Submitted:
07 November 2024
Posted:
08 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Proposal of a New Spliced Widening Structure
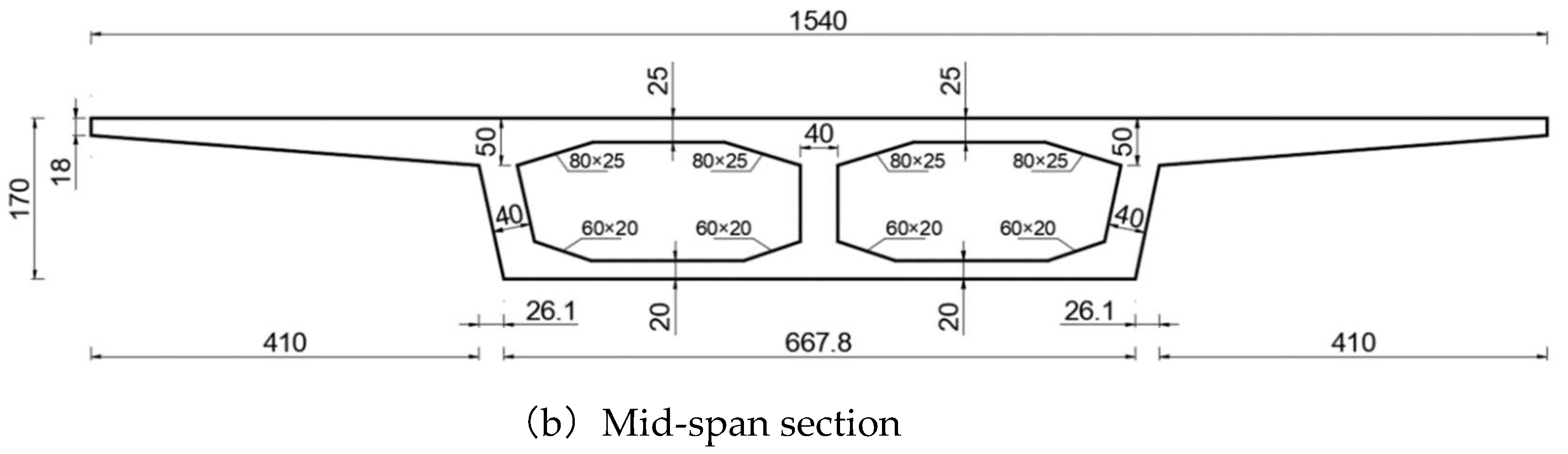
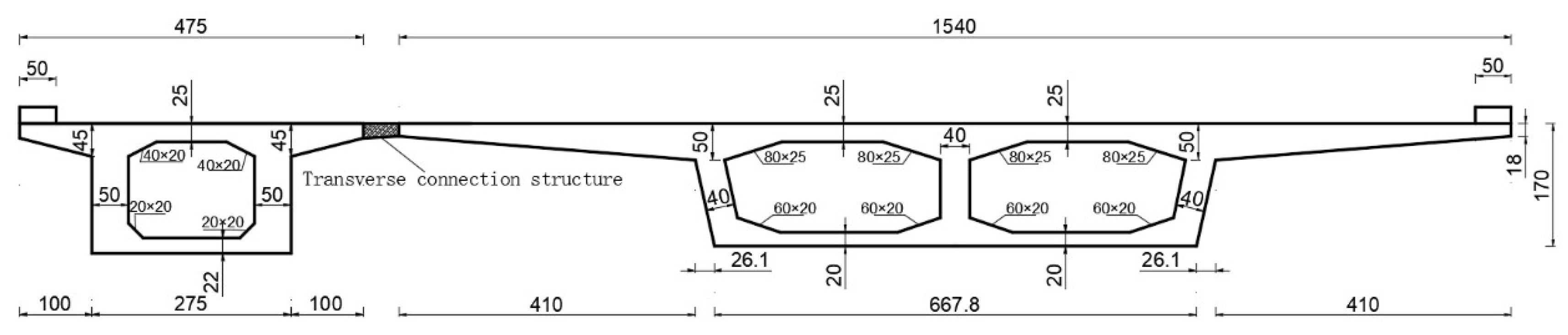
3. Feasibility Study of a Novel Splicing Structure for Widening of Long-Link Concrete Continuous Box Girder Bridges
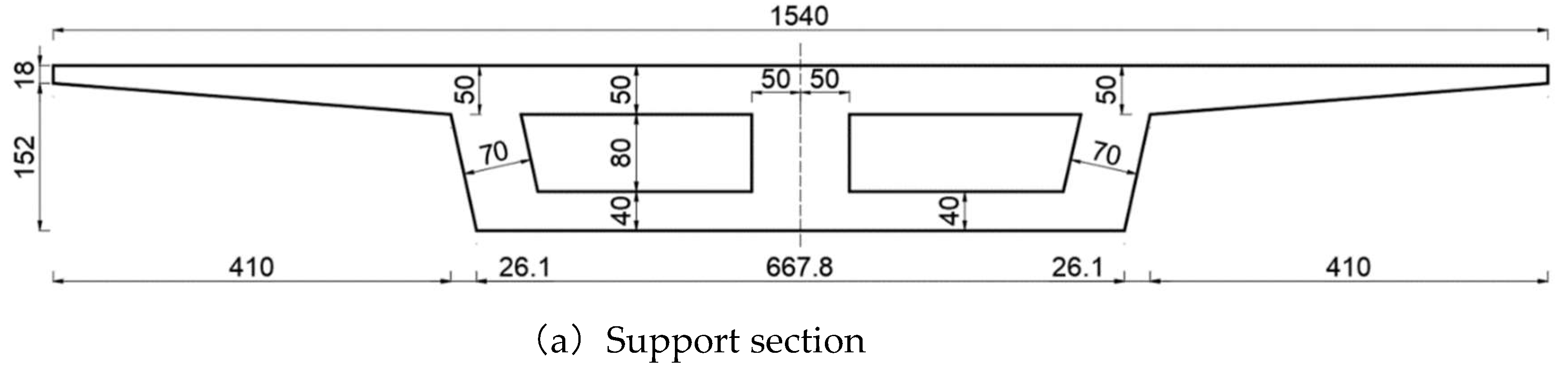
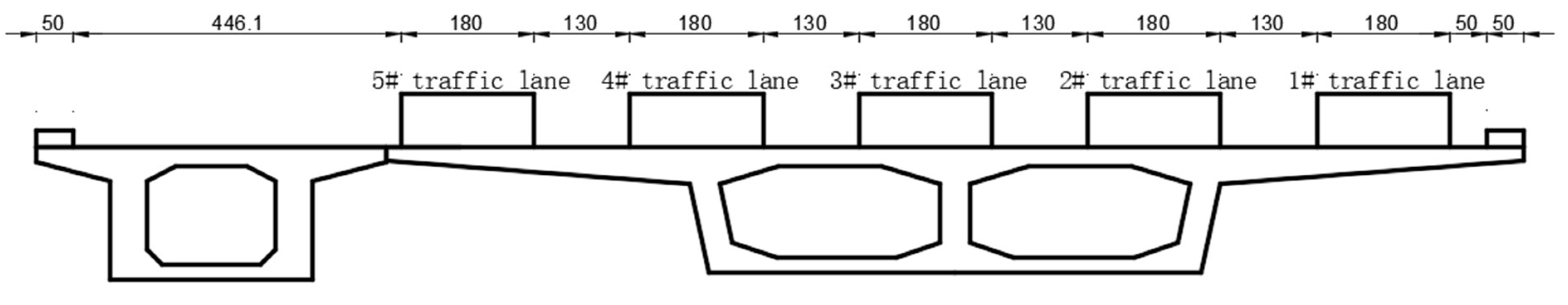
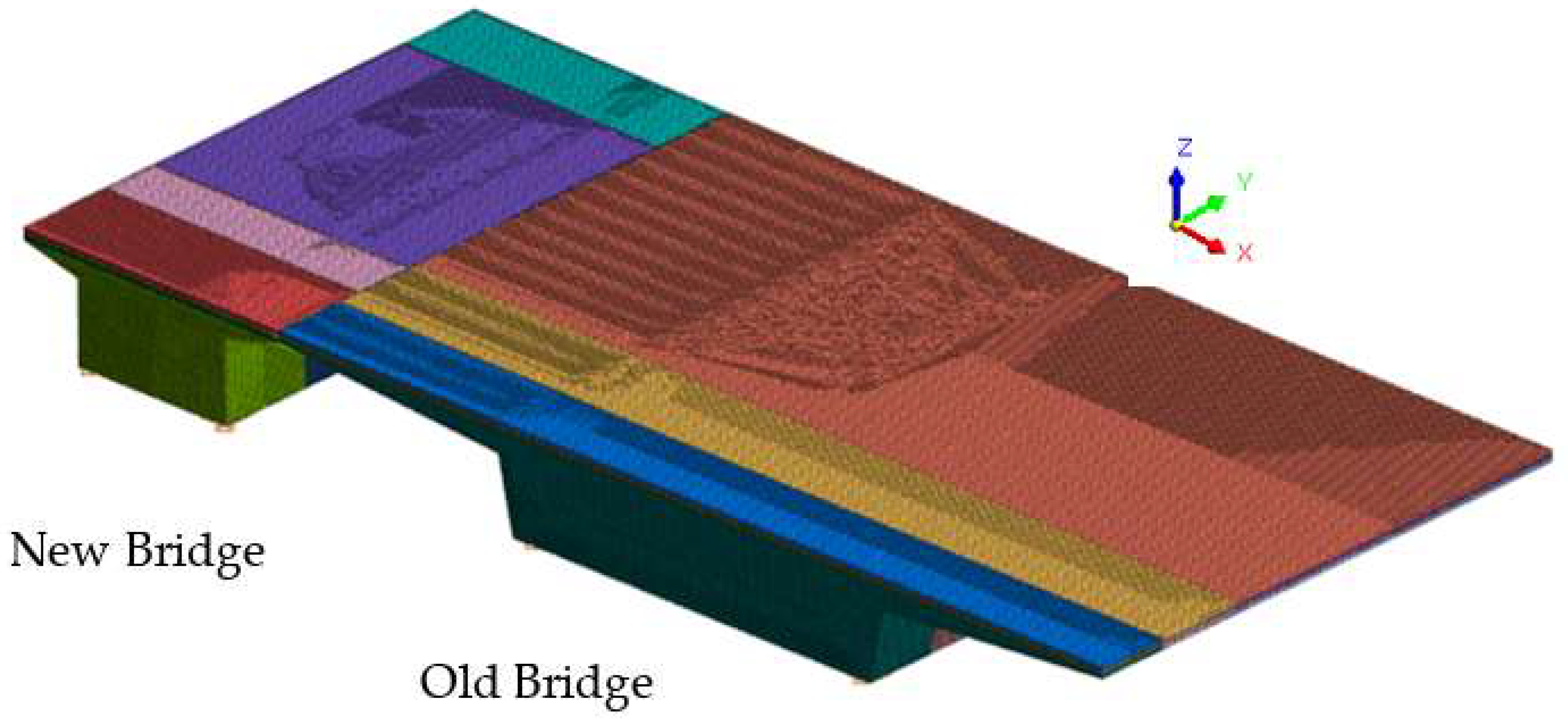
3.1. Finite Element Modeling and Loading Conditions
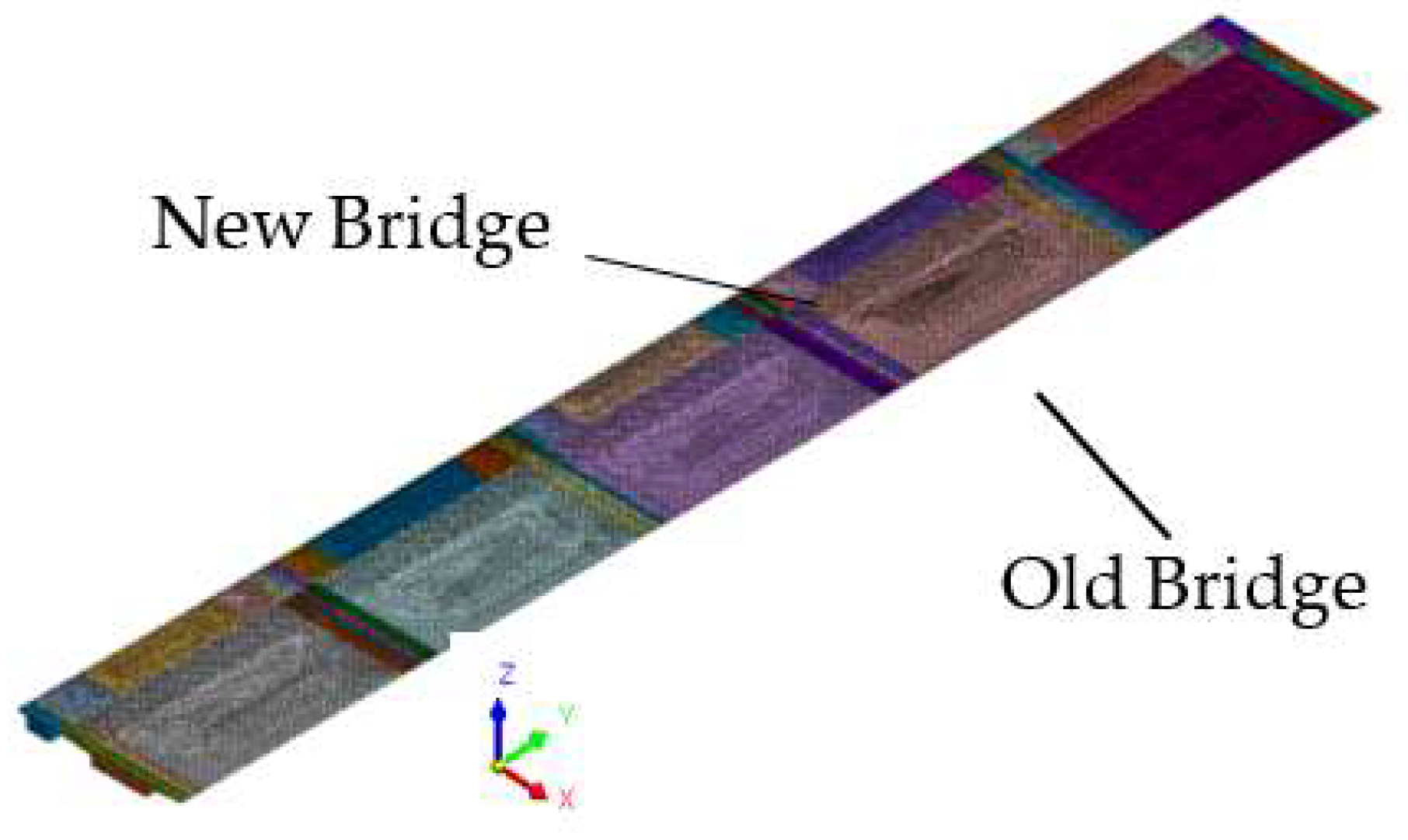
- The Y-axis aligns with the longitudinal direction of the bridge, with positive direction from the small pile number to the big pile number.
- The X-axis corresponds to the transverse direction of the bridge, with positive direction extending from the splicing joints towards the old bridge direction.
