1. Overview
Number theory, " the queen of mathematics
" studies the structures and properties defined on
integers and primes (see Euclid [11],
Hadamard [13], Hardy,
Wright [14], Landau [20], Tchebychev [32]). Numerous
problems have been raised and conjectures made, the statements of which are
often simple but very difficult to prove. These main components include :
Elementary arithmetic :
* Determination and properties of primes, operations on integers (basic operations, congruence, gcd, lcm, ………..).
* Decomposition of integers into products or sums of primes (fundamental theorem of arithmetic, decomposition of large numbers, cryptography, and Goldbach's conjecture).
Analytical number theory :
* Distribution of primes (Prime Number Theorem, Hadamard [
13], De la Vallée-Poussin [
33],
Littlewood [
23] and Erdos [
10], The Riemann hypothesis).
* Gaps between consecutive primes, Bombieri, Davenport, [
3], Cramer [
8], Baker, Harmann, Iwaniec, Pintz [
4], [
5],[
18] , Granville [
12], Shanks [
27], Tchebychev [
32] and Zhang [
36].
Algebraic, probabilistic, combinatorial and algorithmic number theories.
* Modular arithmetic, diophantine approximations, equations, arithmetic functions and algebraic geometry.
2. Definitions, Notations and Background
(2.1) The integers n, k, p, q, r,…….. used in this article are always positive.
(2.2) Let the infinite set of positive primes (called simply primes) :
( = 2 ; = 3 ; = 5 ; = 7 ; = 11 ; = 13 ; ......... ).
(2.3) The writing of large numbers (see appendix 10) is simplified using the following constants
M = ; R = 4. ; G = ; S = ; T = 10 1000
(2.4) ln(x ) denotes the neperian logarithm of the strictly positive real x , (x > 0).
(2.5) Let ( ) be the sequence of primes defined by :
(2.5.1) For any integer n ≥ 3, = Sup( p ∈ : p ≤ 2n - 3 )
(2.6) Any sequence denoted by () = () verifying (2.6.1) is called a Goldbach sequence.:
(2.6.1) ( For any integer nand are primes and + = 2n ).
(2.7) Iwaniec , Pintz [
18] have shown that for a sufficiently large integer
n there is always a prime between
n − and
n . Baker, Harman [
4], [
5] concluded that, there is a prime in the interval
[n ; n + o ( Thus this results provides an increase of the gap between two consecutive primes and of the form :
(2.7.1)
> 0
∈
such that : ∀ k ∈
with k >
-
<
(2.8) According to the Cramer-Maier-Nicely conjecture [
1], [
3], [
8], [
12], [
24], [
25],
for any real c > 2 , for any integer k ≥ 500 ,
(2.8.1) - ≤ 0.7 (with probability one).
3. Introduction
Chen [
6], Hardy, Littlewood [
15], Hegfollt, Platt [
16], Ramaré, Saouter [
26], Tao [
31], Tchebychev [
32] and Vinogradov [
34] have taken important steps and obtained promising results on the Goldbach conjecture. Indeed, Helfgott, Platt [
16] proved the weak Goldbach conjecture in 2013.
Silva, Herzog, Pardi [
29]held the record for calculating the terms of Goldbach sequences after determining pairs of primes (
) verifying :
(3.1) For any integer n, (4 ≤ 2n≤ 4.1018) : ( + = 2n ) .
In previous research work, there is no explicit construction of recurrent sequences of Goldbach primes of the form : () = (; ) satisfying for any integer n ≥ 2 the equality : ( + = 2n ).
In this article, two sequences of primes are developed using a simple and efficient algorithm to compute for any integer
n by successive iterations any term
and
of a Goldbach sequence. Using Maxima scientific software on a personal computer, Silva's record is broken, and the values 2
n = 10
500 and even 2
n = 10
1000 are reached. The proof of the binary Goldbach conjecture can be established on the same principle, using reasoning by recurrence. Moreover, the Lagrange-Lemoine-Lévy conjectures [
9], [
17], [
19], [
24], [
25], [
30], [
35] and its generalization, the Bezout-Goldbach conjecture are validated.
Using case disjunction reasoning, we construct two recurrent sequences of primes () and ()
according to the sequence () by the following process. For any integer n ≥ 2 ,
(3.2) ( = 2 ; = 2 )
Let n be an integer : (n).
1 Either,
( 2n - ) is a prime, then and are defined directly in terms of .
2 Either,
( 2n - ) is a composite number, then and are defined from the preceding terms of the sequence ().
4. Principle of Proof
To determine pairs of primes that verify the Goldbach conjecture, three sequences of primes (( ), ( are defined and verify the following properties :
(4.1) lim = +(4.2) For any integr n ≥ 2 , is defined as a function of = Sup( p ∈ Ƥ : p ≤ 2n - 3 ).
(4.3) ( ) is an increasing sequence that contains all primes except the prime = 2.
(4.4) lim (4.5) ( ) is a complementary sequence of negligible primes with respect to (2n).
(4.6) For any integer n ,
If ( 2n - ) is a prime " special case ",
then and are defined by :
(4.7) = and = 2n - Otherwise, if ( 2n - ) is a composite number “general case”
we search for two previous terms of the sequence (), ) and satisfying the following conditions :
(4.8) , and + 2k are primes + = 2( n - k )
( which is always possible ; see the proof in Theorem 5 ).
Thus, by setting :
(4.9) = and = + 2k
two new primes and satisfying (4.10) are generated.
(4.10) + = 2n .
This process is then repeated, incrementing n by one unit : ( n → n + 1 ).
5. Theorem
There exists a recursive Goldbach sequence of primes () = ( for any integer
n ≥ :
and are primes and their sum is equal to 2n.
(5.1) ( ,
and + = 2n )
(5.2) An algorithm can be used to explicitly compute any term and .
Proof of Theorem 5.
FIRST METHOD :
For any integer n ,
If ( 2n - ) is a prime,
then and are defined by :
(5.3) = and = 2n - Otherwise, if (2n - ) is a composite number ,
we use the previous terms of the sequence ().
For any integer q such that : (1 ≤ q ≤ n - 3) , we have : 3 ≤ ≤
n .
For any integer k such that (4 ≤ 2k ≤ n - 1) , there are two primes and (m > r )
in the interval [4 ; n ] such that :
(5.4) - = 2k
(see Bombieri, Davenport [
1], Cramer [
8], Iwaniec, Pintz [
18] , Tchebychev [
32]).
