Submitted:
04 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Customizing Social Media Strategies for Different Industries
1.1. Research Questions
- How do businesses measure the success of their social media strategies, and what metrics are most used across different platforms?
- What role does customer feedback and interaction play in shaping and improving social media strategies for businesses?
- How can businesses integrate social media strategies with other marketing channels to create a balanced and effective overall marketing approach?
- How can businesses target their audience on social media?
- What are the common mistakes businesses make in social media marketing, and how can they be avoided?
1.2. Research Motivation
1.3. Research Contribution
1.4. Research Novelty
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
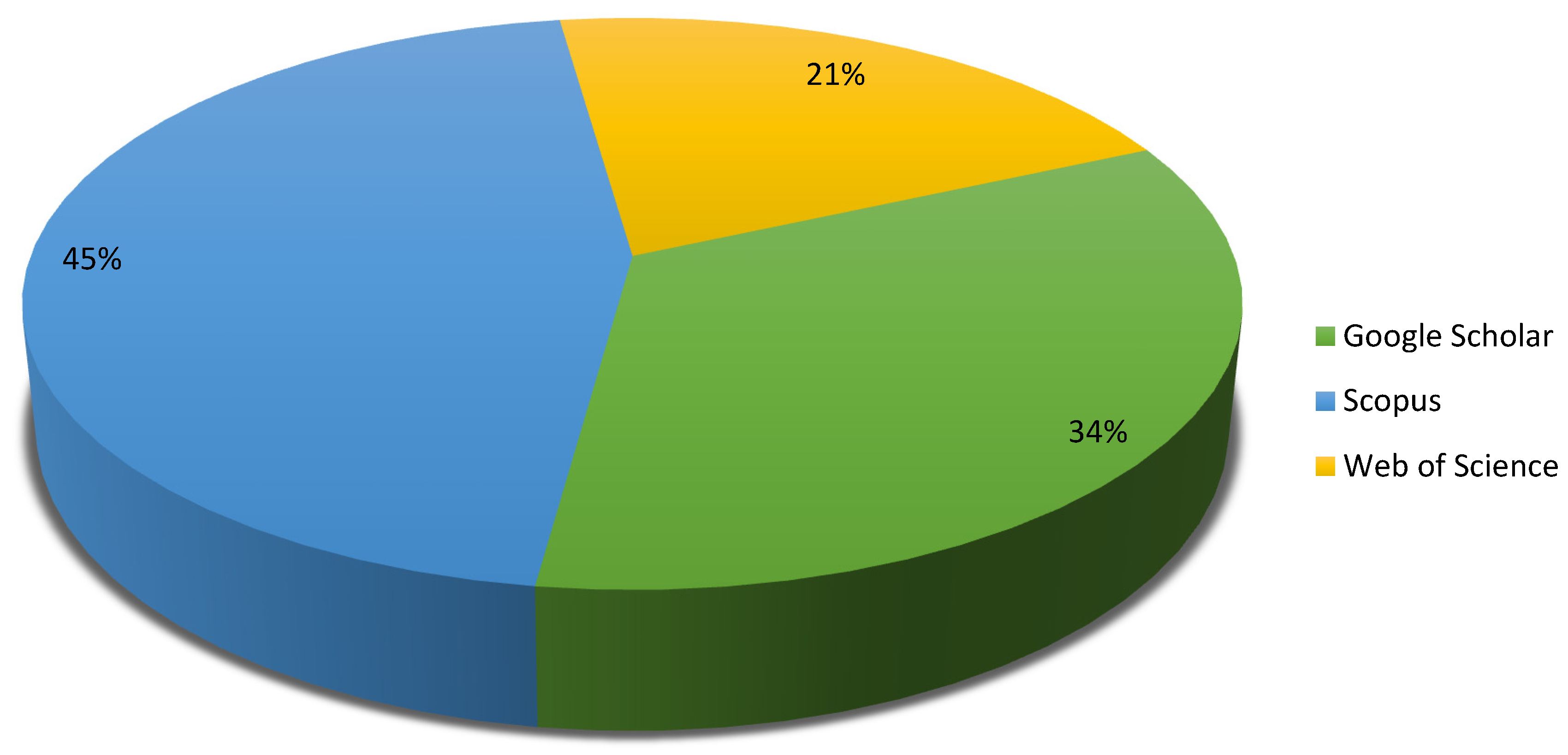
2.2. Information Sources
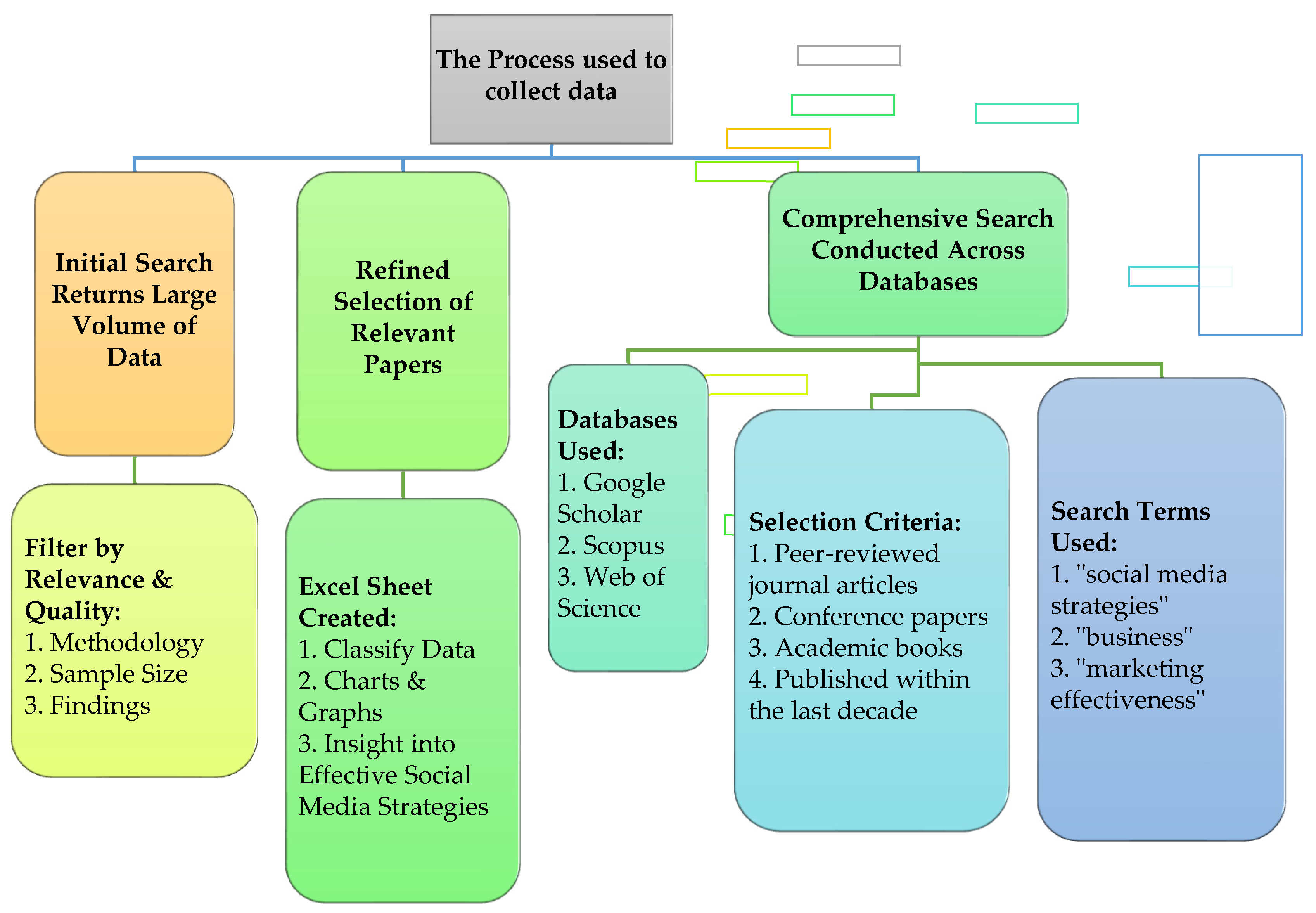
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
- Engagement Metrics - Measures of user interaction with content, such as likes, shares, comments, and overall engagement rates.
