Submitted:
02 December 2024
Posted:
03 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Raw
3.2. SCFr Process Optimization
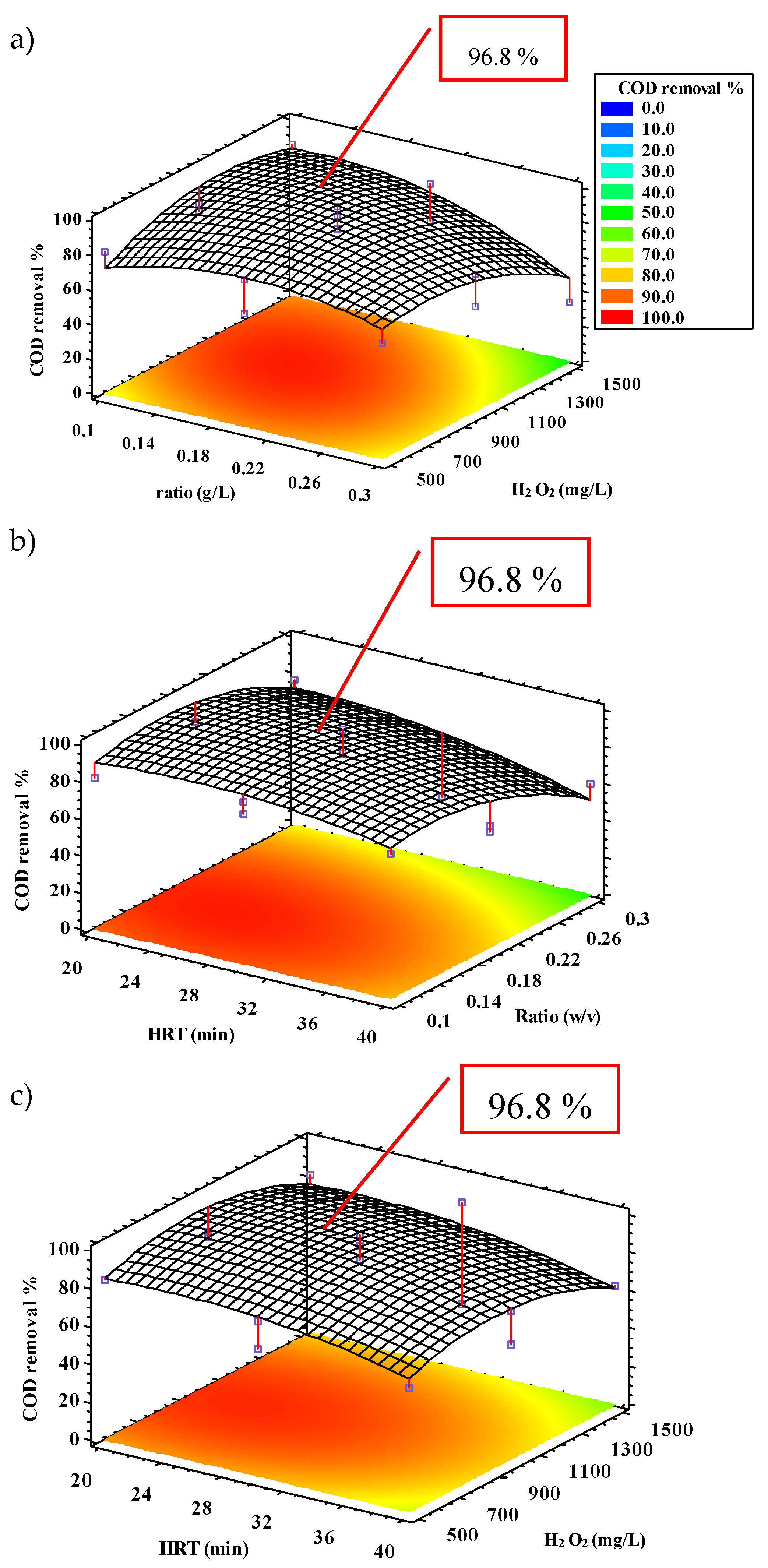
3.2.1. COD Removal
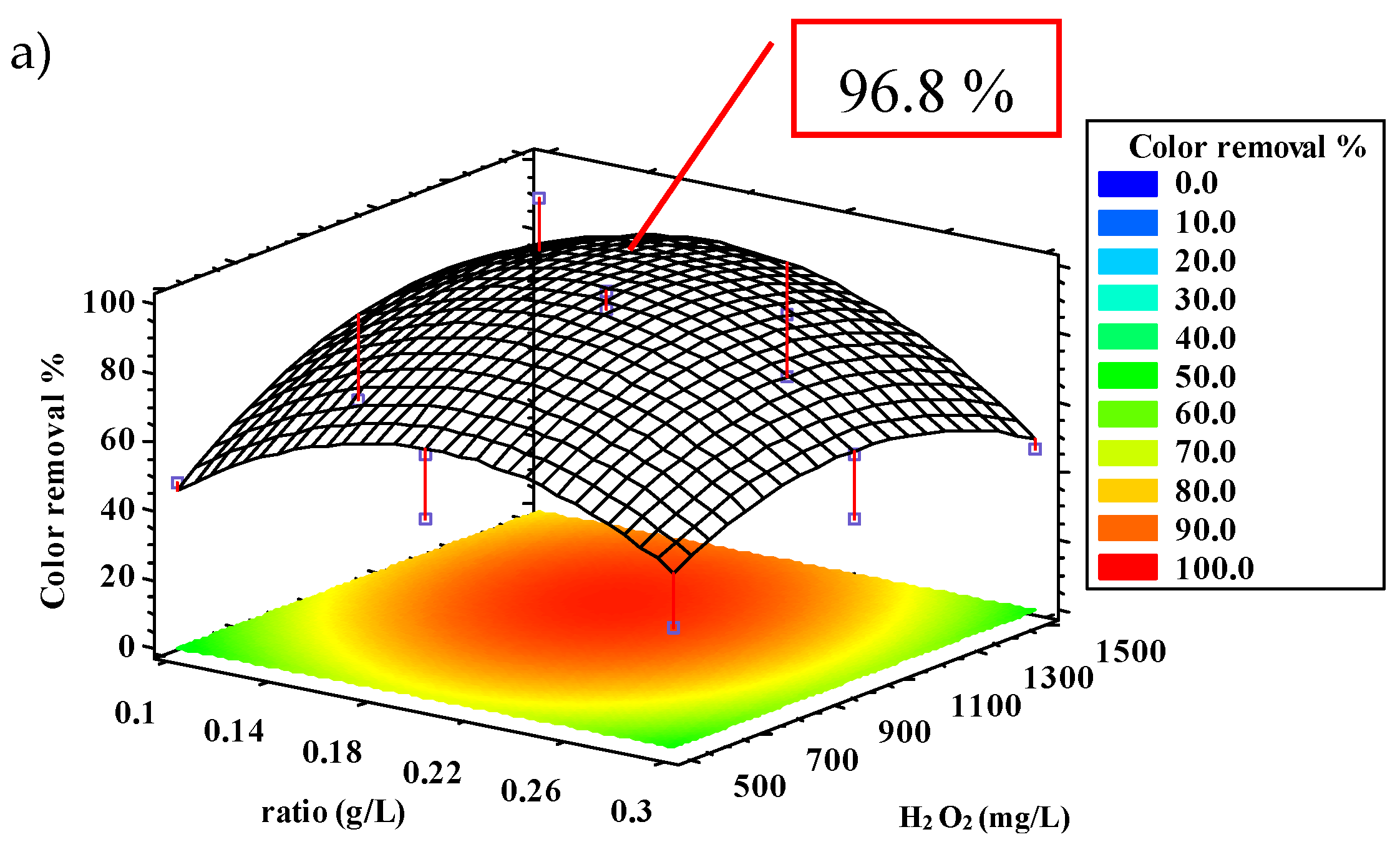
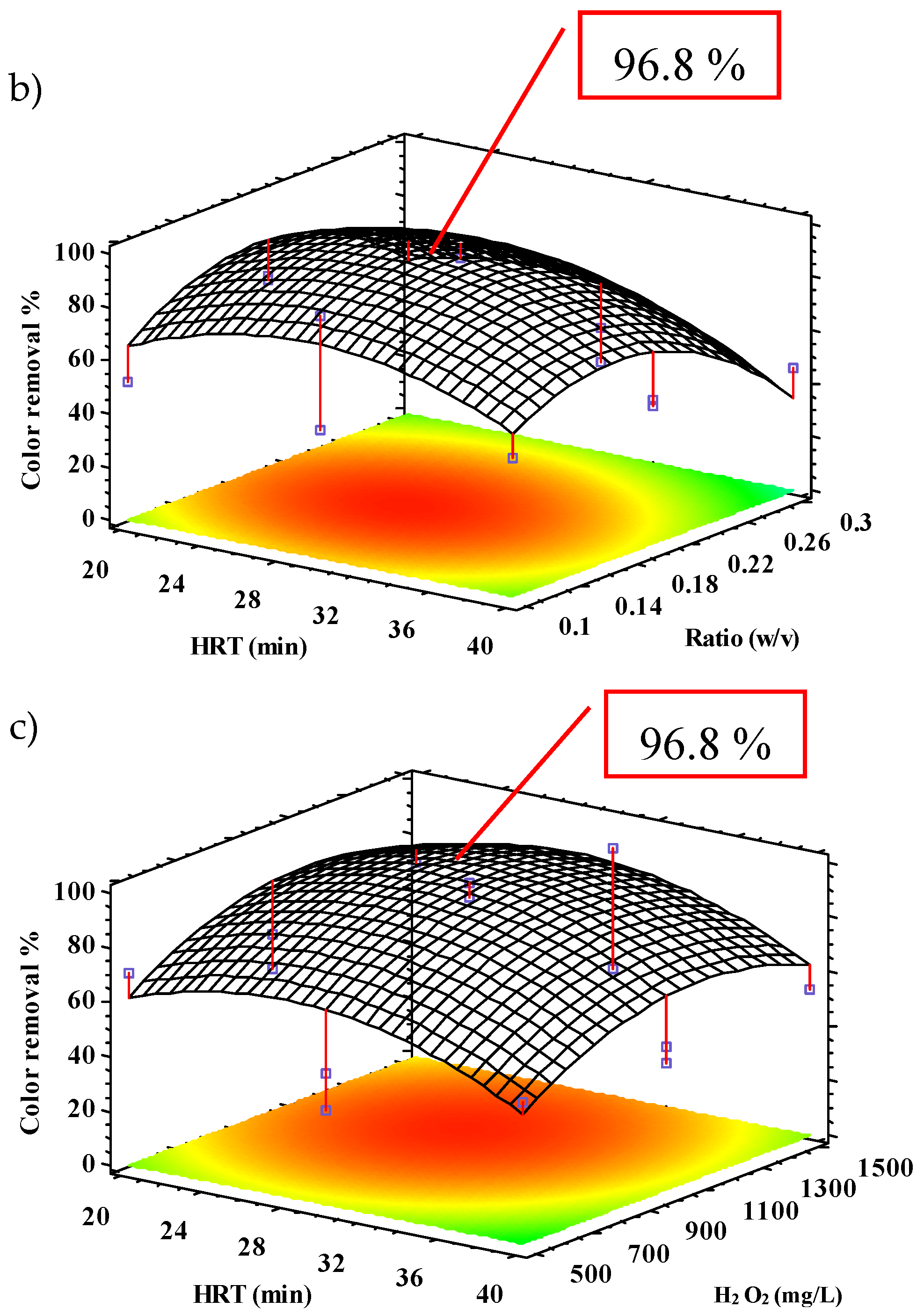
2.2.2. Color Removal
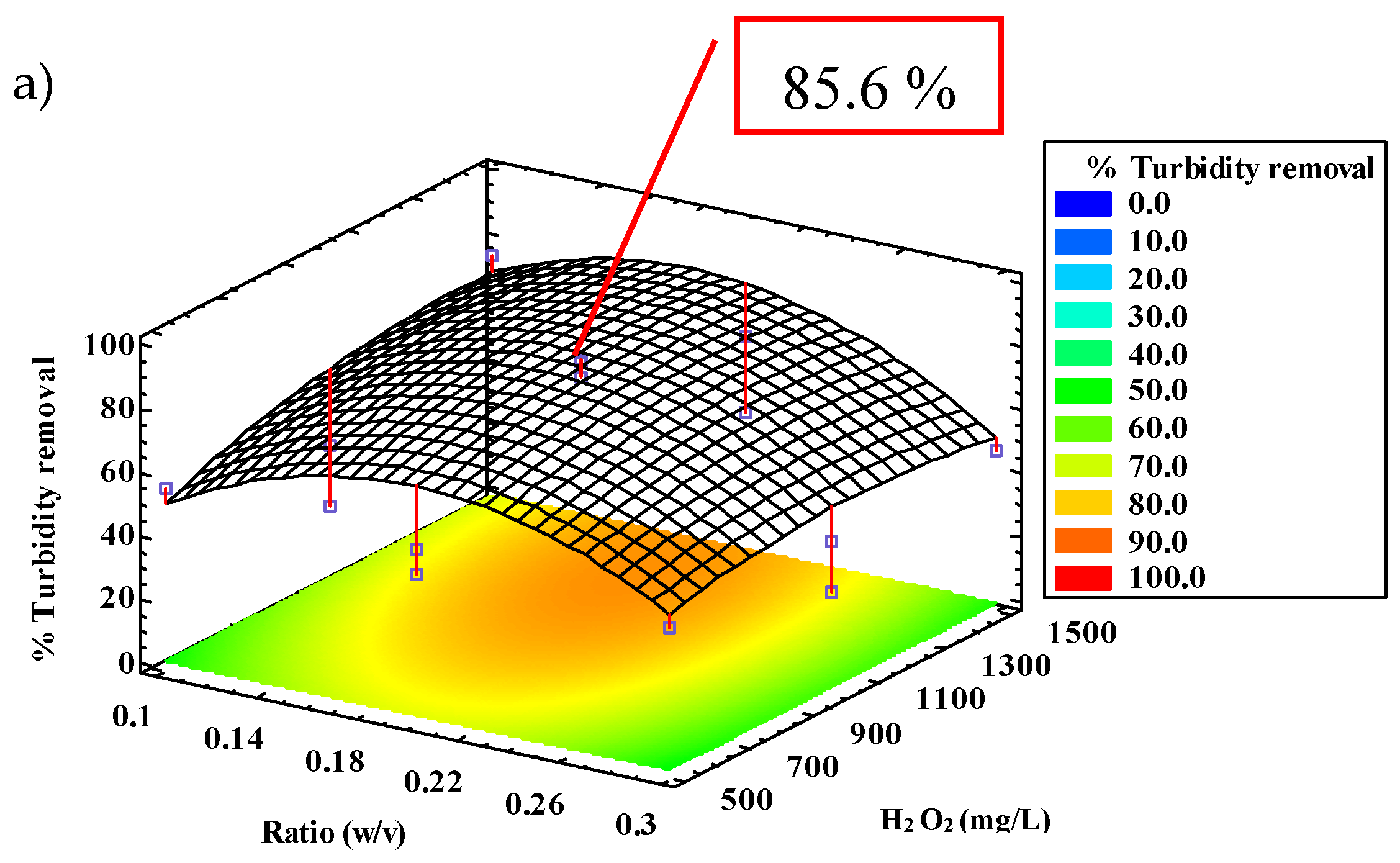
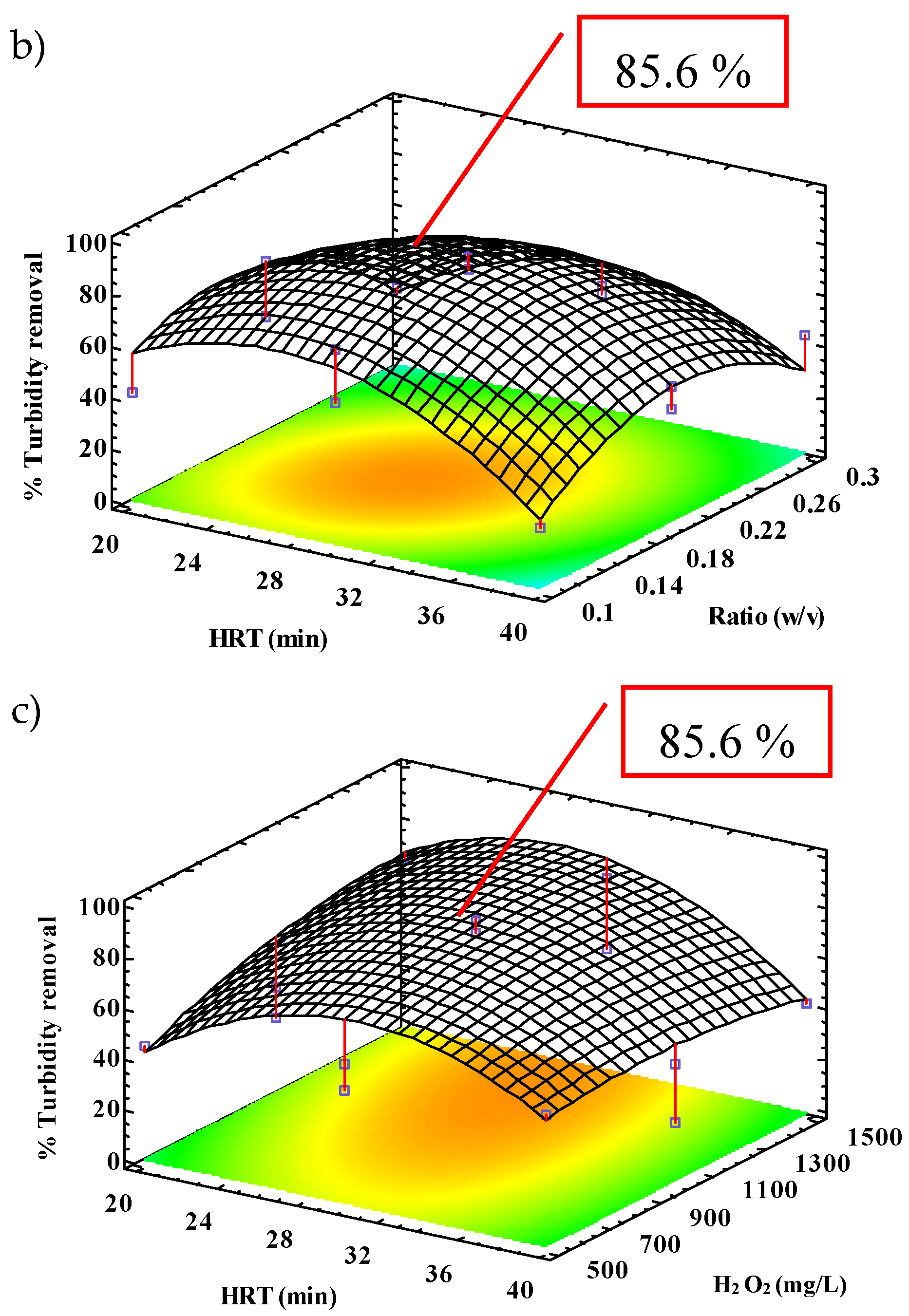
2.2.3. Turbidity Removal
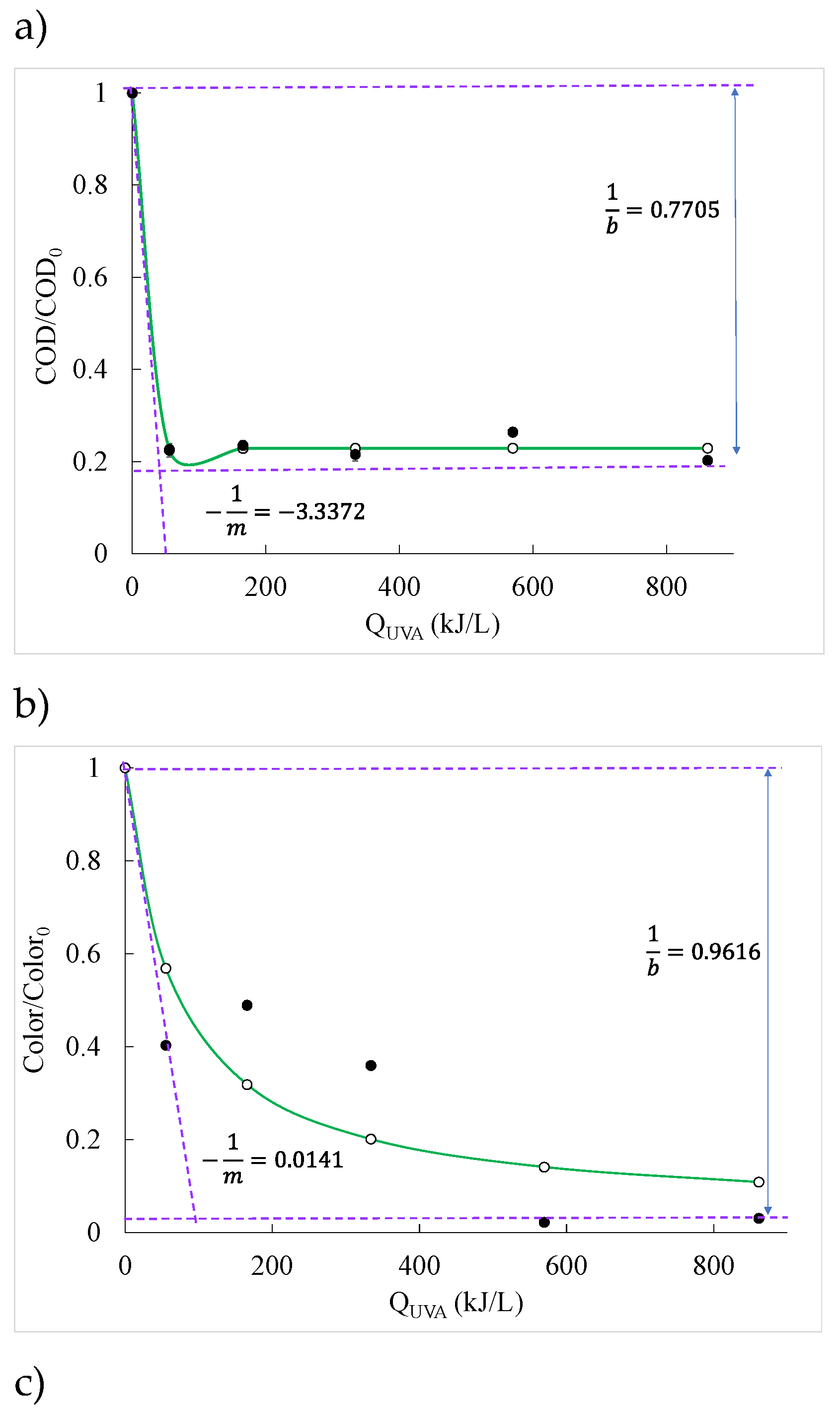
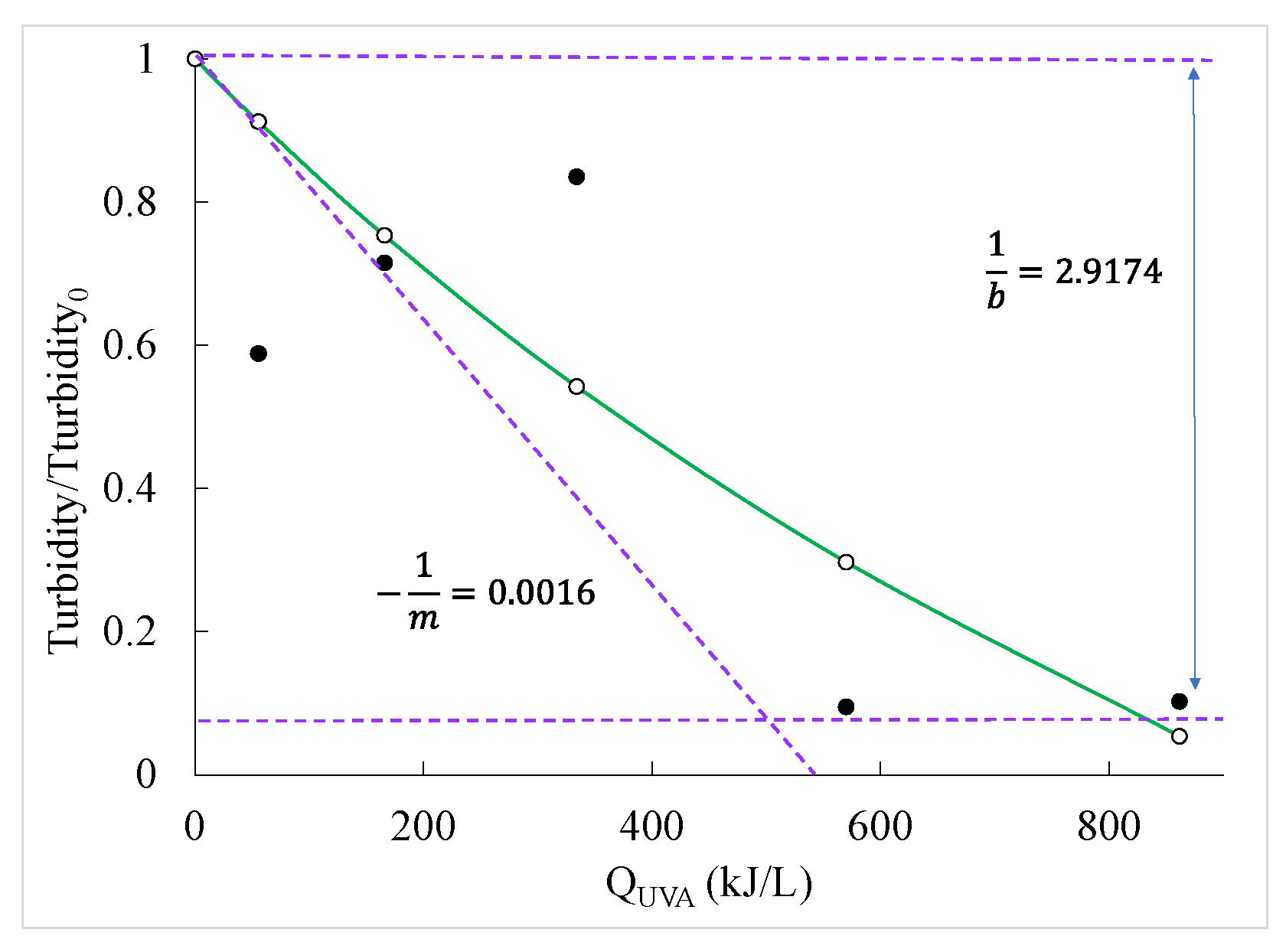
2.3. Kinetic Models
2.4. Effect of Sunlight
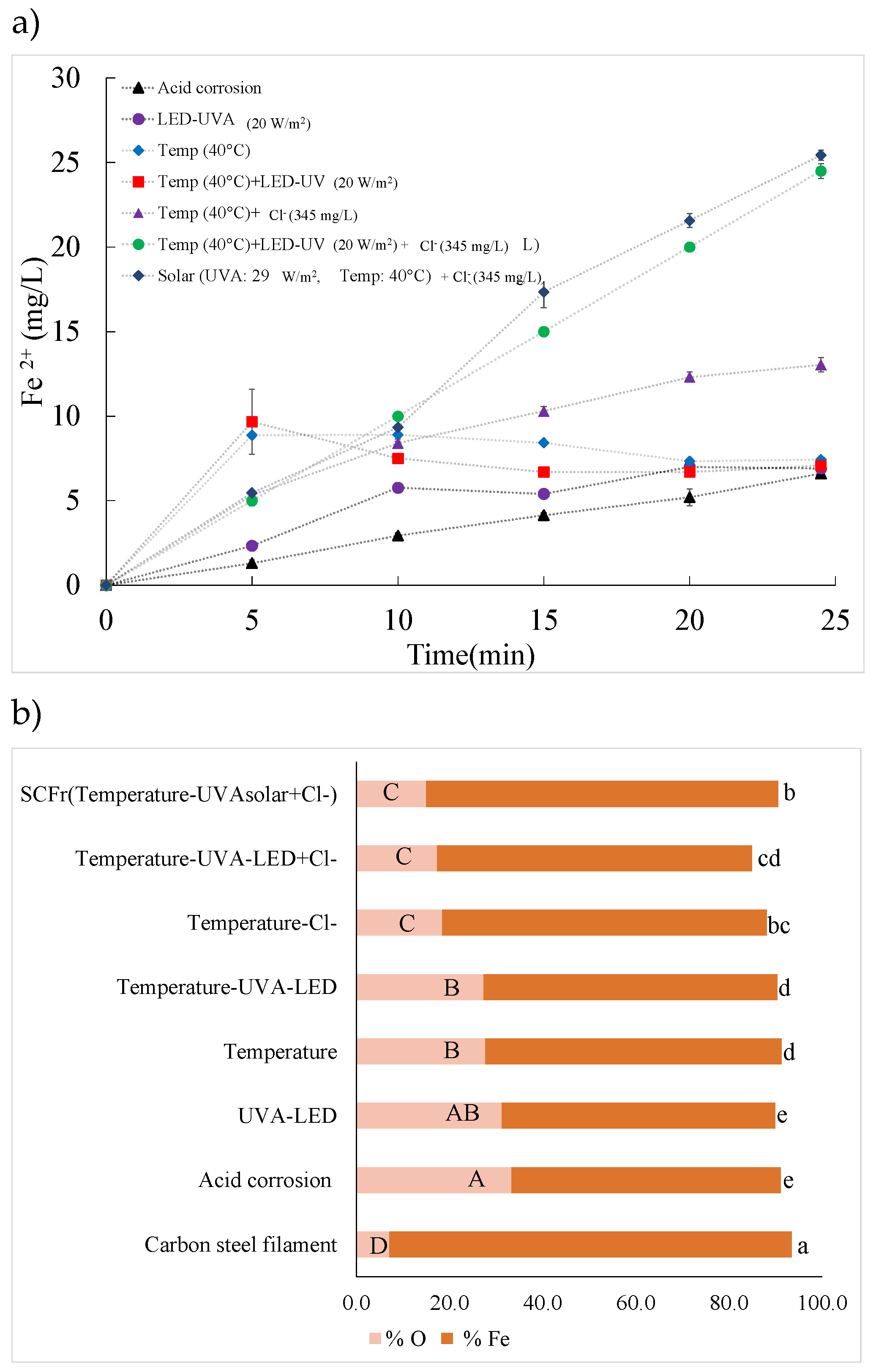
2.5. Fe2+ Release
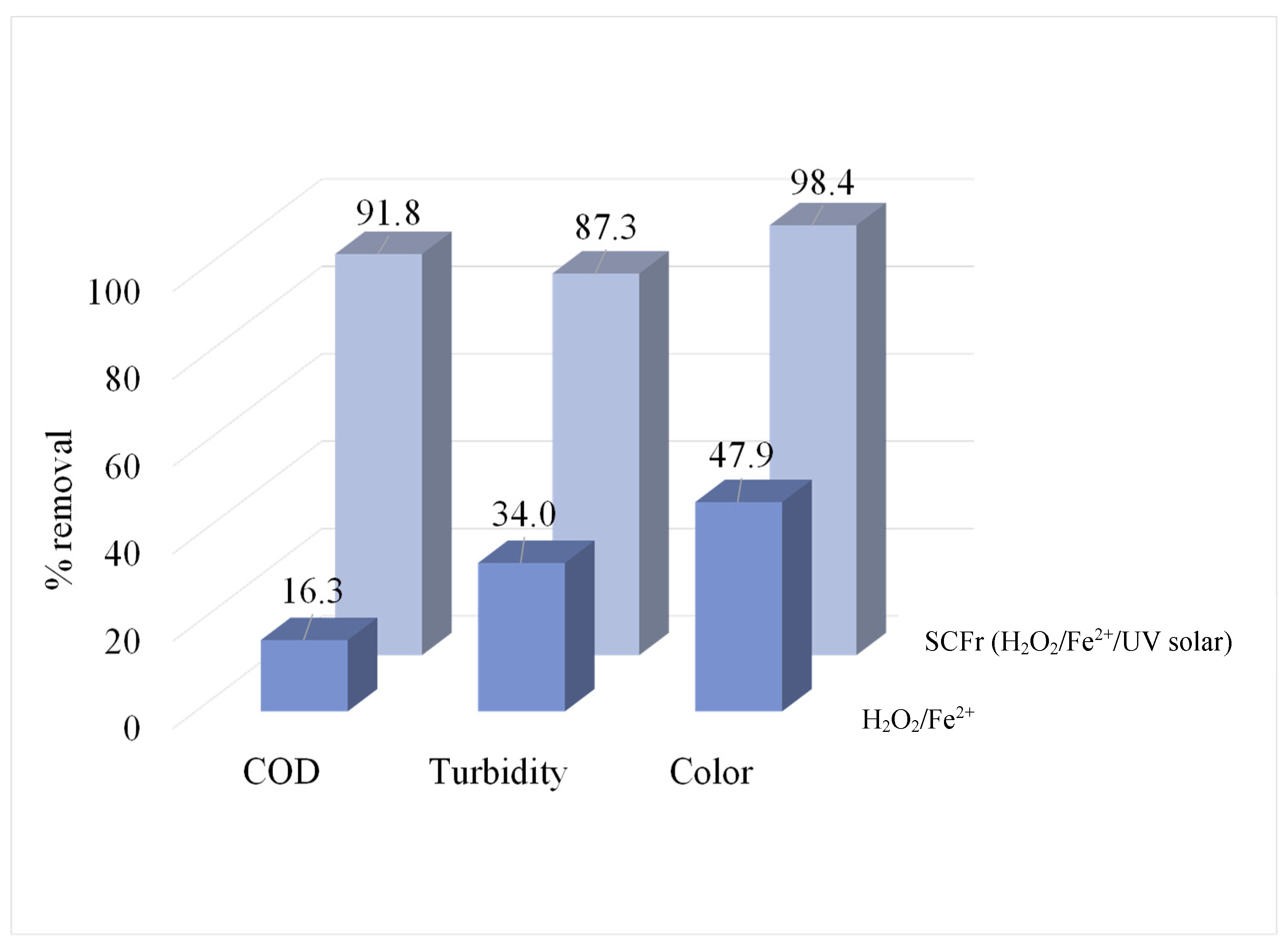
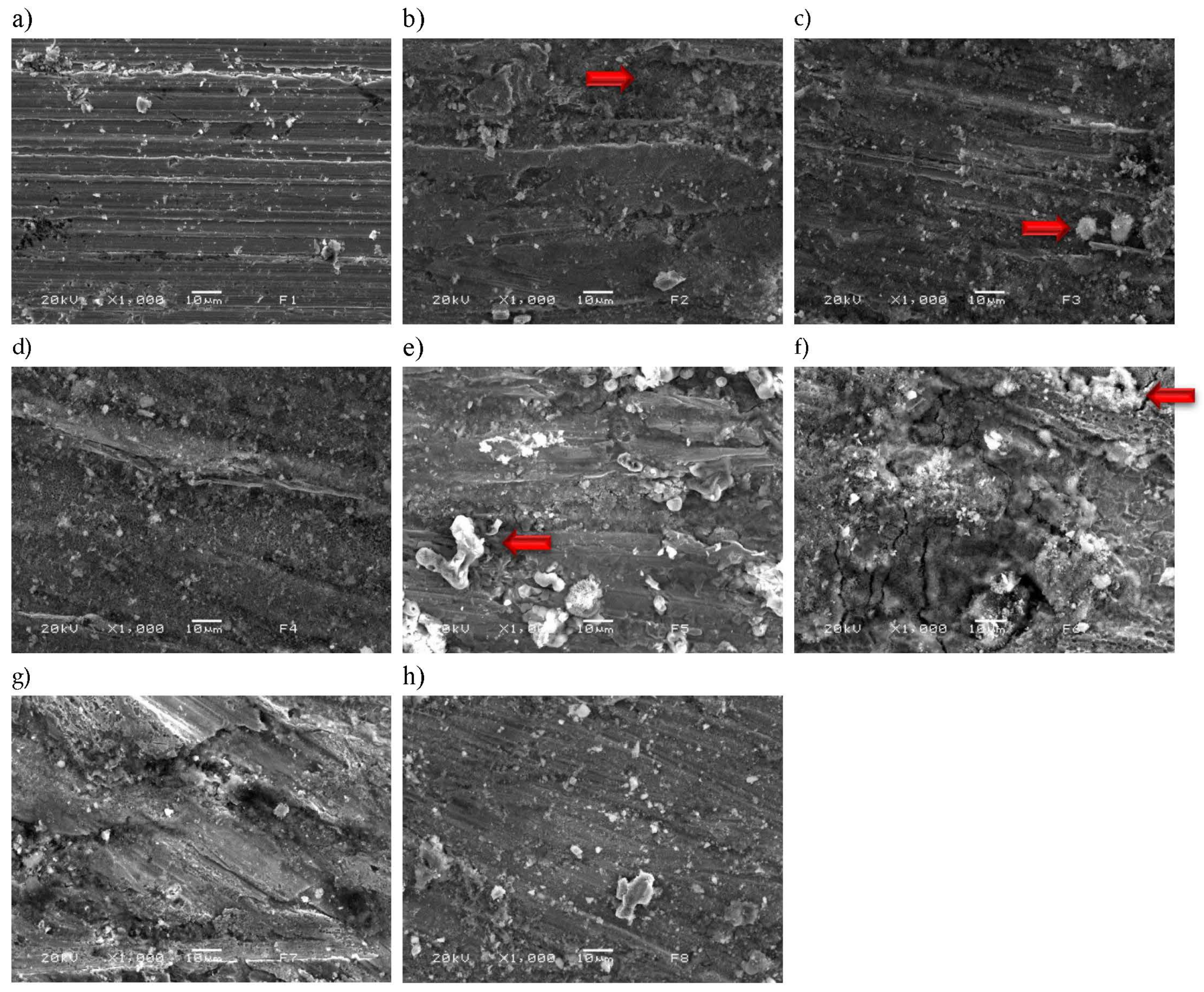
3.6. Final Characterization
