Submitted:
16 November 2024
Posted:
18 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Data normalization is a critical step in machine learning workflows, particularly for clustering algorithms sensitive to feature scaling. This paper introduces a modified Robust Scaling method defined as X1= X−median(X) / mean(X), which combines the resilience of the median with the global sensitivity of the mean. The proposed scaling method is evaluated on standard datasets, including Iris and Wine, using K-means clustering. Results demonstrate that X1 scaling effectively handles outliers, enhances clustering accuracy. Additionally, we provide a detailed analysis of sorted label accuracy, confusion matrices, and the optimal random initialization seed for clustering. The findings highlight the potential of X1 scaling as a robust alternative for preprocessing in machine learning tasks.
Keywords:
I. INTRODUCTION
1. Background
a. Unsupervised Learning Foundation
b. Pattern Discovery and Knowledge Extraction
c. Data Preprocessing and Feature Engineering
d. Applications Across Domains [5]
e. Facilitating Data Visualization
f. Enhancing Machine Learning Models
g. Scalability for Big Data
2. Motivation
3. Limitations of Traditional Scaling Methods in K-means Clustering
a. Sensitivity to Outliers[13]
b. Assumption of Data Distribution
c. Neglect of Median-Based Robustness
d. Lack of Contextual Adaptation
e. Distortion of Cluster Shapes
4. Addressing the Limitations with Advanced Scaling Methods [20]
a. Robust Scaling (e.g., X′=X−median(X) / IQR) or X′=X−median(X) / mean(X)
b. Scaling Based on Domain Knowledge:
5. Objective
a. Mitigate the Impact of Outliers:
b. Improve Cluster Formation:
c. Evaluate Clustering Performance:
d. Enhance Applicability to Real-World Data:
II. BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORK
1. K-means Clustering Overview
a. Objective
b. Distance Metric
c. Cluster Centroid
d. Input Parameters
2. Traditional Scaling Techniques
3. How K-means Works
4. Advantages of K-means Clustering [24]
5. Limitations of K-means Clustering [25]
6. Applications of K-means Clustering [26]
7. Enhancements to K-means
8. Robust Scaling Techniques:
a. Median-Based Scaling
b. Median and Mean Scaling
III. METHODOLOGY
1. Motivation
2. Steps for Implementation
a. Dataset Preparation
b. Calculate Robust Statistics
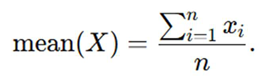
c. Apply the Modified Robust Scaling Formula
3. Application to Clustering
a. K-means Clustering
b. Evaluation Metrics
4. Advantages of the Proposed Method
5. Experimental Validation
6. Conclusion
IV. EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
1. Datasets
a. Iris Dataset Details
b. Wine Dataset Details
2. Preprocessing [32]
a. Feature Scaling Methods for Comparison
b. Handling Missing Values
c. Standardization
3. Experimental Procedure
a. Clustering Algorithm
b. Evaluation Metrics
c. Validation Approach
- Apply the three scaling techniques.
- Perform K-means clustering using each scaled dataset.
- Evaluate performance metrics and identify the best random seed for each method.
d. Implementation Tools
- Programming Language: Python 3.8.
- Libraries:
- ▪
- Scikit-learn: For K-means implementation and scaling methods.
- ▪
- NumPy: For numerical operations.
- ▪
- Pandas: For data manipulation.
4. Experimental Design
a. Comparison Across Scaling Techniques
V. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
VI. DISCUSSION
VII. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
1. Enhanced Robustness
2. Improved Clustering Accuracy
3. Adaptability to Diverse Datasets
4. Practical Applicability
- Integration with other clustering algorithms beyond K-means, such as DBSCAN and hierarchical clustering.
- Adaptations for handling categorical and mixed-type data.
- Development of hybrid scaling methods that combine robust and adaptive features.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. D. V. Prasad and Srikanth, "A Survey on Clustering Algorithms and their Constraints," Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, vol. 11, no. 6s, pp. 165-17917, 2023.
