Submitted:
11 November 2024
Posted:
13 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
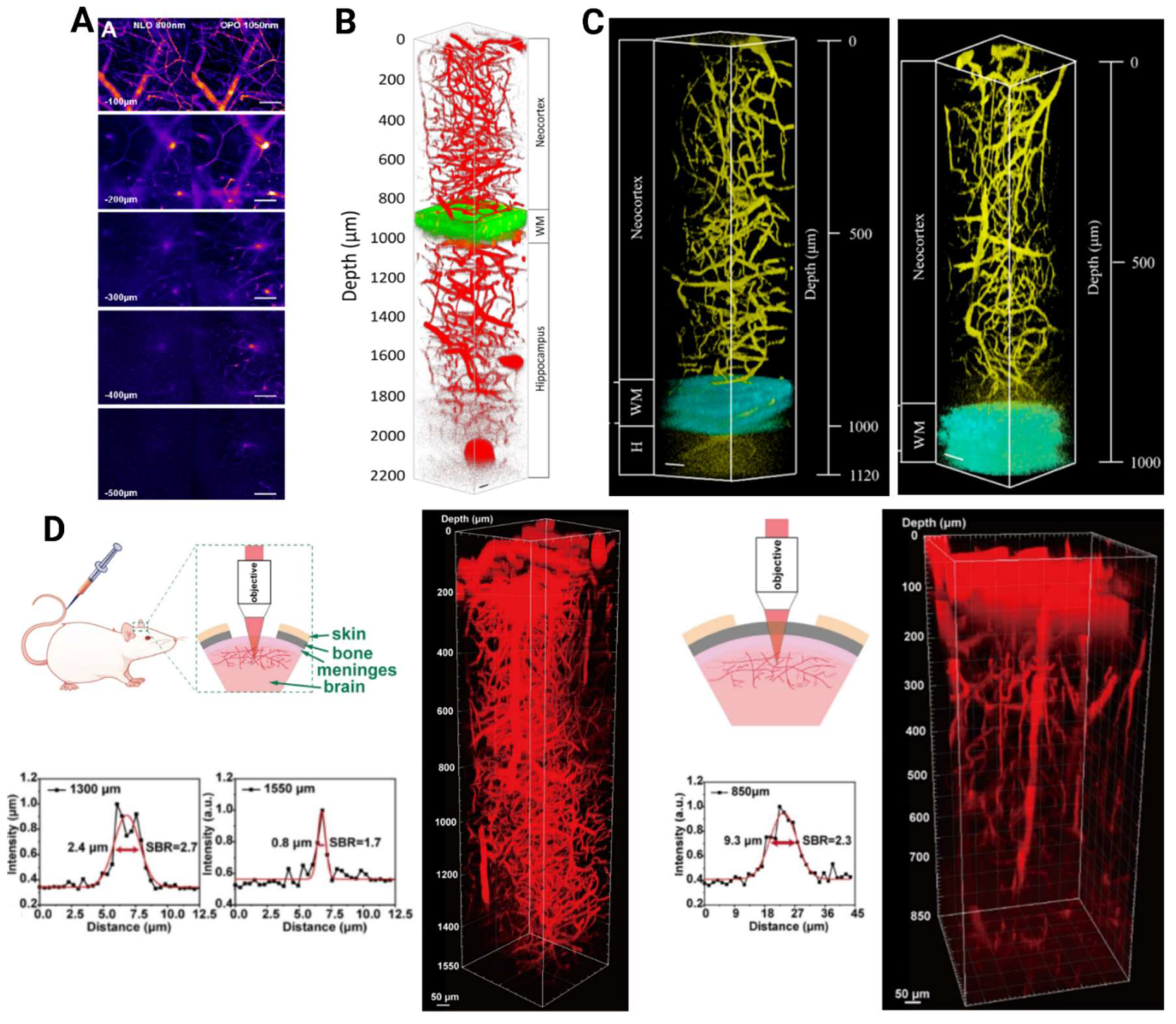
2. Advances in Structural Brain Imaging Using Quantum Dots
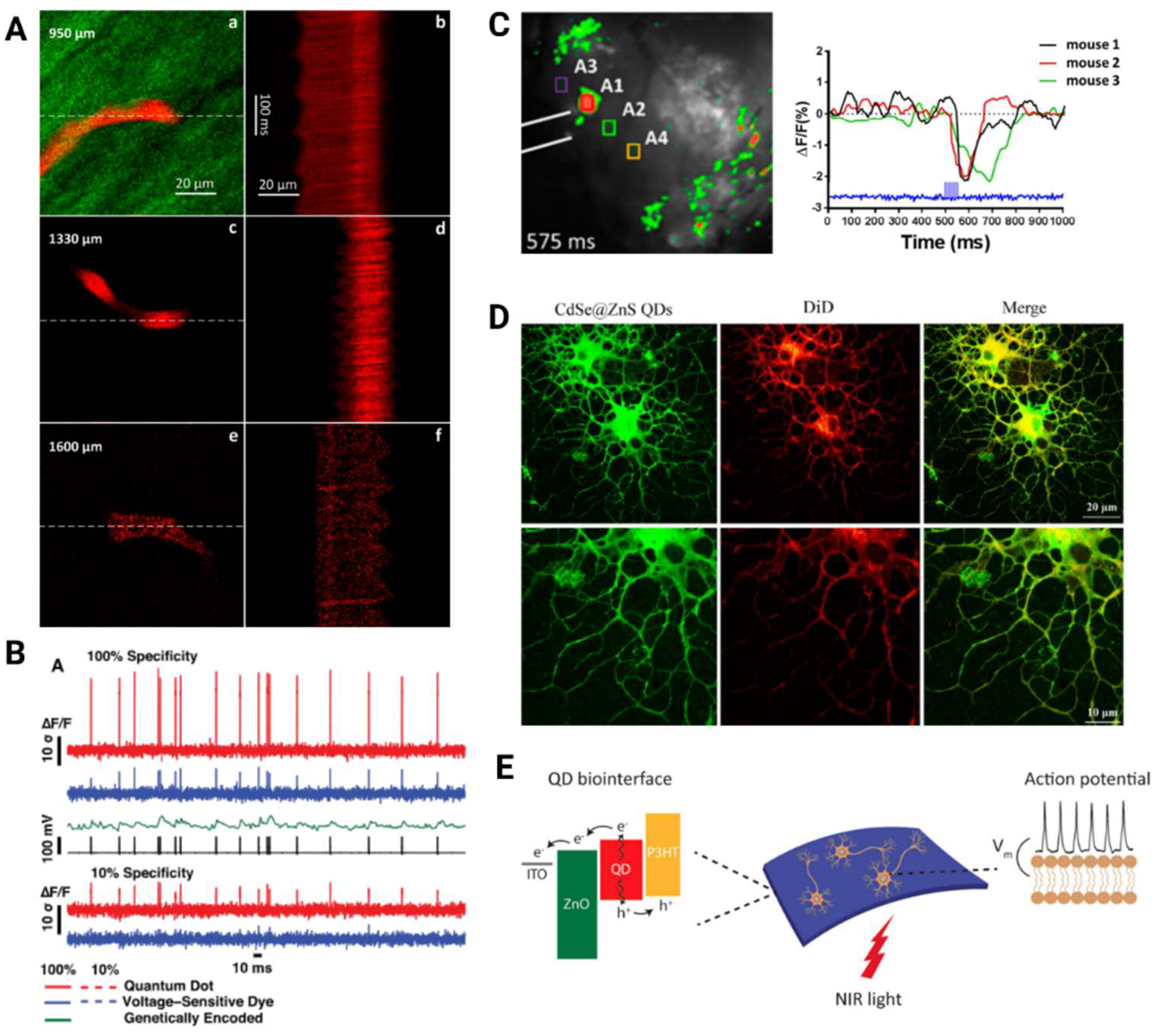
3. Exploring Functional Brain Imaging with Quantum Dots
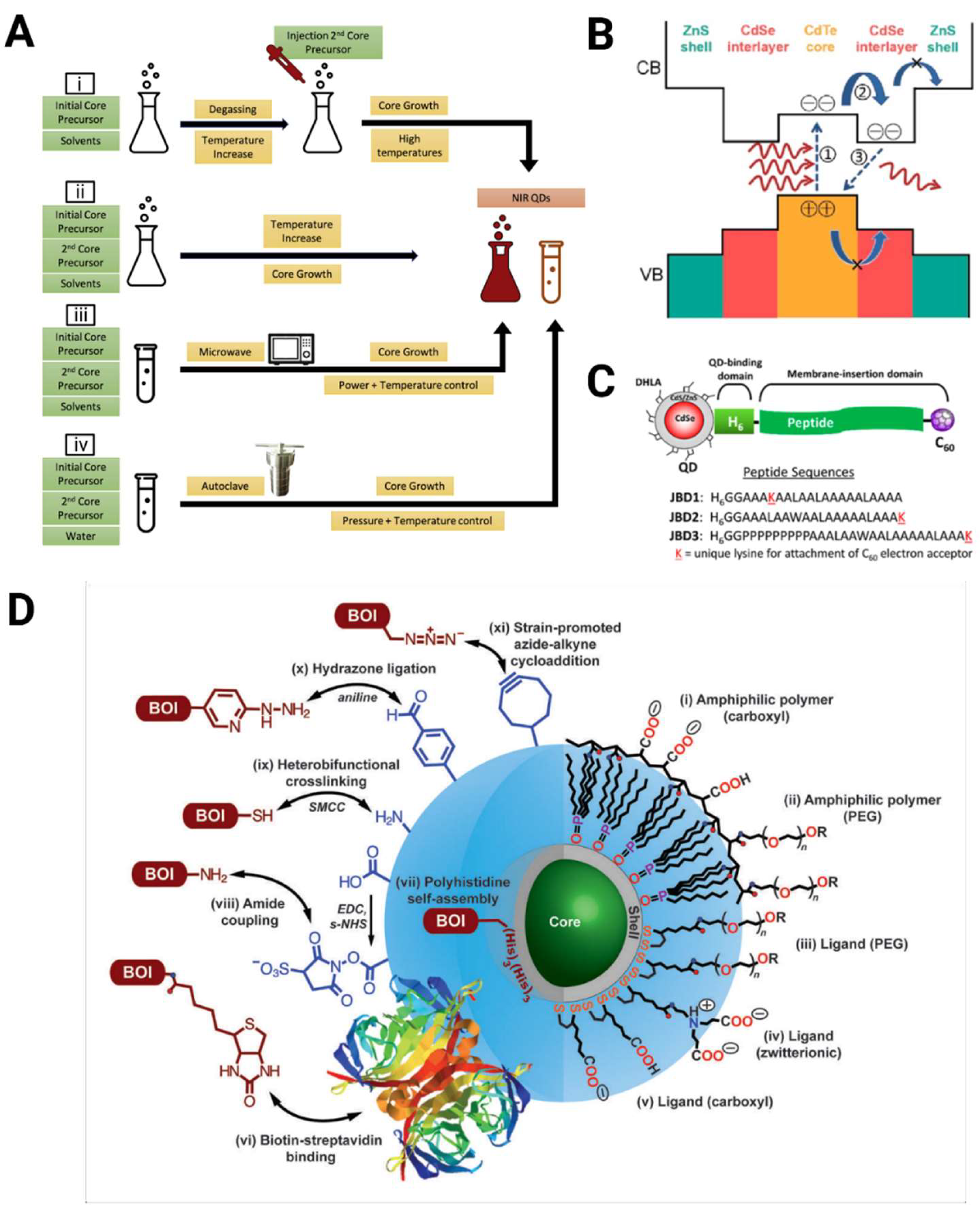
4. Synthesis Mechanisms of Quantum Dots for Enhanced Multiphoton Imaging
5. Quantum Dots in the Study, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Neurological Pathologies and Diseases
6. Conclusions
References
- Xu, C.; Zipfel, W.; Shear, J.B.; Williams, R.M.; Webb, W.W. Multiphoton fluorescence excitation: new spectral windows for biological nonlinear microscopy.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996, 93, 10763–10768. [CrossRef]
- Vellekoop, I.M.; Mosk, A.P. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2309–2311. [CrossRef]
- Horton, N.G., et al., In vivo three-photon microscopy of subcortical structures within an intact mouse brain. Nat Photonics, 2013. 7(3): p. 205-9.