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
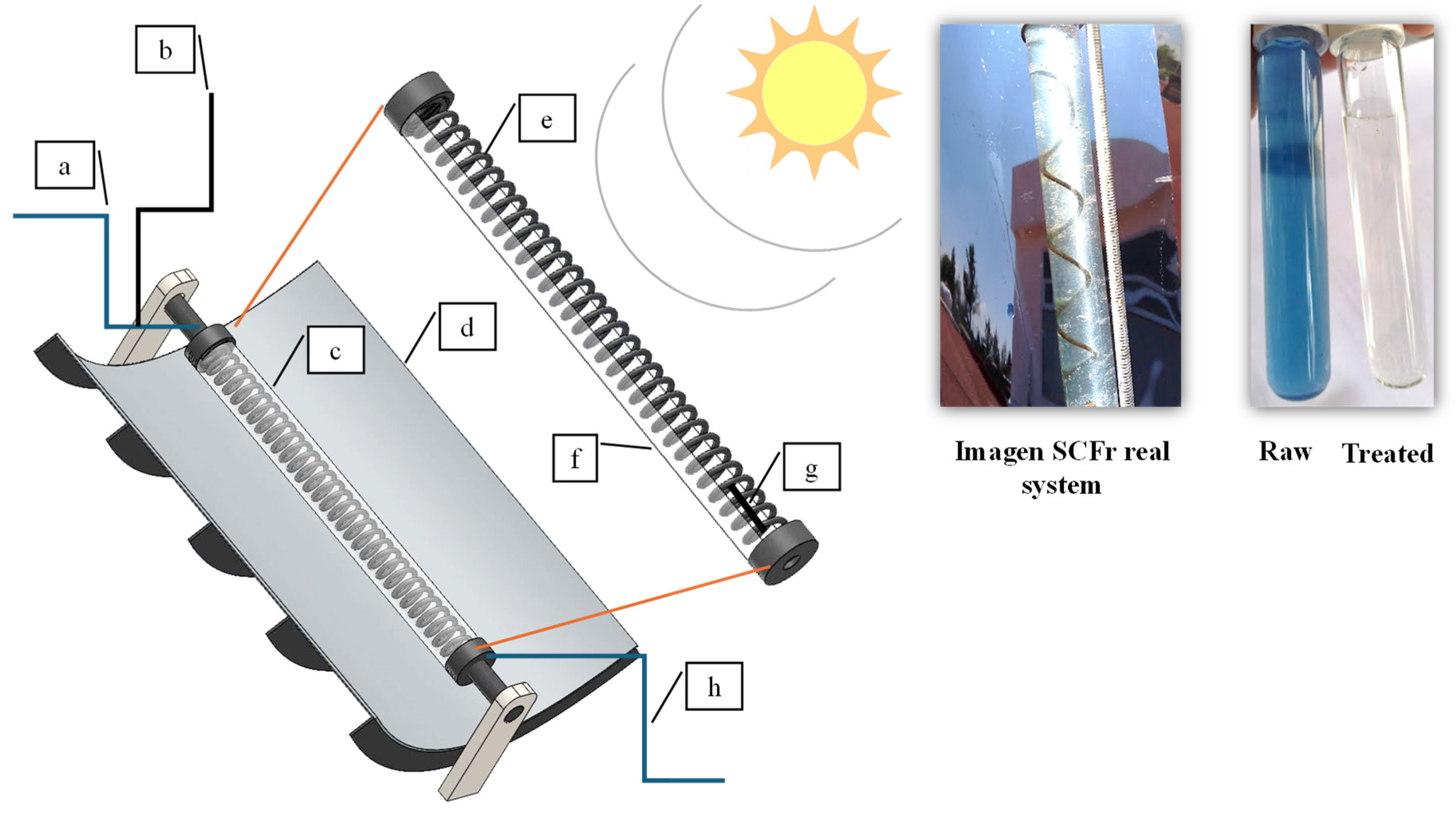
3.2. Solar Corrosion Fenton Reactor (SCFr)
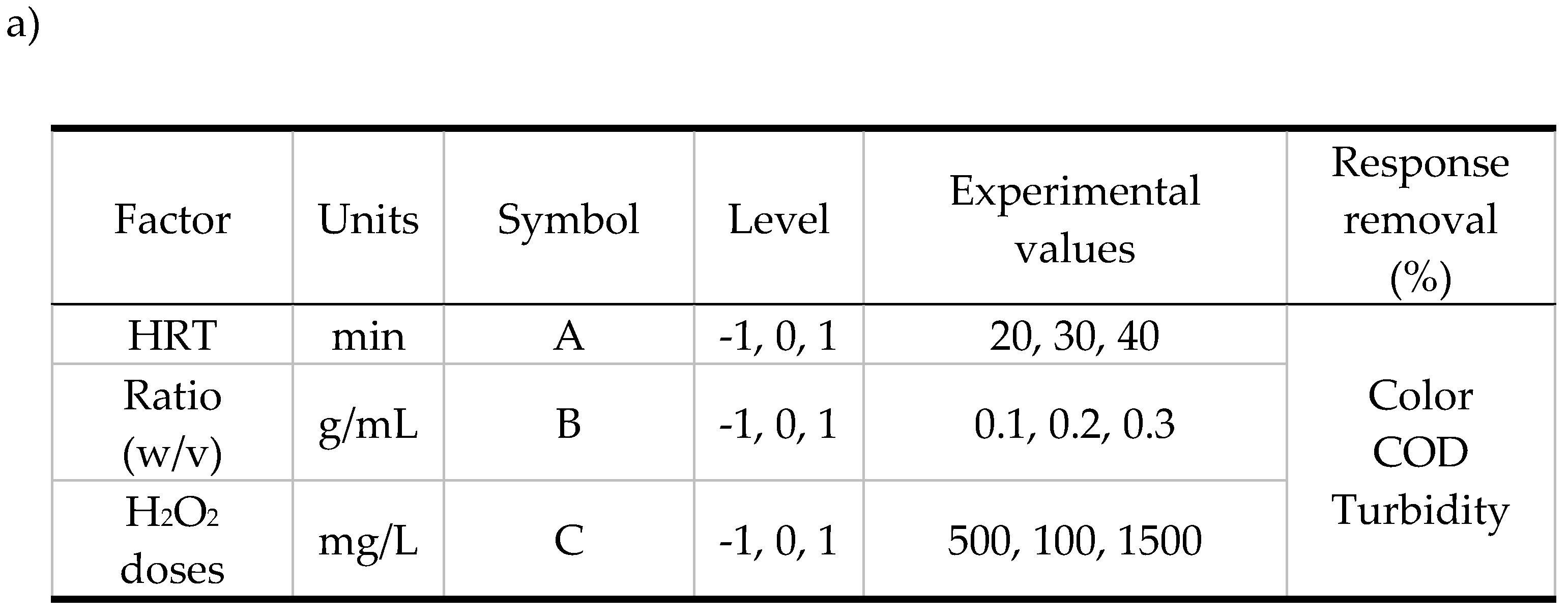
3.3. Optimization of the SCFr
3.4. Kinetic Models
3.5. Effect of the Solar Light
3.6. Fe2+ Release
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- B. Hajjar, “How the textile industry can help countries recover from COVID-19,” Word Economic Forum. Islamic Development Bank.Islamic Development Bank., 2020. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/08/how-the-textile-industry-can-help-countries-recover-from-covid-19/.