- The Z-axis represents the vertical direction, with positive direction pointing upwards.
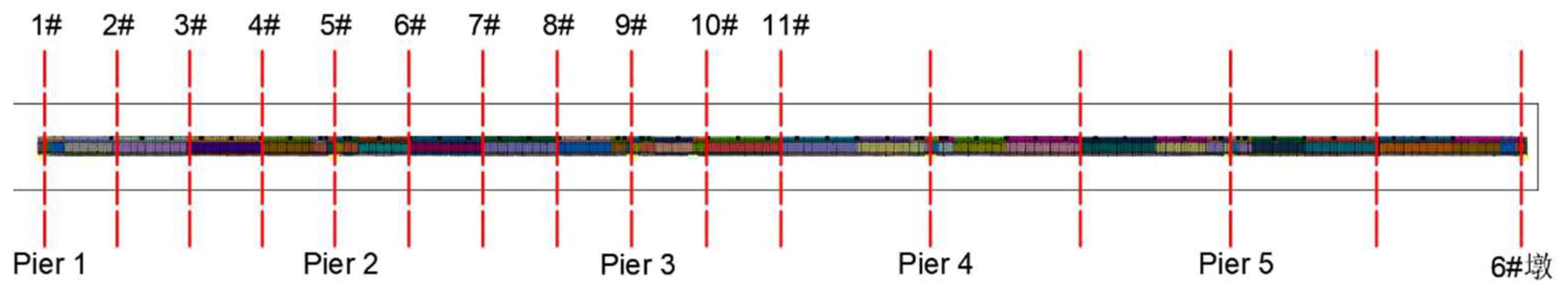
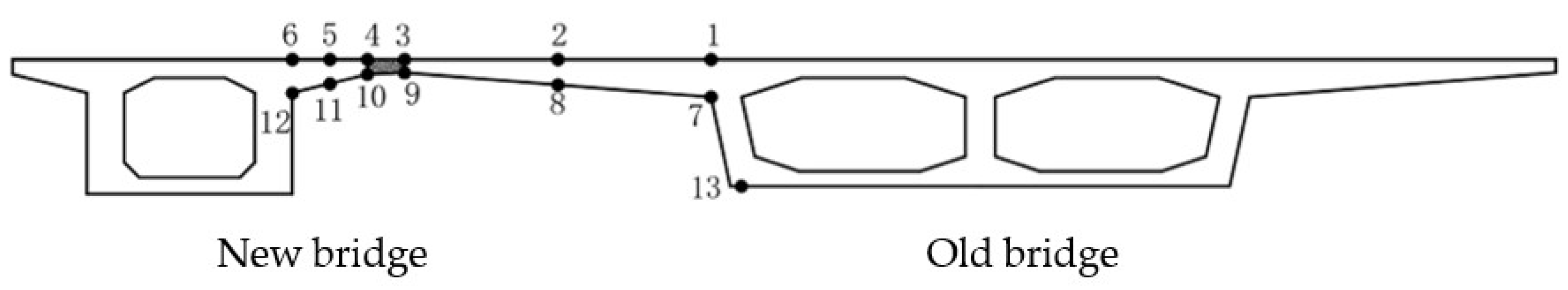
3.2. Analysis of the Effect of Force Characteristics of Widened Structures Under Combined Operating Conditions
3.2.1. Define Combined Operating Conditions
3.2.2. Analysis of Lateral Displacement of Widening Structures
- (1)
- During three years after widening, the trend of transverse displacement along the longitudinal direction for both splicing methods due to the effect of shrinkage creep differential between the old and new bridges is essentially the same. The transverse displacement in the middle part of the bridge is nearly zero, but it increases as it approaches the girder ends.
