Submitted:
18 November 2024
Posted:
19 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical molecular parameter and molecular electrostatic potential analysis
2.2. Chemical synthesis experimental
2.2.1. Materials and methods for the synthesis
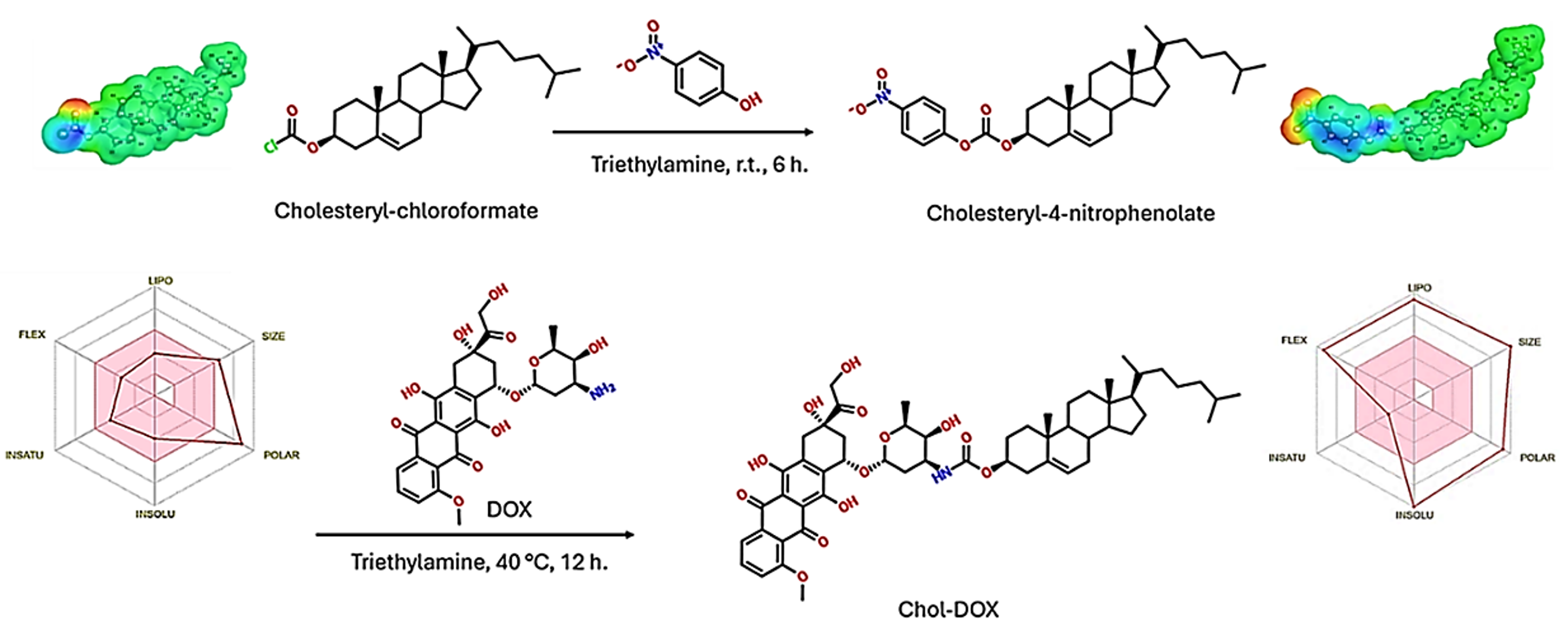
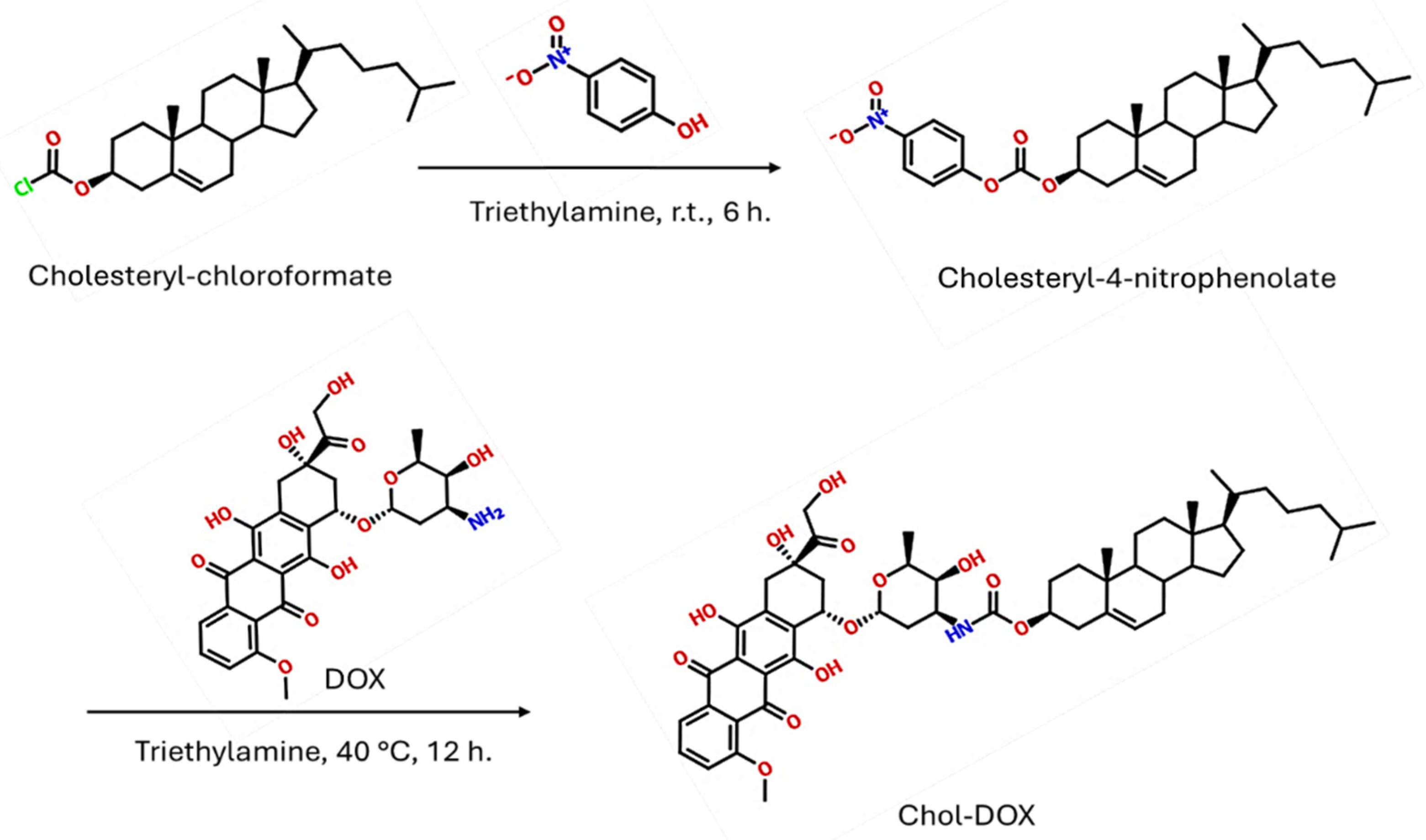
2.2.2. Synthesis of Cholesteryl-4-nitrophenolate (IUPAC name: [(3S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-(6-methylheptan-2-yl)-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]-phenanthren-3-yl] (4-nitrophenyl) carbonate)
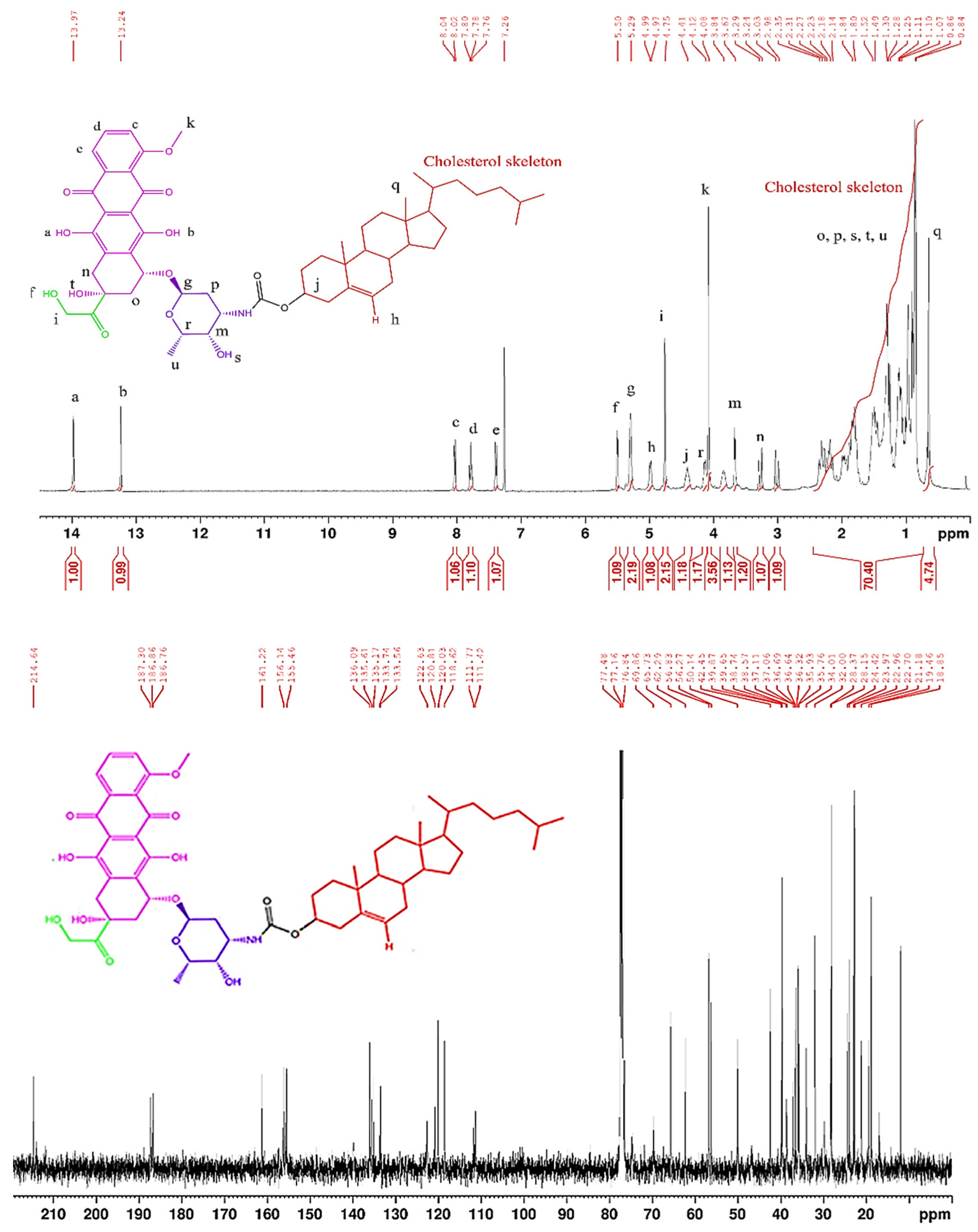
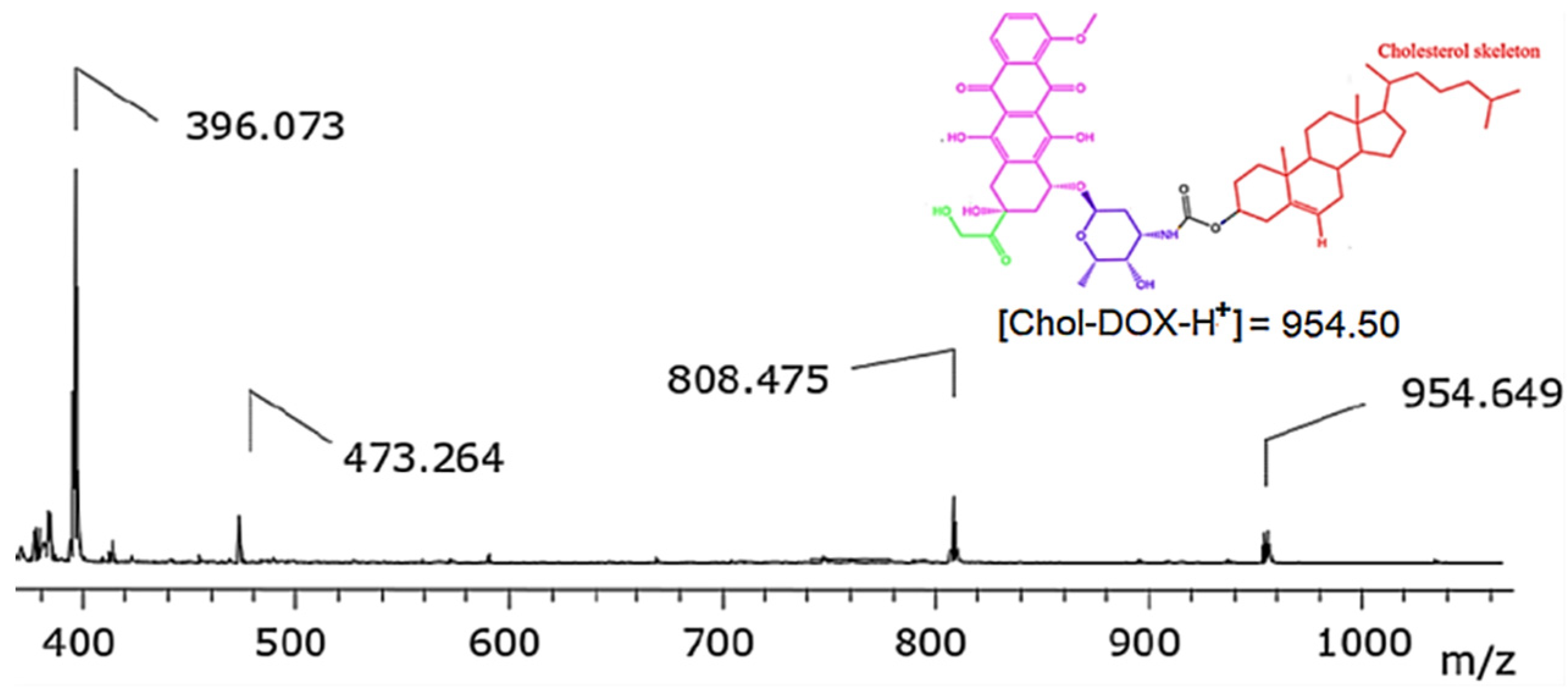
3.2.3. Synthesis of Chol-DOX conjugate (IUPAC name: [(3S,10R,13R,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-(6-methylheptan-2-yl)-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] N-[(2S,3S,4S,6R)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-6-[[(1S,3S)-3,5,12-trihydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-2,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-1-yl]oxy]oxan-4-yl]carbamate)
3. Results and discussion
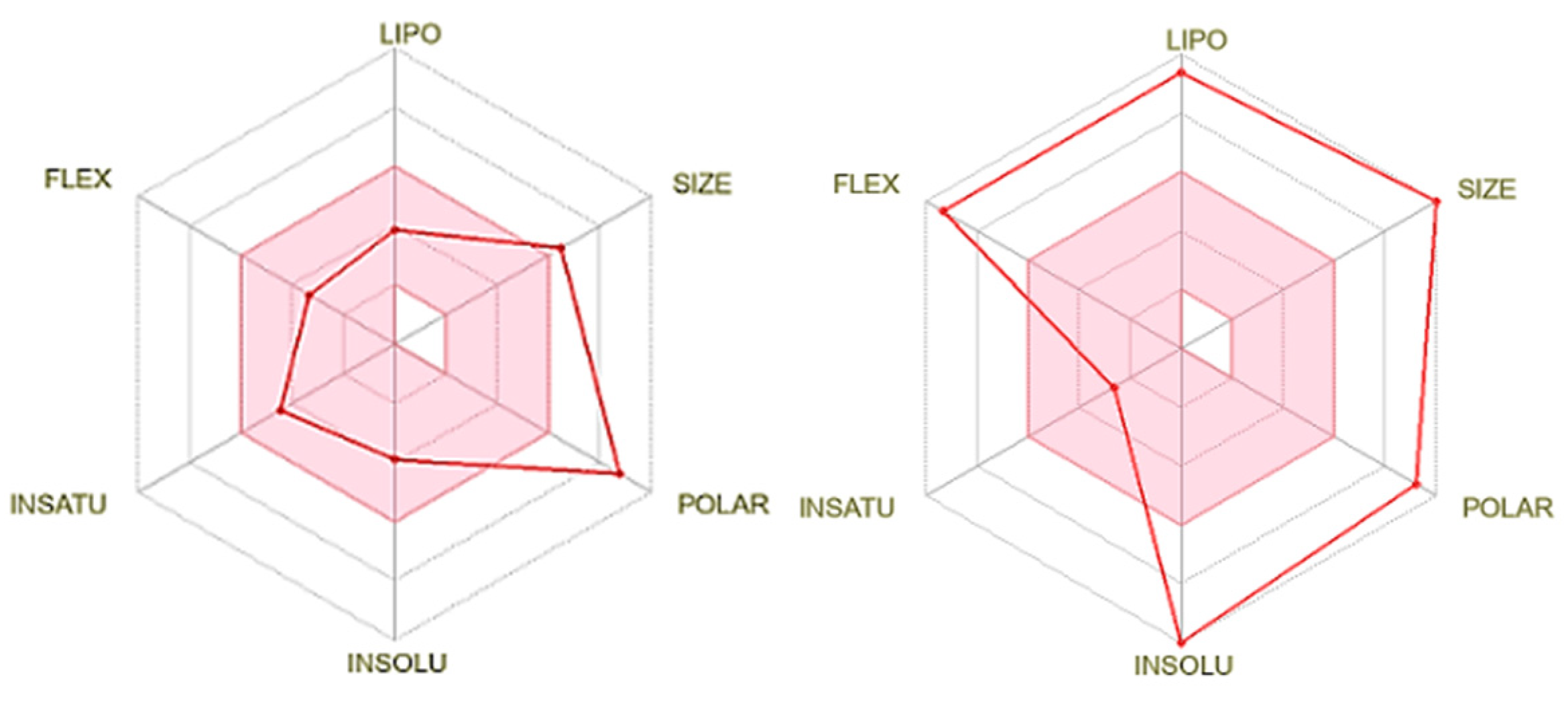
3.1. Theoretical analysis of molecular parameters
