Submitted:
25 November 2024
Posted:
27 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- Data analysis and pattern recognition: Identifying trends and insights from large datasets.
- Predictive modelling: Forecasting future outcomes based on historical data.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Understanding and generating human language.
- Computer vision: Interpreting and responding to visual information.
- The Rise of Data-Driven Marketing: Traces the historical evolution of AI in marketing, from early data analysis techniques to the emergence of CRM systems and programmatic advertising.
- The Two Sides of AI in Marketing: Examines the benefits and challenges of AI adoption and addresses key ethical considerations such as privacy, bias, and transparency.
- Deep Dive: Case Studies of AI Marketing Tools: This section analyses two specific AI marketing tools, Persado and Albert.ai, to illustrate their practical applications and limitations.
- The Future of AI in Marketing: This chapter explores emerging trends such as conversational AI, predictive modelling, and the evolving relationship between AI and marketing creativity.
The Rise of Data-Driven Marketing

Personalisation and the Shift to Customer-Centricity
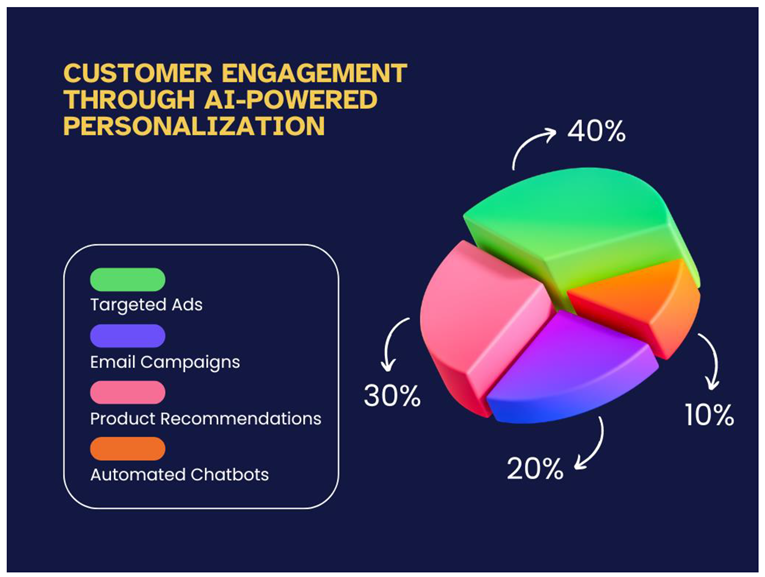
AI and the Transformation of the Marketing Function
The Two Sides of AI in Marketing: Balancing Benefits and Challenges
Hyper-Personalization: Enhanced Engagement vs. Privacy Concerns
Automation: Efficiency Gains vs. Job Displacement and Creativity
Advanced-Data Analysis: Data-Driven Insights vs. Data Dependency and Bias
Dynamic Optimization: Real-Time Adaptability vs. Lack of Transparency
Enhanced Customer Experience: 24/7 Support vs. Impersonal Interactions
Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Responsible Use of AI in Marketing
- Data Privacy and Security: Marketers must prioritise the responsible collection, storage, and use of customer data, ensure compliance with relevant regulations, and obtain informed consent.
- Algorithmic Bias and Fairness: Addressing potential biases in AI algorithms is crucial to prevent discriminatory outcomes in targeting, personalisation, and other marketing decisions.
- Transparency and Accountability: Marketers should strive for transparency in how AI systems are used in their marketing practices, providing clear explanations to customers and stakeholders.
- Consumer Autonomy and Manipulation: AI should not be used to manipulate or exploit consumers. Marketers must respect consumer autonomy and ensure that AI-driven personalisation does not infringe on individual choice and freedom.
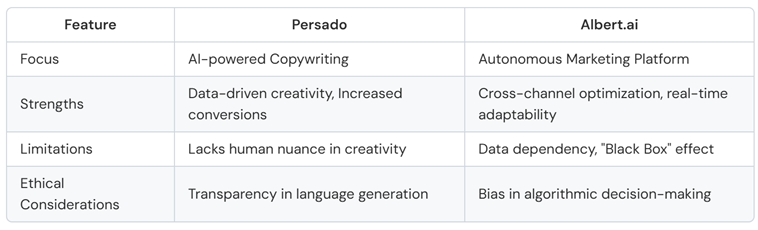
Deep Dive: Case Studies of AI Marketing Tools
Persado: AI-Powered Copywriting
Strengths:
- Data-Driven Creativity: Persado moves beyond subjective interpretations of effective copywriting by using data to identify language patterns that resonate with specific audiences. This data-driven approach can lead to more impactful and persuasive messaging.
