Submitted:
19 December 2024
Posted:
20 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
In the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and large-scale distributed networks, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) face significant challenges in handling complex spatiotemporal features and addressing data imbalance issues. This article systematically reviews recent advancements in applying deep learning techniques in IDS, focusing on the core challenges of spatiotemporal feature extraction and data imbalance. First, this article analyzes the spatiotemporal dependencies of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) in network traffic feature extraction and examines the main methods these models use to solve this problem. Next, the impact of data imbalance on IDS performance is explored, and the effectiveness of various data augmentation and handling techniques, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and resampling methods, in improving the detection of minority class attacks is assessed. Finally, the paper highlights the current research gaps and proposes future research directions to optimize deep learning models further to enhance the detection capabilities and robustness of IDS in complex network environments. This review provides researchers with a comprehensive perspective, helping them identify the challenges in the current field and laying a foundation for future research efforts.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- The paper reviews recent advancements in deep learning applications for IDS, focusing on challenges in spatiotemporal feature extraction.
- It evaluates techniques like CNNs, RNNs, and GANs in handling complex network traffic and addressing data imbalance to improve the detection of minority class attacks.
- The paper identifies key research gaps and proposes future directions to enhance the effectiveness and robustness of deep learning models in IDS.
2. Research Methodology
- “Deep Learning Intrusion Detection Survey”
- “Deep Learning Intrusion Detection Review”
- “Deep Learning Intrusion Detection Overview”
- “Deep Learning Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction Intrusion Detection Survey or Review”
- “Deep Learning Data Imbalance Intrusion Detection Survey or Review”
- “Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction Intrusion Detection”
- “Data Imbalance Intrusion Detection”
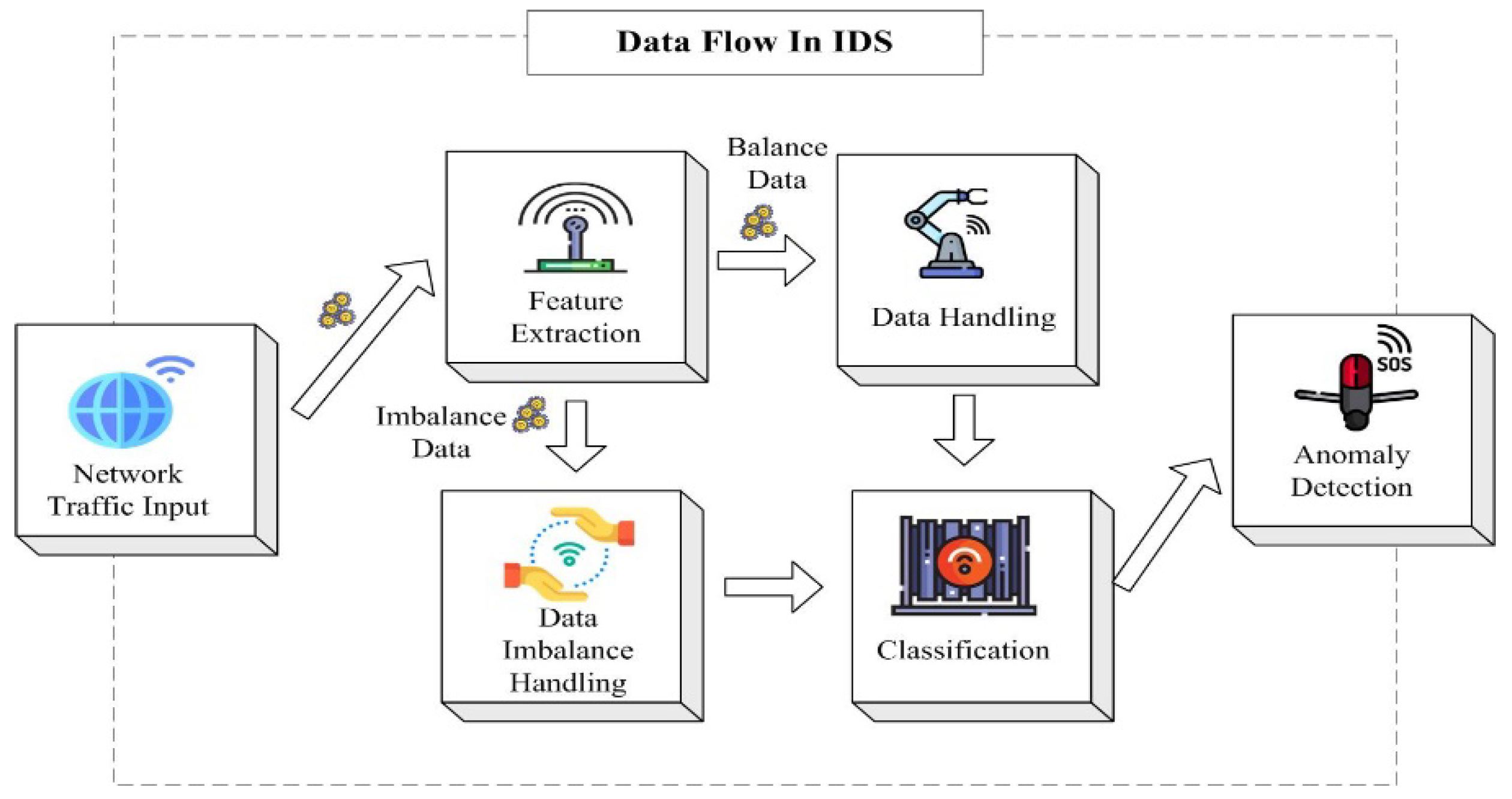
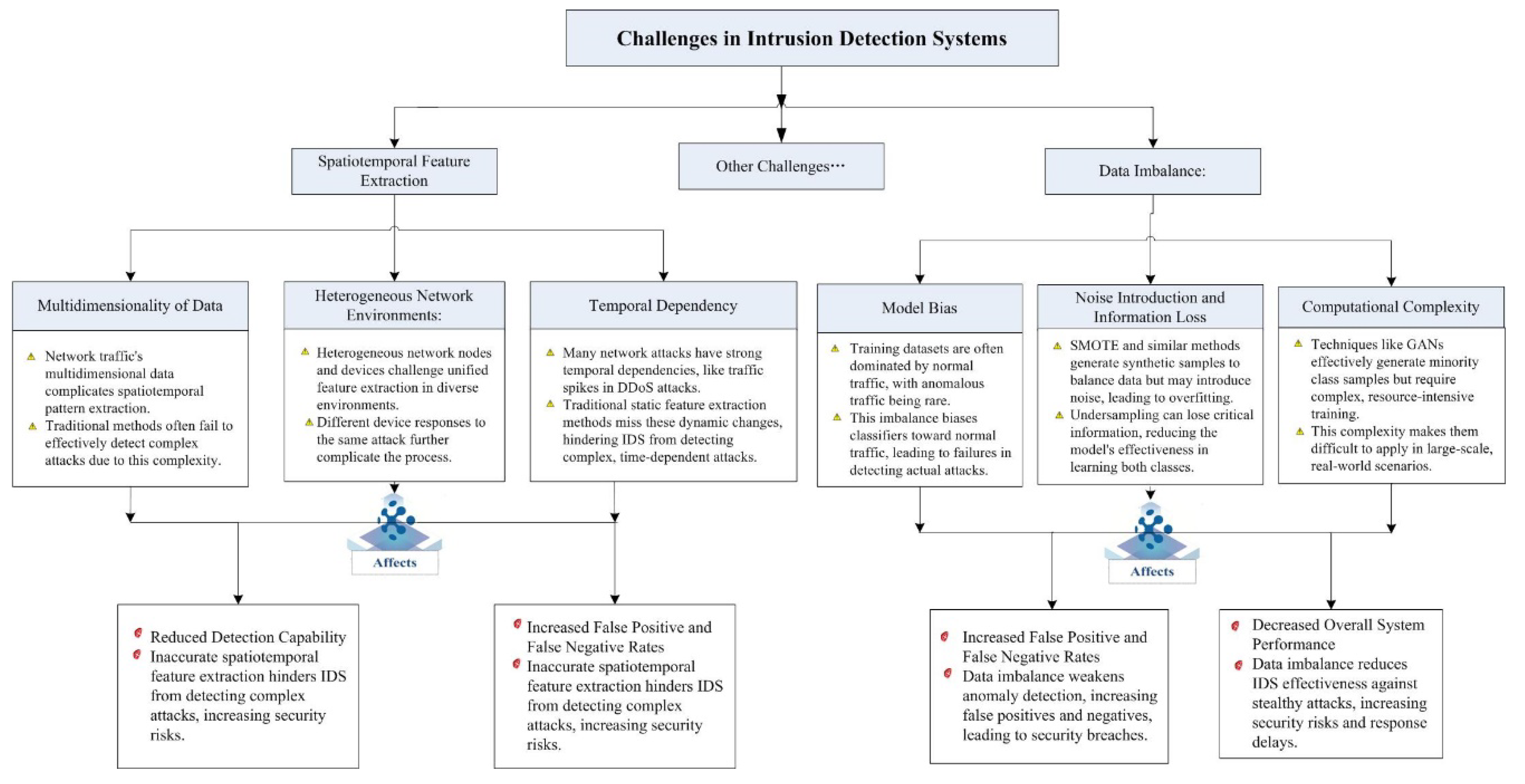
3. Challenges in Intrusion Detection Systems
3.1. Complexity and Importance of Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction
3.2. Challenges of Data Imbalance
4. Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction Techniques
4.1. Traditional Feature Extraction Methods
4.2. Application of Deep Learning Models
4.2.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
4.2.3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
4.3. Autoencoders and Other Enhanced Methods
4.4. Hybrid Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction Models
4.5. Future Research Directions
4.5.1. Optimization of Computational Efficiency and Real-Time Processing
4.5.2. Self-Supervised and Semi-Supervised Learning
4.5.3. 3D Convolutional Neural Network
4.5.4. Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Networks
4.5.5. Attention Mechanisms
4.5.6. Transformer
4.5.7. Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Networks (ST-GNNs)
5. Data Imbalance
5.1. Data Imbalance Handling Techniques
5.1.1. Traditional Oversampling Methods
5.1.2. Undersampling Methods
5.1.3. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
5.2. Limitations of Data Imbalance Handling Techniques
5.2.1. Overfitting and Noise Issues
5.2.2. Computational Complexity and Model Stability
5.2.3. Lack of Adaptability and Scalability
5.3. Future Research Directions
5.3.1. Adaptive Sampling Techniques
5.3.2. Meta-Learning and GAN Integration
5.3.3. Deep Learning and Traditional Methods Integration
5.3.4. Attention Mechanism