- Boyd, R., Nonlienar Optics. Academic Press, 2008. 3.
- Wang, T.; Ouzounov, D.G.; Wu, C.; Horton, N.G.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Schnitzer, M.J.; Xu, C. Three-photon imaging of mouse brain structure and function through the intact skull. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 789–792. [CrossRef]
- Beer, A., Bestimmung der Absorption des rothen Lichts in farbigen Flussigkeiten. Annual Physics, 1852. 162: p. 78-88.
- Lambert, J.H., Photometria siva de mensura et gradibus luminis, coloum et umbrae. 1760.
- Izatt, J.A.; Swanson, E.A.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Hee, M.R.; Owen, G.M. Optical coherence microscopy in scattering media. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 590–592. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Sordillo, L.A.; Rodríguez-Contreras, A.; Alfano, R. Transmission in near-infrared optical windows for deep brain imaging. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 38–43. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, N.; Rebec, M.R.; Xia, F.; Xu, C. Imaging deeper than the transport mean free path with multiphoton microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 452–463. [CrossRef]
- W. Denk, J.S., and W. Webb, Two photon laser scannign fluorescence microscopy. Science, 1990. 248: p. 73-76.
- Theer, P.; Denk, W. On the fundamental imaging-depth limit in two-photon microscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2006, 23, 3139–3149. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Deng, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, B. Three-photon excited fluorescence imaging in neuroscience: From principles to applications. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1085682. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Sugihara, H.; So, P.T.C.; Sur, M. Functional imaging of visual cortical layers and subplate in awake mice with optimized three-photon microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 177. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Delepine, C.; Feldman, D.; A Pham, V.; Chou, S.; Ip, J.; Nott, A.; Tsai, L.-H.; Ming, G.-L.; So, P.T.; et al. Label-free three-photon imaging of intact human cerebral organoids for tracking early events in brain development and deficits in Rett syndrome. eLife 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Hu, M.; Le, N.M.; Sugihara, H.; So, P.T.C.; Sur, M. Quantitative third-harmonic generation imaging of mouse visual cortex areas reveals correlations between functional maps and structural substrates. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 5650–5673. [CrossRef]
- Drobizhev, M.; Tillo, S.; Makarov, N.S.; Hughes, T.E.; Rebane, A. Absolute Two-Photon Absorption Spectra and Two-Photon Brightness of Orange and Red Fluorescent Proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 855–859. [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, R.; Liang, Y.; Ji, N. Adaptive optical versus spherical aberration corrections for in vivo brain imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3891–3902. [CrossRef]
- Ji, N. Adaptive optical fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 374–380. [CrossRef]
- Sinefeld, D.; Xia, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, T.; Wu, C.; Yang, X.; Paudel, H.P.; Ouzounov, D.G.; Bifano, T.G.; Xu, C. Three-Photon Adaptive Optics for Mouse Brain Imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 880859. [CrossRef]
- Sinefeld, D.; Paudel, H.P.; Ouzounov, D.G.; Bifano, T.G.; Xu, C. Adaptive optics in multiphoton microscopy: comparison of two, three and four photon fluorescence. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 31472–83. [CrossRef]
- Streich, L.; Boffi, J.C.; Wang, L.; Alhalaseh, K.; Barbieri, M.; Rehm, R.; Deivasigamani, S.; Gross, C.T.; Agarwal, A.; Prevedel, R. High-resolution structural and functional deep brain imaging using adaptive optics three-photon microscopy. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1253–1258. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, W.; Richie, C.T.; Harvey, B.K.; Betzig, E.; Ji, N. Direct wavefront sensing for high-resolution in vivo imaging in scattering tissue. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7276. [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhong, J.; Chen, X.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, M.; Li, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. In Vivo Deep-Brain 3- and 4-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Subcortical Structures Labeled by Quantum Dots Excited at the 2200 nm Window. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 3686–3695. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Deng, X.; Tong, S.; He, C.; Cheng, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Gan, M.; Li, J.; Xie, W.; Qiu, P.; et al. In Vivo Deep-Brain Structural and Hemodynamic Multiphoton Microscopy Enabled by Quantum Dots. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 5260–5265. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; He, M.; Huang, B.; Tang, T.; Liu, F.; Cui, R.; Qian, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, T. Band Gap Engineering Improves Three-Photon Luminescence of Quantum Dots for Deep Brain Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 10947–10956. [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, S.; Murase, N. Near-infrared emitting CdTe0.5Se0.5/Cd0.5Zn0.5S quantum dots: synthesis and bright luminescence. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 615–615. [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.I.; Kepner, A.D.; Gaponenko, S.V.; Koch, S.W.; Hu, Y.Z.; Peyghambarian, N. Confinement-enhanced biexciton binding energy in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 15449–15452. [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.A.; Randall, J.N.; Aggarwal, R.J.; Matyi, R.J.; Moore, T.M.; Wetsel, A.E. Observation of discrete electronic states in a zero-dimensional semiconductor nanostructure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 60, 535–537. [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-T.; Luo, M.-Y.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, B.; Sun, Z.-J.; Cui, R.; Zhang, M. Molecular Targeting Nanoprobes with Non-Overlap Emission in the Second Near-Infrared Window for in Vivo Two-Color Colocalization of Immune Cells. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12830–12839. [CrossRef]
- Park, J., et al., CuInSe/ZnS core/shell NIR quantum dots for biomedical imaging. Small, 2011. 7(22): p. 3148-52.