- M. Usama et al., "Unsupervised Machine Learning for Networking: Techniques, Applications and Research Challenges," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 65579-65615, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Ahmed, W. H. Wan Ishak, N. Md Norwawi and A. Alkilany, "Pattern discovery using k-means algorithm," 2014 World Congress on Computer Applications and Information Systems (WCCAIS), Hammamet, Tunisia, 2014, pp. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Dwivedi and B. Rawat, "A review paper on data preprocessing: A critical phase in web usage mining process," 2015 International Conference on Green Computing and Internet of Things (ICGCIoT), Greater Noida, India, 2015, pp. 506-510. [CrossRef]
- J. Oyelade et al., "Data Clustering: Algorithms and Its Applications," 2019 19th International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications (ICCSA), St. Petersburg, Russia, 2019, pp. 71-81. [CrossRef]
- J. Wei, H. Yu, J. H. Chen and K. -L. Ma, "Parallel clustering for visualizing large scientific line data," 2011 IEEE Symposium on Large Data Analysis and Visualization, Providence, RI, USA, 2011, pp. 47-55. [CrossRef]
- V. Gulati and N. Raheja, "Efficiency Enhancement of Machine Learning Approaches through the Impact of Preprocessing Techniques," 2021 6th International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC), Solan, India, 2021, pp. 191-196. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Mahdi, K. M. Hosny and I. Elhenawy, "Scalable Clustering Algorithms for Big Data: A Review," in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 80015-80027, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Benkessirat and N. Benblidia, "Fundamentals of Feature Selection: An Overview and Comparison," 2019 IEEE/ACS 16th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2019, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- S. Z. Selim and M. A. Ismail, "K-Means-Type Algorithms: A Generalized Convergence Theorem and Characterization of Local Optimality," in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. PAMI-6, no. 1, pp. 81-87, Jan. 1984. [CrossRef]
- R. Santos, T. Ohashi, T. Yoshida and T. Ejima, "Biased clustering methods for image classification," Proceedings SIBGRAPI'98. International Symposium on Computer Graphics, Image Processing, and Vision (Cat. No.98EX237), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1998, pp. 278-285. [CrossRef]
- S. Dhillon, Yuqiang Guan and J. Kogan, "Iterative clustering of high dimensional text data augmented by local search," 2002 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, 2002. Proceedings., Maebashi City, Japan, 2002, pp. 131-138. [CrossRef]
- P. O. Olukanmi and B. Twala, "Sensitivity analysis of an outlier-aware k-means clustering algorithm," 2017 Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa and Robotics and Mechatronics (PRASA-RobMech), Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2017, pp. 68-73. [CrossRef]
- H. W. Herwanto, A. N. Handayani, A. P. Wibawa, K. L. Chandrika and K. Arai, "Comparison of Min-Max, Z-Score and Decimal Scaling Normalization for Zoning Feature Extraction on Javanese Character Recognition," 2021 7th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Information Engineering (ICEEIE), Malang, Indonesia, 2021, pp. 1-3. [CrossRef]
- N. Fei, Y. Gao, Z. Lu and T. Xiang, "Z-Score Normalization, Hubness, and Few-Shot Learning," 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021, pp. 142-151. [CrossRef]
- Xiaowei Xu, M. Ester, H. . -P. Kriegel and J. Sander, "A distribution-based clustering algorithm for mining in large spatial databases," Proceedings 14th International Conference on Data Engineering, Orlando, FL, USA, 1998, pp. 324-331. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, C. Park, X. Gao and B. Kim, "Robust Model Design by Comparative Evaluation of Clustering Algorithms," in IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 88135-88151, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Xiong, J. Wu and J. Chen, "K-Means Clustering Versus Validation Measures: A Data-Distribution Perspective," in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 318-331, April 2009. [CrossRef]
- B. Bhanu and J. Ming, "Recognition of occluded objects: A cluster structure paradigm," Proceedings. 1986 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1986, pp. 776-781. [CrossRef]
- P. Termont et al., "How to achieve robustness against scaling in a real-time digital watermarking system for broadcast monitoring," Proceedings 2000 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No.00CH37101), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2000, pp. 407-410 vol.1. [CrossRef]
- B. Angelin and A. Geetha, "Outlier Detection using Clustering Techniques – K-means and K-median," 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 2020, pp. 373-378. [CrossRef]