Then there is an integer k verifying , (4 ≤ 2k ≤ n - 3) such that :
(5.5) = + 2k is a prime
The smallest integer k denoted such that is a prime is chosen. So let :
(5.6) = + 2 and = ( These two terms are primes )
In the previous steps two primes and whose sum is equal to 2(n - ) were determined.
(5.7) + = 2(n -)
By adding the term to each member of the equality (5.6), it follows :
(5.8) + 2 + = 2(n - ) + 2(5.9) [ + 2] + = 2n
(5.10) + = 2n
Finally, for any integer n ≥ 3, this algorithm determines two sequences of primes () and () verifying Goldbach's conjecture.
SECOND METHOD :
The demonstration can be made using the following strong recurrence principle.
Let P(n) be the following property defined for any integer n ≥ 2 by :
P(n ) : “ For any integer p satisfying : (2 ≤ p ≤ n) , there exists two primes and such their sum is equal to 2p : ( + = 2p) “ .
Let's show by strong recurrence that P(n) is true for any integer n ≥ 2 .
a) P(2) is true : it suffices to choose = = 2 .
b) Let's show that the property P(n) is hereditary : ( i.e for any integer n ≥ 2 P(n) (n+ 1))
Assume property P(n ) is true,
If ( 2(n + 1) - ) is a prime,
then and are defined by :
(5.11) = and = 2(n+1) - Otherwise, if (2(n+1) - ) is a composite number ,
There exists an integer k to obtain two terms ) and satisfying the following conditions :
(5.12) , and + 2k are primes + = 2( n +1- k )
(which is always possible : see first method ).
Thus, by setting :
(5.13) = and = + 2k
two new primes and satisfying ( + = 2(n + 1)) are generated.
It follows that P(n + 1) is true, then the property P(n ) is hereditary : ( P(n) => P(n + 1) ).
Therefore, for any integer n ≥ 2 the property P(n) is true ; it follows that :
n ≥ 2 there are two primes and and such their sum is 2n : ( + = 2n)
6. Lemma
The sequence () verifies the following increase : For any integer n ≥ 65 ,
(6.1) ≤ (2
Proof of Lemma 6.
According to the programm 9.2 and appendix 10, the increase (6.1) is verified for any integer n such that : (65 ≤ n ≤ 2000) . For any integer n > 2000 , the proof is established by recurrence. For this purpose, let P1(n) be the following property :
(6.2) P1(n) : “ There exists a strictly increasing sequence of positive numbers () such that :
≤ “ .
P1(2000) is true according to program 9.2 and the table in appendix 10.
For any integer n ≥ 2000, let’s show that P1(n ) is hereditary , (i.e P1(n ) ⇒ P1(n+1))
Assume that P1(n ) is true : then,
If (2(n + 1) - ) is a prime ,
then and are defined by :
(6.2)
=
and
= 2(
n + 1) -
According to the results in [
4], [
5], [
18], there is a constant
K > 0 such that :
(n + 1) - K < < 2(n + 1)
⇒ < K ⇒ ≤ Otherwise, if (2(n + 1) - ) is a composite number ,
(6.4) p ∈ / = + 2p
According to [
4], [
5], [
18], the smallest integer
p defined in (6.4) verifies:
(6.5) 2p < K ( and < It follows : < K + Then
(6.6) < and, by setting : = it follows :
(6.7) < P1(n + 1) is true then P1(n ) is hereditary. So for any integer n ≥ 2000, the property P1(n ) is true.
(The inequality (6.7) is verified with the aid of the software Maple studying the functions of the type f : x a + b increased by g : x with a , b > 0).
*Remark. A more precise estimate can be obtained using the Cippola or Axler frames, [
7], [
2].
7. Theorem
For any integer n 3 , it is easy to check :
7.1 ( ) is a positive increasing sequence of primes.
7.2 { : n IN* } = 7.3 lim = +oo
7.4 () is a sequence of primes.
The following results are validated with probability one :
7.5 n ≤ 7.6 3n
7.7 lim = +oo
Proof of Theorem 7.
7.1 For any integer n ≥ 2 let be the following set : = { ∈ : ≤ 2n - 3 } .
therefore, ≤ , so the sequence () is a positive increasing sequence of primes.
7.2 Any prime except = 2 is odd, hence the result.
7.3 lim = lim = +oo
7.4 By definition = or there exits an integer k ≤ n - 2 such that : = ; so, by reccurence the terms of the sequence ( ) are primes ; moreover, there exists a strictly increasing sub-sequence ( ) of ( ) verifying lim ( ) = +oo
7.5 According to Lemma 6, for any integer n ≥ 65 , < ;
therefore < < n and,
= 2n - > 2n - n > n.
For any integer n / (3 ≤ n ≤ 65) verification is carried out according to the computer program in paragraph 9.2 and the table in appendix 10.
7.6 According to 7.5, n ⇒ = 2n - ≤ 2n - n ≤ n ;
moreover,
≤ ⇒ 2n - ≤ 2n - = 7.7 By 7.5, for any integer n ≥ 2 , n ;
so,
lim ( ) = +oo .
8. Remarks
8.1 There are infinitely many integers n such that : = 3, 5, 7 or 11.
8.2 ~ 2n for (n +oo) .
8.3 For any sufficiently large integer n , (n ≥ 5000) : and lim () = 0.
8.4 The smallest integer n such that :
2n - is obtained for n = 49 and = (79 ; 19).
(This type of terms increases in the Goldbach sequence (
) as n increases, in the sense of the Schnirelmann density, and there are an infinite number of them; their proportion per interval can be computed using the results given in [
28]).
8.5 If q ≥ 5 is an odd integer, we could generalize this algorithm with sequences ( ) defined by :
(8.6.1) n ∈ with n ≥ = Sup( p ∈ : p ≤ 2n - q )
Other sequences of Goldbach independent of ()are thus generated.
8.6 The sequence ( ) is extremal in the sense that for any integer n and are the largest
and smallest possible primes such that : + = 2n.
8.7 The Cramer-Maier-Nicely conjecture [
8], [ 12 ], [17 ], [
19], [
21], [
22], [
24], [
25], [
30] is verified with probability one. It leads to the following increase : For any integer
p ≥ 500 ,
(8.7.1 ≤ 0.7( (with probability one )
The proof is similar to that of Lemma 6 using the same type of reasoning by recurrence, validated by the study of functions of the type : f : x a g (x ) + b with a ,b > 0 and c > 2 ,
with g : x 0.7( l and h : x 0.7 using Maple software.
