Submitted:
06 December 2024
Posted:
06 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Information from EEG
2.1. Brain Waves
2.2. Event Related Potentials
2.3. EEG Analysis Steps
3. Hardware Aspects
4. Software Aspects
5. Methodology
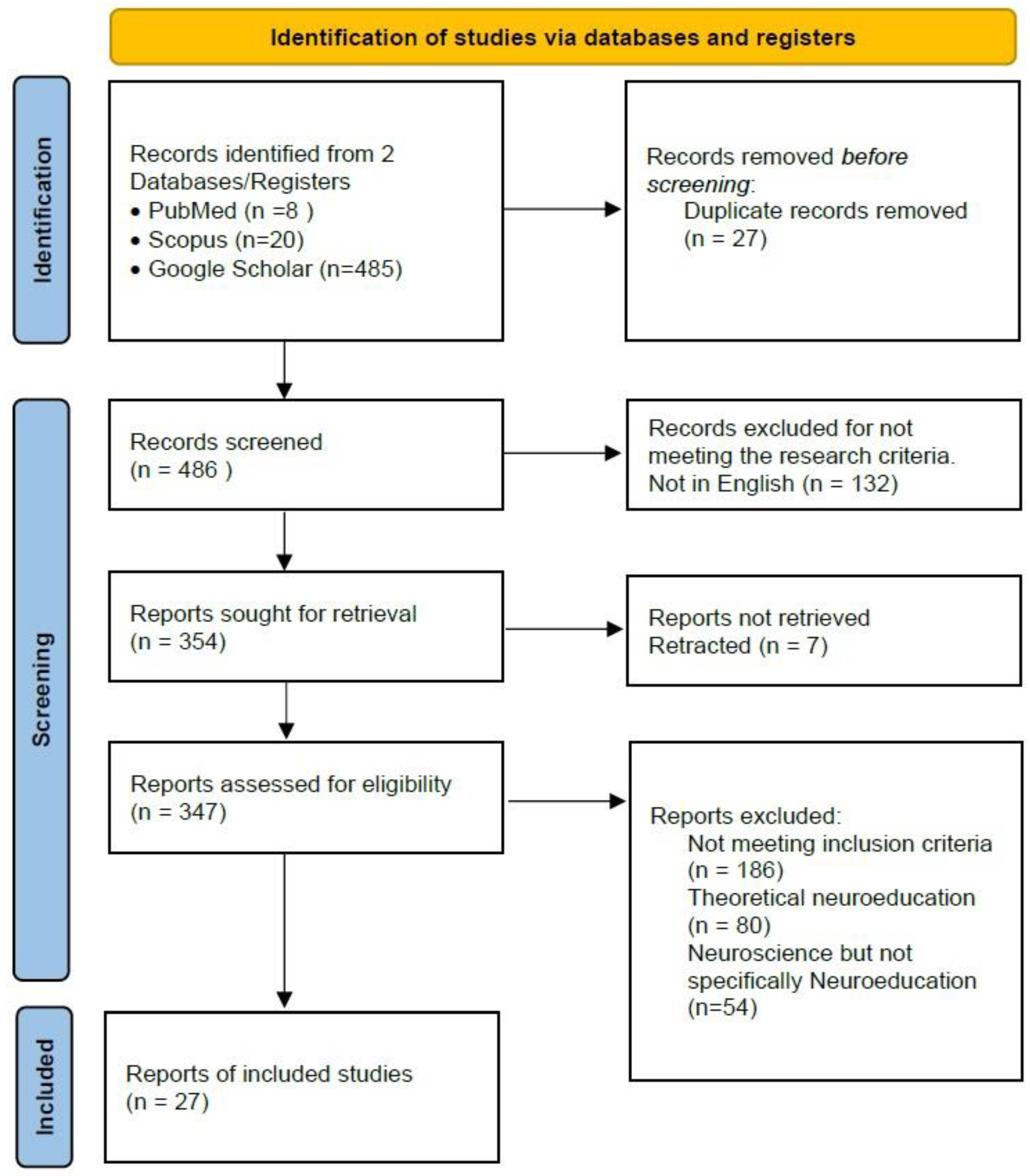
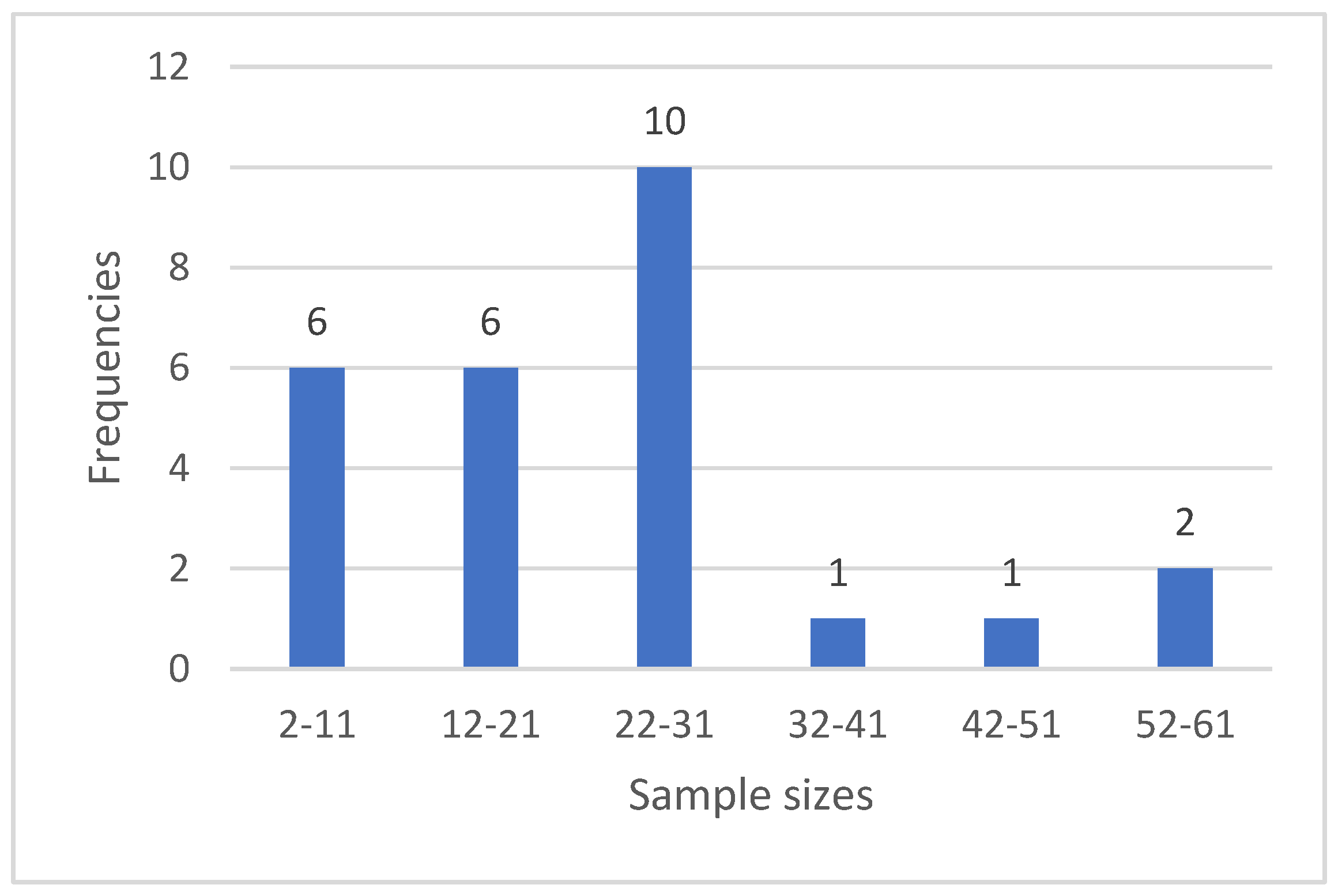
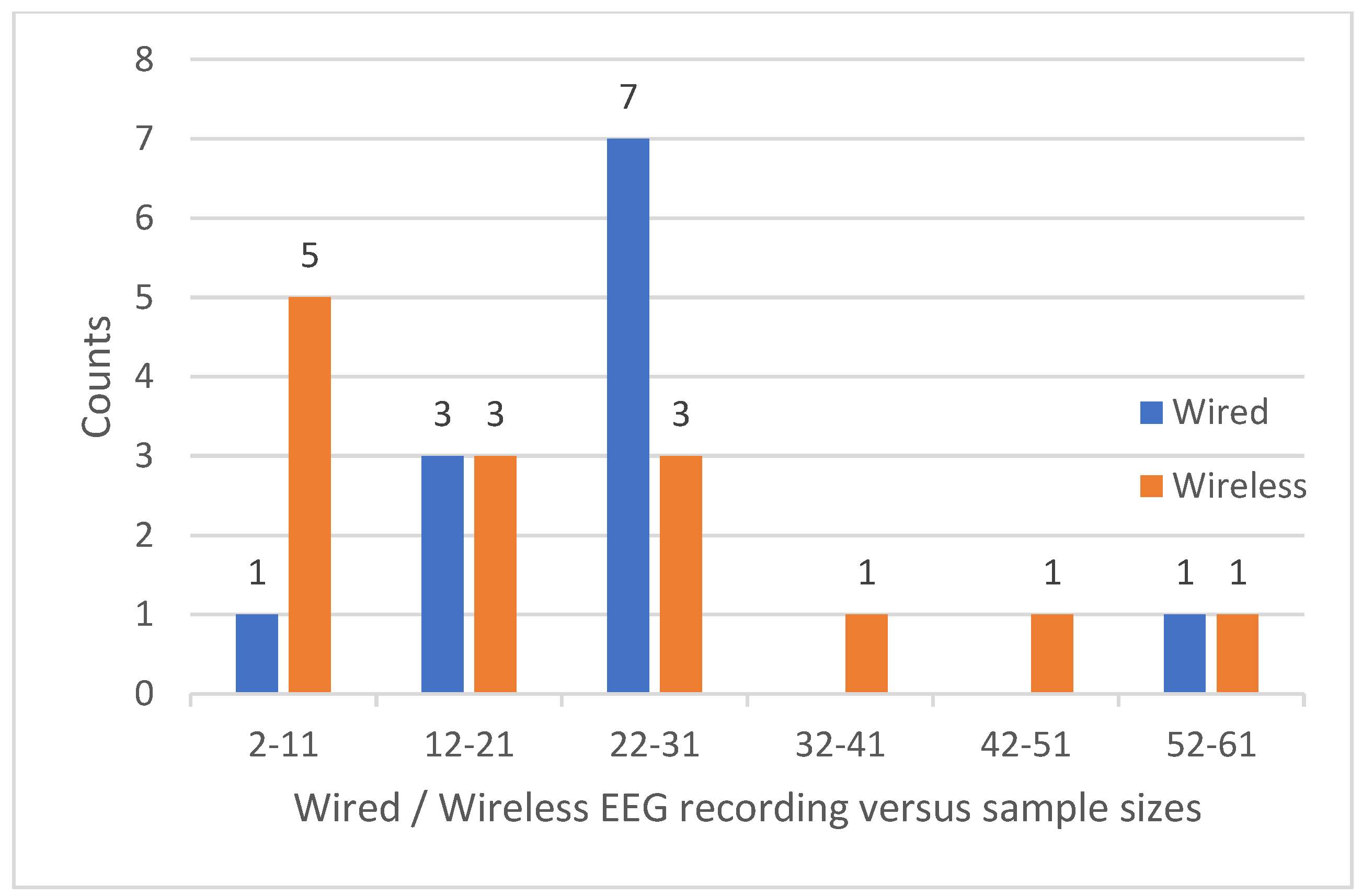
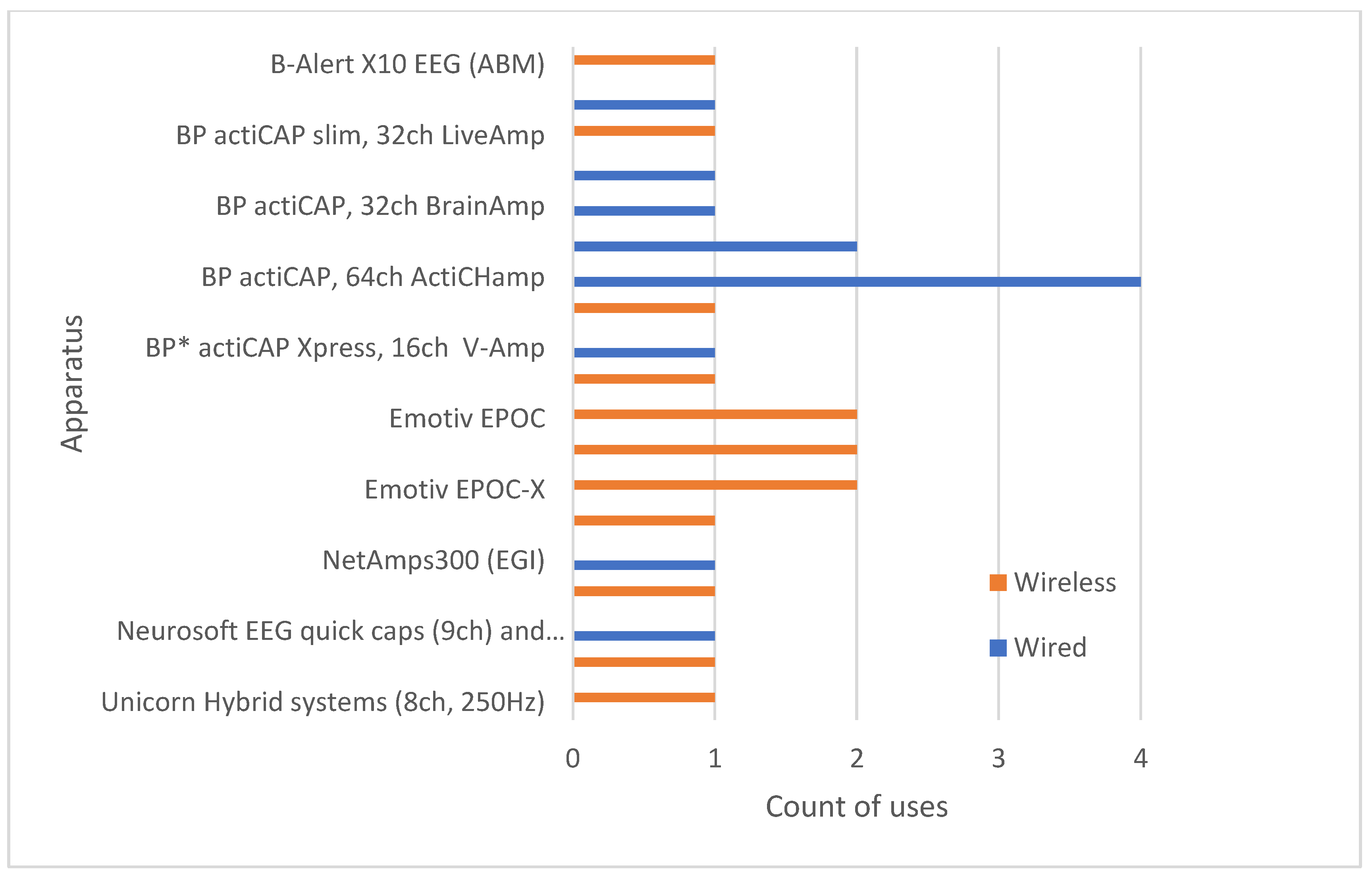
6. Results
7. Discussion
7.1. Q1: Methodological Aspects, Experimental Settings, Sample Sizes, Hardware and Software Used
7.2. Q2: What Is Investigated, What Is the Subject of Research and what Information is Extracted from EEG Signals
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stangor, C.; Walinga, J. Introduction to Psychology; 1st Canadian edition.; BCcampus, BC Open Textbook Project: Victoria, 2014; ISBN 978-1-77420-005-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, D.; De Smedt, B.; Grabner, R.H. Neuroeducation – A Critical Overview of An Emerging Field. Neuroethics 2012, 5, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA APA Dictionary of Psychology. Available online: https://dictionary.apa.org/ (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Bruer, J.T. Education and the Brain: A Bridge Too Far. Educ. Res. 1997, 26, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, C.-H. Basics of EEG: Generation, Acquisition, and Applications of EEG. In Computational EEG Analysis: Methods and Applications; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2018 ISBN 9789811309076.