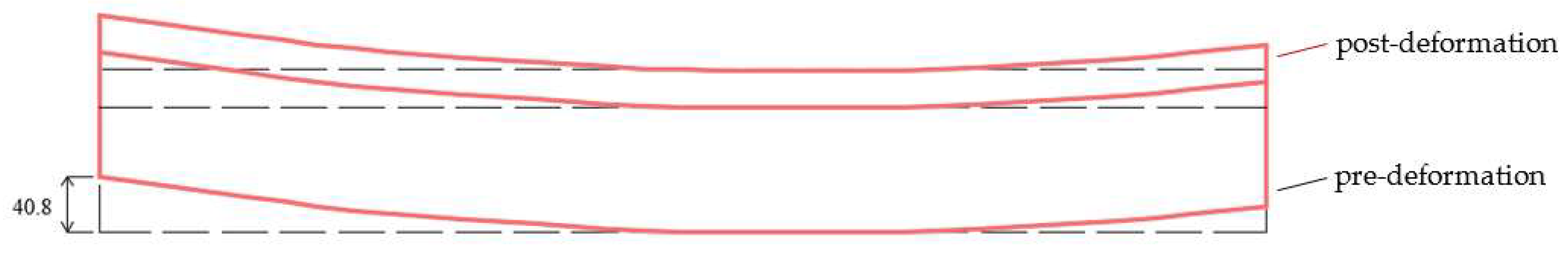
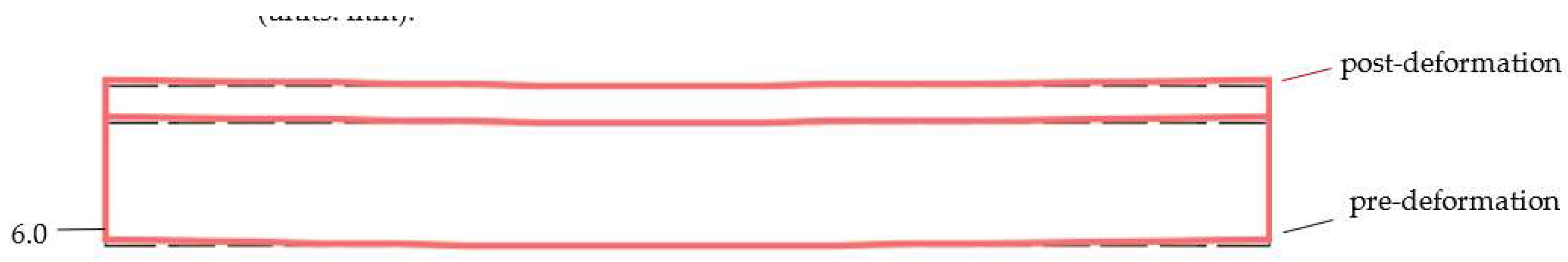
- (2)
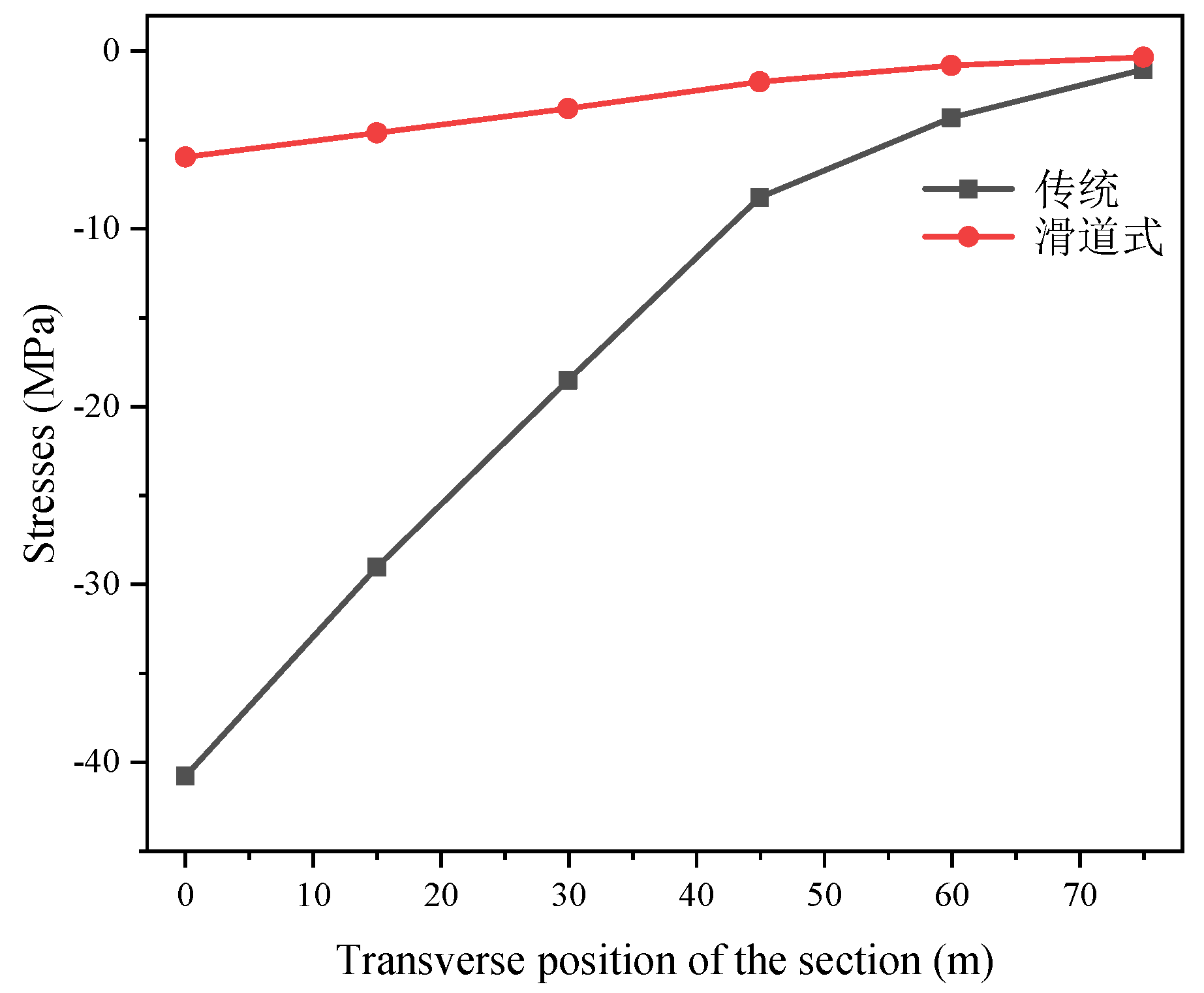
- The maximum transverse displacement at the end of the widened bridge with the traditional articulated splicing structure is about 40.8 mm. In contrast, the maximum transverse displacement at the end corresponding to the slide-type splicing structure is only about 6 mm, which is less than 1/7 of that observed with the traditional splicing structure. This demonstrates that the slide-type splicing structure can significantly mitigate the effect of shrinkage creep differential between two bridges on the widened bridge structure.