* A better estimate can be obtained via [
24], [
25], [
27] .
8.8 According to Bombieri [
3] and using the same method as in the proof of Lemma 6,
on average, we obtain the following estimate of :
(8.8.1) > 0 , = O () , (on average)
9. Algorithm
9.1. Algorithm Written in Natural Language
Inputs :
Input four integer variables : k, N, n, P.
Input : = 2 , = 3 , = 5 , 7 , ................., the first N primes.
: n = 3.
: P = M, R, G, S or T as indicated in paragraph 2Algorithm body :
A Compute : = Sup( p : p ≤ 2n - 3 )
If = (2n - ) is a prime,
Let :
(9.1.1) = and = otherwise ,
B If is a composite number,
Let : k = 1.
B.1) While + 2k is a composite number,
assign to k the value : k + 1 , ( k k + 1 ).
return to B1)
End while .
Assign to k the value : ( k )
(9.1.2) Let : = + 2 and = Assign to n the value n + 1 , ( n and return to A)
End :
Outputs for integers less than Print ( 2n = ... ; 2n - 3 = ... ; = ... ; = ... ; = ... ; = ... ).
Outputs for large integers :
Print ( 2n - P = ... ; 2n - 3 - P = ... ; - P = ... ; = .... ; = ... ).
9.2. Program written with Maxima software for 2n = .
r : 0 ; n1 : 10**500 ; for n :5*10**499 + 10000 thru 5*10**499 + 10010 do
( k :1 , a :2*n , c :a - 3 , test : 0 , b : prev_prime(a - 1) ,
if primep(a - b)
then print(a - n1 , c - n1 , b - n1 , a - b , b - n1 , a - b)
otherwise ( r :r + 1 ,
while test = 0 do
( if ( primep(c ) and primep(a - c ) )
then ( test:1 , print(a-n1 , a-n1-3 , b-n1 , a-b , c-n1 , a-c ," ** " , r))
else ( test : 0 , c : c - 2*k ))) ) ;
10. Appendix
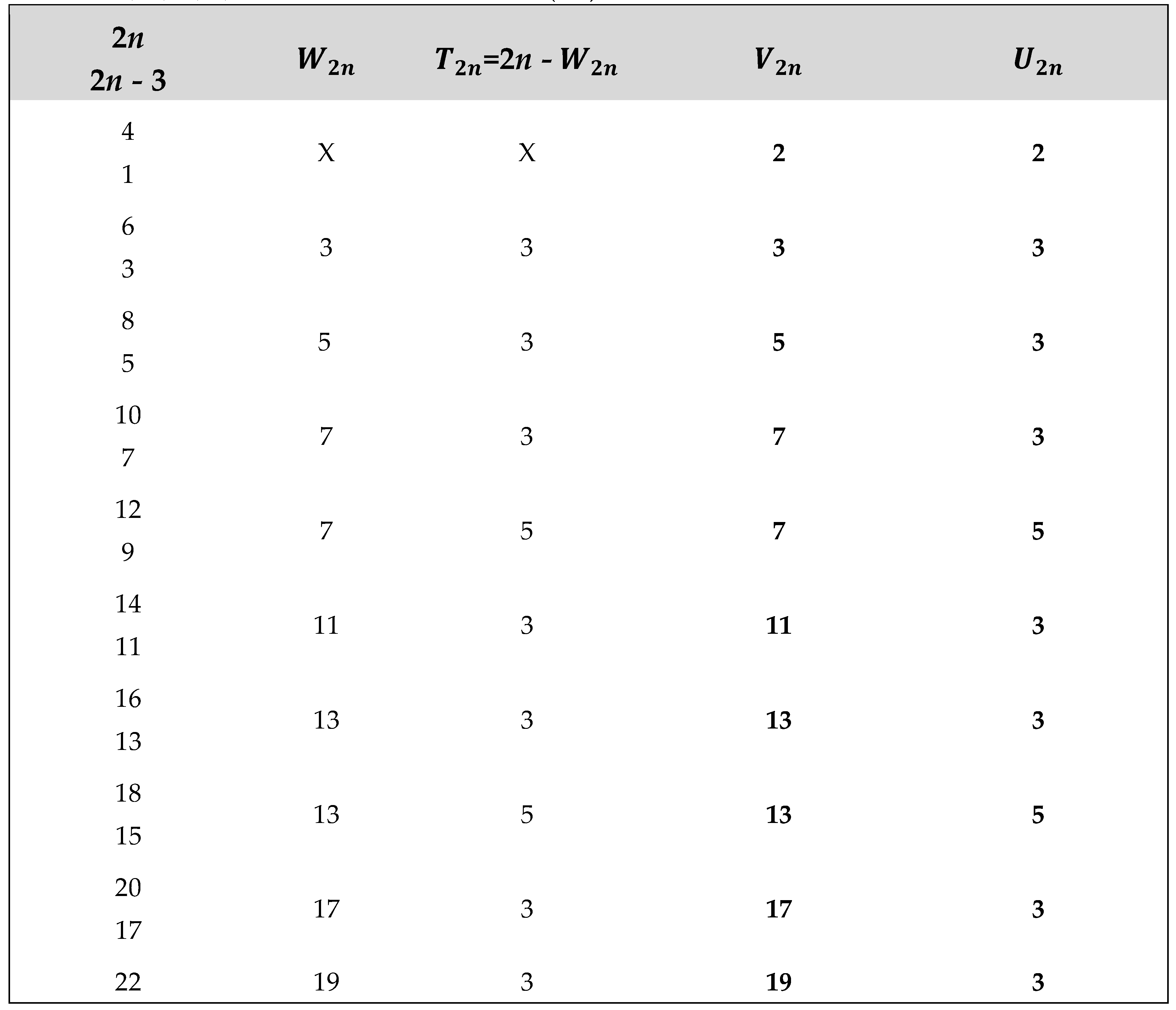
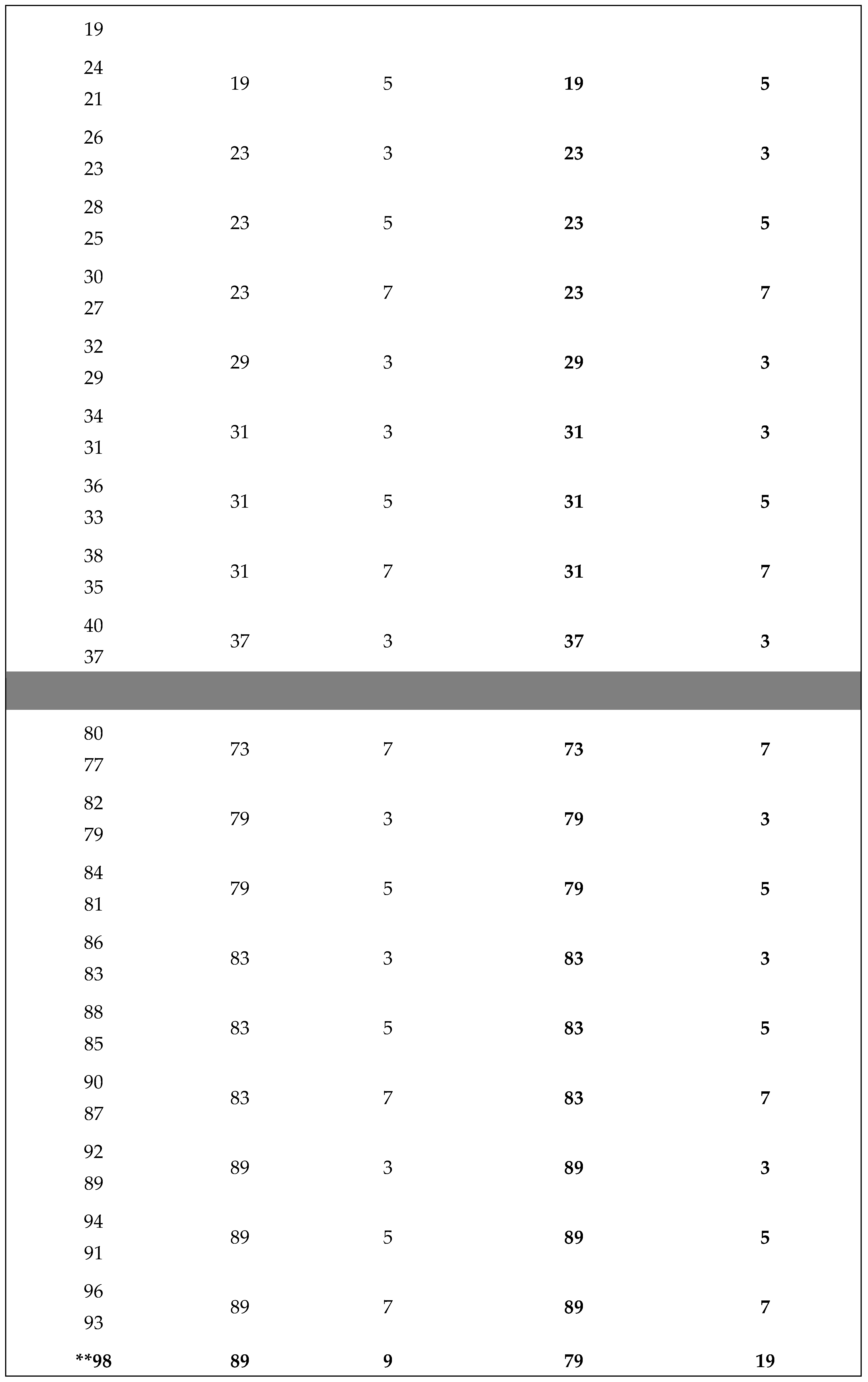
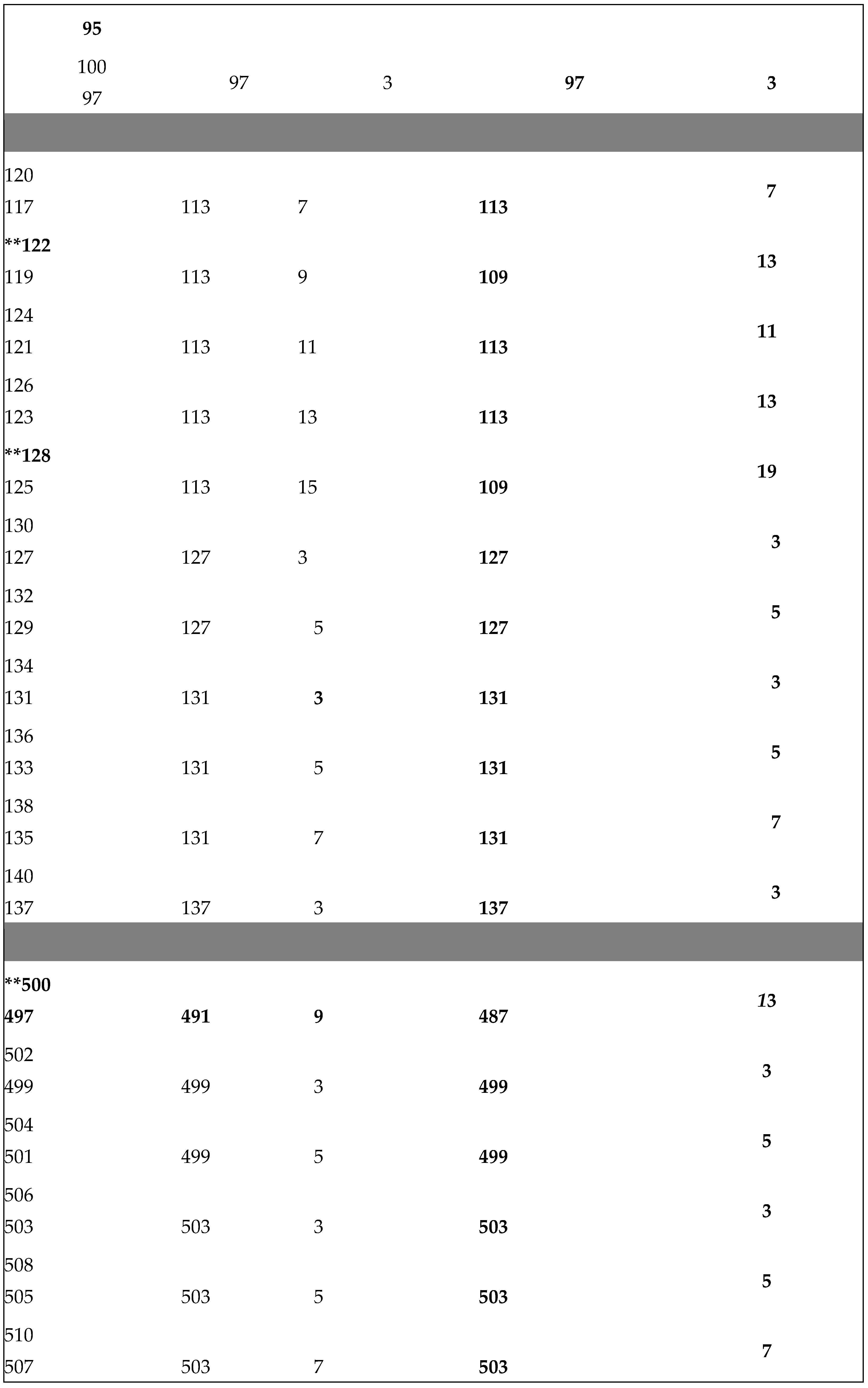
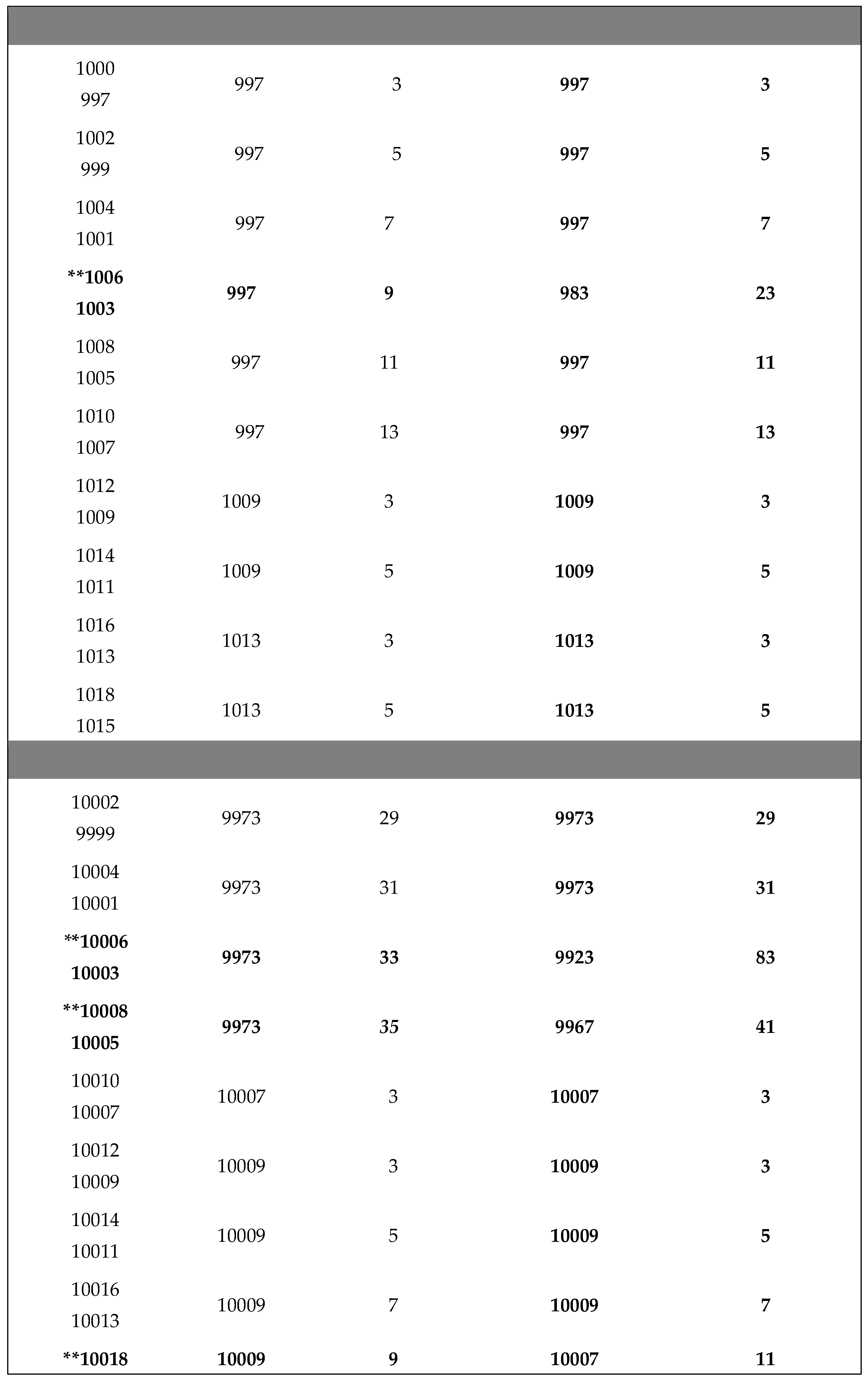
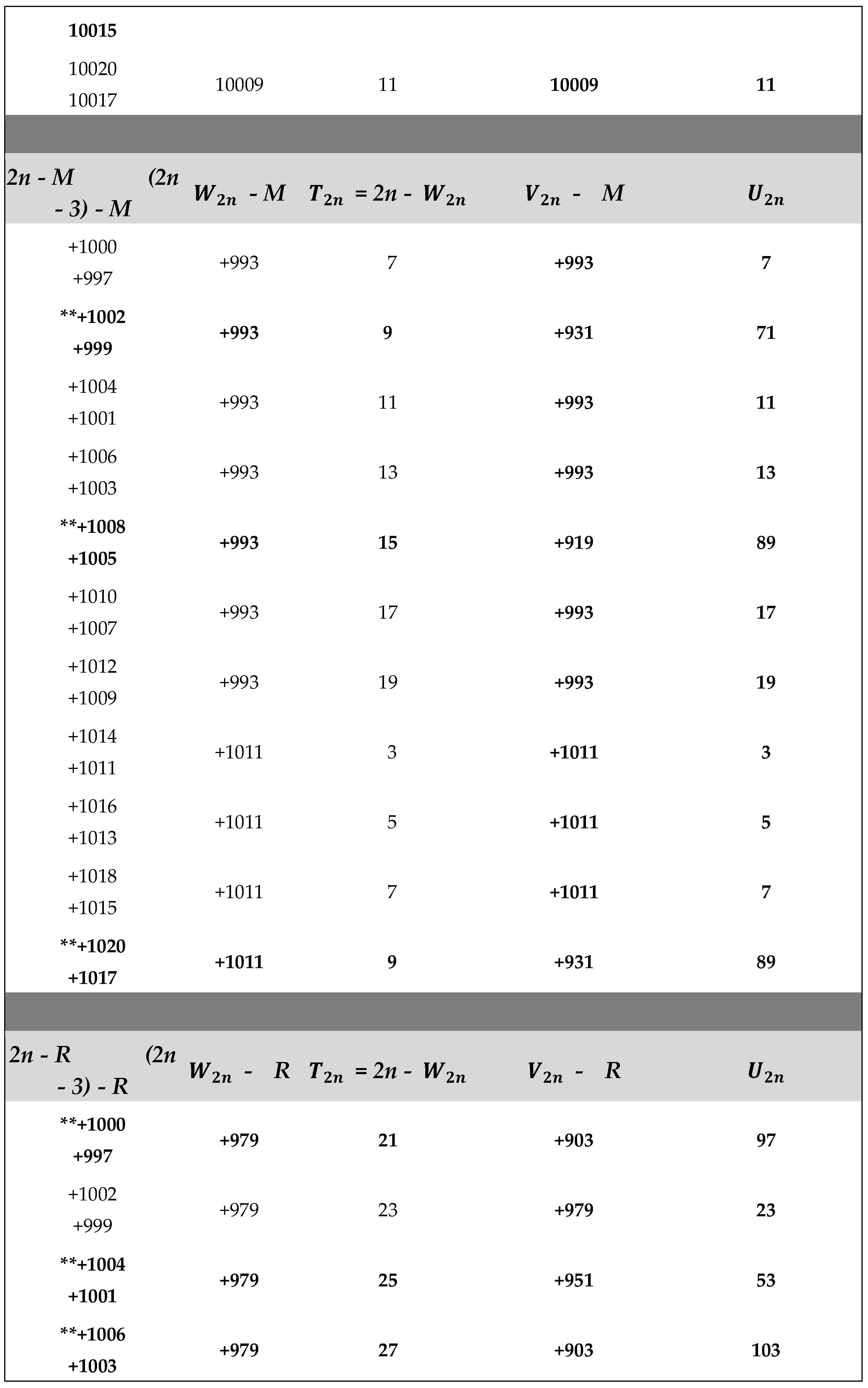
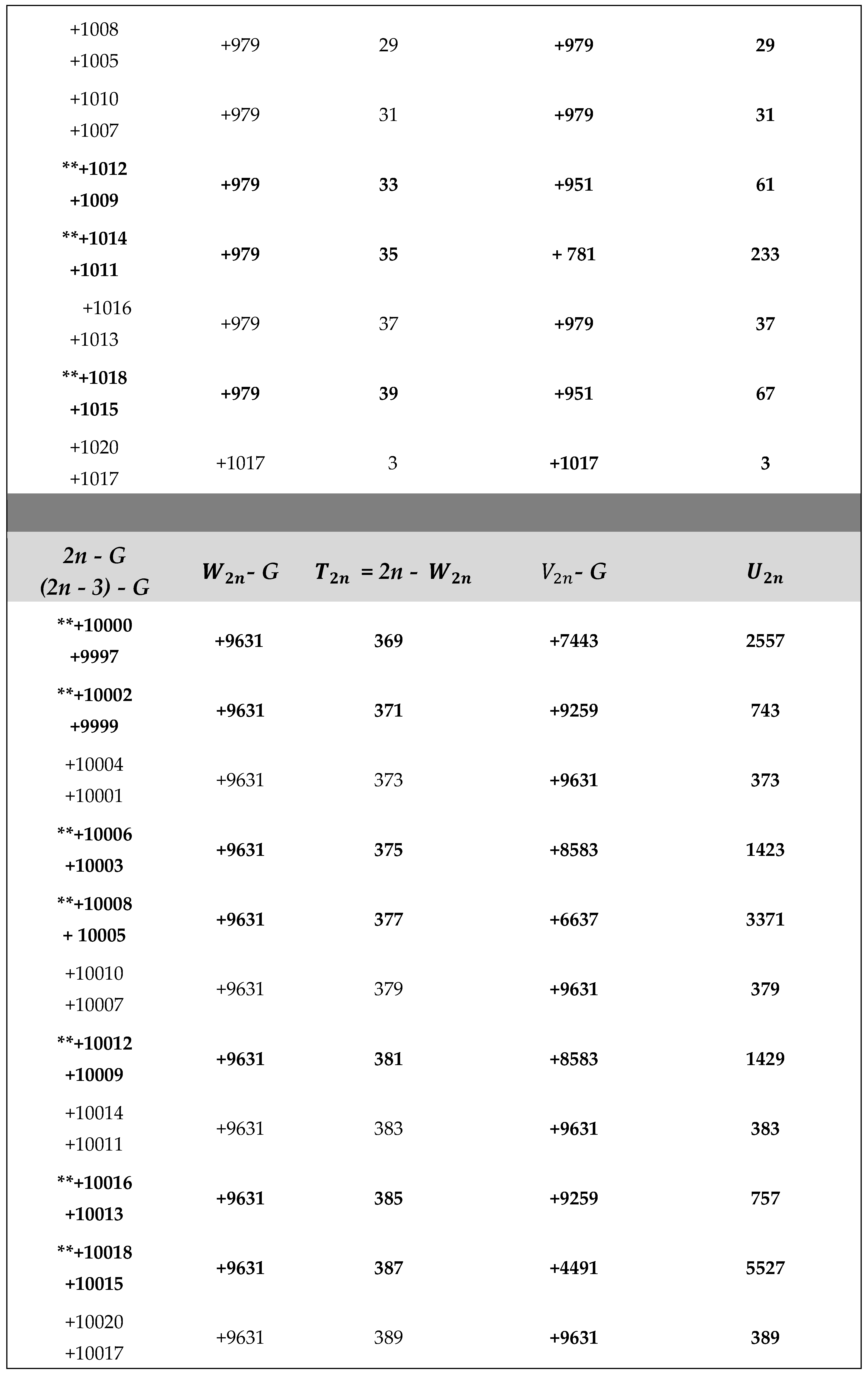
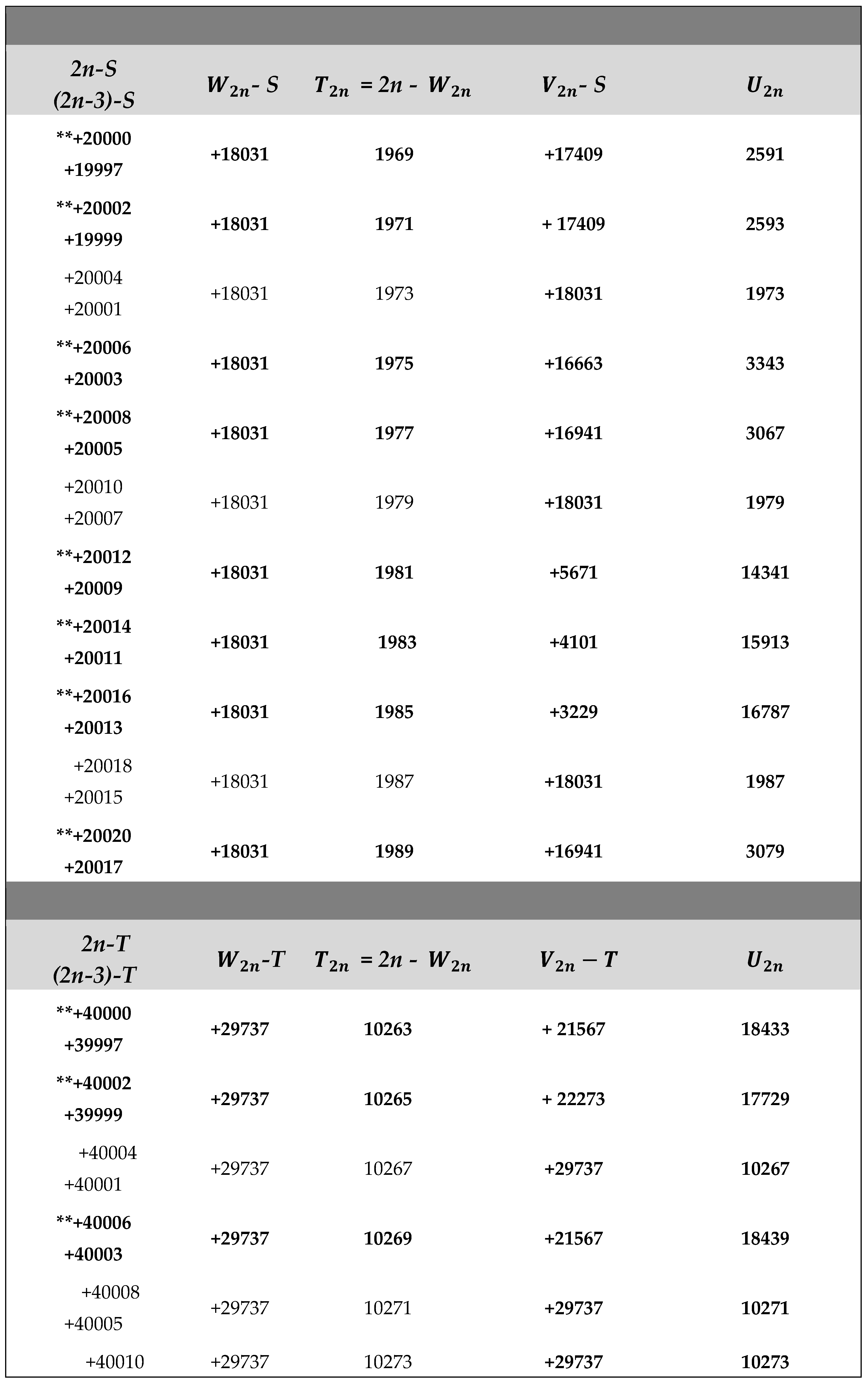
