Submitted:
16 December 2024
Posted:
18 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
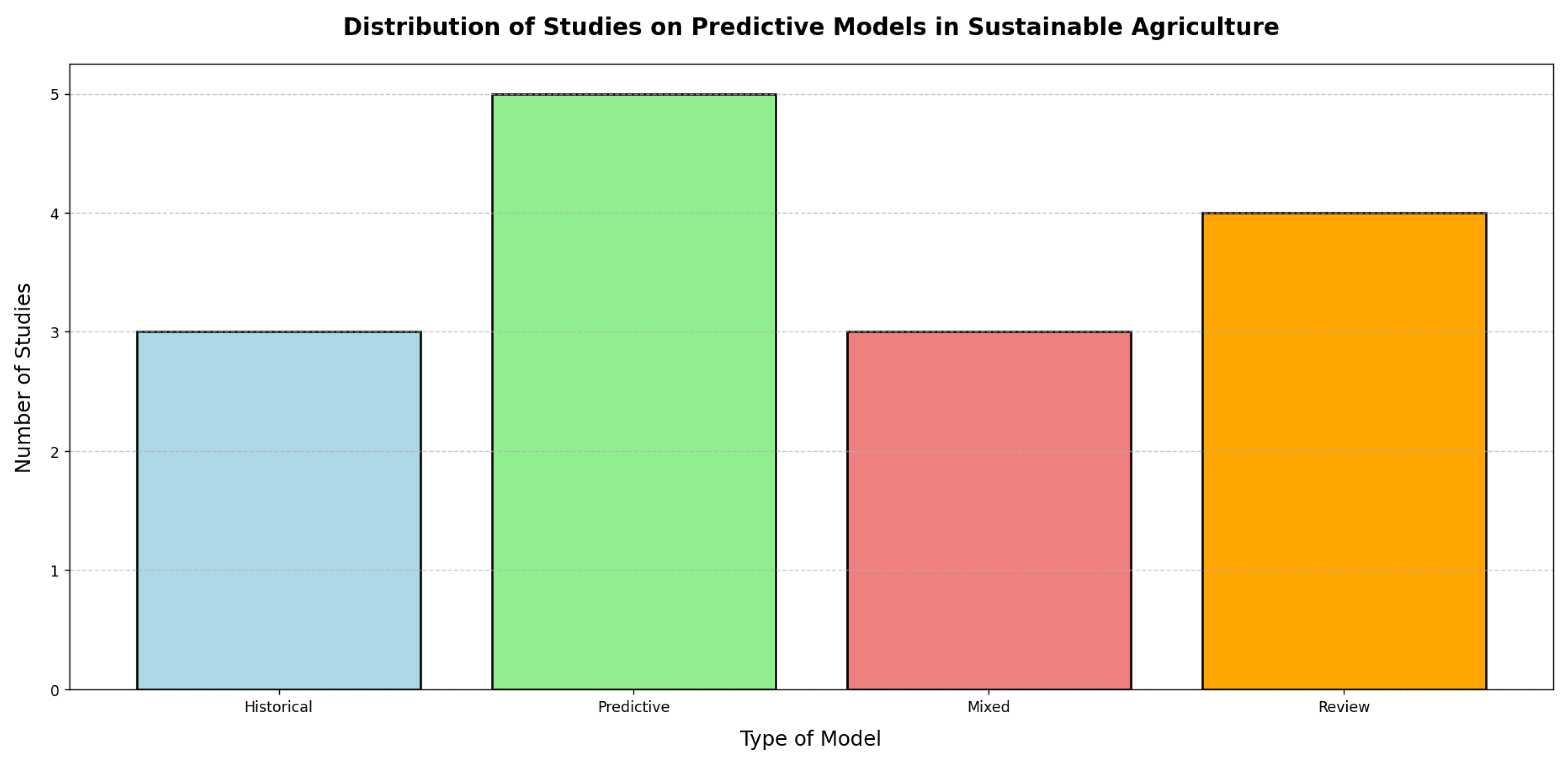
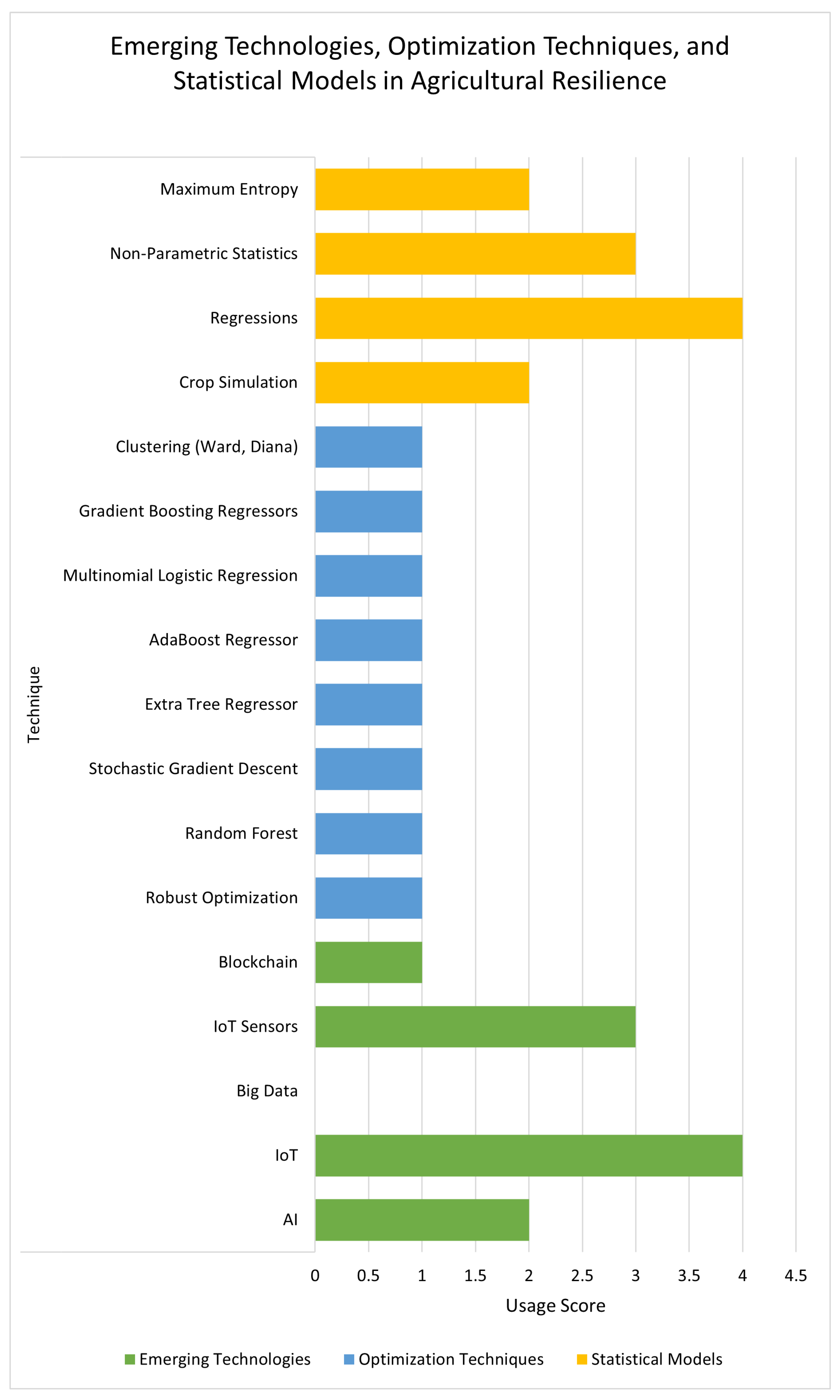
This paper analyses recent advances in predictive models applied to assessing the impact of climate change on sustainable agriculture and reviews optimization techniques, statistical models and emerging technologies. Through a review of 15 studies between 2013 and 2024, predictive techniques were identified to improve yields and manage resources such as water and fertilizers. The results show that most studies on sustainable agriculture focus on predictive models, followed by historical combinations and reviews, reflecting the interest in using data to improve sustainability. It also highlights the use of emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, Big Data and Blockchain, together with optimization techniques and statistical models, to improve efficiency and adaptation in agriculture to climate and production changes. It concludes that these technologies are essential to strengthen food security and agricultural resilience in the face of an uncertain climate environment.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
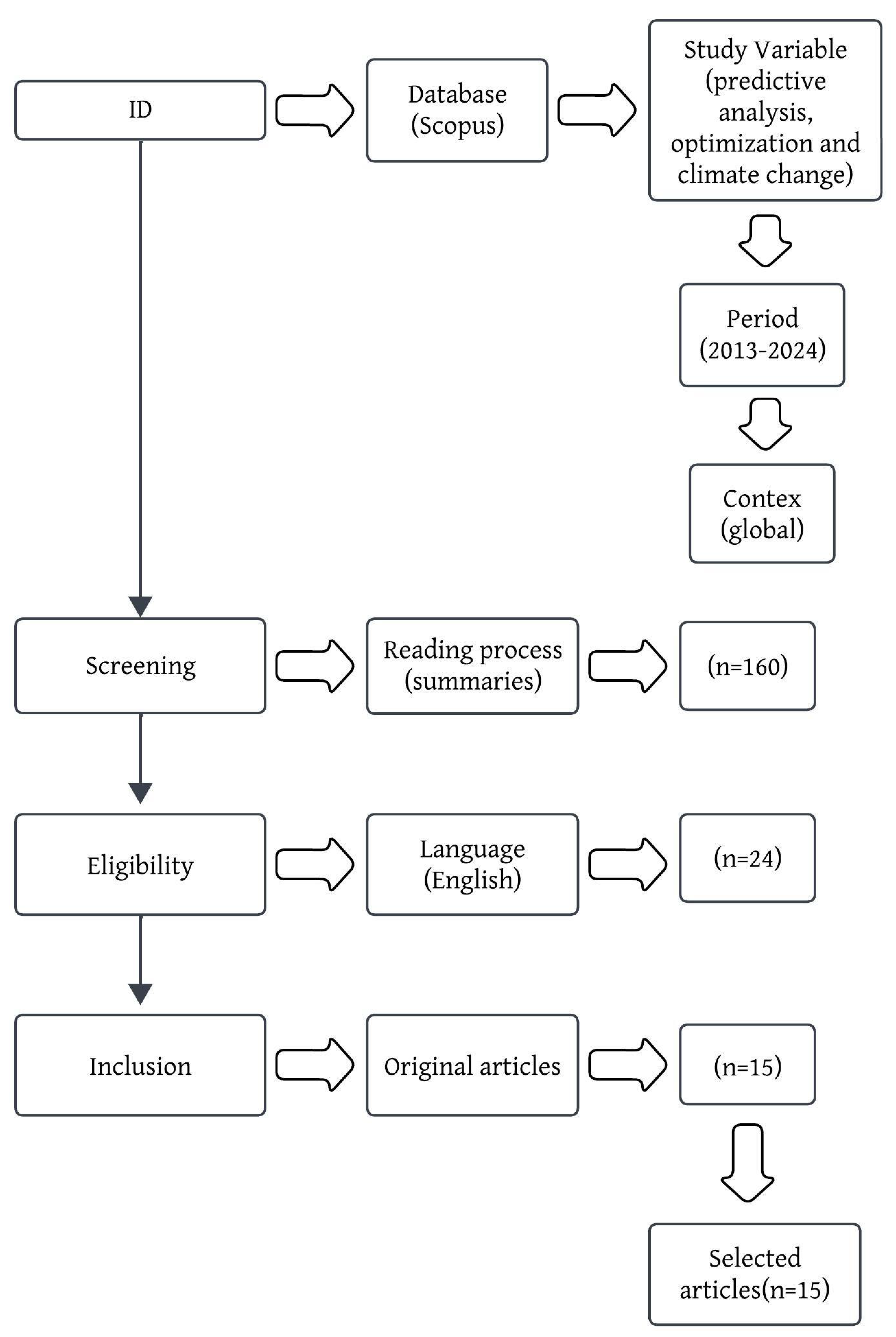
2. methodology
2.1. Type of Study
2.2. Techniques and Tools
2.3. Literature Search Procedure
2.4. Analysis of Studies
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
References
- Y.S. Say, M.W. Kei-Fong, E.N. Yin-Kwee. Adversarial Autoencoders for Agriculture Yield Forecasting. Carpathian Journal of Food Science and Technology 2022, 14, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Yin, D. Wei. Study on the Crop Suitability and Planting Structure Optimization in Typical Grain Production Areas under the Influence of Human Activities and Climate Change: A Case Study of the Naoli River Basin in Northeast China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al A. Lewis, J. Montgomery, M. Lewis; et al. Business As Usual Versus Climate-responsive, Optimised Crop Plans – A Predictive Model for Irrigated Agriculture in Australia in 2060. Water Resources Management 2023, 37, 2721–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E., Alreshidi. Smart Sustainable Agriculture (SSA) Solution underpinned by Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2019, 10, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.J. Roberts, N.O., Braun. Comparing and Combining Process-based Crop Models and Statistical Models with Some Implications for Climate Change. Environmental Research Letters 2017, 12, 095010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Okesola, O., Ifeoluwa. Predictive Analytics on Crop Yield Using Supervised Learning Techniques. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 2024, 36, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Ray, J., Gerber; et al. Climate Variation Explains a Third of Global Crop Yield Variability. Nature Communications 2015, 6, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W.N.W.A. Rahman, W.N.W., Zulkifli. Model for Responsive Agriculture Hub via e-Commerce to Sustain Food Security. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2024, 15, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. El-Maayar, M.A. Lange, "A Methodology to Infer Crop Yield Response to Climate Variability and Change Using Long-Term Observations", Atmosphere, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 365-382, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H.A. Hamid, Y.B., Wah. The Effect of Divisive Analysis Clustering Technique on Goodness-of-Fit Test for Multinomial Logistic Regression. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 39-48, 2025 2025, 48, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Vizcaíno, F., Cañizares. Internet of Things Based Predictive Crop Yield Analysis: A Distributed Approach. Fusion: Practice and Applications 2023, 1, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpa Gowri, D. , Ramachander, A., "Digital Agriculture", in Digital Agricultural Ecosystem (eds. K. Singh & P. Kolar), 2024. [CrossRef]
- N.H. Hussain, N.S.N. S. Ahmed, "Detection of spatiotemporal patterns of rainfall trends, using non-parametric statistical techniques, in Karnataka state, India", Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, vol. 195, art. no. 909, 2023. [CrossRef]
- T.S. Kumar, S. Arunprasad, A. Eniyan, P.A. Azeez, S.B. Kumar, P. Sushanth, "Crop Selection and Cultivation using Machine Learning", 2023 Intelligent Computing and Control for Engineering and Business Systems (ICCEBS), Chennai, India, 2023, pp. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Y.M. Leong, E.H. Lim, N.F.B. Subri, N.B.A. Jalil, "Transforming Agriculture: Navigating the Challenges and Embracing the Opportunities of Artificial Intelligence of Things", 2023 IEEE International Conference on Agrosystem Engineering, Technology & Applications (AGRETA), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 2023, pp. 142-147. [CrossRef]