5.3.5. Multi-Task Learning
5.3.6. Transfer Learning
5.3.7. Signing of a New Loss Function
5.3.8. Strategy of Combining Data Augmentation with Contrastive Learning
6. Conclusion
7. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullahi, M.; Baashar, Y.; et al. Detecting cybersecurity attacks in internet of things using artificial intelligence methods: a systematic literature review. Electron 2022, 11(2), 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraisat, A.; Alazab, A. A critical review of intrusion detection systems in the internet of things: techniques, deployment strategy, validation strategy, attacks, public datasets and challenges. Cybersecurity 2021, 4(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Sun, Z. GHM-DenseNet intrusion detection method based on GAN. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE 4th International Conference on Civil Avi-ation Safety and Information Technology, ICCASIT 2022, Chengdu, China, 12-14 Oct. 2022; pp. 1341–48. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L. Network intrusion detection based on Dual-Encoder generative adversarial network. EEI 2022 - 4th Int Conf Electron Eng Informatics, Guiyang, China, 24-26 June 2022; pp. 625–631. [Google Scholar]
- Zuech, R.; Hancock, J.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Detecting web attacks in severely imbalanced network traffic data. Proceedings - 2021 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration for Data Science, IRI 2021, San Diego, CA, USA, 10-12 Aug. 2021; pp. 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Rahma, F.; Rachmadi, R.F.; et al. Assessing the effectiveness of oversampling and undersampling techniques for intrusion detection on an imbalanced dataset. IEACon 2023 - 2023 IEEE Ind Electron Appl Conf, Singapore, 16-19 Oct. 2023; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Imrana, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Ali, L.; et al. CNN-GRU-FF: a double-layer feature fusion-based network intrusion detection system using convolutional neural network and gated recurrent units. Complex Intell. Syst. [Internet] 2024, 10(3), 3353–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, P.; et al. DL-IDS: extracting features using CNN-LSTM hybrid network for intrusion detection system. Secur. Commun. Networks 2020, special issue, 8890306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakidis, S.; Karlsson, P. A novel feature extraction methodology using Siamese convolutional neural networks for intrusion detection. Cybersecurity 2020, 3(1), 221114272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, K.M.E.; Santhi, M.E. Unified deep learning approach for efficient intrusion detection system using integrated spatial–temporal features. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2021, 226(17), 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.N.; Suresh, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Babu, K.S. An imbalanced generative adversarial network-based approach for network intrusion detection in an imbalanced dataset. Sensors (Basel) 2023, 23(1), 23010550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Sharma, L.; Lal, C.; Roy, S. Anomaly based network intrusion detection for IoT attacks using deep learning technique. Comput. Electr. Eng. [Internet] 2023, 107, 108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, S.; Han, Q.; Li, Q. CNN spatiotemporal features and fusion for surveillance video forgery detection. Signal Process Image Commun. 2021, 90, 116066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Spatiotemporal co-attention recurrent neural networks for human-skeleton motion prediction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal Mach. Intell. 2022, 44(6), 3300–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Tian, T.; et al. A CVAE-GAN-Based approach to process imbalanced datasets for intrusion detection in marine meteorological sensor networks. Proceedings-2022 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking, Melbourne, Australia, 2022, 197–203.
