1. Introduction
Pakistan is plentiful in mineral assets, offering an extraordinary potential for financial turn of events and prosperity. In light of accessible data, the country’s in excess of 600,000 square kilometers of outcrops region supports fluctuated geographical potential for metallic and non-metallic mineral stores. Marble contribute 0.008% to GDP and rank 5th among all the minerals. This shows that this industry has a great potential in Pakistan and this share can rise in future and incoming years, marble industry can rank 2nd among all minerals (Mansoor and Nadeem, 2012). Balochistan is by a wide margin the most extravagant territory regarding mineral assets in Pakistan. Punjab has the second largest reserves of rock salt on the planet, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) is the most extravagant region as far as gem stones. Recently, tremendous stores of coal have been found in Sindh. The execution of the First National Mineral Policy (NMP 1995) at both federal and provincial levels paved the way for an extension of mining area movement in Pakistan. The execution, too, ended up being a vital stage toward drawing in interest in the mining area. Although, the mining area presently offers less than 1% to Pakistan’s Gross domestic product, recent discoveries have provided strong evidence of significant mineral deposits and a great potential for the sector to contribute to the national and local economies ( (PMDC, 2009).
2. Marble Industry; A Prominent Source of Air Pollution
Concrete is the most commonly used construction material in the world. The main constituent of the concrete is cement which requires huge amount of energy for the production. The marble business is likewise one type of development movement, and it comprises of cycles and tasks in particular cutting, polishing, and cleaning which create a lot of residue particles.(El-Gammal et al.,2011). The undesirable endowment of the modern transformation, population blast, and the fast extension of metropolitan regions is air contamination, which is an issue being confronted worldwide, particularly in emerging nations (Arbex et al.,2012). Pakistan is one of the most air-contaminated nations on the planet. The high concentration of PM2.5 and PM10 in the Peshawar area is because of the residue particles that scope from Afghanistan, which adds air contamination to the neighborhood district. The prevalence of air contamination levels outperforming the WHO rules past the satisfactory degrees of particulate matter focus represents ecological corruption and wellbeing crumbling of individuals.
3. Felonious Marble Dumping in Water Courses Leading to Serious Human Health Implications
In Pakistan, countless marble handling units dump their marble squander straightforwardly into streams, waterways, and rich marshes, which cover the dirt pores since there is a shortfall of mindfulness and no regulation about the removal of waste material. Thus, soil penetrability is diminished, which expands the alkalinity of the soil (Haider et al.,2015). The marble reserves in Pakistan are assessed to be over 297 billion tons. Because of such a wealth of regular stores of marbles, there is a multitudinous number of marble manufacturing plants in Pakistan and presently, there is no regulation for legitimate permit and unloading of marble squander. Individuals living close by marble processing plants are experiencing contaminated water, kidney stones, radioactive illnesses , work related wellbeing risks and polluted landfills because of the marble dust (Iqbal et al.,2018).
Sodium is one more waste produced by marble dust. The overabundance expansion of sodium influences plants and would upset the chemical equilibrium in the water, animals and people influencing vegetation, animal survival and coronary illness among people separately. Magnesium is likewise a significant constituent of fish and vegetables. Magnesium intake is in many cases hindered by the aggregation of marble dust in the soil, which diminished the necessary magnesium fixation; this absence of magnesium can cause hypomagnesaemia, prompting diabetes, low pulse, and heart failures (Smedley et al.,2015).
4. Fine Marble Particulate Matter; A Cause of Fatal Human diseases
During marble manufacturing, 40% of the marble squander is equivalent to comprises of the made volume, which is created when the rock debris is unloaded in adjacent fields, horticultural terrains, and stream beds, which produces ecological risks. The subsequent residue particles from marble processing plants have elevated degrees of poisonous PM particles and its openness is a main driver of numerous lethal respiratory and cancer-causing illnesses — like nasal disease, bronchitis, asthma, and lung contamination — in marble laborers. A comparable report was directed in the Hayatabad local location in Peshawar, Pakistan that played out the air contamination examination and its air quality evaluation. In view of the outcomes, it was found that the air quality close to the neighborhood had higher TSP, PM2.5, and PM10 levels than the WHO suggested rules (Akbulut et al., 2003).
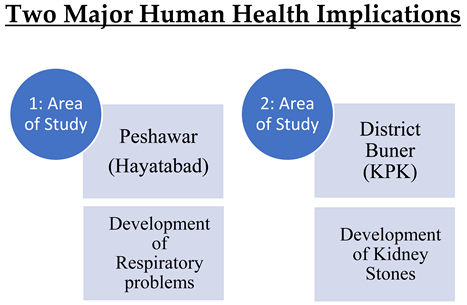
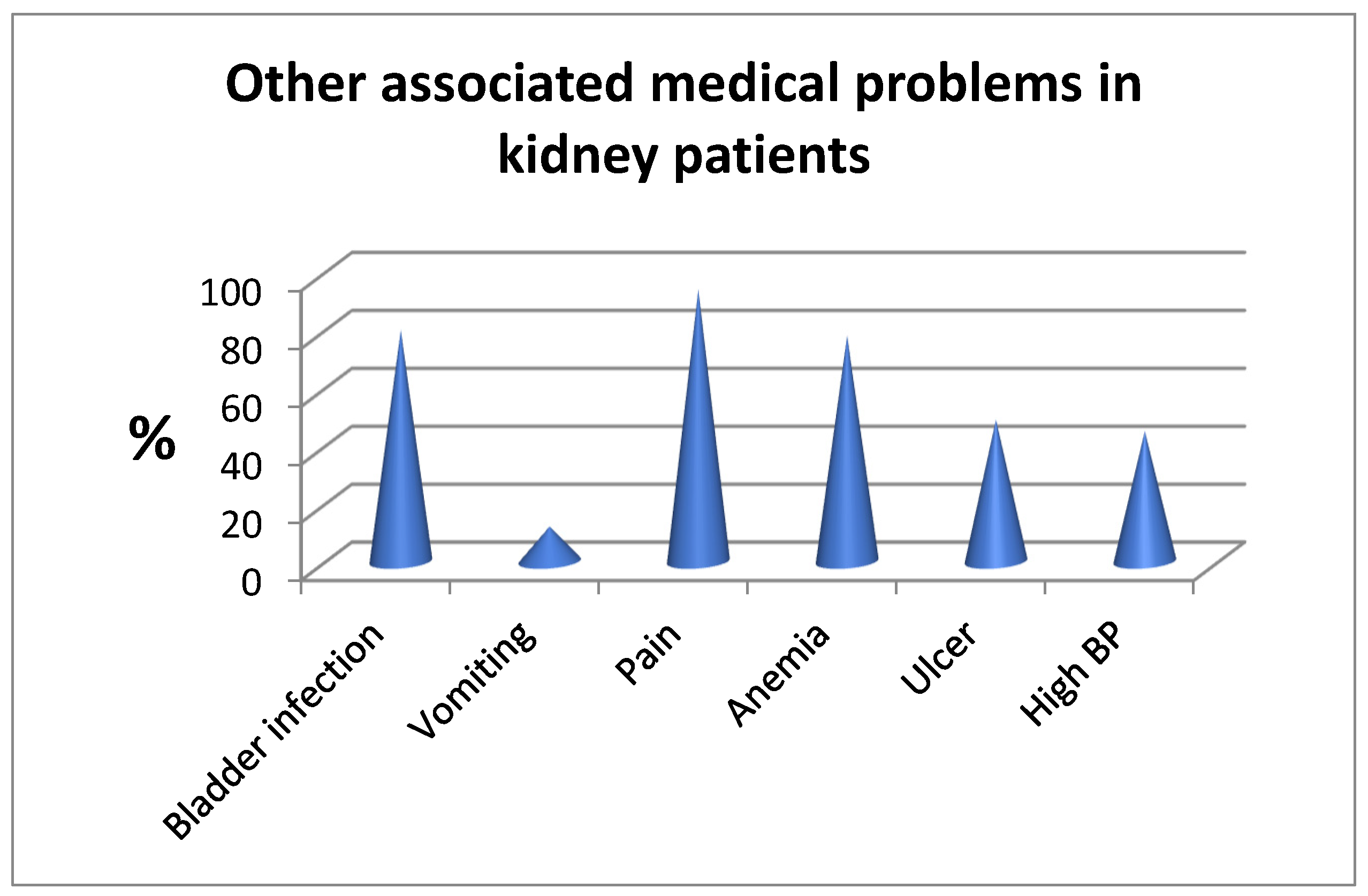
Figure 1.
Associated medical problems witnessed in kidney patients (Khan, 2015).
Figure 1.