3.2.3. Transverse Stress Analysis of Widened Bridge
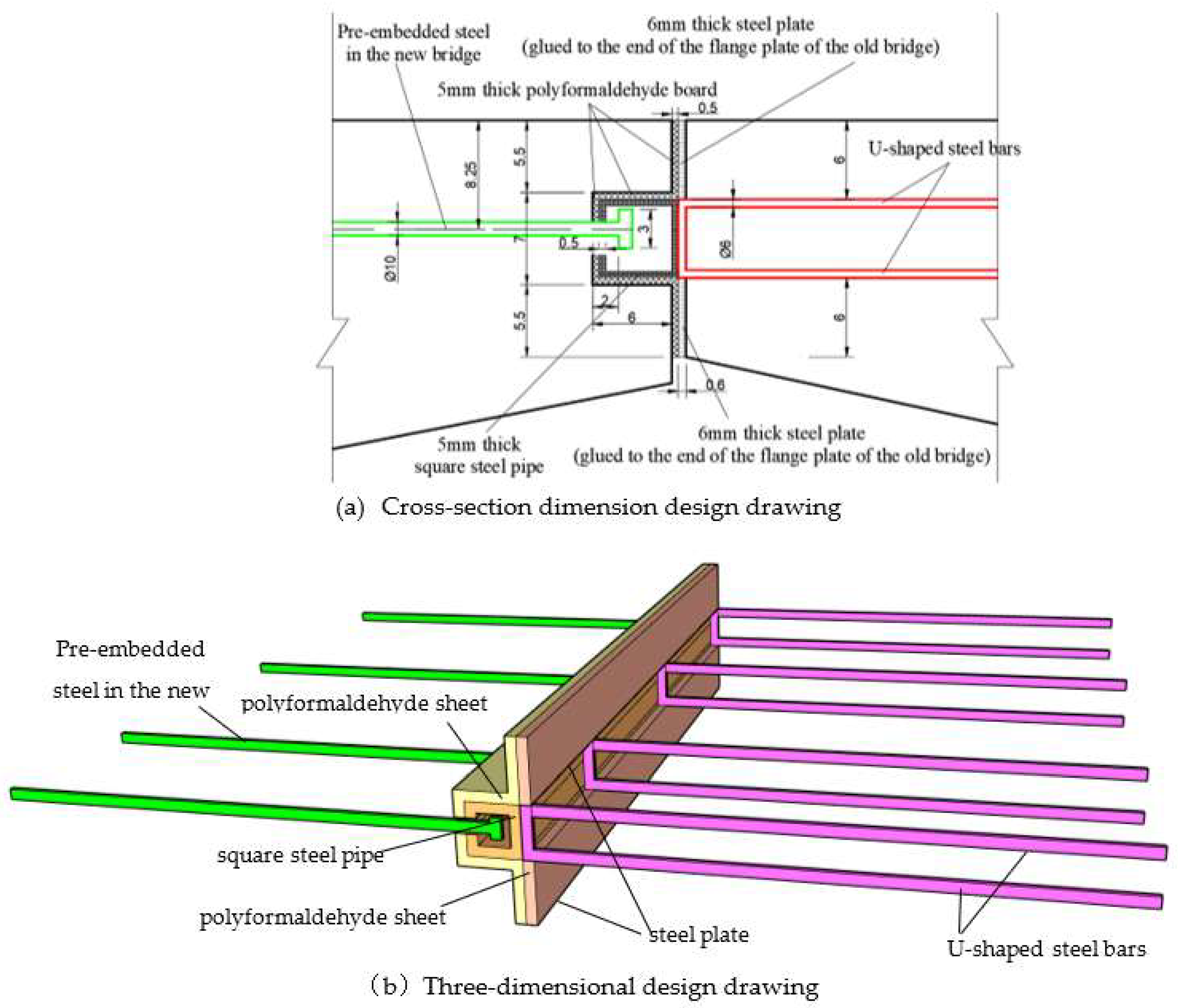
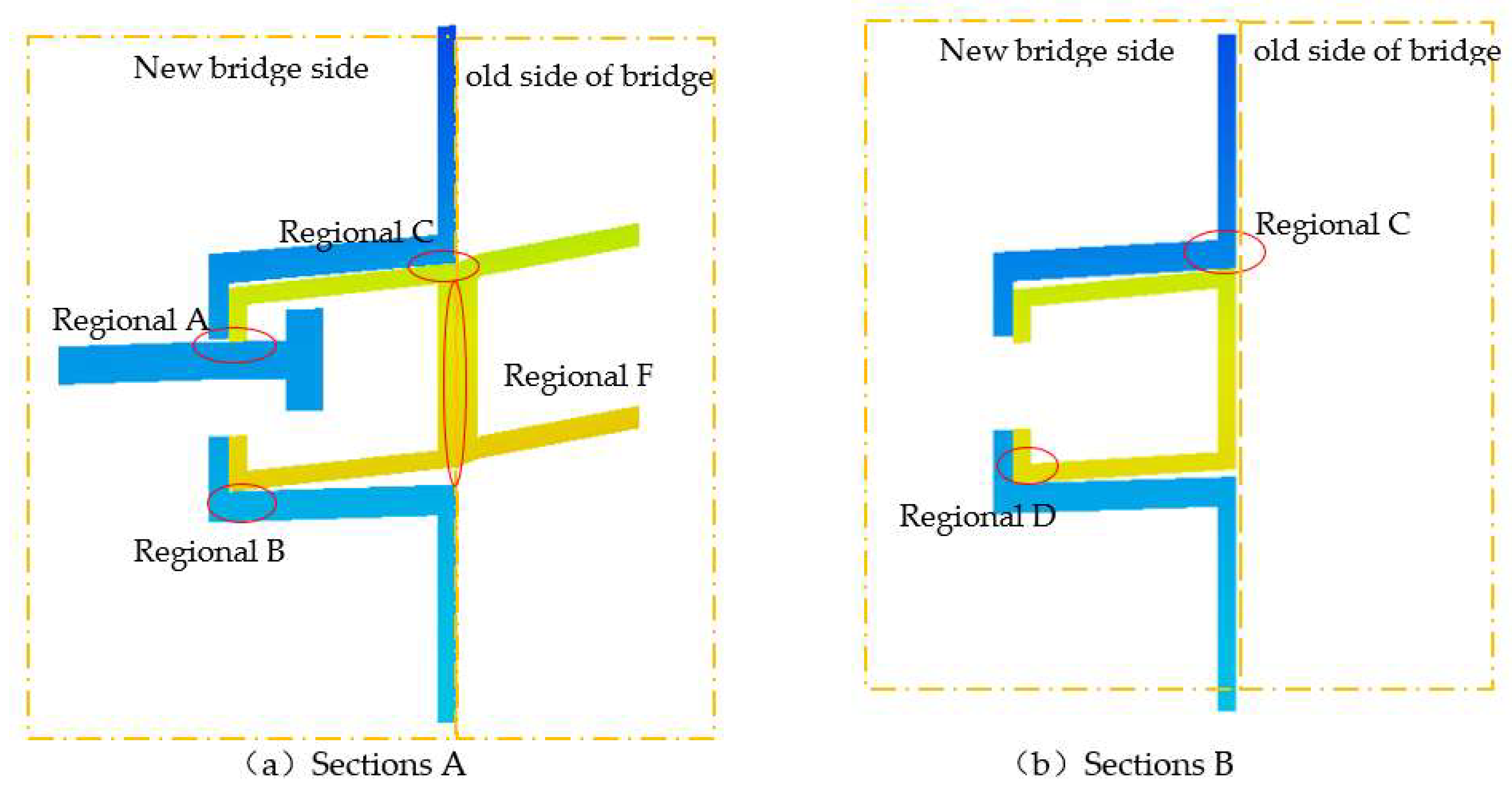
4. Mechanism of Force Transfer and Detailed Analysis of Transverse Spliced Structures
4.1. Finite Element Modeling and Loading Conditions
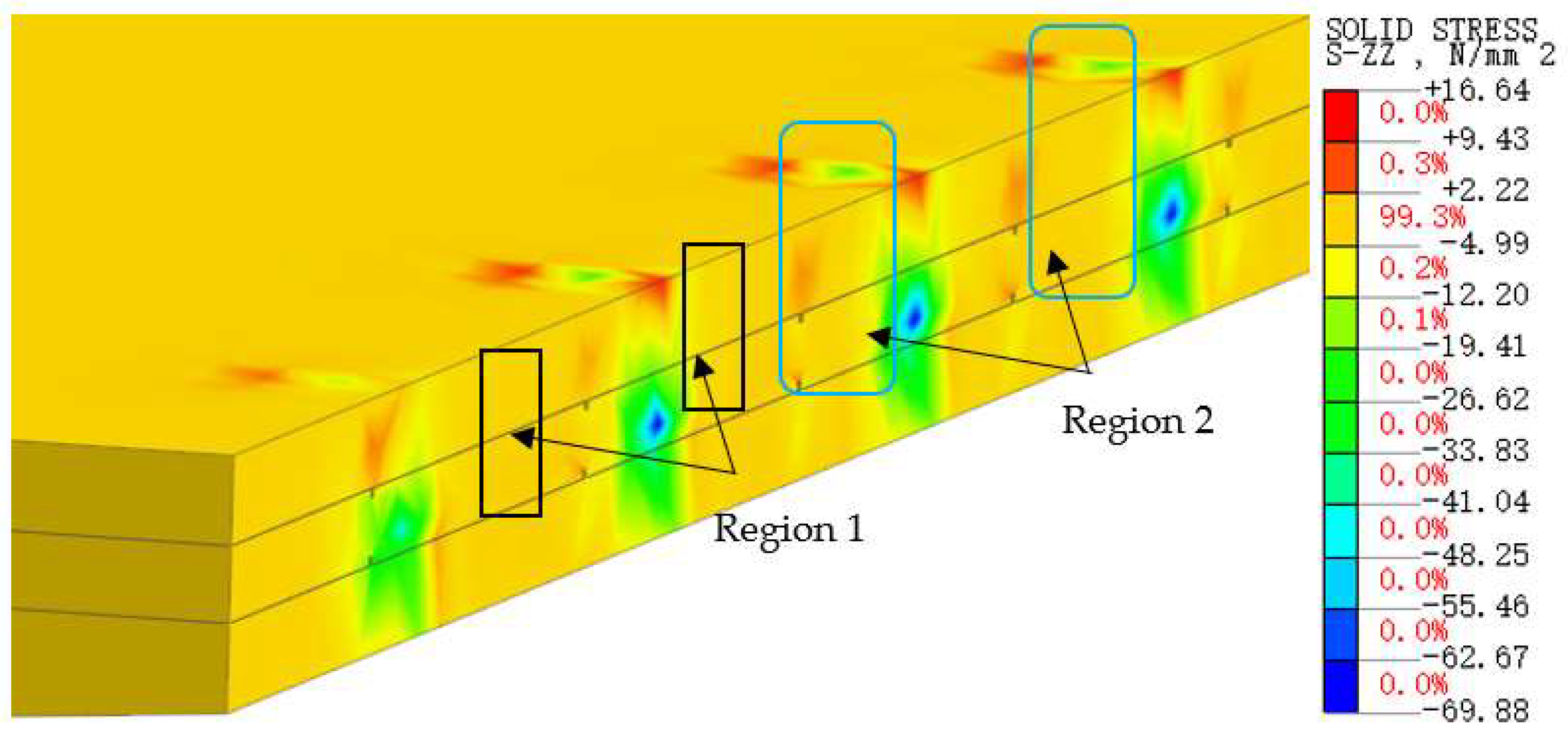
4.2. Vertical Deformation Analysis
4.2.1. Differential Settlement between the Foundations of the New and Old Bridges
4.2.2. Shear Force Transfer Mechanism in Slideway-Spliced Structures.
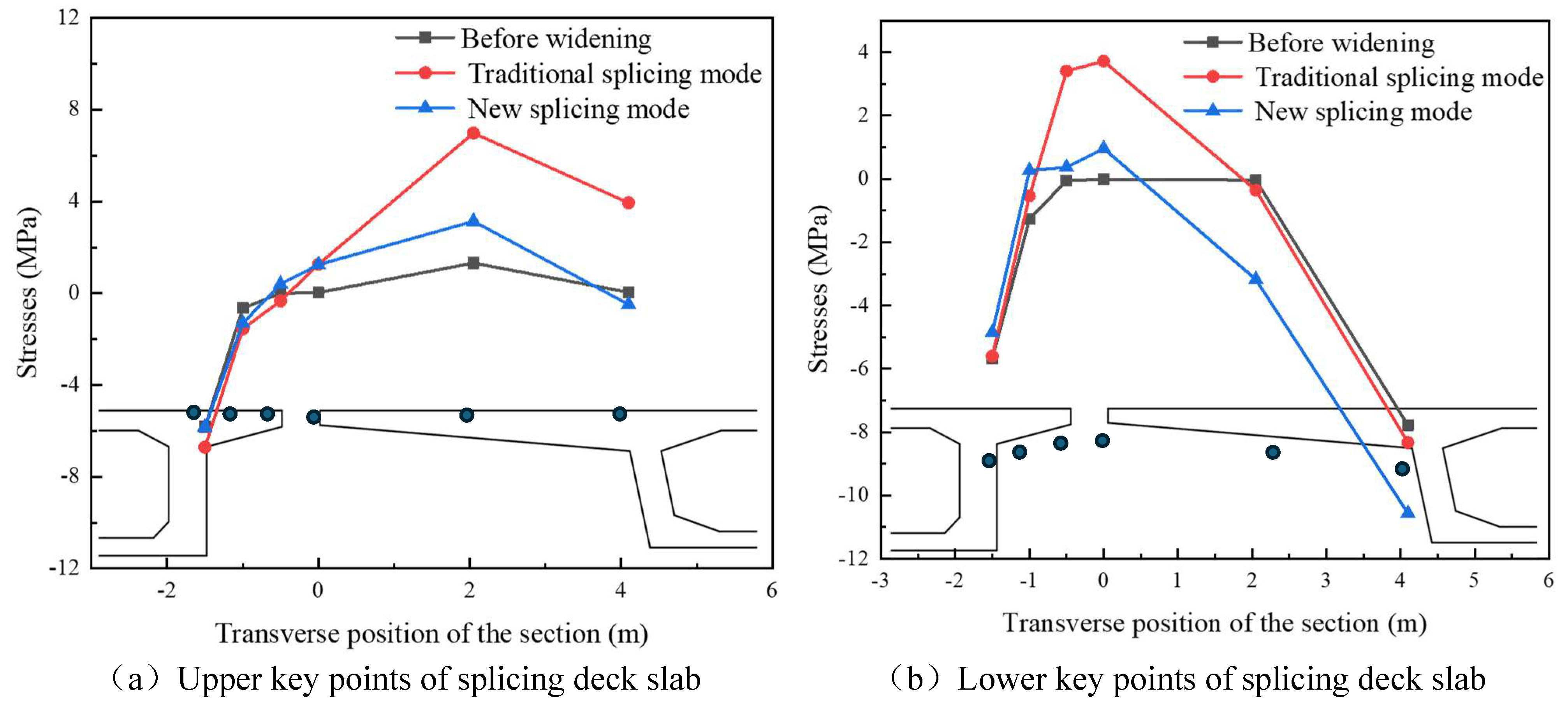
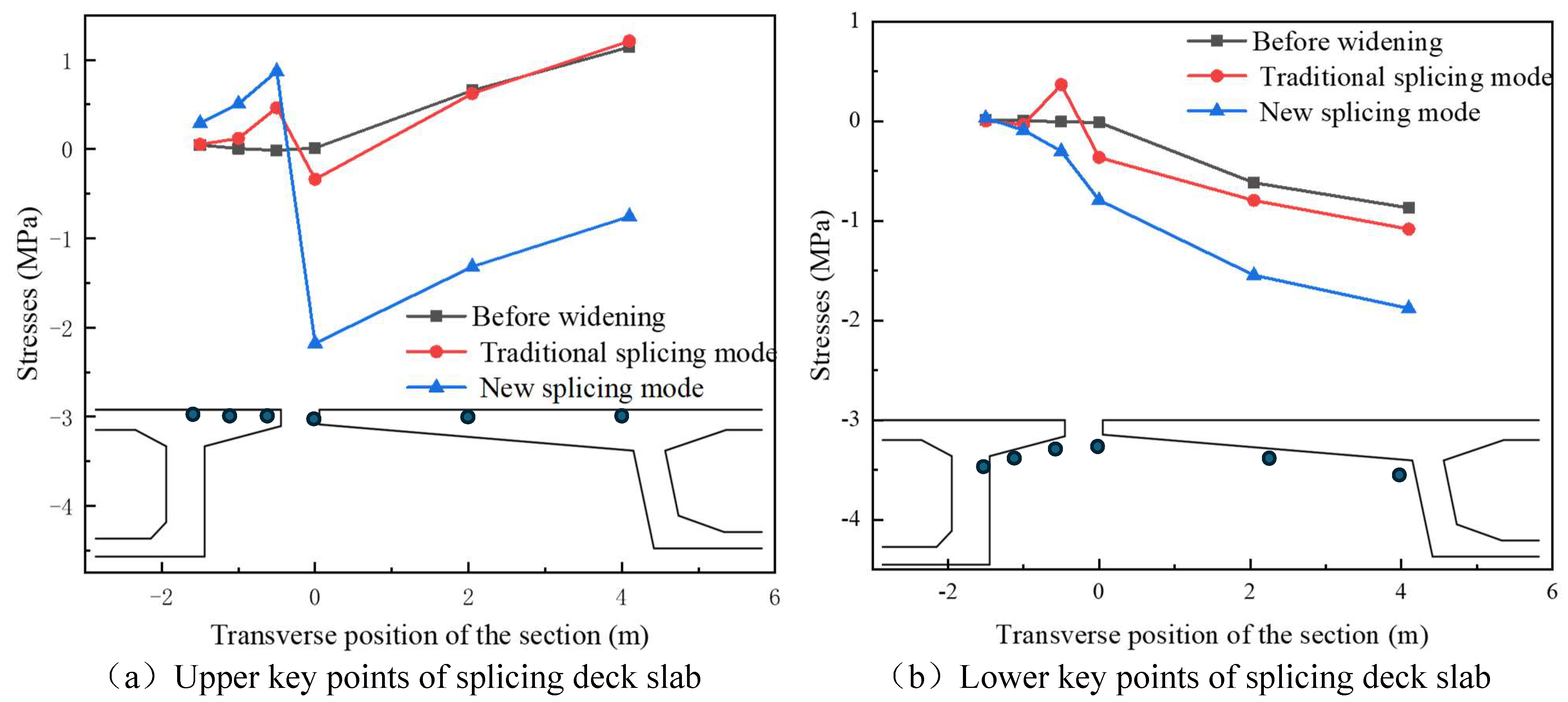
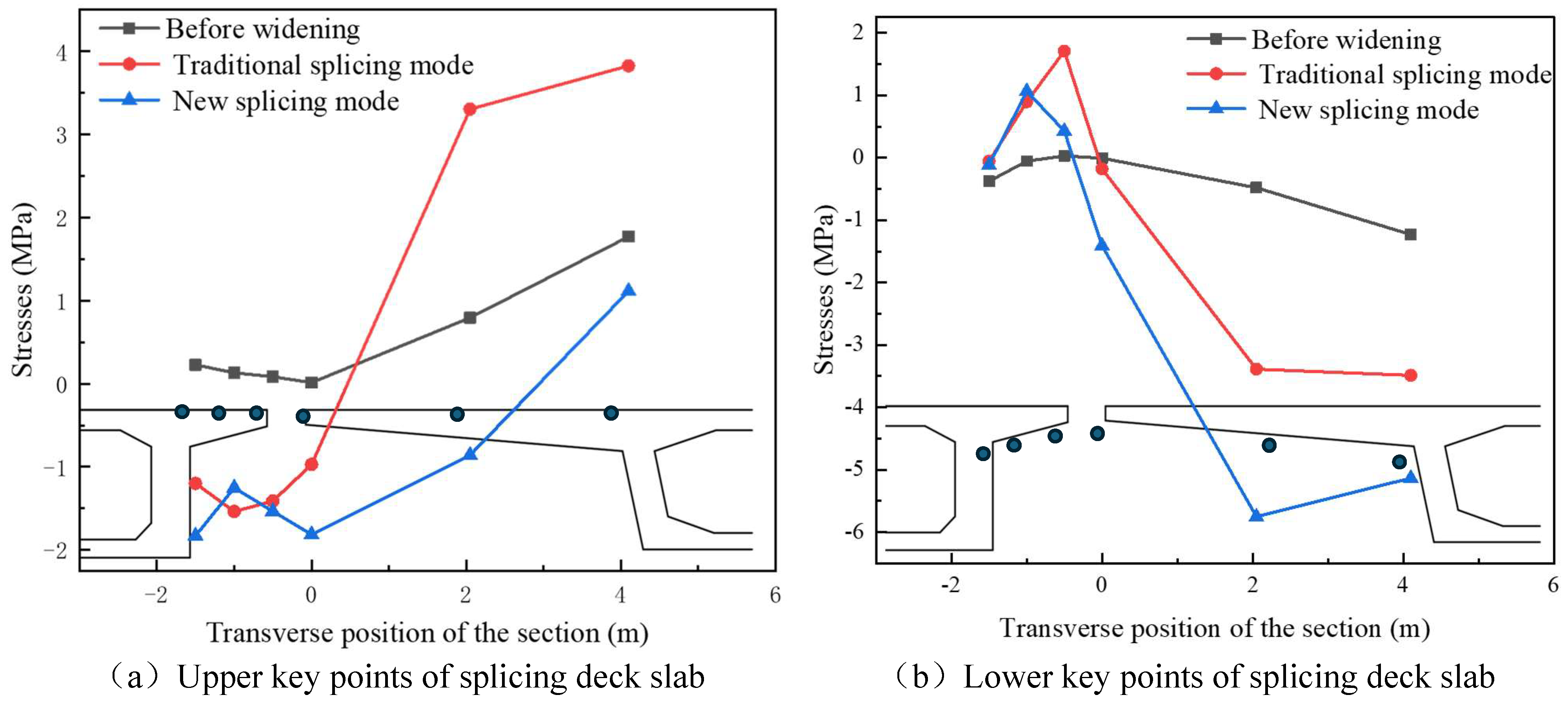
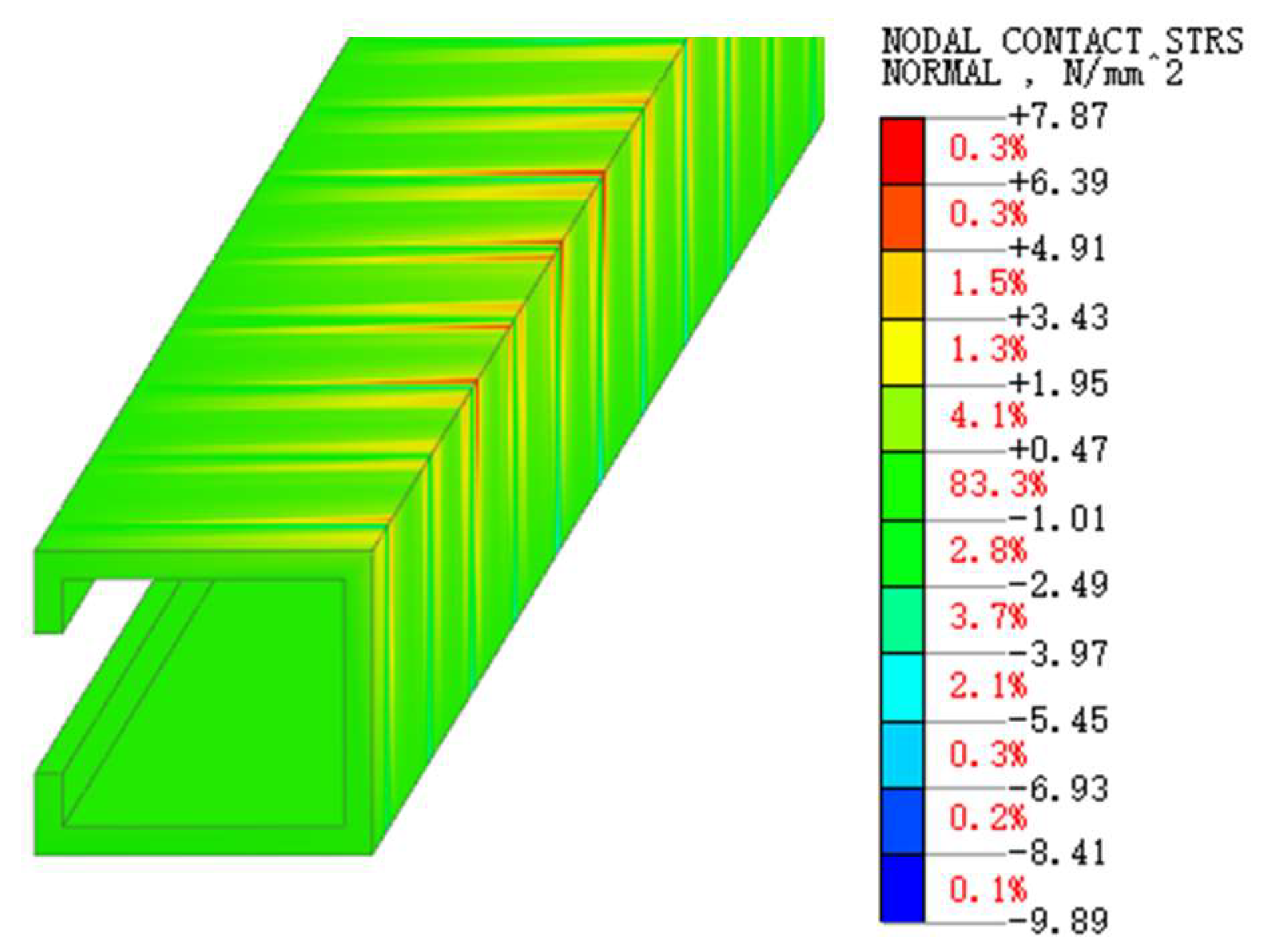
4.3. Stress Analysis
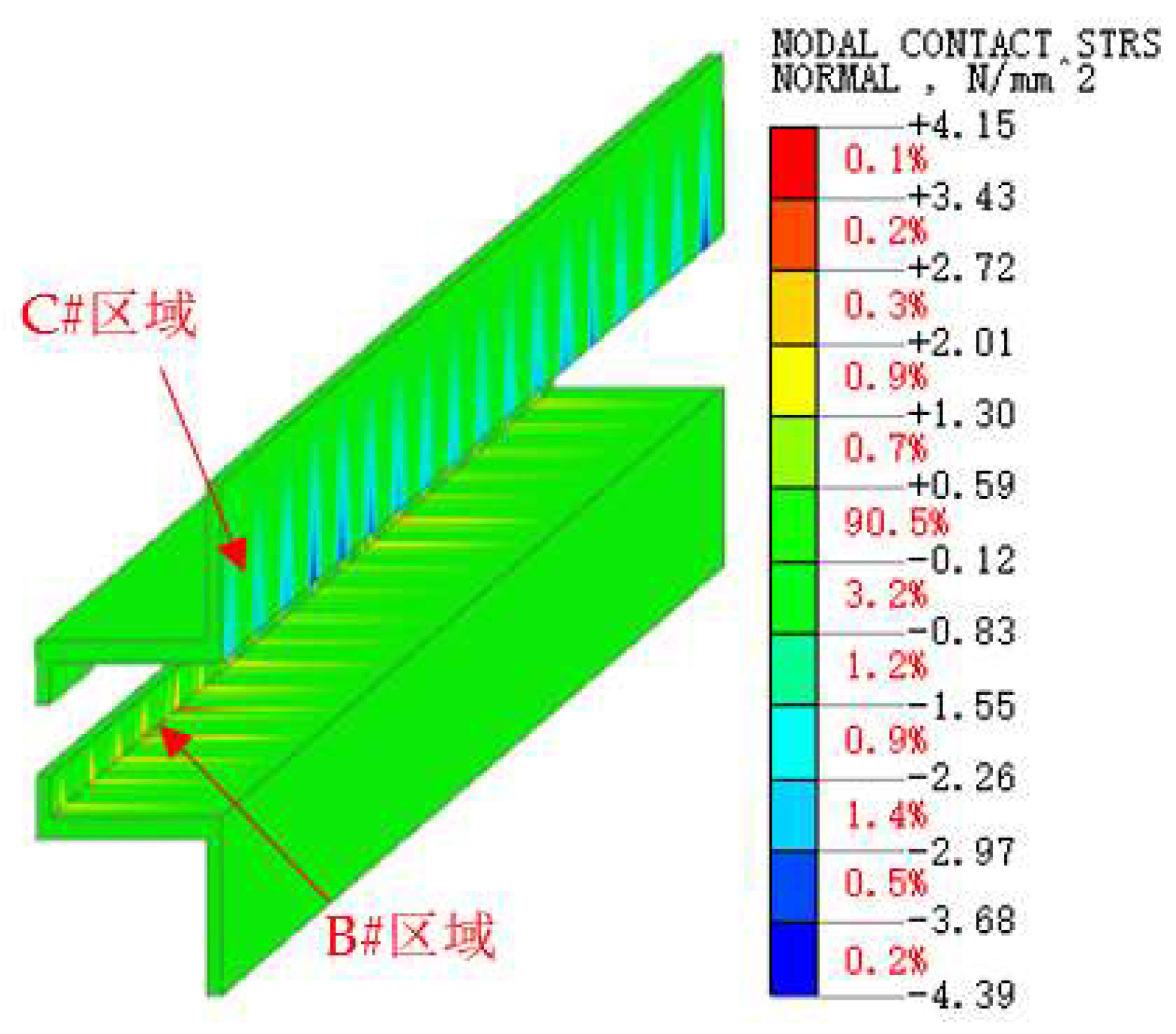
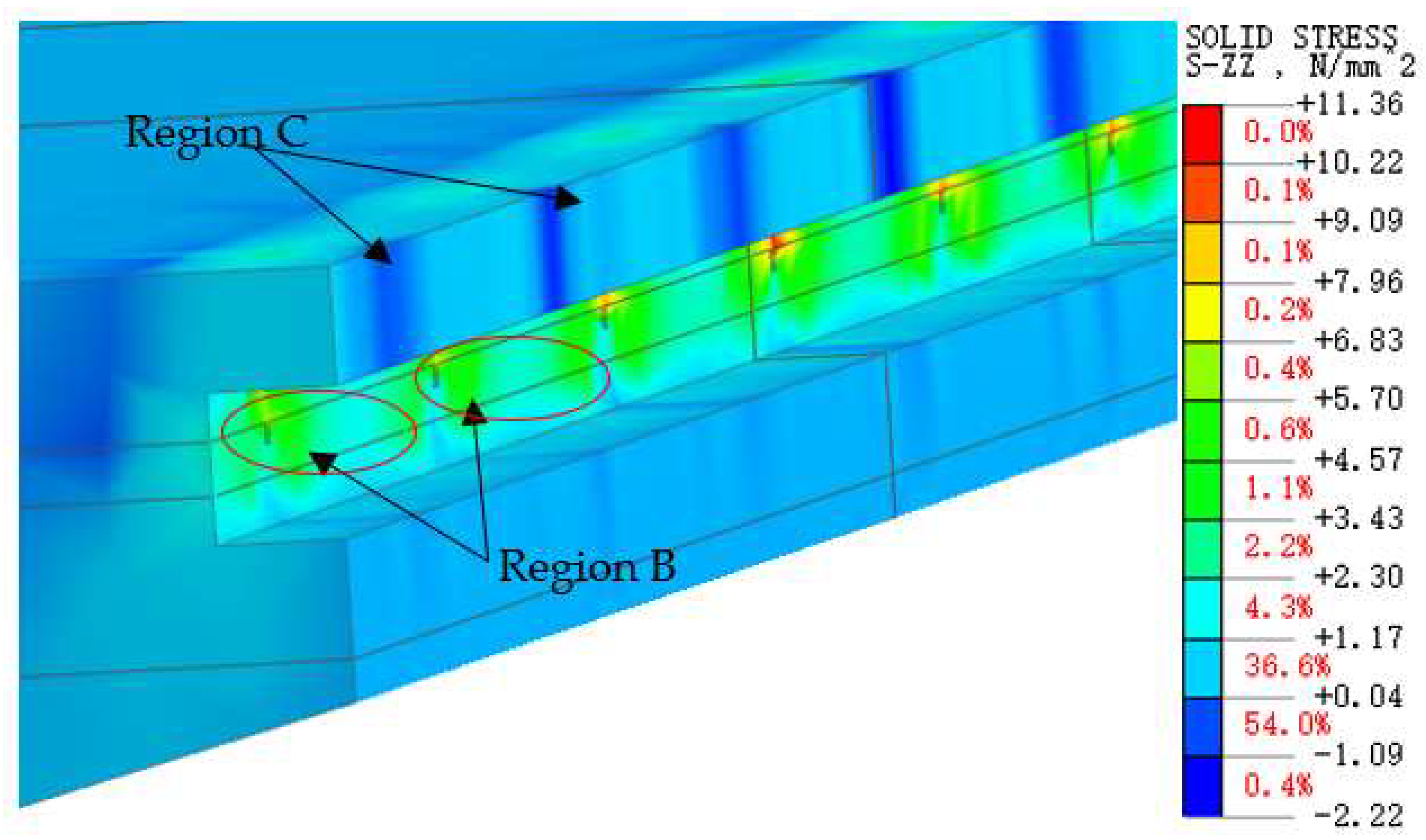
4.3.1. Contact Stresses on Splice Structures
Stress in the Inner Flange of New Bridge
Stress in the Inner Flange of Old Bridge
5. Analysis of Design Parameters for Slide-Type Lateral Connection Structures
5.1. Calculation Description
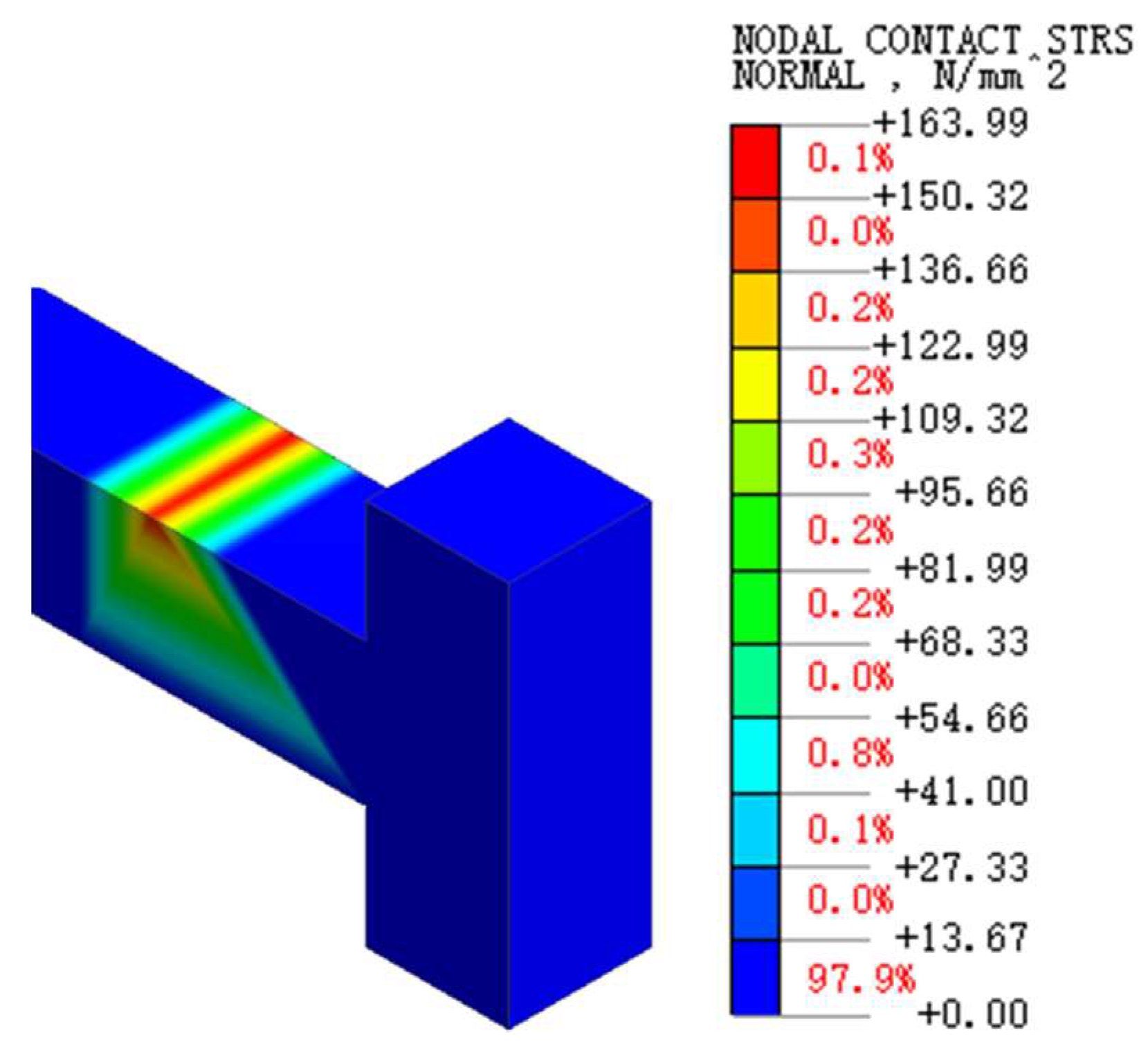
5.2. Stress State Under Combined Conditions
- Both the principal stress of concrete at the inner flange plate ends of the new and old bridges (taking regions B and C as examples) and the maximum contact stress at the weld significantly increase.
