. This situation underscores the necessity for more refined methods to address such biases in cognitive assessments.
Item Response Theory (IRT) offers a valuable statistical framework for analyzing psychological and educational tests, playing a crucial role in evaluating test validity [
10,
11]. IRT allows for a detailed assessment of the quality of a test’s items, offering insights into individual item difficulty, test-taker ability, and overall test performance. This information is instrumental in identifying the strengths and weaknesses of a test guiding decisions regarding which items should be included or excluded. By employing IRT, researchers can ensure that a test accurately measures the intended construct and yields reliable results, thus enhancing the overall effectiveness and precision of cognitive assessments [
12]. Moreover, IRT provides a means to assess and mitigate item bias, allowing for developing of more equitable and culturally appropriate cognitive screening tools.
The MoCA has been extensively examined using the IRT framework in various contexts. For instance, a study conducted in Taiwan revealed that executive function tasks—including attention, working memory, and abstract thinking items—were more effective than language and visual-spatial subscales in distinguishing individuals with mild and moderate cognitive impairment [
13]. Conversely, orientation items proved less effective in differentiating between cognitively unimpaired individuals and those with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia. Similarly, in Portugal, Rasch-based IRT models demonstrated a strong overall fit between MoCA items and individual values, underscoring the test's scalability and appropriateness [
14]. These findings suggest that the discriminative power of MoCA items can vary significantly across different cognitive domains and levels of impairment, highlighting the necessity for a comprehensive understanding of the test's psychometric properties. However, despite these international insights, the analysis of MoCA using the IRT framework in Brazil remains limited.
Applying the Graded Response Model (GRM), one of the IRT models for polytomous items, to the MoCA could improve the estimation of individual cognitive abilities [
15,
16]. GRM can identify the most informative items, potentially resulting in a more concise MoCA. Additionally, GRM may offer insights into the psychometric properties of test items, helping to refine the test by pinpointing poorly performing or redundant items. Utilizing GRM, researchers can develop a more efficient and precise cognitive screening tool tailored to the target population's specific needs.
This study aims to analyze the performance of specific test domains and the overall scores of the Brazilian version of the MoCA using IRT in varying degrees of PD-related cognitive dysfunction and conduct a Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes model approach to investigate the impact of educational level and age on test performance. By examining the MoCA's psychometric properties in a diverse PD sample, this study seeks to contribute to the growing body of evidence on the test's validity and reliability while also exploring potential sources of item bias. The findings could inform the development of more accurate and equitable cognitive screening strategies for PD patients in Brazil and beyond.
3. Results
3.1. Participants
The study sample consisted of 484 patients diagnosed with PD. Participants ranged from 26 to 90 years old (mean ± SD: 59.9 ± 11.1 years). PD duration varied substantially, spanning 1 to 35 years (mean ± SD: 9.1 ± 5.8 years). The average educational attainment was 9.1 ± 5.4 years. The majority of participants were male (57.6%), aligning with the known higher PD prevalence among males.
Table 1 summarizes the demographic and clinical characteristics, including education levels, PD duration categories, gender proportions, and MoCA scores. The mean total MoCA score for the full cohort was 20.61 ± 5.80 (SD).
Table 2 shows score distribution across MoCA's seven cognitive domains. Naming and Orientation exhibited ceiling effects, with 70% and 80.4% of participants scoring maximum points, respectively. Visuospatial/Executive scores were evenly distributed, peaking at 5 (21.5%). Attention centered around 6 (26%). Language and Abstraction had modal scores of 2 (36% and 39.3%). Memory showed wide distribution, with 0 most frequent (30%). These patterns indicate varying cognitive performance across domains, with Naming and Orientation showing strongest performance, while Visuospatial/Executive and Memory displayed more variability. This suggests differential sensitivities to PD-related cognitive impairment across MoCA domains, emphasizing the need for domain-specific score interpretation.
3.2. IRT Graded Response Model
3.2.1. Dimensionality Analysis, Model Fit, and Reliability Assessment
The correlation matrix's factorability was confirmed by Bartlett's test (χ² = 808.03, df = 21.0, p < 0.001) and KMO (0.867). Parallel analysis supported a unidimensional model (first eigenvalue: 3.205 vs. 1.176 in simulated data). High factor loadings across MoCA domains validated its use as a unidimensional cognitive assessment tool. EFA indicated satisfactory model fit (χ2 = 26.106, df = 14, p = 0.025; RMSEA = 0.042, 90% CI: 0.015-0.067; TLI = 0.977), reinforcing the model's robustness.
