Submitted:
11 February 2025
Posted:
13 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The mRNA- and DNA-based “genetic” COVID-19 vaccines can induce a broad range of adverse events (AEs), with statistics showing significant variation depending on timing and data analysis methods. Focusing only on lipid nanoparticle-enclosed mRNA (mRNA-LNP) vaccines, this review traces the evolution of statistical conclusions on AE prevalence and incidence associated with these vaccines, from initial underestimation of atypical, severe toxicities to recent claims suggesting the possible contribution of Covid-19 vaccinations to the excess deaths observed in many countries over the past few years. Among hundreds of different AEs listed in Pfizer’s pharmacovigilance survey, the present analysis categorizes the main symptoms according to organ systems, nearly all being affected. Using data from the US Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and a global vaccination dataset, a comparison of the prevalence and incidence rates of AEs induced by genetic versus flu vaccines revealed an average 26-fold increase in AEs with genetic vaccines. The difference is especially pronounced in the case of severe ‘Brighton-listed’ AEs, which are also observed in COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions. Among these, the increases of incidence rates relative to flu vaccines, given as x-fold rises, were 1,152x, 455x, 226x, 218x, 162x, 152x; and 131x, for myocarditis, thrombosis, death, myocardial infarction, tachycardia, dyspnea, and hypertension, respectively. The review delineates the concepts that genetic vaccines can be regarded as prophylactic immuno-gene therapies, and that the chronic disabling AEs might be categorized as iatrogenic orphan diseases. It also examines the unique vaccine characteristics that could be causally related to abnormal immune responses potentially leading to adverse events and complications. These new insights may contribute to improving the safety of this platform technology and assessing the risk-benefit balance of various products.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The “special interest” symptoms of post-vaccination syndrome and public reaction
3. The unique features of mRNA vaccines and their adverse effects
4. Prevalence and incidence of adverse events caused by mRNA-LNP vaccines: Inconsistent statistics
5. Comparison of mRNA-LNP and flu vaccines
6. Complement activation as a possible contributor to acute AEs
7. Regulatory classification of mRNA vaccines
8. The orphan disease proposition for categorizing persistent and/or disabling vaccine-induced chronic AEs