3.2. Synthesis and characterization of Chol-DOX conjugate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sritharan, S.; Sivalingam, N. A comprehensive review on time-tested anticancer drug doxorubicin. Life Sciences 2021, 278, 119527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Mignani, S.; Rodrigues, J.; Tomás, H. A glance over doxorubicin based-nanotherapeutics: From proof-of-concept studies to solutions in the market. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 317, 347–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; Cao, A.; Sun, J.; Jia, L.; Sheng, R. Morphology-Variable Aggregates Prepared from Cholesterol-Containing Amphiphilic Glycopolymers: Their Protein Recognition/Adsorption and Drug Delivery Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; Cao, A.; Sun, J.; Kinsella, J.M. Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, A. Cholesterol-based cationic lipids for gene delivery: Contribution of molecular structure factors to physico-chemical and biological properties. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Luo, T.; Shen, Y.; Cao, A.; Sheng, R. Natural steroid-based cationic copolymers cholesterol/diosgenin-r-PDMAEMAs and their pDNA nanoplexes: impact of steroid structures and hydrophobic/hydrophilic ratios on pDNA delivery. RSC Advances 2021, 11, 19450–19460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, R.; Chen, J. Microfluidic-Based Cationic Cholesterol Lipid siRNA Delivery Nanosystem: Highly Efficient In Vitro Gene Silencing and the Intracellular Behavior. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, W.; Sheng, R.; Guo, X.; Hao, L.; Zhang, X. Controlled preparation of cholesterol-bearing polycations with pendent l-lysine for efficient gene delivery. International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials 2023, 72, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Hao, L.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Q.; Sheng, R. Charge-Convertible and Reduction-Sensitive Cholesterol-Containing Amphiphilic Copolymers for Improved Doxorubicin Delivery. Materials 2022, 15, 6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olim, F.; Neves, A.R.; Vieira, M.; Tomás, H.; Sheng, R. Self-Assembly of Cholesterol-Doxorubicin and TPGS into Prodrug-Based Nanoparticles with Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Lysosome-Dependent Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2021, 123, 2000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polik, W.F.; Schmidt, J.R. WebMO: Web-based computational chemistry calculations in education and research. WIREs Computational Molecular Science 2022, 12, e1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amić, A.; Gotal, E. Selected Thermodynamic Parameters of Antioxidant Activity of Coumarin Based Heterocyclic Compounds. Chemistry Proceedings 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Paci, I.; Leitch, D.C. A broadly applicable quantitative relative reactivity model for nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) using simple descriptors. Chemical Science 2022, 13, 12681–12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvishmanesh, S.; Vanneste, J.; Tocci, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Tasselli, F.; Degrève, J.; Drioli, E.; Van der Bruggen, B. Physicochemical Characterization of Solute Retention in Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration: the Effect of Solute Size, Polarity, Dipole Moment, and Solubility Parameter. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2011, 115, 14507–14517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmachari, G.; Nayek, N.; Nurjamal, K.; Karmakar, I.; Begam, S. Triethylamine — A Versatile Organocatalyst in Organic Transformations: A Decade Update. Synthesis 2018, 50, 4145–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, S. Elucidating Colorization in the Functionalization of Hydroxyl-Containing Polymers Using Unsaturated Anhydrides/Acyl Chlorides in the Presence of Triethylamine. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, N.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, R.; Wang, F.; Wu, W.; et al. Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives: A New Class of Coumarin-Based G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activators and Inhibitors. Polymers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolier, J.P.E.; Roux-Desgranges, G.; Berkane, M.; Jiménez, E.; Wilhelm, E. Heat capacities and densities of mixtures of very polar substances 2. Mixtures containing N, N-dimethylformamide. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics 1993, 25, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokbel, I.; Razzouk, A.; Sawaya, T.; Jose, J. Experimental Vapor Pressures of 2-Phenylethylamine, Benzylamine, Triethylamine, and cis-2,6-Dimethylpiperidine in the Range between 0.2 Pa and 75 kPa. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 2009, 54, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakchi, B.; Krishna, A.D.; Sreecharan, E.; Ganesh, V.B.J.; Niharika, M.; Maharshi, S.; Puttagunta, S.B.; Sigalapalli, D.K.; Bhandare, R.R.; Shaik, A.B. An overview on applications of SwissADME web tool in the design and development of anticancer, antitubercular and antimicrobial agents: A medicinal chemist's perspective. Journal of Molecular Structure 2022, 1259, 132712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Mei, L.; Quach, T.; Porter, C.; Trevaskis, N. Lipophilic Conjugates of Drugs: A Tool to Improve Drug Pharmacokinetic and Therapeutic Profiles. Pharmaceutical Research 2021, 38, 1497–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Carballo, K.; Lamoureux, G.V.; Perez, A.L.; Bella Cruz, A.; Cechinel Filho, V. Novel one-pot synthesis of a library of 2-aryloxy-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives. Determination of antifungal and antibacterial activity. RSC Advances 2022, 12, 18507–18523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
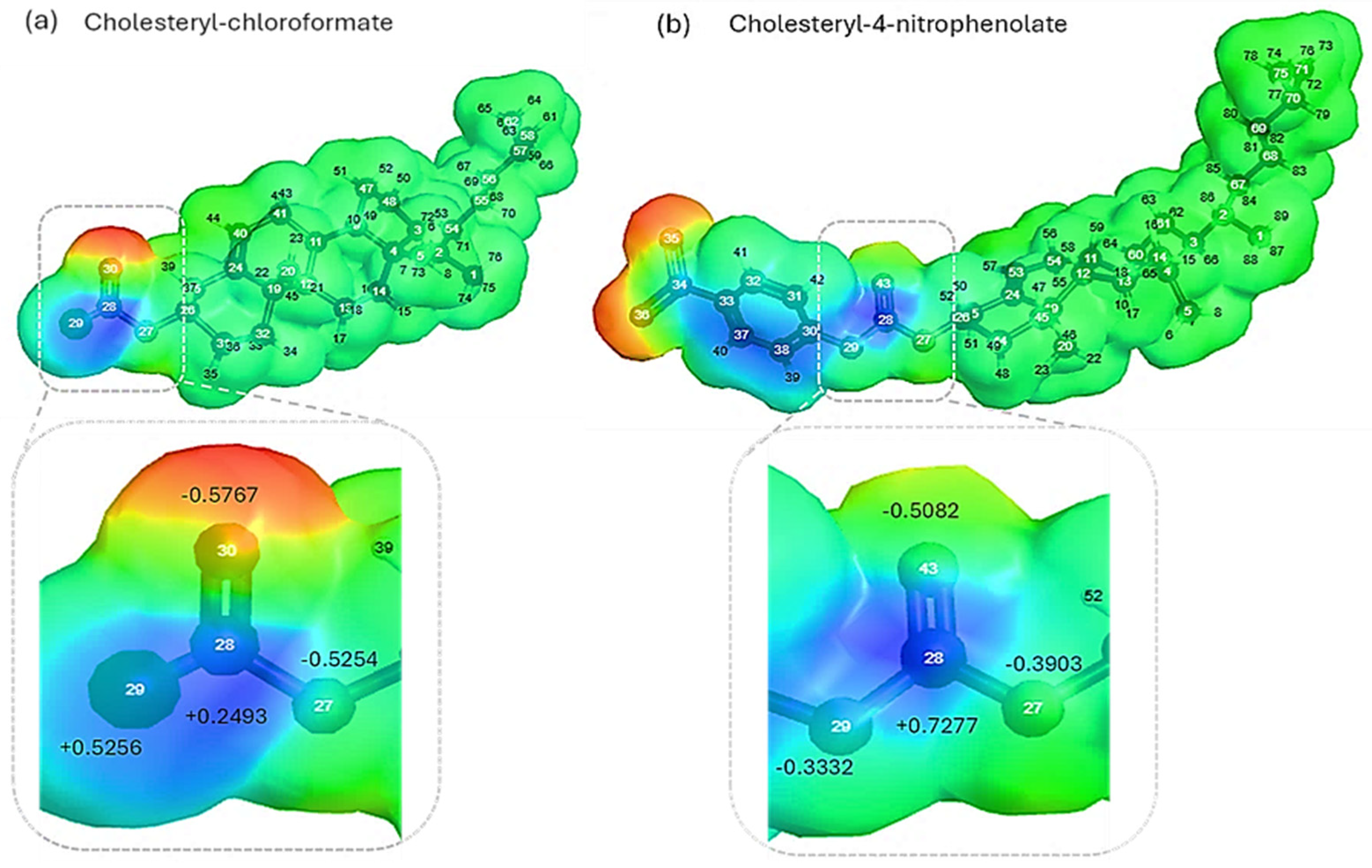
| Molecular parameters | Cholesteryl-chloroformate | Cholesteryl-4-nitrophenolate |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C28H45O2Cl | C34H49NO5 |
| Molecular weight (MW) | 449.115 | 551.765 |
| Heat of formation (Kcal/mol) | 98.164 | 469.093 |
| Molecular area (Å2) | 465.440 | 576.180 |
| Molecular volume (Å2) | 595.540 | 713.880 |
| LUMO energy (ELUMO, eV) | +0.088 | -12.812 |
| HOMO energy (EHOMO, eV) | -9.000 | -13.946 |