- Alghamdi, R.; Bellaiche, M. An ensemble deep learning based IDS for IoT using Lambda architecture. Cybersecurity 2023, 6(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musafer, H.; Abuzneid, A.; Faezipour, M.; Mahmood, A. An enhanced design of sparse autoencoder for latent features extraction based on trigonometric simplexes for network intrusion detection systems. Electron 2020, 9(2), 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsameraee, A.; Alsameraee, A.; Ibrahem, M.K. ; Toward constructing a balanced intrusion detection dataset. Samarra J. Pure. Appl. Sci. 2021, 2(3), 132–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, V.; Maurtua, I.; et al. A survey on generative adversarial networks for imbalance problems in computer vision tasks. Journal of Big Data 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, F.; Hussain, R.; et al. Machine learning in IoT security: current solutions and future challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22(3), 1686–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Garadi, M.A.; Mohamed, A.; et al. A survey of machine and deep learning methods for internet of things (IoT) security. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22(3), 1646–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotunde, J.B.; Misra, S. ; Feature extraction and artificial intelligence-based intrusion detection model for a secure internet of things networks. Lect. Notes Data Eng. Commun. Technol. 2022, 109, 21–44. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Chakraborty, P.; Sharma, A. Deep convolutional generative adversarial networks for traffic data imputation encoding time series as images. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12(1), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, P.; Brzychczy, E.; Zimroz, R. Decision tree-based classification for planetary gearboxes’ condition monitoring with the use of vibration data in multidimensional symptom space. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20(21), 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharipuddin, S.; Winanto, E.A.; Purnama, B.; et al. Enhanced deep learning intrusion detection in iot heterogeneous network with feature extraction. Indones J Electr Eng Informatics 2021, 9(3), 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, F.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zou, Q. Non-local spatial and temporal attention network for video-based person re-identification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10(15), 225471111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatani, A.; Dahou, A.; et al. Advanced feature extraction and selection approach using deep learning and aquila optimizer for iot intrusion detection system. Sensors 2022, 22(1), 35009682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, X. ; Sequence feature extraction-based APT attack detection method with provenance graphs. Sci. Sin. Informationis 2022, 52(8), 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboaoja, F.A.; Zainal, A.; et al. Malware detection issues, challenges, and future directions: a survey. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2022, 12, 8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S. Model robustness optimization method using GAN and feature pyramid. J Front Comput Sci Technol 2023, 17(5), 1139–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wongvorachan, T.; He, S.; Bulut, O. A comparison of undersampling, oversampling, and SMOTE methods for dealing with imbalanced classification in educational data mining. Inf. 2023, 14(1), 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapre, S.; Islam, K.; Ahmadi, P. A comprehensive data sampling analysis applied to the classification of rare IoT network intrusion types. 2021 IEEE 18th Annu Consum Commun Netw Conf CCNC. Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9-12 Jan. 2021, 21–2.
- Saikam, J.; Koteswararao, C. A Comprehensive review of machine learning and deep learning techniques for addressing class imbalance issues in network intrusion detection systems. Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Recent Trends in Advance Computing, ICRTAC 2023, New Delhi, India, 14-15 Dec. 2023, 678–83.
- Narender, M.; Yuvaraju, B.N. Deep regularization mechanism for combating class imbalance problem in intrusion detection system for defending DDoS attack in SDN. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 19(3), 334–344. [Google Scholar]
- Mbow, M.; Koide, H.; Sakurai, K. An intrusion detection system for imbalanced dataset based on deep learning. Proceedings - 2021 9th International Symposi-um on Computing and Networking, CANDAR 2021, Fukuoka, Japan, 23-26 Nov. 2021, 38–47.
- Joloudari, J.H.; Marefat, A.; et al. Effective class-imbalance learning based on SMOTE and convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(6), 252070746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Tian, T.; Cai, L.; Ye, B.; Xing, H. A CVAE-GAN-based approach to process imbalanced datasets for intrusion detection in marine meteorological sensor networks. Proc - 2022 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking, Melbourne, Australia, 17-19 Dec. 2022, 1-8.