- Singh, S.P. Magnetoencephalography: Basic Principles. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2014, 17, S107–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, G.H. Overview of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-L.; Wagner, J.; Heugel, N.; Sugar, J.; Lee, Y.-W.; Conant, L.; Malloy, M.; Heffernan, J.; Quirk, B.; Zinos, A.; et al. Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Its Clinical Application in the Field of Neuroscience: Advances and Future Directions. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, H.; Hill, R.M.; Feys, O.; Holmes, N.; Osborne, J.; Doyle, C.; Bobela, D.; Corvilian, P.; Wens, V.; Rier, L.; et al. A Novel, Robust, and Portable Platform for Magnetoencephalography Using Optically Pumped Magnetometers 2024, 2024.03.06.583313.
- Hramov, A.E.; Maksimenko, V.A.; Pisarchik, A.N. Physical Principles of Brain–Computer Interfaces and Their Applications for Rehabilitation, Robotics and Control of Human Brain States. Phys. Rep. 2021, 918, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mustieles, M.A.; Lima-Carmona, Y.E.; Pacheco-Ramírez, M.A.; Mendoza-Armenta, A.A.; Romero-Gómez, J.E.; Cruz-Gómez, C.F.; Rodríguez-Alvarado, D.C.; Cruz-Garza, J.G.; Arceo, A.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.A. Wearable Biosensor Technology in Education: A Systematic Review. 2024.
- SAYGINER, Ş.; BALAMAN, F.; TİRYAKİ, S.H. The Current Trend in Educational Neuroscience Research: A Descriptive and Bibliometric Study. J. Comput. Educ. Res. 2022, 10, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.; Chambers, J. EEG Signal Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, England; Hoboken, NJ, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-02581-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lotte, F.; Bougrain, L.; Cichocki, A.; Clerc, M.; Congedo, M.; Rakotomamonjy, A.; Yger, F. A Review of Classification Algorithms for EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces: A 10 Year Update. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 031005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raufi, B.; Longo, L. An Evaluation of the EEG Alpha-to-Theta and Theta-to-Alpha Band Ratios as Indexes of Mental Workload. Front. Neuroinformatics 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, L.; Chu, J.; Zhu, W.; Hu, B.; He, H.; Yang, L. An Augmented Reality Based Mobile Photography Application to Improve Learning Gain, Decrease Cognitive Load, and Achieve Better Emotional State. Int. J. Human–Computer Interact. 2023, 39, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emy Nguyen What Are the Performance Metrics Detection Suite? EMOTIV 2019.
- Halderman, L.K.; Finn, B.; Lockwood, J. r.; Long, N.M.; Kahana, M.J. EEG Correlates of Engagement During Assessment. ETS Res. Rep. Ser. 2021, 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollan, J.K.; Hoxha, D.; Chihade, D.; Pflieger, M.E.; Rosebrock, L.; Cacioppo, J. Frontal Alpha EEG Asymmetry before and after Behavioral Activation Treatment for Depression. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 99, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Espinal, E.; Aupperle, R.L.; Nikulina, V.; Stewart, J.L. The Electrical Aftermath: Brain Signals of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Filtered Through a Clinical Lens. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, M.F.; Gable, P.A. Frontal Asymmetry in an Approach–Avoidance Conflict Paradigm. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.F.; Bolger, D.J. The Neurophysiological Bases of EEG and EEG Measurement: A Review for the Rest of Us: Neurophysiological Bases of EEG. Psychophysiology 2014, 51, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappenman, E.S.; Farrens, J.L.; Zhang, W.; Stewart, A.X.; Luck, S.J. ERP CORE: An Open Resource for Human Event-Related Potential Research. NeuroImage 2021, 225, 117465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Oxford Handbook of Event-Related Potential Components; Kappenman, E.S., Luck, S.J., Eds.; 1st ed.; Oxford University Press, 2011; ISBN 978-0-19-537414-8.
- Luck, S.J. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique; Second edition.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2014; ISBN 978-0-262-52585-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bentin, S.; Allison, T.; Puce, A.; Perez, E.; McCarthy, G. Electrophysiological Studies of Face Perception in Humans. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.M.; Schweinberger, S.R.; Burton, A.M. N250 ERP Correlates of the Acquisition of Face Representations across Different Images. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutas, M.; Hillyard, S.A. Reading Senseless Sentences: Brain Potentials Reflect Semantic Incongruity. Science 1980, 207, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comerchero, M.D.; Polich, J. P3a and P3b from Typical Auditory and Visual Stimuli. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näätänen, R.; Paavilainen, P.; Rinne, T.; Alho, K. The Mismatch Negativity (MMN) in Basic Research of Central Auditory Processing: A Review. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2544–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, W.J.; Goss, B.; Coles, M.G.H.; Meyer, D.E.; Donchin, E. The Error-Related Negativity. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 13, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.M.; Eberhard, A.C.; Walker, M.S.; Bennion, A.; South, M.; Larson, M.J. Dissociating the Effect of Reward Uncertainty and Timing Uncertainty on Neural Indices of Reward Prediction Errors: A Reward Positivity (RewP) Event-Related Potential (ERP) Study. Biol. Psychol. 2021, 163, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudfit, G.H. The Reward Positivity: From Basic Research on Reward to a Biomarker for Depression. Psychophysiology 2015, 52, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Wu, Y.; Kateb, R.; Bouridane, A. Electroencephalography Signal Processing: A Comprehensive Review and Analysis of Methods and Techniques. Sensors 2023, 23, 6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-P. Preprocessing of EEG. In Computational EEG Analysis: Methods and Applications; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2018 ISBN 9789811309076.
- Cohen, M.X. Analyzing Neural Time Series Data: Theory and Practice; The MIT Press, 2014; ISBN 978-0-262-31955-3.
- Lotte, F.; Congedo, M.; Lécuyer, A.; Lamarche, F.; Arnaldi, B. A Review of Classification Algorithms for EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, R1–R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Koester, J.; Mack, S.H.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Principles of Neural Science, Sixth Edition; McGraw Hill, 2021; ISBN 978-1-259-64224-1.