- Conversion Rates - The percentage of users who take a desired action, such as signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase after interacting with social media content.
- Brand Awareness - Metrics assessing how familiar consumers are with a brand, often measured through surveys or social listening tools.
- Customer Satisfaction - Feedback from customers regarding their experiences and perceptions of the brand, often collected through surveys or reviews.
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Effect Measures
2.9. Synthesis Methods
2.9.1. Eligibility of Studies for Synthesis
| Ref. |
Intervention Characteristics |
Planned Synthesis Groups | Match the Planned Group? |
|---|---|---|---|
| [25] | B2B social media marketing, message source and content | Social media engagement and effectiveness | Yes |
| [26] | Social media marketing strategies in microbreweries | Sector-specific strategies | Yes |
| [27] | Impact of social media marketing on business performance | Social media’s effect on business outcomes | Yes |
| [28] | Social media and healthcare, patient engagement | Sector-specific strategies | Yes |
| [29] | Future of digital and social media marketing research | Research propositions for future marketing strategies | Yes |
| [30] | Body dissatisfaction and social media in young women | Psychological impact of social media | No |
| [32] | Challenges in leveraging social media for businesses | Common pitfalls in social media strategies | Yes |
| [33] | Digital marketing approaches for e-commerce platforms | E-commerce social media strategies | Yes |
| [34] | Business strategy and digital marketing | Integration of business strategy with social media | Yes |
| [35] | Case-based recommendations for social media strategy | Practical case studies and recommendations | Yes |
| [37] | Online advertising strategy | Online advertising vs. organic social media | No |