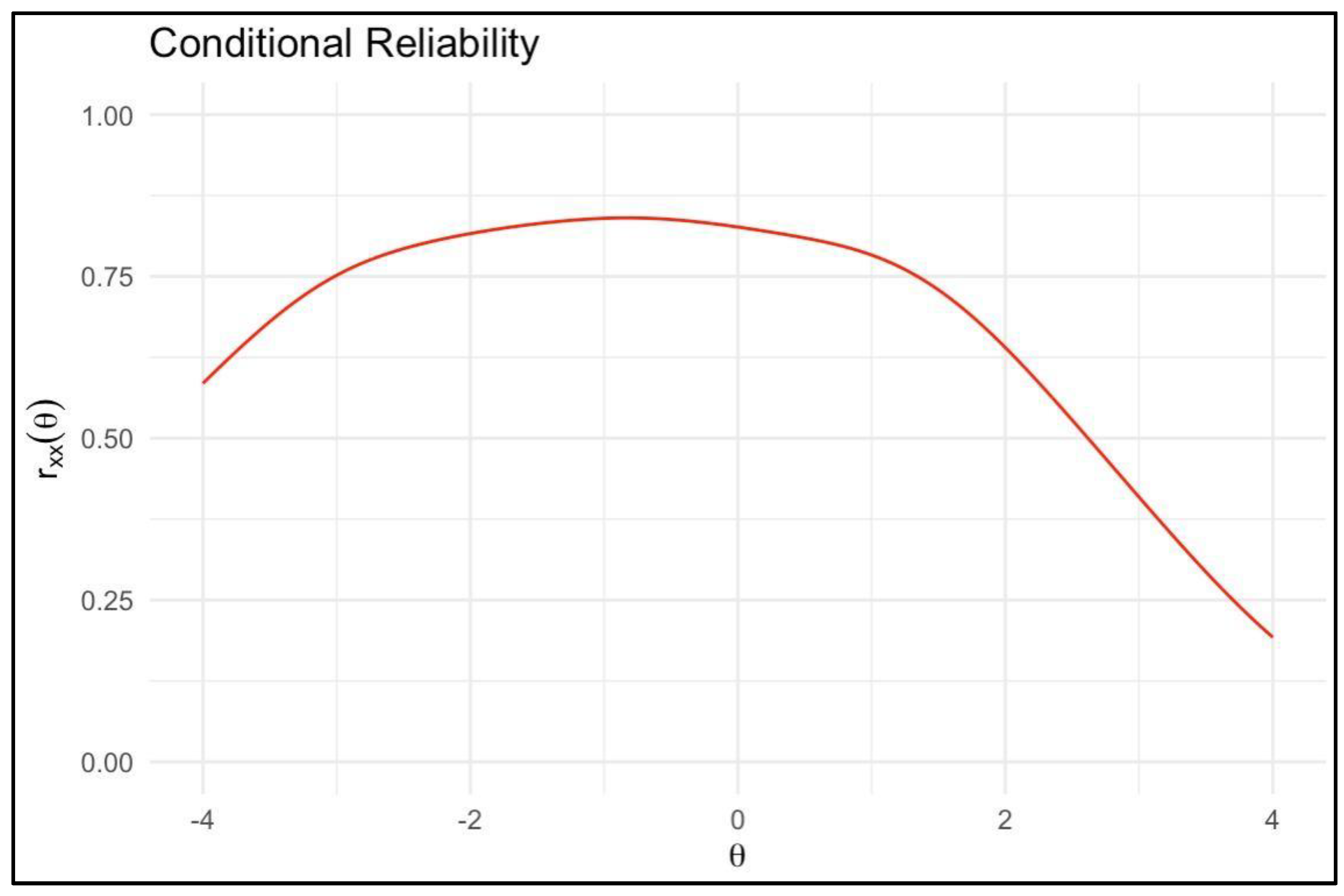
Figure 1 shows MoCA's conditional reliability peaks at moderate trait levels (θ between -1 and 1), indicating optimal precision for average cognitive abilities. Reliability decreases at cognitive spectrum extremes. The marginal reliability coefficient (
rxx=0.806) demonstrates good overall precision. These findings support MoCA's suitability for assessing cognitive function in PD populations, especially for mild to moderate impairments.
Legend. The x-axis shows the latent cognitive trait (θ) continuum. The y-axis displays reliability coefficients (rxx(θ)) at corresponding trait levels. The peak conditional reliability indicates the cognitive ability range at which the MoCA provides optimal measurement precision. As θ diverges from this peak, score reliability declines, reflecting variable consistency across the spectrum of cognitive faculties indexed by the MoCA.
3.2.2. Evaluation of Model and Item Fit
The GRM exhibited a robust overall fit to the MoCA data (M2 = 12.94, degrees of freedom (df) = 14, p = 0.53; RMSEA = 0.000 [90% CI: 0.000-0.041]; standardized root mean square residual [SRMSR] = 0.040), affirming its suitability for this analysis.
Table 3 details the item-level fit statistics for each cognitive domain, all demonstrating good concordance with the model.
Specifically, the Visuospatial/Executive domain aligned well with the model's assumptions (S-χ2 = 40.918, df = 50, RMSEA = 0.000, p = 0.817). Similarly, acceptable fits were observed in the Naming (S-χ2 = 34.498, df = 27, RMSEA = 0.024, p = 0.152), Attention (S-χ2 = 69.589, df = 50, RMSEA = 0.028, p = 0.035), Language (S-χ2 = 41.125, df = 41, RMSEA = 0.003, p = 0.465), Abstraction (S-χ2 = 21.000, df = 26, RMSEA = 0.000, p = 0.742), Memory (S-χ2 = 49.590, df = 49, RMSEA = 0.005, p = 0.450), and Orientation domains (S-χ2 = 34.239, df = 29, RMSEA = 0.019, p = 0.231). These findings strongly support GRM-based analysis of the psychometric properties of the MoCA in a PD population.
3.2.3. Analysis of Item and Person Parameters
The GRM analysis was employed to evaluate how effectively each domain of the MoCA discriminates between levels of cognitive abilities and to assess item difficulty levels (as detailed in
Table 3). Notably, the Attention and Naming domains exhibited the highest discrimination values, indicating their strong capability to differentiate individuals across various latent trait levels. The particularly high discrimination value in the Attention domain (1.985) highlights its sensitivity in identifying subtle cognitive impairment.
On the other hand, the Memory domain demonstrated the lowest discrimination (1.265), implying a relatively weaker capacity to differentiate between varying levels of cognitive abilities. This lower discrimination in Memory could affect its effectiveness, particularly in identifying early stages of cognitive decline.