- Niso, G.; Romero, E.; Moreau, J.T.; Araujo, A.; Krol, L.R. Wireless EEG: A Survey of Systems and Studies. NeuroImage 2023, 269, 119774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Di Florio, A.; Babiloni, F. The Dry Revolution: Evaluation of Three Different EEG Dry Electrode Types in Terms of Signal Spectral Features, Mental States Classification and Usability. Sensors 2019, 19, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eeg10-20 10–20 System (EEG). Wikipedia 2023.
- openEEG Welcome to the OpenEEG Project. Available online: https://openeeg.sourceforge.net/doc/ (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Sawangjai, P.; Hompoonsup, S.; Leelaarporn, P.; Kongwudhikunakorn, S.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. Consumer Grade EEG Measuring Sensors as Research Tools: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3996–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleichner, M.G.; Mirkovic, B.; Debener, S. Identifying Auditory Attention with Ear-EEG: cEEGrid versus High-Density Cap-EEG Comparison. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 066004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlogl, A.; Brunner, C. BioSig: A Free and Open Source Software Library for BCI Research. Computer 2008, 41, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillet, S.; Friston, K.; Oostenveld, R. Academic Software Applications for Electromagnetic Brain Mapping Using MEG and EEG. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.W.; Bateman, D.; Hauberg, S.; Wehbring, R. GNU Octave Version 7.2.0 Manual: A High-Level Interactive Language for Numerical Computations. 2022.
- Lopez-Calderon, J.; Luck, S.J. ERPLAB: An Open-Source Toolbox for the Analysis of Event-Related Potentials. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, F.C.; Thorne, J.; Edmonds, B.; Schneider, T.; Eichele, T.; Debener, S. Semi-Automatic Identification of Independent Components Representing EEG Artifact. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, Y.; Lotte, F.; Gibert, G.; Congedo, M.; Maby, E.; Delannoy, V.; Bertrand, O.; Lécuyer, A. OpenViBE: An Open-Source Software Platform to Design, Test, and Use Brain–Computer Interfaces in Real and Virtual Environments. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2010, 19, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.-M. FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG, and Invasive Electrophysiological Data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memmott, T.; Koçanaoğulları, A.; Lawhead, M.; Klee, D.; Dudy, S.; Fried-Oken, M.; Oken, B. BciPy: Brain–Computer Interface Software in Python. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2021, 8, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramfort, A.; Luessi, M.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.A.; Strohmeier, D.; Brodbeck, C.; Parkkonen, L.; Hämäläinen, M.S. MNE Software for Processing MEG and EEG Data. NeuroImage 2014, 86, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirce, J.; Gray, J.R.; Simpson, S.; MacAskill, M.; Höchenberger, R.; Sogo, H.; Kastman, E.; Lindeløv, J.K. PsychoPy2: Experiments in Behavior Made Easy. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, M.; Brainard, D.; Pelli, D.; Ingling, A.; Murray, R.; Broussard, C. What’s New in Psychtoolbox-3. Perception 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Brainard, D.H. The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spat. Vis. 1997, 10, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.J.; Hecker, K.G.; Krigolson, O.E.; Jamniczky, H.A. A Reinforcement-Based Learning Paradigm Increases Anatomical Learning and Retention-A Neuroeducation Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.J.; Warren, A.L.; Abdullayeva, N.; Krigolson, O.; Hecker, K.G. Pathologists Aren’t Pigeons: Exploring the Neural Basis of Visual Recognition and Perceptual Expertise in Pathology. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukakis, S. Exploring Brain Activity and Transforming Knowledge in Visual and Textual Programming Using Neuroeducation Approaches. AIMS Neurosci. 2019, 6, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukakis, S.; Papalaskari, M.-A.; Vlamos, P.; Plerou, A.; Giannopoulou, P. Undergraduate Students’ Brain Activity in Visual and Textual Programming. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1194, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, G.L.; Innis, I.J. Electroencephalography ( Eeg ). In The International Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods; Matthes, J., Davis, C.S., Potter, R.F., Eds.; Wiley, 2017; pp. 1–18 ISBN 978-1-118-90176-2.
- Fard, M.H.; Petrova, K.; Doborjeh, M.; Kasabov, N. Using EEG Data and NeuCube for the Study of Transfer of Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), IEEE; 2020; pp. 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, A.T.; Kamronn, S.; Dmochowski, J.; Parra, L.C.; Hansen, L.K. EEG in the Classroom: Synchronised Neural Recordings during Video Presentation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmochowski, J.; Sajda, P.; Dias, J.; Parra, L. Correlated Components of Ongoing EEG Point to Emotionally Laden Attention – A Possible Marker of Engagement? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopczynski, A.; Stahlhut, C.; Larsen, J.E.; Petersen, M.K.; Hansen, L.K. The Smartphone Brain Scanner: A Portable Real-Time Neuroimaging System. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e86733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroer, J.E.; Thomas, R.D. Learning the Law of Reflection: Event-Related Potentials of Children Aged 6–12 during Educational Video Game Play. Mind Brain Educ. 2020, 14, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutafina, E.; Heiligers, A.; Popovic, R.; Brenner, A.; Hankammer, B.; Jonas, S.M.; Mathiak, K.; Zweerings, J. Tracking of Mental Workload with a Mobile EEG Sensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Monge, A.; Rodríguez-Navarro, H.; Marbán, J.-M. Potentialities and Limitations of the Use of EEG Devices in Educational Contexts. Comun. Media Educ. Res. J. 2023, 31, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhdana, I.; P, C.; Lb, F.; Hg, L.; Pm, L.; G, A.-D.; P, P.; S, M.; M, R.; Ma, M. Effects of Reading Contextualized Physics Problems among Men and Women: A Psychophysiological Approach. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 2023, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, A.S.; Donato, L.G.; Vettori, M.; Zaro, M.A. Effects of the Binaural Wave as a Stimulus for Student Hyperattention: Brain Frequency Records without Interactive Media Context. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2020, 7, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onieva López, J.L.; Maqueda Cuenca, E.; Felipe Morales, A.; García Ruiz, M.A. E-Textbooks vs. Print Textbooks: A Neuroscientific Study on Reading and Completing Exercises in Primary School Students. 2021.
