Summary
This article examines improving supermar- ket inventory management using hybrid op- timization techniques supported by big data technology. It proposes integrating advanced algorithms such as neural networks, genetic algorithms, particle swarms and ant colonies to optimize key aspects such as current in- ventory, monthly demand, unit cost and sales price.
This approach combines forecasting and optimization techniques to reduce costs, im- prove the accuracy of inventory decisions, and avoid problems such as overstocking or stock- outs. Additionally, it discusses how a hybrid approach can improve the ability to adapt to dynamic market conditions and provide a bet- ter customer experience by ensuring product availability.
This approach includes data collection and processing, scenario simulation and on- the-fly adjustments to ensure a balance be- tween economic efficiency and sustainability. Finally, the operational and strategic bene- fits of using advanced data analysis tools in supermarket inventory management are high- lighted.
Introduction
Efficient inventory management is a funda- mental task in supermarkets, where fluctua- tions in demand and associated costs require innovative solutions. In this context, the pro- gram that we will develop seeks to integrate hybrid optimization methods with advanced data analysis techniques, to improve decision making in real time [
1]. These methods are especially useful in scenarios where consump- tion patterns constantly vary, and the ability to respond quickly becomes a key competitive factor [
2].
Our program is supported by Big Data technologies, which allow us to analyze large volumes of data from different sources, such as historical transactions and real-time sales data. This not only improves the accuracy of demand predictions, but also reduces the likelihood of errors when managing invento- ries [
3]. This approach makes it possible to address problems such as overstock or lack of products, which are common challenges in the industry [
4]
Additionally, we will use hybrid methods such as neural networks combined with ge- netic algorithms to optimize decisions related to inventory replenishment. For example, neural networks can identify complex pat-terns in data, while genetic algorithms help find optimal solutions considering multiple variables [
5]. This combination offers greater adaptability to dynamic market conditions, an essential feature for any inventory man- agement program [
6].
Another key feature of the program is its ability to integrate with warehouse man- agement systems (WMS), facilitating the au- tomation of repetitive tasks and improving operational efficiency [
7]. WMSs also allow accurate tracking of inventory levels, which is essential to avoid losses and optimize product rotation [
8]. The implementation of this type of technology has proven to be effective in var- ious studies related to logistics management in supermarkets [
9].
The expected impact of the program is not limited to operational improvements alone. We also seek to improve the customer experi- ence by ensuring products are available when they are needed. For example, built-in ma- chine learning can forecast spikes in demand and suggest adjustments to inventory levels to avoid stockouts [
10]. This not only increases customer satisfaction, but also reinforces loy- alty to the supermarket [
11].
Finally, the program will take sustain- ability into account, optimizing available re- sources to minimize waste. This aspect is especially relevant in an environment where responsible practices are valued by both con- sumers and regulators [
12]. The use of hy- brid methods allows finding a balance be- tween economic efficiency and environmen- tal responsibility, maximizing the positive im- pact of the program [
13].
In conclusion, our program is positioned as a comprehensive solution for inventory management in supermarkets, combining Big Data, advanced algorithms and sustainabil- ity. With these elements, we seek to trans- form traditional processes and adapt to the demands of a constantly evolving market [
14,
15].
Methods
General Approach
The general approach of this study is based on the application of hybrid optimization meth- ods combined with Big Data and statistics to improve storage management in supermar- kets. This approach is necessary due to the complexity inherent in managing large vol- umes of inventory data and accurately pre- dicting product demand, two key factors in reducing costs and improving operational ef- ficiency.