Associated medical problems witnessed in kidney patients (Khan, 2015).
5. Minimize Magnesium and Calcium Mass by Boiling Water
Local individuals have revealed the presence of Calcium mass/precipitants at the lower part of the pots in the wake of heating up the water in pots/pots. This shows that the water has enormous tainting of Calcium mass of marble industrial facilities. This may be the explanation that individuals living close to or in the modern regions experienced more kidney contaminations. Be that as it may, individuals who were utilizing boiled water (liberated from Calcium mass) for drinking intentions were seen to be less tainted from kidney stones. The solidified carbonate minerals, most regularly calcite or dolomite are interfered with in the kidney tubules and subsequently these crystals become bigger when there is steady intake of water defiled with the marble business effluents (Jehangir khan et al.,2015). Magnesium is additionally a significant constituent of fish and vegetables. Magnesium intake is many times obstructed by the collection of marble dust in the soil, which decreased the necessary magnesium concentration; this absence of magnesium can cause hypo-magnesemia, prompting diabetes, low pulse, and heart failures.
6. Other Trace Constituents of Marble Dust Particles
Copper is additionally delivered in marble dust and its high focus in water is hazardous to the both people and yields, which can damage kidneys and can cause malignant growth in individuals living and working in marble processing plants.
Zinc is another important component, which forestalls heart sicknesses, goes about as a calming specialist, and helps in connective tissue development. Hints of a high measure of zinc were found in marble laborers’ blood, any amount higher than the needed intake is hurtful .
Arsenic is a significant constituent of residue particles. Arsenic contamination is a worldwide residue issue — particularly in South Asian nations like Pakistan, India, and Bangladesh — which can cause hyperkeratosis as well as kidney, liver, cardiovascular, and neurological problems(Mosley et al.,2005).
7. Cement Production; A Step towards Sustainability
The utilization of marble powder or slurry for the creation of cement is a significant stage from the supportability point of view. The total aggravate produced from the marble mining squander were utilized as coarse total in substantial blends (Silva, Gameiro, and de Brito 2014). The fine aggravate delivered from the marble squander utilized in the creation of cement clearing blocks (Gencel et al. 2012). It was tracked down that, utilization of this marble squander diminished the creation cost of cement clearing block by 12%. In India roughly 95% creation of marble is gotten from the territory of Rajasthan alone. There are around 4000 marble mines and 1100 handling units working in the territory of Rajasthan, India.
Marble squander has been tried as a potential substitution of fine total for the development of substantial blends having w/c proportion in the reach 0.4-0.6. The majority of the examinations have utilized calcite based marble squander for their investigations. As on account of supplanting coarse total by marble squander, Hanifi Binici here also was the trailblazer in completing the exploration in this area. (Binici, Kaplan and Yilmaz ,2007) utilized marble squander better than 1 mm to supplant sand of similar size, in extents of 5%, 10% and 15%. They expressed that with consideration of marble squander, compressive strength of the substantial blends worked on by 24% at 15% replacement level. After openness to a 7% sulfate arrangement the compressive strength of a similar blend diminished by as it were 15% when contrasted with control substantial which lost 58% of unique compressive strength. This blend had the best obstruction to rough wear and water infiltration too. These upgrades were credited to marble squanders’ pore filling capacity however at the cost of decreased functionality. Subsequently a super-plasticizer must be utilized to repay this misfortune.
8. Use of Waste Marble in Concrete Production; Fulfilling Green Building Norms
By the consolidation of marble as coarse and fine aggregates, the mining business would in a manner figure out their waste administration issues by redirecting the loss to the development industry as opposed to heedless unloading in open land. This would make the mining action more feasible and ecological amicable. Indeed, even financial advantages can be somewhat long by exchanging the marble as totals. The development business can source the aggregates by close to marble mines as opposed to acquiring from far off committed total creating mines. This would diminish transportation cost make the substantial ‘green’ by obtaining the locally ‘accessible materials’ to satisfy green building norms. This would all in a manner lessen the need of badly arranged unloading of waste as slurry and aggregates along engine ways what’s more, stream banks, cutting down air, water and soil contamination. The wellbeing perils brought about by the slurry suspended in air and water can be forestalled. Vegetation can be safeguarded from harm. In short this would help the whole environment both in transient contamination and long haul an Earth-wide temperature boost (Sudarshan et al.,2019).
