Submitted:
16 October 2024
Posted:
17 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review-Related Work
1.2. Paper Outline
2. Comparisons and Constructions of Fuzzy Implications. Materials, Methods and Data.
2.1. Theoretical Framework of Fuzzy Implication
- If then (decreasing as to the first variable)
- If then(increasing as to the second variable)
- This means that falsehood implies anything (dominion of false)
- Τhis means that truth does not implies anything (neutrality of truth)
- identity
- (property of change)
- If then (border condition). It means that the fuzzy implications are true if and only if the following condition is at least as true as much as the preceding term.
- That is, two fuzzy implications are identical if o abbot and the following term are interchanged, having previously taken their denial. Essentially, this postulate is a generalization of its method of indiscriminately abducting classical logic,
- The function is continuous
- and
- The n is a genuinely decreasing function.
- (commutativity property)
- (associative property)
- (border condition)
- if (monotonicity)
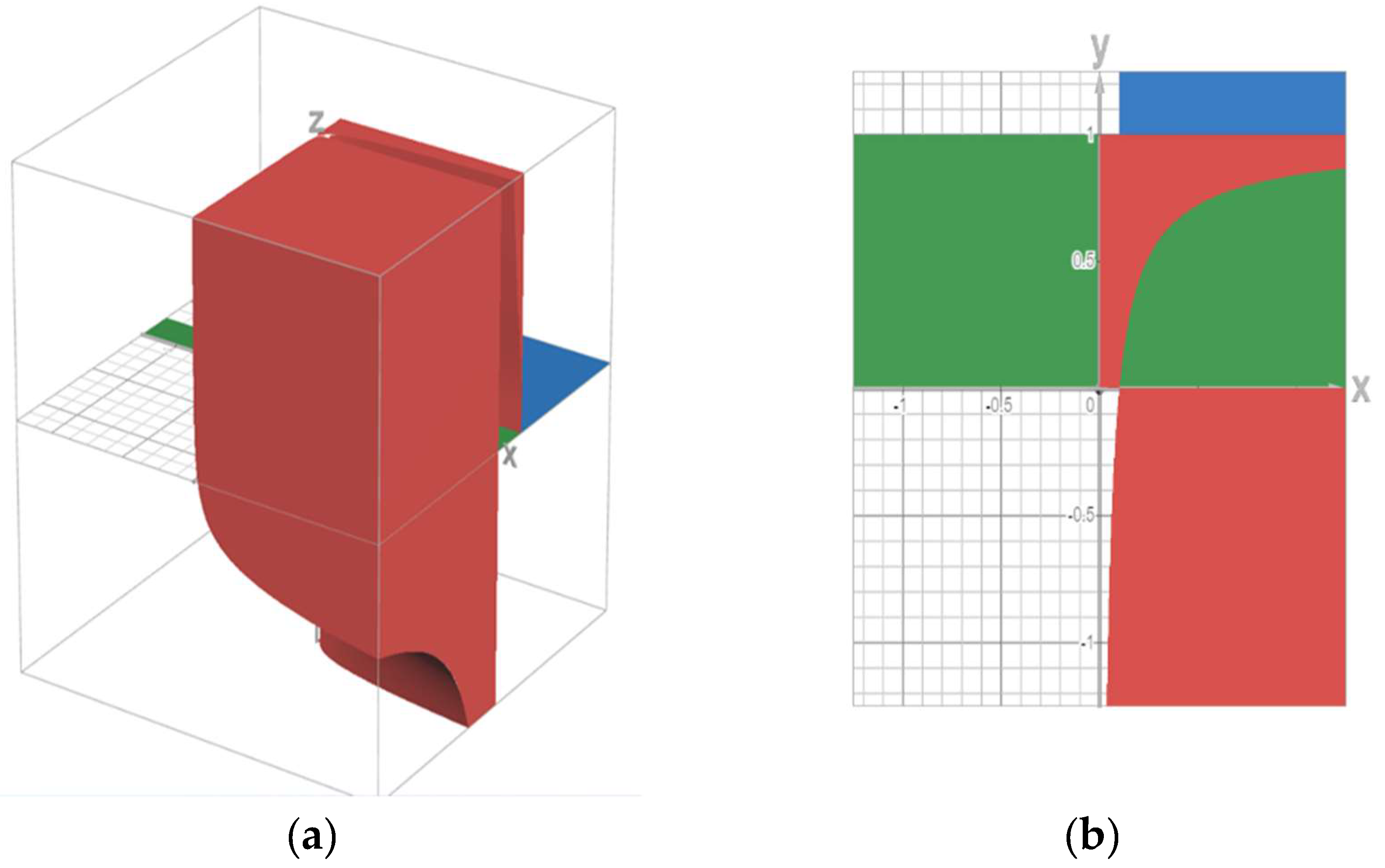
2.2. Comparison of Fuzzy Implications Using Different t-Conorm

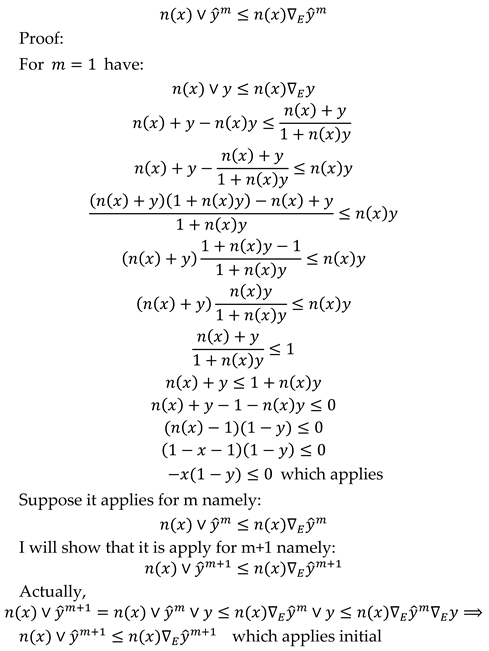
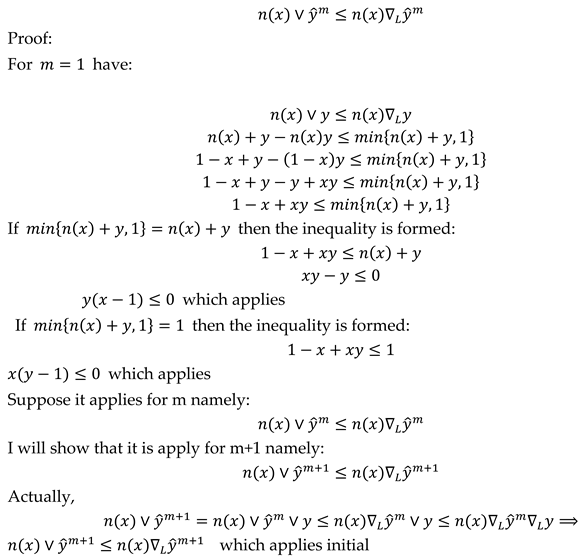

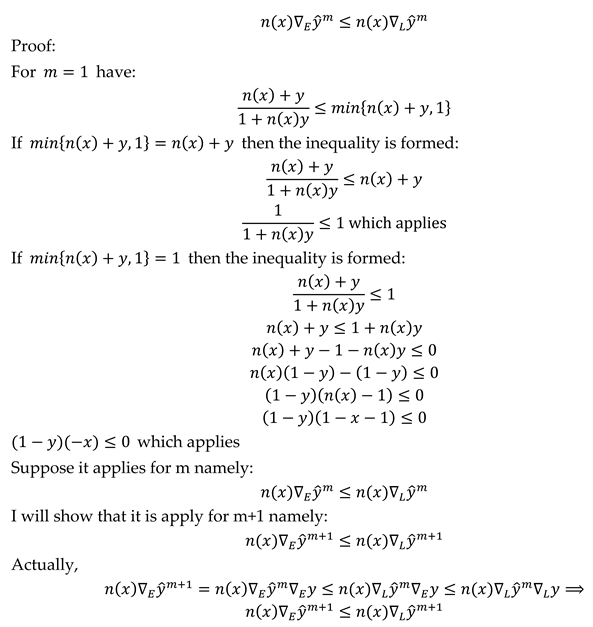

| T-CONORMS | GENERAL FORMULA | SYMBOL |
|---|---|---|
| Probor | x+y-xy | |
| Max | ||
| Einstein | ||
| Lukasiewicz | ||