- Zhao, P.; Xu, Q.; Tao, J.; Jin, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yu, C.; Yu, Z. Near infrared quantum dots in biomedical applications: current status and future perspective. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2017, 10, e1483. [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Yu, W.; Li, D.; He, M.; Chen, R.; Zhang, M.; Qian, J. Quantum dots assisted in vivo two-photon microscopy with NIR-II emission. Photon- Res. 2021, 10, 189–196. [CrossRef]
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.M.; Leach, J.; Gong, L.Y.; Ding, J.; Zheng, B.Y. Aberration corrections for free-space optical communications in atmosphere turbulence using orbital angular momentum states. Opt. Express 2011, 20, 452–461. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Peng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, T.; Guo, J.; Cui, R.; Sun, T.; Zhang, M. Improving Three-Photon Fluorescence of Near-Infrared Quantum Dots for Deep Brain Imaging by Suppressing Biexciton Decay. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 6706–6713. [CrossRef]
- H Liu, X.D., Shen Tong, Chen He, Hui Cheng, Ziwei Zhuang, Mengyao Gan, Jia Li, Weixin Xie, Ping Qiu, Ke Wang, In vivo deep brain structural and hemodynamic multiphoton miroscopy enabled by quantum dots. Nano Letters, 2019. 19.
- Ricard, C.; Lamasse, L.; Jaouen, A.; Rougon, G.; Debarbieux, F. Combination of an optical parametric oscillator and quantum-dots 655 to improve imaging depth of vasculature by intravital multicolor two-photon microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2362–2372. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Alifu, N.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z.; Qian, J. Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen with Deep-Red Emission for Through-Skull Three-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Mouse. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10452–10461. [CrossRef]
- Shen Tong, J.Z., X Chen, X Deng, J Huang, Y Zhang, M Qin, Z Li, Hui Cheng, W Zhang, Lei Zheng, Weixin Xie, Ping Qui, Ke Wang, In vivo deep brain 3 and 4 photon fluorescence imaging of subbcortical structures labeled by quantum dots excited at the 2200 nm window. ACS Nano, 2023. 17: p. 3686-3695.
- Zhong, J., et al., In vivo deep brain multiphoton fluorescence imaging emitting at NIR-I and NIR-II and excited at NIR-IV. J Biophotonics, 2024. 17(4): p. e202300422.
- Li, D.; Deng, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, D.; Xu, G.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, P.; Xie, W.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Molecular Engineering of NIR-II AIE Luminogen Excited at 1700 nm for Ultradeep Intravital Brain Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33. [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.X.a.W., Multiphoton Excitation of Molecular Fluorophores and Nonlinear Laser Microscopy, in Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy, J.L.P. Press, Editor. 1997. p. 471-540.
- Yusaku Hontani, F.X., Chris Xu, Multicolor Three-Photon Fluorescence Imaging with Single-Wavelength Excitation Deep in Mouse Brain. Science Advances, 2021. 7.
- Zhang, K., et al., Second Near-Infrared (NIR-II) Window for Imaging-Navigated Modulation of Brain Structure and Function. Small, 2023. 19(14): p. e2206044.
- Tang, T.; Chang, B.; Zhang, M.; Sun, T. Nanoprobe-mediated precise imaging and therapy of glioma. Nanoscale Horizons 2021, 6, 634–650. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Qiu, P.; Wang, D.; et al. In Vivo 3-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Mouse Subcortical Vasculature Labeled by AIEgen Before and After Craniotomy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32. [CrossRef]
- Hontani, Y., et al., Deep-Tissue Three-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy in Intact Mouse and Zebrafish Brain. J Vis Exp, 2022(179).