9. The European experience: Paul-Ehrlich-Institute statistics
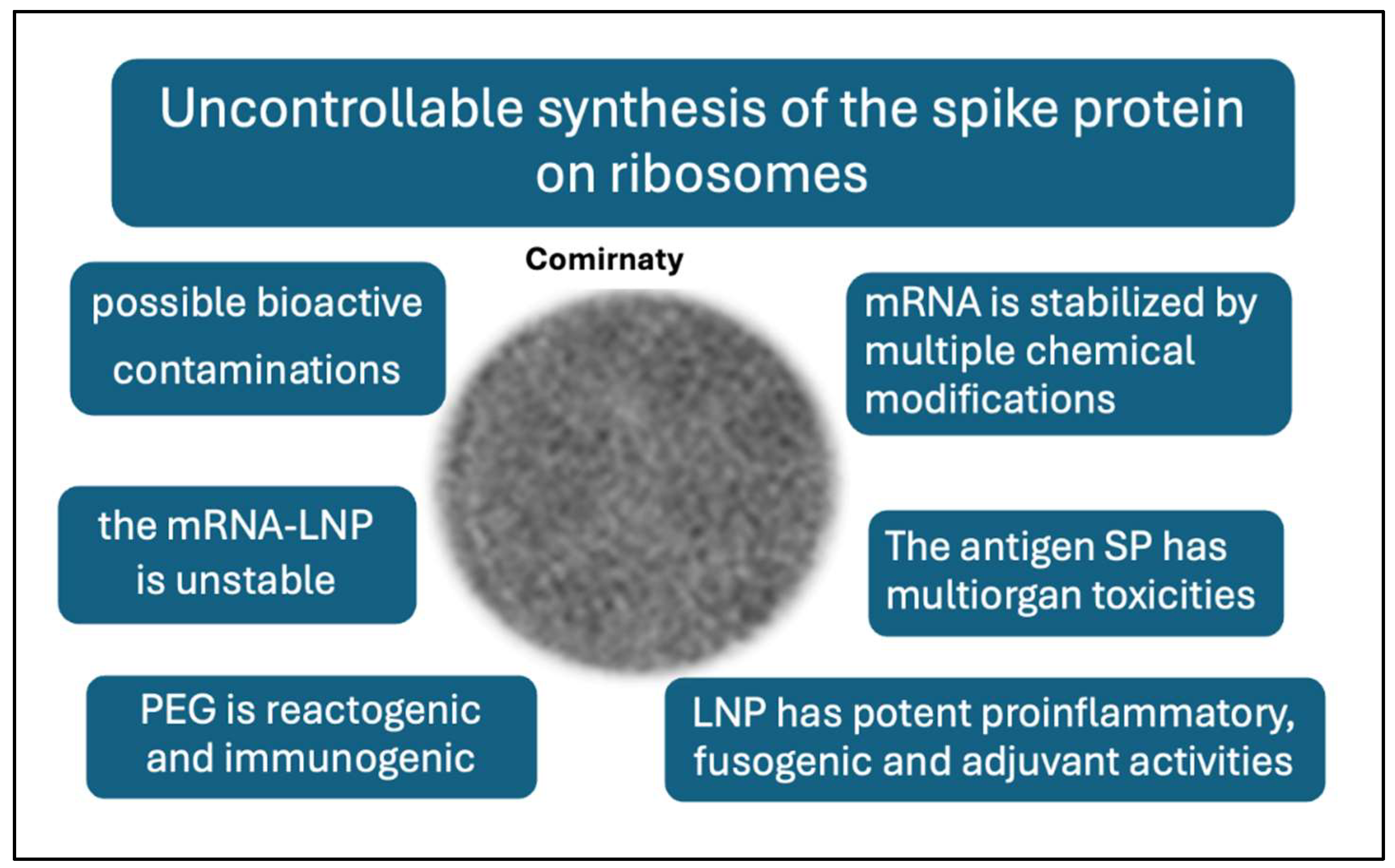
10. Potential plausible causes of adverse events inherent to the mRNA-LNP platform
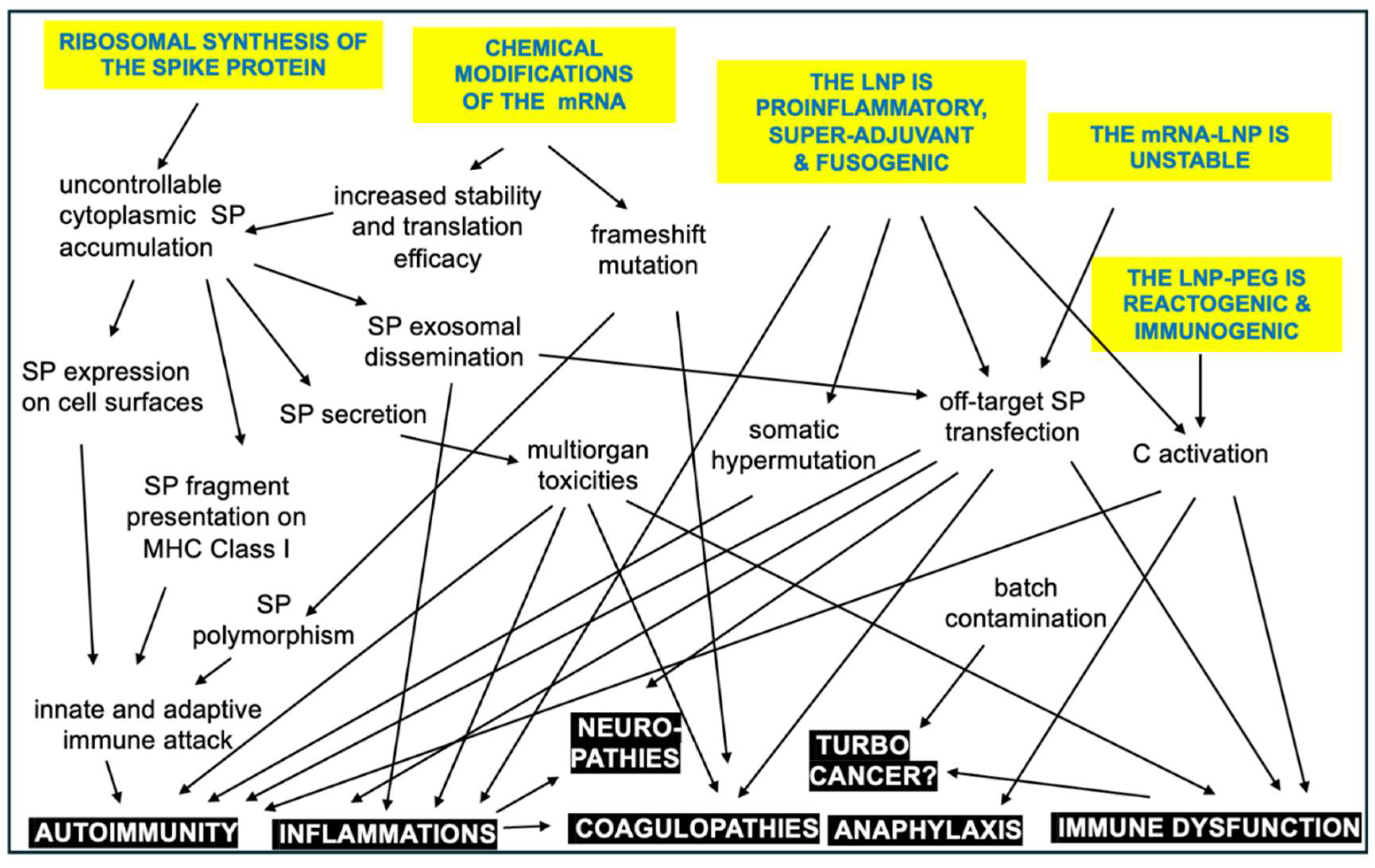
11. Outlook
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahin, U., Kariko, K., & Tureci, O. (2014). mRNA-based therapeutics: Developing a new class of drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 13(10), 759-780. [CrossRef]
- Kariko, K., Whitehead, K., & van der Meel, R. (2021). What does the success of mRNA vaccines tell us about the future of biological therapeutics? Cell Systems, 12(8), 757-758. [CrossRef]
- Cullis, P. R., & Felgner, P. L. (2024). The 60-year evolution of lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. [CrossRef]
- Igyarto, B. Z., Jacobsen, S., & Ndeupen, S. (2021). Future considerations for the mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine platform. Current Opinion in Virology, 48, 65-72. [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, R., & Ladapo, J. A. (2023). Health alert on mRNA COVID-19 vaccine safety. Florida Health. https://www.floridahealth.gov/_documents/newsroom/press-releases/2023/02/20230215-updated-health-alert.pdf.
- FDA. (2024). FDA approves and authorizes updated mRNA COVID-19 vaccines to better protect against currently circulating variants. FDA News Release. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-and-authorizes-updated-mrna-covid-19-vaccines.
- Oueijan, R. I., Hill, O. R., Ahiawodzi, P. D., Fasinu, P. S., & Thompson, D. K. (2022). Rare heterogeneous adverse events associated with mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines: A systematic review. Medicines (Basel), 9(8), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Krumholz, H. M., Wu, Y., Sawano, M., Shah, R., Zhou, T., Arun, A. S., ... & Iwasaki, A. (2023). Post-vaccination syndrome: A descriptive analysis of reported symptoms and patient experiences after COVID-19 immunization. medRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M., Bhakdi, S., Hooker, B., Holland, M., DesBois, M., Rasnick, D., & Fitts, C. A. (2023). mRNA vaccine toxicity. Doctors for COVID Ethics.
- Shrestha, Y., & Venkataraman, R. (2024). The prevalence of post-COVID-19 vaccination syndrome and quality of life among COVID-19-vaccinated individuals. Vacunas, 25(1), 7-18. [CrossRef]
- Law, B. "Priority List of Covid-19 Adverse Events of Special Interest: Quarterly Update December 2020." Safety Platform for Emergency Vaccines (SPEAC) https://brightoncollaboration.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/SO2_D2.1.2_V1.2_COVID-19_AESI-update_V1.3-1.pdf (2021).