| Hamacher | ||
| RANKING |
2.3. Construction of Fuzzy Implications Using Different t-Conorm

- If m is odd number, then:
- If m is even number then:
- ➢
- If
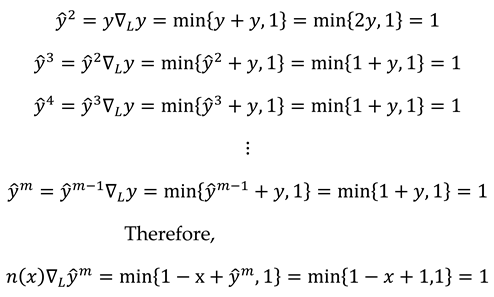
- ➢
- If
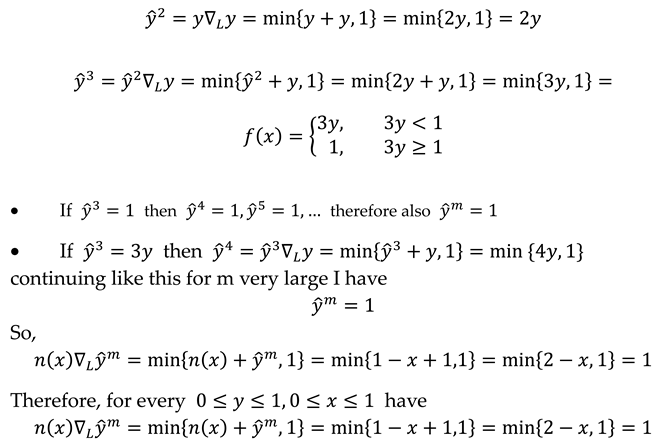
| T-CONORMS | GENERAL FORMULA | SYMBOL | IMPLICATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| probor | x+y-xy | ||
| max | |||
| Einstein | |||
| Lukasiewicz |
2.4. A General Framework of Seven Steps of Methodology
2.4.1. Real Data and Area of Study
3. Results
3.1. General Outcomes of Comparisons of Fuzzy Implications Using Different t-conorm-The Results from the 1st Step of the Methodology
- Fuzzy implication with t-conorm max which is less than or equal to probor.
- Fuzzy implication with t-conorm probor which is less than or equal to all other three t-conorms Einstein, Lukasiewicz, Hamacher
- Fuzzy implication with t-conorm Hamacher which is less than or equal to Einstein and fuzzy implication with t-conorm Einstein less than or equal to Lukasiewicz
- The fuzzy implication with t-conorm Einstein which is greater than or equal to Hamacher and less than or equal to Lukasiewicz.
- Fuzzy implication with t-conorm Lukasiewicz which is greater than or equal to Einstein and Einstein is greater than or equal to Hamacher than probor and max.
- The fuzzy implication with t-conorm Lukasiewicz is greater than or equal to the other four fuzzy implications created with Einstein, Hamacher, probor and max.