- J. Rovira and J. L. Domingo, “Human health risks due to exposure to inorganic and organic chemicals from textiles: A review,” Environ. Res., vol. 168, no. September 2018, pp. 62–69, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. U. Khan, S. Ahmed, Y. Dhoble, and S. Madhav, “A critical review of hazardous waste generation from textile industries and associated ecological impacts,” J. Indian Chem. Soc., vol. 100, no. 1, p. 100829, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Koszewska, “Circular Economy - Challenges for the Textile and Clothing Industry,” Autex Res. J., 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. P. Periyasamy and J. Militky, Denim processing and health hazards. Elsevier Ltd., 2017.
- A. K. Roy Choudhury, “Finishing of denim fabrics,” in Principles of Textile Finishing, Elsevier, 2017, pp. 383–415.
- D. Sharma, Water footprint of denim industry (Read from pg 111) in Sustainability in denim (Elsevier), no. July. 2020.
- M. C. Tomei, J. Soria Pascual, and D. Mosca Angelucci, “Analysing performance of real textile wastewater bio-decolourization under different reaction environments,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 129, pp. 468–477, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Yaseen and M. Scholz, “Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review,” Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 1193–1226, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Sánchez-Sánchez, M. Tejocote-Pérez, R. M. Fuentes-Rivas, I. Linares-Hernández, V. Martínez-Miranda, and R. M. G. Fonseca-Montes De Oca, “Treatment of a textile effluent by electrochemical oxidation and coupled system electooxidation- salix babylonica,” Int. J. Photoenergy, vol. 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. O. Ramos, M. V. C. Albuquerque, W. S. Lopes, J. T. Sousa, and V. D. Leite, “Degradation of indigo carmine by photo-Fenton, Fenton, H2O2/UV-C and direct UV-C: Comparison of pathways, products and kinetics,” J. Water Process Eng., vol. 37, p. 101535, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. P. Singh, P. K. Singh, R. Gupta, and R. L. Singh, Treatment and Recycling of Wastewater from Textile Industry. 2019.