- Cui, J.; Zong, L.; Xie, J.; Tang, M. A novel multi-module integrated intrusion detection system for high-dimensional imbalanced data. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53(1), 272–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakthivelu, U.; Vinoth Kumar, C.N.S. A multi-step APT attack detection using hidden Markov models by molecular magnetic sensors. Opt. and Quantum. Electron. 2024, 56(3), 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, M.; Abbas, H.M.; Moustafa, N.; Sitnikova, E.; Sadek, R.A. Few-Shot learning for discovering anomalous behaviors in edge networks. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 69(2), 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.; Layeghy, S.; Moustafa, N.; Gallagher, M.; Portmann, M. Feature extraction for machine learning-based intrusion detection in IoT networks. Digit. Commun. Networks 2024, 10(1), 205–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.H.; Qiu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Z. A depthwise separable CNN-based interpretable feature extraction network for automatic pathological voice detection. Biomed Signal Process Control 2024, 88, 264948156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y. A new AI-based approach for automatic identification of tea leaf disease using deep neural network based on hybrid pooling. Heliyon 2024, 10(5), e26465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Khan, S.A.; Shaheen, M.; Saba, T.; et al. Prosperous human gait recognition: an end-to-end system based on pre-trained CNN features selection. Multimed Tools Appl. 2024, 83(5), 14979–14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagrabi, A.O. A deep CNN-LSTM-Based feature extraction for Cyber-Physical system monitoring. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 76(2), 2079–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, K.; Sasirekha, V.; Devi, S. Detection of sarcastic sentiment analysis in tweets using lstm with improved attention based feature extraction. J Theor Appl Inf Technol. 2023, 101(18), 264380718. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y. Design of english teaching speech recognition system based on LSTM network and feature extraction. Soft Comput. 2023, 05 June, 08550w. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corizzo, R.; Zdravevski, E.; Russell, M.; Vagliano, A.; Japkowicz, N. Feature extraction based on word embedding models for intrusion detection in network traffic. J. Surveill. Secur. Saf. 2020, 1, 140–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Guan, W. Intrusion detection method based on wasserstein generative adversarial network. Proceedings - 2022 2nd International Con-ference on Frontiers of Electronics, Information and Computation Technologies, ICFEICT 2022, Bhubaneswar, India, 2022, 599–603.
- Chao, W.; Wenhui, W.; Jiahan, D.; et al. Research on network intrusion detection yechnology based on DCGAN. 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12-14 March 2021, 1418-1422.
- Li, F.; Ma, W.; Li, H.; Li, J. Improving intrusion detection system using ensemble methods and over-sampling technique. 2022 4th International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation (IAECST), Guangzhou, China, 9-11 Dec. 2022, 1200-1205.
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Research on intrusion detection method based on generative adversarial network. 2021 International Conference on Big Data Analysis and Computer Science (BDACS), Kunming, China, 25-27 June 2021; pp. 264–268. [Google Scholar]
- Dener, M.; Al, S.; Orman, A. STLGBM-DDS: an efficient data balanced DoS detection system for wireless sensor networks on big data environment. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 92931–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.S.; Danyali, H. Nuclear atypia grading in breast cancer histopathological images based on CNN feature extraction and LSTM classification. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2021, 6(4), 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Xu, L.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, J. Web traffic anomaly detection using a hybrid spatio-temporal neural network. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Honolulu, Oahu, HI, USA, 1-4 Oct. 2023; pp. 5009–5014. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.R.; Arun, K.U.; Gopinath, S.; et al. A novel deep learning-based approach for detecting attacks in social IoT. Soft Comput. 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, F.; et al. CNN-LSTM hybrid model to promote signal processing of ultrasonic guided lamb waves for damage detection in metallic pipelines. Sensors 2023, 23(16), 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, B.; Lacerda, P.; Albuquerque, C.; Conci, A. Pulmonary COVID-19: learning spatiotemporal features combining CNN and LSTM networks for lung ultrasound video classification. Sensors 2021, 21(16), 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y. Res-TranBiLSTM: An intelligent approach for intrusion detection in the Internet of Things. Comput Networks 2023, 235, 109982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gong, X.; Fan, J. Spatiotemporal distance and multiple networks mutual learning-relevant pedestrian re-identification. J. Image Graph. 2023, 28(5), 273257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, B.; Bhosale, S. Hybrid optimization enabled robust CNN-LSTM technique for network intrusion detection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 65611–65622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.; Bao, X.; Cui, H. Outlet water temperature prediction of energy pile based on spatial-temporal feature extraction through CNN–LSTM hybrid model. Energy 2023, 264, 126190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttala, R.; Subramanian, R.; Oruganti, V.R.M. Multimodal hierarchical CNN feature fusion for stress detection. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 6867–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Ju, F.R. A method of hierarchical feature fusion and connected attention architecture for pavement crack detection. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. 2022, 23(9), 16038–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, W.; Zou, X.; Xia, W.; et al. Smart-DNN+: A memory-efficient neural networks compression framework for the model inference. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. 2023, 20(4), 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Tan, S.H.; Lambrechts, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, K. A 400MHz NPU with 7.8TOPS2/W high-performance guaranteed efficiency in 55nm for multi-mode pruning and diverse quantization using pattern-kernel encoding and reconfigurable MAC units. In Proceedings of the Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 25-30 April 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Olatinwo, D.D.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.; Hancke, G.; Myburgh, H. IoT-Enabled WBAN and machine learning for speech emotion recognition in patients. Sensors 2023, 23(6), 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Tian, X.; Wei, Q.; Liu, Y. A self-attention based contrastive learning method for bearing fault diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, J.; Asil, H. A review of various semi-supervised learning models with a deep learning and memory approach. Iran. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 2(2), 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Wang, G. Deep vision multimodal learning: methodology, benchmark, and trend. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2022, 12(13), 6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; He, R.; Feng, J. Source data-absent unsupervised domain adaptation through hypothesis transfer and labeling transfer. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2022, 44(11), 8602–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7-13 Dec. 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.; Min, X.; Luo, T.; et al. Computed tomography-based 3D convolutional neural network deep learning model for predicting micropapillary or solid growth pattern of invasive lung adenocarcinoma. Radiol Medica. 2024, 129(5), 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Yan, L.; Li, J.; Plaza, A.; Li, B. A new spatio-temporal fusion method for remotely sensed data based on convolutional neural networks. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium(IGARSS), Yokohama, Japan, 2019, 835-838.