3.2. General Outcomes from the Construction and Calculation of General Types of Fuzzy Implications - The Results from the 2nd Step of the Methodology
3.3. General Outcomes of Fuzzy Model-The Results from the 3rd Step of the Methodology
3.4. General Outcomes of Fuzzy model-The Results from the 4rth Step of the Methodology
3.5. General and Optimal Outcomes after Extensive Tests at Four Membership Functions and Four Types of Fuzzy Implications When the Value of m Is Equal to 1-The Results from the 5th Step of the Methodology
3.6. General and Optimal Outcomes after Extensive Tests to the Value of Parameter m at Four Membership Functions from the Results of the Type of Fuzzy Implication Probor -The Results from the 6th Step of the Methodology
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 23 | 22 | 1 | 8 |
| m=11-14 | 27 | 23 | 4 | 4 |
| m=15 | 29 | 23 | 6 | 2 |
| m=62 | 29 | 24 | 5 | 2 |
| m=127,128 | 29 | 26 | 3 | 2 |
| m=135-138 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=139 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 16 |
| m=31 | 28 | 22 | 6 | 3 |
| m=34 | 29 | 22 | 7 | 2 |
| m=195 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=308 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=311 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 22 |
| m=30 | 28 | 19 | 9 | 3 |
| m=34 | 29 | 19 | 10 | 2 |
| m=310 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=317 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=320 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 24 |
| m=20 | 28 | 12 | 16 | 3 |
| m=36 | 29 | 20 | 9 | 2 |
| m=127 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=128 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=495 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 20 | 17 | 3 | 11 |
| m=15 | 28 | 21 | 7 | 3 |
| m=16 | 28 | 23 | 5 | 3 |
| m=22 | 29 | 26 | 3 | 2 |
| m=36 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=75 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=204 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 14 | 9 | 5 | 17 |
| m=16 | 28 | 20 | 8 | 3 |
| m=24 | 29 | 24 | 5 | 2 |
| m=51 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=100 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=263 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 19 |
| m=18 | 28 | 18 | 10 | 3 |
| m=27 | 29 | 23 | 6 | 2 |
| m=52 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=104 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=275 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
| Probor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m=1 | 14 | 2 | 12 | 17 |
| m=9 | 28 | 8 | 20 | 3 |
| m=15 | 29 | 15 | 14 | 2 |
| m=45 | 29 | 27 | 2 | 2 |
| m=71 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 2 |
| m=192 | 29 | 29 | 0 | 2 |
3.6. General and Optimal Outcomes after Extensive Tests at Four Membership Functions and at Two Types of Fuzzy Implications (Probor and Einstein) when the Value of m Is Equal to 1, 2, 3 and 10 - The Results from the 7th Step of the Methodology
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 23 | 22 | 1 | 8 |
| Einstein m=1 | 21 | 20 | 1 | 10 |
| Probor m=2 | 25 | 22 | 3 | 6 |
| Einstein m=2 | 25 | 22 | 3 | 6 |
| Probor m=3 | 25 | 22 | 3 | 6 |
| Einstein m=3 | 25 | 22 | 3 | 6 |
| Probor m=10 | 26 | 23 | 3 | 5 |
| Einstein m=10 | 27 | 23 | 4 | 4 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 16 |
| Einstein m=1 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 19 |
| Probor m=2 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 11 |
| Einstein m=2 | 22 | 15 | 7 | 9 |
| Probor m=3 | 23 | 15 | 8 | 8 |
| Einstein m=3 | 24 | 15 | 9 | 7 |
| Probor m=10 | 25 | 15 | 10 | 6 |
| Einstein m=10 | 27 | 17 | 10 | 4 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 22 |
| Einstein m=1 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 26 |
| Probor m=2 | 16 | 4 | 12 | 15 |
| Einstein m=2 | 21 | 4 | 17 | 10 |
| Probor m=3 | 21 | 4 | 17 | 10 |
| Einstein m=3 | 25 | 4 | 21 | 6 |
| Probor m=10 | 26 | 9 | 17 | 5 |
| Einstein m=10 | 26 | 13 | 13 | 5 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 24 |
| Einstein m=1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 28 |
| Probor m=2 | 15 | 4 | 11 | 16 |
| Einstein m=2 | 17 | 4 | 13 | 14 |
| Probor m=3 | 20 | 4 | 16 | 11 |
| Einstein m=3 | 21 | 4 | 17 | 10 |
| Probor m=10 | 26 | 6 | 20 | 5 |
| Einstein m=10 | 28 | 7 | 21 | 3 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 20 | 17 | 3 | 11 |
| Einstein m=1 | 20 | 17 | 3 | 11 |
| Probor m=2 | 25 | 17 | 8 | 6 |
| Einstein m=2 | 26 | 17 | 9 | 5 |
| Probor m=3 | 26 | 17 | 9 | 5 |
| Einstein m=3 | 26 | 17 | 9 | 5 |
| Probor m=10 | 28 | 20 | 8 | 3 |
| Einstein m=10 | 28 | 20 | 8 | 3 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 14 | 9 | 5 | 17 |
| Einstein m=1 | 14 | 8 | 6 | 17 |
| Probor m=2 | 24 | 9 | 15 | 7 |
| Einstein m=2 | 24 | 9 | 15 | 7 |
| Probor m=3 | 26 | 9 | 17 | 5 |
| Einstein m=3 | 26 | 9 | 17 | 5 |
| Probor m=10 | 28 | 13 | 15 | 3 |
| Einstein m=10 | 28 | 18 | 10 | 3 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 19 |
| Einstein m=1 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 25 |
| Probor m=2 | 23 | 2 | 21 | 8 |