9. Analysis of Water Quality, Marble slurry and Major Oxides in Marble Slurry Generating From Various Marble Polishing and Cutting Industries
9.1. Water Quality Analysis
The samples were gathered from various industrial streams and dissected in the lab. The outcomes were then contrasted with sindh environmental quality standards(SEQS). The marble area industry produces squander water that has high turbidity and contains suspended solids. In the marble business, water is predominantly used to cool cutting edges. The gushing is then assembled in the sedimentation tanks, and suspended solids settle. The wastewater is reused a few times prior to being released in semi strong structure for definite removal. The wastewater samples from the power source of sedimentation tanks of marble businesses were gathered and examined for physico-substance and organic qualities. A sum of three examples from the different marble modern units were gathered. It tends to be seen that the TDS and turbidity values were extremely high. The explanation is that the industrial’s influent water is as of now high in TDS , and the cutting system increments turbidity. High TDS values confirm it in each of the three examples. The chemical oxygen demand(COD) values were additionally over the breaking point set by sindh EPA. In any case, low bio-chemical oxygen demand (BOD) values demonstrated that the natural matter in the examples was basically not biodegradable. Mercury was committed in one example, the worth was over the sindh environmental quality standards set by sindh EPA. The mercury source is obscure and tracked down in just a single example. It might have started from marble rocks in a disconnected way. Any remaining boundaries stayed underneath the cutoff points set by sindh EPA (Ahmed,2023).
9.2. Marble Slurry Analysis
The marble slurry squander was broke down in which the Molybdenum(Mo) was not recognized, and manganese(Mn) and palladium(Pb) were identified underneath recognition limit. Notwithstanding, the sodium was distinguished 301.4 mg/g of marble slurry which is higher when contrasted with different components. The centralizations of calcium and magnesium in marble slurry was distinguished as 274.4 and 224.6 mg/g. The justification for the presence of sodium , calcium and magnesium in the marble slurry may be the presence of sodium, calcium and magnesium in unique marble blocks or chunks and it became packed in the marble slurry dust during the cutting and cleaning process (Khan et al.,2017).
9.3. Major Oxides Analysis in Marble Slurry
In the review, the marble slurry squander was additionally examined to know its fixations. The examination of significant oxides in marble slurry test is given as in
Table 1. The CaO has higher convergences of 42.3% than all, loss of ignition is 55% and humidity is 11.9%. These have higher concentrations in marble slurry(Ahmed,2023).
10. Socio-Economic Zone Improvement Leading to Economic Growth and Social Development
These zones work on generally speaking financial development and social improvement of local area. Also, he featured that social economic zones (SEZs) are not any more connected with financial advantages just; rather SEZs socially affect networks encompassing SEZs (Aggarwal, 2012). In (2014, Aharonson) did explore on creative result that can be accomplished by modern bunching. It was featured in concentrate on that item development increments with modern grouping that outcomes in expanded enhancement with gigantic monetary advantages (Aharonson, 2014).