- A. Othmani, A. Kesraoui, and M. Seffen, “The alternating and direct current effect on the elimination of cationic and anionic dye from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation and coagulation flocculation,” Euro-Mediterranean J. Environ. Integr., vol. 2, no. 1, p. 6, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- B. Keskin, M. E. Ersahin, H. Ozgun, and I. Koyuncu, “Pilot and full-scale applications of membrane processes for textile wastewater treatment: A critical review,” J. Water Process Eng., vol. 42, no. March, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. GilPavas and S. Correa-Sanchez, “Assessment of the optimized treatment of indigo-polluted industrial textile wastewater by a sequential electrocoagulation-activated carbon adsorption process,” J. Water Process Eng., vol. 36, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ö. Kahraman and İ. Şimşek, “Color removal from denim production facility wastewater by electrochemical treatment process and optimization with regression method,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 267, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Yin et al., “Textile wastewater treatment for water reuse: A case study,” Processes, vol. 7, no. 1, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Chowdhury, S. Khandaker, F. Sarker, A. Islam, M. T. Rahman, and M. R. Awual, “Current treatment technologies and mechanisms for removal of indigo carmine dyes from wastewater: A review,” J. Mol. Liq., vol. 318, p. 114061, 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. B. de Leon, B. A. F. de Negreiros, C. Z. Brusamarello, G. Petroli, M. Di Domenico, and F. B. de Souza, “Artificial neural network for prediction of color adsorption from an industrial textile effluent using modified sugarcane bagasse: Characterization, kinetics and isotherm studies,” Environ. Nanotechnology, Monit. Manag., vol. 14, no. October, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Hendaoui, M. Trabelsi-Ayadi, and F. Ayari, “Optimization and mechanisms analysis of indigo dye removal using continuous electrocoagulation,” Chinese J. Chem. Eng., vol. 29, pp. 242–252, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Leila et al., “Fertilization value of municipal sewage sludge for Eucalyptus camaldulensis plants,” Biotechnol. Reports, vol. 13, no. 2017, pp. 8–12, 2017. [CrossRef]
- O. S. Djandja, L. X. Yin, Z. C. Wang, and P. G. Duan, “From wastewater treatment to resources recovery through hydrothermal treatments of municipal sewage sludge: A critical review,” Process Saf. Environ. Prot., vol. 151, pp. 101–127, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. U. H. Khan et al., “Removal of organic pollutants through hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., vol. 267, no. July, p. 115564, 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. Wang, Y. Zhou, S. Cao, J. Lu, and Y. Zhou, “Degradation of sulfanilamide by Fenton-like reaction and optimization using response surface methodology,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., vol. 172, no. 130, pp. 334–340, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Castañeda-Juárez et al., “Oxidation of N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (acetaminophen) by a galvanic Fenton and solar galvanic Fenton processes,” Sol. Energy, vol. 199, no. November 2019, pp. 731–741, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, C. J. Miller, R. N. Collins, and T. D. Waite, “Key Considerations When Assessing Novel Fenton Catalysts: Iron Oxychloride (FeOCl) as a Case Study,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 55, no. 19, pp. 13317–13325, 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Cheng, L. Liang, J. Ye, N. Li, B. Yan, and G. Chen, “Influence and mechanism of water matrices on H2O2-based Fenton-like oxidation processes: A review,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 888, p. 164086, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Kerboua, N. Haddour, I. Gasmi, and O. Hamdaoui, “Water Remediation from Recalcitrant Pollution Using the Galvano-Fenton Process: A Modeling Approach of the Hydroxyl Radical Generation and the Energy Efficiency,” Eurasia Proc. Sci. Technol. Eng. Math., vol. 21, pp. 506–516, 2022. [CrossRef]
- I. Gasmi, K. Kerboua, N. Haddour, O. Hamdaoui, A. Alghyamah, and F. Buret, “Kinetic pathways of iron electrode transformations in Galvano-Fenton process: A mechanistic investigation of in-situ catalyst formation and regeneration,” J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., vol. 116, pp. 81–91, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. S. Tadayozzi, F. A. dos Santos, E. F. Vicente, and J. C. Forti, “Application of oxidative process to degrade paraquat present in the commercial herbicide,” J. Environ. Sci. Heal. - Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes, vol. 56, no. 7, pp. 670–674, 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Lazorenko, A. Kasprzhitskii, and T. Nazdracheva, “Anti-corrosion coatings for protection of steel railway structures exposed to atmospheric environments: A review,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 288, p. 123115, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zhang, Z. Ye, Z. Zhu, X. Liu, J. Zhang, and F. Cao, “Separation and kinetic study of iron corrosion in acidic solution via a modified tip generation/substrate collection mode by SECM,” Corros. Sci., vol. 139, no. January, pp. 403–409, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Gomes, M. Navas, N. Uranga, T. Paiva, I. Figueira, and T. C. Diamantino, “High-temperature corrosion performance of austenitic stainless steels type AISI 316L and AISI 321H, in molten Solar Salt,” Sol. Energy, vol. 177, no. November 2018, pp. 408–419, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Gomez-Vidal and R. Tirawat, “Corrosion of alloys in a chloride molten salt (NaCl-LiCl) for solar thermal technologies,” Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, vol. 157, pp. 234–244, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Alam and M. R. Islam, “Pre-post Bleaching Behaviors of Cotton Knits Using Reductive and Oxidative bleaches,” Int. J. Polym. Text. Eng., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 42–53, 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. Reddythota and, M. Teferi Timotewos, “Evaluation of Pollution Status and Detection of the Reason for the Death of Fish in Chamo Lake, Ethiopia,” J. Environ. Public Health, vol. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Allemand and D. Osborn, “Ocean acidification impacts on coral reefs: From sciences to solutions,” Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci., vol. 28, p. 100558, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Azanaw, B. Birlie, B. Teshome, and M. Jemberie, “Textile effluent treatment methods and eco-friendly resolution of textile wastewater,” Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng., vol. 6, no. July, p. 100230, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Ben Salah, M. Missaoui, A. Attia, G. Lesage, M. Heran, and R. Ben Amar, “Treatment of real textile effluent containing indigo blue dye by hybrid system combining adsorption and membrane processes,” Front. Membr. Sci. Technol., vol. 3, no. March, pp. 1–14, 2024. [CrossRef]
- F. Uddin, “Environmental hazard in textile dyeing wastewater from local textile industry,” Cellulose, vol. 28, no. 17, pp. 10715–10739, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Ilyas, W. Ahmad, H. Khan, S. Yousaf, M. Yasir, and A. Khan, “Environmental and health impacts of industrial wastewater effluents in Pakistan: A review,” Rev. Environ. Health, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 171–186, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Bijay-Singh and E. Craswell, “Fertilizers and nitrate pollution of surface and ground water: an increasingly pervasive global problem,” SN Appl. Sci., vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 1–24, 2021. [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey, “Hardness of Water,” official website of the United States government, 2018. https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/hardness-water (accessed Jun. 25, 2024).
- S. A. Ibrahim, M. B. Hasan, I. M. Al-Tameemi, T. A. Ibrahim, and M. N. Abbas, “Optimization of adsorption unit parameter of hardness remediation from wastewater using low-cost media,” Innov. Infrastruct. Solut., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 1–12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. F. Couto, L. S. Marques, J. Balmant, A. P. de Oliveira Maia, W. G. Moravia, and M. C. Santos Amaral, “Hybrid MF and membrane bioreactor process applied towards water and indigo reuse from denim textile wastewater,” Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom), vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 725–738, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Zheng, Y. Pan, and X. Xiang, “Oxidation of acidic dye Eosin Y by the solar photo-Fenton processes,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 141, no. 3, pp. 457–464, 2007. [CrossRef]
- P. T. Almazán-Sánchez et al., “Treatment of Indigo-Dyed Textile Wastewater Using Solar Photo-Fenton with Iron-Modified Clay and Copper-Modified Carbon,” Water, Air, Soil Pollut., vol. 228, no. 8, p. 294, Aug. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Mansour, Y. Farid, S. A. Nosier, O. Adli, and M. H. Abdel-Aziz, “Removal of Eosin Yellow dye from industrial wastewater using UV/H2O2 and photoelectro-Fenton techniques,” J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem., vol. 436, no. October 2022, p. 114411, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Qian et al., “The Acceleration of Pitting Corrosion of AISI 304 Stainless Steel by Ultraviolet Light Illumination in Acidic Chloride Solution,” J. Electrochem. Soc., vol. 167, no. 2, p. 021506, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Singh, J. Singh, and H. Singh, “Chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand,” in Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science, Elsevier, 2021, pp. 69–83.