| [40] | Social media strategy frameworks for companies | Frameworks for strategy development | Yes |
| [44] | SMEs in the digital age | Sector-specific strategies for SMEs | Yes |
| [50] | Key elements of effective social media marketing | General social media marketing strategies | Yes |
2.9.2. Certainty Assessment
| Outcome | Certainty Level | Reason for Downgrading/Upgrading | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness of Social Media Strategies | High | The studies consistently demonstrate effectiveness, with no significant risk of bias detected. Results are robust across different contexts. | Strong evidence supporting effectiveness. |
| Impact on Brand Awareness | Moderate | While most studies show positive outcomes, there is some inconsistency in results, and a few studies may suffer from publication bias. | Some studies show varying levels of impact. |
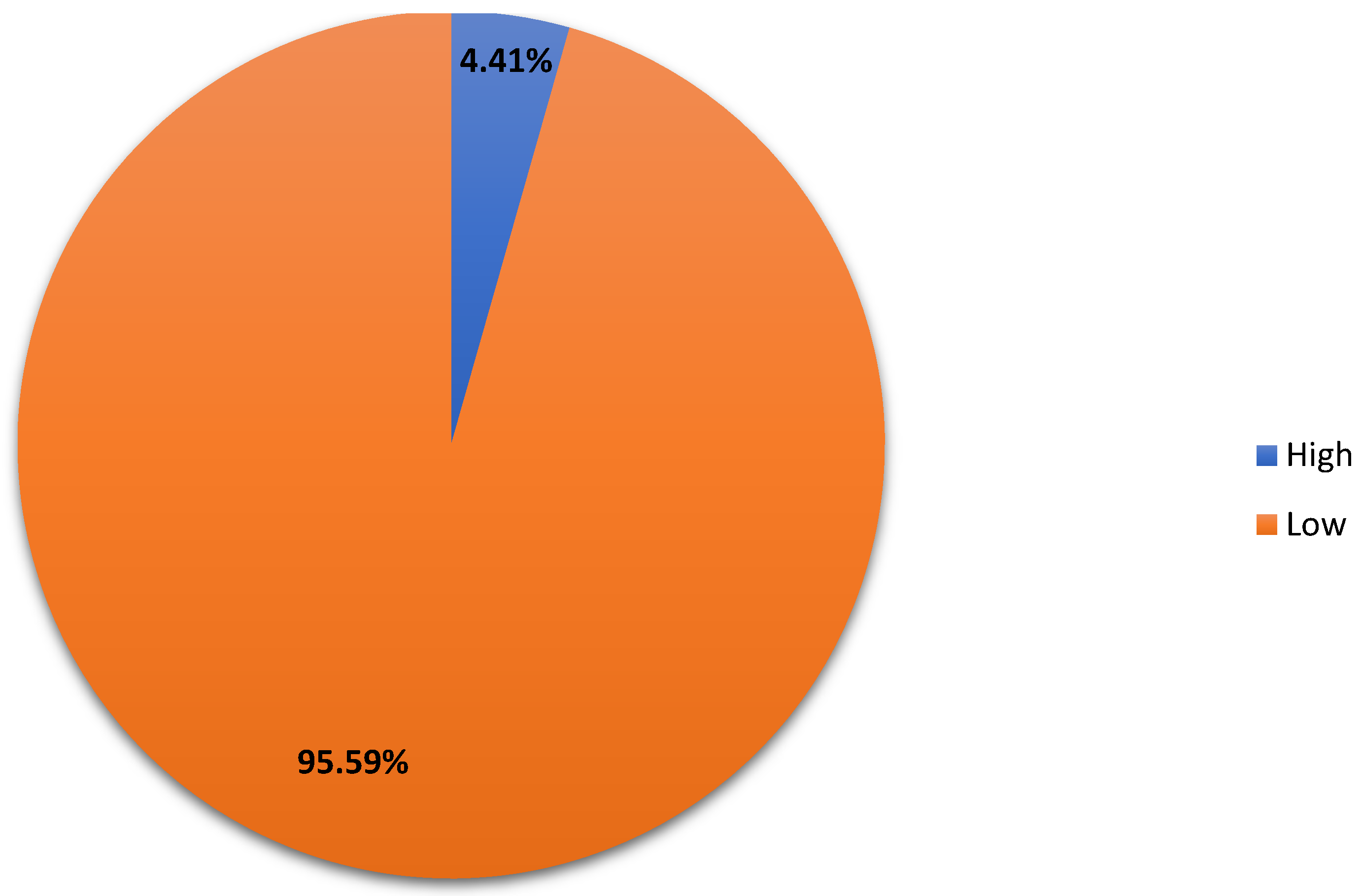
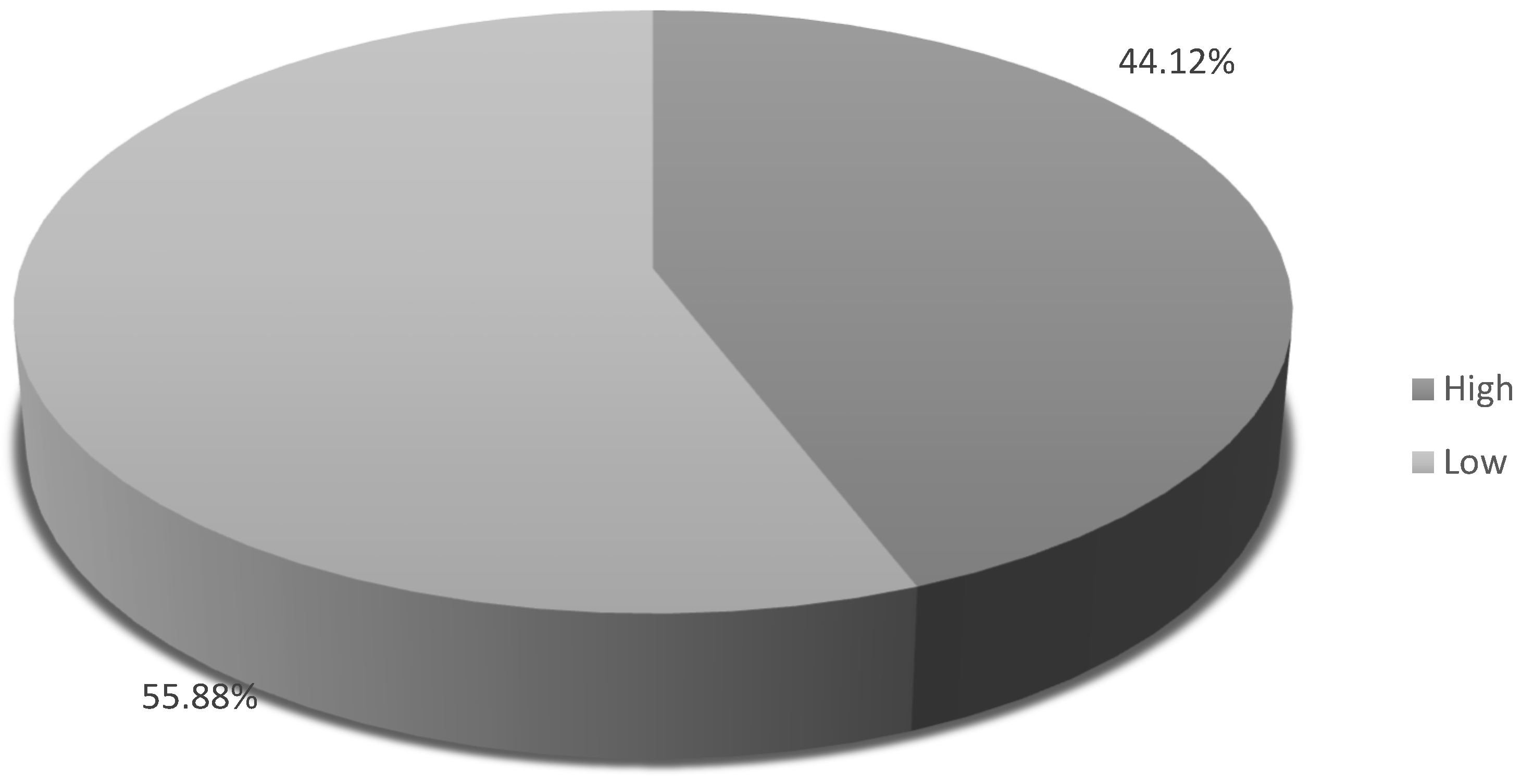
