Submitted:
09 October 2024
Posted:
09 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Research Design
2.1. Conceptual Model of the Emergence of Cluster Enterprises’ Capability for Basic Research
2.2. Measurement Model of the Emergence of Cluster Enterprises’ Capability for Basic Research
2.2.1. Measurement and Assessment of Emergence Degree
2.2.2. Metrics for the Emergence of Cluster Enterprises’ Capability for Basic Research
2.2.2. The Entropy Generation and Entropy Flow of the Basic Research Capability System of Cluster Enterprises and the Emergence Measurement Model
- Calculation Model of Entropy Generation and Entropy Flow in the Basic Research Capability System of Cluster Enterprises
- Emergence Measurement Model of the Enterprise Basic Research Capability System Based on Information Entropy
- Normalization of positive measurement indicators:
- Normalization of negative measurement indicators:
3. Case Study
3.1. Case Selection and Research Approach
3.2. Data Sources and Processing
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of Entropy Variation
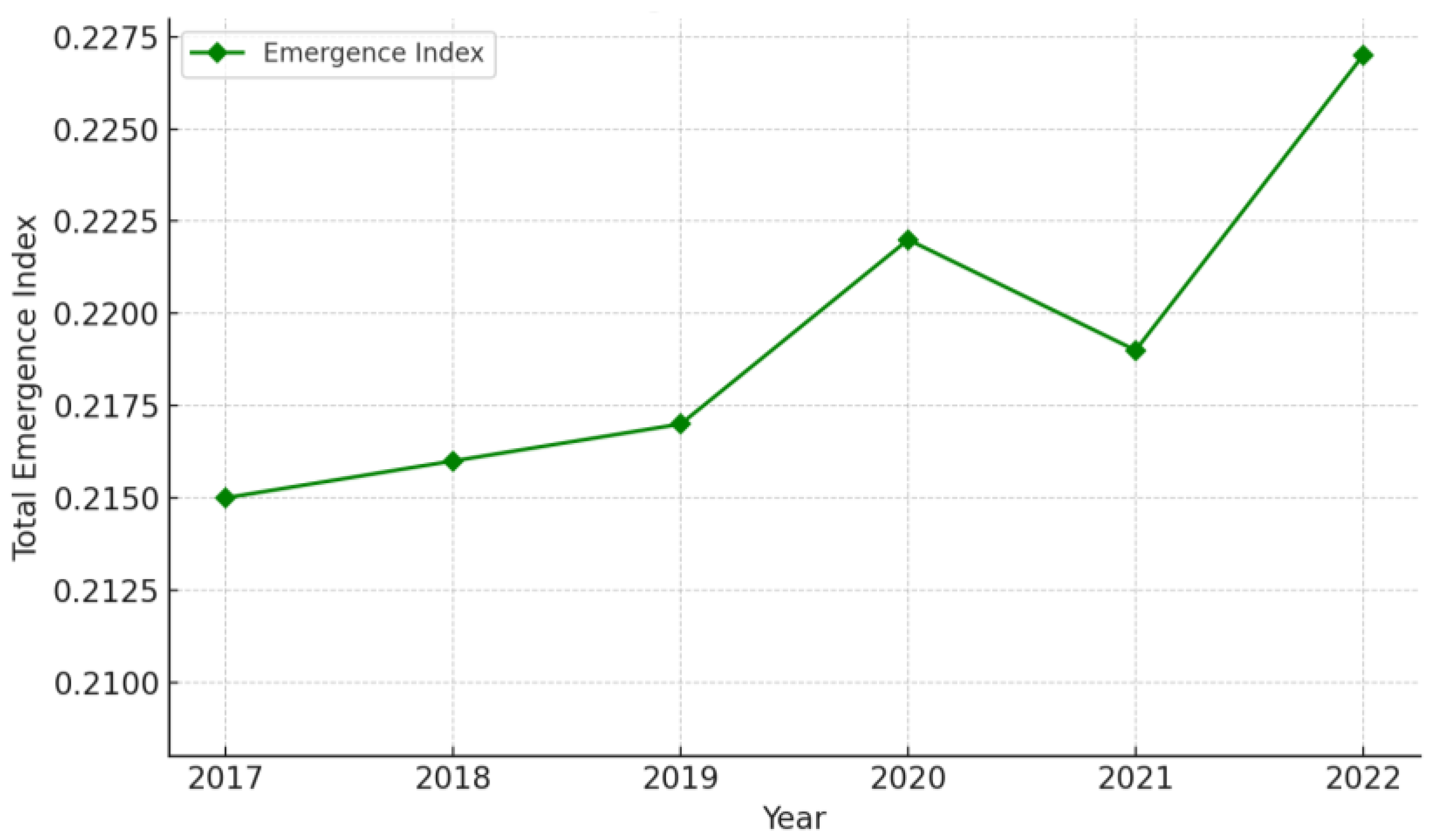
4.2. The Emergence of Cluster Enterprises’ Basic Research Capability as a System
4.3. Analysis of the Emergent Properties in the Basic Research Capability of Cluster Enterprises
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Research Conclusions
5.2. Theoretical Contributions and Practical Implications
5.2.1. Theoretical Contributions
5.2.2. Management Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nestle, V.; Täube, F.A.; Heidenreich, S.; Bogers, M. Establishing open innovation culture in cluster initiatives: The role of trust and information asymmetry. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2019, 146, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Tao, C.; Zhou, X. Connected knowledge spillovers, technological cluster innovation and efficient industrial structure. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge 2022, 7, 100195. [Google Scholar]