Additionally, Caniels has clarified in 2005 that modern and mechanical groups in extraordinary financial zones increment creativity and work on nature of items and subsequently upgraded competitiveness is produced in firms. It was likewise featured that these bunches have immense social advantages as further developed offices and occupation creation (Caniels, 2005). In 2004, Helsley chipped away at financial matters of agglomeration and demonstrated how cognizant and viable agglomeration of ventures can expand cycle of monetary development in territorial setting (Helsley, 2004).
A review led by Hamza in 2016 featured that development in marble and rock handling can give upgraded financial advantages. He featured that even waste of marble and stone is definitely not a loss as it tends to be re-cycled and yet again utilized (Hamza, 2016).Thus, from the contemporary exploration it very well may be securely presumed that improvement of marble industry is productive to economy of country. The favored choice ought to be to make a modern zone with current handling machines inside sensible separation from the marble quarries to create immense amount of marble tiles. Such modern zone will likewise acquire flourishing to families encompassing of modern zone.
11. Major Footprints (Environmental, Water and Energy) of Marble Tile Production
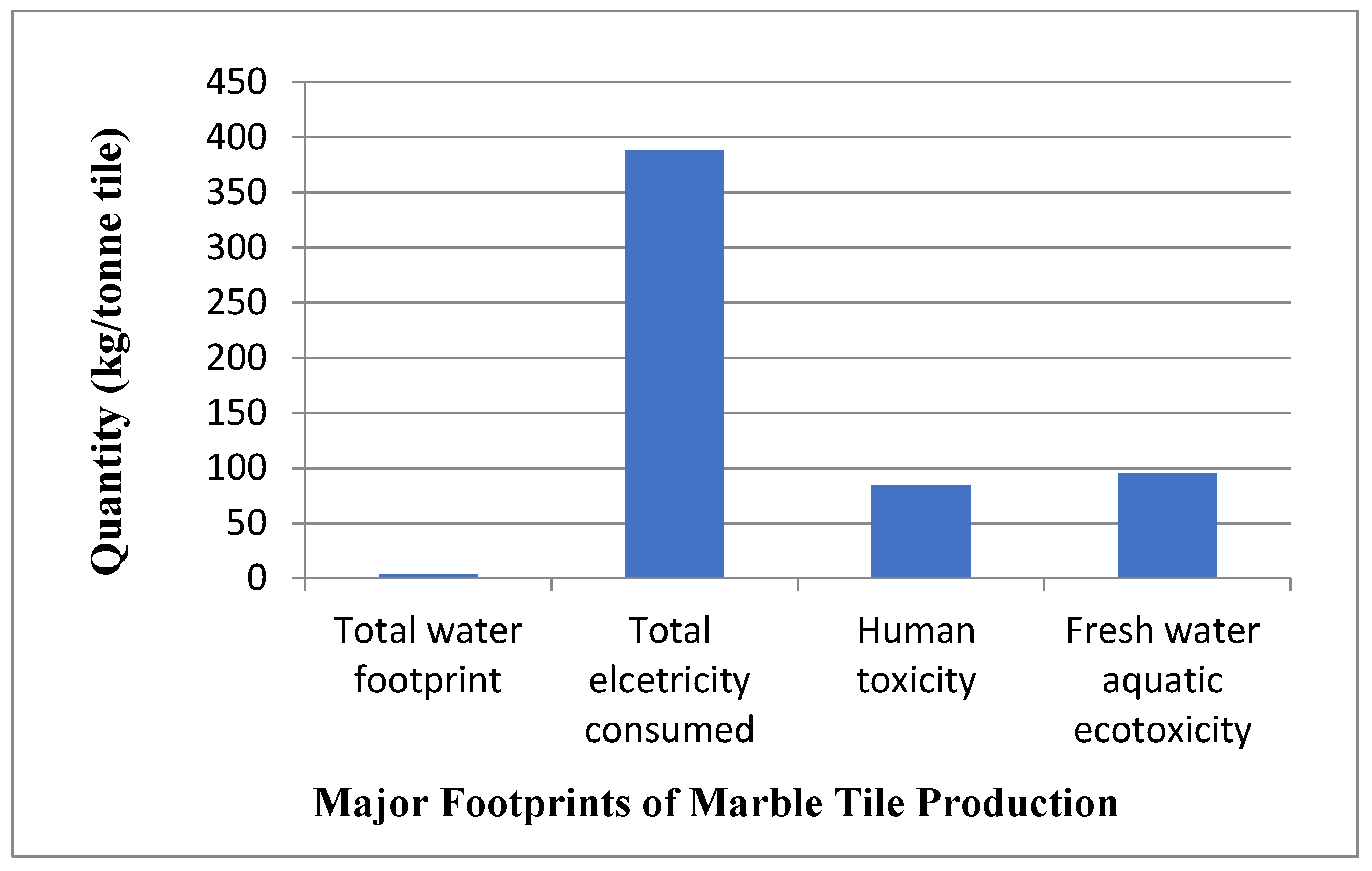
The marble business is filling in Pakistan, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa territory is the biggest maker of marble tiles in Pakistan. Marble creation used a lot of water during its life cycle stages and effects different natural compartments, like air, water, and soil; subsequently, the study planned to evaluate the ecological effects, water impression, and combined energy interest of one-ton marble tile made in a small industrial estate Mardan (SIEM), Pakistan, and give suggestions to further develop its natural effect profile. The review covers water utilization, energy use, and related ecological effects of unrefined substances and cycles through various phases of the marble life-cycle during 2017-2018. The all out water impression expected for one ton of completed marble tile was 3.62 cubic meters per ton (m3/t), with power consumed at handling units adding to ecological weights the most. Likewise, electricity (at handling units and during cleaning) and transportation of completed marble tile to the nearby market were answerable for an world-wide temperature boost potential (388 kg CO2 eq/ton tile), human toxicity (84.34 kg 1,4-DB-eq/ton), freshwater oceanic eco-toxicity (94.97kg 1,4-DB eq/ton). Most of the surveyed industrial units did not have wastewater treatment and recycling plants, and wastewater directly flows to nearby freshwater bodies and terrestrial ecosystems. These wastewaters should be adequately treated before being discharged into freshwater aquatic bodies. Environmental impacts must be improved by using the latest automatic machinery, reducing waste materials generation, reducing the distance between processing units and the market, and installing wastewater recycling plants.
Figure 2.
Major footprints of marble tile production (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
Figure 2.
Major footprints of marble tile production (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
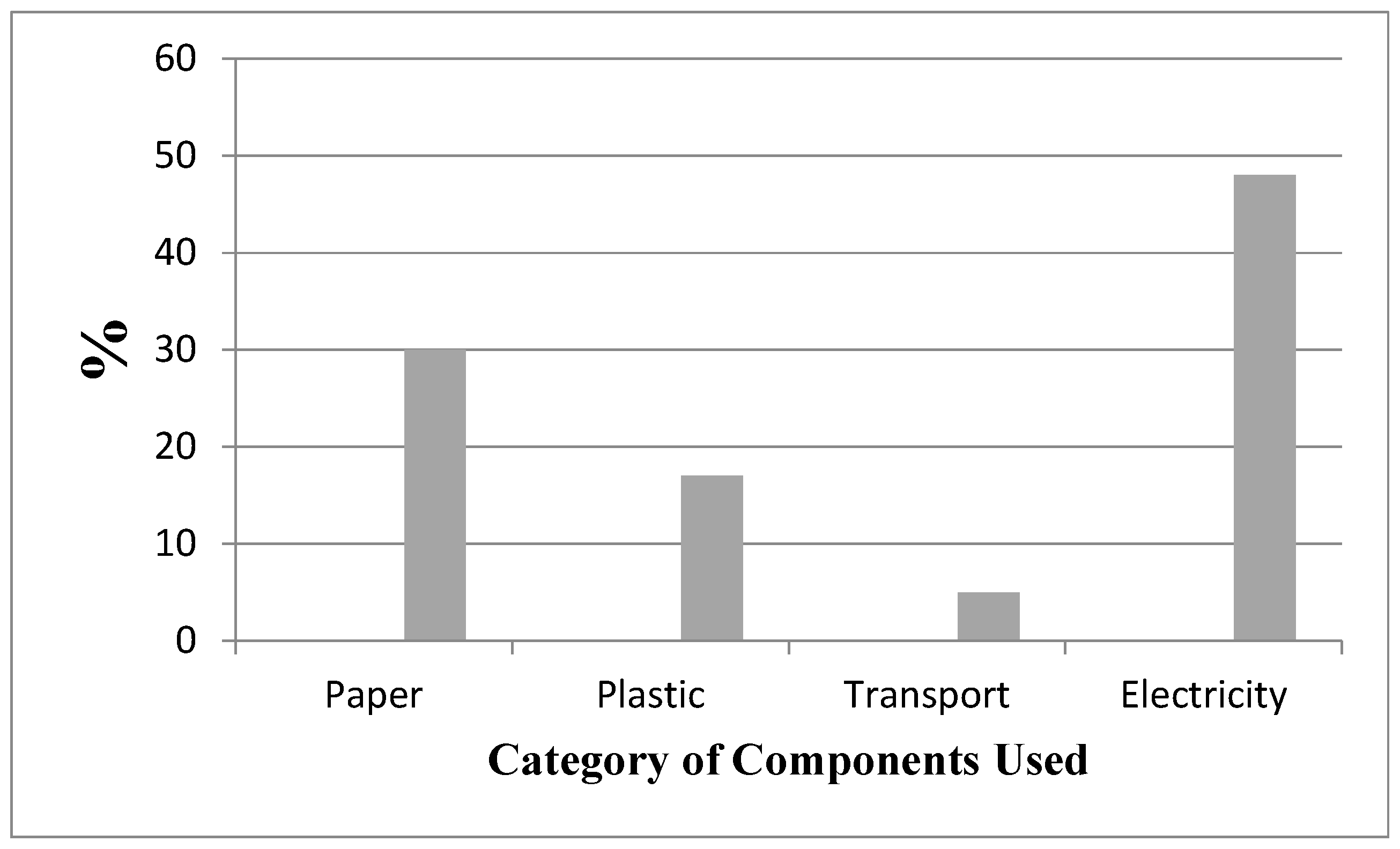
The water shortage record (water impression) was assessed through LCA. The water impression because of marble/stones extraction, handling, and completed marble tile creation is displayed below. In general, 3.63 m3/t water shortage or water impression is brought about by one-ton completed marble tile creation in small industrial estate Mardan (SIEM), Pakistan. Various variables added to ecological impressions including power use during handling represented the vast majority of the effects (48%), trailed by paper bundling at the handling units (30%), plastic use at extraction locales and handling units (17%) and transport of stones/pieces to handling units (5%) ( Ahmad et al.,2022).