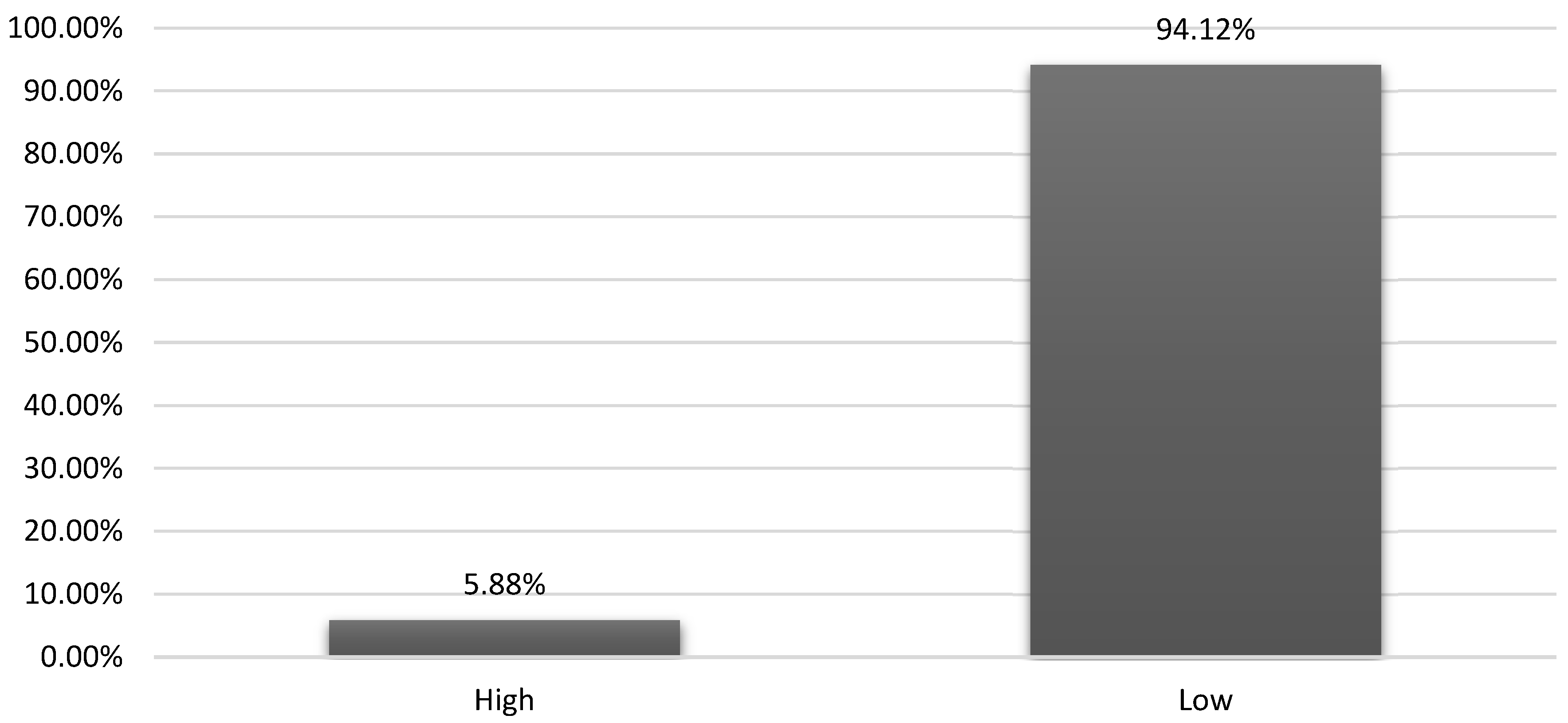
| Lead Generation | Low | Many studies in this area have a high risk of bias, and the effect estimates are often imprecise, leading to uncertainty in the findings. | Limited and uncertain evidence. |
| Customer Engagement | Moderate | The evidence is somewhat indirect, as not all studies focus directly on engagement. Additionally, some estimates lack precision. | Evidence is suggestive but not definitive. |
| Overall Business Success | High | Consistent results across studies with no major limitations indicate a strong link between social media strategies and business success. | Robust evidence linking strategies to business success. |
3. Results
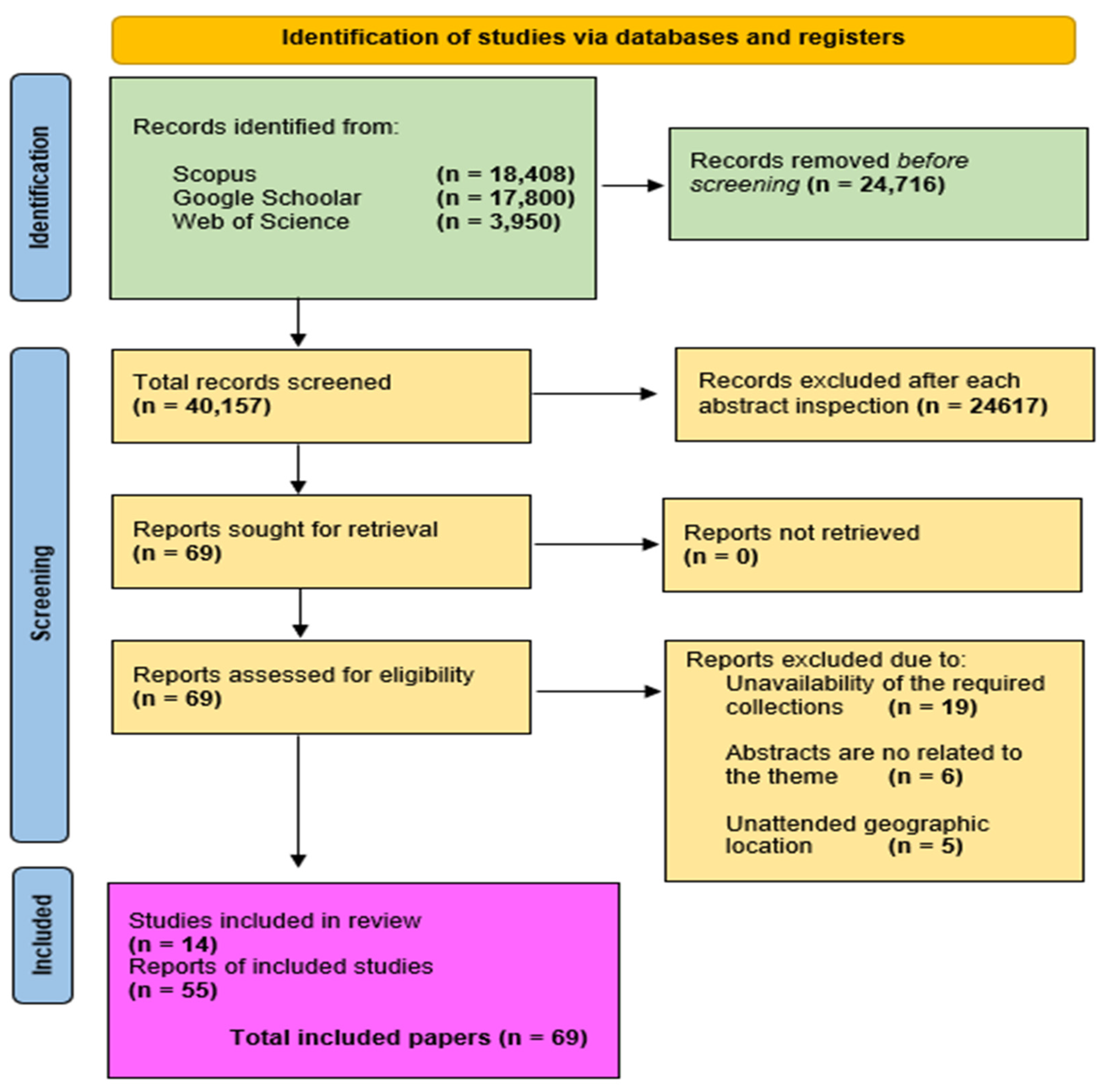
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
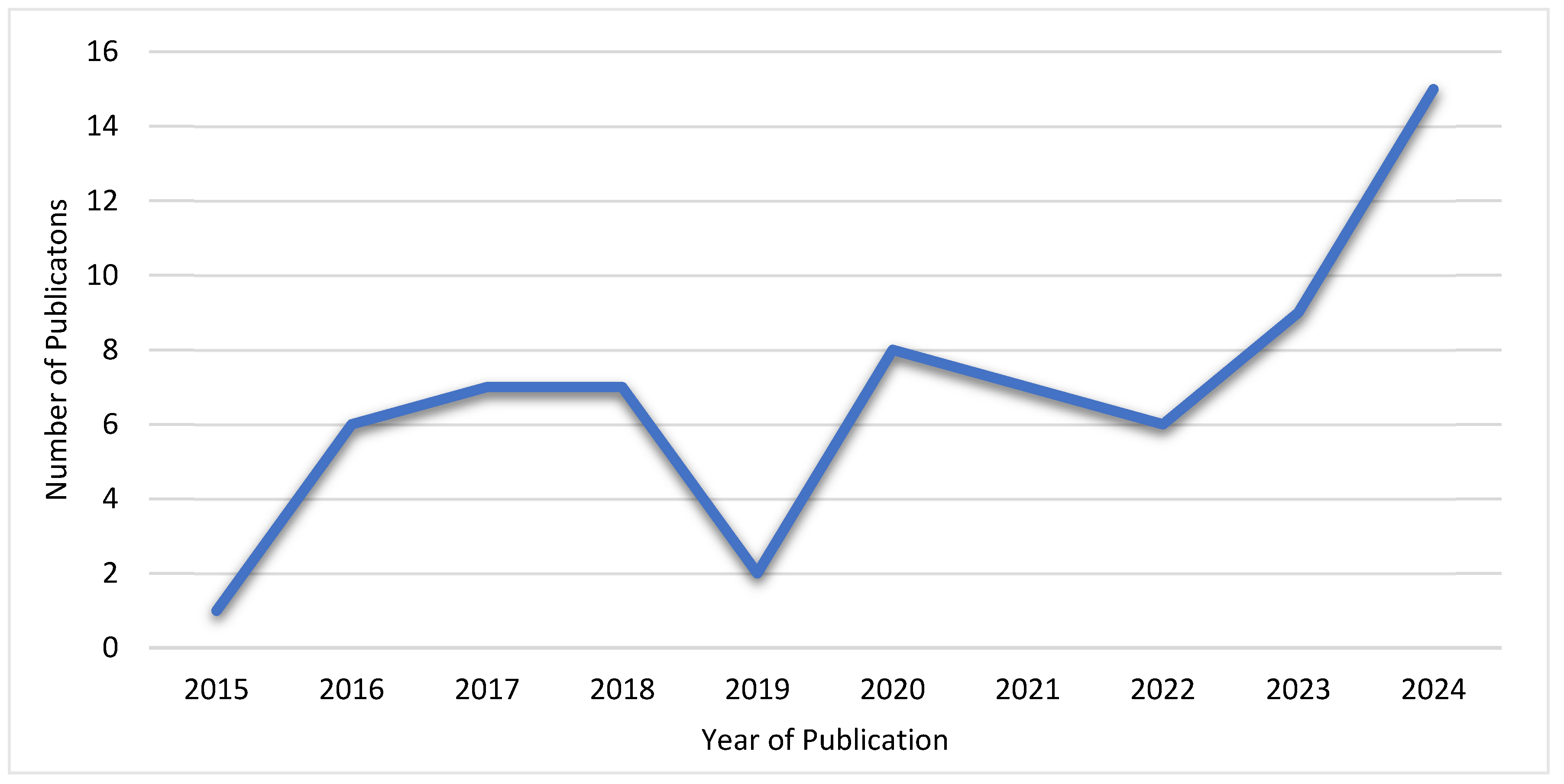