- Fraiman, J., J. Erviti, M. Jones, S. Greenland, P. Whelan, R. M. Kaplan, and P. Doshi. "Serious Adverse Events of Special Interest Following mRNA Covid-19 Vaccination in Randomized Trials in Adults." Vaccine 40, no. 40 (2022): 5798-805. [CrossRef]
- Faksova, K., D. Walsh, Y. Jiang, J. Griffin, A. Phillips, A. Gentile, J. C. Kwong, K. Macartney, M. Naus, Z. Grange, S. Escolano, G. Sepulveda, A. Shetty, A. Pillsbury, C. Sullivan, Z. Naveed, N. Z. Janjua, N. Giglio, J. Perala, S. Nasreen, H. Gidding, P. Hovi, T. Vo, F. Cui, L. Deng, L. Cullen, M. Artama, H. Lu, H. J. Clothier, K. Batty, J. Paynter, H. Petousis-Harris, J. Buttery, S. Black, and A. Hviid. "Covid-19 Vaccines and Adverse Events of Special Interest: A Multinational Global Vaccine Data Network (Gvdn) Cohort Study of 99 Million Vaccinated Individuals." Vaccine 42, no. 9 (2024): 2200-11. [CrossRef]
- Levitan, B., S. C. Hadler, W. Hurst, H. S. Izurieta, E. R. Smith, N. L. Baker, V. Bauchau, R. Chandler, R. T. Chen, D. Craig, J. King, P. Pitisuttithum, W. Strauss, S. Tomczyk, J. Zafack, and S. Kochhar. "The Brighton Collaboration Standardized Module for Vaccine Benefit-Risk Assessment." Vaccine 42, no. 4 (2024): 972-86. [CrossRef]
- Mostert, S., M. Hoogland, M. Huibers, and G. Kaspers. "Excess Mortality across Countries in the Western World since the Covid-19 Pandemic: ‘Our World in Data’ Estimates of January 2020 to December 2022. ." BMJ Public Health 2:e000282. (2024). [CrossRef]
- Rancourt, D.G., J. Hickey, and C Linard. "Spatiotemporal Variation of Excess All-Cause Mortality in the World (125 Countries) During the Covid Period 2020-2023 Regarding Socio-Economic Factors and Public-Health and Medical Interventions." Correlation https://correlation-canada.org/covid-excess-mortality-125-countries/ no. Report I 19 July 2024 (2024).
- Wang, S., K. Zhang, and J. Du. "Pubmed Captures More Fine-Grained Bibliographic Data on Scientific Commentary Than Web of Science: A Comparative Analysis." BMJ Health Care Inform 31, no. 1 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Du, P., N. Li, S. Tang, Z. Zhou, Z. Liu, T. Wang, J. Li, S. Zeng, and J. Chen. "Development and Evaluation of Vaccination Strategies for Addressing the Continuous Evolution Sars-Cov-2 Based on Recombinant Trimeric Protein Technology: Potential for Cross-Neutralizing Activity and Broad Coronavirus Response." Heliyon 10, no. 14 (2024): e34492.
- Polack, F. P., S. J. Thomas, N. Kitchin, J. Absalon, A. Gurtman, S. Lockhart, J. L. Perez, G. Perez Marc, E. D. Moreira, C. Zerbini, R. Bailey, K. A. Swanson, S. Roychoudhury, K. Koury, P. Li, W. V. Kalina, D. Cooper, R. W. Frenck, Jr., L. L. Hammitt, O. Tureci, H. Nell, A. Schaefer, S. Unal, D. B. Tresnan, S. Mather, P. R. Dormitzer, U. Sahin, K. U. Jansen, W. C. Gruber, and C. Clinical Trial Group. "Safety and Efficacy of the Bnt162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine." N Engl J Med 383, no. 27 (2020): 2603-15. [CrossRef]
- Worldwide Safety. "Cumulative Analysis of Post-Authorization Adverse Event Reports of Pf-07302048 (Bnt162b2) Received through 28-Feb-2021." https://phmpt.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/5.3.6-postmarketing-experience.pdf?fbclid=IwAR2tWI7DKw0cc2lj8 (2021).
- Thomas, S. J., E. D. Moreira, Jr., N. Kitchin, J. Absalon, A. Gurtman, S. Lockhart, J. L. Perez, G. Perez Marc, F. P. Polack, C. Zerbini, R. Bailey, K. A. Swanson, X. Xu, S. Roychoudhury, K. Koury, S. Bouguermouh, W. V. Kalina, D. Cooper, R. W. Frenck, Jr., L. L. Hammitt, O. Tureci, H. Nell, A. Schaefer, S. Unal, Q. Yang, P. Liberator, D. B. Tresnan, S. Mather, P. R. Dormitzer, U. Sahin, W. C. Gruber, K. U. Jansen, and C. Clinical Trial Group. "Safety and Efficacy of the Bnt162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine through 6 Months." N Engl J Med 385, no. 19 (2021): 1761-73. [CrossRef]
- VAERS. "VAERS Ids." https://vaers.hhs.gov/data/datasets.html (2023).
- OpenVAERS. "VAERS Covid Vaccine Adverse Event Reports." https://openvaers.com/covid-data https://openvaers.com/covid-data (2024).
- Rosenblum, H. G., J. Gee, R. Liu, P. L. Marquez, B. Zhang, P. Strid, W. E. Abara, M. M. McNeil, T. R. Myers, A. M. Hause, J. R. Su, L. E. Markowitz, T. T. Shimabukuro, and D. K. Shay. "Safety of mRNA Vaccines Administered During the Initial 6 Months of the Us Covid-19 Vaccination Programme: An Observational Study of Reports to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and V-Safe." Lancet Infect Dis 22, no. 6 (2022): 802-12. [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. "Timeline of the Covid-19 Pandemic in the United States." Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_the_COVID-19_pandemic_in_the_United_States_%282021%29?utm_source=chatgpt.com (2025).
- Ross, L., and M. Klompas. "Electronic Support for Public Health–Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (Esp:Vaers)." In Grant Final Report: Grant ID: R18 HS 017045, 2010.
- word, CDC Our. "Our World in Data." https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/covid-vaccine-doses-by-manufacturer?country=European+Union~HUN~USA (2024).