The analysis of location thresholds provided insights into the range of item difficulties. The Orientation domain was marked by the lowest difficulty levels (thresholds: -4.135 to -1.225), suggesting that these items are more easily endorsed across a range of cognitive abilities. Conversely, the Memory domain presented the highest difficulty (thresholds: -0.860 to 2.402), requiring a higher level of cognitive functioning for successful performance. These findings highlight MoCA's capabilities in capturing diverse cognitive performance profiles with varying levels of sensitivity and challenge across its different domains. Identifying highly discriminating domains (Attention and Naming) and those with a broader range of difficulty (Memory) can guide the refinement of the MoCA for optimal use in PD populations.
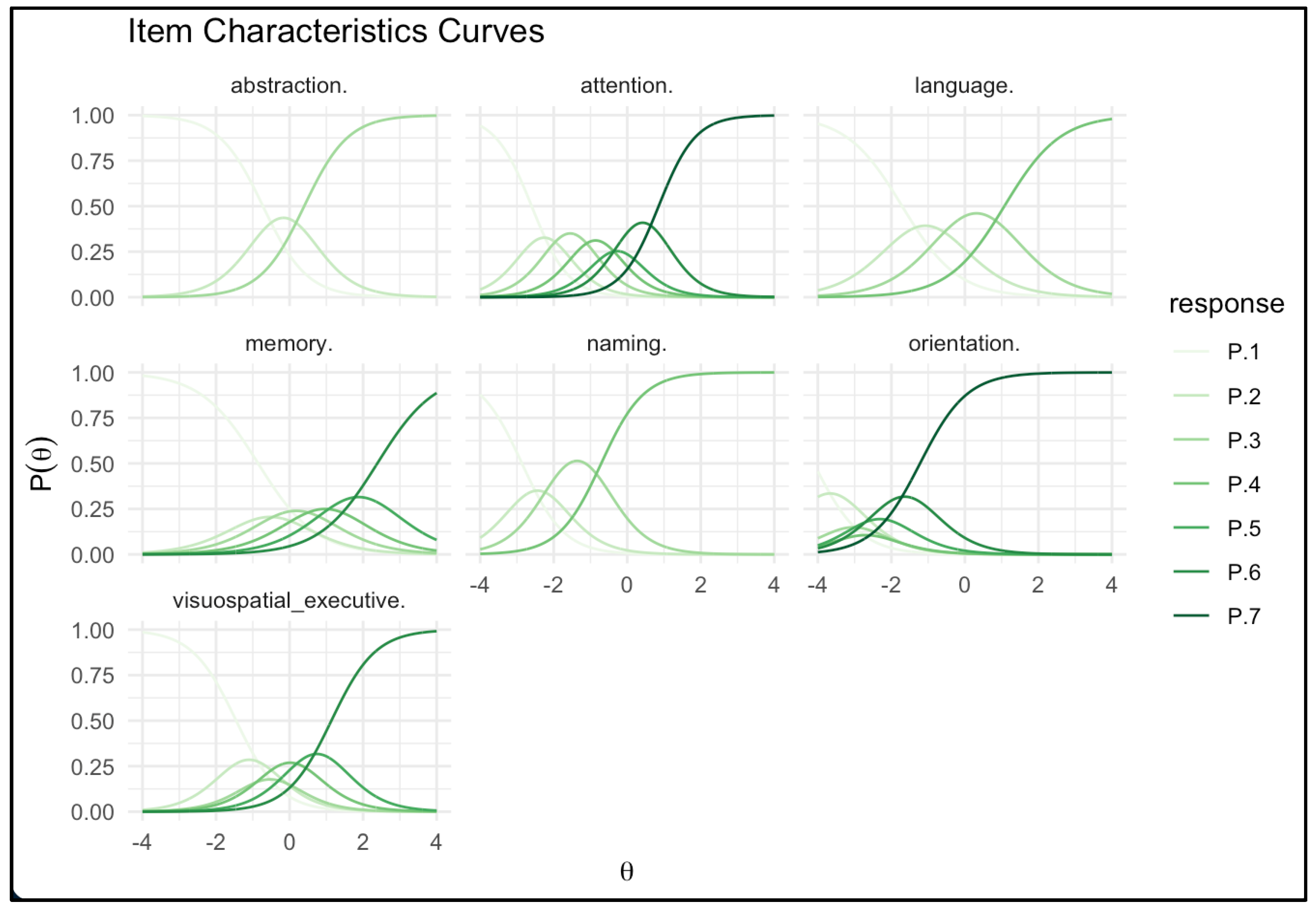
Figure 2 presents Item Characteristic Curves (ICCs) for each MoCA domain, illustrating the relationship between latent cognitive abilities (θ) and response category endorsement probabilities. Steeper curves (e.g., Attention, Naming) indicate higher discrimination, while gradual slopes (e.g., Memory) suggest lower discrimination. Curve positioning along the x-axis reflects domain difficulty, with Orientation being the easiest and Memory the most challenging. These ICCs visually represent how difficulty and discrimination parameters influence response patterns across the cognitive ability spectrum.
Legend. The graph presents Item Characteristic Curves (ICCs) for polytomous item responses within the cognitive domains of the MoCA. The x-axis (θ) represents the latent trait of cognitive ability, ranging from -4 (indicating lower ability) to +4 (indicating higher ability). The y-axis depicts the probability [P(θ)] of a participant endorsing a particular response category at a given level of θ. Curves labeled P.1 through P.7 correspond to the ascending response categories for each domain, with P.1 representing the lowest category (e.g., no correct responses) and P.7 representing the highest category (e.g., all correct responses). A higher curve position on the y-axis reflects a higher probability of a participant with a corresponding θ level selecting that response category, providing a visual representation of the probability of achieving each score based on cognitive ability.