- K. J. Shou, C. C., Wu. Predictive analysis of landslide susceptibility under climate change conditions—A study on the Ai-Liao Watershed in Southern Taiwan. Journal of GeoEngineering 2018, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C.Y. Rojo Ávila, B.P. Rojo Ávila, "Aplicación de la Inteligencia Artificial para hacer frente al cambio climático en el mundo", Congreso del Estado de Sinaloa, Instituto de Investigaciones Parlamentarias, Derecho y Opinión Ciudadana, 2024. https://iip.congresosinaloa.gob.mx/Rev_IIP/rev/015/007.
- I.J. Mirón, "La seguridad e inocuidad alimentarias frente al cambio climático. Adaptación y mitigación", Revista de Salud Ambiental, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 123-140, 2023. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=8999797.
- P. Pekárová, Z. Bajtek, J. Pekár, R. Výleta, O. Bonacci, P. Miklánek, J. U. Belz, and L. Gorbachova, "Monthly stream temperatures along the Danube River: Statistical analysis and predictive modelling with incremental climate change scenarios," Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, vol. 71, no. 4, pp. 382–398, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. S., Kimuyu. Comparative spatial–temporal analysis and predictive modeling of climate change-induced malaria vectors’ invasion in new hotspots in Kenya. SN Applied Sciences 2021, 3, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. Chen, M. X. Lin, L. P. Wang, et al., "Driving role of climatic and socioenvironmental factors on human brucellosis in China: machine-learning-based predictive analyses," Infect Dis Poverty, vol. 12, no. 36, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Sánchez-García, C., Rubio Bellido. El control adaptativo en instalaciones existentes y su potencial en el contexto del cambio climático. Revista Hábitat Sustentable 2017, 7, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Lozano-Povis, C. E. Alvarez-Montalván, and N. Moggiano-Aburto, "El cambio climático en los Andes y su impacto en la agricultura: una revisión sistemática," Scientia Agropecuaria, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 101–108, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. M. Mah, I., Skalna. Integration of sensors and predictive analysis with machine learning as a modern tool for economic activities and a major step to fight against climate change. J. Green Econ. Low-Carbon Dev. 2022, 1, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Author(s) | Year | Country | Type of Study | Sample Size | Techniques | Instruments | Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yueyang Symus Say, Mark Wong Kei-Fong, Eddie Ng Yin-Kwee | 2022 | Singapore | Research study on agricultural yield prediction using machine learning models. | 3 batches of Romaine lettuce images. | Adversarial Autoencoder (AAE), Machine Vision. | Smartphone, OpenCV | Predictive |