- Madanaguli, A.; Dhir, A.; Talwar, S.; Clauss, T.; Kraus, S.; Kaur, P. Diving into the uncertainties of open innovation: A systematic review of risks to uncover pertinent typologies and unexplored horizons. Technovation 2023, 119, 102582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, M.; Filieri, R.; O’Malley, L. Establishing successful university–industry collaborations: barriers and enablers deconstructed. The Journal of Technology Transfer 2023, 48, 900–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Song, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G. Innovation network, technological learning and innovation performance of high-tech cluster enterprises. Journal of Knowledge Management 2019, 23, 1729–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnekpe, C.; Coeurderoy, R.; Mulotte, L. How a firm’s knowledge base influences its external technology sourcing strategy: the case of biopharmaceutical firms. Industry and Innovation 2023, 30, 233–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abootorabi, H.; Wiklund, J.; Johnson, A.R.; Miller, C.D. A holistic approach to the evolution of an entrepreneurial ecosystem: An exploratory study of academic spin-offs. Journal of Business Venturing 2021, 36, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsanzumuhire, S.U.; Groot, W. Context perspective on University-Industry Collaboration processes: A systematic review of literature. Journal of cleaner production 2020, 258, 120861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoraki, C.; Dana, L.-P.; Caputo, A. Building sustainable entrepreneurial ecosystems: A holistic approach. Journal of Business Research 2022, 140, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, L.J.; de Villiers Scheepers, M.J.; Miles, M.P.; de Klerk, S. Understanding entrepreneurial ecosystems using complex adaptive systems theory: Getting the big picture for economic development, practice, and policy. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development 2022, 34, 911–934. [Google Scholar]
- Mnif, M.; Müller-Schloer, C. Quantitative emergence. Organic Computing—A Paradigm Shift for Complex Systems 2011, 39-52.