| Einstein m=2 | 24 | 2 | 22 | 7 |
| Probor m=3 | 24 | 2 | 22 | 7 |
| Einstein m=3 | 26 | 2 | 24 | 5 |
| Probor m=10 | 27 | 7 | 20 | 4 |
| Einstein m=10 | 28 | 16 | 12 | 3 |
| Fuzzy implication / value of m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor m=1 | 14 | 2 | 12 | 17 |
| Einstein m=1 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 24 |
| Probor m=2 | 21 | 2 | 19 | 10 |
| Einstein m=2 | 23 | 2 | 21 | 8 |
| Probor m=3 | 24 | 2 | 22 | 7 |
| Einstein m=3 | 27 | 2 | 25 | 4 |
| Probor m=10 | 28 | 8 | 20 | 3 |
| Einstein m=10 | 29 | 14 | 15 | 2 |
4. Discussion
| Isosceles trapezium | Random trapezium | Isosceles Triangle | Scalene Triangle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humidity ≥0.9 | 37 from 62 | 24 from 62 | 10 from 62 | 8 from 62 |
| Temperature ≥0.9 | 34 from 62 | 19 from 62 | 12 from 62 | 5 from 62 |
| Humidity = 1 | 40 from 62 | 20 from 62 | 0 from 62 | 0 from 62 |
| Temperature = 1 | 34 from 62 | 19 from 62 | 3 from 62 | 0 from 62 |
| Isosceles trapezium August and January |
Random trapezium August and January |
Isosceles Triangle August and January |
Scalene Triangle August and January |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy Implication Probor receive value=1 |
y=1 and x=1, y=1 and x=0, y=1 and x=[0,1], y=[0,1] and x=0 |
y=1 and x=1, y=1 and x=0, y=1 and x=[0,1], y=[0,1] and x=0 |
y=[0,1] and x=0 | y=[0,1] and x=0 |
| Fuzzy Implication Max receive value=1 |
y=1 and x=1, y=1 and x=0, y=1 and x=[0,1], y=[0,1] and x=0 |
y=1 and x=1, y=1 and x=0, y=1 and x=[0,1], y=[0,1] and x=0 |
y=[0,1] and x=0 | y=[0,1] and x=0 |
| Fuzzy Implication Einstein receive value=1 |
y=1 and x=1, y=1 and x=0, y=1 and x=[0,1] |
y=1 and x=1, y=1 and x=0, y=1 and x=[0,1] |
| Fuzzy Implications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Probor Isosceles trapezium | 43 | 39 |
| Max Isosceles trapezium | 42 | 39 |
| Einstein Isosceles trapezium | 41 | 37 |
| Probor Random trapezium | 29 | 23 |
| Max Random trapezium | 27 | 24 |
| Einstein Random trapezium | 26 | 20 |
| Probor Isosceles triangle | 21 | 6 |
| Max Isosceles triangle | 15 | 6 |
| Einstein Isosceles triangle | 11 | 0 |
| Probor Scalene triangle | 21 | 6 |
| Max Scalene triangle | 13 | 6 |
| Einstein Scalene triangle | 10 | 0 |
| Probor August | 1 | |
| Isosceles Trapezium m=15 | 29 | 23 |
| Isosceles Trapezium m=139 | 29 | 29 |
| Random Trapezium m=34 | 29 | 22 |
| Random Trapezium m=311 | 29 | 29 |
| Isosceles Triangle m=34 | 29 | 19 |
| Isosceles Triangle m=320 | 29 | 29 |
| Scalene Triangle m=36 | 29 | 20 |
| Scalene Triangle m=495 | 29 | 29 |
| Probor January | 1 | |
| Isosceles Trapezium m=22 | 29 | 26 |
| Isosceles Trapezium m=204 | 29 | 29 |
| Random Trapezium m=24 | 29 | 24 |
| Random Trapezium m=263 | 29 | 29 |
| Isosceles Triangle m=27 | 29 | 23 |
| Isosceles Triangle m=275 | 29 | 29 |
| Scalene Triangle m=15 | 29 | 15 |
| Scalene Triangle m=192 | 29 | 29 |
| Einstein August | 1 | |
| Isosceles Trapezium m=10 | 27 | 23 |
| Random Trapezium m=10 | 27 | 17 |
| Isosceles Triangle m=10 | 26 | 13 |
| Scalene Triangle m=10 | 28 | 7 |
| Einstein January | 1 | |
| Isosceles Trapezium m=10 | 28 | 20 |
| Random Trapezium m=10 | 28 | 18 |
| Isosceles Triangle m=10 | 28 | 16 |
| Scalene Triangle m=10 | 29 | 14 |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 | 17/8/2021 | 36/0.2500 | 0.32/0.5714 |
| 2/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.49/1.0000 | 18/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.3/0.2857 |
| 3/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 | 19/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.32/0.5714 |
| 4/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.35/1.0000 | 20/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.34/0.8571 |
| 5/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 | 21/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.31/0.4286 |
| 6/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.38/1.0000 | 22/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.29/0.1429 |
| 7/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.4/1.0000 | 23/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.28/0.0000 |
| 8/8/2021 | 28/0.5000 | 0.58/0.1429 | 24/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.43/1.0000 |
| 9/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.29/0.1429 | 25/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.43/1.0000 |
| 10/8/2021 | 26/0.0000 | 0.48/1.0000 | 26/8/2021 | 34/0.7500 | 0.36/1.0000 |
| 11/8/2021 | 28/0.5000 | 0.45/1.0000 | 27/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.49/1.0000 |
| 12/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.29/0.1429 | 28/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.52/1.0000 |
| 13/8/2021 | 29/0.7500 | 0.43/1.0000 | 29/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 |
| 14/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.4/1.0000 | 30/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.52/1.0000 |
| 15/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.59/0.0000 | 31/8/2021 | 30/1.0000 | 0.52/1.0000 |
| 16/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.43/1.0000 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/2024 | 15/0.8000 | 0.63/0.9000 | 17/1/2024 | 14/1.0000 | 0.59/1.0000 |
