Submitted:
14 October 2024
Posted:
15 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model Setup
2.1. General Deterministic Model for Ontogenetic Growth
2.2. Stochastic Models for Ontogenetic Growth
3. Parameter Fitting
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Fitting Method
3.3. Drift Term Fitting
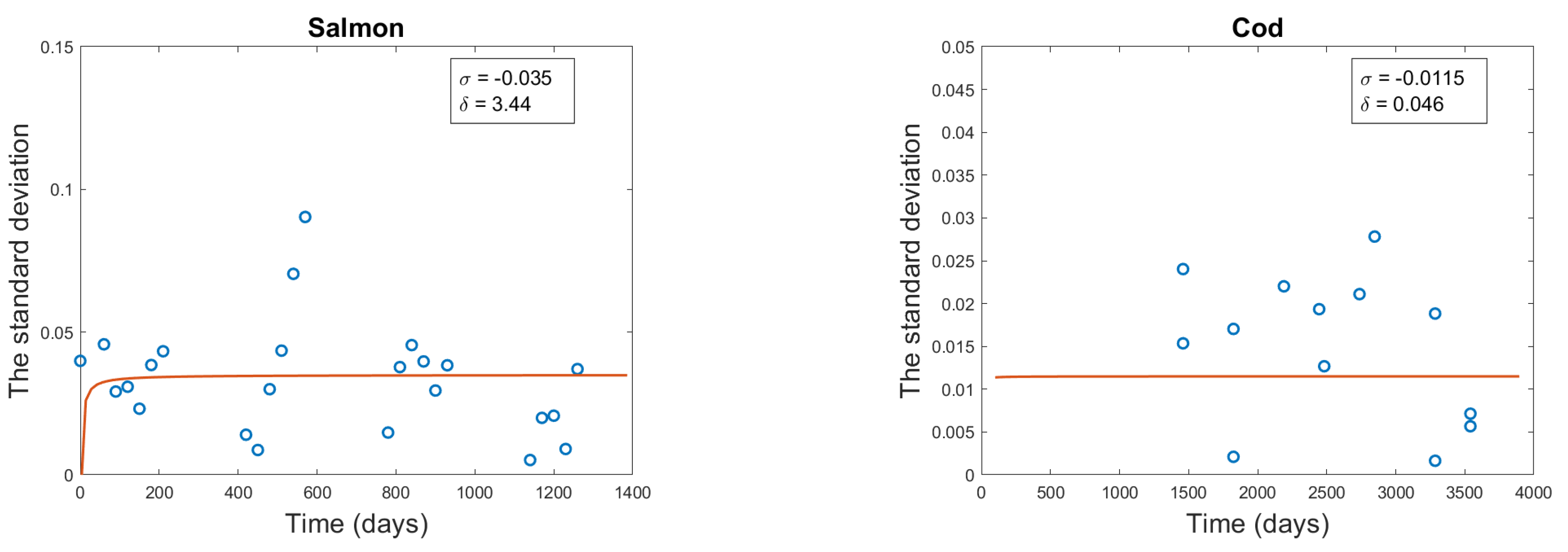
3.4. Diffusion Term Fitting
Noise intensity
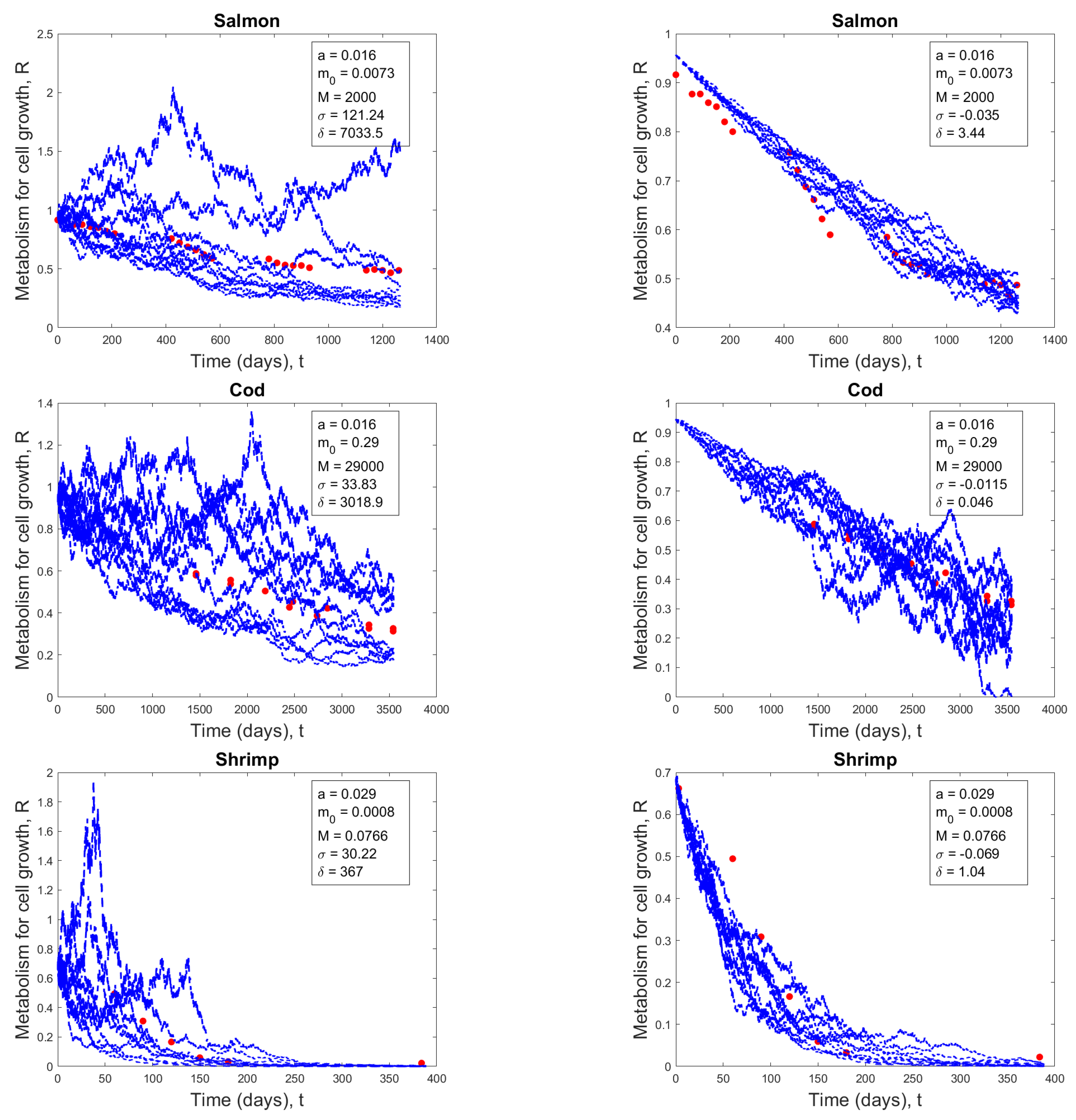
Stochastic solution paths
4. Theoretical Analysis
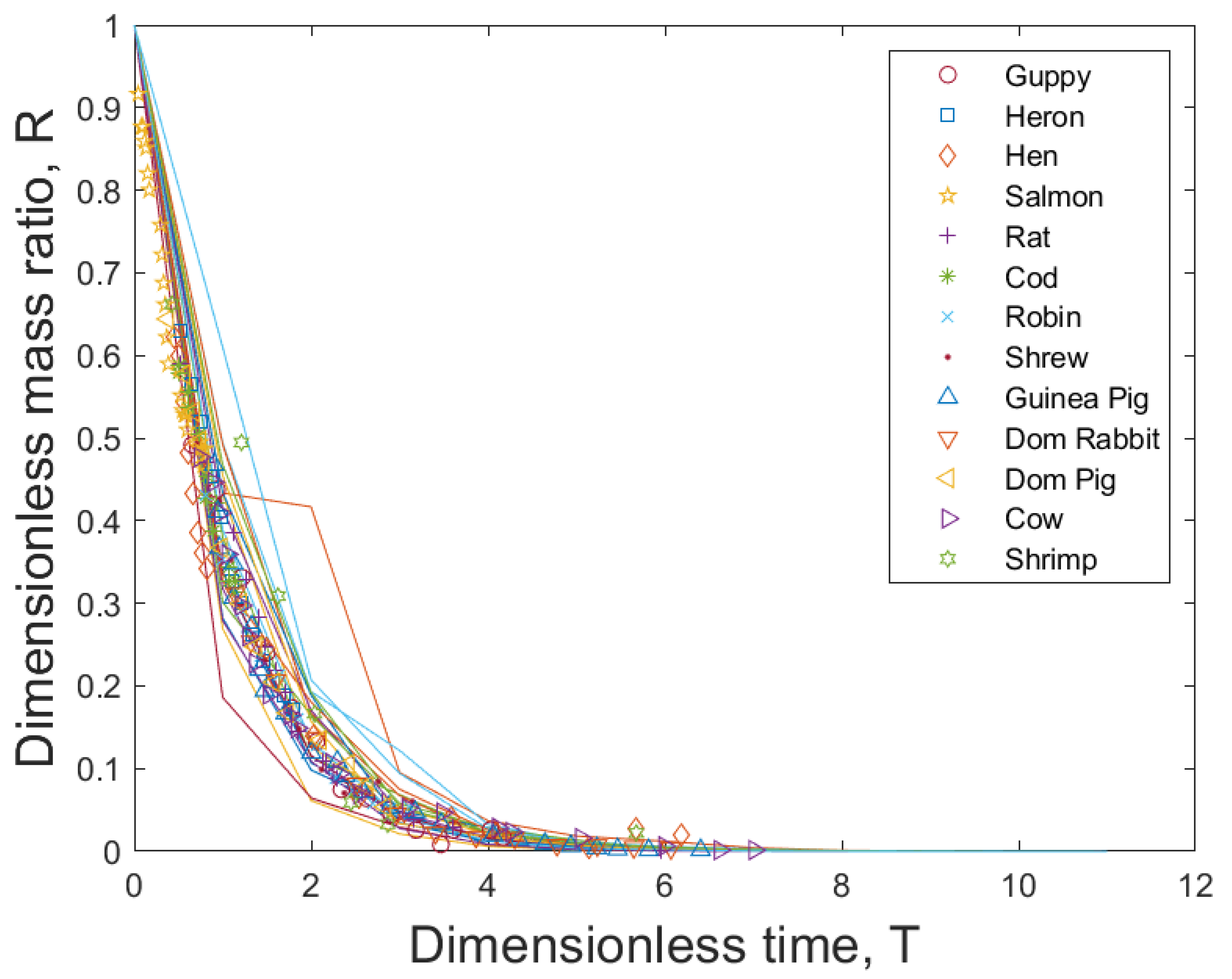
5. Universal Stochastic Growth Process
6. Discussion
Acknowledgments
References
- Carrel, A. (1931) Physiological time. Science 74, 618.
- Brody, S. (1945) Bioenergetics and Growth. Hafner, New York.
- von Bertalanffy, L. (1938) A quantitative theory of organic growth. Human Biology 10, 181–213.
- von Bertalanffy, L. (1957) Quantitative laws in metabolism and growth. Quarterly Review of Biology 32, 217–231.
- Sibly, R.M. & Calow, P. (1987) Growth and resource allocation. Evolutionary Physiological Ecology, pp. 37–52. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Reiss, M.J. (1989) The allometry of growth and reproduction.
- Kooijman, S.A.L.M. (1993) Dynamic Energy Budgets in Biology Systems. Theory and Applications in Ecotoxicology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Ricklefs, R.E. (1967) A graphical method of fitting equations to growth curves. Ecology 48, 978–983.
- Ricklefs, R.E. (2003) Is rate of ontogenetic growth constrained by resource supply or tissue growth potential? A comment on West et al. 17.