Figure 3 and
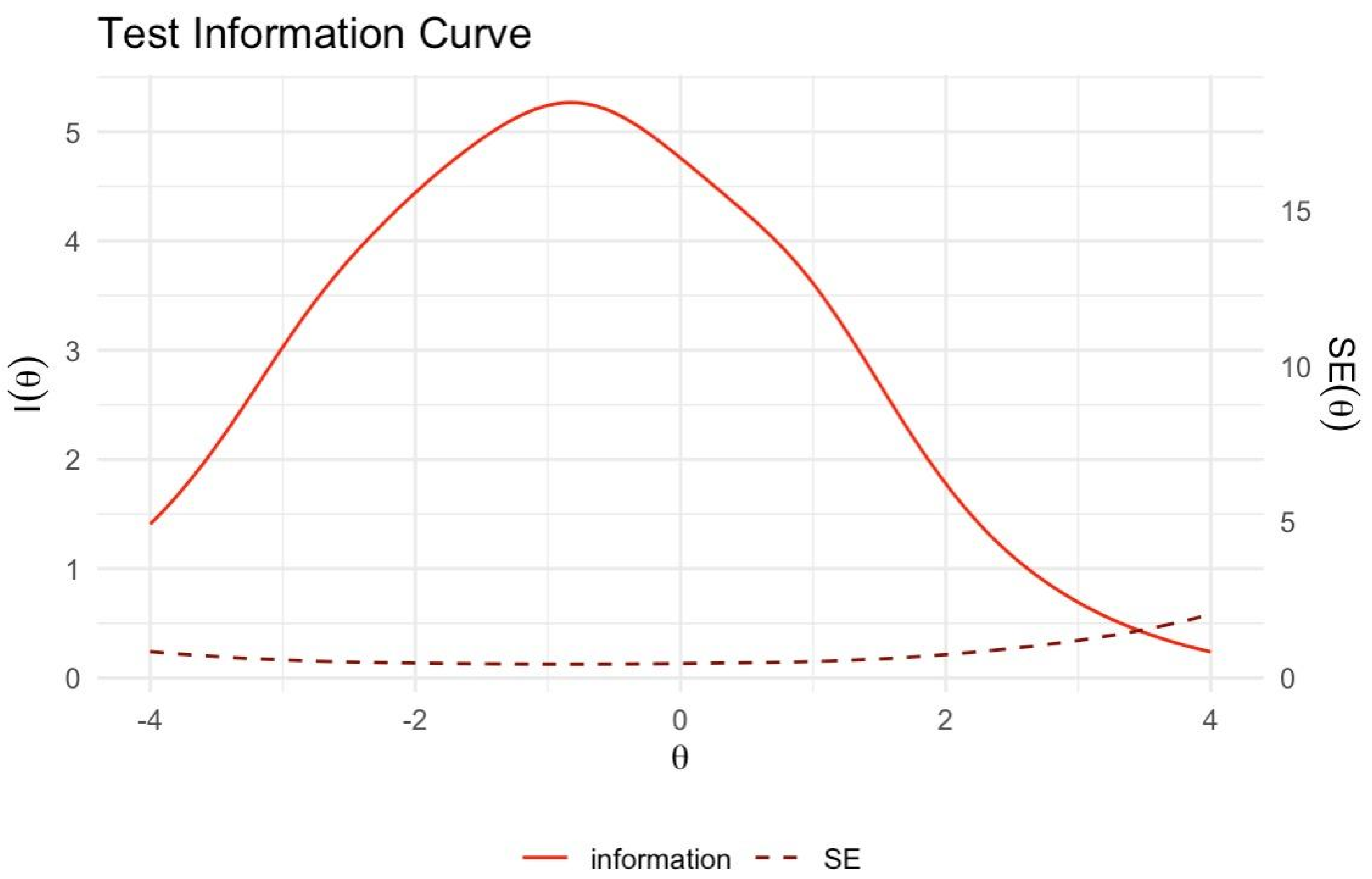
Figure 4 offer insights into item and test information functions.
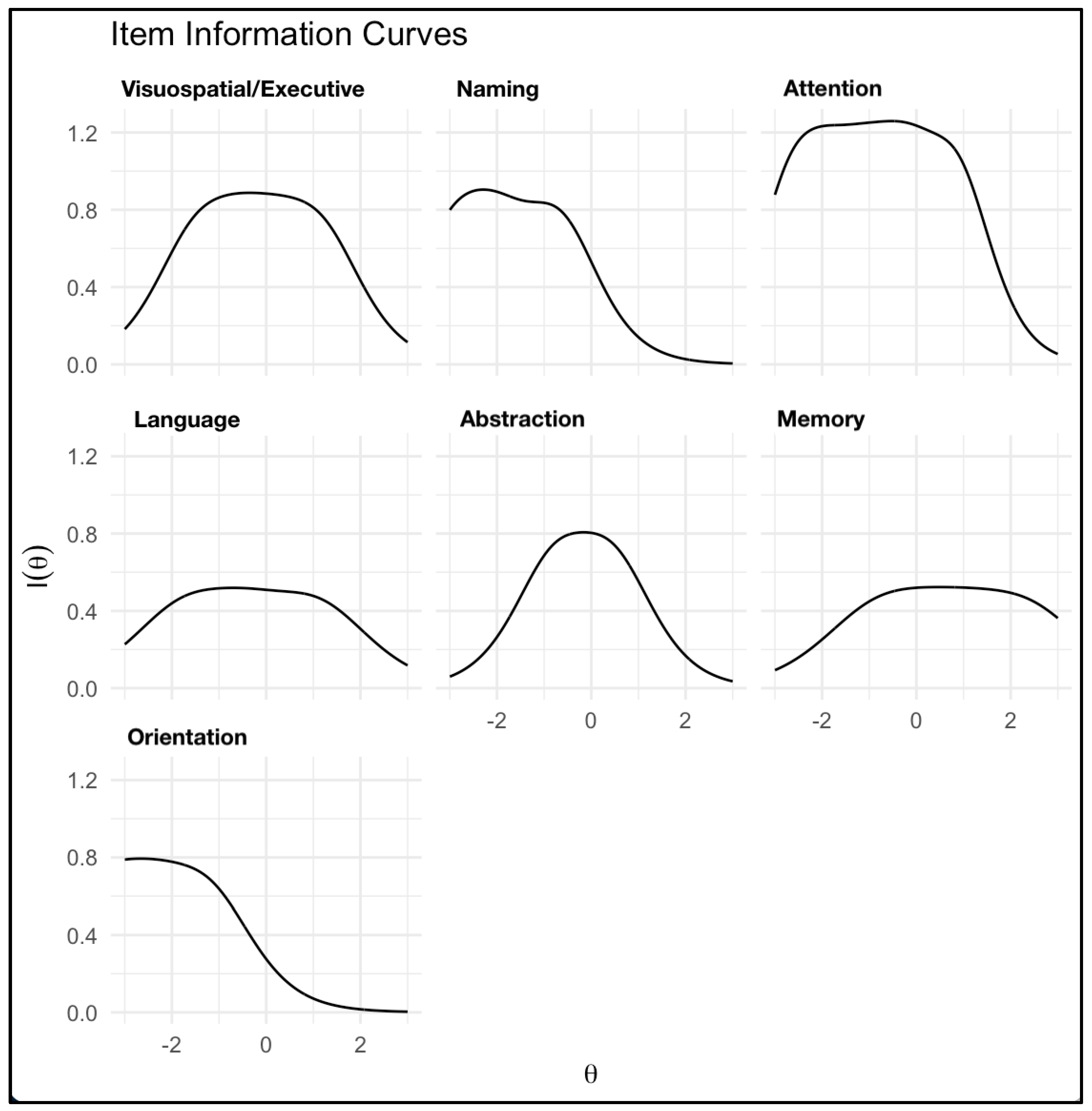
Figure 3's item information curves show psychometric information provided by each MoCA domain across the cognitive ability spectrum. Domains with higher peaks (e.g., Attention and Naming) offer more information, indicating greater reliability and discrimination at specific ability levels.
Figure 4 displays the test information function, representing aggregate information from the entire MoCA. The curve's peak indicates the ability level where MoCA provides the most precise measurement. It also illustrates the inverse relationship between test information and standard error of measurement.
Legend. This figure illustrates the item information functions (IIFs) associated with the cognitive domains assessed by the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Each graph represents the sensitivity of the respective domain to detect changes in cognitive ability, denoted as theta (θ). The θ parameter is normatively scaled, ranging from -3 to +3, signifying low to high cognitive abilities, respectively. The acme of each curve symbolizes the juncture at which the domain is most informative, i.e., where it most accurately discerns between different levels of cognitive function. A steeper ascent and peak of the curve connote a higher information density, indicating a domain's heightened precision in measuring cognitive abilities around its peak θ value. Conversely, the flattening of the curve at the tails suggests diminishing informational yield for extreme ability levels.
Figure 4.
- Test information and standard error curves for the MoCA.
Figure 4.
- Test information and standard error curves for the MoCA.