- Nakagawa, A.; Sukigara, M.; Benga, O. The temporal relationship between reduction of early imitatitve responses and the development of attention mechanisms. BMC Neuroscience 2003, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plisiecki, H.; Sobieszek, A. Extrapolation of affective norms using transformer-based neural networks and its application to experimental stimuli selection. Behav. Res. Methods 2023, 56, 4716–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, G.; Ragazzi, L.; Valgimigli, L.; Frisoni, G.; et al. Efficient memory-enhanced transformer for long-document summarization in low-resource regimes. Sensors 2023, 23(7), 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, X.X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; et al. Adaptive spatio-temporal graph neural network for traffic forecasting. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2022, 242, 108199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Son, J.; Seo, D.H.; et al. ST-GAT: A spatio-temporal graph attention network for accurate traffic speed prediction. The 31st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17-21 Oct., 2022, 252904856.
- Khlaisamniang, P.; Phoomvuthisarn, S. ST-CopulaGNN: A multi-view spatio-temporal graph neural network for traffic forecasting. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 10 - 12 July, 2023, 1-12.
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.P.; Shen, X.; et al. PWG-IDS: An intrusion detection model for solving class imbalance in IIoT networks using generative adversarial networks. arXiv:2110.03445 2021, arXiv:2110.03445. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, S.; Sun, C.; Yuwen, L. A novel early diagnostic framework for chronic diseases with class imbalance. Sci. Rep. [Internet] 2022, 12(1), 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kafhali, S.; Tayebi, M. Generative adversarial neural networks based oversampling technique for imbalanced credit card dataset. 2022 6th SLAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (SLAAI-ICAI), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1-2 Dec. 2022, 1-5.
- Ding, H.; Chen, L.; Dong, L.; et al. Imbalanced data classification: A KNN and generative adversarial networks-based hybrid approach for intrusion detection. Futur Gener Comput Syst. [Internet] 2022, 131, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y.; et al. Learning-based intrusion detection for high-dimensional imbalanced traffic. Comput Commun. 2023, 212, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, A.; El-Fishawy, N.; Badawy, M.; Radad, M. RN-SMOTE: reduced noise SMOTE based on DBSCAN for enhancing imbalanced data classification. J. King Saud Univ - Comput Inf Sci. 2022, 24(8), 5059–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.D.; Vuong, T.C.; Van-Luong, T.; Tran, H. ; Machine learning-based intrusion detection: feature selection versus feature extraction. Cluster Comput. 2024, 27(3), 2365–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X. Intrusion detection method for internet of vehicles based on parallel analysis of spatio-temporal features. Sensors 2023, 23(9), 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefnezhad, M.; Hamidzadeh, J.; Aliannejadi, M. Ensemble classification for intrusion detection via feature extraction based on deep Learning. Soft Comput. 2021, 25(20), 12667–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.P.; Wang, J.J.; Dong, S.L.; et al. Selective ensemble learning for soft sensor development based on deep learning for feature extraction and multi-objective optimization for ensemble pruning. Kongzhi yu Juece/Control Decis. 2023, 38(3), 738–750. [Google Scholar]
- Sayegh, H.R.; Dong, W.; Al-madani, A.M. Enhanced intrusion detection with LSTM-Based model, feature selection, and SMOTE for imbalanced data. Appl Sci. 2024, 14(2), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.W.; Xiong, M.; Yang, Z.H. Real and fake channel: GAN-based wireless channel modeling and generating. Physical Communication 2023, 61, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.A.; Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.A.; et al. Machine learning-based network intrusion detection for big and imbalanced data using oversampling, stacking feature embedding and feature extraction. J. Big Data [Internet]. 2024, 11(1), 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.T.; Khandokar, I.A.; Shatabda, S. New boosting approaches for improving cluster-based undersampling in problems with imbalanced data. Decis Anal J. 2023, 8, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, R.A.; Pardede, H.F.; Subekti, A. Oversampling based on generative adversarial networks to overcome imbalance data in predicting fraud insurance claim. Kuwait J Sci. 2022, Special Issue, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndichu, S.; Ban, T.; Takahashi, T.; Inoue, D. AI-Assisted security alert data analysis with imbalanced learning methods. Appl Sci. 2023, 13(3), 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, F.A.H.; Syed, I.S.P. Multi-stage deep investigation pipeline on detecting malign network traffic. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 62, 4726–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, A.; Habaebi, M.H.; Elsheikh, E.A.A.; et al. The effect of dataset imbalance on the performance of SCADA intrusion detection systems. Sensors 2023, 23(2), 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkah, A.S.; Selamat, S.R.; Abidin, Z.Z.; Wahyudi, R. Impact of data balancing and feature selection on machine learning-based network intrusion detection. Int. J. Informatics Vis. 2023, 7(1), 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Antypenko, R.; Sushko, I.; Zakharchenko, O. Intrusion detection system after data augmentation schemes based on the VAE and CVAE. IEEE Trans Reliab. 2022, 71(2), 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedzadeh, N.; Jacobs, M. A reinforcement learning framework with oversampling and undersampling algorithms for intrusion detection system. Appl Sci. 2023, 13(20), 11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaddi, H.; Jouhari, M.; Ibrahimi, K.; et al. Anomaly detection in industrial IoT using distributional reinforcement learning and generative adversarial networks. Sensors 2022, 22(21), 8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Li, Q.; Li, M. A method for network intrusion detection based on GAN-CNN-BiLSTM. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14(5), 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lei, K. IGAN-IDS: An imbalanced generative adversarial network towards intrusion detection system in ad-hoc networks. Ad. Hoc. Networks 2020, 105, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xia, S.; Chen, Z.; et al. RSMOTE: A self-adaptive robust SMOTE for imbalanced problems with label noise. Inf. Sci (Ny). 2021, 553, 397–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuningsih, L.; Pradipta, G.A.; Hermawan, D.; et al. IRS-BAG-Integrated Radius-SMOTE algorithm with bagging ensemble learning model for imbalanced data set classification. Emerg. Sci. J. 2023, 7(5), 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Li, Y. An imbalanced learning method by combining SMOTE with Center Offset Factor. Appl Soft Comput. 2022, 120, 108618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaeddini, A.; Majidi, B.; Souri, A.; Eshghi, M. Data augmentation using fast converging CIELAB-GAN for efficient deep learning dataset generation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2023, 26(4), 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Kang, S.J. A generative adversarial network-based image denoiser controlling heterogeneous losses. Sensors (Switzerland) 2021, 21(4), 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megahed, M.; Mohammed, A. A comprehensive review of generative adversarial networks: Fundamentals, applications, and challenges. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics 2024, 16(1), e1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yao, X.; Chen, Y. An imbalanced-data processing algorithm for the prediction of heart attack in stroke patients. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 25394–25404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanat, A.B.; Tarawneh, A.S.; Abed, S.S.; et al. RDPVR: Random data partitioning with voting rule for machine learning from class-imbalanced datasets. Electron. 2022, 11(2), 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, S.; Senvar, O. Comparing performances and effectiveness of machine learning classifiers in detecting financial accounting fraud for turkish SMEs. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2021, 14(1), 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, H.; Nguyen, X.; Dang, T.K.; Tran-Truong, P.T. Money laundering detection using a transaction-based graph learning approach. 2024 18th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (IMCOM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3-5 Jan. 2024, 1-8.