Our outcomes revealed the water footprint for coke and coal as 1.03 m3/t and 0.38 m3/t, separately, which is not exactly our review on the grounds that the marble creation chain is a more water-escalated process. Likewise, water footprint for the iron and steel industry as 6.7 × 108 m3/t having a higher water impression than the current review on the grounds that the iron and steel creation chain is more water-escalated than the marble tile creation chain (Gu et al.,2015).
Figure 3.
Showing higher consumption rate of electricity than other components in production (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
Figure 3.
Showing higher consumption rate of electricity than other components in production (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
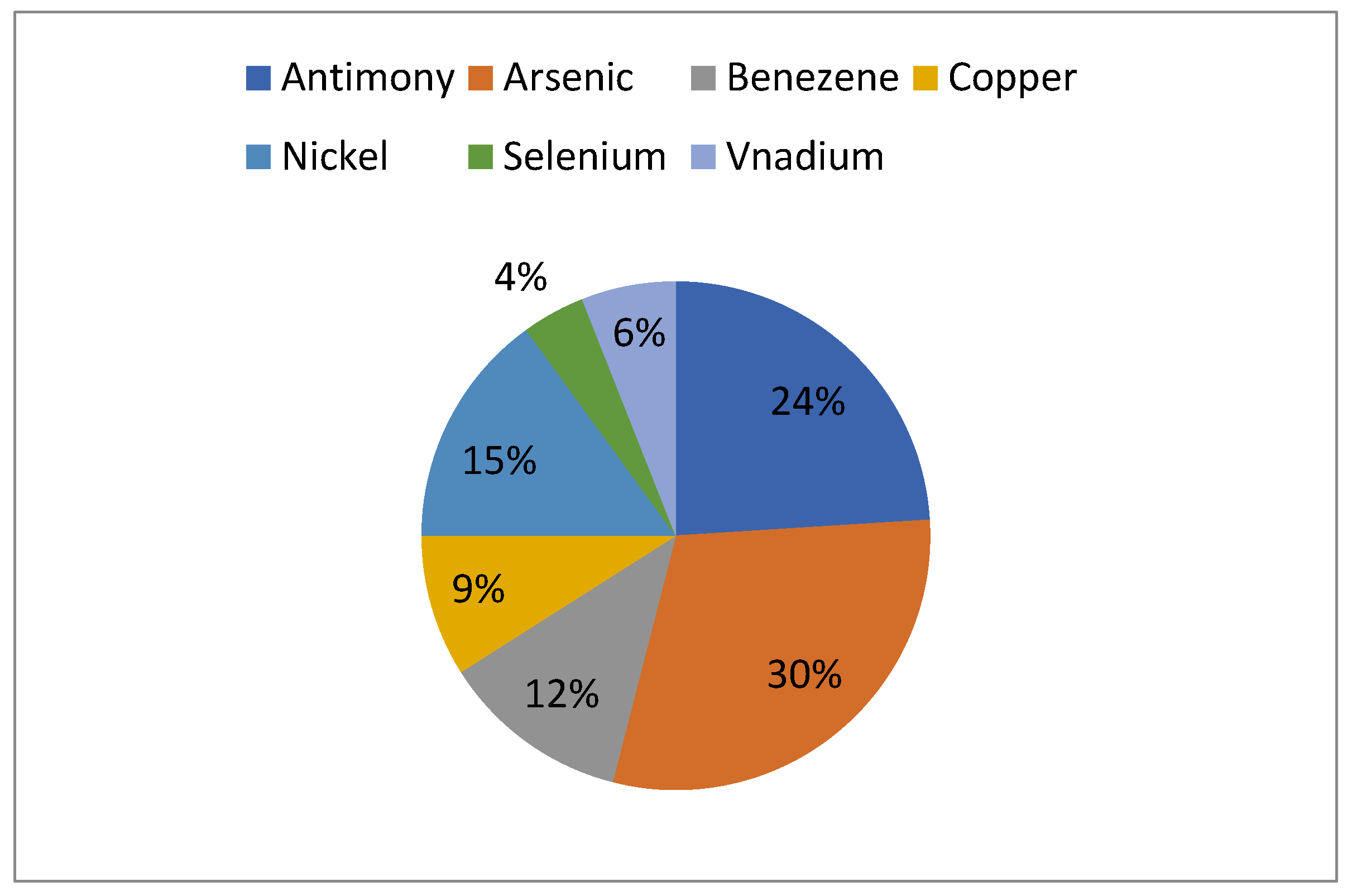
Human Toxicity (HT) to various ecological compartments like air, water and soil was surveyed impartially to kg 1,4 dichlorobenzene (kg 1,4-DB-eq). To the air, 38.5 kg 1,4-DB-eq of human harmfulness was brought about by one ton of marble tile from extraction to completed item. Transportation (95%), squander created from marble units, and power utilized were various sources. The most elevated commitment from transport, squanders, and power were arsenic, antimony, nickel, benzene, copper, vanadium, and selenium as shown below.