- Ç. Çalık and D. İ. Çifçi, “Comparison of kinetics and costs of Fenton and photo-Fenton processes used for the treatment of a textile industry wastewater,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 304, p. 114234, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. M. R. Santana et al., “Photo-Fenton process under sunlight irradiation for textile wastewater degradation: monitoring of residual hydrogen peroxide by spectrophotometric method and modeling artificial neural network models to predict treatment,” Chem. Pap., vol. 75, no. 6, pp. 2305–2316, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Lanzarini-Lopes, S. Garcia-Segura, K. Hristovski, and P. Westerhoff, “Electrical energy per order and current efficiency for electrochemical oxidation of p-chlorobenzoic acid with boron-doped diamond anode,” Chemosphere, vol. 188, pp. 304–311, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. Tuncer and G. Sönmez, “Removal of COD and Color from Textile Wastewater by the Fenton and UV/H2O2 Oxidation Processes and Optimization,” Water. Air. Soil Pollut., vol. 234, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- F. Hussin, M. K. Aroua, and M. Szlachtac, “Combined solar electrocoagulation and adsorption processes for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution,” Chem. Eng. Process. - Process Intensif., vol. 143, no. March, p. 107619, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Q. Guo et al., “A green solar photo-Fenton process for the degradation of carbamazepine using natural pyrite and organic acid with in-situ generated H2O2,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 784, p. 147187, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Rahman and G. A. Gagnon, “Bench-scale evaluation of drinking water treatment parameters on iron particles and water quality,” Water Res., vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 137–147, 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. D. N. Ramos, C. S. Santana, C. C. V. Velloso, A. H. M. da Silva, F. Magalhães, and A. Aguiar, “A review on the treatment of textile industry effluents through Fenton processes,” Process Saf. Environ. Prot., vol. 155, pp. 366–386, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. A. De León-Condés et al., “Sulfonated and gamma-irradiated waste expanded polystyrene with iron oxide nanoparticles, for removal of indigo carmine dye in textile wastewater,” Heliyon, vol. 5, no. 7, 2019. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Castillo-Suárez, A. G. Sierra-Sánchez, I. Linares-Hernández, V. Martínez-Miranda, and E. A. Teutli-Sequeira, “A critical review of textile industry wastewater: green technologies for the removal of indigo dyes,” Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., no. Ic, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. U. Okoro, S. Sharifi, M. A. Jesson, and J. Bridgeman, “Natural organic matter (NOM) and turbidity removal by plant-based coagulants: A review,” J. Environ. Chem. Eng., vol. 9, no. 6, p. 106588, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. T. Nguyen et al., “Synthesis of natural flowerlike iron-alum oxide with special interaction of Fe-Si-Al oxides as an effective catalyst for heterogeneous Fenton process,” J. Environ. Chem. Eng., vol. 9, no. 4, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Ferreira da Silva, A. Daniane Barbosa, A. E. Da Hora Machado, and L. Santos Andrade, “Combining Chemical and Photo-Fenton Solar Coagulation Processes in the Treatment of Real Wastewater from Paint Industry,” Orbital Electron. J. Chem., vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 1–25, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. S. S. Abujazar, S. U. Karaağaç, S. S. Abu Amr, M. Y. D. Alazaiza, and M. J. Bashir, “Recent advancement in the application of hybrid coagulants in coagulation-flocculation of wastewater: A review,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 345, p. 131133, Apr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Bener, Ö. Bulca, B. Palas, G. Tekin, S. Atalay, and G. Ersöz, “Electrocoagulation process for the treatment of real textile wastewater: Effect of operative conditions on the organic carbon removal and kinetic study,” Process Saf. Environ. Prot., vol. 129, pp. 47–54, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. Ertugay and F. N. Acar, “Removal of COD and color from Direct Blue 71 azo dye wastewater by Fenton’s oxidation: Kinetic study,” Arab. J. Chem., vol. 10, pp. S1158–S1163, 2017. [CrossRef]
- F. Li, T. S. Y. Choong, S. Soltani, L. C. Abdullah, and S. N. A. M. Jamil, “Kinetic Study of Fenton-Like Degradation of Methylene Blue in Aqueous Solution Using Calcium Peroxide,” Pertanika J. Sci. Technol., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 1087–1102, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. P. P. Lima, C. H. B. Tabelini, M. D. N. Ramos, and A. Aguiar, “Kinetic Evaluation of Bismarck Brown Y Azo Dye Oxidation by Fenton Processes in the Presence of Aromatic Mediators,” Water. Air. Soil Pollut., vol. 232, no. 8, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. H. Chan and W. Chu, “Modeling the reaction kinetics of Fenton’s process on the removal of atrazine,” Chemosphere, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 305–311, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li and H. Cheng, “Chemical kinetic modeling of organic pollutant degradation in Fenton and solar photo-Fenton processes,” J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., vol. 123, pp. 175–184, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Umar, H. A. Aziz, and M. S. Yusoff, “Trends in the use of Fenton, electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton for the treatment of landfill leachate,” Waste Manag., vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 2113–2121, 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Ahmadi, F. Ghanbari, A. Alvarez, and S. Silva Martinez, “UV-LEDs assisted peroxymonosulfate/Fe2+ for oxidative removal of carmoisine: The effect of chloride ion,” Korean J. Chem. Eng., vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 2154–2161, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. López-Vinent et al., “Synergies, radiation and kinetics in photo-Fenton process with UVA-LEDs,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 380, p. 120882, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. S. B. de Souza, M. P. Silva, T. J. M. Fraga, and M. A. Motta Sobrinho, “A comparative study of photo-Fenton process assisted by natural sunlight, UV-A, or visible LED light irradiation for degradation of real textile wastewater: factorial designs, kinetics, cost assessment, and phytotoxicity studies,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., vol. 28, no. 19, pp. 23912–23928, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Shirato et al., “Synergistic effect of thermal energy on bactericidal action of photolysis of H 2O 2in relation to acceleration of hydroxyl radical generation,” Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 295–301, 2012. [CrossRef]
- X. Duan et al., “Temperature-dependent evolution of hydroxyl radicals from peroxymonosulfate activation over nitrogen-modified carbon nanotubes,” Sustain. Mater. Technol., vol. 18, p. e00082, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. M. Sakthi, “ENHANCEMENT OF WASTE ACTIVATED SLUDGE REDUCTION POTENTIAL BY THERMO-FENTON TREATMENT,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol., vol. 07, no. 08 | Aug 2020, pp. 3600–3605, 2020, doi: https://www.irjet.net/archives/V7/i8/IRJET-V7I8616.pdf.
- F. R. Omi, M. Rastgar, and M. Sadrzadeh, “Synergistic effect of thermal dehydrating on the emerging contaminants removal via Electro-Fenton,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 356, p. 131880, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Y. Yew et al., “Thermal-Fenton mechanism with sonoprocessing for rapid non-catalytic transesterification of microalgal to biofuel production,” Chem. Eng. J., vol. 408, p. 127264, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. M. Herrera-Ibarra, R. M. Ramírez-Zamora, A. Martín-Domínguez, M. Piña-Soberanis, D. Schnabel-Peraza, and J. A. Bañuelos-Díaz, “Treatment of Textile Industrial Wastewater by the Heterogeneous Solar Photo-Fenton Process Using Copper Slag,” Top. Catal., vol. 65, no. 9–12, pp. 1163–1179, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Bello, A. A. Abdul Raman, and A. Asghar, “A review on approaches for addressing the limitations of Fenton oxidation for recalcitrant wastewater treatment,” Process Saf. Environ. Prot., vol. 126, pp. 119–140, 2019. [CrossRef]
- I. Gasmi, K. Kerboua, N. Haddour, O. Hamdaoui, A. Alghyamah, and F. Buret, “The Galvano-Fenton process: Experimental insights and numerical mechanistic investigation applied to the degradation of acid orange 7,” Electrochim. Acta, vol. 373, p. 137897, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- O. García-Rodríguez, J. A. Bañuelos, A. El-Ghenymy, L. A. Godínez, E. Brillas, and F. J. Rodríguez-Valadez, “Use of a carbon felt-iron oxide air-diffusion cathode for the mineralization of Malachite Green dye by heterogeneous electro-Fenton and UVA photoelectro-Fenton processes,” J. Electroanal. Chem., vol. 767, pp. 40–48, 2016. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Castillo-Suárez et al., “Commercial herbicide degradation by solar corrosion Fenton processes of iron filaments in a continuous flow reactor and its computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation,” J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem., vol. 412, no. August 2020, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. C. Namkung, A. E. Burgess, and D. H. Bremner, “A fenton-like oxidation process using corrosion of iron metal sheet surfaces in the presence of hydrogen peroxide: A batch process study using model pollutants,” Environ. Technol., vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 341–352, 2005. [CrossRef]
- P. Li and M. Du, “Effect of chloride ion content on pitting corrosion of dispersion-strengthened-high-strength steel,” Corros. Commun., vol. 7, pp. 23–34, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Kaczmarczyk and S. Gurgul, “Thermodynamic Analysis of Chloride Corrosion in Steel for Energy System Applications in Fe-O-Cl-Na Environments,” 2024.
- C. Zhao, K. Dai, P. Li, Z. Cheng, and K. Xiao, “Effect of UV Illumination on the Corrosion Behavior of Under a Thin NaCl Electrolyte Layer,” Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., vol. 17, no. 11, p. 221164, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Kanjana, P. Ampornrat, and J. Channuie, “Gamma-radiation-induced corrosion of aluminum alloy: low dose effect,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 860, p. 012041, Jun. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. de M. A. y R. N. SEMARNAT, “NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2021 Límites permisibles de contaminantes en las descargas de aguas residuales en cuerpos recptores propiedad de la nacion.,” 2021. https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5645374&fecha=11/03/2022#gsc.tab=0 (accessed Jul. 10, 2024).
- B. T. N. VÀ and M. TRƯỜNG, “C Ộ NG HÒA XÃ H Ộ I CH Ủ NGH Ĩ A VI Ệ T NAM QCVN 13-MT: 2015 / BTNMT QUY CHU Ẩ N K Ỹ THU Ậ T QU Ố C GIA QUY CHU Ẩ N K Ỹ THU Ậ T QU Ố C GIA V Ề N ƯỚ C TH Ả I CÔNG NGHI Ệ P D Ệ T NHU Ộ M National technical regulation on the effluent of textile industry,” 2015. https://thuvienphapluat.vn/van-ban/Tai-nguyen-Moi-truong/Thong-tu-13-2015-TT-BTNMT-Quy-chuan-ky-thuat-quoc-gia-ve-moi-truong-270027.aspx (accessed Jun. 25, 2021).
- “Official Newspape, W. National Water Pollution Control Reg ulation..,” 2004. https://www.mfa.gov.tr/turkiye_s-policy-on-water-issues.en.mfa (accessed Jul. 10, 2024).
- V. Katheresan, J. Kansedo, and S. Y. Lau, “Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review,” J. Environ. Chem. Eng., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 4676–4697, 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. Alvarez-Bastida, V. Martínez-Miranda, M. Solache-Ríos, I. Linares-Hernández, A. Teutli-Sequeira, and G. Vázquez-Mejía, “Drinking water characterization and removal of manganese. Removal of manganese from water,” J. Environ. Chem. Eng., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 2119–2125, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Shekoohiyan, S. Rtimi, G. Moussavi, S. Giannakis, and C. Pulgarin, “Enhancing solar disinfection of water in PET bottles by optimized in-situ formation of iron oxide films. From heterogeneous to homogeneous action modes with H2O2 vs. O2 – Part 1: Iron salts as oxide precursors,” Chem. Eng. J., vol. 358, no. October 2018, pp. 211–224, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. El-Nahas, A. I. Osman, A. S. Arafat, A. H. Al-Muhtaseb, and H. M. Salman, “Facile and affordable synthetic route of nano powder zeolite and its application in fast softening of water hardness,” J. Water Process Eng., vol. 33, p. 101104, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st ed. Washington, DC.: Water Environment Federation, W, 2005.