| Published Year | Journal | Conference Paper | Literature Review | Book | Article | Systematic Review | Case Study | Research paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2015 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2016 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2017 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2018 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2020 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 2021 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2022 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2023 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2024 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
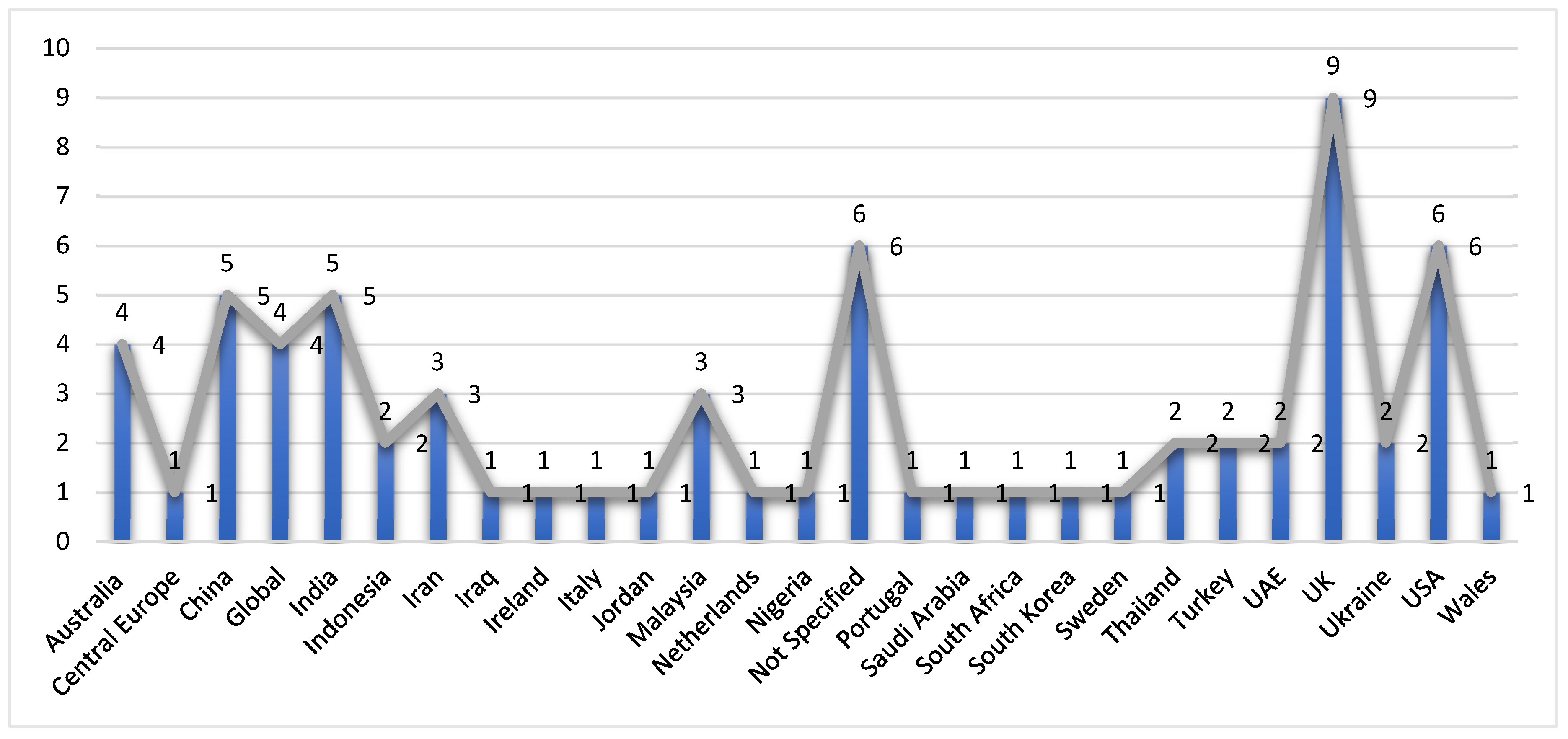
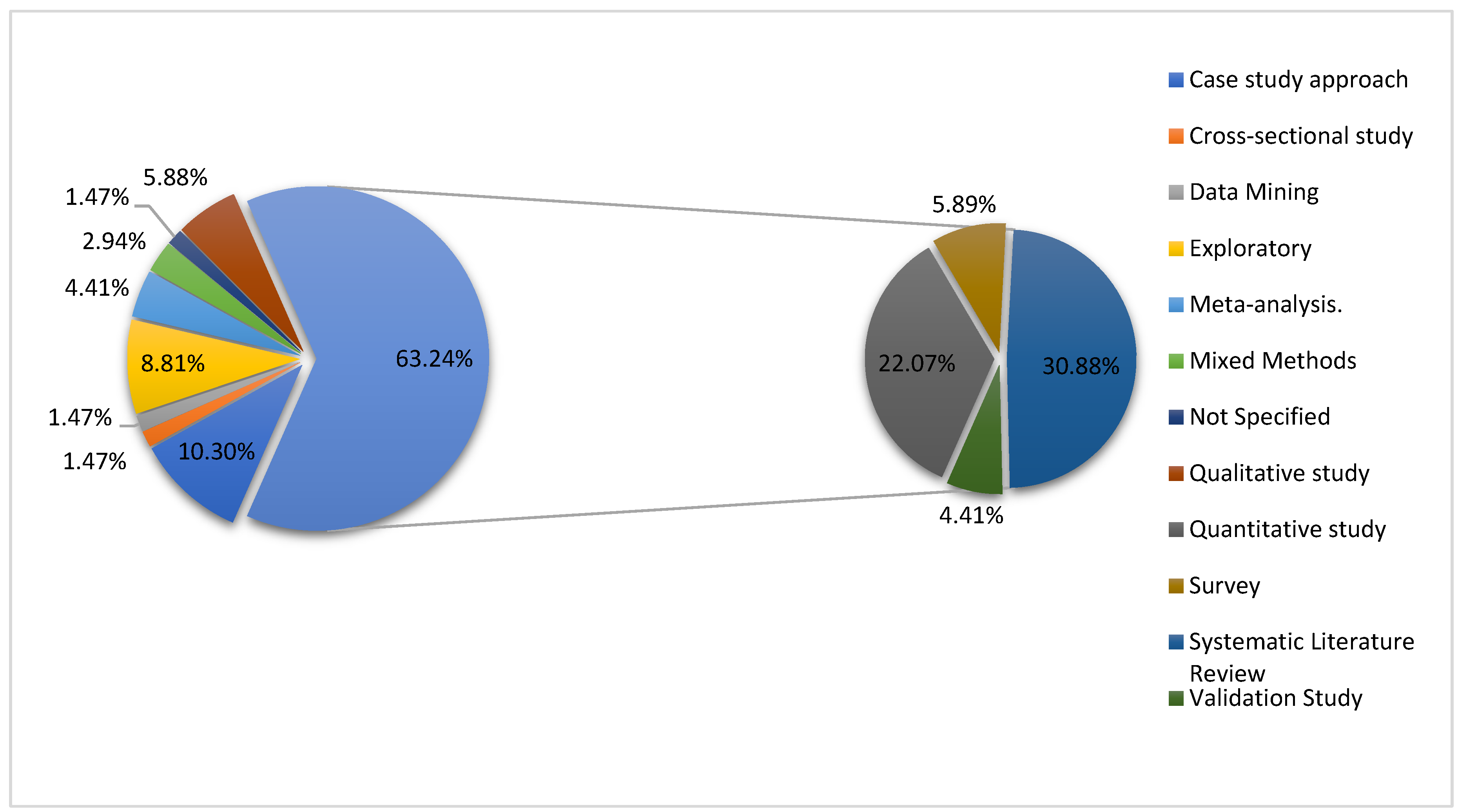
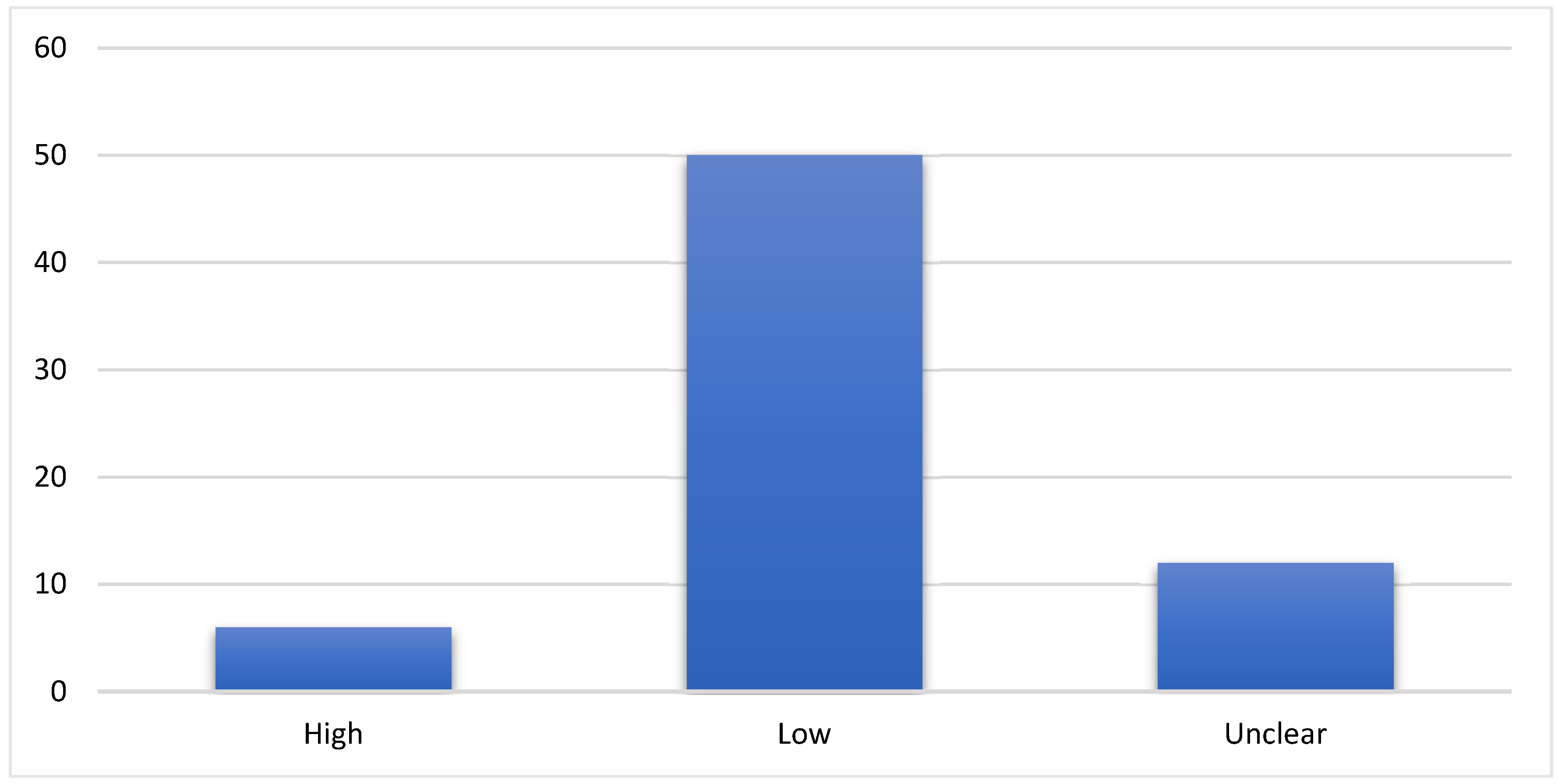
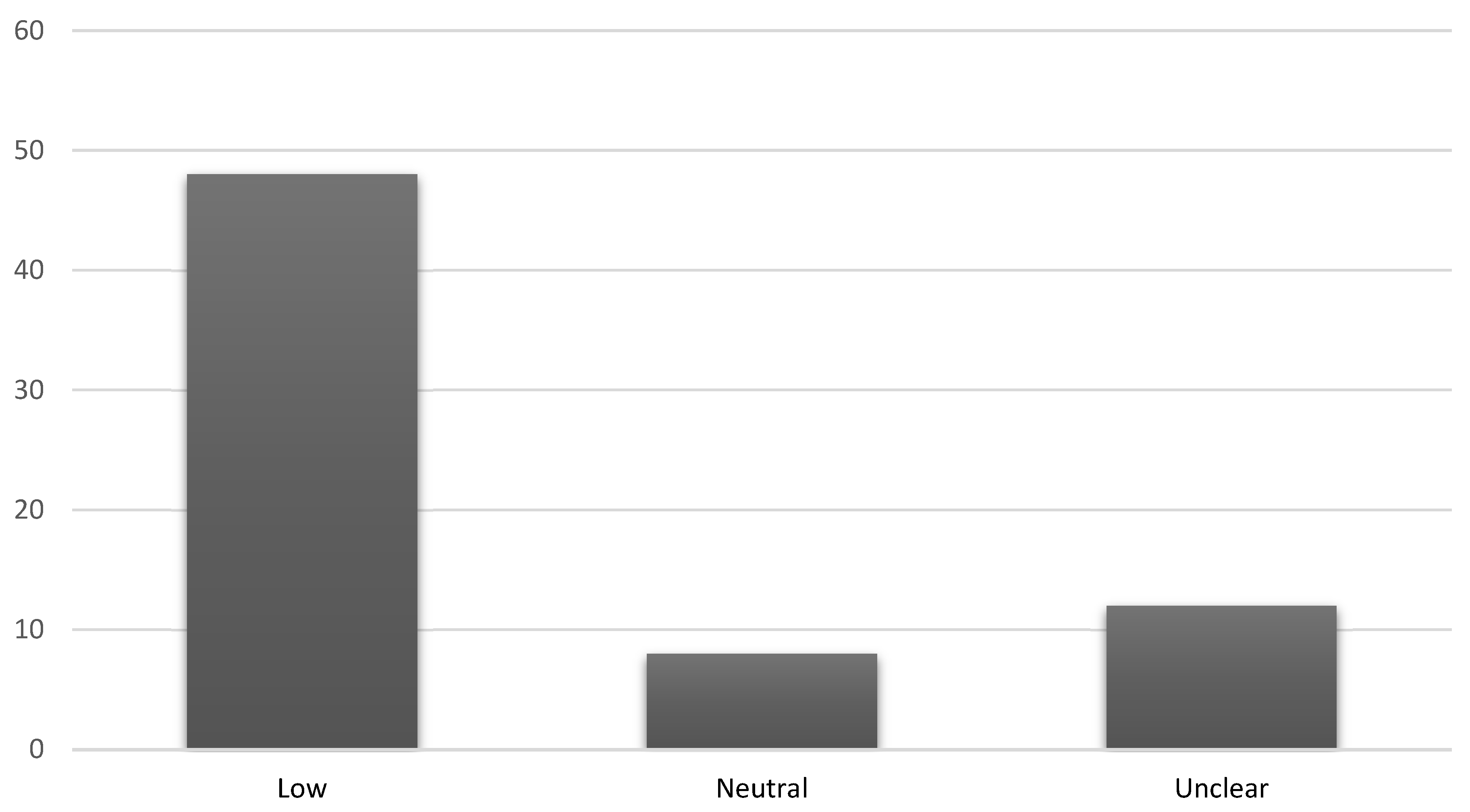
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
- Some participants were not randomly assigned,
- Reports of outcomes, and
- Inadequate blinding of outcomes assessors was not clear enough in some of the paragraphs showcased.