- Byczynski, G.E.; D’Angiulli, A. Frontal P300 Asymmetry and Congruence Judgment: Retroactive Switching Is Impaired during School Day Mornings in Female Adolescents. Curr. Res. Neurobiol. 2024, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, P.; Zeng, J. Inhibiting the Whole Number Bias in a Fraction Comparison Task: An Event-Related Potential Study. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2020, Volume 13, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelling-Desmeules, Y.; Brault Foisy, L.-M.; Potvin, P.; Lapierre, H.G.; Ahr, E.; Léger, P.-M.; Masson, S.; Charland, P. Persistence of the “Moving Things Are Alive” Heuristic into Adulthood: Evidence from EEG. CBE Life Sci. Educ. 2021, 20, ar45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.C.; Kappen, M.; Hassall, C.D.; Wright, B.; Krigolson, O.E. Thinking Theta and Alpha: Mechanisms of Intuitive and Analytical Reasoning. NeuroImage 2019, 189, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez Varón, D.; Bellido-García, I.; Gupta, B.B. Analysis of Stress, Attention, Interest, and Engagement in Onsite and Online Higher Education: A Neurotechnological Study. Comunicar 2023, 31, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Monge, A.; Rodríguez-Navarro, H.; González-Calvo, G.; Bores-García, D. Brain Activity during Different Throwing Games: EEG Exploratory Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khramova, M.V.; Kuc, A.K.; Maksimenko, V.A.; Frolov, N.S.; Grubov, V.V.; Kurkin, S.A.; Pisarchik, A.N.; Shusharina, N.N.; Fedorov, A.A.; Hramov, A.E. Monitoring the Cortical Activity of Children and Adults during Cognitive Task Completion. Sensors 2021, 21, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.C.; Hecker, K.G.; Paget, M.K.; Coderre, S.P.; Burak, K.W.; Wright, B.; Krigolson, O.E. The Application of Reward Learning in the Real World: Changes in the Reward Positivity Amplitude Reflect Learning in a Medical Education Context. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2018, 132, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.C.; Hassall, C.D.; Lindenbach, T.; Krigolson, O.E. Reward Prediction Errors Reflect an Underlying Learning Process That Parallels Behavioural Adaptations: A Trial-to-Trial Analysis. Comput. Brain Behav. 2020, 3, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassall, C.D.; Hajcak, G.; Krigolson, O.E. The Importance of Agency in Human Reward Processing. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 19, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrella, E.M.; Cowan, C.; Girdner, J.; Watson, M.K.; Anderson, R. Measuring Connections: Engineering Students’ Cognitive Activities and Performance on Complex Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE); IEEE; 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Mustieles, M.A.; Lima-Carmona, Y.E.; Mendoza-Armenta, A.A.; Hernandez-Machain, X.; Garza-Vélez, D.A.; Carrillo-Márquez, A.; Rodríguez-Alvarado, D.C.; Lozoya-Santos, J. de J.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.A. An EEG Dataset of Subject Pairs during Collaboration and Competition Tasks in Face-to-Face and Online Modalities. Data 2024, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Armenta, A.A.; Blanco-Téllez, P.; García-Alcántar, A.G.; Ceballos-González, I.; Hernández-Mustieles, M.A.; Ramírez-Mendoza, R.A.; Lozoya-Santos, J. de J.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.A. Implementation of a Real-Time Brain-to-Brain Synchrony Estimation Algorithm for Neuroeducation Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-De León, R.; Cham-Pérez, M.L.L.; Elizondo-Villegas, V.A.; Villarreal-Villarreal, A.; Ortiz-Espinoza, A.A.; Vélez-Saboyá, C.S.; Lozoya-Santos, J.D.J.; Cebral-Loureda, M.