- Institute, Paul Erlich. "Safety Report." https://www.pei.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/newsroom-en/dossiers/safety-reports/safety-report-27-december-2020-31-march-2022.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=8 (2022).
- Mathieu, E., H. Ritchie, E. Ortiz-Ospina, M. Roser, J. Hasell, C. Appel, C. Giattino, and L. Rodes-Guirao. "A Global Database of Covid-19 Vaccinations." Nat Hum Behav 5, no. 7 (2021): 947-53. [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, J. "Complement Activation-Related Pseudoallergy: A New Class of Drug-Induced Acute Immune Toxicity." Toxicology 216, no. 2-3 (2005): 106-21. [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, J. "Complement Activation-Related Pseudoallergy: A Stress Reaction in Blood Triggered by Nanomedicines and Biologicals." Mol. Immunol. 61 (2014): 163-73. [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, J., G. Storm, J. Y. Ljubimova, M. Castells, E. J. Phillips, K. Turjeman, Y. Barenholz, D. J. A. Crommelin, and M. A. Dobrovolskaia. "Applying Lessons Learned from Nanomedicines to Understand Rare Hypersensitivity Reactions to mRNA-Based Sars-Cov-2 Vaccines." Nat Nanotechnol 17, no. 4 (2022): 337-46. [CrossRef]
- Ruf, Wolfram. "Links between Complement Activation and Thrombosis." Blood 134, no. Supplement_1 (2019): SCI-40-SCI-40.
- Luo, S., D. Hu, M. Wang, P. F. Zipfel, and Y. Hu. "Complement in Hemolysis- and Thrombosis- Related Diseases." Front Immunol 11 (2020): 1212. [CrossRef]
- Rawish, E., M. Sauter, R. Sauter, H. Nording, and H. F. Langer. "Complement, Inflammation and Thrombosis." Br J Pharmacol 178, no. 14 (2021): 2892-904. [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, B., A. Mubarak, M. E. Hamed, A. Z. Almutairi, A. A. Alrashed, A. AlJuryyan, M. Enani, F. Q. Alenzi, and W. Alturaiki. "Complement Anaphylatoxins and Inflammatory Cytokines as Prognostic Markers for Covid-19 Severity and in-Hospital Mortality." Front Immunol 12 (2021): 668725. [CrossRef]
- Lim, E. H. T., R. B. E. van Amstel, V. V. de Boer, L. A. van Vught, S. de Bruin, M. C. Brouwer, A. P. J. Vlaar, and D. van de Beek. "Complement Activation in Covid-19 and Targeted Therapeutic Options: A Scoping Review." Blood Rev 57 (2023): 100995. [CrossRef]
- Siggins, M. K., K. Davies, R. Fellows, R. S. Thwaites, J. K. Baillie, M. G. Semple, P. J. M. Openshaw, W. M. Zelek, C. L. Harris, B. P. Morgan, and Isaric C. Investigators. "Alternative Pathway Dysregulation in Tissues Drives Sustained Complement Activation and Predicts Outcome across the Disease Course in Covid-19." Immunology 168, no. 3 (2023): 473-92. [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P. L., S. Croci, P. A. Lonati, F. Pregnolato, L. Spaggiari, G. Besutti, M. Bonacini, I. Ferrigno, A. Rossi, G. Hetland, I. Hollan, M. Cugno, F. Tedesco, M. O. Borghi, and C. Salvarani. "Complement Activation Predicts Negative Outcomes in Covid-19: The Experience from Northen Italian Patients." Autoimmun Rev 22, no. 1 (2023): 103232. [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, C. R., Z. Chen, M. T. Xiao, C. Qian, C. Wang, M. S. Khatun, S. Liu, M. Islamuddin, N. J. Maness, J. A. Halperin, R. V. Blair, J. K. Kolls, S. Tomlinson, and X. Qin. "Enhanced Complement Activation and Mac Formation Accelerates Severe Covid-19." Cell Mol Life Sci 81, no. 1 (2024): 405. [CrossRef]
- Mastellos, D. C., D. Ricklin, E. Hajishengallis, G. Hajishengallis, and J. D. Lambris. "Complement Therapeutics in Inflammatory Diseases: Promising Drug Candidates for C3-Targeted Intervention." Mol Oral Microbiol 31, no. 1 (2016): 3-17. [CrossRef]
- Dezsi, L., T. Meszaros, G. Kozma, H. Velkei M, C. Z. Olah, M. Szabo, Z. Patko, T. Fulop, M. Hennies, M. Szebeni, B. A. Barta, B. Merkely, T. Radovits, and J. Szebeni. "A Naturally Hypersensitive Porcine Model May Help Understand the Mechanism of Covid-19 mRNA Vaccine-Induced Rare (Pseudo) Allergic Reactions: Complement Activation as a Possible Contributing Factor." Geroscience 44, no. 2 (2022): 597-618. [CrossRef]
- Bakos, T., T. Meszaros, G. T. Kozma, P. Berenyi, R. Facsko, H. Farkas, L. Dezsi, C. Heirman, S. de Koker, R. Schiffelers, K. A. Glatter, T. Radovits, G. Szenasi, and J. Szebeni. "mRNA-LNP Covid-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions." Int J Mol Sci 25, no. 7 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Barta, B. A., T. Radovits, A. B. Dobos, G. Tibor Kozma, T. Meszaros, P. Berenyi, R. Facsko, T. Fulop, B. Merkely, and J. Szebeni. "Comirnaty-Induced Cardiopulmonary Distress and Other Symptoms of Complement-Mediated Pseudo-Anaphylaxis in a Hyperimmune Pig Model: Causal Role of Anti-Peg Antibodies." Vaccine X 19 (2024): 100497. [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, J., L. Baranyi, S. Savay, M. Bodo, J. Milosevits, C. R. Alving, and R. Bunger. "Complement Activation-Related Cardiac Anaphylaxis in Pigs: Role of C5a Anaphylatoxin and Adenosine in Liposome-Induced Abnormalities in ECG and Heart Function." Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290, no. 3 (2006): H1050-8. [CrossRef]
- Kozma, G. T., T. Meszaros, P. Berenyi, R. Facsko, Z. Patko, C. Z. Olah, A. Nagy, T. G. Fulop, K. A. Glatter, T. Radovits, B. Merkely, and J. Szebeni. "Role of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Antibodies in the Allergic Reactions to PEG-Containing Covid-19 Vaccines: Evidence for Immunogenicity of PEG." Vaccine 41, no. 31 (2023): 4561-70. [CrossRef]
- Schanzenbacher, J., J. Kohl, and C. M. Karsten. "Anaphylatoxins Spark the Flame in Early Autoimmunity." Front Immunol 13 (2022): 958392. [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D., D. C. Mastellos, and J. D. Lambris. "Therapeutic Targeting of the Complement System." Nat Rev Drug Discov (2019). [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M. Kolu, N. Yeh, M. Parikh, A. and Deschatelets, P. "The Future of Complement Therapeutics." Exploration of immunology 4, no. 5 (2024): 577-615. [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J. A., and G. Gaudernack. "Immuno-Gene Therapy of Cancer with Tumour- mRNA Transfected Dendritic Cells." Cancer Immunol Immunother 55, no. 11 (2006): 1432-42. [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M. G., T. M. Pawlik, A. N. Fader, N. F. Esnaola, and M. A. Makary. "The Orphan Drug Act: Restoring the Mission to Rare Diseases." Am J Clin Oncol 39, no. 2 (2016): 210-3. [CrossRef]
- Gabay, M. "The Orphan Drug Act: An Appropriate Approval Pathway for Treatments of Rare Diseases?" Hosp Pharm 54, no. 5 (2019): 283-84. [CrossRef]
- Schouten, A. "Ei Briefing Note 2020:4 Selected Government Definitions of Orphan or Rare Diseases Selected Government Definitions of Orphan or Rare Diseases". ." Knowledge Ecology International. R Nov 3 2020 (2020).