| 2 | Jian Yin and Danqi Wei | 2023 | China | Study on crop suitability and optimization of planting structure. | Total area of the Nile River Basin (26,480.25 km²). | Maximum entropy model (MaxEnt). | Climatic, ecological, hydrological, soil and socioeconomic data. | Predictive |
| 3 | Andrew Lewis, James Montgomery, Max Lewis, Marcus Randall, Karin Schiller | 2023 | Australia | Predictive model for irrigated agriculture. | Simulation models | Robust optimization and simulation models. | Climate data, crop requirements, costs and crop returns. | Predictive |
| 4 | Julius Olatunji Okesola, Olaniyi Ifeoluwa, Sunday Adeola Ajagbe, Olubunmi Okesola, Adeyinka O. Abiodun, Francis Bukie Osang, Olakunle O. Solanke | 2024 | Nigeria | Research study on predictive analysis of crop performance using supervised learning techniques. | 104 records | Random Forest, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Extra Tree Regressor, AdaBoost Regressor y Linear Regression | Python, Web Interface and Performance Metrics. | Predictive |
| 5 | Michael J Roberts, Noah O Braun, Thomas R Sinclair, David B Lobell, Wolfram Schlenker | 2017 | United States | Comparative research study on process-based crop models and statistical models. | 1,121,601 corn field observations in 741 counties. | Crop simulation models (simple simulation model) and statistical models (regressions). | Crop yield data, climate data (temperatures, precipitation), and simulation models. | Mixed |
| 6 | Deepak K. Ray, James S. Gerber, Graham K. MacDonald, Paul C. West | 2015 | United States | Global data analysis on crop yield variability and its relationship with climate variability. | 13,500 political units worldwide | Statistical analysis using time data on crops and climate variability (temperature and precipitation). | Data from the Climate Research Unit (CRU) and crop statistics. | Historical |
| 7 | Mustapha El-Maayar, Manfred A. Lange | 2013 | Egypt, Greece and Morocco | Study on the impact of climate change on crop yield. | National-level data (1961-2006) | Regression analysis, first difference approach (FDA). | Crop yield and climate data. | Historical |
| 8 | Fausto Vizca0edno Naranjo, Fredy Ca0f1izares Galarza, Edmundo Jal0f3n Arias | 2023 | Ecuador | Study on the integration of IoT and machine learning techniques for crop yield prediction. | Environmental data is collected in real time. | Integration of IoT sensors and machine learning techniques (specifically gradient boosting regressors). | IoT sensors (soil moisture sensors, weather stations, drones). | Predictive |