| 2/1/2024 | 16/0.6000 | 0.55/1.0000 | 18/1/2024 | 17/0.4000 | 0.68/0.6500 |
| 3/1/2024 | 13/1.0000 | 0.59/1.0000 | 19/1/2024 | 18/0.2000 | 0.6/1.0000 |
| 4/1/2024 | 16/0.6000 | 0.48/1.0000 | 20/1/2024 | 6/0.6000 | 0.81/0.0000 |
| 5/1/2024 | 16/0.6000 | 0.48/1.0000 | 21/1/2024 | 9/1.0000 | 0.27/0.0000 |
| 6/1/2024 | 19/0.0000 | 0.52/1.0000 | 22/1/2024 | 7/0.8000 | 0.42/0.7500 |
| 7/1/2024 | 16/0.6000 | 0.63/0.9000 | 23/1/2024 | 8/1.0000 | 0.5/1.0000 |
| 8/1/2024 | 16/0.6000 | 0.52/1.0000 | 24/1/2024 | 11/1.0000 | 0.47/1.0000 |
| 9/1/2024 | 3/0.0000 | 0.6/1.0000 | 25/1/2024 | 10/1.0000 | 0.58/1.0000 |
| 10/1/2024 | 6/0.6000 | 0.42/0.7500 | 26/1/2024 | 14/1.0000 | 0.36/0.4500 |
| 11/1/2024 | 8/1.0000 | 0.46/0.9500 | 27/1/2024 | 12/1.0000 | 0.51/1.0000 |
| 12/1/2024 | 9/1.0000 | 0.29/0.1000 | 28/1/2024 | 11/1.0000 | 0.41/0.7000 |
| 13/1/2024 | 7/0.8000 | 0.49/1.0000 | 29/1/2024 | 10/1.0000 | 0.32/0.2500 |
| 14/1/2024 | 8/1.0000 | 0.53/1.0000 | 30/1/2024 | 8/1.0000 | 0.43/0.8000 |
| 15/1/2024 | 11/1.0000 | 0.58/1.0000 | 31/1/2024 | 10/1.0000 | 0.4/0.6500 |
| 16/1/2024 | 17/0.4000 | 0.52/1.0000 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.46/1.0000 | 17/8/2021 | 36/0.2500 | 0.32/0.2667 |
| 2/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.49/1.0000 | 18/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.3/0.1333 |
| 3/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 | 19/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.32/0.2667 |
| 4/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.35/0.5667 | 20/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.34/0.4000 |
| 5/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 | 21/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.31/0.2000 |
| 6/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.38/0.6667 | 22/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.29/0.0667 |
| 7/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.4/0.8000 | 23/8/2021 | 35/0.5000 | 0.28/0.0000 |
| 8/8/2021 | 28/0.4000 | 0.58/0.1000 | 24/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.43/1.0000 |
| 9/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.29/0.0667 | 25/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.43/1.0000 |
| 10/8/2021 | 26/0.0000 | 0.48/1.0000 | 26/8/2021 | 34/0.7500 | 0.36/0.5333 |
| 11/8/2021 | 28/0.4000 | 0.45/1.0000 | 27/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.49/1.0000 |
| 12/8/2021 | 32/1.0000 | 0.29/0.0667 | 28/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.52/0.7000 |
| 13/8/2021 | 29/0.6000 | 0.43/1.0000 | 29/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.46/1.0000 |
| 14/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.4/0.8000 | 30/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.52/0.7000 |
| 15/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.59/0.0000 | 31/8/2021 | 30/0.8000 | 0.52/0.7000 |
| 16/8/2021 | 31/1.0000 | 0.43/1.0000 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/2024 | 15/1.0000 | 0.63/0.8571 | 17/1/2024 | 14/1.0000 | 0.59/1.0000 |
| 2/1/2024 | 16/1.0000 | 0.55/1.0000 | 18/1/2024 | 17/0.6670 | 0.68/0.6190 |
| 3/1/2024 | 13/1.0000 | 0.59/1.0000 | 19/1/2024 | 18/0.3330 | 0.6/1.0000 |
| 4/1/2024 | 16/1.0000 | 0.48/0.8077 | 20/1/2024 | 6/0.3330 | 0.81/0.0000 |
| 5/1/2024 | 16/1.0000 | 0.48/0.8077 | 21/1/2024 | 9/0.6670 | 0.27/0.0000 |
| 6/1/2024 | 19/0.0000 | 0.52/0.9615 | 22/1/2024 | 7/0.4440 | 0.42/0.5769 |
| 7/1/2024 | 16/1.0000 | 0.63/0.8571 | 23/1/2024 | 8/0.5560 | 0.5/0.8846 |
| 8/1/2024 | 16/1.0000 | 0.52/0.9615 | 24/1/2024 | 11/0.8890 | 0.47/0.7692 |
| 9/1/2024 | 3/0.0000 | 0.6/1.0000 | 25/1/2024 | 10/0.7780 | 0.58/1.0000 |
| 10/1/2024 | 6/0.3330 | 0.42/0.5769 | 26/1/2024 | 14/1.0000 | 0.36/0.3462 |
| 11/1/2024 | 8/0.5560 | 0.46/0.7308 | 27/1/2024 | 12/1.0000 | 0.51/0.9231 |
| 12/1/2024 | 9/0.6670 | 0.29/0.0769 | 28/1/2024 | 11/0.8890 | 0.41/0.5385 |
| 13/1/2024 | 7/0.4440 | 0.49/0.8462 | 29/1/2024 | 10/0.7780 | 0.32/0.1923 |
| 14/1/2024 | 8/0.5560 | 0.53/1.0000 | 30/1/2024 | 8/0.5560 | 0.43/0.6154 |
| 15/1/2024 | 11/0.8890 | 0.58/1.0000 | 31/1/2024 | 10/0.7780 | 0.4/0.5000 |
| 16/1/2024 | 17/0.6670 | 0.52/0.9615 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.46/0.8387 | 17/8/2021 | 36/0.1818 | 0.32/0.2581 |
| 2/8/2021 | 31/0.9091 | 0.49/0.6452 | 18/8/2021 | 35/0.3636 | 0.3/0.1290 |
| 3/8/2021 | 32/0.9091 | 0.46/0.8387 | 19/8/2021 | 35/0.3636 | 0.32/0.2581 |
| 4/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.35/0.4516 | 20/8/2021 | 35/0.3636 | 0.34/0.3871 |
| 5/8/2021 | 31/0.9091 | 0.46/0.8387 | 21/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.31/0.1935 |
| 6/8/2021 | 32/0.9091 | 0.38/0.6452 | 22/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.29/0.0645 |
| 7/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.4/0.7742 | 23/8/2021 | 35/0.3636 | 0.28/0.0000 |
| 8/8/2021 | 28/0.3636 | 0.58/0.0645 | 24/8/2021 | 32/0.9091 | 0.43/0.9677 |
| 9/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.29/0.0645 | 25/8/2021 | 32/0.9091 | 0.43/0.9677 |
| 10/8/2021 | 26/0.0000 | 0.48/0.7097 | 26/8/2021 | 34/0.5455 | 0.36/0.5161 |
