Submitted:
12 December 2024
Posted:
13 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
2.2. Search and Screening Strategy
- TOPIC: ("serious game" OR "serious games") AND ("socio-emotional" OR "social" OR "emotional") AND ("adolescents" OR "children")
- Timespan: 1900–2024 (third trimester of 2024)
- Database: Web of Science (WOS) – All Databases
3. Results
3.1. Evolution and Trends of Published and Cited Articles
3.2. Publishing Journals
3.3. The Most Influential Articles
3.4. The Most Prolific and Influential Authors
3.5. The Most Productive and Influential Institutions
3.6. Country Analysis
3.7. Title and Abstrat Co-Ocurrence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gergely, G. , & Watson, J. S. Early socio-emotional development: Contingency perception and the social-biofeedback model. Early social cognition: Understanding others in the first months of life, 1999, 60, 101–136. [Google Scholar]
- Espoz-Lazo, S., Rodríguez Huete. Emotional education for the development of primary and secondary school students through physical education: Literature review. Education Sciences 2020, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Núñez, M. T., García-Rubio. Emotional intelligence and mental health in the family: The influence of emotional intelligence perceived by parents and children. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youell, B. (2018). The importance of play and playfulness. In Childhood, well-being and a therapeutic ethos (pp. 183-194). Routledge.
- Stone, S. J. The essential role of play in school contexts for the well-being of children. LEARNing Landscapes 2017, 10, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Pesántez, D. , Rivera, L. A., & Alban, M. S. (2017). Approaches for serious game design: A systematic literature review. Computers in education journal, 8(3).
- Lameras, P., Arnab. Essential features of serious games design in higher education: Linking learning attributes to game mechanics. British journal of educational technology, 2017, 48, 972–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondi, C. F., Giovanelli. Fostering socio-emotional learning through early childhood intervention. International Journal of Child Care and Education Policy, 2021, 15, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M. D. (2021). Socio-Emotional learning. Springer, 10, 978-3.
- McClelland, M. M. , Tominey, S. L., Schmitt, S. A., & Duncan, R. SEL interventions in early childhood. The Future of Children, 2017, 27, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Váradi, J. A review of the literature on the relationship of music education to the development of socio-emotional learning. Sage Open, 2022, 12, 21582440211068501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncu, A., Costea, I., & Minulescu, M. (2017). A meta-analytic study investigating the efficiency of socio-emotional learning programs on the development of children and adolescents. Romanian Journal of Psychology, 19(2).
- Yorke, L., Rose, P., Bayley, S., Wole, D., & Ramchandani, P. (2021). The importance of students’ socio-emotional learning, mental health and wellbeing in the time of COVID-19. Rise Insights, 25, 1-11.
- Fleming, T. M. , Bavin, L., Stasiak, K., Hermansson-Webb, E., Merry, S. N., Cheek, C.,... & Hetrick, S. Serious games and gamification for mental health: current status and promising directions. Frontiers in psychiatry, 2017, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dewhirst, A. , Laugharne, R., & Shankar, R. Therapeutic use of serious games in mental health: scoping review. BJPsych open, 2022, 8, e37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yusof, N. , Mohd Rias, R., & Yusoff, E. H. (2014). Serious games in mental health treatment: Review of literature.
- Laamarti, F. , Eid, M., & El Saddik, A. An overview of serious games. International Journal of Computer Games Technology, 2014, 2014, 358152. [Google Scholar]
- Cangas, A. J. , Navarro, N., Aguilar-Parra, J. M., Trigueros, R., Gallego, J., Zárate, R., & Gregg, M. Analysis of the usefulness of a serious game to raise awareness about mental health problems in a sample of high school and university students: relationship with familiarity and time spent playing video games. Journal of clinical medicine, 2019, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides, M. K., Lazaridou, I. Z., & Papanas, N. (2023). Bibliometric analysis: Bridging informatics with science. The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds, 15347346231153538. [CrossRef]
- Broadus, R. Toward a definition of “bibliometrics” Scientometrics. 1987, 12, 373–379.