Legend. The solid red line shows the test information function [I(θ)] across cognitive ability levels (θ). The peak indicates where the MoCA provides optimal measurement information. The dashed line represents the standard error of measurement [SE(θ)], which inversely relates to test information. Lower SE(θ) reflects greater precision in estimating θ. SE(θ) is minimized where test information is maximized, delineating the optimal range of measurement precision.
3.3. Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC) Modeling of Age and Education Effects on Latent Trait
The Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC) model was employed to examine differential item functioning (DIF) across demographic variables. The model demonstrated adequate fit (χ2 p = 0.606, CFI and TLI > 0.95, RMSEA < 0.001 for standard model, 0.050 for scaled model). Regression analysis revealed significant associations between cognitive performance and demographics: age negatively impacted performance (β = -0.149, p = 0.016), while education showed a positive influence (β = 1.001, p < 0.001). Cognitive domains were differentially affected by age and education, with Memory Recall and Executive/Visuospatial tasks benefiting more from education, and Working Memory/Attention showing a moderate correlation with age but stronger association with education. A negative correlation between age and education (β = -0.126, p = 0.008) was observed. Educational attainment significantly affected the MoCA's latent trait, accounting for 70% of its variance. These findings underscore the complex interplay between age and education in cognitive performance, emphasizing the need for age- and education-adjusted norms in MoCA interpretation.