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.A. EEG and Physiological Signals Dataset from Participants during Traditional and Partially Immersive Learning Experiences in Humanities. Data 2024, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.; Belkacem, A.N. Investigating the Phenomenon of Brain-to-Brain Synchronization and Cognitive Dynamics in Remote Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 80086–80098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubov, V.V.; Khramova, M.V.; Goman, S.; Badarin, A.A.; Kurkin, S.A.; Andrikov, D.A.; Pitsik, E.; Antipov, V.; Petushok, E.; Brusinskii, N.; et al. Open-Loop Neuroadaptive System for Enhancing Student’s Cognitive Abilities in Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 49034–49049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.A.A.; Moreira, J.A.M.; Zambrano, M.J.Z.; Rivas, F.E.C.; Pilligua, M.L.B. Applied Neuroscience in Early Childhood and High School Education. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2021, 5, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusz, P.J.; Dikker, S.; Huth, A.G.; Perrodin, C. Are We Ready for Real-World Neuroscience? J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadina, J.N. The Synergy Zone: Connecting the Mind, Brain, and Heart for the Ideal Classroom Learning Environment. Brain Sci. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience; 1st ed.; Harper & Row: New York, 1990; ISBN 978-0-06-016253-5. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, A.U.; Madathil, D.; Fan, Y.-T.; Tzeng, O.J.L.; Huang, C.-M.; Huang, H.-W. Neurofeedback for the Education of Children with ADHD and Specific Learning Disorders: A Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
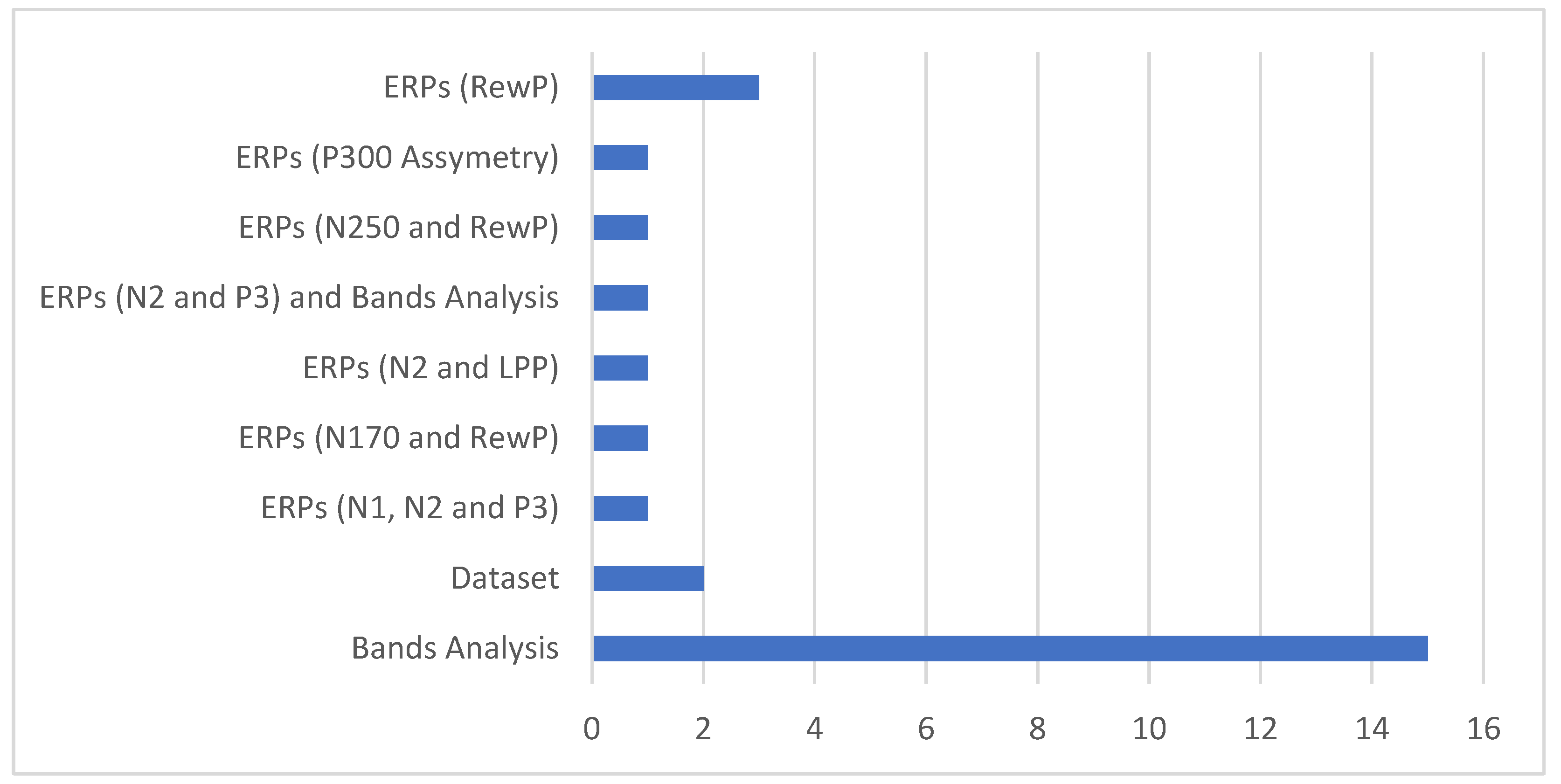
| Project | Subject | Sample | EEG metrics | H/W used | S/W used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anderson et al (2018), [59] | Efficacy of Just in Time teaching in anatomy education. | 24 students (11m.+23 f.), m.age=20.74 | N250 and RewP ERPs | BP* actiCAP Xpress + 16ch V-Amp | Psychophysics Matlab Toolbox, Brain Vision Recorder |
| Anderson et al (2023), [60] | Diagnostic accuracy factors examination | 26 students(23f.+3m.), m.age=19.8 and 9 experts (6f+3m), m.age=44.1 | RewP and N170 ERPs | BP 32ch actiCAP slim + LiveAmp | Psychophysics Matlab Toolbox, Brain Vision Recorder |
| Doukakis et al (2019-20), [61,62] | Students’ performance in programming tasks | 8 first year students (3f. + 5m.) | EEG negative means value and time. | BIOPAC MP150 | AckKnowledge 4.3 |
| Fard et al (2020), [64] | Transfer learning during computer programming tasks | 8 male students (18-21 y.o) | EEG alpha and theta bands power spectrums and models of neuronal connectivity | Emotiv EPOC-X | OpenSesame, EEGLAB, NeuCube with Spike Neural Networks (SNNs) models. |
| Poulsen et al (2017), [65] | Brain synchronization and engagement while watching videos | 42 f. (m.age=22.4) | Intersubject correlation (ISC) | Emotiv EPOC | Corrmap Matlab Toolbox |
| Schroer et al (2020), [68] | Spatial reasoning | 21 children (11m.+10f.), 6-12 y.old | N2 and P3 ERPs, Joint time frequencies of alpha | NetAmps300 (EGI) | Nestation 4.5 (EGI) |
| Zhao et al (2023), [16] | Effectiveness of AR app to assist learning | 28 persons (7m.+21f.) m.age=20 | Emotional state indexes from Brain waves | Emotiv EPOC+ | EmotivPro |
| García-Monge et al, (2023), [70] | Exploration of potentialities and issues using portable EEG in classrooms | 17 primary sch. Children, (10f.+7m.), 8-9 y.o | 2’ EEG recording with eyes closed and 2’ with eyes open. Frequency domain analyses. | Brainlink Pro, Emotiv Epoc, Epoc Flex, Muse | EEGLAB, Lucid Scribe, Emotiv TestBench, EmotivPro, Mind monitor |
| Bouhdana et al (2023), [71] | Effects of context and gender in physics problems | 60 participants, (32f.+28m.), m.age=23.7 | Cognitive engagement indexes β/(α+θ) | BP ActiCAP + 32ch BrainAmp | BrainVision Analyzer (v2.0), Matlab |