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, J.; Lyu, A.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Liu, K.; Mou, M.; Cui, P. Emergence and causality in complex systems: A survey of causal emergence and related quantitative studies. Entropy 2024, 26, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, B.; Pellens, M.; Blind, K.; Gruber, S.; Schubert, T. Are firms withdrawing from basic research? An analysis of firm-level publication behaviour in Germany. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 9677–9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yang, X.; Yu, Z. Effect of basic research and applied research on the universities’ innovation capabilities: The moderating role of private research funding. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5387–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, S.; Nazemi, E.; Masoumi, B. Emergence phenomena in self-organizing systems: a systematic literature review of concepts, researches, and future prospects. Journal of organizational computing and electronic commerce 2020, 30, 224–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegenfeld, A.F.; Bar-Yam, Y. An introduction to complex systems science and its applications. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaria, K. Negation and entropy: Effectual knowledge management equipment for learning organizations. Expert Systems with Applications 2020, 157, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, A.; Demir, H.; Sezen, B. The role of negative entropy within supply chain sustainability. Sustainable Production and Consumption 2021, 28, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, W.; Baozhong ,S.; Xi, C.. Situation Analysis of Basic Endowment Insurance for the Urban Working Group System from the Perspective of Dissipative Structure Theory. China Soft Science 2015, 173–183.
- Choi, J.-U.; Lee, C.-Y. The differential effects of basic research on firm R&D productivity: The conditioning role of technological diversification. Technovation 2022, 118, 102559. [Google Scholar]
- Sheer, L. Sitting on the fence: Integrating the two worlds of scientific discovery and invention within the firm. Research Policy 2022, 51, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, W. Evaluation of the performance of regional innovation systems based on the dissipative structure. Science Research Management 2018, 39, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zheng, J. The cyclical and nonlinear impact of R&D and innovation activities on economic growth in OECD economies: A new perspective. Journal of the Knowledge Economy 2023, 14, 544–593. [Google Scholar]
- Blomsma, F.; Bauwens, T.; Weissbrod, I.; Kirchherr, J. The ‘need for speed’: Towards circular disruption—What it is, how to make it happen and how to know it's happening. Business Strategy and the Environment 2023, 32, 1010–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J. There and back again: Revisiting Vannevar Bush, the linear model, and the freedom of science. Research Policy 2022, 51, 104610. [Google Scholar]