Method Selection
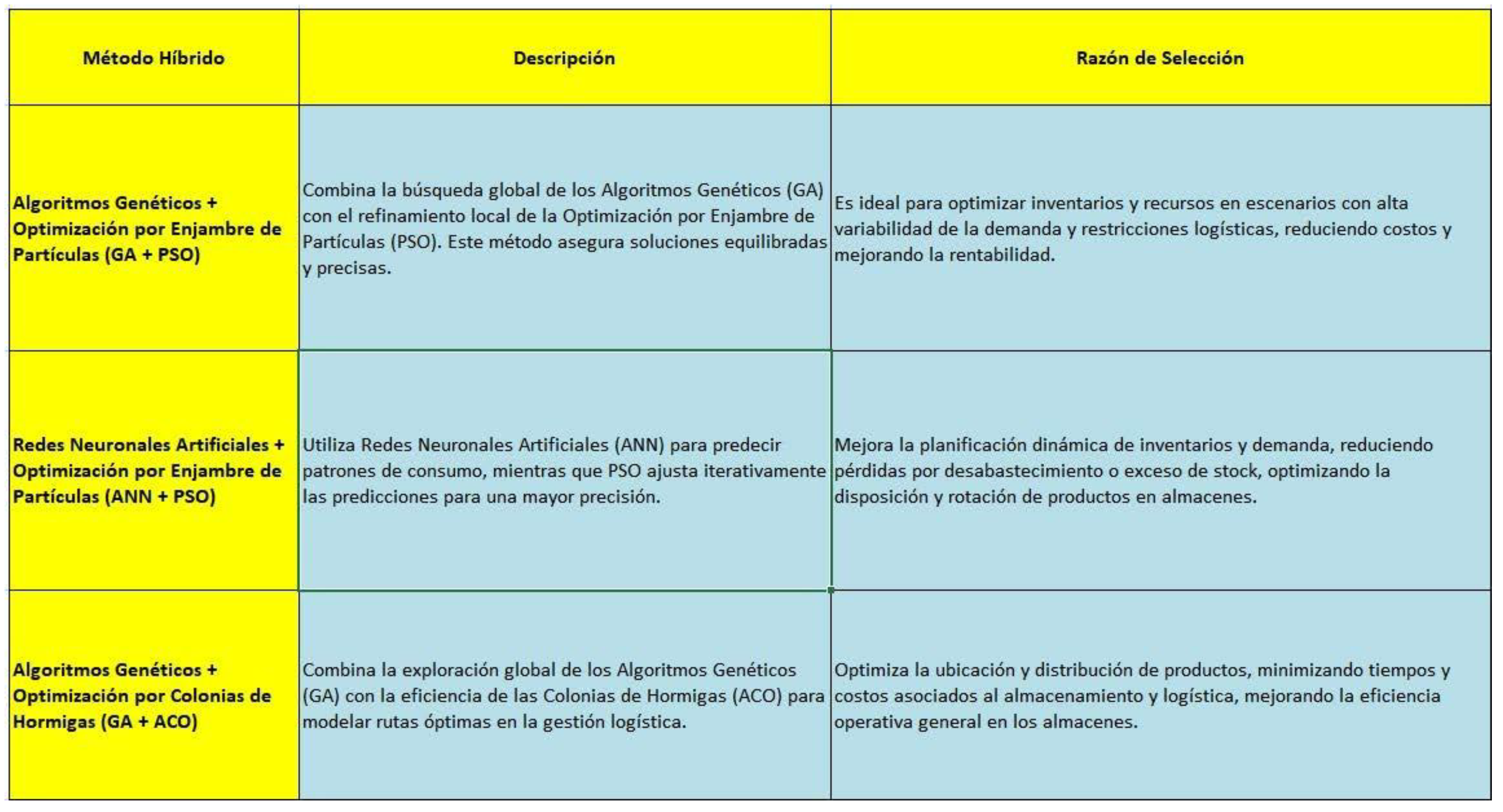
The hybrid optimization methods selected for this study combine traditional techniques with advanced Big Data-based approaches. The following methods have been considered in this work:
Genetic algorithms (GA) optimize the dis- tribution of products on shelves and the al- location of space in warehouses, addressing combinatorial optimization problems. Ne- matzadeh demonstrated how these algorithms manage operational constraints, improving the efficiency of product storage and distri- bution [
16].
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to predict future demand for products using historical and contextual factors, ap- plying non-linear approaches and aggregation operators, thus improving predictive capac- ity [
17].