- Bar-Ilan, J. Informetrics at the beginning of the 21st century—A review. Journal of informetrics, 2008, 2, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerola-Navarro, V. , Oltra-Badenes, R., Gil-Gomez, H., & Gil-Gomez, J. A. Customer relationship management (CRM): a bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Services Operations and Informatics, 2020, 10, 242–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N. , Kumar Badhotiya, G., Kumar, S., Soni, G., & Pandey, N. A retrospective overview of Journal of Enterprise Information Management using bibliometric analysis. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 2022, 35, 504–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Navarrete, S. , Palacios-Marqués, D., Lassala, C., & Ulrich, K. Key factors of information management for crowdfunding investor satisfaction. International Journal of Information Management, 2021, 59, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P. M. , MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, N. P., & Bachrach, D. G. Scholarly influence in the field of management: A bibliometric analysis of the determinants of university and author impact in the management literature in the past quarter century. Journal of Management, 2008, 34, 641–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merigo, J. M. , Miranda, J., Modak, N. M., Boustras, G., & De La Sotta, C. Forty years of Safety Science: A bibliometric overview. Safety science, 2019, 115, 66–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Gomez, H., Oltra-Badenes, R., Guerola-Navarro, V. & Zegarra Saldaña, P. Crowdfunding: a bibliometric analysis. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 2021, 19, 27–45. [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J. E. An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences, 2005, 102, 16569–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijhof, S. L. , Vinkers, C. H., van Geelen, S. M., Duijff, S. N., Achterberg, E. M., Van Der Net, J.,... & Lesscher, H. M. Healthy play, better coping: The importance of play for the development of children in health and disease. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 2018, 95, 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Schoneveld, E. A. , Malmberg, M., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A., Verheijen, G. P., Engels, R. C., & Granic, I. A neurofeedback video game (MindLight) to prevent anxiety in children: A randomized controlled trial. Computers in Human Behavior, 2016, 63, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kaimara, P. , Oikonomou, A., & Deliyannis, I. Could virtual reality applications pose real risks to children and adolescents? A systematic review of ethical issues and concerns. Virtual Reality, 2022, 26, 697–735. [Google Scholar]