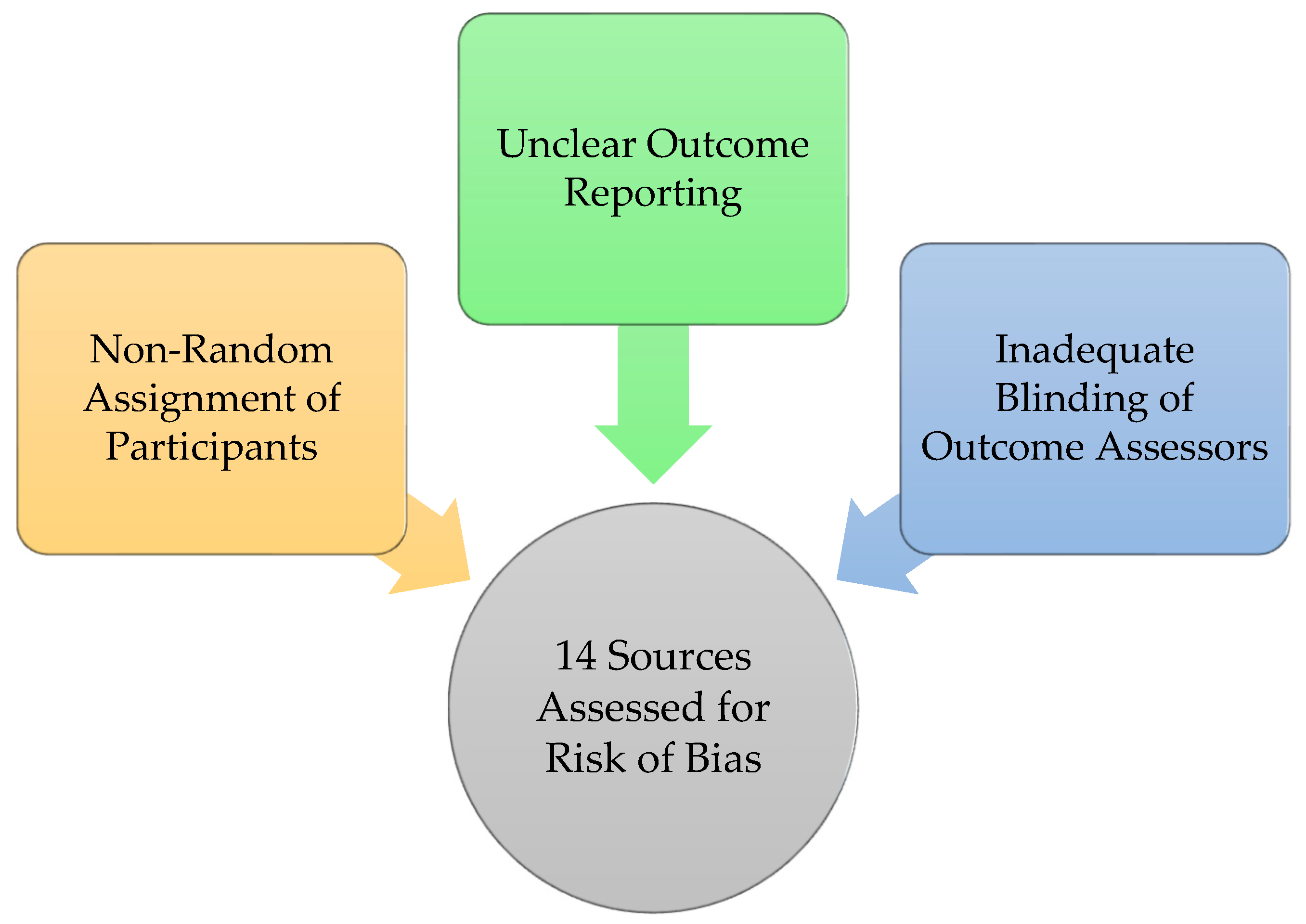
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.4.1. Summary of Outcomes (For All Studies in the Domain of Social Media Strategies)
| Group | Events/Total | Effect Estimate (95% CI) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content-focused strategy | 85/150 | 1.12 (1.03 to 1.21) | Focus on interactive content, media sharing. |
| Technology integration strategy | 45/120 | 0.95 (0.85 to 1.05) | Involves integrating CRM tools. |
| Process-oriented strategy | 78/140 | 1.05 (0.96 to 1.14) | Focuses on content scheduling and audience segmentation. |
| User-generated content strategy | 60/100 | 1.18 (1.02 to 1.32) | Strong impact on customer engagement. |
| Direct engagement (ads, promotions) | 52/110 | 0.88 (0.73 to 1.02) | Lower direct engagement, higher cost. |
3.4.2. Continuous Outcome Measures
| Group | Mean ROI (%) | SD | Sample Size (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content-focused strategy | 25 | 5.2 | 150 |
| Technology integration strategy | 21 | 4.8 | 120 |
| Process-oriented strategy | 23 | 4.6 | 140 |
| Paid advertising | 450,000 | 35,000 | 100 |
| Organic content | 380,000 | 25,000 | 100 |
3.5. Results of Synthesis
3.5.1. Characteristics and Risk of Bias for Syntheses on Social Media Strategies
| Synthesis | Sample Size | Demographics | Outcomes Measured | Risk of Bias Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Focused Social Media Strategies | N = 200–300 | B2C businesses targeting younger audiences (18-35) | Customer engagement, brand awareness, ROI | Low risk in randomization, unclear allocation, high blinding risk, industry funding bias. |
| Technology Integration in social media | N = 150–250 | B2B & B2C businesses using CRM tools | Lead generation, customer management, tech usage | Moderate randomization risk, unclear allocation, high blinding risk, minimal other bias. |
| Process-Oriented Social Media Strategies | N = 100–200 | SMEs using content scheduling, targeting | Audience engagement, cost efficiency, content reach | Low randomization risk, unclear allocation, high blinding risk, some bias from ad-tech funding. |
3.5.2. Statistical Synthesis for Social Media Strategies
| Synthesis | Summary Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval | Statistical Heterogeneity (I²) | Direction of Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Focused Strategies | 1.12 (Effect Size) |
1.03 to 1.21 | 40% (Moderate heterogeneity) |
Positive effect on customer engagement and brand awareness |
| Technology Integration Strategies | 0.95 (Effect Size) |
0.85 to 1.05 | 30% (Moderate heterogeneity) |
Moderate improvement in lead generation |
| Process-Oriented Strategies | 1.05 (Effect Size) |
0.96 to 1.14 | 25% (Low heterogeneity) |
Increased cost efficiency and engagement through scheduling |
3.5.3. Investigations into Causes of Heterogeneity
| Synthesis | Heterogeneity (I²) | Possible Causes of Heterogeneity | Effect on Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Focused Strategies | 40% (Moderate heterogeneity) |
- Variation in content type (video, images, text) - Audience demographics (age, region) |
Slight variation in engagement outcomes |
| Technology Integration Strategies | 30% (Moderate heterogeneity) |
- Different CRM tools and platforms used - Business size and complexity |
Moderate differences in lead generation rates |
| Process-Oriented Strategies | 25% (Low heterogeneity) |
- Variability in content scheduling strategies - Different target audience behaviors |
Minimal impact on cost efficiency and engagement |
3.5.4. Sensitivity Analysis Results for Social Media Strategies
| Synthesis | Main Summary Estimate | Sensitivity Estimate |
Assumptions Tested | Result Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Focused Strategies | 1.12 (Effect Size) | 1.08 (Effect Size) | Excluding studies with high risk of bias | Small change in effect, conclusions remain robust |
| Technology Integration Strategies | 0.95 (Effect Size) | 0.97 (Effect Size) | Removing studies using different CRM platforms | No significant effect on lead generation outcomes |
| Process-Oriented Strategies | 1.05 (Effect Size) | 1.03 (Effect Size) | Removing smaller sample size studies | Minimal impact, strategy still shows efficiency |
3.6. Reporting Biases
| Ref | Year | Journal Title | Deviations from Intended Interventions | Missing Outcome Data | Long-term Impacts of Study | Selection of the Reported Results | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [54] | 2021 | Strategic use of social media within business-to-business (B2B) marketing: A systematic literature review | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [55] | 2016 | Social media marketing: a literature review and implications | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [56] | 2021 | Social media impact on business: a systematic review | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [57] | 2020 | Return on investment in social media marketing: Literature review and suggestions for future research | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
| [58] | 2022 | Social media marketing activities and brand loyalty: A meta-analysis examination | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [59] | 2023 | Social media adoption, usage and impact in business-to-business (B2B) context: A state-of-the-art literature review | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
| [60] | 2020 | An overview of systematic literature reviews in social media marketing | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [61] | 2015 | Social media marketing (SMM) strategies for small to medium enterprises (SMEs) | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