- Kaminsky, A.L.; Wang, Y.; Pant, K. An efficient batch K-fold cross-validation voronoi adaptive sampling technique for global surrogate modeling. J. Mech. Des. 2021, 43(1), MD-19-1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghalhoud, O.; Naik, K.; Zaman, M.; at, al. Data balancing and CNN based network intrusion detection system. 2023 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Glasgow, United Kingdom, 26-29 March 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zakariah, M.; AlQahtani, S.A.; Al-Rakhami, M.S. Machine learning-based adaptive synthetic sampling technique for intrusion detection. Appl Sci. 2023, 13(11), 6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.R.; McDaniel, W.L. Adaptive sampling technique. IEEE Trans Automat Control 1969, 14(2), 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, Y.K.; Abdulganiyu, O.H.; Tchakoucht, T.A. ; Modified genetic algorithm and fine-tuned long short-term memory network for intrusion detection in the internet of things networks with edge capabilities. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 155, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospedales, T.; Antoniou, A.; Micaelli, P.; Storkey, A. Meta-Learning in neural networks: a Survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2022, 44(9), 5149–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauata, N.; Hosseini, S.; Chang, K.H.; et al. House-GaN++: Generative adversarial layout refinement network towards intelligent computational agent for professional architects. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20-25 June 2021; pp. 13627–13636. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Huang, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, X.; Peng, S.J. Unsupervised meta-learning via spherical latent representations and dual VAE-GAN. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53(19), 22775–22788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Pandya, S. Internet of things applications, security challenges, attacks, intrusion detection, and future visions: a systematic review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 59353–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Peng, Z.; Wei, J.; et al. An effective integrated intrusion detection model based on deep neural network. 2021 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), Kunming, China, 25-27 June 2021, 146-152.
- Kk, S.; Shrivastava, S.; Sangeetha, V. Anomaly-based intrusion detection using GAN for industrial control systems. 2022 10th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 2022, 1-6.
- Dina, A.S.; Siddique, A.B.; Manivannan, D. ; Effect of balancing data using synthetic data on the performance of machine learning classifiers for intrusion detection in computer networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 96731–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, Y. EIFDAA: evaluation of an IDS with function-discarding adversarial attacks in the IIoT. Heliyon [Internet] 2023, 9(2), e13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, Y. Ida-GAN: A novel imbalanced data augmentation GAN. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10-15 Jan. 2021, 8299-8305.
- An, C.S.; Sun, J.T.; Wang, Y.F.; Wei, Q.J. A K-means improved CTGAN oversampling method for data imbalance problem. 2021 IEEE 21st International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability and Security (QRS), Hainan, China, 6-10 Dec. 2021, 883-887.
- Dang, X.; Li, Z. Network Intrusion detection approach based on convolutional neural network. 2022 4th International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE), Shenzhen, China, 27-29 May 2022, 247-251.
- Abdulkareem, S.A.; Foh, C.H.; Carrez, F.; Moessner, K. SMOTE-Stack for network intrusion detection in an IoT environment. 2022 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Rhodes, Greece, 30 June 2022, 1-6.
- Mahalakshmi, M.; Ramkumar, M.P.; Emil Selvan, G.S.R. SCADA intrusion detection system using cost sensitive machine learning and SMOTE-SVM. 2022 4th International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICAC3N), Greater Noida, India, 16-17 Dec. 2022, 332-337.
- Sridhar, S.; Sanagavarapu, S. Handling data imbalance in predictive maintenance for machines using SMOTE-based oversampling. 2021 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Lima, Peru, 22-23 Sept. 2021, 44-49.
- Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Fei, M.; Du, D.; Rakić, A. An intrusion detection method using ADASYN and bayesian optimized lightGBM. 2022 34th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Hefei, China, 15-17 Aug. 2022, 4622-4627.
- Liang, X.; Xing, H.; Hou, T. Network intrusion detection method based on CGAN and CNN-BiLSTM. 2023 IEEE 16th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Harbin, China, 9-11 Aug. 2023, 396-400.
- Kalita, I.; Chakraborty, S.; Reddy, T.G.G.; Roy, M. A deep learning-based technique for firm classification and domain adaptation in land cover classification using time-series aerial images. Earth Sci. Informatics 2024, 17(1), 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Shen, S.; Xu, M.; et al. Single model deep learning on imbalanced small datasets for skin lesion classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2022, 41(5), 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, I.F.; Megret, R.; Acuna, E.; at, al. Recognition of pollen-bearing bees from video using convolutional neural Nnetwork. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12-15 March 2018, 314-322.