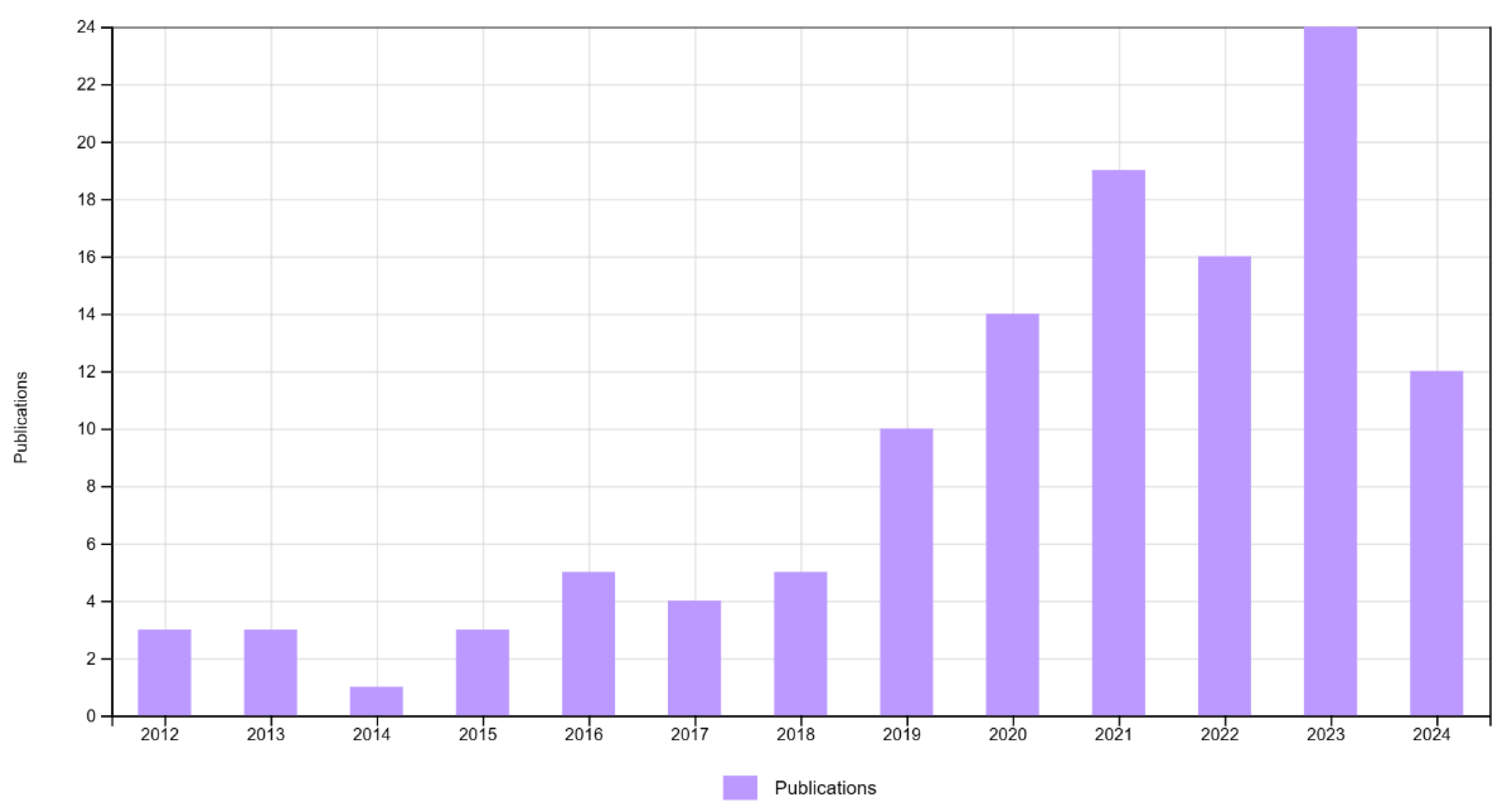
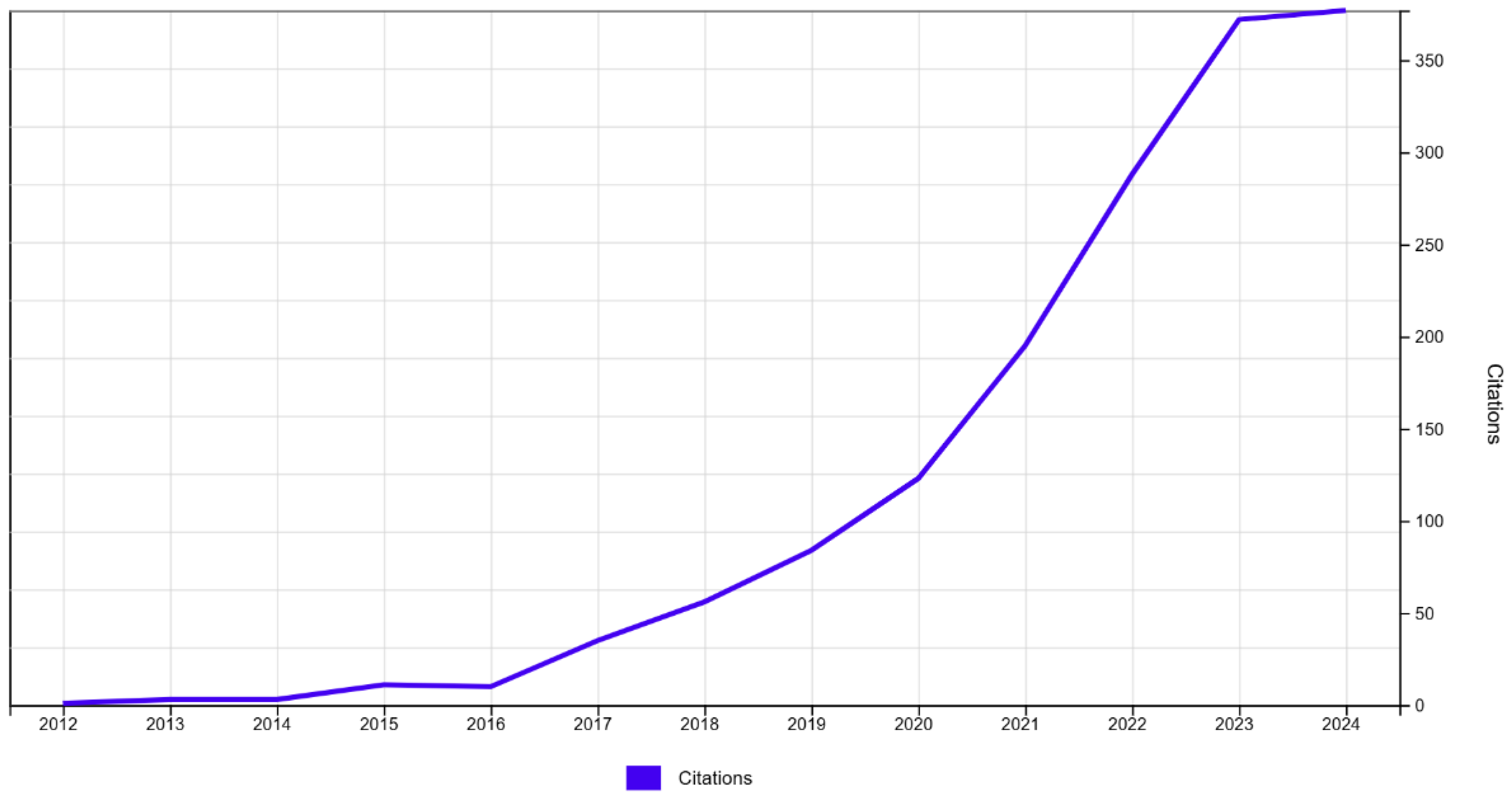
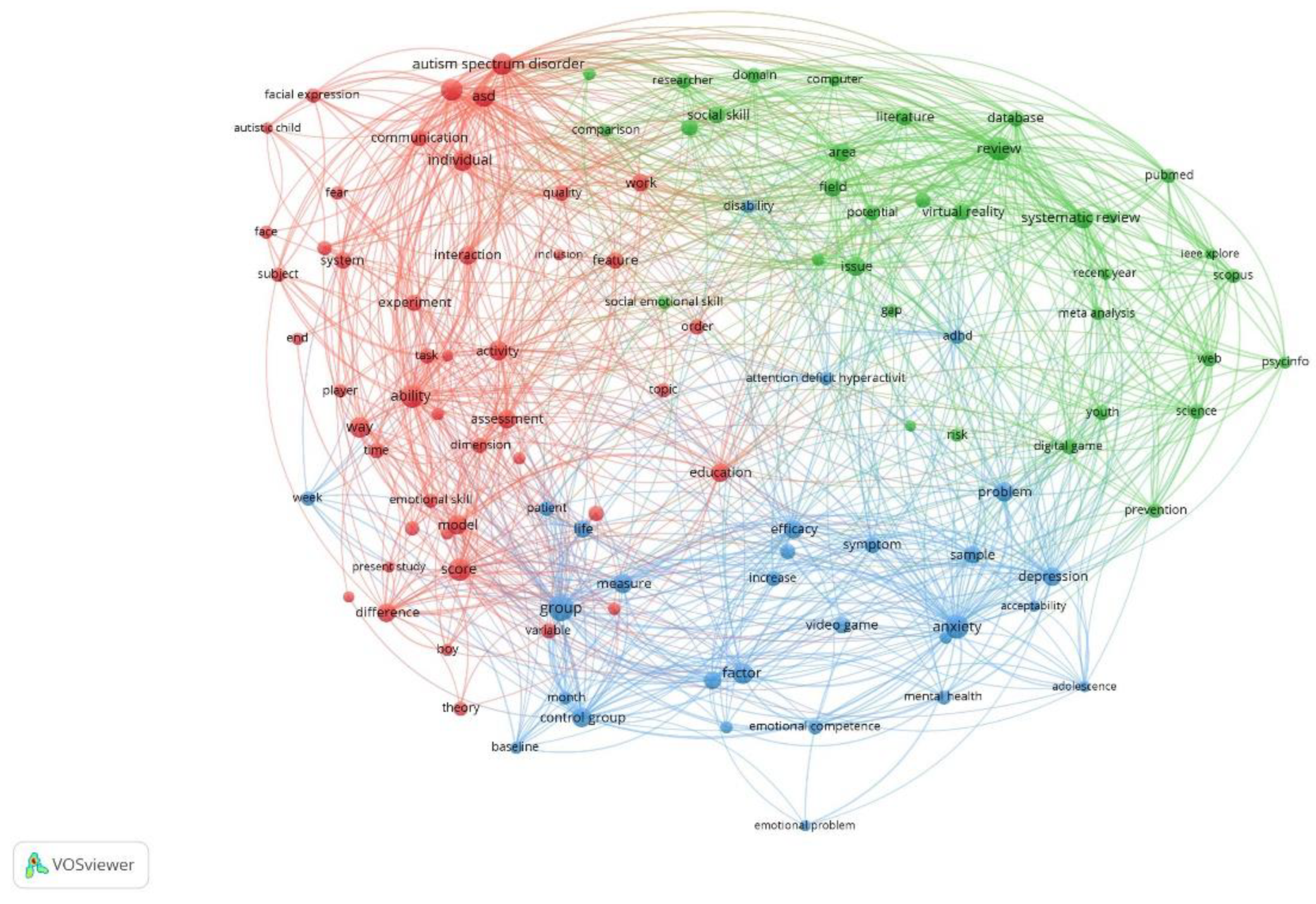
| Citations | All time | 2020 - 2024 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of papers | % Papers | Number of papers | % Papers | |
| > 100 citations | 2 | 1,68% | 0 | 0,00% |
| > 50 citations | 6 | 5,04% | 1 | 1,18% |
| > 25 citations | 15 | 12,61% | 7 | 8,24% |
| > 10 citations | 37 | 31,09% | 19 | 22,35% |
| <= 10 citations | 82 | 68,91% | 66 | 77,65% |
| Total | 119 | 100% | 85 | 100% |
| Rank | Name | h-index | TC | TP | TC/TP | >50 | >20 | >10 | >5 | IF (2023) | 5-IF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JMIR SERIOUS GAMES | 4 | 56 | 8 | 7,00 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3.8 | 3.9 |
| 2 | APPLIED SCIENCES | 4 | 53 | 6 | 8,83 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2.5 | 2.7 |
| 3 | Journal of The Korean Society for Computer Game | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0,00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | --- | --- |
| 4 | UNIVERSAL ACCESS IN THE INFORMATION SOCIETY | 3 | 64 | 3 | 21,33 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2.1 | 2.8 |
| 5 | BRITISH JOURNAL OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY | 3 | 37 | 3 | 12,33 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6.7 | 7.2 |
| 6 | IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AFFECTIVE COMPUTING | 2 | 13 | 3 | 4,33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9.6 | 11 |
| 7 | NEUROSCIENCE AND BIOBEHAVIORAL REVIEWS | 2 | 167 | 2 | 83,50 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7.6 | 8.7 |
| 8 | COMPUTERS IN HUMAN BEHAVIOR | 2 | 141 | 2 | 70,50 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 9.5 |
| 9 | VIRTUAL REALITY | 2 | 69 | 2 | 34,50 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4.4 | 5.4 |
| 10 | JOURNAL OF AUTISM AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS | 2 | 55 | 2 | 27,50 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3.1 | 4.2 |
| 11 | EDUCATION AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES | 2 | 23 | 2 | 11,50 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4.8 | 4.8 |
| 12 | CHILDREN-BASEL | 2 | 22 | 2 | 11,00 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2.1 |
| 13 | PLOS ONE | 2 | 21 | 2 | 10,50 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 | 3.3 |
| 14 | FRONTIERS IN PSYCHIATRY | 2 | 15 | 2 | 7,50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.2 | 3.9 |
| 15 | IEEE ACCESS | 2 | 10 | 2 | 5,00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.4 | 3.7 |