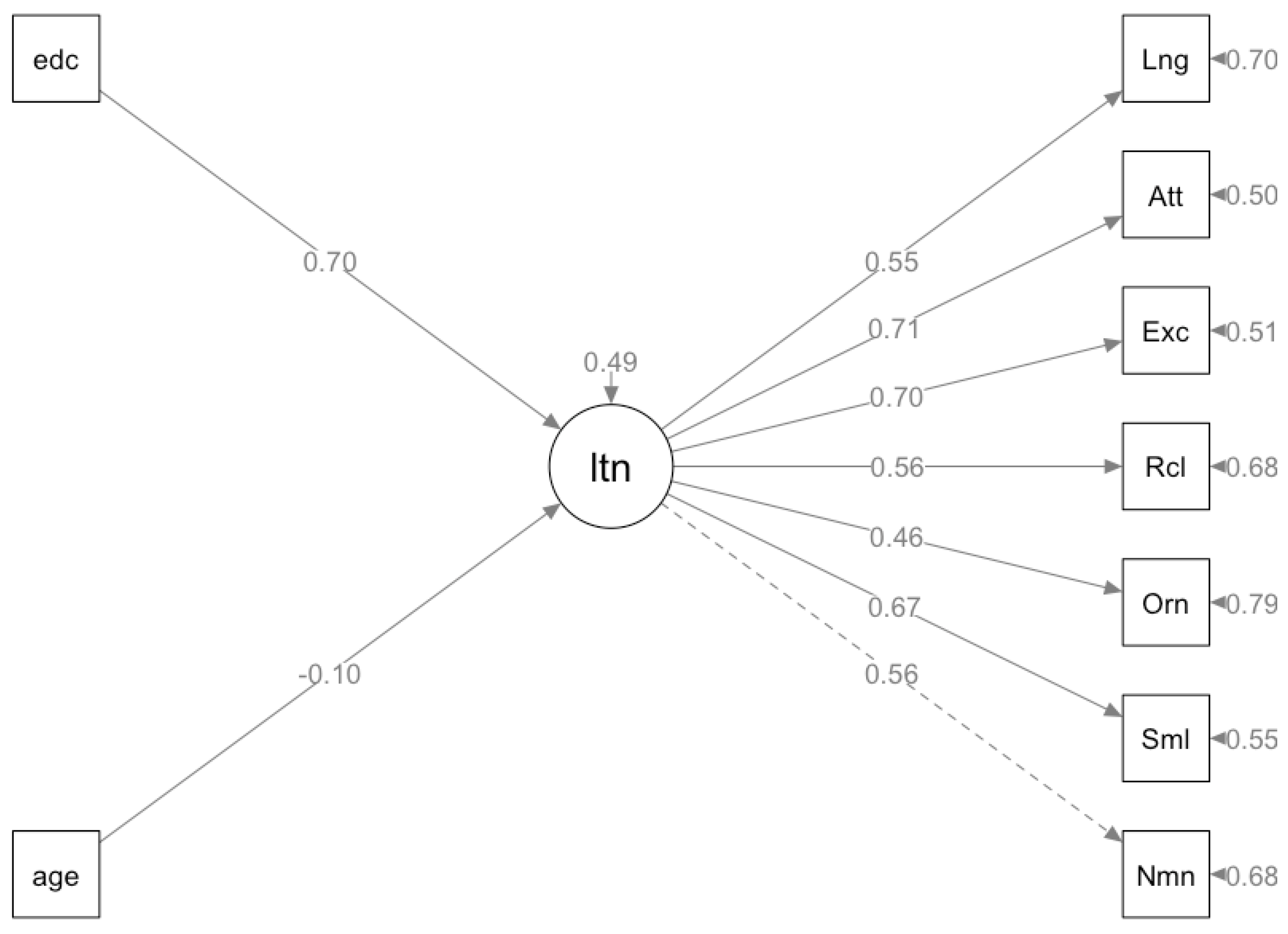
Figure 5.
- Influence of Age and Education on Latent Cognitive Traits: A MIMIC Model Representation.
Figure 5.
- Influence of Age and Education on Latent Cognitive Traits: A MIMIC Model Representation.
Legend. In the presented model, 'age' and 'education' (edc) are depicted as influencing factors, represented by the rectangles labeled 'age' and 'edc'. These factors impact the latent trait (ltn) of cognitive performance, which is represented by the central circle. The latent trait, in turn, influences various cognitive domains assessed by the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), including Language (Lng), Attention (Att), Executive Functions (Exc), Recall (Rcl), Orientation (Orm), Similarities (Sml), and Naming (Nnm). These domains are represented by the squares connected to the latent trait by arrows, indicating the strength and direction of their relationship. Solid arrows reflect significant positive associations, while dashed arrows indicate non-significant or weaker associations. The numbers on the arrows represent the standardized path coefficients, reflecting the strength of the relationships. This model aims to illustrate how age and education affect overall cognitive abilities and their subsequent impact on specific cognitive domains within the MoCA framework.
A second MIMIC model explored the influences of age and education on MoCA domain performance. The model demonstrated strong fit (CFI and TLI ~0.99, RMSEA ≤0.035). Educational attainment significantly impacted Language, Attention, Executive Functions, and Similarities (Abstraction) domains (βs from 0.76 to 2.677, p < 0.05), while age had a smaller, negative effect on Naming, Similarities, Orientation, and Executive Functions (βs from -0.175 to -0.283, p < 0.05). Age's impact on Memory, Attention, and Language was marginal (p > 0.05). These findings highlight the differential impact of age and education across cognitive domains, emphasizing the need for demographic-specific norms in MoCA interpretation to enhance assessment accuracy and fairness in diverse populations.