- Fermaglich, L. J., and K. L. Miller. "A Comprehensive Study of the Rare Diseases and Conditions Targeted by Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals over the Forty Years of the Orphan Drug Act." Orphanet J Rare Dis 18, no. 1 (2023): 163. [CrossRef]
- Sanders, T. I. "The Orphan Drug Act." Prog Clin Biol Res 127 (1983): 207-15.
- Tian, J., Z. Xu, J. S. Smith, S. E. Hofherr, M. A. Barry, and A. P. Byrnes. "Adenovirus Activates Complement by Distinctly Different Mechanisms in Vitro and in Vivo: Indirect Complement Activation by Virions in Vivo." J Virol 83, no. 11 (2009): 5648-58. [CrossRef]
- Radmer, A., and J. Bodurtha. "Prospects, Realities, and Safety Concerns of Gene Therapy." Va Med Q 119, no. 2 (1992): 98-100.
- Szebeni, János. "The Unique Features and Collateral Immune Effects of mRNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccines: Potential Plausible Causes of Adverse Events and Complications." In Preprints: Preprints, 2025.
- Kariko, K., H. Muramatsu, F. A. Welsh, J. Ludwig, H. Kato, S. Akira, and D. Weissman. "Incorporation of Pseudouridine into mRNA Yields Superior Nonimmunogenic Vector with Increased Translational Capacity and Biological Stability." Mol Ther 16, no. 11 (2008): 1833-40.
- Kariko, K., H. Muramatsu, J. Ludwig, and D. Weissman. "Generating the Optimal mRNA for Therapy: Hplc Purification Eliminates Immune Activation and Improves Translation of Nucleoside-Modified, Protein-Encoding mRNA." Nucleic Acids Res 39, no. 21 (2011): e142. [CrossRef]
- Moghaddar, M., R. Radman, and I. Macreadie. "Severity, Pathogenicity and Transmissibility of Delta and Lambda Variants of Sars-Cov-2, Toxicity of Spike Protein and Possibilities for Future Prevention of Covid-19." Microorganisms 9, no. 10 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L., M. Aparicio-Alonso, M. Henry, M. Radman, R. Attal, and A. Bakkar. "Toxicity of the Spike Protein of Covid-19 Is a Redox Shift Phenomenon: A Novel Therapeutic Approach." Free Radic Biol Med 206 (2023): 106-10. [CrossRef]
- Boros, L. G., A. M. Kyriakopoulos, C. Brogna, M. Piscopo, P. A. McCullough, and S. Seneff. "Long-Lasting, Biochemically Modified mRNA, and Its Frameshifted Recombinant Spike Proteins in Human Tissues and Circulation after Covid-19 Vaccination." Pharmacol Res Perspect 12, no. 3 (2024): e1218. [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N., S. Tuyishime, H. Muramatsu, K. Kariko, B. L. Mui, Y. K. Tam, T. D. Madden, M. J. Hope, and D. Weissman. "Expression Kinetics of Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Delivered in Lipid Nanoparticles to Mice by Various Routes." J Control Release 217 (2015): 345-51. [CrossRef]
- Ltd, Pfizer Australia Pty. "Nonclinical Evaluation Report: Bnt162b2 [mRNA] Covid-19 Vaccine (Comirnatytm)." https://www.tga.gov.au/sites/default/files/foi-2389-06.pdf https://t.co/Zrhakh7Xgv (2021).
- Sharma, P., D. Hoorn, A. Aitha, D. Breier, and D. Peer. "The Immunostimulatory Nature of mRNA Lipid Nanoparticles." Adv Drug Deliv Rev 205 (2024): 115175. [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, L., R. Rossi, F. Sechi, D. Buonocore, M. Sorrenti, S. Perteghella, M. Peviani, and M. C. Bonferoni. "Effect of Lipid Nanoparticle Physico-Chemical Properties and Composition on Their Interaction with the Immune System." Pharmaceutics 16, no. 12 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Cullis, P. R., and M. J. Hope. "Lipid Nanoparticle Systems for Enabling Gene Therapies." Mol Ther 25, no. 7 (2017): 1467-75.
- Ferraresso, F., K. Badior, M. Seadler, Y. Zhang, A. Wietrzny, M. F. Cau, A. Haugen, G. G. Rodriguez, M. R. Dyer, P. R. Cullis, E. Jan, and C. J. Kastrup. "Protein Is Expressed in All Major Organs after Intravenous Infusion of mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticles in Swine." Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 32, no. 3 (2024): 101314.