| 16 | MULTIMEDIA TOOLS AND APPLICATIONS | 1 | 7 | 2 | 3,50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2.9 |
| 17 | MULTIMODAL TECHNOLOGIES AND INTERACTION | 1 | 6 | 2 | 3,00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.4 | |
| 18 | INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED COMPUTER SCIENCE AND APPLICATIONS | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2,50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 19 | INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH AND PUBLIC HEALTH | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2,50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.6 | 4.8 |
| 20 | FRONTIERS IN PSYCHOLOGY | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1,00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.6 | 3.3 |
| 21 | INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONLINE AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0,50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 | 1.3 |
| Journal | Rank | TC | Title | Author/s | Year | C/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEUROSCIENCE AND BIOBEHAVIORAL REVIEWS | 1 | 160 | Healthy play, better coping: The importance of play for the development of children in health and disease | Nijhof, SL; Vinkers, CH; (...); Lesscher, HMB | 2018 | 22,86 |
| COMPUTERS IN HUMAN BEHAVIOR | 2 | 120 | A neurofeedback video game (MindLight) to prevent anxiety in children: A randomized controlled trial | Schoneveld, EA; Malmberg, M; (...); Granic, I | 2016 | 13,33 |
| EUROPEAN CHILD & ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY | 3 | 89 | Emotiplay': a serious game for learning about emotions in children with autism: results of a cross-cultural evaluation | Fridenson-Hayo, S; Berggren, S; (...); Golan, O | 2017 | 11,13 |
| AGGRESSION AND VIOLENT BEHAVIOR | 4 | 80 | Anti-bullying programs and Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs): A systematic review | Nocentini, A; Zambuto, V and Menesini, E | 2015 | 8,00 |
| ETR&D-EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT | 5 | 64 | Supporting struggling readers with digital game-based learning | Ronimus, M; Eklund, K; (...); Lyytinen, H | 2019 | 10,67 |
| VIRTUAL REALITY | 6 | 59 | Could virtual reality applications pose real risks to children and adolescents? A systematic review of ethical issues and concerns | Kaimara, P; Oikonomou, A and Deliyannis, I | 2022 | 14,75 |
| CURRENT PEDIATRIC REVIEWS | 7 | 48 | Serious Game-based Intervention for Children with Developmental Disabilities | Kokol, P; Vosner, HB; (...); Peinemann, F | 2020 | 9,60 |