- The maximum extrusion contact stress between the end of the embedded rebar and the square steel tube decreases significantly.
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- CCCC Highway Consultants Co., Ltd. (2015). JTG D60-2015 General code for design of highway bridges and culverts [In Chinese]. China Communications Press.
- Chen, K.M., Wu, Q.X., Chen, B.C., & Zhang, G. (2016). Method and Tests for Partially Splicing and Widening Long-span Bridges. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 29(11), 99-107. (In Chinese).
- Cousins, D.P. (2017). Reinforced Concrete Beam Hinge Joint Fatigue Assessment. Bridge Engineering, 1–11.
- Elsafty, A., Okeil, A.M., Torres, K., Tawfiq, K., & Fallaha, S. (2020). Investigation of Empirical Deck Design in Bridge Widening. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 25(10), 04020079.
- Fang, Z., Chang, H.H., Yang, X.Q., & Yuan, Y. (2013). Lateral Effects Caused by Shrinkage and Creep in Widened and Spliced Concrete Box Girder Bridges. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 26(6), 65-72. (In Chinese).
- Guo, Q., Sun, Y., & Mi, T. (2021). Assessment on Long-term Deflection of Concrete Beam Bridges Based on Uncertainty Quantification Method. Structures, 34, 3013-3027.
- Hosseini, M., & Jefferson, A.D. (1998). Time-Dependent Behavior of Widened Reinforced Concrete Under-bridge. Materials and Structures, 31(10), 714-719.