- 7, J., B. Kiss, T. Bozo, K. Turjeman, Y. Levi-Kalisman, Y. Barenholz, and M. Kellermayer. "Insights into the Structure of Comirnaty Covid-19 Vaccine: A Theory on Soft, Partially Bilayer-Covered Nanoparticles with Hydrogen Bond-Stabilized mRNA-Lipid Complexes." ACS Nano 17, no. 14 (2023): 13147-57. [CrossRef]
- König, Brigitte, and Jürgen O. Kirchner. "Methodological Considerations Regarding the Quantification of DNA Impurities in the Covid-19 mRNA Vaccine Comirnaty®." Methods and Protocols, no. 3 (2024).
- Diblasi, L. , M. Monteverde, D. Nonis, and M. Sangorrín. "At Least 55 Undeclared Chemical Elements Found in Covid-19 Vaccines from Astrazeneca, Cansino, Moderna, Pfizer, Sinopharm and Sputnik V, with Precise Icp-Ms." International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research 3 (2024): 1367-93.
- Verbeke, R., M. J. Hogan, K. Lore, and N. Pardi. "Innate Immune Mechanisms of mRNA Vaccines." Immunity 55, no. 11 (2022): 1993-2005.
- Fineberg, H. V. "Swine Flu of 1976: Lessons from the Past. An Interview with Dr Harvey V Fineberg." Bull World Health Organ 87, no. 6 (2009): 414-5. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E., J. Goswami, A. H. Baqui, P. A. Doreski, G. Perez-Marc, K. Zaman, J. Monroy, C. J. A. Duncan, M. Ujiie, M. Ramet, L. Perez-Breva, A. R. Falsey, E. E. Walsh, R. Dhar, L. Wilson, J. Du, P. Ghaswalla, A. Kapoor, L. Lan, S. Mehta, R. Mithani, C. A. Panozzo, A. K. Simorellis, B. J. Kuter, F. Schodel, W. Huang, C. Reuter, K. Slobod, S. K. Stoszek, C. A. Shaw, J. M. Miller, R. Das, G. L. Chen, and R. S. V. Study Group Conquer. "Efficacy and Safety of an mRNA-Based Rsv Pref Vaccine in Older Adults." N Engl J Med 389, no. 24 (2023): 2233-44.
- ModernaTX, Inc. "Prescribing Information: Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine) Injectable Suspension, for Intramuscular Use." https://www.fda.gov/media/179005/download?attachment=&utm_source=chatgpt.com https://www.fda.gov/media/179005/download?attachment=&utm_source=chatgpt.com (2024).
- Wang, Y. S., M. Kumari, G. H. Chen, M. H. Hong, J. P. Yuan, J. L. Tsai, and H. C. Wu. "mRNA-Based Vaccines and Therapeutics: An in-Depth Survey of Current and Upcoming Clinical Applications." J Biomed Sci 30, no. 1 (2023): 84. [CrossRef]
- Ladak, R. J., A. J. He, Y. H. Huang, and Y. Ding. "The Current Landscape of mRNA Vaccines against Viruses and Cancer-a Mini Review." Front Immunol 13 (2022): 885371. [CrossRef]
- Sayour, E. J., D. Boczkowski, D. A. Mitchell, and S. K. Nair. "Cancer mRNA Vaccines: Clinical Advances and Future Opportunities." Nat Rev Clin Oncol 21, no. 7 (2024): 489-500. [CrossRef]

| Organ System | Adverse Events |
| Cardiovascular | acute coronary syndrome, aneurysm, arrhythmia, arrhythmias, arteriosclerosis, cardiac tamponade, coronary artery disease, deep vein thrombosis, cardiomyopathy, edema of the lip, tongue, face, endothelial dysfunction, heart failure, hypertension, hypotension, ischemia, large-vessel vasculitis, microangiopathy, myocardial infarction, myocarditis, non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis, pericarditis, postural tachycardia syndrome, stroke, sudden death, Takotsubo syndrome (stress cardiomyopathy), vascular inflammation (Kawasaki disease) |