- Case, T.J. (1978) On the evolution and adaptive significance of postnatal growth rates in the terrestrial vertebrates. Quarterly Review of Biology 29, 103–137.
- Geoffrey, B. West, James H. Brown & Brian J. Enquist, A general model for ontogenetic growth, Nature volume 413, pages628–631 (2001).
- West, G.B. , Brown, J. J. ( 1997) A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 276, 122–126.
- West, G.B. , Enquist, B.J. & Brown, J.H. (2002) Modelling universality and scaling: reply. Nature 420, 626–627.
- Makarieva A.M., V. G. Gorshkov, B.-L. Li, Ontogenetic growth: models and theory, Ecological Modelling 176 (2004) 15–26.
- Moses M.E., C. Hou, W.H. Woodruff, G.B. West, J.C. Nekola, W. Zuo, and J.H. Brown, Revisiting a model of ontogenetic growth: estimating model parameters from theory and data, the American Naturalist, 2008. Vol. 171, (3) 632–645.
- Hou, C. , Bolt K. R. Soc. B ( 2011) 278, 2881–2890.
- Shi P-J., X-Y Men, H.S. Sandhu, A Chakraborty, B-L Li, F Ou-Yang, Y-C Sun, F Ge, The “general”ontogenetic growth model is inapplicable to crop growth, Ecological Modelling 266 (2013) 1– 9.
- Sibly, R. M, J. Baker, J.M. Grady, S.M. Luna, A. Kodric-Brownb, C. Venditti, and J.H. Brown, Fundamental insights into ontogenetic growth from theory and fish, PNAS, 2015, Vol. 112, (45) 13934-13939.
- Hatton I.A., A. P. Dobson, D. Storch, E.D. Galbraithe, and M. Loreau, Linking scaling laws across eukaryotes, PNAS, 2019, 116(43):21616–21622.
- Escala A, Universal ontogenetic growth without fitted parameters: implications for life history invariants and population growth, Theoretical Ecology (2023) 16:315–325.
- West, B.J. , and D. West, Stochastic ontogenetic growth model, A Letter Journal Exploring the Frontiers of Physics, 2012, 97, 48002. [Google Scholar]
- Ziwei Ma, Ben Niu, Tuan Anh Phan, Anne Line Stensjoen, Chibawanye Ene, Timothy Woodiwiss, Tonghui Wang, Philip K. Maini, Eric C. Holland & Jianjun Paul Tian, Stochastic growth pattern of untreated human glioblastomas predicts the survival time for patients, Scientific Reports, Volume 10, Article number: 6642 (2020).
- Phan, T.A.; Wang, S.; Tian, J.P. Analysis of a new stochastic Gompertz diffusion model for untreated human glioblastomas. Stochastics Dyn. 2022, 2250019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, C., P. G. Degiorgis, P.P. Delsanto, P. Gabriele, T.S. Deisboeck, 2003. Does tumor growth follow a “universal law”? J. Theor. Biol. 225, 147–151.
- 2024; 86.
- Bernt Oksendal, An introduction to stochastic differential equations with applications, 5th edition, Springer-Verlag Heidelberg New York.