- Increased Conversion Rates: Case studies have shown that Persado's AI-generated copy can significantly outperform human-written copy regarding click-through rates, conversion rates, and overall campaign performance (Persado, 2024). For example, a campaign for a major credit card company saw a 41% increase in conversions after implementing Persado's AI-generated copy.
- Scalability and Efficiency: Persado enables marketers to generate high-quality copy across multiple channels and formats with speed and efficiency, freeing up human copywriters to focus on more strategic tasks.
Limitations:
- Lack of Nuance and Creativity: While Persado excels at optimising language for specific outcomes, it may not always capture the nuance, creativity, or brand voice that can be achieved through human copywriting.
- Over-Reliance on Data: Overreliance on data-driven insights could lead to formulaic or generic copy lacking originality or emotional depth.
Ethical Considerations:
- Transparency and Control: As with any AI system, transparency in how Persado's algorithms make decisions is crucial. Marketers must retain control over the messaging and ensure it aligns with their brand values and ethical standards.
Albert.ai: Autonomous Marketing Platform
Strengths:
- Cross-Channel Optimization: Albert.ai analyses data across all digital channels to identify the most effective strategies and allocate marketing budgets accordingly. This holistic approach ensures that campaigns are optimised for maximum impact.
- Real-Time Adaptability: The platform continuously monitors campaign performance and makes real-time adjustments based on changing market conditions, audience behaviour, and other relevant factors.
- Improved ROI and Efficiency: By automating many time-consuming tasks and optimising performance campaigns, Albert.ai can significantly improve marketing ROI and free marketers to focus on strategic planning and creative initiatives.
Limitations:
- Data Dependency: Albert.ai's effectiveness highly depends on the quality and quantity of data it receives. Insufficient or inaccurate data can lead to suboptimal campaign performance.
- Black Box Effect: Albert.ai's algorithms' complexity can make it challenging for marketers to understand decisions, potentially leading to a lack of trust or control.
Ethical Considerations:
- Bias and Discrimination: As with any AI system, Albert.ai's algorithms are subject to bias, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes in ad targeting or campaign optimisation. Marketers must be vigilant in monitoring for and mitigating bias.
- Job Displacement: The increasing automation of marketing tasks raises concerns about job displacement. Marketers must adapt their skills and embrace new roles focusing on strategy, creativity, and human-centred marketing.
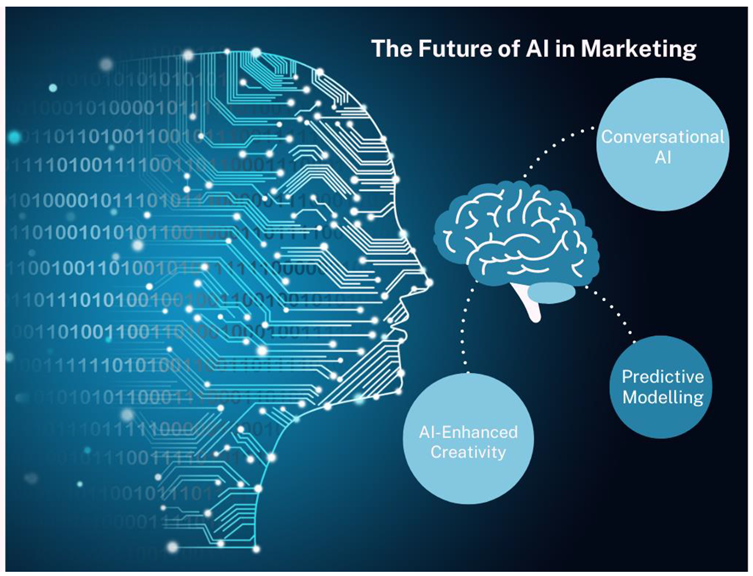
The Future of AI in Marketing: Beyond Automation, Towards Collaboration
The Rise of Conversational AI: Humanizing the Customer Journey
Predictive Modelling: Anticipating Needs, Respecting Boundaries
The Evolving Relationship Between AI and Marketing Creativity
Conclusion
Key Takeaways:
- AI is shifting from a tool to a partner: Marketers must evolve from simply using AI tools to strategically collaborating with AI systems.