| HOMO-LUMO energy gap (ΔE= ELUMO-EHOMO, eV) | 9.088 | 0.134 |
| Dipole moment (Debye) | 2.855 | 10.721 |
| Biological Properties | Free DOX | Chol-DOX |
|---|---|---|
| GI absorption a | Low | Low |
| BBB permeant a | No | No |
| P-gp substrate a | Yes | Yes |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor a | No | No |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor a | No | No |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor a | No | No |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor a | No | No |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor a | Yes | Yes |
| Log Kp (skin permeation, cm/s) a | -8.71 | -4.37 |
| Log Po/w (iLOGP) a | 2.58 | 5.80 |
| Lipinski Druglikeness a | No (3 violations): MW>500; number of N or O atoms >10; NH or OH groups >5) | No (3 violations): MW>500, number of N or O atoms >10, NH or OH groups >5 |
| Bioavailability Score a | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| MDA-MB-231 cell viability (%) with 2, 6, 10ug/mL DOX, respectively.b | 87.1, 74.3, 70.2 | 98.9, 94.3, 82.1 |
| MCF-7 cell viability (%) with 2, 6, 10ug/mL DOX, respectively.b | 67.3, 64.1, 60.7 | 95.9, 79.4, 62.4 |
| Intracellular localization b | cell nuclei | lysosome |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