- Yin, C.; Chen, S.; Yin, Z. Clustering-based active learning classification towards data stream. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2023, 14(2), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Han, S.; Li, W.; Shao, H.; Yang, X. A new framework for intelligent fault diagnosis of spiral bevel gears with unbalanced data. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53(18), 21312–21324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.R.; Yu, D.W.; Wu, M.H.; Jin, C.H.; Yu, H.C. Adversarial supervised contrastive learning. Mach. Learn. 2023, 112(6), 2105–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Hate speech detection via dual contrastive learning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang Process. 2023, 31, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Wang, R.; Chen, R.; Luo, S. A novel contrastive self-supervised learning framework for solving data imbalance in solder joint defect detection. Entropy 2023, 25(2), 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
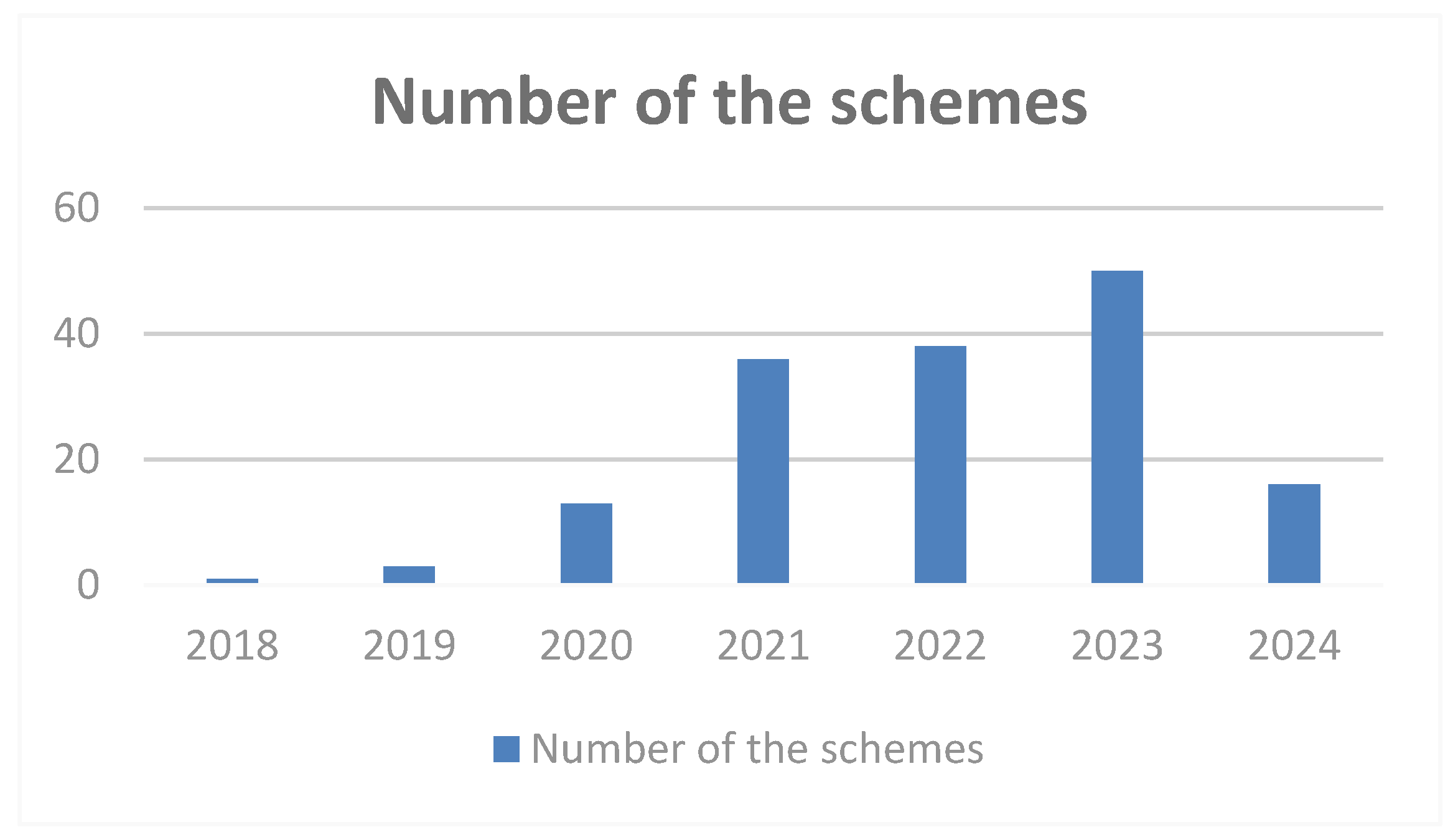
| ID | Site | Website | Introduce |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Google Scholar | https://scholar.google.com/ | A free academic search engine that searches across all disciplines for scholarly literature. |
| 2 | Web of Science | https://www.webofscience.com | Covers high-quality academic literature in natural sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities |
| 3 | Cnki | https://www.cnki.net/ | One of China’s largest digital academic literature publishing and retrieval platforms. It provides a wide range of academic journals, theses and dissertations, conference papers, newspapers, yearbooks, statistical data, and other resources. |
| 4 | IEEE Explore | http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/ | Covers high-quality academic literature in natural sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities |
| 5 | Science Direct | https://www.sciencedirect.com | Offers a broad range of scientific, technical, and medical journal articles and book chapters |
| 6 | Wiley Online Library | https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com | It provides a comprehensive online platform for academic research resources, covering a wide range of disciplinary fields, including natural sciences, engineering and technology, biomedical sciences, social sciences, and humanities. |
| 7 | ACM Digital Library | http://dl.acm.org/ | A leading digital library operated by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), focused on academic research in the fields of computer science and information technology. |
| 8 | Springer | www.springer.com | Provides a wide range of scientific, technical, and medical content, including books and journal articles. |
| ID | Dataset | Class Distribution | Model | Presion | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NSL-KDD dataset | Dos:53387、Normal: 7052 Probe: 14077、R2L: 3880 U2R: 119 |
RF | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.70 | - | [49,50] |
| SVM | 0.75 | 0.60 | 0.65 | - | ||||
| MLP | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.72 | - | ||||
| 2 | CIC-IDS-2017 | BENIGN:2273097 WebAttck:673 Bot:1966 PortScan:158930 |
RF | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.63 | 0.98 | [51] |
| LightGBM | 0.59 | 0.97 | 0.64 | 0.98 | ||||
| Xgboost | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.52 | 0.99 | ||||
| CatBoost | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.99 | ||||
| 3 | KDD-CUP99 | DoS 3,883,370 R2L: 1,126 U2R: 52 Probe: 41,102 Precision, Recall, and F1-Score are focused on the minority class data U2R |
CNN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.784 | [52] The situation where zeros appear, It may be due to the severe data imbalance. |
| CNN+GAN | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.807 | ||||
| CNN+VAE+GAN | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.814 | ||||
| MLP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.80 | ||||
| MLP+GAN | 0.44 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.812 | ||||
| MLP+VAE+GAN | 0.52 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.83 | ||||
| RNN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.76 | ||||
| RNN+GAN | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.80 | ||||
| RNN+VAE+GAN | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.81 | ||||
| 4 | WSN-DS dataset | Normal: 340066 Grayhole: 10049 TDMA: 3312 Flooding:6038 |
Decision Treee | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.975 | [53] |
| Random Forest | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.976 | ||||
| Naïve Bayes | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.925 | ||||
| STLGBM-DDS approach | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.995 | ||||
| 5 | UNSWNB15 | Normal: 77500 Exploits: 37104 DoS: 13628 Reconnaissance: 11656 Analysis: 2231 Backdoor: 1940 Shellcode: 1259 Worms: 145 |
Without sampling | 0,7772 | 0,5085 | 0,5295 | 0,9654 | [6] |
| Random OverSampling | 0,5757 | 0,6771 | 0,5895 | 0,9530 | ||||
| SMOTE | 0,5521 | 0,6764 | 0,5710 | 0,9528 | ||||