- Pramanik, A.; Gates, K.; Patibandla, S.; Davis, D.; Begum, S.; Iftekhar, R.; Alamgir, S.; Paige, S.; Porter, M.M.; Ray, P.C. Water-Soluble and Bright Luminescent Cesium–Lead–Bromide Perovskite Quantum Dot–Polymer Composites for Tumor-Derived Exosome Imaging. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5872–5879. [CrossRef]
- Ricard, C.; Lamasse, L.; Jaouen, A.; Rougon, G.; Debarbieux, F. Combination of an optical parametric oscillator and quantum-dots 655 to improve imaging depth of vasculature by intravital multicolor two-photon microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2362–2372. [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Rivera, J.A.; Sun, W.; Peterson, J.; Haeberle, H.; Rubin, S.; Ji, N. High-speed volumetric two-photon fluorescence imaging of neurovascular dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Vérant, P.; Serduc, R.; van der Sanden, B.; Chantal, R.; Ricard, C.; Coles, J.A.; Vial, J.-C. Subtraction method for intravital two-photon microscopy: intraparenchymal imaging and quantification of extravasation in mouse brain cortex. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 011002–011002-11. [CrossRef]
- Nag, O.K., et al., Quantum Dot-Peptide-Fullerene Bioconjugates for Visualization of in Vitro and in Vivo Cellular Membrane Potential. ACS Nano, 2017. 11(6): p. 5598-5613.
- Sakmann, B.; Edwards, F.; Konnerth, A.; Takahashi, T. PATCH CLAMP TECHNIQUES USED FOR STUDYING SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN SLICES OF MAMMALIAN BRAIN. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 1989, 74, 1107–1118. [CrossRef]
- Sakmann, B.; Neher, E. Patch Clamp Techniques for Studying Ionic Channels in Excitable Membranes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1984, 46, 455–472. [CrossRef]
- Broussard, G.J.; Liang, R.; Tian, L. Monitoring activity in neural circuits with genetically encoded indicators. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 97. [CrossRef]
- Tsytsarev, V.; Liao, L.-D.; Kong, K.V.; Liu, Y.-H.; Erzurumlu, R.S.; Olivo, M.; Thakor, N.V. Recent progress in voltage-sensitive dye imaging for neuroscience.. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 4733–4744. [CrossRef]
- Karatum, O.; Kaleli, H.N.; Eren, G.O.; Sahin, A.; Nizamoglu, S. Electrical Stimulation of Neurons with Quantum Dots via Near-Infrared Light. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8233–8243. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.D.; Schnitzer, M.J. Optical Strategies for Sensing Neuronal Voltage Using Quantum Dots and Other Semiconductor Nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4601–4609. [CrossRef]
- Dombeck, D.A.; Khabbaz, A.N.; Collman, F.; Adelman, T.L.; Tank, D.W. Imaging Large-Scale Neural Activity with Cellular Resolution in Awake, Mobile Mice. 2007, 56, 43–57. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Huang, D.; Li, C.; Wang, Q. Glutathione-capped quantum dots for plasma membrane labeling and membrane potential imaging. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1321–1326. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Larimer, P.; Pressler, R.T.; Strowbridge, B.W.; Burda, C. Wireless Activation of Neurons in Brain Slices Using Nanostructured Semiconductor Photoelectrodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2407–2410. [CrossRef]
- Qtracker non-targeted quantum dots for in vivo imaging, in Thermofisher, ThermoFisher, Editor. 2007: Thermofisher.com.
- Gil, H.M.; Price, T.W.; Chelani, K.; Bouillard, J.-S.G.; Calaminus, S.D.; Stasiuk, G.J. NIR-quantum dots in biomedical imaging and their future. 2021, 24. [CrossRef]
- Wegner, D., Hildebrandt, N, Quantum dots: Bright and Versitile in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging biosensors. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2015. 44.
- Sonawane, G.H., Patil, S.P., Sonawane, S.H, Nanocomposities and its Applications. Applications of Nanomaterials, Esevier. 2018: Elsevier.
- Li, C.; Wu, P. Cu-doped quantum dots: a new class of near-infrared emitting fluorophores for bioanalysis and bioimaging. Luminescence 2019, 34, 782–789. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Controlled Synthesis of Ag(2) Te@Ag(2) S Core-Shell Quantum Dots with Enhanced and Tunable Fluorescence in the Second Near-Infrared Window. Small, 2020. 16(14): p. e2001003.
- Van Embden, J., Chesman, A., Jasieniak, J, The Heat-Up Synthesis of Collodial Nanoparticles. Chemistry of Materials, 2015. 27: p. 2246-2285.
- Wei, X., Al Muyeed, S.A., Peart, M.R., Sun, W., Tansu, N., Wierer Jr, J.J, Room Temperature Luminescence of Passivated Ingan Quantum Dots formed by Quantum Sized Controlled Photoelectrochemical Etching. Applied Physics, 2018. 113: p. 121106.
- Ballou, B.; Lagerholm, B.C.; Ernst, L.A.; Bruchez, M.P.; Waggoner, A.S. Noninvasive Imaging of Quantum Dots in Mice. Bioconjugate Chem. 2003, 15, 79–86. [CrossRef]
- Daou, T.J.; Li, L.; Reiss, P.; Josserand, V.; Texier, I. Effect of Poly(ethylene glycol) Length on the in Vivo Behavior of Coated Quantum Dots. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3040–3044. [CrossRef]
- Al-Jamal, W.T., et al., Lipid-quantum dot bilayer vesicles enhance tumor cell uptake and retention in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano, 2008. 2(3): p. 408-18.