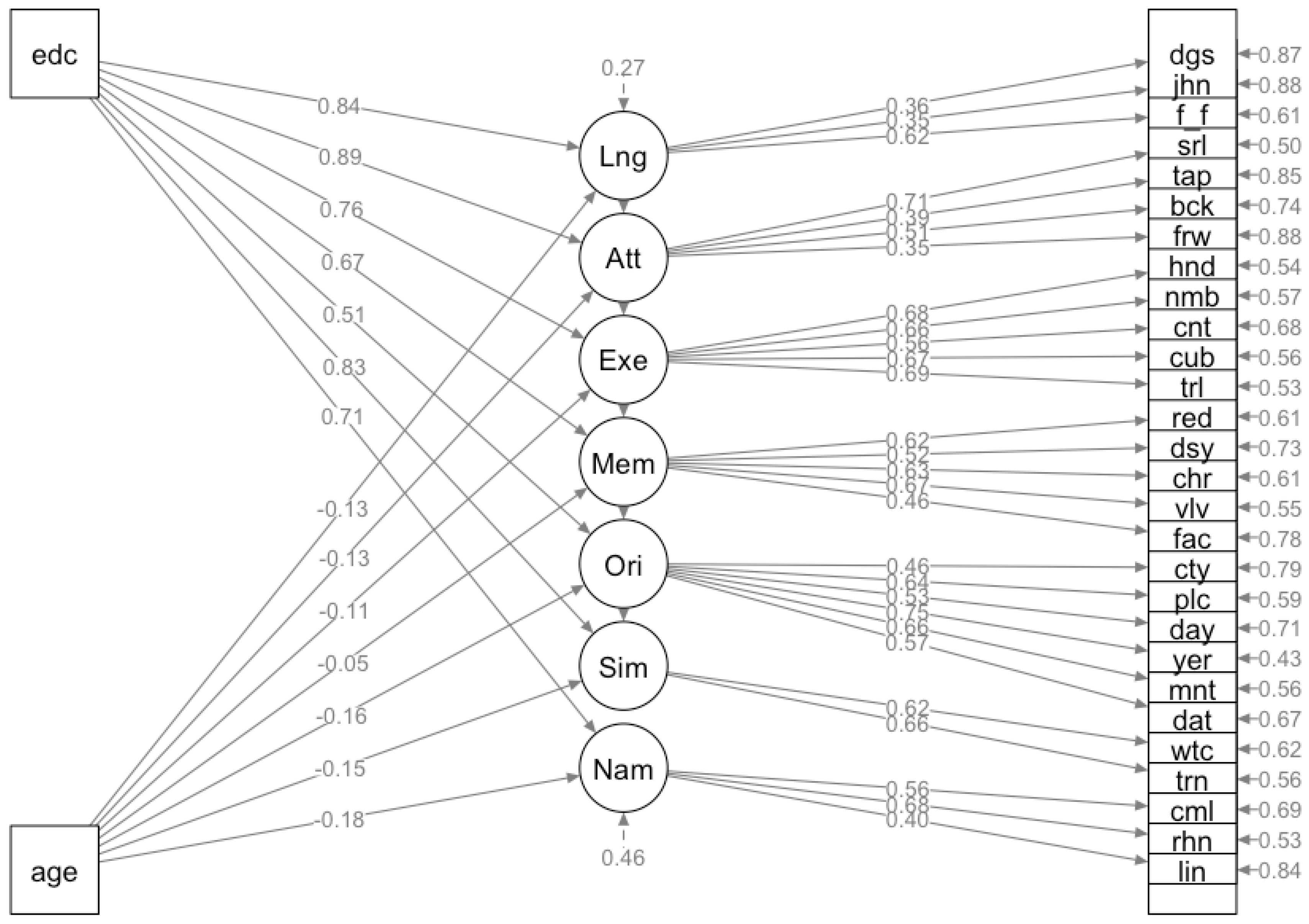
Figure 6.
- Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC) model quantifies age and education's effects on MoCA domains rather than on a latent trait.
Figure 6.
- Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC) model quantifies age and education's effects on MoCA domains rather than on a latent trait.
Legend. The model provides specific insights into how these variables impact different cognitive domains within the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Rectangles indicate the predictor variables ('age' and 'edc'), and the circles represent the cognitive domains: Language (Lng), Attention (Att), Executive/Visuospatial (Exe), Memory Recall (Mem), Orientation (Ori), Abstraction/Similarities (Sim) and Naming (Nam). The numerical values next to the single-headed arrows from 'age' and 'edc' denote the strength and direction of the effects on each domain, with negative values indicating an inverse relationship.
4. Discussion
Our investigation into the MoCA using the GRM within a Brazilian PD patient cohort offers detailed insights into the test's psychometric attributes. The findings on dimensionality align with the MoCA’s design as a tool for globally assessing cognitive function, reinforcing its suitability as a comprehensive cognitive evaluation instrument. This aligns with previous research, such as a study from Portugal, which also upheld the MoCA's unidimensional nature [
14]. However, our study sets itself apart by employing the GRM to address the polytomous characteristics of the MoCA items, offering a distinct analytical perspective.
Contrasting with the findings of Smith et al., who were unable to definitively determine a factor structure for the MoCA in a large cohort of recent-onset PD patients (n=1738) with normal to mildly impaired cognition [
24], our results demonstrate a unidimensional factor structure for the Brazilian Portuguese MoCA in a PD context. The IRT analysis underpins the reliability of the MoCA, as evidenced by its adequate model fit and robust factor loadings. This suggests that within our study's framework, the MoCA effectively captures the cognitive dimensions it intends to measure in PD patients, offering a reliable assessment tool in this population.
The MIMIC model revealed significant effects of age and education on MoCA performance. Age negatively correlated with Naming domain scores (β = -0.175 to -0.283, p < 0.05), suggesting decreased semantic memory and language fluency with aging. Conversely, higher education positively influenced various cognitive domains, including Executive Functions and Naming, indicating enhanced cognitive reserve. The pronounced impact of education on Similarities (Abstraction) domain highlights its role in strengthening abstract reasoning. These findings emphasize the importance of considering both age and educational background when interpreting MoCA results, as higher education may mask early cognitive decline. Clinicians should adjust their interpretations accordingly to ensure accurate cognitive assessments.
Our findings partially align with those of Luo et al. (2020) in Hong Kong, where an IRT analysis of the MoCA was conducted among older Cantonese-speaking individuals. Using a sample of 1873 participants and the Chinese version of MoCA, the study implemented exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses along with the GRM. It revealed significant variation in MoCA item performance by educational background, particularly in visuospatial items, and found greater reliability of MoCA among uneducated participants. This advocated for the broader use of IRT to improve the measurement precision of clinical scales.