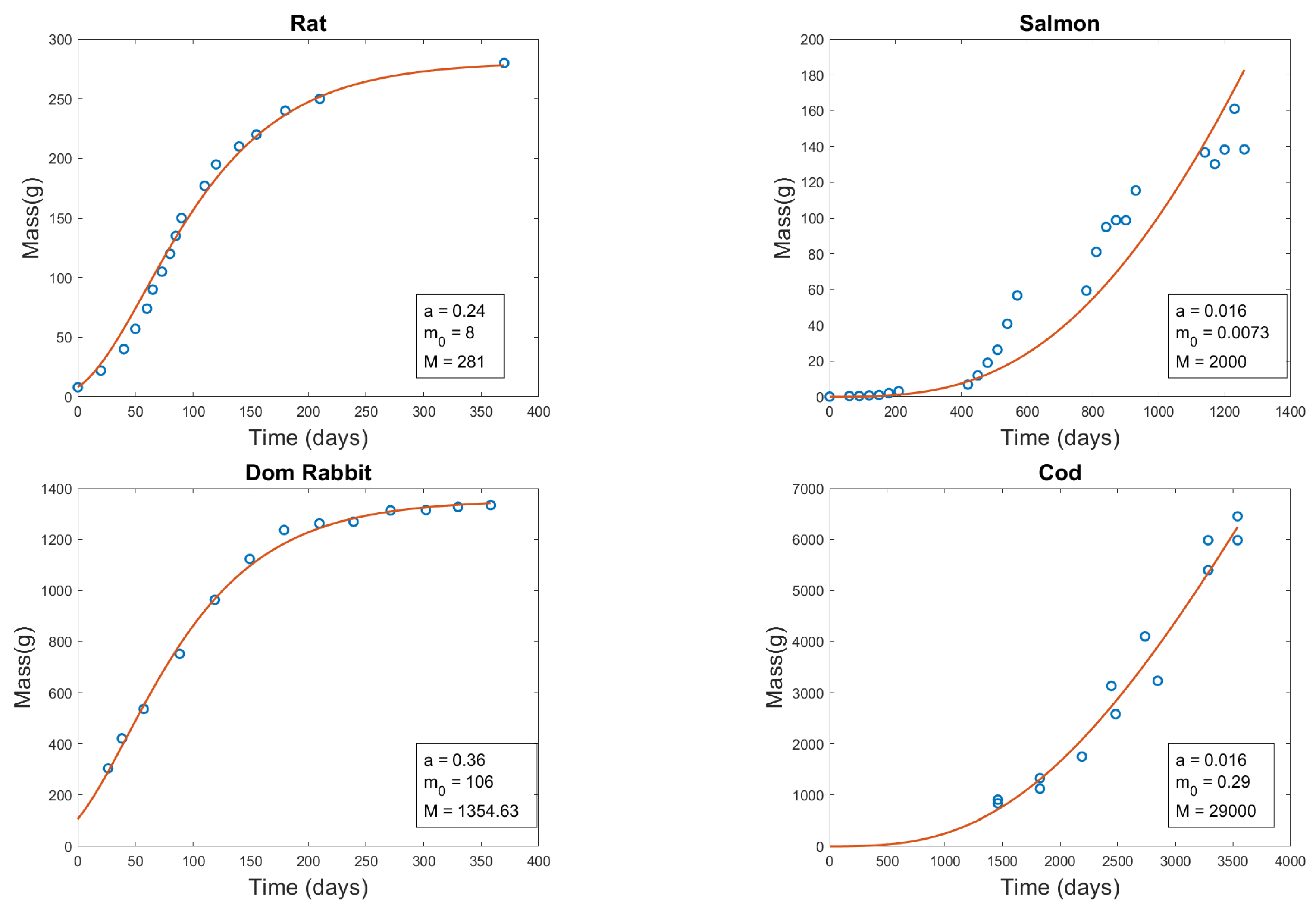
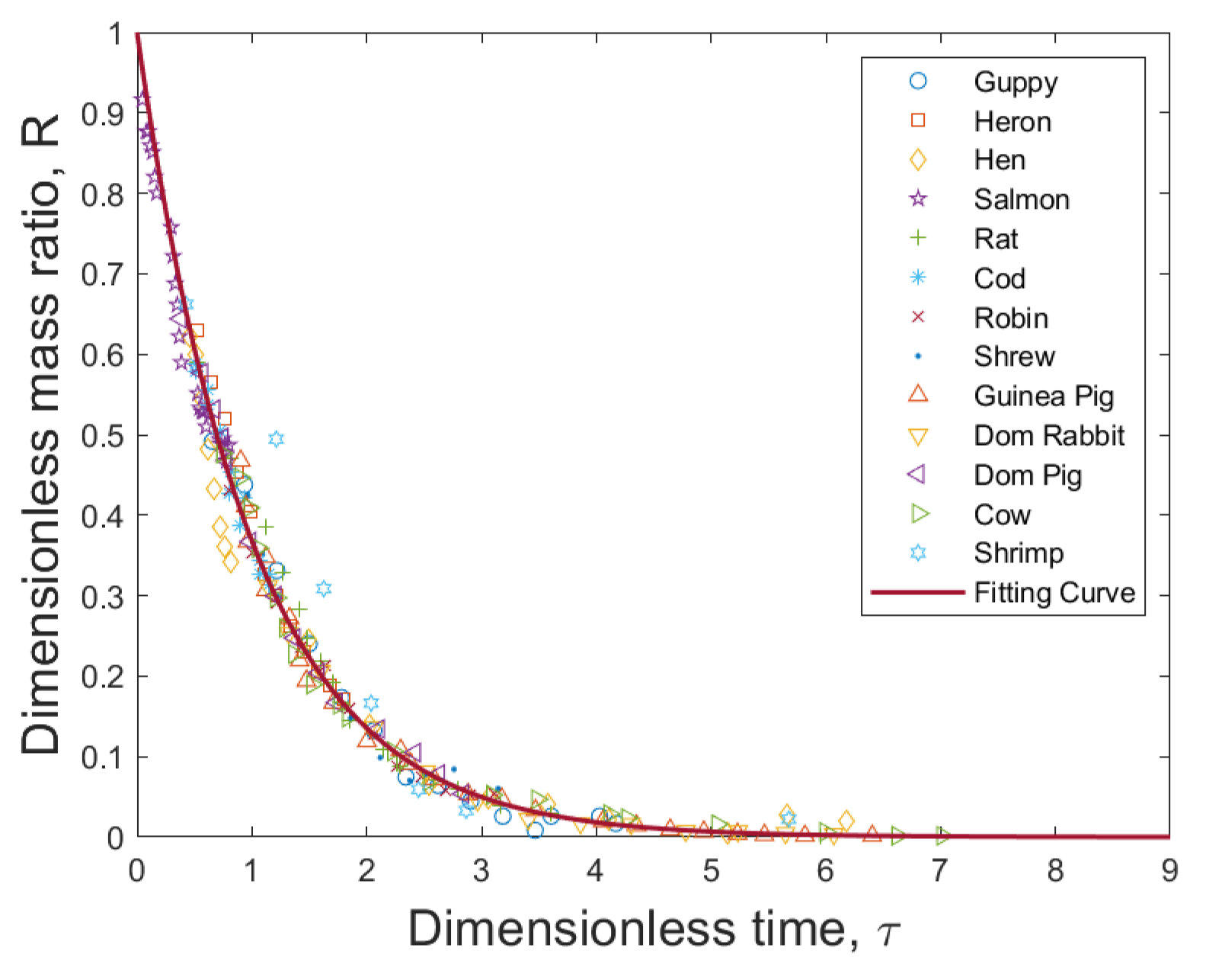
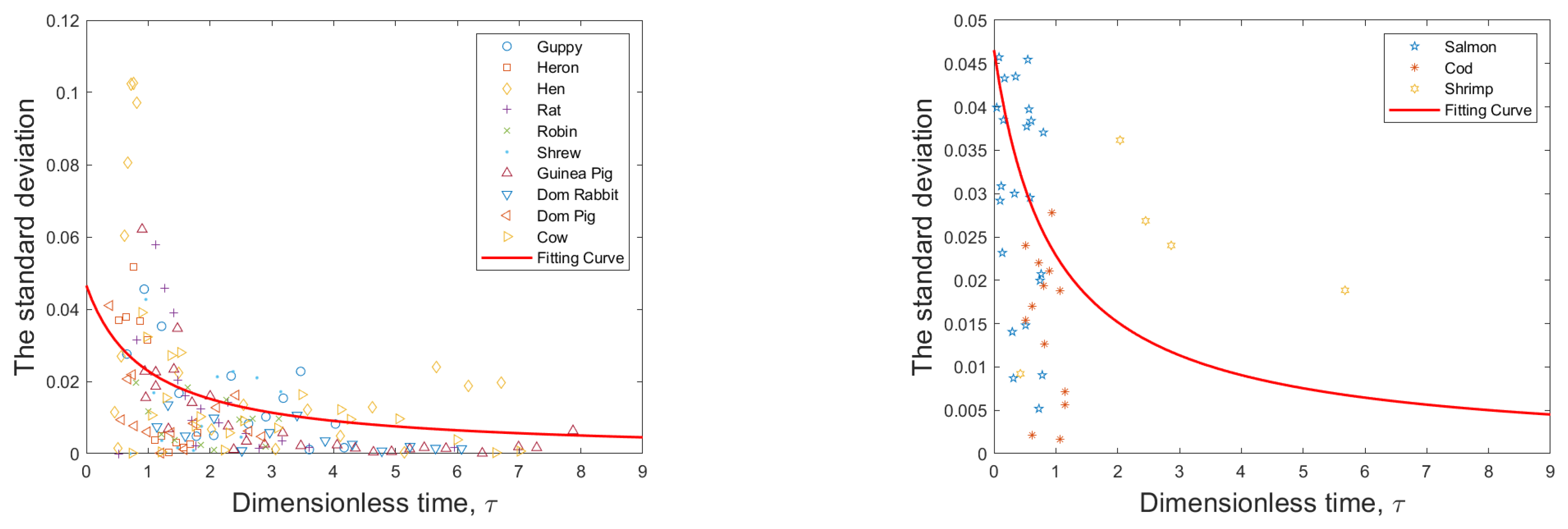
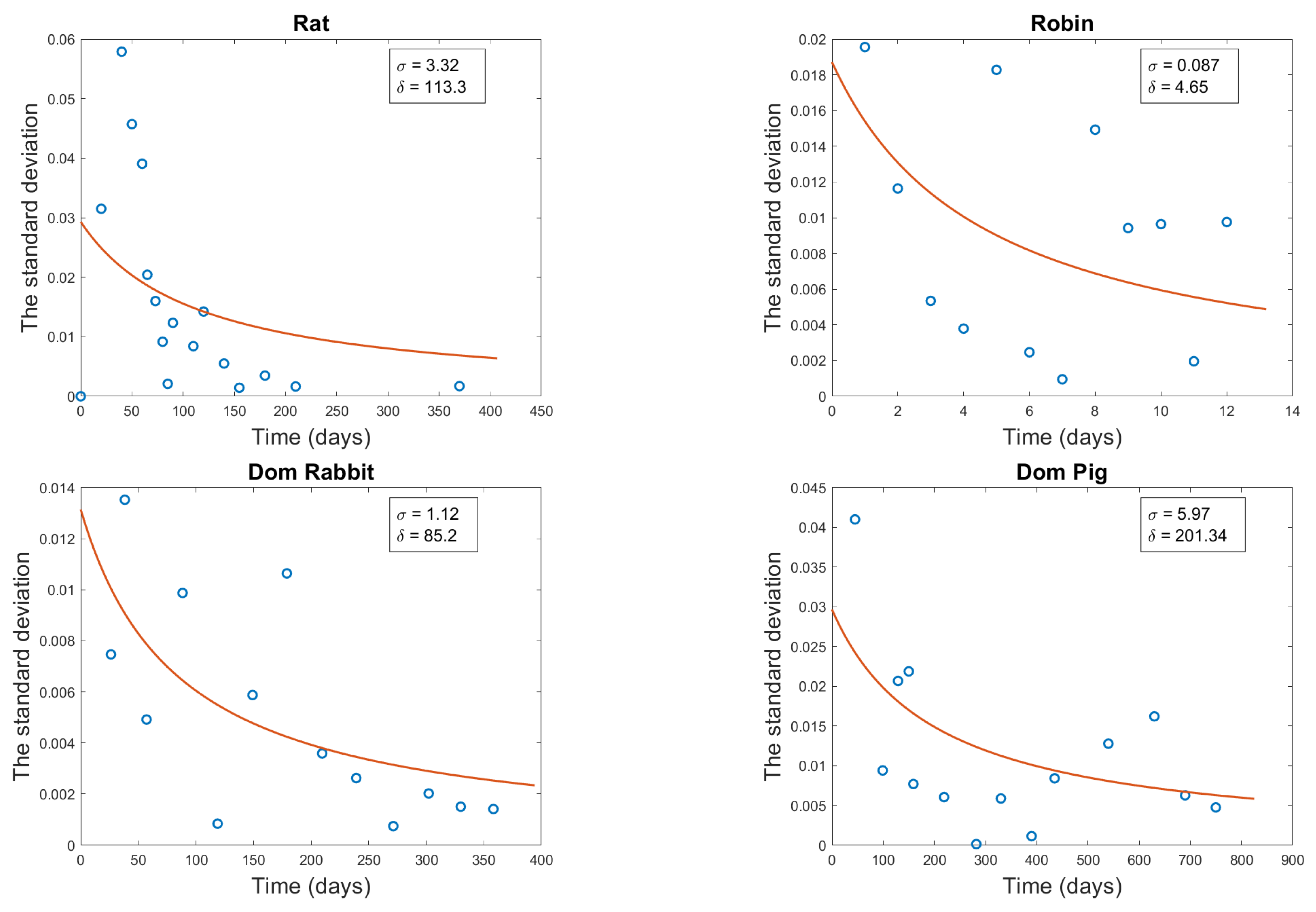

| Organism | a | (g) | M (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guppy | 0.1 | 0.008 | 0.15 |
| Heron | 1.62 | 4.52 | 2,370 |
| Hen | 0.47 | 38 | 2,100 |
| Rat | 0.24 | 8 | 281 |
| Robin | 1.84 | 0.89 | 22.88 |
| Shrew | 0.75 | 0.3 | 4.55 |
| Guinea Pig | 0.21 | 1.78 | 830.15 |