| 11/8/2021 | 28/0.3636 | 0.45/0.9032 | 27/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.49/0.6452 |
| 12/8/2021 | 32/0.9091 | 0.29/0.0645 | 28/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.52/0.4516 |
| 13/8/2021 | 29/0.5455 | 0.43/0.9677 | 29/8/2021 | 31/0.9091 | 0.46/0.8387 |
| 14/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.4/0.7742 | 30/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.52/0.4516 |
| 15/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.59/0.0000 | 31/8/2021 | 30/0.7273 | 0.52/0.4516 |
| 16/8/2021 | 31/0.9091 | 0.43/0.9677 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/2024 | 15/0.5000 | 0.63/0.6667 | 17/1/2024 | 14/0.6250 | 0.59/0.8148 |
| 2/1/2024 | 16/0.3750 | 0.55/0.9630 | 18/1/2024 | 17/0.2500 | 0.68/0.4815 |
| 3/1/2024 | 13/0.7500 | 0.59/0.8148 | 19/1/2024 | 18/0.1250 | 0.6/0.7778 |
| 4/1/2024 | 16/0.3750 | 0.48/0.7778 | 20/1/2024 | 6/0.3750 | 0.81/0.0000 |
| 5/1/2024 | 16/0.3750 | 0.48/0.7778 | 21/1/2024 | 9/0.7500 | 0.27/0.0000 |
| 6/1/2024 | 19/0.0000 | 0.52/0.9259 | 22/1/2024 | 7/0.5000 | 0.42/0.5556 |
| 7/1/2024 | 16/0.3750 | 0.63/0.6667 | 23/1/2024 | 8/0.6250 | 0.5/0.8519 |
| 8/1/2024 | 16/0.3750 | 0.52/0.9259 | 24/1/2024 | 11/1.0000 | 0.47/0.7407 |
| 9/1/2024 | 3/0.0000 | 0.6/0.7778 | 25/1/2024 | 10/0.8750 | 0.58/0.8519 |
| 10/1/2024 | 6/0.3750 | 0.42/0.5556 | 26/1/2024 | 14/0.6250 | 0.36/0.3333 |
| 11/1/2024 | 8/0.6250 | 0.46/0.7037 | 27/1/2024 | 12/0.8750 | 0.51/0.8889 |
| 12/1/2024 | 9/0.7500 | 0.29/0.0741 | 28/1/2024 | 11/1.0000 | 0.41/0.5185 |
| 13/1/2024 | 7/0.5000 | 0.49/0.8148 | 29/1/2024 | 10/0.8750 | 0.32/0.1852 |
| 14/1/2024 | 8/0.6250 | 0.53/0.9630 | 30/1/2024 | 8/0.6250 | 0.43/0.5926 |
| 15/1/2024 | 11/1.0000 | 0.58/0.8519 | 31/1/2024 | 10/0.8750 | 0.4/0.4815 |
| 16/1/2024 | 17/0.2500 | 0.52/0.9259 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.46/0.5306 | 17/8/2021 | 36/0.1538 | 0.32/0.6154 |
| 2/8/2021 | 31/0.9231 | 0.49/0.4082 | 18/8/2021 | 35/0.3077 | 0.3/0.3077 |
| 3/8/2021 | 32/0.7692 | 0.46/0.5306 | 19/8/2021 | 35/0.3077 | 0.32/0.6154 |
| 4/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.35/0.9796 | 20/8/2021 | 35/0.3077 | 0.34/0.9231 |
| 5/8/2021 | 31/0.9231 | 0.46/0.5306 | 21/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.31/0.4615 |
| 6/8/2021 | 32/0.7692 | 0.38/0.8571 | 22/8/2021 | 37/0.0000 | 0.29/0.1538 |
| 7/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.4/0.7755 | 23/8/2021 | 35/0.3077 | 0.28/0.0000 |
| 8/8/2021 | 28/0.4444 | 0.58/0.0408 | 24/8/2021 | 32/0.7692 | 0.43/0.6531 |
| 9/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.29/0.1538 | 25/8/2021 | 32/0.7692 | 0.43/0.6531 |
| 10/8/2021 | 26/0.0000 | 0.48/0.4490 | 26/8/2021 | 34/0.4615 | 0.36/0.9388 |
| 11/8/2021 | 28/0.4444 | 0.45/0.5714 | 27/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.49/0.4082 |
| 12/8/2021 | 32/0.7692 | 0.29/0.1538 | 28/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.52/0.2857 |
| 13/8/2021 | 29/0.6667 | 0.43/0.6531 | 29/8/2021 | 31/0.9231 | 0.46/0.5306 |
| 14/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.4/0.7755 | 30/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.52/0.2857 |
| 15/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.59/0.0000 | 31/8/2021 | 30/0.8889 | 0.52/0.2857 |
| 16/8/2021 | 31/0.9231 | 0.43/0.6531 |
| Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
Kavala 14:50 o' clock measurement |
Temperature / membership degrees |
Humidity / membership degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/2024 | 15/0.9600 | 0.63/0.5217 | 17/1/2024 | 14/0.8800 | 0.59/0.6377 |
| 2/1/2024 | 16/0.8570 | 0.55/0.7536 | 18/1/2024 | 17/0.5710 | 0.68/0.3768 |
| 3/1/2024 | 13/0.8000 | 0.59/0.6377 | 19/1/2024 | 18/0.2860 | 0.6/0.6087 |
| 4/1/2024 | 16/0.8570 | 0.48/0.9565 | 20/1/2024 | 6/0.2400 | 0.81/0.0000 |
| 5/1/2024 | 16/0.8570 | 0.48/0.9565 | 21/1/2024 | 9/0.4800 | 0.27/0.0000 |
| 6/1/2024 | 19/0.0000 | 0.52/0.8406 | 22/1/2024 | 7/0.3200 | 0.42/0.7692 |
| 7/1/2024 | 16/0.8570 | 0.63/0.5217 | 23/1/2024 | 8/0.4000 | 0.5/0.8986 |
| 8/1/2024 | 16/0.8570 | 0.52/0.8406 | 24/1/2024 | 11/0.6400 | 0.47/0.9855 |
| 9/1/2024 | 3/0.0000 | 0.6/0.6087 | 25/1/2024 | 10/0.5600 | 0.58/0.6667 |
| 10/1/2024 | 6/0.2400 | 0.42/0.7692 | 26/1/2024 | 14/0.8800 | 0.36/0.4615 |
| 11/1/2024 | 8/0.4000 | 0.46/0.9744 | 27/1/2024 | 12/0.7200 | 0.51/0.8696 |
| 12/1/2024 | 9/0.4800 | 0.29/0.1026 | 28/1/2024 | 11/0.6400 | 0.41/0.7179 |
| 13/1/2024 | 7/0.3200 | 0.49/0.9275 | 29/1/2024 | 10/0.5600 | 0.32/0.2564 |
| 14/1/2024 | 8/0.4000 | 0.53/0.8116 | 30/1/2024 | 8/0.4000 | 0.43/0.8205 |
| 15/1/2024 | 11/0.6400 | 0.58/0.6667 | 31/1/2024 | 10/0.5600 | 0.4/0.6667 |
| 16/1/2024 | 17/0.5710 | 0.52/0.8406 |
References
- Kandel, A. Fuzzy Expert Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Florida, USA, 1992; pp.336, ISBN-10: 084934297X, ISBN-13: 978-0849342974.
- Ruan, D.; Kerre, E.E. Fuzzy implication operators and generalized fuzzy method of cases. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1993, 54, 1, 23–37. ISSN: 01650114. [CrossRef]
- Kecman, V. Learning and Soft Computing, 1st ed.; MIT Press: London, England, 2001; pp.576, ISBN 10: 0262527901 ISBN-13: 9780262527903.