| Neurological | acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, ageusia, anosmia, aseptic meningitis, Bell’s palsy, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, CNS bleed, cranial polyneuropathy, dysesthesia with exanthem, dysgeusia, encephalitis, encephalopathy, facial nerve palsy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, hypogeusia, hypoglossal nerve palsy, hyposmia, myelitis, myoclonus, myoclonus-ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, oropharyngeal dysphagia, persistent hiccups, seizures, seizures, sensorineural hearing loss, Stroke (hemorrhagic, ischemic), vestibular neuritis |
| Respiratory | acute chest syndrome, acute respiratory distress syndrome, bronchospasm, bullous lung disease, coughing, dyspnea, pulmonary vasculitis, hemopneumothorax, hemoptysis, hilar lymphadenopathy, hoarseness, hypoxia, pediatric croup, platypnea orthodeoxia syndrome, pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pulmonary embolism, stridor |
| Gastrointestinal | acute acalculous cholecystitis, angular cheilitis, appendicitis, cholecystitis, colitis, enteritis, enterocolitis, fulminant hepatic failure, hepatitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, paralytic ileus, parotitis, spontaneous hemoperitoneum, spontaneous splenic rupture, tongue ulcers |
| Musculoskeletal | arthralgia, arthritis, aseptic arthritis, muscle spasms, myalgia, myositis, rhabdomyolysis |
| Dermatological | angioedema, chilblain, chronic urticaria, cutaneous vasculitis, dermatographia, epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, follicular eruption, Gianotti-Crosti rash, Gilbert type erythema nodosum, Grover-like eruption, hyperkeratosis, lower extremity bullae, maculopapular rash, nail bed red half-moon sign, oral vesiculobullous lesions, painful cystic lesion, pityriasis rosea, pustular eruption, rash, seborrheic dermatitis, Steven-Johnson syndrome, unilateral thoracic exanthema, urticaria (hives), vasculitis. |
| Hematological | anemia, coagulopathy, cold agglutinin syndrome, hemophagocytic lymph histiocytosis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, lymphopenia, methemoglobinemia, stroke, thromboembolism, thrombocytopenia, thrombosis, thrombosis with thrombocytopenia |
| Endocrine/Metabolic | adrenal injury, diabetes, hyperglycemia, myxedema, orchitis, pancreatitis, parotitis, prostatitis, prostatic infarction, sexual dysfunction, thyroiditis |
| Renal/Genitourinary | glomerulopathy, hematuria, hypernatremia, IgA vasculitis with nephritis, nephrosis, proteinuria, renal failure, renal infarction, urinary retention, vasculitis with glomerulonephritis |
| Immune System | anaphylaxis, autoimmune flare-ups, autoimmune glomerulonephritis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, autoimmune hepatitis, autoimmune rheumatological diseases, CARPA, hypersensitivity reactions, lymphadenopathy, lymphadenopathy |
| General/Systemic | abscess, alopecia, hyperferritinemic syndrome, hyperglycemia, hyponatremia, multisystem inflammatory syndrome, sepsis, septic shock |