Figure 4.
Participatory elements contributing Human Toxicity(HT) (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
Figure 4.
Participatory elements contributing Human Toxicity(HT) (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
12. Waste water Treatment; A Step Towards for an Effective Heavy Metals Remediation Released from Marble Production
Wastewater treatment can work on the nature of modern effluents, yet monetary limitations and the execution of compelling waste administration approaches are significant difficulties for legitimate quality control in emerging nations . In Pakistan, wastewater assortment and treatment plans at the optional or tertiary level are missing, and just a small portion (< 8%) of modern wastewater is appropriately treated. The rest is released straightforwardly into streams, streams, water system trenches, and different waterways without compulsory treatment per ecological security organization necessities. Safeguarding the accessibility of adequate measures of great water is a significant mechanical and cultural test that should be addressed. In Pakistan, the idea of utilizing developed wetlands to eliminate poisonous metals from wastewater was as of recently introduced(Batool and Saleh,2020).
In non-industrial nations, including Pakistan, unfortunate ranchers frequently depend on the utilization of wastewater to develop different yields for transient financial advantages, overlooking the natural and related wellbeing gambles because of an absence of fundamental information. Wastewater contains microbes (microscopic organisms, infections, protozoa, and molds) and possibly harmful components in extreme fixations that can cause critical medical issue. Openness to wastewater can happen through ingestion, dermal, and inward breath courses while working in wastewater-creating ventures, involving wastewater for water system and swimming (Kinuthia et al.,2020). In this manner, the utilization of wastewater for water system and family purposes can present short-and long term risks. The utilization of bio-char is likewise one of the most exceptional procedures for eliminating poisonous mixtures from water and soil(Tariq M et al.,2022). Furthermore, natural and compound remediation advancements, for example, plant development advancing rhizobacteria (PGPR) and the utilization of diatomite are viable in weighty metal remediation.
In the Malakand Division, the marble business creates squander in various structures that are released straightforwardly into streams and water system channels, delivering the surface water unacceptable for water system and family purpose. This rising pattern of surface water contamination has turned into a difficult issue. Health risk assessments , for example, hazard index and cancer risk could be used to determine non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic health risks from exposure to potentially toxic elements through ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact(Fadel et al.,2022).
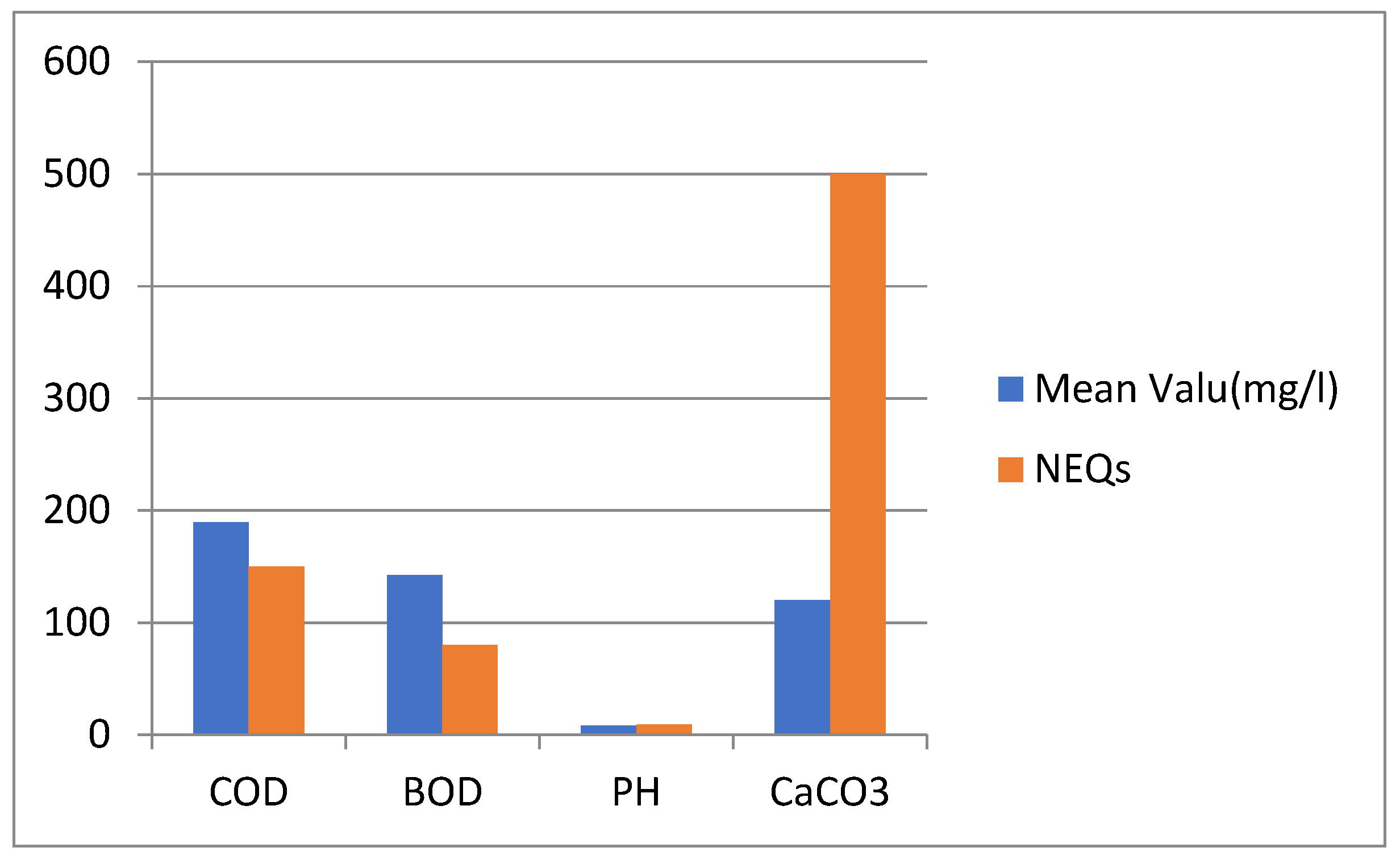
High BOD in wastewater drains the oxygen content of the water and prompts the passing of sea-going life forms .Like BOD, COD is additionally used to address in general water quality . The BOD and COD focuses in the ongoing review went from 74 to 197 mg/L and 98.30 to 248.70 mg/L, with mean upsides of 142.14 and 189.38 mg/L, separately. As far as possible for BOD and COD in wastewater are 80 and 150 mg/L, separately. The convergences of BOD and COD in the water test (89%) surpassed as far as possible for water system(Khan et al.,2022).