- Daniilidou, A.; Konguetsof, A.; Souliotis, G.; Papadopoulos, B. Generator of Fuzzy Implications. Algorithms 2023, 16, 569. [CrossRef]
- Makariadis, S.; Souliotis, G.; Papadopoulos, B. Parametric fuzzy implications produced via fuzzy negations with a case study in environmental variables. Symmetry 2021, 13, 509–529. [CrossRef]
- Pagouropoulos, P.; Tzimopoulos, C.D.; Papadopoulos, B.K. A method for the detection of the most suitable fuzzy implication for data applications. In Communications in Computer and Information Science, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks (EANN), Athens, Greece, 25-27 August 2017; Iliadis L., Likas A., Jayne C., Boracchi G. Eds.; Springer Verlag: Volume 744, pp. 242-255. ISSN: 18650929, ISBN: 978-331965171-2. [CrossRef]
- Pagouropoulos, P.; Tzimopoulos, C.D.; Papadopoulos, B.K. A method for the detection of the most suitable fuzzy implication for data applications. Evolving Systems 2020, 11, 467-477. [CrossRef]
- Botzoris, G.N.; Papadopoulos, K. Papadopoulos, B.K. A method for the evaluation and selection of an appropriate fuzzy implication by using statistical data. Fuzzy Economic Review 2015, 20, 19-29. [CrossRef]
- Rapti, M.N.; Papadopoulos, B.K. A method of generating fuzzy implications from n increasing functions and n + 1 negations. Mathematics 2020, 8, 886. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Van Gasse, B.; Ruan, D.; and Kerre, E.E. On Dependencies and Independencies of Fuzzy Implication Axioms. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2010, 161, 1388-1405. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Peralta, R.; Massanet, S.; Mesiarová-Zemánková, A.; Mir, A. A general framework for the characterization of (S, N)-implications with a non-continuous negation based on completions of t-conorms. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2022, 441, 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, J.; Kolesárová, A.; Mesiar, R., Quesada-Molina, J.J.; Úbeda-Flores, M. A generalization of a copula-based construction of fuzzy implications. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2023, 456, 197-207. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lu, J. On the distributivity for the ordinal sums of implications over t-norms and t-conorms. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 2023, 152, 284-296. [CrossRef]
- Souliotis, G.; Papadopoulos, B. Fuzzy Implications Generating from Fuzzy Negations. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN 2018), Part 1, Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning, Rhodes, Greece, 4–7 October 2018; Kurkova V., Hammer B., Manolopoulos Y., Iliadis L., Maglogiannis I. Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Volume 11139 LNCS, p.p. 736-744, ISSN: 03029743, ISBN: 978-303001417-9. [CrossRef]
- Karbassi Yazdi, A.; Hanne, T.; Wang, Y.J.; Wee, H.M.A. Credit Rating Model in a Fuzzy Inference System Environment. Algorithms 2019, 12, 139. [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Yazir, D.; Hamid, A.A.; Abdul Rahman, N.S.F. Maritime Supply Chain Optimization by Using Fuzzy Goal Programming. Algorithms 2021, 14, 234. [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.K.; Wei, Y.C.; Chen, B.C. A Study on the Fuzzy-Logic-Based Solar Power MPPT Algorithms Using Different Fuzzy Input Variables. Algorithms 2015, 8, 100-127. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; You, X. Some linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy Heronian mean operators based on Einstein T-norm and T-conorm and their application to decision-making, Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2018, 35, 2433-2445. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.; Abdullah, S.; Ghani, F. Some new generalized interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy aggregation operators using Einstein t-norm and t-conorm, Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2019, 37, 3721-3742. [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. Generalized Pythagorean Fuzzy Geometric Aggregation Operators Using Einstein t-Norm and t-Conorm for Multicriteria Decision-Making Process. International Journal of Intelligent Systems 2017, 32, 597-630. [CrossRef]
- Boixader, D.; Recasens, J. Vague and fuzzy t-norms and t-conorms, Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2022, 433, 156-175. [CrossRef]
- Grigorenko, O.; Miñana, J.J.; Šostak, A.; Valero, O. On t-Conorm Based Fuzzy (Pseudo)metrics. Axioms 2020, 9, 78. [CrossRef]
- Von Schmidt, B.; Klawonn, F. Construction of fuzzy classification systems with the Lukasiewicz-t-norm. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society-NAFIPS (PEACH FUZZ 2000), Atlanta, GA, USA, 13-15 July 2000. pp. 109-113. ISSN: 10987789. Print ISBN: 0-7803-6274-8. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Y. Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Aggregation Operators Based on the Hamacher t-norm and t-conorm. Symmetry 2018, 10, 189. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ali, Z.; Mahmood, T.; Liu, P. Power aggregation operators based on hamacher t-norm and t-conorm for complex intuitionistic fuzzy information and their application in decision-making problems. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45, pp. 8383-8403. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Mesiarova-Zemankova, A. Choosing t-norms and t-conorms for fuzzy controllers (2007) In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, FSKD 2007, Haikou, Hainan, China, 24-27 August 2007. ISBN: 0-7695-2874-0. [CrossRef]
- Gaxiola, F.; Melin, P.; Valdez, F.; Castillo, O.; Castro, Juan, R. Comparison of T-Norms and S-Norms for interval type-2 fuzzy numbers in weight adjustment for neural networks. Information 2017, 8, pp. 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Olej, V.; Hajek, P. Comparison of fuzzy operators for IF-inference systems of Takagi-Sugeno type in ozone prediction. Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations - 12th INNS EANN-SIG International Conference, EANN 2011 and 7th IFIP WG 12.5 International Conference, AIAI 2011, Corfu, Greece, September 15-18, 2011, Proceedings, Part II. In IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, Part 2.; Lazaros, S. Iliadis, Ilias, Maglogiannis, Harris, Papadopoulos Eds.; Springer, New York LLC, 2011; Volume 364 AICT, Issue PART 2, pp. 92 – 97 ISBN: 978-364223959-5, ISSN:18684238. [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhou, H.; Yan, X. Characterizations for the migrativity of continuous t-conorms over fuzzy implications. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2023, 456, pp. 173 – 196. [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.W. On alpha-cross-migrativity of t-conorms over fuzzy implications. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2023, 466. Art.no. 108463. [CrossRef]
- Yang, E. Fixpointed Idempotent Uninorm (Based) Logics. Mathematics 2019, 7, 107. [CrossRef]
- Massanet, S.; Torrens, J.; Shi, Y.; Van Gasse, B.; Kerre, E.E.; Qin, F.; Baczyński, M.; Deschrijver, G.; Bedregal, B.; Beliakov, G.; Bustince, H.; Fernández, J.; Pradera, A.; Reiser, R.; Hliněná, D.; Kalina, M.; Král’, P.; Drewniak, J.; Sobera, J.; Baczyński, M.; Jayaram, B. Advances in Fuzzy Implication Functions, 1st ed.; (Book Series: Studies in Fuzziness and soft Computing STUDFUZZ, volume 300 Series editor Kacprzyk J); Baczynski, M.; Beliakov, G.; Sola, H.B.; Pradera, A. Eds.; Springer Berlin, Heidelberg Germany, 2013; Volume VII, p. 209, ISBN: 978-3-642-35676-6, e-book ISBN: 978-3-642-35677-3, ISSN: 1434-9922, E-ISSN: 1860-0808. [CrossRef]
- Baczynski, M.; Jayaram, B. Fuzzy Implications, 1st ed.; (Book Series: Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing STUDFUZZ volume 231, Series editor Kacprzyk J); Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume XVIII, p. 310; ISBN: 978-3-540-69080-1, e-book ISBN: 978-3-540-69082-5, ISSN: 1434-9922, E-ISSN: 1860-0808. [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, G.; Montagna, F. Substructural Fuzzy Logics. Journal of Symbolic Logic 2007, 72, 834–864. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Aguilera, D., Torrens, J. Residual implications and co-implications from idempotent uninorms. Kybernetika, 2004, 40, 21–38. ISSN: 0023-5954.