However, this study also contrasts with Sala et al.'s research in Japan, which thoroughly examined MoCA's psychometric properties in a large elderly cohort [
25]. With 2408 participants across three age groups, their study identified multidimensionality in initial tests, followed by a hierarchical EFA revealing a general factor and seven first-order factors. A confirmatory factor analysis confirmed this structure, and importantly, measurement invariance was established across diverse demographics, including age, education, sex, and economic status, indicating MoCA's robustness across these variables. This finding differs from our study's emphasis on the impact of age and education. These divergent findings could be due to several factors, including differences in sample characteristics (elderly Japanese vs. PD patients in Brazil), analytical approaches (hierarchical EFA vs. GRM), and the handling of item scores (dichotomous vs. polytomous). Further research is needed to clarify these discrepancies and establish the generalizability of MoCA's psychometric properties across different populations and contexts.
In Portugal, MoCA's analysis by Freitas et al. (2014) using the Rasch model for dichotomous items and DIF analysis also provides a relevant comparison [
14]. Assessing MoCA in 897 participants, including healthy individuals and a clinical group with various dementia forms, the study evaluated the test's fit and reliability. It explored DIF related to pathology, gender, age, and education. The results showed good item and person fits with no severe misfit among items and strong discriminant validity, especially between control and clinical groups. Although some items exhibited DIF, it was balanced across variables, mitigating score bias concerns. This balanced DIF contrasts with our findings, where educational background significantly influenced domain performance. These differences might stem from the use of distinct IRT models (Rasch vs. GRM), the handling of item scores (dichotomous vs. polytomous), and the focus on different clinical populations (dementia vs. PD). Future studies could directly compare these analytical approaches and populations to highlight these discrepancies.
Our study provides novel insights into the MoCA's application in PD patients. The Attention and Naming domains demonstrated high discrimination ability, underscoring their importance in detecting cognitive impairments. However, the Orientation and Naming domains showed limitations in differentiating individuals with higher cognitive abilities, suggesting a potential ceiling effect. Clinicians should interpret perfect or near-perfect scores in these domains cautiously and consider supplementing the MoCA with more challenging tasks when assessing individuals with previously high cognitive functioning. The significant effect of educational attainment on MoCA scores necessitates careful consideration in clinical practice. Adjusting cutoff scores based on patients' educational backgrounds could mitigate the risk of misdiagnosing cognitive impairment, while developing education-specific norms for PD populations could enhance diagnostic accuracy.
The MIMIC analysis revealed the differential impact of age and education on MoCA domains. Age exhibited a modest negative effect on cognitive performance, while education demonstrated a strong positive influence, particularly on Executive Functions (96%) and Naming (19%). These findings emphasize the importance of considering patients' educational backgrounds when interpreting MoCA performance and suggest the potential for education-based interventions to promote cognitive resilience in PD. The analysis also indicated that age and education independently influenced MoCA performance, with no significant covariance between them. This suggests that the cognitive benefits of education may persist across the lifespan, potentially buffering against age-related decline. Clinically, these results highlight the importance of lifelong learning and cognitive stimulation in maintaining brain health, especially in neurodegenerative disorders like PD.
To address the psychometric limitations of the MoCA identified in our study, we propose a refined approach for its application in PD patients. We advocate for the calibration of test items using IRT to account for educational variability and the development of tailored MoCA versions with reduced educational bias. Additionally, we recommend supplemental assessments to better evaluate high cognitive performers and the establishment of large sample demographic-specific norms for more accurate score interpretation. The integration of technology, such as a web-based application utilizing the GRM for automated MoCA scoring, could significantly enhance diagnostic precision by individualizing item weighting. These refinements could substantially improve the MoCA's utility in diagnosing and tracking cognitive impairment in PD patients across diverse educational backgrounds.
We acknowledge the limitations of the study. The relatively small sample size and non-random participant selection may challenge the generalizability of our findings. Our sample, drawn from specialized clinics, might not fully represent the broader PD population, potentially excluding patients with more severe cognitive or motor impairments. Future research should aim to recruit larger, more diverse PD samples using random sampling methods. Additionally, while our analysis focused on the impact of education and age on Differential Item Functioning (DIF), it did not explore other potential contributing factors such as gender or cultural influences. Future studies should investigate a broader range of sociodemographic and cultural variables on MoCA performance in PD and develop strategies to mitigate their influence. Furthermore, the cross-sectional design of our study limits causal inferences about the relationships between demographic factors and cognitive performance. Longitudinal studies are necessary to elucidate the temporal dynamics of these associations and investigate the protective role of education against cognitive decline in PD over time.
Furthermore, our study focused on the MoCA as a global cognitive screening tool and did not include a comprehensive neuropsychological assessment battery. While the MoCA has demonstrated utility in detecting cognitive impairment in PD, it may not capture the full spectrum of cognitive deficits associated with the disease. Future research should explore the relationship between MoCA performance and more comprehensive cognitive assessments in PD and its predictive validity for clinical outcomes such as dementia risk and functional decline.
In conclusion, our study demonstrates the utility of the IRT GRM approach in assessing the MoCA test's psychometric properties, revealing unidimensionality with variable domain discrimination and significant age and education influences. The findings highlight the necessity of considering these factors in MoCA score interpretation and advocate for refined, education-adjusted norms in clinical practice. MIMIC analysis indicates a strong positive impact of education and a modest negative effect of age on MoCA performance, suggesting education is a protective factor against cognitive decline in PD. Future research should expand DIF investigations, develop strategies to address measurement invariance and conduct longitudinal studies to explore the protective role of education over time. Integrating IRT and MIMIC modeling in cognitive screening tool validation promises to enhance our understanding of socio-demographic influences on cognitive health, leading to more personalized and equitable cognitive assessments in PD and other neurological conditions.