- Joergensen, H.B., & Hoang, L.C. (2013). Tests and Limit Analysis of Loop Connections Between Precast Concrete Elements Loaded in Tension. Engineering Structures, 52, 558-569.
- Li, Z.F. (2019). Verification Method for Widening Long-Span Bridges Using Steel Plate Splicing at Both Ends. Fujian Traffic Technology, (1), 54-57. (In Chinese).
- Nie, J.G., Wang, Y.H., Zhang, X.G., & Fan, J.S., & Cai, C.S. (2012). Mechanical Behavior of Composite Joints for Connecting Existing Concrete Bridges and Steel–Concrete Composite Beams. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 75, 11-20.
- Ru, Y. (2014). Research on Several Issues in the Widening Structure of In-service Concrete Box Girder Bridges. [PhD dissertation, Southeast University]. (In Chinese).
- Tu, B., Fang, Z., Dong, Y., et al. (2017). Time-Variant Reliability Analysis of Widened Deteriorating Prestressed Concrete Bridges Considering Shrinkage and Creep. Engineering Structures, 153, 1-16.
- Wen, Q.J. (2011).Long-term Effect Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Box-Girder Bridge Widening. Construction and Building Materials, 25(4), 1580-1586.
- Wen, Q.J., & Jing, H.W. (2014).Numerical Simulation of Creep and Shrinkage in Widened Concrete Bridges. Magazine of Concrete Research, 66, 661-673.