| Indicator Type | Metric Indicator | Definition | Attribute | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
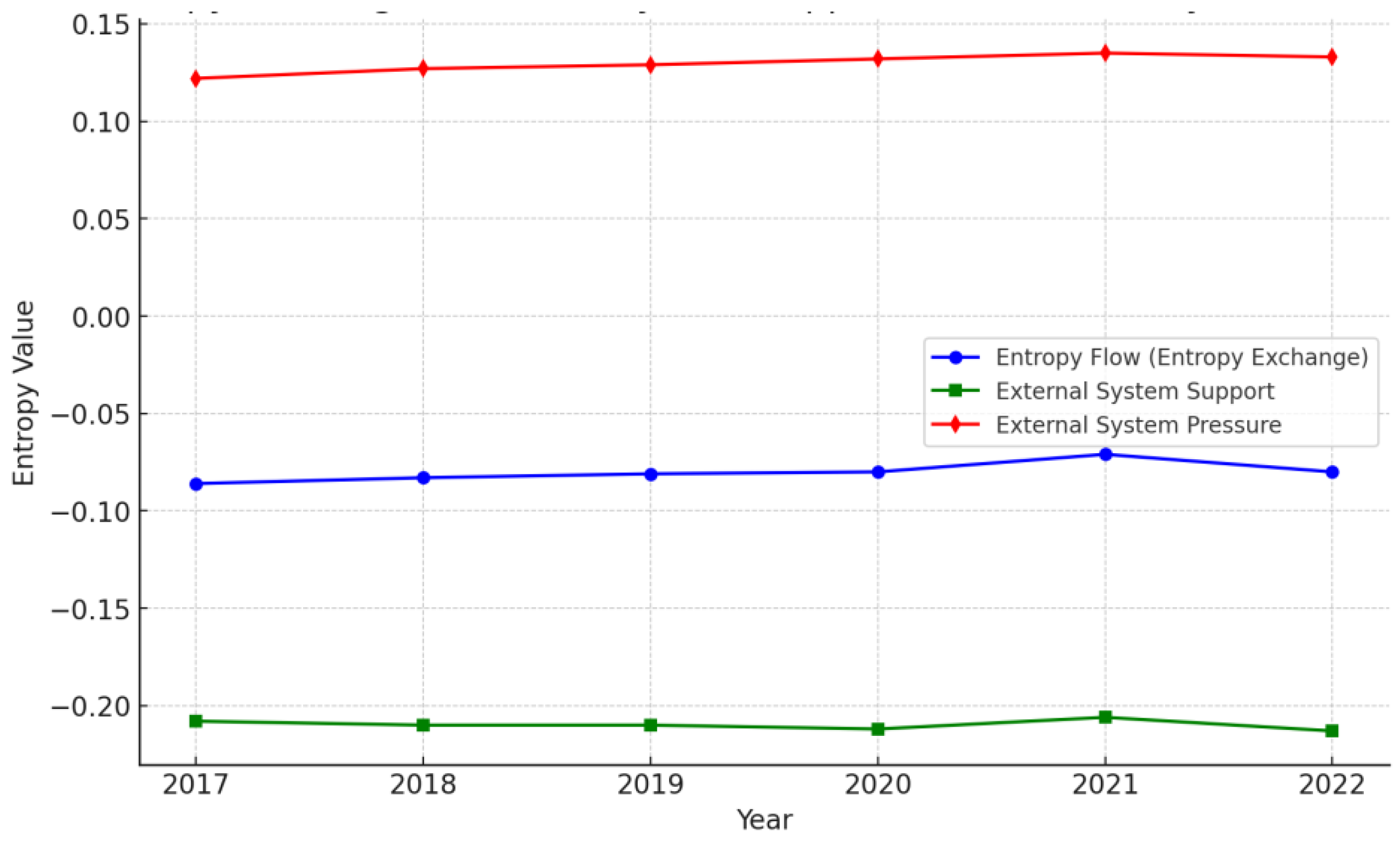
| Entropy Flow (Entropy Exchange) |
Support from Other Systems | R&D Subsidies | Proportion of government innovation subsidies received by the enterprise to its total assets | Negative |
| Tax Incentives | Actual tax incentives enjoyed by the enterprise | Negative | ||
| Foreign Investment | Total amount of foreign enterprise investment in the region | Negative | ||
| Regional R&D Intensity | Regional R&D expenditure / GRDP | Negative | ||
| Market Environment | Depicts changes in the market environment based on the "China Marketization Index" by Fan Gang et al. | Negative | ||
| Pressure from Other Systems | Market Competition Degree | Herfindahl index, sum of squares of the percentage of industry revenue generated by other companies except the company itself | Positive | |
| Corporate Debt Level | Estimated corporate debt-to-asset ratio, total debt / total assets | Positive | ||
| Number of Jobs Created | Natural logarithm of the number of employees | Positive | ||
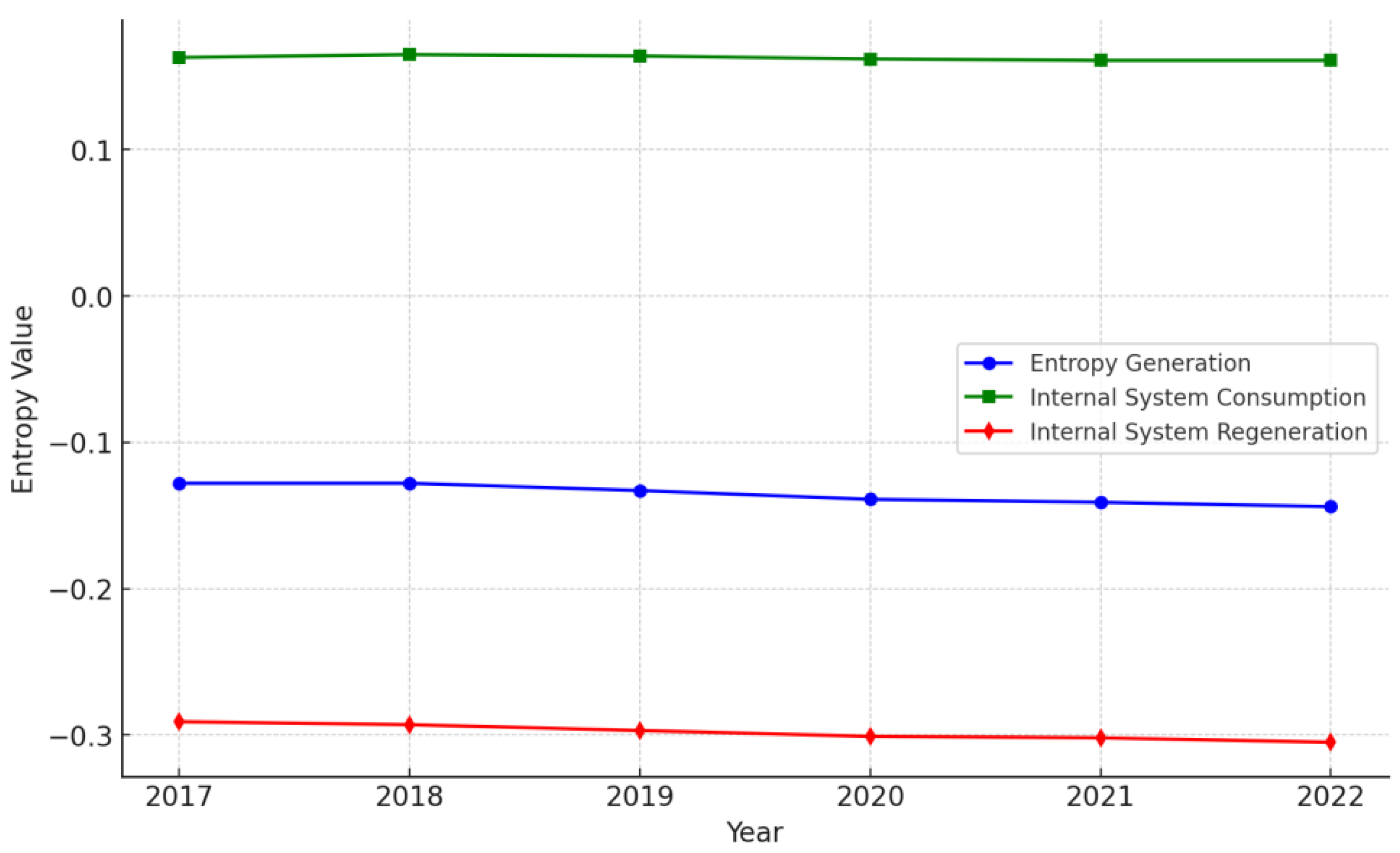
| Entropy Generation | Internal System Consumption | Internal R&D Investment | Proportion of R&D investment to total revenue | Positive |
| Corporate Scale Maintenance | Natural logarithm of total assets | Positive | ||