| 9 | Harishnaika N, Shilpa N, S A Ahmed | 2023 | India | Analysis of long-term rainfall variability (2000-2020). | Rainfall data from various districts in Karnataka. | Non-parametric tests (LOWESS curve method, Mann-Kendall, SNHT test, Pettitt test, Buishand range test). | Statistical analysis of rainfall data series. | Historical |
| 10 | D. Pushpa Gowri, Anitha Ramachander | 2024 | India | Review article on the implementation of digital technologies in agriculture. | Not applicable (review article) | Analysis of technologies like AI, IoT, robotics, blockchain. | Literature review on technological innovations applied in agriculture. | Revision |
| 11 | T. Sathies Kumar, S. Arunprasad, A. Eniyan, P.Abdul Azeez, S. Bharath | 2023 | India | Research on the use of Machine Learning (ML) in crop selection and cultivation. | Not applicable. | Analysis of Machine Learning algorithms (neural networks, decision trees, assembly models) for crop selection. | Real-time data collection via IoT sensors and satellite images; analysis of datasets on soil quality, climate, and historical crop yield. | Mixed |
| 12 | Arlitt Amy Lozano Povis, Carlos E. Alvarez-Montalv0e1n, Nabi lt Moggiano. | 2021 | Peru | Systematic review on the impact of climate change on agriculture in the Andes. | Not applicable. | Analysis of climatological data and regional model simulations. | Not mentioned as it is based on the collection and analysis of previous studies. | Revision |
| 13 | Isidro J. Mirón | 2023 | Spain | Literature review on food safety and security in the face of climate change, focusing on adaptation and mitigation. | Not applicable. | Analysis of adaptive and mitigation proposals for climate change in the context of food security. | No specific instruments are mentioned, since the study is a literature review. | Revision |
| 14 | Ying Mei Leong; Ean Heng Lim; Nor Fatiha Binti Subri; Norazira Binti A Jalil | 2023 | Malaysia | Technical review and analysis. | Not applicable. | Literature review on AIoT applications, including real-time data analysis, automation, and resource optimization. | AI technologies (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Decision support systems, and Advanced AI algorithms. | Revision |
| 15 | Hamzah Abdul Hamid, Yap Bee Wah, Khatijahhusna Abdul Rani, Xian Jin Xie3 | 2024 | Malaysia | Simulation study. | 100 and 400 | Multinomial logistic regression, simulation, clustering techniques (Ward and DIANA). | Goodness-of-fit tests, data simulation, logistic regression models. | Mixed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