Application of Algorithm 9 : Table of and terms of the Goldbach sequence () computed from program 9.2 , ( 2 ≤ 2n ≤ + 4020).
The ** sign in the table below indicates the results given by the algorithm 9 in case B) of return to the previous terms of the sequence (. WATCH OUT ! , for large integers n (2n > for example), to simplify the display of large numbers, the results are entered as follows :
2n - P , (2n - 3) - P , - P , , - P and with ,
P = M, R, G, S,or T constants defined in (2.3).
11. Perspectives and Generalizations
11.1 Other Goldbach sequences () and () independent of may be studied using the increasing sequences of primes ( and () defined by :
For any integer n = Sup( p f (n) ), f being a function defined on the interval
I = [3 ; +[ and satisfying the following conditions:
* f is strictly increasing on the interval I .
* = + f (3) = 3 .
*
For example, one of the following functions defined on I can be selected.
- (a)
f : x a x + 3 - 3a ; (a : 0 < a
- (b)
g : x[49] ( [x ] being the integer part of the real number x ).
- (c)
h : x + 3 .
11.2 Using this method, it would be interesting to study the Schnirelmann density [
28] of certain primes such as 3 , 5 , 7, 11
,..... ... in the sequence (
) for
n [
; ] as a function of
N .
11.3 It is possible to exceed the values shown in the table (2n = ) by optimizing this algorithm, Maple .
11.4 Diophantine equations and conjectures of the same nature (Lagrange-Lemoine-Levy conjecture [
9], [
17], [
19],[
21],[
22], [
30]) can be processed using similar reasoning and algorithms.
1) To validate the Lagrange_Lemoine-Levy conjecture, we can study the following sequences of primes (), ( (= Sup( p a) If = (2n + 1 - 2 ) is aprime , then let : = and = b) If is a composite number, then there exists an integer k , (1 such hat :
+ 2k is a prime ; then let : = and =+ 2k .
2) Using the same type of reasoning , a generalized Bezout-Goldbach conjecture of the following form can be validated :
a) Let K and Q be two odd integers, prime to each other : for any integer n such that : 2n(K + Q), there exist two primes and verifying :
K + Q = 2n.
b) Let K and Q be two integers of different parity, prime to each other : for any integer n such that :
2n (K + Q ), there are two primes and verifying:
K + Q = 2n + 1.
12. Conclusion
12.1 An unique recursive and explicit Goldbach sequence () = (; ), verifying :
( n ∈ and are primes += 2n) ,
has been developed using an simple and efficient "local" algorithm.
12.2 Silva's [
29] record is broken on a personal computer, and it is possible to reach values of the order of 2
n =
with a reasonable computation time (
less than three hours for the evaluation of ten terms
and
) .