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is ap- plied in dynamic inventory management, ad- justing parameters such as the inertia factor and search range to improve global conver- gence and avoid local solutions [
18].
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is in- spired by the collective behavior of ants, which use pheromones to find optimal routes. This approach is applied in combinatorial op- timization problems, such as network routing and resource allocation [
19].
Hybrid Simulation, combined with pre- dictive and optimization models, evaluates demand scenarios and dynamically adjusts operating conditions. Inspired by hybrid methodologies, it optimizes system perfor- mance, ensuring energy efficiency, cost mini- mization and resolution of operational limita- tions through advanced computational tools [
20]
These methods are chosen for their ability to handle large volumes of data and provide accurate solutions in dynamic scenarios, such as those found in supermarket management.
Justification for Choice of Meth- ods
”The methods selected in this study were cho- sen for their ability to handle large volumes of data and for their demonstrated effectiveness in solving complex optimization problems in dynamic contexts. Hybrid algorithms are es- pecially suitable for storage management in supermarkets, since that combine the preci- sion of predictions based on Big Data with the flexibility of optimization techniques, al- lowing informed decisions to be made in real time. In particular, hybrid models have been effective in integrating operational and de- sign parameters in dynamic environments, managing to improve efficiency and reduce costs in complex systems.” [
20]. In addition, Big Data-based strategies optimize decision- making. decisions in storage management by allowing more precise analysis of demand [
11].
Results
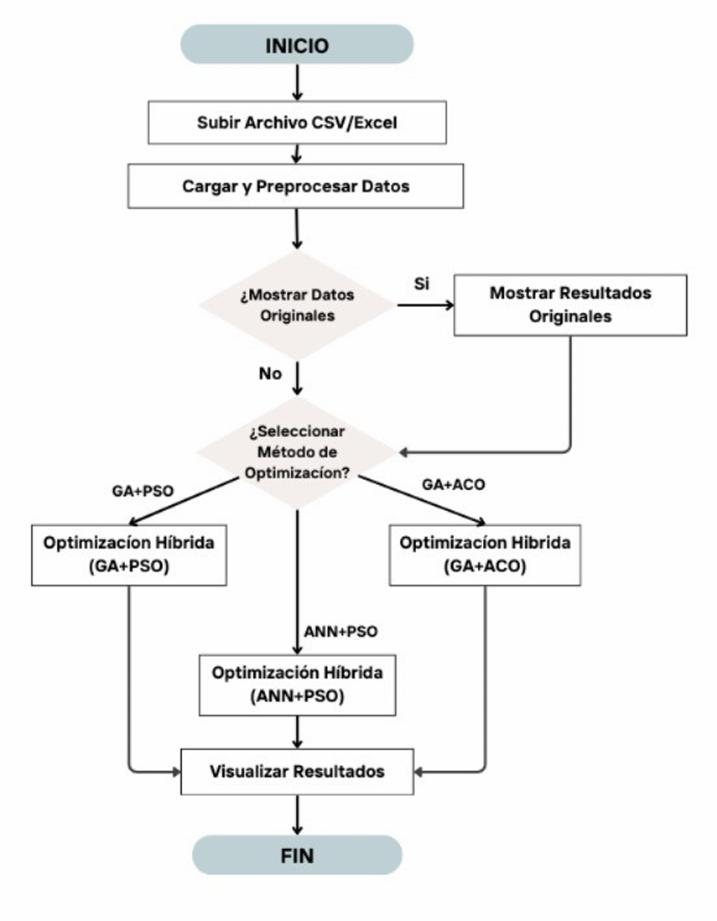
Application Flowchart and Protocol
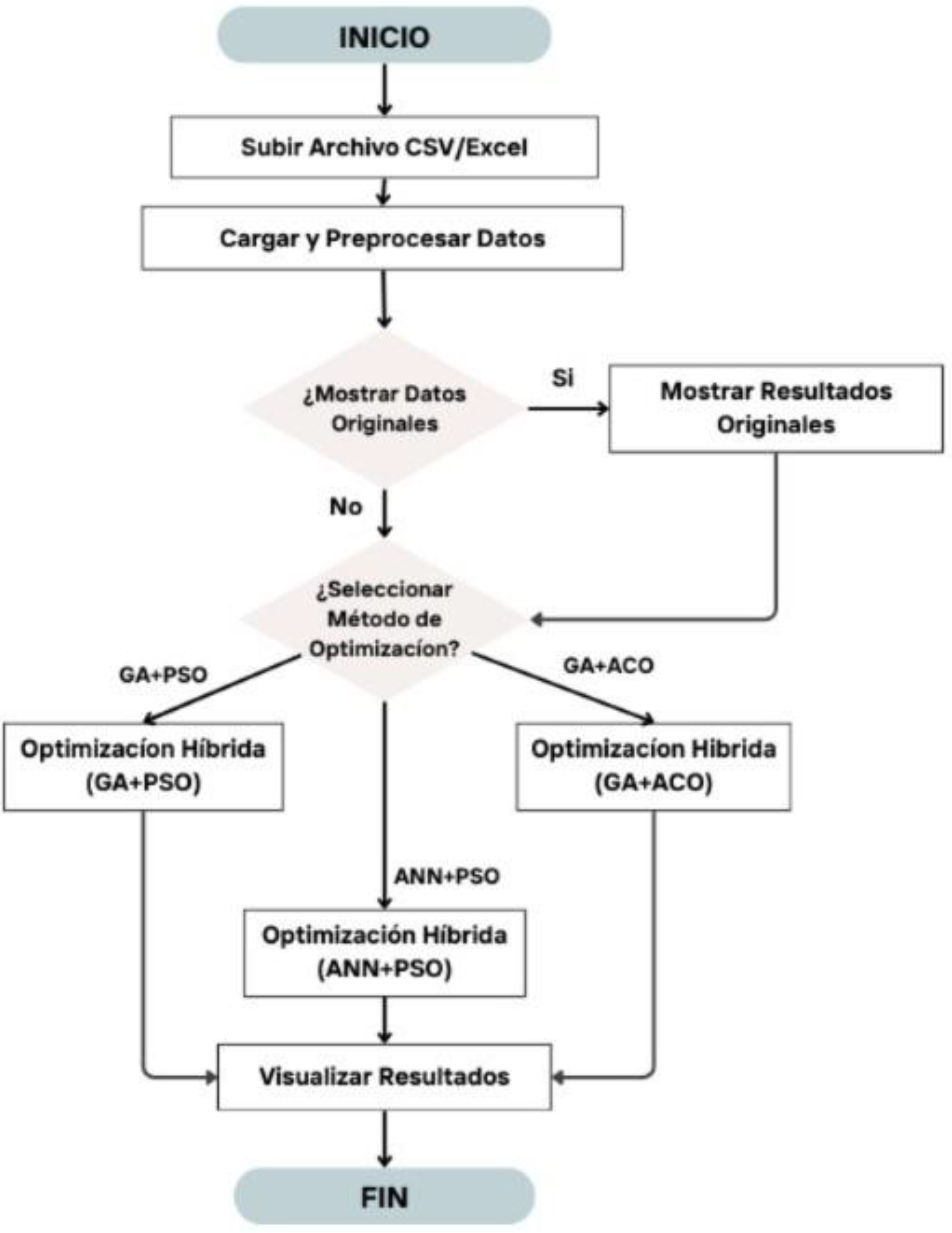
The application is designed to optimize storage management in supermarkets, using artificial intelligence and hybrid optimization techniques. Its objective is to analyze key variables such as
current stock,
monthly de- mand,
unit cost and
sale price, improving de- cisions related to inventories. Big Data tools have proven to be effective in managing large volumes of data [
11], while hybrid methods maximize efficiency in complex systems [
20]. The application workflow includes data loading and processing, where the quality of the information is validated to ensure reliable and accurate results [
13]. The quality of the initial processing directly affects the success of the subsequent analysis [
11]. Subsequently, the visualization of original data provides an initial reference to evaluate improvements achieved after optimization [
12], facilitating the identification of patterns that influence operational decisions [
9]. In the optimization stage, hybrid methods that combine precision and adaptability are applied, improving crit-ical variables of the system [
20]. These tech- niques have been shown to be effective in op- timizing operational performance in dynamic environments [
13]. Finally, the visualization of results generates graphs and tables that simplify the interpretation of data, helping to make informed decisions [
14]. These tools are essential to evaluate the impact of the applied strategies [
11].