| Psychiatric | akathisia, altered mental status, catalepsy, convulsions, delirium, insomnia, mania, multiple sclerosis, narcolepsy, psychosis, seizures, status epilepticus, sudden and persistent dysphonia, suicide attempt |
| Ocular | bilateral macular bleed, bilateral visual loss, conjunctivitis, episcleritis, ocular myasthenia gravis, ocular/orbital inflammation, retinopathy, uveo-retinitis |
| Reproductive | abortion, ectopic pregnancy, fetal HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) |
| Gynecological/obstetric | amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, endometritis, menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, oligomenorrhea, pelvic inflammatory disease, premenstrual syndrome |
| Oncological | acute lymphocytosis, lymphoid leukemias, “turbo cancer” |
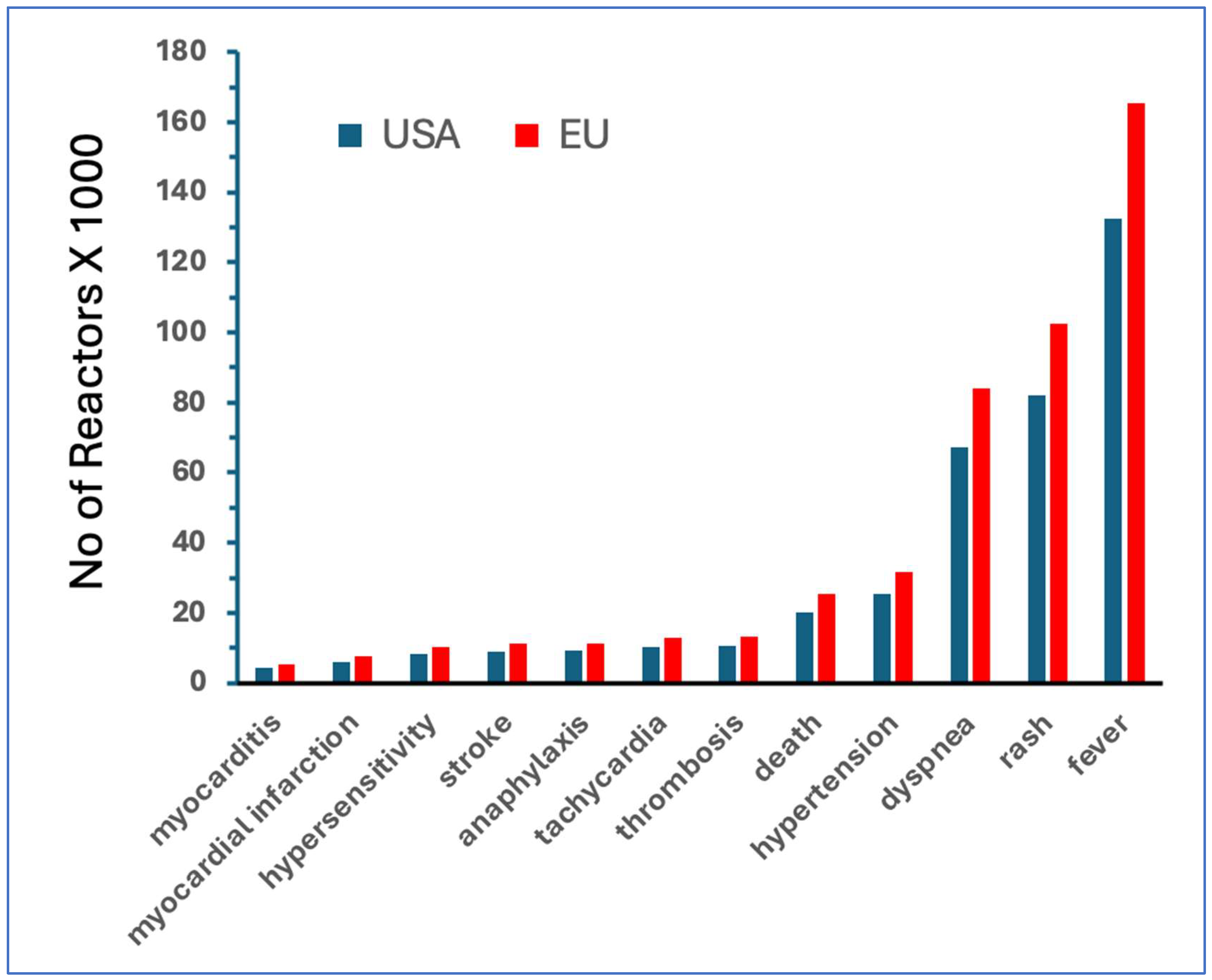
| Vaccine | AE+n* | Doses | AE+/M** | AE-/AE+*** | COVID/flu |
| Comirnaty | 434,821 | 401,685,954 | 1,082 | 924 | 20 |
| Spikevax | 426,714 | 251,852,502 | 1,694 | 590 | 32 |
| Combined mRNA | 861,535 | 653,538,456 | 1,318 | 759 | 25 |
| Jcovden (Janssen) | 54,728 | 18,991,177 | 2,882 | 347 | 54 |
| All genetic | 934,959 | 672,529,633 | 1,390 | 719 | 26 |
| Flu | 18,696 | 352,670,000 | 53 | 18,863 | 1 |
| Flu vaccines | mRNA vaccines | Fold increase | ||||||||
| AE | AE/M | AE | AE/M | AE | AE/M | |||||
| fever | 4294 | 7.9 | 132,447 | 201.70 | 31 | 26 | ||||
| rash | 1118 | 2.06 | 82,113 | 125.05 | 73 | 61 | ||||
| dyspnea | 622 | 1.14 | 67355 | 102.57 | 204 | 152 | ||||
| hypertension | 160 | 0.29 | 25,292 | 38.52 | 158 | 131 | ||||
| death | 74 | 0.14 | 20,227 | 30.8 | 273 | 226 | ||||
| thrombosis | 19 | 0.03 | 10,439 | 15.9 | 549 | 455 | ||||
| tachycardia | 52 | 0.1 | 10,205 | 15.54 | 196 | 162 | ||||
| anaphylaxis | 117 | 0.22 | 9,094 | 13.85 | 78 | 64 | ||||
| stroke | 280 | 0.52 | 8,939 | 13.61 | 32 | 26 | ||||
| hypersensitivity | 122 | 0.22 | 8,153 | 12.42 | 67 | 55 | ||||
| MI | 23 | 0.04 | 6,067 | 9.24 | 264 | 218 | ||||
| myocarditis | 3 | 0.01 | 4,176 | 6.36 | 1392 | 1,152 | ||||
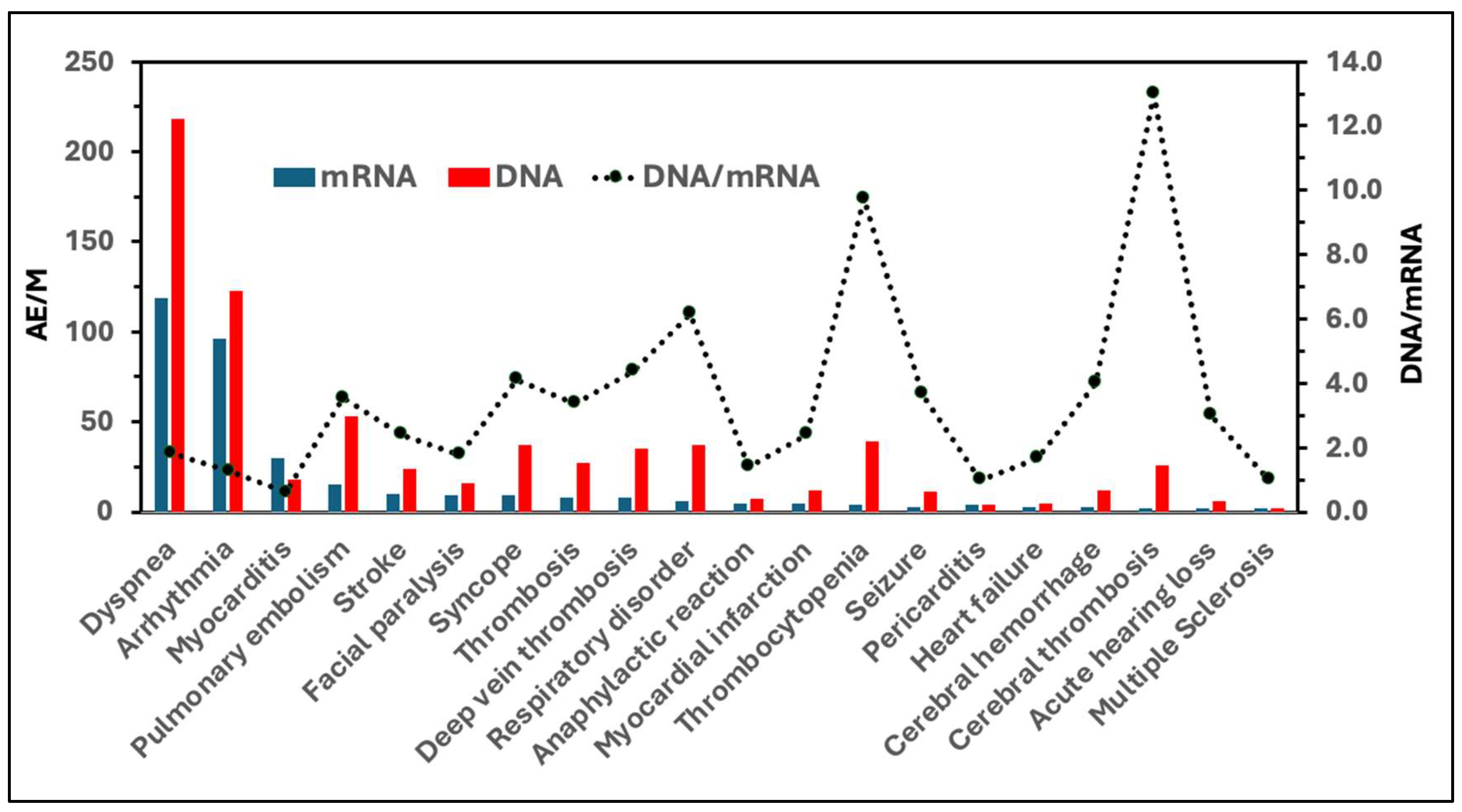
| AE of special interest | AEs/Million | |||
| Comirnaty | Spikevax | Vaxzevria | Jcovden | |
| Dyspnea | 55 | 64 | 110 | 108 |
| Arrhythmia | 46 | 50 | 57 | 66 |
| Myocarditis | 14 | 16 | 6 | 12 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 8 | 7 | 33 | 20 |
| Stroke | 6 | 4 | 15 | 9 |
| Facial paralysis | 5 | 4 | 7 | 9 |
| Syncope | 5 | 4 | 25 | 12 |
| Thrombosis | 4 | 4 | 19 | 8 |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 4 | 4 | 27 | 8 |
| Respiratory disorder | 3 | 3 | 33 | 4 |
| Anaphylactic reaction | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Myocardial infarction | 3 | 2 | 6 | 6 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 3 | 1 | 32 | 7 |
| Seizure | 2 | 1 | 7 | 4 |
| Pericarditis | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Heart failure | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Cerebral hemorrhage | 2 | 1 | 8 | 4 |
| Cerebral thrombosis | 1 | 1 | 20 | 6 |
| Acute hearing loss | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| Multiple Sclerosis | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