High BOD and COD levels were likewise acquired by while concentrating on the effect of marble overflow on the Barandu Stream in Pakistan(Mulk et al.,2015). Alkalinity is vital for sea-going life because of its buffering limit against quick pH changes that happen normally because of the photosynthetic movement of plants. In the ongoing review, alkalinity went from 60.7 to 195 mg/L with a mean of 120.03 mg/L CaCO3. The alkalinity levels of all water tests were permissible as far as possible (500 mg/L) for water system purposes as shown below.
Figure 5.
Major wastewater parameters and their comparison with NEQS (Asghar Khan, 2022).
Figure 5.
Major wastewater parameters and their comparison with NEQS (Asghar Khan, 2022).
Wastewater stream rate and not entirely settled for ten different marble fabricating units at SIEM, Pakistan. The typical wastewater release in SIEM was 318 ± 34 m3/day, while the typical wastewater per ton of marble tile created was 3.1 ± 1.7 m3/d/t. The typical slurry delivered was 49 ± 5 g/L, with the most elevated commitment from Two-Star Marble Processing plant (58.02 g/L) and Al-Noor Marble Industrial facility (54.34 g/L), SIEM, Pakistan. From the correlation, obviously the marble unit with additional wastewater and slurry creation had more apparatus for marble handling and by and large more creation volume of marble tiles as shown below.
Figure 6.
Estimating slurry and wastewater flow rate from various industrial unit of Mardan, Pakistan (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
Figure 6.
Estimating slurry and wastewater flow rate from various industrial unit of Mardan, Pakistan (Ahmad, et al., 2022).
13. Global Importance of Pakistan’s Marble Reserves; Globally Competitive and Socially Responsible Industry
As per Pakistan Stone Development Company (PASDEC), Pakistan has approximately 300 billion tons of marble resources spread generally in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, the ancestral belt, Balochistan and Sindh. Around, 98% marble resources are thought to be in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and FATA. In any case, high expected regions for colossal and quality marble repositories are arranged in Buner, Chitral, Hazara, Kohistan, Nowshera, Mardan, Smack and Kohat, Bajaur, Kurram, Khyber, Mohmand and Orakzai Organizations from Governmentally Controlled Ancestral Regions (FATA) (Khan, 2009; Hadi, 2014).
The marble business has potential in export area. In this way, a portion of the important marble is sent out to European nations. While the assessed overall trade in marble and stone is circuitous 45 dollar billion every year (Hadi, 2014). However, tragically, marble sent out from Pakistan was simply of $33 million last year (Khan, 2009). As of late, Pakistan offered large venture potential open doors in mining. Subsequently, Saudi Arabia has focused on purchase Pakistani marble results of around $260 billion to fabricate its new urban areas (Khan, 2009). Pakistan Stone Development Company (PASDEC) is devoted to change over the ongoing Pakistani marble area in to a universally serious and socially mindful industry in Pakistan. The cutting edge procedures will change over the current marble industry of Pakistan in to a universally cutthroat industry which thusly will improve the financial development of the country.
14. Eco-Innovative Options for Marble Sector
The major ecological issues marble area enterprises face incorporates the age of marble powder slurry(Semi-strong fluid), drainage of water from marble slurry in unloading regions, air borne particulates produce after drying of marble slurry in open unloading regions , and high energy utilization of marble cuttings(Ahmed et al.,2021). The marble business is energy escalated and utilizes energy to cut enormous marble stones into little pieces of required sizes. Alongside energy necessities, significant water is expected to cool cutting sharp edges. Marble dust, when unloaded transparently as slurry, adds to air contamination when it gets dried and compromises the region’s environment(Shah and Mohammad,2019). The eco-development choice distinguished or the marble area industry is introduced below:
Use marble slurry in fired clay bricks as an alternative source to reduce flue gases from the brick kilns.
Use marble slurry as a limestone(Calcium) source in chicken feed production.
Use of automatic motor controllers(PID controllers and VFDs).
Use of solar energy.
15. Thorough Reviewing on Research Gaps
- ▪
Research gap in accessing durability:
Not many investigations were led by the researchers on durability properties of substantial utilizing marble squander. Hence with this restricted information accessible, concrete with marble total consolidated cement can be utilized in the development of superstructures in provincial and semi metropolitan regions from industrial zones.
- ▪
Research gap to use marble waste as an alternative to sulphate environments:
It has been accounted for that marble, which is a carbonate rock is equipped for responding with calcium aluminate to shape calcium alumino carbonates. Since it is surely known that calcium aluminate is the most reactive part when presented to sulphates. If the outcomes end up being positive, marble waste can be solely utilized in sulphate conditions.
- ▪
Research gap in judging the strength of marble aggregates for low grade construction purposes:
The majority of the examinations were done by embracing low water- concrete proportions for the investigation of low to medium strength grades of concrete. These have demonstrated that use of marble aggregates should be possible at lower levels of development like private units and low ascent structures. Since in low-and medium-strength cements the strength is for the most part administered by the concrete paste and interfacial progress zone, the strength of the aggregate is barely used. By the investigation of high strength concrete the job of the marble aggregate can be decided to additional degree. This would assist in the judgment whether with marbling aggregate can be utilized where execution is out a right standards.
- ▪
Research gap in checking the drying and shrinking property of marble in comparison with basalt and granite:
Cracks bringing about shrinkage can speed up crumbling of concrete because of the expanded openness to the inward center of the part. Marble is perceived to have lesser modulus of flexibility when contrasted with rocks of basalt and stone. Furthermore, drying shrinkage is a function of aggregates modulus of versatility likewise for example lesser the flexible modulus of total, more noteworthy the drying shrinkage when every one of the contributing elements are kept consistent. Consequently preceding assessment of marble consolidated substantial’s presentation in forceful climate, drying shrinkage can likewise be checked.