| Specific Investment | (Fixed assets + intangible assets) / total assets | Positive | ||
| Technology Introduction Investment | Proportion of expenditures on technology introduction, absorption, and digestion to sales revenue | Positive | ||
| Internal System Regeneration | Corporate Growth Rate | (Current period revenue - previous period revenue) / previous period revenue | Negative | |
| Corporate Profitability | Corporate profit margin | Negative | ||
| Corporate Age | Observation period year - year of establishment + 1 | Negative | ||
| Knowledge Integration Ability | Number of patents applied for by the enterprise in different domestic and international patent classifications (logarithm) | Negative | ||
| Breakthrough Innovation | Number of times domestic and international patents of the enterprise have been cited (logarithm adjusted to overcome right-skew problem) | Negative | ||
| Labor Productivity | Ratio of profit to total number of employees | Negative | ||
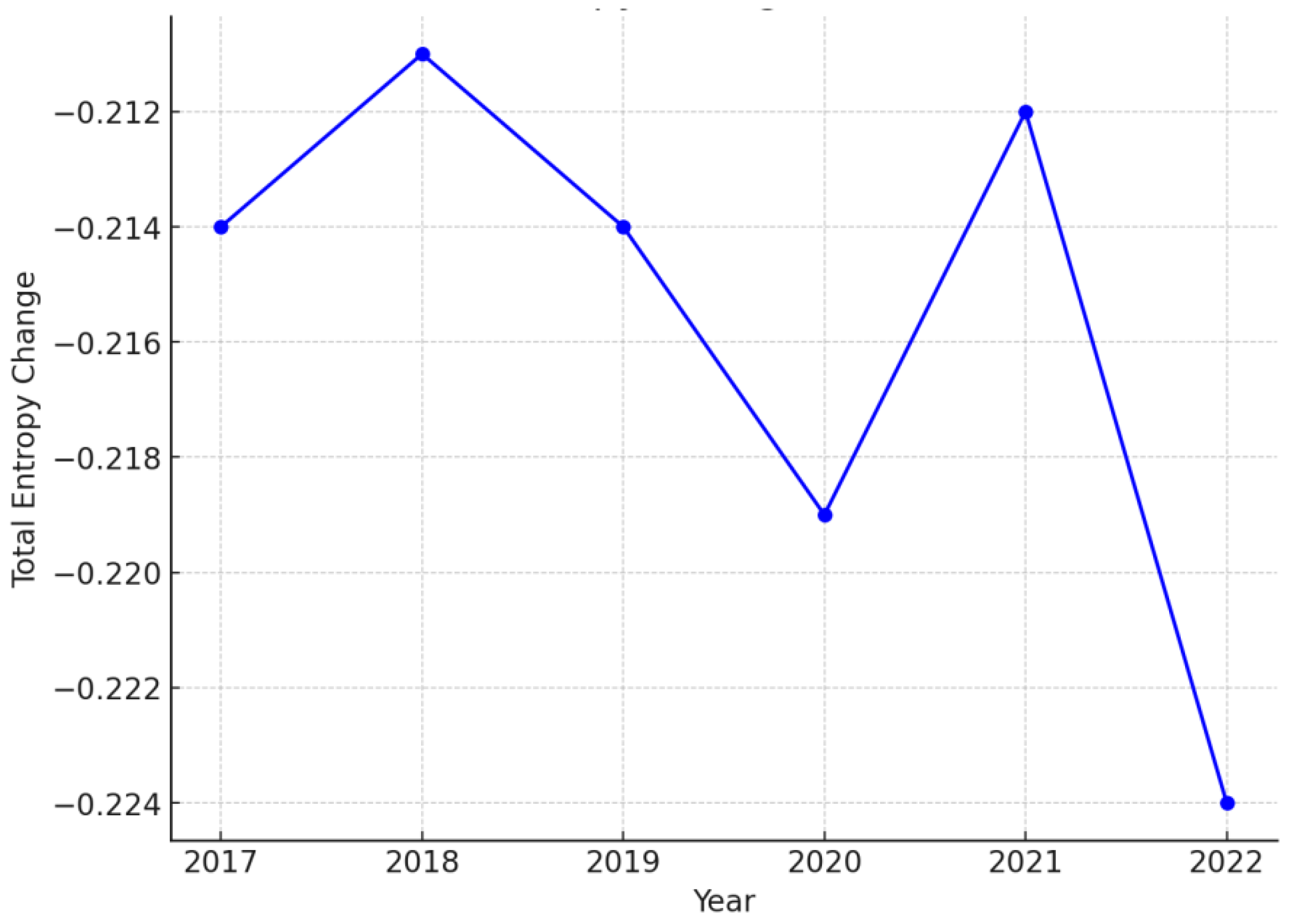
| Entropy Type | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External System Support | -0.208 | -0.21 | -0.21 | -0.212 | -0.206 | -0.213 |
| External System Pressure | 0.122 | 0.127 | 0.129 | 0.132 | 0.135 | 0.133 |
| Internal System Consumption | 0.163 | 0.165 | 0.164 | 0.162 | 0.161 | 0.161 |
| Internal System Regeneration | -0.291 | -0.293 | -0.297 | -0.301 | -0.302 | -0.305 |
| Total Entropy Change | -0.214 | -0.211 | -0.214 | -0.219 | -0.212 | -0.224 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