| Domestic Rabbit | 0.36 | 106 | 1,354.63 |
| Domestic Pig | 0.33 | 482 | 311,800 |
| Cow | 0.27 | 33,300 | 444,490 |
| Salmon | 0.016 | 0.0073 | 2,000 |
| Cod | 0.016 | 0.29 | 29,000 |
| Shrimp | 0.029 | 0.0008 | 0.0766 |
| Organism | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Guppy | 0.93 | 24.87 | 0.0098 |
| Heron | 0.26 | 5.12 | 0.0132 |
| Hen | 5.54 | 96.19 | 0.0315 |
| Rat | 3.32 | 113.3 | 0.0162 |
| Robin | 0.087 | 4.65 | 0.0061 |
| Shrew | 4.28 | 313.34 | 0.0133 |
| Guinea Pig | 1.11 | 40.6 | 0.0083 |
| Domestic Rabbit | 1.12 | 85.2 | 0.0033 |
| Domestic Pig | 5.97 | 401.34 | 0.0066 |
| Cow | 15.53 | 778.43 | 0.0102 |
| Organism | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cod | -0.0115 | 0.046 | 0.0087 |
| Salmon | -0.035 | 3.44 | 0.00218 |
| Shrimp | -0.069 | 1.04 | 0.0726 |
| Organism | K | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Guppy | 4.64 | 24.87 | 0.1866 |
| Heron | 1.08 | 5.12 | 0.2108 |
| Hen | 42.05 | 96.19 | 0.4372 |
| Rat | 27.43 | 113.3 | 0.2421 |
| Robin | 0.19 | 4.65 | 0.0408 |
| Shrew | 11.95 | 313.34 | 0.0381 |
| Guinea Pig | 11.22 | 40.6 | 0.2764 |
| Domestic Rabbit | 9.2 | 85.2 | 0.1079 |
| Domestic Pig | 101.04 | 401.34 | 0.2517 |
| Cow | 303.74 | 778.43 | 0.3902 |
| Cod | -0.66 | 0.092 | -7.1397 |
| Salmon | -1.43 | 3.44 | -0.416 |
| Shrimp | -0.59 | 1.04 | -0.5652 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