- Ethical considerations are paramount: Responsible AI adoption requires addressing privacy concerns, mitigating bias, and ensuring transparency.
- Human skills remain essential: Creativity, empathy, ethical judgment, and strategic thinking will be increasingly vital in an AI-driven marketing landscape.
Recommendations for Marketers:
- Embrace lifelong learning: Continuously update skills to stay ahead of AI advancements and leverage new tools effectively.
- Prioritize data quality and ethics: Ensure data accuracy, address potential biases, and be transparent about data usage.
- Focus on strategic and creative roles: Delegate routine tasks to AI and focus on high-level strategy, creative campaign development, and building authentic customer relationships.
Recommendations for Policymakers:
- Develop ethical guidelines for AI in marketing: Establish clear regulations regarding data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and responsible AI use.
- Support workforce transition: Provide resources and training programs to help marketers adapt their skills for an AI-driven future.
- Foster collaboration between industry and academia: Encourage research and development of ethical and responsible AI applications in marketing.
Conflicts of Interests
References
- Burrell, J. How the Machine ‘Thinks’: Understanding Opacity in Machine Learning. journal Big Data & Society 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L. (2024, August 14). The Impact of Conversational AI on Customer Experience. From innovative dev: https://www.smartdev.com/the-impact-of-conversational-ai-on-customer-experience/.
- Darrell, K.; Rigby, F. F. Avoid the Four Perils of CRM. Harvard Business Review 2002, 80, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- etc. (2024, July 25). Improved Customer Satisfaction With Advanced Conversational AI. From EDC: https://edc.ae/blog/improved-customer-satisfaction-with-advanced-conversational-ai/.
- Hoffman, C. v. (2023, February 22). How can bias in AI damage marketing data, and what can you do about it? From martech: https://martech.org/bias-in-ai-chatgpt-marketing-data/.
- Joseph, A.; Konstan, J. T. E-commerce recommendation applications. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2001, 5, 115–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M. H. A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On Messages and Messengers. California Management Review 2019, 61, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. (2024). The future of marketing in the era of AI: 2024 outlook. From out: https://owdt.com/article/the-future-of-marketing-in-the-era-of-ai-2024-outlook/.
- Marr, B. (2019). Marketing Automation: Explained. Bernard Marr & Co.
- Martin, K. Ethical Implications of Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Business Ethics 2019, 155, 937–948. [Google Scholar]
- McAfee, E. B. (2014). The Second Machine Age: Work, Progress, and Prosperity in a Time of Brilliant Technologies. W. W. Norton & Company.
- Persado. (2024, Jun 18). Persado case studies. From Persado: https://www.persado.com/resource-library/articles/.
- Phukan, P. (2024, February 20). AI Overdose in Marketing: How to Balance AI and Human Creativity. From species: https://www.specbee.com/blogs/ai-overdose-marketing-how-to-balance-ai-and-human-creativity.
- Rakesh Agrawal, R. S. (1994). Fast algorithms for mining association rules. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, VLDB, 1215, pp. 487–499. From https://www.vldb.org/conf/1994/P487.PDF#:~:text=Proceedings%20of%20the%2020th%20VLDB%20Conference%20and%20AprioriTid,%20that%20differ.
- Rust, M.-H. H. Artificial Intelligence in Service. Journal of Service Research, 2018, 21, 155–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J. (2017). Artificial Intelligence for Marketing: Practical Applications. Wiley.
- Sweeney, M. (2024). What is Programmatic Advertising? The Definitive Guide for 2024. From clear code: https://clearcode.cc/blog/programmatic-advertising/.
- Thewritecure. (2024). How is AI Impacting Marketing Strategies? From Write Cure: https://www.writecure.com/marketing-in-the-age-of-ai.
- Thomas Davenport, A. G. How artificial intelligence will change the future of marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 2020, 48, 24–42. Available online: https://onwork.edu.au/bibitem/2020-Davenport,T-Guha,A-etal-How+artificial+intelligence+will+change+the+future+of+marketing/. [CrossRef]
- V. Kumar, B. R. I understand the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 2019, 47, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Welser, O. a. (2017). An Intelligence in Our Image: The Risks of Bias and Errors in Artificial Intelligence. Rand Corporation.
- Winer, R. S. Mathematical programming for profitable marketing decisions. Marketing Science 1964, 3, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