| TELEMEDICINE AND E-HEALTH | 8 | 40 | Time for a Change: College Students' Preference for Technology-Mediated Versus Face-to-Face Help for Emotional Distress | Lungu, A and Sun, M | 2016 | 4,44 |
| UNIVERSAL ACCESS IN THE INFORMATION SOCIETY | 9 | 39 | Inclusion of third-person perspective in CAVE-like immersive 3D virtual reality role-playing games for social reciprocity training of children with an autism spectrum disorder | Tsai, WT; Lee, IJ and Chen, CH | 2021 | 7,80 |
| IEEE COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND APPLICATIONS | 10 | 36 | A VR-Based Serious Game for Studying Emotional Regulation in Adolescents | Rodríguez, A; Rey, B; (...); Pérez-López, D | 2015 | 3,60 |
| PSYCHNOLOGY JOURNAL | 11 | 34 | LIFEisGAME Prototype: A Serious Game about Emotions for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders | Alves, S; Marques, A; (...); Orvalho, V | 2013 | 2,83 |
| ENTERTAINMENT COMPUTING | 12 | 33 | Serious games to improve social and emotional intelligence in children with autism | Hassan, A; Pinkwart, N and Shafi, M | 2021 | 8,25 |
| APPLIED SCIENCES | 13 | 33 | SoundFields: A Virtual Reality Game Designed to Address Auditory Hypersensitivity in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder | Johnston, D; Egermann, H and Kearney, G | 2020 | 6,60 |
| JOURNAL OF AUTISM AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS | 14 | 30 | Pilot Study of an Attention and Executive Function Cognitive Intervention in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders | Macoun, SJ; Schneider, I; (...); Sung, A | 2021 | 6,00 |
| SUSTAINABILITY | 15 | 28 | Virtual Reality and Metacognition Training Techniques for Learning Disabilities | Drigas, A; Mitsea, E and Skianis, C | 2022 | 9,33 |
| JOURNAL OF AUTISM AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS | 16 | 25 | Designing a Serious Game for Youth with ASD: Perspectives from End-Users and Professionals | Tang, JSY; Falkmer, M; (...); Girdler, S | 2019 | 4,17 |
| RESEARCH IN AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS | 17 | 24 | A systematic review and meta-analysis of social emotional computer based interventions for autistic individuals using the serious game framework | Tang, JLSY; Chen, NTM; (...); Girdler, S | 2019 | 4,00 |
| DEVELOPMENTAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGY | 18 | 23 | Interventions with Serious Games and Entertainment Games in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review | Silva, GM; Souto, JJD; (...); Santos, NA | 2021 | 5,75 |
| BRITISH JOURNAL OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY | 19 | 22 | Children like it more but don't learn more: Effects of esthetic visual design in educational games | Javora, O; Hannemann, T; (...); Brom, C | 2019 | 3,67 |
| INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING PEDAGOGY | 20 | 22 | Games for Empathy for Social Impact | Papoutsi, C and Drigas, AS | 2016 | 2,44 |
| COMPUTERS IN HUMAN BEHAVIOR | 21 | 21 | A game for emotional regulation in adolescents: The (body) interface device matters | Vara, MD; Baños, RM; (...); Alcañiz, M | 2016 | 2,33 |
| JMIR SERIOUS GAMES | 22 | 20 | Awareness, Prevention, Detection, and Therapy Applications for Depression and Anxiety in Serious Games for Children and Adolescents: Systematic Review | Martinez, K; Menéndez-Menéndez, MI and Bustillo, A | 2021 | 5,00 |
| SENSORS | 23 | 19 | Augmented Reality, Serious Games and Picture Exchange Communication System for People with ASD: Systematic Literature Review and Future Directions | Almurashi, H; Bouaziz, R; (...); Kammoun, S | 2022 | 6,33 |
| INTERNET INTERVENTIONS-THE APPLICATION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN MENTAL AND BEHAVIOURAL HEALTH | 24 | 19 | Effectiveness of the REThink therapeutic online video game in promoting mental health in children and adolescents | David, OA; Predatu, R and Cardos, RAI | 2021 | 4,75 |
| CHILDREN | 25 | 19 | Digital Attention-Related Augmented-Reality Game: Significant Correlation between Student Game Performance and Validated Clinical Measures of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | Keshav, NU; Vogt-Lowell, K; (...); Sahin, NT | 2019 | 3,17 |
| Rank | Name / Author | Institution / Affiliation | Country | TP | TC | TC/TP | h-index | > 50 | > 20 | > 10 | >5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alcañiz, Mariano | Universitat Politècnica de València | Spain | 4 | 63 | 15,75 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | Rey, Beatriz | Universitat Politècnica de València | Spain | 4 | 63 | 15,75 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | Rodríguez Ortega, Alejandro | Universitat Politècnica de València | Spain | 4 | 63 | 15,75 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | Wrzesien, Maja | Universitat Politècnica de València | Spain | 4 | 63 | 15,75 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | David, Oana | University Cluj-Napoca | Romania | 4 | 34 | 8,50 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | Drigas, Athanasios | National Centre of Scientific Research "Demokritos" | Greece | 4 | 50 | 12,50 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 7 | Bölte, Sven | Karolinska Institutet | Sweden | 3 | 138 | 46,00 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 8 | Rasal, Paloma | Universitat de Valencia | Spain | 3 | 27 | 9,00 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| R | Institution | Country | TP | TC | TC/TP | H-index | > 50 | > 20 | > 10 | > 5 | ARWU | QS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Universitat Politècnica De València | Spain | 7 | 88 | 12,57 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 401-500 | 436 |