- Petryayeva, E.; Algar, W.R.; Medintz, I.L. Quantum Dots in Bioanalysis: A Review of Applications across Various Platforms for Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Imaging. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 67, 215–252. [CrossRef]
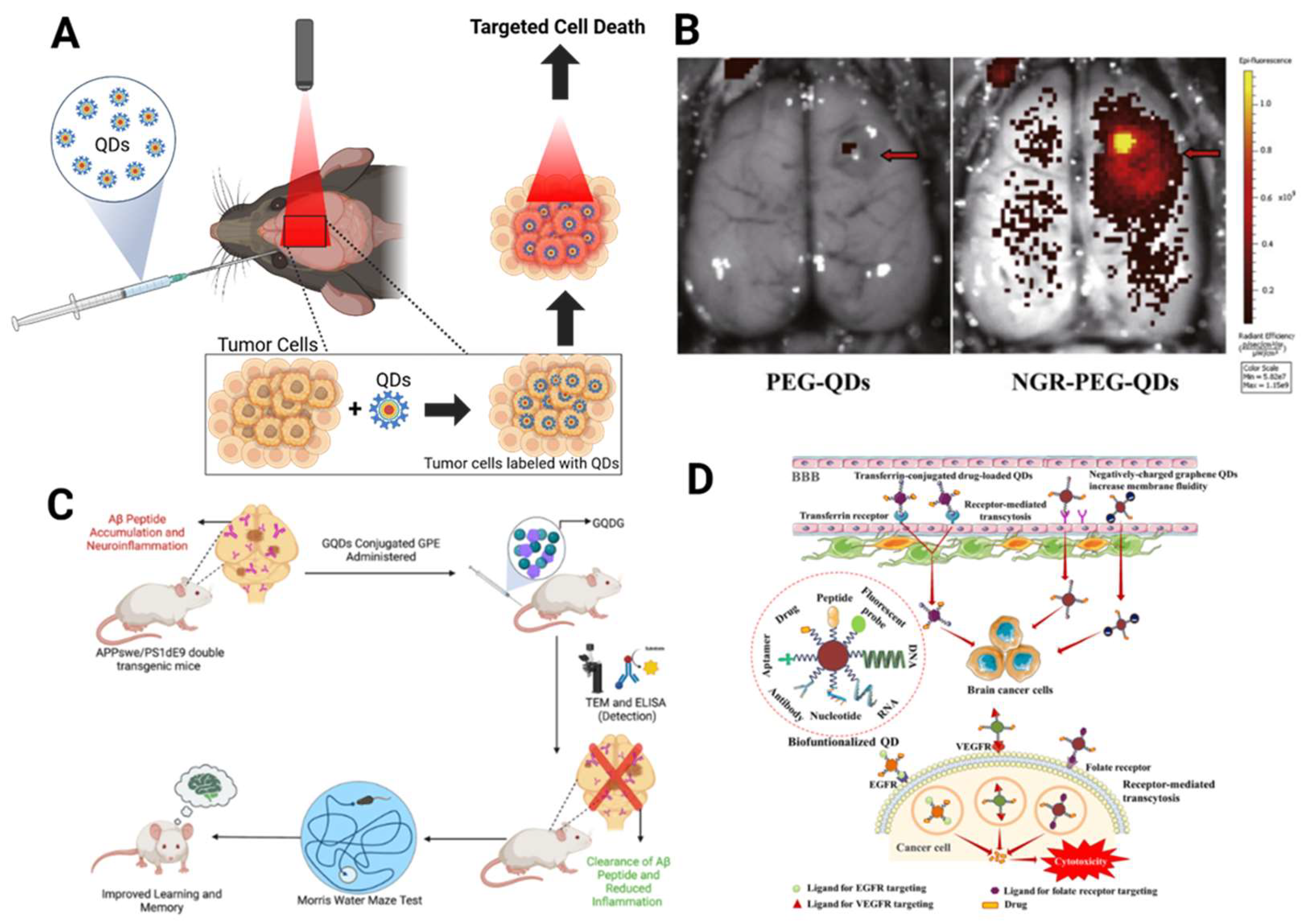
- Huang, N.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Pi, J.; Tang, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z.; et al. Efficacy of NGR peptide-modified PEGylated quantum dots for crossing the blood–brain barrier and targeted fluorescence imaging of glioma and tumor vasculature. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 83–93. [CrossRef]
- Shampa Ghosh, B.S., Punya Sachdeva, Vishal Chaudhary, Gokana Mohana Rani, Jitendra Kumar Sinha, Graphene Quntum Dots as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease. Carbon Letters, 2022. 32: p. 1381-1394.
- Xiao, S.; Zhou, D.; Luan, P.; Gu, B.; Feng, L.; Fan, S.; Liao, W.; Fang, W.; Yang, L.; Tao, E.; et al. Graphene quantum dots conjugated neuroprotective peptide improve learning and memory capability. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 98–110. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Das, S.S.; Dey, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Bhattacharyya, C.; Kandimalla, R.; Mukherjee, B.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Singh, S.K.; Kant, S.; et al. Quantum dots: The cutting-edge nanotheranostics in brain cancer management. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 698–715. [CrossRef]
- Das, S. and P.A. Marsden, Angiogenesis in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med, 2013. 369(16): p. 1561-3.