| Bos et al (2020), [72] | Effects of low frequency binaural waves to attention levels | 2 students with ages from 20 to 28 y.o | Frequencies analysis performed by the proprietary software | Neurosky Mindwave | Effective Learner app. (Neurosky) |
| Onieva et al (2021), [73] | Brain responses differences and similarities while reading digital or paper textbooks | 3 pupils (1m. +2f.), 12 y.o | Emotional state indexes from Brain waves and FAA | Emotiv EPOC | Emotiv software |
| Byczynski and Angiulli (2024), [74] | Congruence judgement in relation to school days and starting times | 24 female students, m.age=16.9 | Frontal P300 assymentry | Neurosoft EEG quick caps (9ch) and SynAmps2 (Compumedics Neuroscan) | SCAN 4.3 (Compumedics Neuroscan) and Stim2 for stimuli presentation |
| Fu et al (2020), [75] | Inhibitory control performing fraction comparisons | 28 students, m.age=20.8 | N1, N2 and P3 ERPs | BP ActiCAP, 64ch | BrainVision Analyzer (v2.0) |
| Skelling-Desmeules et al (2021), [76] | Persistence of minconceptions in biological studies | 28 students, (13f.+15m.),m.age= 23.7 | N2 and LPP ERPs | BP ActiCAP, 64ch | BrainVision Analyzer (v2.0), E-prime |
| Williams et al (2019), [77] | Intuitive and analytical thinking | 30 undergrad students (22f.+8m.), (m.age=22.8) | Alpha and theta activity in parietal and frontal areas. | BP ActiCAP, 64ch + ActiCHamp | BrainVision (v.1.10), EEGLAB and R language |
| Juarez-Varon et al (2023), [78] | Analysis of stress, attention, interest, and engagement in onsite and online learning | 20 pg students (22-25 y.o, 10m.+10f.) | Alpha, beta, and theta activity | Emotiv EPOC + | EmotivPRO (v2.0) and R language |
| Garcia-Monge et al (2020), [79] | Brain activity differences in various types of throwing games | 8 children (m.age=7.2) | Brain bands (mostly beta) activity | Emotiv EPOC-X | Emotiv Brain Activity Map and Emotiv TestBench, EEGLAB |
| Khramova et al (2021), [80] | Differences in cortical activities of adults and children | 12 children (3f.+9m.) 7-8 y.o. and 10 adults (3f+7m) (18-20 y.o.) | Brain bands (mostly alpha and beta) activity | BP ActiCAP, 32ch + ActiCHamp | EEGLAB and FieldTrip |
| Williams et al (2018), [81] | Reflection of reinforcement learning in RewP ERP | 30 students (23f.+7m.), m.age=20 | RewP ERP | BP ActiCAP, 64ch ActiCHamp | BrainVision Analyzer |
| Williams et al (2020), [82] | Reward Predictions errors as indications of learning processes | 30 students (19f.+11m.), m.age=20 | RewP ERP | BP ActiCAP, 64ch ActiCHamp | Brain Vision Analyzer and Psychophysics Toolbox for stimuli presentation |
| Hassal et al (2019), [83] | The role of control over actions in reward processing | 26 students (13m.+13f.), m.age=21.54) | RewP ERP | BP ActiCAP, 64ch ActiCHamp | BrainVision (v.2.1.2) and EEGLAB |
| Barrella et al (2019), [84] | Measurement of cognitive load in concept handling tasks | 23 students (13m.+10f.), m.age=19.25) | Alpha over theta waves ratio | B-Alert X10 EEG (ABM) | ABM’s B-Alert Live software |
| Hernandez-Mustieles et al (2024), [85] | Public Dataset of parallel EEG recordings during Collaboration and Competition Tasks | 16 subject pairs by 1 m. and 1 f. (aged 18-24) | Enophones | EEGLAB | |
| Rome-De Leon et al (2024), [87] | Public dataset of EEG and other physiological signals recordings during two teaching scenarios for humanities studies | 24 students (10 m. and 14 f.., aged 18-25, mean=21.33, sd=1.4) | OpenBCI Ultracortex Mark IV | OpenBCI GUI and EEGLAB |
|
| Jamil et al (2024), [88] | Brain to brain synchronization during remote learing. | 10 students aged 18-28 and one instructor | Time series and frequency domain correlations. | Unicorn Hybrid systems (8ch, 250Hz) | |
| Grubov et al (2024), [89] | Cognitive abilities assessment and feedback in form of recommendations | 60 pupils in two age groups, 9-10 and 11-12 years old, 36 boys and 24 girls. | Alpha band power variance. | BP LiveAmp (64ch, 500Hz) | EEGLAB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