| 2 | Universitat de Valencia | Spain | 6 | 82 | 13,67 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 201-300 | 445 |
| 3 | Babes Bolyai University From Cluj | Romania | 4 | 34 | 8,50 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | --- | 781-790 |
| 4 | Ciber Centro De Investigacion Biomedica En Red | Spain | 4 | 34 | 8,50 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | --- | --- |
| 5 | National Centre Of Scientific Research Demokritos | Greece | 4 | 50 | 12,50 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | --- | --- |
| 6 | Karolinska Institutet | Sweden | 3 | 138 | 46,00 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 43 | --- |
| 7 | Stockholm County Council | Sweden | 3 | 138 | 46,00 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | --- | --- |
| 8 | Ludwig Boltzmann Institute | Austria | 3 | 16 | 5,33 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | --- | --- |
| 9 | University Of Birmingham | UK | 3 | 21 | 7,00 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 151-200 | 80 |
| Rank | Country | TP | TC | TC/TP | H-index | Population | TP/Pop | TC/Pop | > 50 | > 20 | > 10 | >5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spain | 22 | 187 | 8,50 | 7 | 48.373,34 | 0,45 | 3,87 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 13 |
| 2 | USA | 12 | 217 | 18,08 | 7 | 334.914,89 | 0,04 | 0,65 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 7 |
| 3 | Greece | 11 | 126 | 11,45 | 5 | 10.361,29 | 1,06 | 12,16 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | UK | 10 | 180 | 18,00 | 6 | 68.350,00 | 0,15 | 2,63 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 5 | Italy | 9 | 138 | 15,33 | 5 | 58.761,15 | 0,15 | 2,35 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| 6 | Portugal | 8 | 77 | 9,63 | 5 | 10.525,34 | 0,76 | 7,32 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| 7 | Austria | 5 | 33 | 6,60 | 3 | 9.132,38 | 0,55 | 3,61 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | Brazil | 5 | 50 | 10,00 | 4 | 212.422,45 | 0,02 | 0,24 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 9 | Germany | 5 | 111 | 22,20 | 4 | 84.482,27 | 0,06 | 1,31 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 10 | Netherlands | 5 | 306 | 61,20 | 4 | 17.879,49 | 0,28 | 17,11 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 11 | Romania | 4 | 34 | 8,50 | 3 | 19.056,12 | 0,21 | 1,78 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