- Kitambi, S.S.; Toledo, E.M.; Usoskin, D.; Wee, S.; Harisankar, A.; Svensson, R.; Sigmundsson, K.; Kalderén, C.; Niklasson, M.; Kundu, S.; et al. Retraction Notice to: Vulnerability of Glioblastoma Cells to Catastrophic Vacuolization and Death Induced by a Small Molecule. Cell 2017, 170, 407. [CrossRef]
- Dorand, R.D.; Barkauskas, D.S.; A Evans, T.; Petrosiute, A.; Huang, A.Y. Comparison of intravital thinned skull and cranial window approaches to study CNS immunobiology in the mouse cortex. IntraVital 2014, 3, e29728. [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Gallagher, J.; Myers, J.T.; Li, M.; Vasanji, A.; McLendon, R.E.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Huang, A.Y.; Rich, J.N. Direct In Vivo Evidence for Tumor Propagation by Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e24807. [CrossRef]
- Osswald, M.; Jung, E.; Sahm, F.; Solecki, G.; Venkataramani, V.; Blaes, J.; Weil, S.; Horstmann, H.; Wiestler, B.; Syed, M.; et al. Brain tumour cells interconnect to a functional and resistant network. Nature 2015, 528, 93–98. [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Tanev, D.I.; Strahle, C.; Studier-Fischer, A.; Fankhauser, L.; Kessler, T.; Körber, C.; Kardorff, M.; Ratliff, M.; Xie, R.; et al. Glutamatergic synaptic input to glioma cells drives brain tumour progression. Nature 2019, 573, 532–538. [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Yang, Y.; Schubert, M.C.; Reyhan, E.; Tetzlaff, S.K.; Wißmann, N.; Botz, M.; Soyka, S.J.; Beretta, C.A.; Pramatarov, R.L.; et al. Glioblastoma hijacks neuronal mechanisms for brain invasion. 2022, 185, 2899–2917.e31. [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.C.; Soyka, S.J.; Tamimi, A.; Maus, E.; Schroers, J.; Wißmann, N.; Reyhan, E.; Tetzlaff, S.K.; Yang, Y.; Denninger, R.; et al. Deep intravital brain tumor imaging enabled by tailored three-photon microscopy and analysis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Wen, C.-J.; Zhang, L.-W.; Suwayeh, A.; Yen, T.-C.; Zhang, L.-W. Theranostic liposomes loaded with quantum dots and apomorphine for brain targeting and bioimaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1599–611. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.; Muhammad, O.; Daneshvar, H.; Nelms, J.; Popescu, A.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Bruchez, M.; Toms, S.A. QUANTUM DOTS ARE PHAGOCYTIZED BY MACROPHAGES AND COLOCALIZE WITH EXPERIMENTAL GLIOMAS. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 524–530. [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-Y.; Yu, X.-H.; Wang, K.; Yin, Y.-J.; Tang, Y.-L.; Liang, X.-H. Graphene quantum dots (GQDs)-based nanomaterials for improving photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111620. [CrossRef]
- Nobari, S.A., Doustvandi, M.A., Yaghoubi, S.M., Oskouei, S.S., Alizadeh, E., Nour, M.A., Khiabani, N.A., Baradaran,B., Rahmati, M., Emerging Trends in Quantum Dot Based Photosensitzers for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 2024.
- Doustvandi, M.A.; Mohammadnejad, F.; Mansoori, B.; Tajalli, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Baghbani, E.; Khaze, V.; Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; Moghaddam, M.M.; et al. Photodynamic therapy using zinc phthalocyanine with low dose of diode laser combined with doxorubicin is a synergistic combination therapy for human SK-MEL-3 melanoma cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 28, 88–97. [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Doustvandi, M.A.; Mohammadnejad, F.; Kamari, F.; Gjerstorff, M.F.; Baradaran, B.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic therapy for cancer: Role of natural products. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 26, 395–404. [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; McCarron, P.A.; Tunney, M.M. Antifungal photodynamic therapy. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Cai, P.; Yang, X.; McHugh, K.J.; Zheng, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, P.; Luo, X.; et al. Aqueous Grown Quantum Dots with Robust Near-Infrared Fluorescence for Integrated Traumatic Brain Injury Diagnosis and Surgical Monitoring. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 19038–19053. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.-P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of GQDs–Tramiprosate Covalent Binding on Amyloid Aggregation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 9, 817–823. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; He, K.; Tang, M. Application of quantum dots in brain diseases and their neurotoxic mechanism. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 3733–3746. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-Z.; Yu, R.-N.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-D. Targeted quantum dots fluorescence probes functionalized with aptamer and peptide for transferrin receptor on tumor cells. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 485104. [CrossRef]