- Grammatikopoulos, D.S.; Papadopoulos, B.K. A Method of Generating Fuzzy Implications with Specific Properties. Symmetry 2020, 12, 155. [CrossRef]
- Massanet, S.; Torrens, J. The law of importation versus the exchange principle on fuzzy implications. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2011, 168, 47-69. [CrossRef]
- Mayor, G. “Sugeno’s negations and t-norms”. Mathware and Soft Computing 1994, 1, 93–98.
- Smets, P.; and Magrez, P. Implications in fuzzy logic. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 1987 1, 327-347. [CrossRef]
- Cintula, P. Weakly Implicative (Fuzzy) Logics I: Basic properties. Archive for Mathematical Logic 2006, 45, 673-704. [CrossRef]
- Klir, G.J.; and Yuan, Bo. Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy Logic: Theory and Applications, 1st Ed.; Prentice Hall Press, UpperSaddle River, New Jersey, United States, 1995; pp. 574. ISBN-10 0131011715, ISBN-13 978-0131011717.
- Trillas, E.; Mas, M.; Monserrat, M.; Torrens, J. On the representation of fuzzy rules. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 2008, 48, 583–597. [CrossRef]
- Botzoris, G.; Papadopoulos, B. Fuzzy Sets: Applications in Design-Management of Engineer Projects, 1st ed.; Sofia : Greece, Xanthi, 2015; p. 424, ISBN-13: 9789606706868 (In Greek).
- Dombi, J.; Jónás, T. On a strong negation-based representation of modalities. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2021. 407, 142–160. [CrossRef]
- Asiain, M.J.; Bustince, H.R.; Mesiar, R.; Kolesárová, A.; Takác, Z. Negations with respect to admissible orders in the interval-valued fuzzy set theory. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems 2018, 26, 2, 556-568, ISSN:10636706. [CrossRef]
- Bustince, H.; Burillo, P.; Soria, F. Automorphisms, negations and implication operators. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2003, 134, 2, 209-229, ISSN: 01650114. [CrossRef]
- Drygas, P. Some remarks about idempotent uninorms on complete lattice. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Proceedings of the 10th Conference of the European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology, Warsaw, Poland 11-15 September 2017; In Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Technology 2017, Proceedings of the EUSFLAT 2017 and 16th International Workshop on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets and Generalized Nets (IWIFSGN 2017), Warsaw, Poland 13-15 September 2017; Kacprzyk, J., Szmidt, E., Zadrozny, S., Atanassov, K.T, Krawczak, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, volume 641, p.p. 648-657, ISSN 21945357, ISBN 978-331966829-1. [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://freemeteo.gr/mobile/kairos/kavala/istoriko/imerisio-istoriko/?gid=735861&station=5222&date=2023-08-01&language=greek&country=greece&fbclid=IwAR3Ph3AbGLWjGn39AWnLMqarYsgjypBRAtAG9gtcEITSWAVkDwEz4Hffn7M (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Available online: https://freemeteo.gr/mobile/kairos/kavala/istoriko/imerisio-istoriko/?gid=735861&station=5222&date=2024-01-01&language=greek&country=greece&fbclid=IwAR3Ph3AbGLWjGn39AWnLMqarYsgjypBRAtAG9gtcEITSWAVkDwEz4Hffn7M (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Baczynski, M.; Jayaram, B.; Massanet S.; Torrens, J. Fuzzy Implications: Past, Present, and Future. In Springer Handbook of Computational Intelligence Part of the Springer Handbooks book series (SHB), 1st ed.; Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp.183-202. ISBNonline: 978-366243505-2, ISBNprint:978-366243504-5. [CrossRef]
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 23 | 22 | 1 | 8 |
| Max | 22 | 22 | 0 | 9 |
| Einstein | 21 | 20 | 1 | 10 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 15 | 15 | 0 | 16 |
| Max | 15 | 15 | 0 | 16 |
| Einstein | 12 | 12 | 0 | 19 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 9 | 4 | 5 | 22 |
| Max | 9 | 4 | 5 | 22 |
| Einstein | 5 | 0 | 5 | 26 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 7 | 4 | 3 | 24 |
| Max | 6 | 4 | 2 | 25 |
| Einstein | 3 | 0 | 3 | 28 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 20 | 17 | 3 | 11 |
| Max | 20 | 17 | 3 | 11 |
| Einstein | 20 | 17 | 3 | 11 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 14 | 9 | 5 | 17 |
| Max | 12 | 9 | 3 | 19 |
| Einstein | 14 | 8 | 6 | 17 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 12 | 2 | 10 | 19 |
| Max | 6 | 2 | 4 | 25 |
| Einstein | 6 | 0 | 6 | 25 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
| Fuzzy Implications | and < 1 | < 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probor | 14 | 2 | 12 | 17 |
| Max | 7 | 2 | 5 | 24 |
| Einstein | 7 | 0 | 7 | 24 |
| Lukasiewicz | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