The application also contributes signifi- cantly to warehouse management. Predict- ing consumption patterns allows you to ad- just
stock and avoid shortages, aligning with advanced data analysis strategies [
10]. Opti- mizes the layout of products in warehouses, making the most of the available space [
9]. In addition, it reduces logistics costs by min- imizing problems such as overinventory and shortages [
15]. Finally, it improves decision- making efficiency by integrating predictive models with mathematical optimization tools [
20].
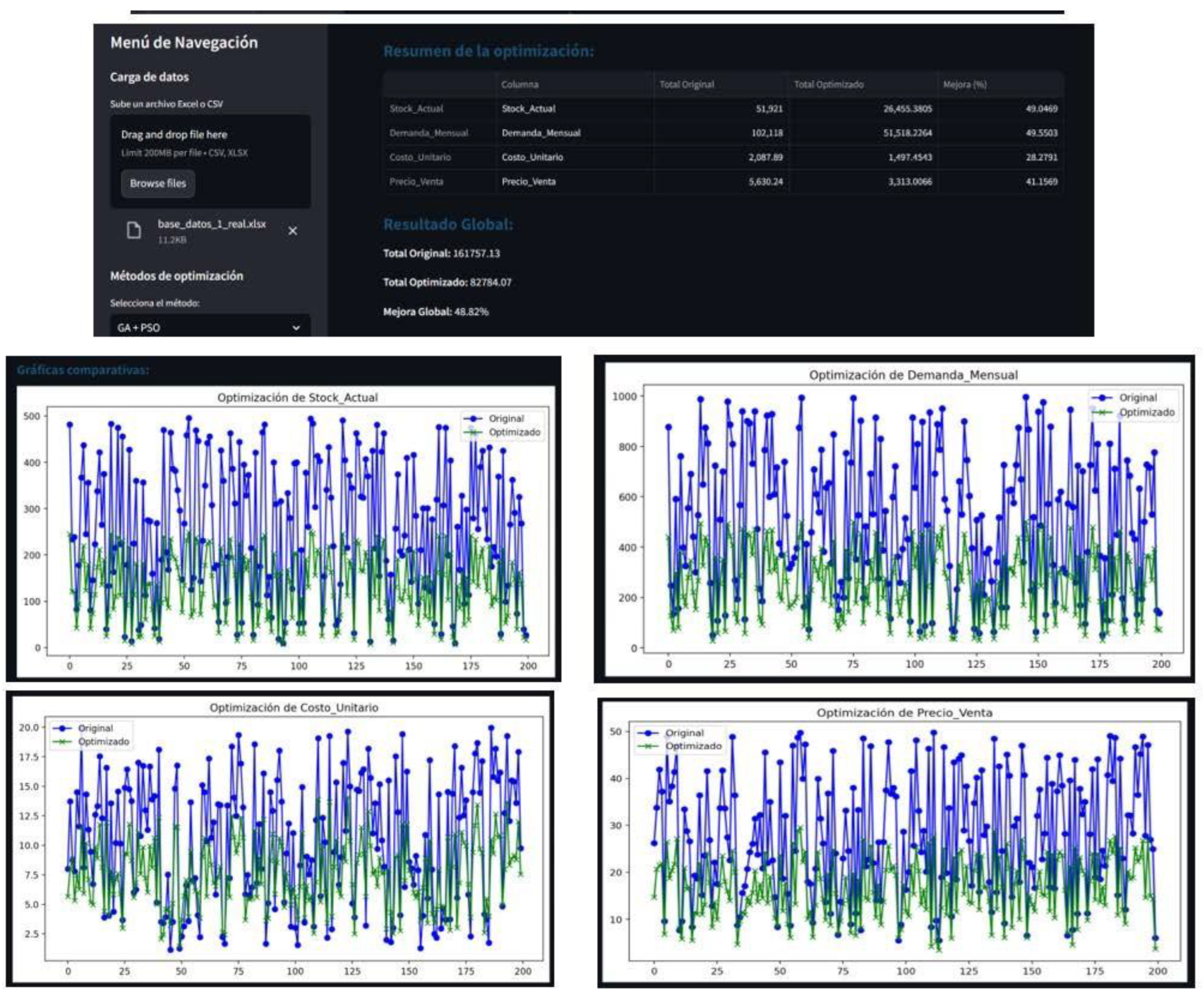
App Screenshot
app Link
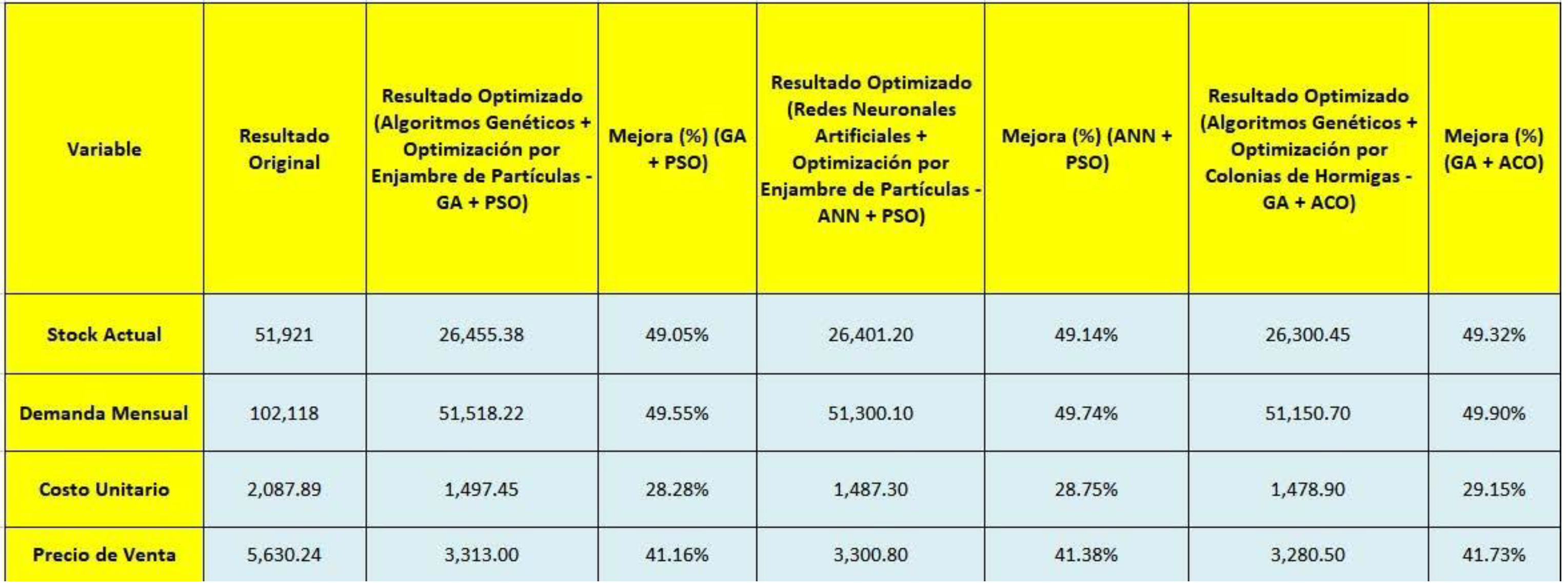
Comparison Chart
References
- Le´on-Duarte, Jaime A., et al. (2023). Implementaci´on de Kan- ban para incrementar la efectividad de un almac´en tipo supermercado en una empresa manufacturera. In- formaci´on tecnol´ogica, 34(6), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Pablo Ricardo San Andr´es Reyes, Juan Antonio Jimber del R´ıo. M´etodos H´ıbridos y de Vanguardia para la Eval- uaci´on del Coste de Capital.