- ▪
Research gap in reducing carbon footprint of construction industry by reusing marble aggregates:
On the economy front, marble is in demand as an aesthetic dimensional stone. Its quarrying and handling will unintentionally produce squander as blocks, powder and slurry. Subsequently as opposed to opening committed quarries for total production of marble aggregates can be utilized in substantial assembling. This would lessen the creation cost of aggregates furthermore, concrete both the same. This would prompt supportability of the marble industry with lessen or try and zero waste. Construction enterprises’ carbon footprint can likewise be diminished by considerable amount.
- ▪
Some research limitations while collecting data due to diverse localities:
As monitoring points are random—having diverse localities—it may be possible that the readings of one area differ from the other area. Moreover, the readings can be affected by various factors in settings, such as unpaved roads dust and residential dust, that can interfere with the actual marble dust concentration.
16. Valuable Recommendations To Reduce Above Research Gaps
- ▪
The public authority ought to upgrade the transportation office for the easy accessibility of the natural substance, the public authority ought to give incentives based on simple conditions to the business proprietors, Credit ought to be given to marble modern proprietors in the review region.
- ▪
Marble modern proprietors ought to be excluded from the public authority charge for elevating to this area in the review region; Water accessibility offices should be guaranteed in the review region, training institutions ought to be laid out in the review region for covering the lack of expertise work, free electricity ought to be given to marble industry proprietor to inspiring marble industry in the review region.
17. Conclusion
Effluents from the marble industry are the main source of surface water pollution in the study area. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to move the marble processing plants from the nearby river canals and agricultural land to the industrial area. Many of the physio-chemical parameters were not within the limits of NEQS when they were analyzed. This is due to the lack of proper policy and environmental laws. Some eco-innovation options have been suggested to save processing cost water, energy and waste disposal costs instead of open dumping.
For the determination of air pollution, the areas near marble factories and non-marble factories were compared and it was found that people living near marble factories are more prone to diseases associated with dust inhalation. Based on the results of the air pollution test, the Peshawar area air is unfit to breathe, and it would worsen with time due to the unlicensed and haphazard location of factories because of the absence of regulation. There is a strong need for legislation of establishment of factories in the industrial zone only.
Depending on the particle size distribution of marble waste and cement, utilization of 10–15% of marble slurry as cement replacement can give satisfactory performance of concrete mixes; this would result in reduction in utilization of cement by 10% and consequently reduce the CO2 emission. The extent of using marble waste as a replacement for conventional coarse aggregate depends on the geological origin of the conventional aggregate. Complete replacement of limestone aggregate is possible, whereas for the other types the replacement value depends on the dry bulk density of the concrete making constituents.
The study finally concluded that after marble industry the level of income of the sample respondents were increased which play great role in expenditure, saving, educational institution availability and health services center availability in the study area.
References
- Ahmad,T., Hussain,M., Iqbal,M., Ali,A., Manzoor,W., Hamida,B., Ali,S., Rehamn,F., Rashedi,A., Amin,M., Tabassum,A., Raza,G&Shams,D.(2022).Environmental, Energy, and Water Footprints of Marble Tile Production Chain in a Life Cycle Perspectivehttps://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/14/8325. [CrossRef]
- Khan,A., Khan,M., Egozcue,J., Shafique,M., Nadeem,S&Saddiq,G.(2022).Irrigation suitability, health risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in surface water used for irrigation near marble industry in Malakand, Pakistan https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0279083. [CrossRef]
- Khan,I., Rehan,R., Shahzada,K., Ahmad,M&Shah,A.(2022) Critical Analysis of Multi Sectoral Policies related to Marble Industry in Pakistan. [CrossRef]
-
https://publications.muet.edu.pk/index.php/muetrj/article/view/2368.
- Khan,J.(2015) Burden of Marble Factories and Health Risk Assessment of Kidney (renal) Stones Development in District Buner, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
-
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275621942_Burden_of_Marble_Factories_and_Health_Risk_Assessment_of_Kidney_renal_Stones_Development_in_District_Buner_Khyber_Pakhtunkhwa_Pakistan.
- Neelab,N., Ullah,S., Faiz,P., Rashid,S., Rahim,F., Akbar,F., Yousufzai,M,. Lashari,A., Rashid,W&Hussain,W.(2022). Effects of Marble Industry Effluents on Soil Quality, Growth and Productivity of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) in District Swat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. https://www.pjoes.com/Effects-of-Marble-Industry-Effluents-non-Soil-Quality-Growth-and-Productivity-nof,144659,0,2.html. [CrossRef]
- Ahmas,S.(2019). Marble Industry Role in the Socio Economic Development of Marble Industrial Owners of District Mohmand Federal Administered Tribal Area-Pakistan. [CrossRef]
-
https://www.iiste.org/Journals/index.php/IEL/article/view/47308/0.
- Kakakhel,S., Ahmad,K&Tariq,M.(2017). Determinants of Safe Organizational Climate and its Impact on Employee Performance: A Case of Marble Industries Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
-
https://journal.suit.edu.pk/index.php/sjms/article/view/84.
- Noreen,U., Ahmed,Z., Khalid,A&(2019). Water pollution and occupational health hazards caused by the marble industries in district Mardan, Pakistan. [CrossRef]
-
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335457664_Water_pollution_and_occupational_health_hazards_caused_by_the_marble_industries_in_district_Mardan_Pakistan.
Table 1.
Analysis of major Oxides of Marble Slurry. (Ahmed, 2023)
Table 1.
Analysis of major Oxides of Marble Slurry. (Ahmed, 2023)
| Oxides |
Symbols |
Content(%) |
| Calcium Oxide |
CaO |
42.3 |
| Aluminum Oxide |
Al2O3 |
0.16 |
| Ferric Oxide |
Fe2O3 |
0.028 |
| Magnesium Oxide |
MgO |
0.93 |
| Sulfur Trioxide |
SO3 |
0.73 |
| Sodium Oxide |
Na2O3 |
0.027 |
| Potassium Oxide |
K2O |
0.036 |
| Phosphorus Pentoxide |
P2O5 |
0.013 |
| Chlorine Monoxide |
Cl- |
0.039 |
| Strontium Oxide |
SrO |
0.018 |
| Loss of Ignition |
LOI |
55.1 |
| Water content |
W |
0.73 |
| Humidity |
- |
11.9 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).