- Wu, W.Q, Zhang, H., Liu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2022).Numerical Analysis on Transverse Splicing Structure for the Widening of a Long Multi-Span Highway Concrete Continuous Box Girder Bridge. Materials, 15, 6805.
- Wu, W.Q., Shan, H., Yang, S., et al. (2017).Key Assumption to Evaluate the Mechanical Performance of Widened Voided-Slab Bridge Due to Foundation Settlement. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 22(4), 1225-1234.
- Wu, W.Q., Tang, Z.X., Zhang, H., et al. (2018).Analysis of Deck Damage in Existing Prestressed Concrete Continuous Box Girder Bridges After Widening and Splicing. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 31(5), 63-73. (In Chinese).
- Wu, W.Q., et al. (2012).Comparison of Transverse Widened Structure of Wide-size Voided Slab Beam Bridge on Expressway. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 29(3), 92-97, 117.
- Yan, G.B. (2013).Research on Influencing Factors and Countermeasures for Widening and Splicing Long-span Prestressed Concrete Continuous Box Girder Bridges. [Doctoral dissertation, China Academy of Railway Sciences]. (In Chinese).
- Yang, Y., Wu, E.J., Lan, W.J., & Wang, J.Y. (2013).Analysis of Solutions for Disengagement in Continuous Bridge Lifting and Reconstruction. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 11(6), 35-39. (In Chinese).