- P. Carbajal-Palacios, P. Balderas-Hernández, G. Roa-Morales, and J. G. Ibanez, “A Greener UV and Peroxide-Based Chemical Oxygen Demand Test,” Water. Air. Soil Pollut., vol. 228, no. 8, 2017. [CrossRef]
- L.A. Castillo-suárez, V. Lugo-lugo, I. Linares-hernández, V. Martínez-miranda, M. Esparza-soto, and M. D. L. Á. Mier-quiroga, “Biodegradability index enhancement of land fi ll leachates using a Solar Galvanic-Fenton and Galvanic-Fenton system coupled to an anaerobic – aerobic bioreactor,” Sol. Energy, vol. 188, no. March, pp. 989–1001, 2019. [CrossRef]
- I. Linares-Hernández et al., “Degradation of commercial paraquat in a solar-Fenton pilot lagoon using iron oxalate as a chelating agent: Hydro-thermal analysis with CFD,” J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem., vol. 429, no. October 2021, p. 113914, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Ruíz-Delgado, M. A. Roccamante, I. Oller, A. Agüera, and S. Malato, “Natural chelating agents from olive mill wastewater to enable photo-Fenton-like reactions at natural pH,” Catal. Today, vol. 328, pp. 281–285, May 2019. [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Raw | + | Treatment† | + | % removal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.44 | 0.06 | 2.6 | 0.07 | - |
| COD (mg/L) | 1020.0 | 10.1 | 83.5 | 6.1 | 91.8 |
| Color (Pt-Co) | 1808.3 | 23.5 | 29.3 | 0.7 | 98.4 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 237.0 | 1.5 | 30.0 | 0.0 | 87.3 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) | 2.971 | 0.15 | 4.12 | 0.12 | - |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | 345.4 | 3.6 | 280.7 | 1.9 | 18.7 |
| Nitrates (mg/L) | 4.0 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 0.01 | 52.5 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.7 | 0.01 | 5.15 | 0.02 | - |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 200.0 | 1.5 | 22.0 | 1.4 | 89.0 |
| Alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 77.2 | 5.2 | 0.0 | 0.54 | 100.0 |
| Acidity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 1200.0 | 10.2 | 629.2 | 4.4 | 47.5 |
| Total dissolved solids (g/L) | 1.483 | 0.01 | 2.018 | 0.06 | - |
| Total solids (mg/L) | 3540.0 | 70.8 | 3160.0 | 63.2 | 10.7 |
| Suspended solids (mg/L) | 412.0 | 2.8 | 28.0 | 0.56 | 93.2 |
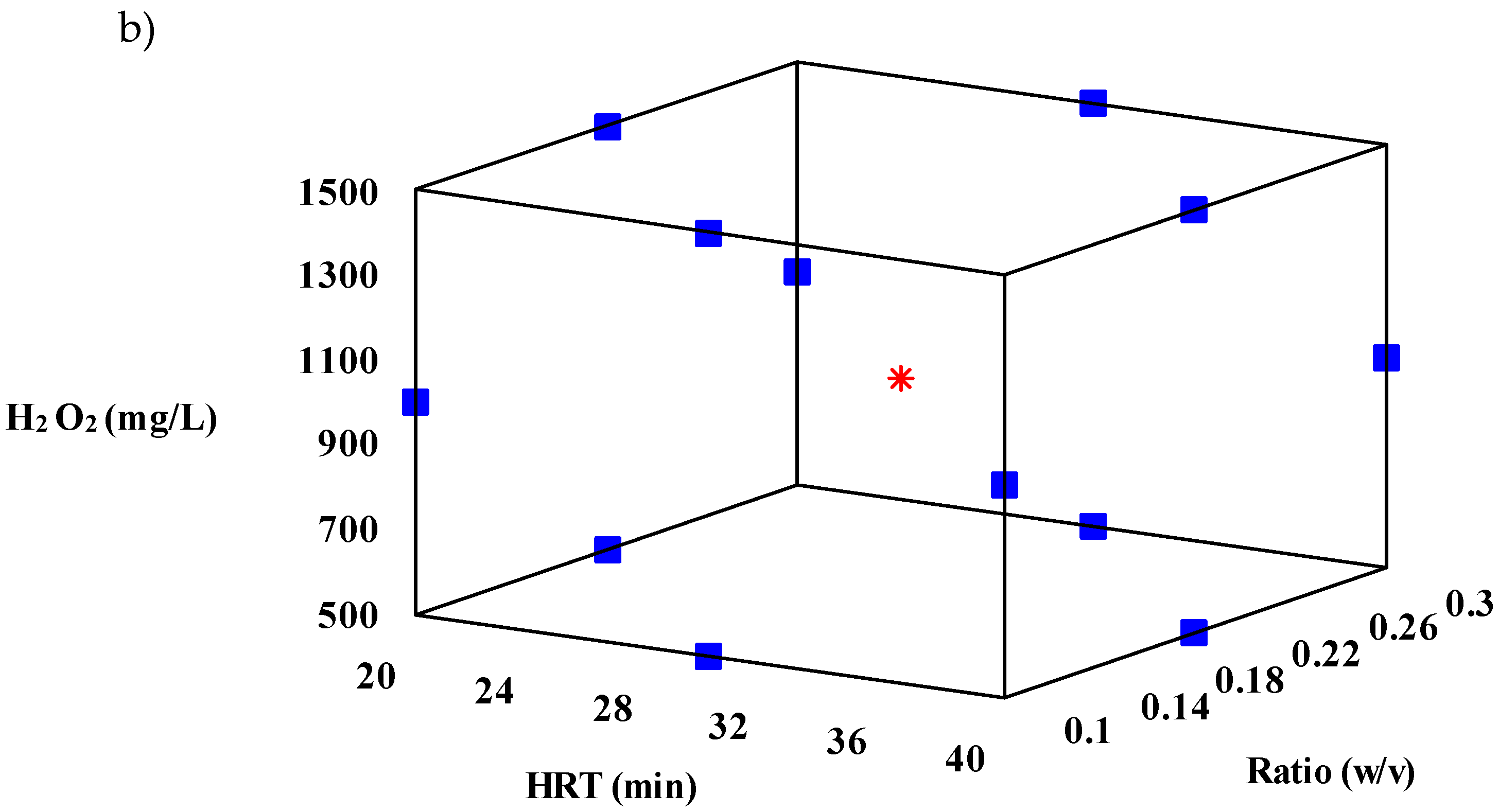
| % Removal (Predicted) | % Removal (Observed) | HRT (min) | Ratio (w/v) | H2O2 doses (mg/L) |
R2 | SEE (%) * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | 96.8 | 91.8 | 24.5 | 0.16 | 1006.9 | 86.6 | 9.8 |
| Color | 96.6 | 98.4 | 28.2 | 0.18 | 1134.9 | 84.3 | 13.6 |
| Turbidity | 85.6 | 87.3 | 28.4 | 0.18 | 1277.0 | 93.6 | 8.2 |
| # run | HRT (min) | Ratio | Dose H2O2 (mg/L) | COD removal (%) | Color removal (%) | Turbidity removal (%) | Solar UVA radiation (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 0.2 | 1000 | 93.40% | 92.6% | 80.3% | 46.5abcd |
| 2 | 30 | 0.2 | 1000 | 98.71% | 98.2% | 85.2% | 53.2ab |
| 3 | 30 | 0.2 | 1000 | 85.84% | 92.8% | 86.2% | 55.3a |
| 4 | 20 | 0.1 | 1000 | 81.51 | 51.9% | 41.8% | 50.7abc |
| 5 | 40 | 0.1 | 1000 | 77.79 | 52.1% | 22.8% | 30.5cde |
| 6 | 20 | 0.3 | 1000 | 78.94 | 65.1% | 29.8% | 26.5de |
| 7 | 40 | 0.3 | 1000 | 60.31 | 46.3% | 45.4% | 40.5abcd |
| 8 | 20 | 0.2 | 500 | 84.21% | 70.2% | 44.7% | 33.4 bcde |
| 9 | 40 | 0.2 | 500 | 65.17 | 51.6% | 52.1% | 51.2abc |
| 10 | 20 | 0.2 | 1500 | 83.72% | 71.4% | 66.7% | 13.6e |
| 11 | 40 | 0.2 | 1500 | 62.72 | 53.7% | 43.2% | 46.7abcd |
| 12 | 30 | 0.1 | 500 | 81.51% | 47.6% | 54.6% | 47.0abcd |
| 13 | 30 | 0.3 | 500 | 66.72% | 34.3% | 44.6% | 40.7abcd |
| 14 | 30 | 0.1 | 1500 | 88.09% | 90.9% | 75.2% | 33.8abcde |
| 15 | 30 | 0.3 | 1500 | 34.12% | 46.9% | 47.6% | 25.2de |
| First order | Second order | BMG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k(L/kJ) | R2 | k2(L/mg L/kJ) | R2 | 1/m (L/kJ) | 1/b | R2 | |
| COD | 0.0893 | 0.7667 | 0.1133 | 0.8784 | -3.3372 | 0.7705 | 0.9978 |
| Color | 0.0198 | 0.8680 | 0.0474 | 0.9171 | 0.0141 | 0.9616 | 0.9179 |
| Turbidity | 0.0081 | 0.8053 | 0.0136 | 0.7750 | 0.0016 | 2.9174 | 0.8202 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