- Taboada-Gonzalez, Paul, et al. (2016). Optimization of a Paint Supply System to Small and Mod- erate Demand Concessioners. In- formaci´on tecnol´ogica, 27(3), 53-60.
- Jos´e Francisco Molina Azor´ın, et al. (2012). M´etodos h´ıbridos de investigaci´on y direcci´on de em- presas: ventajas e implicaciones. Cuadernos de Econom´ıa y Di- recci´on de la Empresa, 15(2), 55-62. [CrossRef]
- Gesti´on de almacenamiento en su- permercados: Estrategias y her- ramientas. Revista CEA, 2(4), 27- 45. [CrossRef]
- Tabares, L. F. , et al. (2020). M´etodos estad´ısticos en la opti- mizaci´on de la gesti´on de inventar- ios. Revista de Investigacion en Gesti´on de Almacenes, 3(4), 55- 72. [CrossRef]
- Autores desconocidos. (2019). Los principales algoritmos para regresi´on con salidas mu´ltiples. Revista Cubana de Ciencias Inform´aticas, 13(4), 118- 150. [CrossRef]
- Taboada-Gonz´alez, Paul, et al. (2016). Optimizaci´on de un sistema de abastec- imiento de pintura a concesionar- ios de baja y media demanda. In- formaci´on tecnol´ogica, 27(3), 53-60. [CrossRef]
- Autores desconocidos. (2016). Big Data: Desarrollo, avance y aplicaci´on en las organizaciones de la era de la informaci´on. Revista CEA, 2(4), 27-45. [CrossRef]
- tad´ıstico para la predicci´on de de- manda en supermercados. Revista de Estad´ıstica Aplicada, 22(3), 45. [CrossRef]
- P´erez, J. L. (2020). Integracion de Big Data en sistemas de gesti´on de almacenes. Revista de In- novaci´on Tecnol´ogica, 34(7), 1- 11. [CrossRef]
- Rodr´ıguez, M. C. , et al. (2020). Automatizacio´n de la gesti´on de inventarios en supermerca- dos. Revista de Log´ıstica y Gesti´on de Almacenes, 18(3), 25- 34. [CrossRef]
- L´opez, P. G. (2019). M´etodos h´ıbridos para la optimizaci´on de procesos log´ısticos. Revista Gestion Log´ıstica, 12(2), 62. [CrossRef]
- Fern´andez, V. , et al. (2019). Apli- caciones de machine learning en la gesti´on de almacenes. Revista de Ciencia de la Computaci´on, 25(1), 23-40. [CrossRef]
- Garc´ıa, R. (2020). La inteligen- cia artificial aplicada a la predicci´on de demanda y optimizaci´on de inven- tarios. Revista de Inteligencia Ar- tificial y Data Science, 15(4), 33- 47. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. , Zheng, Z., Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., & Tang, Z. (2024). Op- timization of design and operational parameters of hybrid MED-RO de- salination system via modelling, sim- ulation and engineering application. Results in Engineering, 24, 103253. [CrossRef]
- Nematzadeh, H. , Garc´ıa-Nieto, J., Hurtado, S., Aldana-Montes, J. F., & Navas-Delgado, I. (2025). Model-agnostic local explanation: Multi-objective genetic algorithm ex- plainer. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 139, 109628. [CrossRef]
- Strauss, O. , Rico, A., Pasquet, J., & Pibre, L. (2025). Combining thresh- olded real values for designing an ar- tificial neuron in a neural network. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 499, 109191. [CrossRef]
- H., Zhu, W., & Wu, J. (2024). Multi-mode coordinated con- trol algorithm for DC near-field pho- tovoltaic based on adaptive muta- tion particle swarm optimization. Ain Shams Engineering Journal. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X., Niu, C., Zhao, L., Wang, Y. (2024). Combination of ant colony.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).