- P. Sinaga and M. -S. Yang, "Unsupervised K-Means Clustering Algorithm," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 80716-80727, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. E. M. Gonzales, L. C. Uy, J. A. L. Sy and M. O. Cordel, "Distance Metric Recommendation for k-Means Clustering: A Meta-Learning Approach," TENCON 2022 - 2022 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2022, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Xie and S. Jiang, "A Simple and Fast Algorithm for Global K-means Clustering," 2010 Second International Workshop on Education Technology and Computer Science, Wuhan, China, 2010, pp. 36-40. [CrossRef]
- S. Na, L. Xumin and G. Yong, "Research on k-means Clustering Algorithm: An Improved k-means Clustering Algorithm," 2010 Third International Symposium on Intelligent Information Technology and Security Informatics, Jian, China, 2010, pp. 63-67. [CrossRef]
- D. Chi, "Research on the Application of K-Means Clustering Algorithm in Student Achievement," 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China, 2021, pp. 435-438. [CrossRef]
- Kapoor and A. Singhal, "A comparative study of K-Means, K-Means++ and Fuzzy C-Means clustering algorithms," 2017 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology (CICT), Ghaziabad, India, 2017, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, S. Guan, S. Deng and M. Li, "Improved Weighting K-Means Algorithm Based on Covariance Matrix," 2022 6th Asian Conference on Artificial Intelligence Technology (ACAIT), Changzhou, China, 2022, pp. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Feizollah, N. B. Anuar, R. Salleh and F. Amalina, "Comparative study of k-means and mini batch k-means clustering algorithms in android malware detection using network traffic analysis," 2014 International Symposium on Biometrics and Security Technologies (ISBAST), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2014, pp. 193-197. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, Y. Zhang, Q. Tang, W. Huang, Y. Jiang and S. -T. Xia, "t-k-means: A ROBUST AND STABLE k-means VARIANT," ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 2021, pp. 3120-3124. [CrossRef]
- S. Kapil and M. Chawla, "Performance evaluation of K-means clustering algorithm with various distance metrics," 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), Delhi, India, 2016, pp. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- D. U. Ozsahin, M. Taiwo Mustapha, A. S. Mubarak, Z. Said Ameen and B. Uzun, "Impact of feature scaling on machine learning models for the diagnosis of diabetes," 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Everything (AIE), Lefkosa, Cyprus, 2022, pp. 87-94. [CrossRef]
- R. Houari, A. Bounceur, A. K. Tari and M. T. Kecha, "Handling Missing Data Problems with Sampling Methods," 2014 International Conference on Advanced Networking Distributed Systems and Applications, Bejaia, Algeria, 2014, pp. 99-104. [CrossRef]
- P. Cerda and G. Varoquaux, "Encoding High-Cardinality String Categorical Variables," in IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 1164-1176, 1 March 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Tang and T. M. Khoshgoftaar, "Noise identification with the k-means algorithm," 16th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004, pp. 373-378. [CrossRef]
AUTHOR DETAILS
 |
Dr. Srikanth Thota received his Ph.D in Computer Science Engineering for his research work in Collaborative Filtering based Recommender Systems from J.N.T.U, Kakinada. He received M.Tech. Degree in Computer Science and Technology from Andhra University. He is presently working as an Associate Professor in the department of Computer Science and Engineering, School of Technology, GITAM University, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India. His areas of interest include Machine learning, Artificial intelligence, Data Mining, Recommender Systems, Soft computing. |
 |
Mr. Maradana Durga Venkata Prasad received his B. TECH (Computer Science and Information Technology) in 2008 from JNTU, Hyderabad and M. Tech. (Software Engineering) in 2010 from Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Kakinada, He is a Research Scholar with Regd No: 1260316406 in the department of Computer Science and Engineering, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management (GITAM) Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA. His Research interests include Clustering in Data Mining, Big Data Analytics, and Artificial Intelligence. He is currently working as an Assistant Professor in Department of Computer Science Engineering, GURUNANAK University, Hyderabad, Ranga Reddy, India. |
| Type of normalization | Data Set | Attributes Considered | Seed | Kmeans Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without | Iris | All | 2 | 0.8933333333333333 |
| With Robust Scaled | Iris | All | 3 | 0.8133333333333334 |
| Modified Robust Scaled | Iris | All | 0 | 0.96 |
| Without | Wine | All | 0 | 0.702247191011236 |
| With Robust Scaled | Wine | All | 0 | 0.702247191011236 |
| Modified Robust Scaled | Wine | All | 22 | 0.9382022471910112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