12.3 For a given integer n ≥ 49 , the evaluation of the terms and does not require the computing of all previous terms and , (1 k < n - 1). we just need to know the primes , such that :
(12.3.1) ≤ 7( and 2n - 7( ≤ ≤ 2n (on average ).
This property allows quick computing of and even for values of 2n of the order of .
12.4 Therefore, the binary Goldbach and the Lagrange-Lemoine-Levy conjectures are true.
References
- L. Adleman, K. L. Adleman, K. Mc Curley, Open Problems in Number Theoretic Complexity, II. Algorithmic number theory (Ithaca, NY,1994), 291–322, Lecture Notes in Comput. Sci., 877, Springer, Berlin, (1994).
- C., Axler. New Estimates for the nth Prime” 19.4.2 2. Journal of Integer Sequences 2019, 22, 30. [Google Scholar]
- E. Bombieri, Davenport, "Small differences between prime numbers", Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser. A293, pp. 1-18, (1966).
- R. C. Baker, and Harman, G. The difffference between consecutive primes. Proc. London Math. Soc. 1996, 72, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. C. Baker, Harman, G., and Pintz, J. “The difffference between consecutive primes”. II. Proc. London Math. Soc. 2001, 83, 532–562.
- J. R. Chen, "On the representation of a large even integer as the sum of a prime and the product of at most two primes". Kexue Tongbao 17 (1966), pp. 385-386 (Chinese).
- M. Cipolla, “La determinazione assintotica dell n imo numero primo”, Rend. Acad. Sci. Fis. Mat. Napoli 8(3) (1902).
- H. Cramer, "On the order of magnitude of the difference between consecutive prime numbers", Acta Arithmetica vol. 2, (1986), p.23-46.
- N. Dawar, “Lemoine's Conjecture: A Limited Solution Using Computers”, TechRxiv [ Archive online ] (2023).
- P. Erdos. On a new method in elementary number theory which leads to an elementary proof of the prime number theorem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1949, 36, 374–384. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euclid, (trans. Bernard Vitrac), "Les éléments d'Euclide", Ed. PUF Paris, vol.2, p. 444-446 and p. 339-341, (1994).
- A. Granville, "Harald Cramér and the distribution of prime numbers", Scandinavian Actuarial Journal, 1995, 1, 12–28.
- J. Hadamard, "On the zeros of the function ζ(s) of Riemann". C. R. 122, p.1470-1473 (1896), and "On the distribution of zeros of the function ζ'(s) and its arithmetical consequences". S. M. F. Bull. 24, pp. 199-220 (1896).
- G. H. Hardy & Wright , "An introduction to the Theory of numbers", Oxford : Oxford University Press 621 p. (2008).
- G. H. Hardy, J. E. Littlewood: Some problems of 'partitio numerorum'; III: On the expression of a number as a sum of primes (Acta Math. Vol. 44: pp. 1 – 70, (1922).
- H. Helfgott, Platt, The ternary Goldbach conjecture", Gaz. Math. Soc. Math. Fr. 140, pp. 5-18 (2014). "The weak Goldbach conjecture", Gac. R. Soc. Mat. Esp. 16, no. 4, 709-726 (2013). "Numerical verification of the ternary Goldbach conjecture up to 8.875.1030. Exp. Math. 22, n° 4, 406-409 (2013).
- L. Hodges, "A lesser-known Goldbach conjecture", Math. Mag., 1993, 66, 45–47.
- H. Iwaniec, Pintz, Primes in short intervals. Monatsh. Math. 1984, 98, 115–143. [CrossRef]
- J. O. Kiltinen and P. B. Young, "Goldbach, Lemoine, and a Know/Don't Know Problem", Mathematics Magazine, 58(4) (Sep., 1985), p. 195–203.
- E. Landau, "Handbuch der Lehre von der Verteiligung der Primzahlen", vol. 1 and vol. 2 (1909), published by Chelsea Publishing Company (1953).
- E. Lemoine, “L’intermédiaire de mathématiciens”, vol. 1, 1894, p. 179, vol. 3, 1896, p. 151.
- H. Levy, “On Goldbach’s conjecture”, Math. Gaz." 1963, 47, 274.
- J., Littlewood. Sur la distribution des nombres premiers. CRAS Paris 1914, 158, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar]
- H. Maier. Primes in short intervals. Michigan Math. J. 1985, 32, 221–225. [CrossRef]
- T. R. Nicely, "New maximal prime gaps and first occurrences", Mathematics of Computation, 68 (227): 1311–1315, (1999).
- O. Ramaré, Saouter, "Short effective intervals containing primes", J. Number theory, 98, No. 1, p..10-33 (2003).
- D. Shanks, "On Maximal Gaps between Successive Primes", Mathematics of Computation, American Mathematical Society, 18 (88): 646–651, (1964).
- L. Schnirelmann, "Schnirelmann density", Wikipedia, (on line, internet) and "A proof of the fundamental theorem on the density of sums of sets of positive integers", Annals of Math, 2nd series, vol. 43, no. 3, (1942), pp. 523-527.
- T. O. e Silva, Herzog, Pardi, "Empirical verification of the even Goldbach conjecture and computation of prime gaps up to 4.1018. Math. Comput. 83, no. 288, pp. 2033-2060 (2014).
- Z-W. Sun, "On sums of primes and triangular numbers" » [archive], arXiv, 2008 (arXiv 0803.3737).
- T. Tao, "Every odd number greater than 1 is the sum of at most five primes", Math. Comput. 83, no. 286, pp.997-1038 (2014).
- P. Tchebychev, "Mémoire sur les nombres premiers" J. math. pures et appliquées, 1ère série, t.17, p. 366-390 et p. 381-382, (1852).
- C.- J. de La Vallée-Poussin, "Recherches analytiques sur la théorie des nombres premiers", Brux. S. sc. 21 B, pp. 183-256, 281-362, 363-397, vol.21 B, pp. 351-368, (1896).
- A. Vinogradov, "Representation of an odd number as a sum of three primes". Dokl. Akad.Nauk. SSR, 15:291-294, (1937).
- E.W. Weisstein, "Levy's Conjecture" » [archive], sur MathWorld, CRC Concise Encyclopédie de mathématiques (CRC Press, ), 733-4, (1999).
- Y. Zhang, "Bounded gaps between primes", Ann. Math. (2) 179, no. 3, pp.1121-1174 (2014).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).