- Paris-Robidas, S.; Brouard, D.; Emond, V.; Parent, M.; Calon, F. Internalization of targeted quantum dots by brain capillary endothelial cells in vivo. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 36, 731–742. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-X.; Zhu, B.-J. The Research and Applications of Quantum Dots as Nano-Carriers for Targeted Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- McHugh, K.J.; Jing, L.; Behrens, A.M.; Jayawardena, S.; Tang, W.; Gao, M.; Langer, R.; Jaklenec, A. Biocompatible Semiconductor Quantum Dots as Cancer Imaging Agents. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706356. [CrossRef]
| Material | Preparation | MPM | Absorption Cross-Section | Surgery | Excitation Wavelength Used (nm) | Imaging Depth (μm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescein | Commercial | 4PF | ησ4=10.5x10-16 cm8 (s/photons)3 | - | 1680 | - | [24] |
| Qtracker655 | Commercial | 4 PF | ησ4=7.8x10-108 cm8 (s/photons)3 | Intact Skull | 2200 | 330 | [24] |
| Craniotomy | 2200 | 940 | |||||
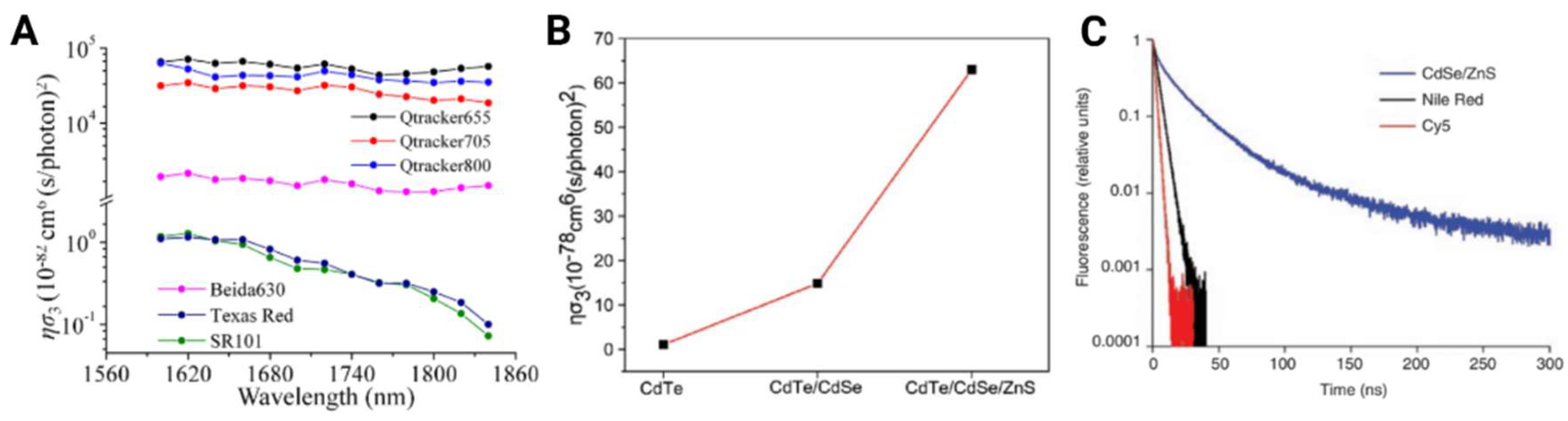
| Qtracker655 | Commercial | 3PF | ησ3=7.1x10-78 cm6 (s/photons)2 | Craniotomy | 1700 | 2100 | [25] |
| Commercial | 3PF | - | Intact Skull | 1700 | 750 | [3] | |
| Qtracker800 | Commercial | 3PF | ησ3=1.68x10-78 cm6 (s/photons)2 | Intact Skull | 2200 | 460 | [24] |
| Craniotomy | 2200 | 1060 | |||||
| CdSe/5.8CdS/ZnS QDs | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=2.10x10-78 cm6 (s/photons)2 | Intact Skull | 1600 | 850 | [26] |
| Craniotomy | 1600 | 1550 | |||||
| CdSe/ZnS QDs | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=2.0x10-77 cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1600 | - | [26] |
| CdTe QDs | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=2.42x10-77cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1600 | - | [36] |
| ησ3=1.05x10-78 cm6 (s/photons)2 | |||||||
| CdTe/CdSe QDs | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=6.34x10-77cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1600 | - | [36] |
| ησ3=14.84x10-78cm6 (s/photons)2 | |||||||
| CdTe/CdSe/ZnS QDs | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=25.6x10-77cm6 (s/photons)2 | Craniotomy | 1600 | 1300 | [36] |
| ησ3=62.98x10-78cm6 (s/photons)2 | |||||||
| DCzPDI | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=6.8x10-80 cm6 (s/photons)2 | Craniotomy | 1550 | 450 | [45] |
| DCDPP-2TPA | Lab Modified | 3PF | σ3=2.95x10-79cm6 (s/photons)2 | Intact Skull | 1550 | 300 | [46] |
| Lab Modified | Craniotomy | 1550 | 785 | ||||
| MTTCM NP | Lab Modified | 3PF | ησ3=1.13x10-81cm6 (s/photons)2 | Intact Skull | 1600 | 1100 | [47] |
| Craniotomy | 1660 | 1900 | [47] | ||||
| SR101 | Commercial | 3PF | ησ3=9.4x10-83cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1600 | - | [47] |
| Texas Red dextran | Commercial | 3PF | - | Craniotomy | 1675 | 1340 | [48] |
| 3PF | σ3=0.97x10-82 cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1650 | - | [44] | ||
| 3PF | σ3=11x10-82cm6(s/photons)2 | Craniotomy | 1340 | 1200 | [44] | ||
| 3PF | ησ3=1.2x10-82 cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1700 | - | [25] | ||
| 3PF | - | Craniotomy | 510 | 510 | [5] | ||
| mCherry | Commercial | 3PF | σ3=1.9x10-83cm6 (s/photons)2 | - | 1340 | - | [44] |
| Thy1-EGFP THG imaging | Transgenic | 3PF | - | Craniotomy | 1300 | 1400 | [22] |
| mCherry | Commercial | 2PF | σ2=94 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 640-1000 | - | [17] |
| 2PF | σ2=25 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 1020-1100 | - | |||
| DsRed2 | Commercial | 2PF | σ2=104 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 640-1000 | - | |
| 2PF | σ2=96 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 1020-1100 | - | |||
| PbS/CdS QD | Lab Modified | 2PF | - | Craniotomy | 1550 | 220 | [33] |
| - | Intact Skull | 1550 | 110 | ||||
| CsPbNr3 PQD | Lab Modified | 2PF | σ2=1.8x105 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 800 | - | [49] |
| CsPbI3 QDs | Lab Modified | 2PF | σ2=2.1x106 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 800 | - | |
| CsPbCl3 QDs | Lab Modified | 2PF | σ2=3.8x104 cm4 (s/photons) | - | 800 | - | |
| Qtracker655 | Commercial | 2PF | - | Craniotomy | 1050 | ~630 | [50] |
| - | 800 | ~560 | |||||
| Texas Red dextran | Commercial | 2PF | - | Craniotomy | 920 | 420 | [51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