| ADASYN | 0,5376 | 0,6719 | 0,5592 | 0,9512 | ||||
| RandomUnderSampling | 0,4233 | 0,5633 | 0,3832 | 0,9307 | ||||
| AllKNN | 0,5543 | 0,4762 | 0,4952 | 0,9582 | ||||
| TomekLinks | 0,7586 | 0,5059 | 0,5327 | 0,9646 | ||||
| SMOTEENN | 0,5152 | 0,6425 | 0,5114 | 0,9432 | ||||
| SMOTETomek | 0,5577 | 0,6609 | 0,5778 | 0,9555 |
| ID | Model | Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction | Advantages | Challenges | Empirical Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) | Excels in capturing spatial features; limited in temporal feature extraction. Effective for image-like data but less so for time series without modifications (e.g., with Temporal Convolution Networks). | Strong spatial feature extraction, adaptable to various data formats (e.g., images, video). | High computational cost, struggles with temporal dependencies without architectural modifications. | [8,9,22,27,55,56,87,88] |
| 2 | Automatic Encoder(Autoencoder) | Extract essential features through data reconstruction; can learn latent spatiotemporal representations in sequence-based AEs (e.g., LSTM Autoencoders). | Reduces dimensionality, effective noise removal. | Sensitive to anomalies and outliers, potentially requiring large datasets. | [17,48,89,90] |
| 3 | Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) | It specializes in capturing temporal dependencies, ideal for sequential data where timing is crucial (e.g., sensor data, IoT). | Handles long-term dependencies well, resilient to abrupt changes in data streams. | It is computationally expensive, prone to gradient vanishing, requires extensive tuning. | [8,88,91] |
| 4 | Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) | Can generate synthetic temporal data to augment datasets, improving robustness in spatiotemporal models. | Enriches training datasets, and improves model generalization. | Training complexity, risk of mode collapse, difficult to stabilize. | [30,92] |
| 5 | Principal Component Analysis (PCA) | Reduces dimensionality, helping models focus on major spatiotemporal patterns by filtering out noise. | Simplifies data, and accelerates training. | Can miss nonlinear spatiotemporal relationships, potential loss of important features. | [41,93] |
| 6 | K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN ) | Simple, distance-based method; can be adapted for temporal sequences with dynamic time warping. | Easy to implement, adaptable to various data distributions. | Computationally intensive on large datasets, sensitive to noise, not ideal for imbalanced data. | [89] |
| ID | Method | Detection Accuracy | False Positive Rate | Dataset | Advantages | Challenges | Empirical Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Generative Adversarial Network (gan) | High accuracy in generating realistic data, improving detection of minority classes. | Low due to high-quality synthetic data reducing misclassification. | UNSW-NB15, NSL-KDD, CIC-IDS2017 | Produces realistic data, handles data scarcity, versatile across domains. | Complex training is sensitive to hyperparameters and dependent on original data quality. | [3,52,123,124] [125,126,127] [437,49,50] [3,49,84,125,128] |
| 2 | Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Network | Significantly improves detection, especially with imbalanced datasets. | Reduced due to better data representation. | UNSW-NB15、NSL-KDD、CIC-IDS2017 | High-quality synthetic data, effective on tabular data, handles imbalanced datasets well. | High training complexity, sensitive to parameters, depends on original data quality. | [51,126,129] |
| 3 | Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) | improves detection by balancing the dataset with synthetic samples. | This can increase due to potential misalignment with true data distribution. | UNSW-NB15、NSL-KDD、CIC-IDS2017 | Easy to implement, enhances minority class detection, reduces overfitting. | It may introduce noise, less effective on complex data, potential for increased false positives. | [35] [130] [131] [132,133] |
| 4 | Positive and Unlabeled learning with Oversampling Strategy | Improves detection by oversampling positive samples and using unlabeled data. | Generally reduced, but the risk of overfitting exists. | NSL-KDD and CICIIDS2017 | Effective with limited labeled data, balances datasets, reduces impact of unlabeled data. | It may introduce noise, overfitting risk, increased complexity. | [130] |
| 5 | Adaptive Synthetic Sampling | Enhances detection by focusing on difficult-to-classify samples. | Reduced by selective sample generation, avoiding overfitting. | CIC-IDS2017 | Targets challenging samples, reduces overfitting, improves performance on imbalanced datasets. | Higher complexity, noise risk, sensitive to parameters. | [134] |
| 6 | Random Oversampling | Improves detection by increasing minority class instances. | May increase due to potential overfitting. | NSL-KDD and UNSW-NB15 | Simple to implement, improves class representation, compatible with various models. | Overfitting risk, increased false positives, limited enhancement of true data distribution. | [126] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