- Ye, Y.C., Li, S.Q., & Zhang, Y. (2013).Analysis and Countermeasures of Influencing Factors in Widening and Splicing Long-span Highway Bridges. Railway Engineering, (10), 24-27. (In Chinese).
- Zhou, J.Y., Li, T., Ye, X.J., et al. (2020).Safety Assessment of Widened Bridges Considering Uneven Multilane Traffic-Load Modeling: Case Study in China. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 25(9), 1-12.



| No | construction phase |
| 1 | Completion of the old bridge |
| 2 | old bridge in operation for ten years |
| 3 | New bridge built |
| 4 | Six months after new bridge built |
| 5 | Completion of bridge widening |
| 6 | Operation together for 3 years |
| Mechanical Response Indicators | Square Steel Tube Thickness (mm) | |||
| 5 | 10 | 15 | ||
| Principal tensile stress in the concrete at the ends of the inner flange plates of the new and old bridges (MPa) | Region B | 1.33 | 1.87 | 2.49 |
| Region C | 2.41 | 2.89 | 3.50 | |
| Maximum compressive contact stress between the embedded steel bar ends and the square steel tubes (MPa) | 163.99 | 0.15 | 0 | |
| Maximum weld contact stress at the welded joints (MPa) | 125.70 | 129.73 | 142.05 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