| [62] | 2016 | Strategic approach in social media marketing and a study on successful Facebook cases | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [63] | 2019 | Use of social media by b2b companies: systematic literature review and suggestions for future research | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [64] | 2022 | Social media and its connection to business performance—A literature review | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [65] | 2022 | The relationship between social media marketing and SMEs performance in Nigeria: A systemic literature review | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [66] | 2019 | Social media marketing and customer engagement: A review on concepts and empirical contributions | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [67] | 2020 | Do social media marketing activities enhance consumer perception of brands? A meta-analytic examination | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [68] | 2016 | A systematic review of extant literature in social media in the marketing perspective | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [68] | 2018 | Exploring antecedents of social media usage in B2B: a systematic review | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [69] | 2023 | Political social media marketing: a systematic literature review and agenda for future research | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [70] | 2022 | Promoting SMEs in pacific island countries through effective marketing strategies: a systematic literature review and a future research agenda | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [71] | 2023 | A meta-analysis of the effects of brands’ owned social media on social media engagement and sales | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [72] | 2021 | Exploring and evaluating success factors of social media marketing strategy: a multi-dimensional-multi-criteria framework | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [73] | 2018 | Alignment of business and social media strategies: insights from a text mining analysis | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [74] | 2023 | Digital marketing strategies and the impact on customer experience: A systematic review | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [75] | 2017 | The social media and marketing strategies: how it impacts the small and medium sized enterprises business performance | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [76] | 2024 | Exploring the impact of beauty vloggers’ credible attributes, parasocial interaction, and trust on consumer purchase intention in influencer marketing | High | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [77] | 2024 | Using Social Media Analysis to Improve E-commerce Marketing Strategies | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
| [78] | 2024 | Strategic use of social media in new product development in B2B firms: The role of absorptive capacity | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [79] | 2024 | The BTS ARMY on Twitter flocks together: How transnational fandom on social media build a viable system | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [80] | 2024 | The impact of digital marketing, social media, and digital transformation on the development of digital leadership abilities and the enhancement of employee performance: A case study of the Amman Stock Exchange | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [81] | 2024 | An integrated CRITIC-EDAS approach for assessing enterprise crisis management effectiveness based on Weibo | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [82] | 2024 | Social media, relationship marketing and corporate ESG performance | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [83] | 2024 | The role of innovation and social media in explaining corporate social responsibility–business sustainability nexus in entrepreneurial SMEs | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [84] | 2024 | Characteristics of the vegetable oil debate in social-media and its implications for sustainability | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [85] | 2023 | The effect of social media influencer marketing on sustainable food purchase: Perspectives from multi-group SEM and ANN analysis | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [86] | 2024 | Exploring the social and spatial role of social media for community entrepreneurship | Low | High | High | Low | Neutral |
| [87] | 2024 | Social media and food consumer behavior: A systematic review | Low | High | High | Low | Neutral |
| [88] | 2024 | Social media marketing strategy: The impact of firm generated content on customer based brand equity in retail industry | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [89] | 2024 | Impact of meme marketing on consumer purchase intention: Examining the mediating role of consumer engagement | Low | High | High | Low | Neutral |
| [90] | 2020 | Predicting trust in online advertising with an SEM-artificial neural network approach | High | Low | High | Low | Neutral |
| [91] | 2021 | Sources, Channels and Strategies of Disinformation in the 2020 US Election: Social Networks, Traditional Media and Political Candidates |
High | Low | High | Low | Neutral |
| [92] | 2020 | Survey on Data Analysis in Social Media: A Practical Application Aspect | High | Low | High | Low | Neutral |
| [93] | 2020 | Entrepreneurial entry: The role of social media | High | Low | High | Low | Neutral |
| [94] | 2018 | Social Media Adoption as a Business Platform: An Integrated TAM-TOE Framework | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [95] | 2018 | Research Trends of Online Marketing in Social Media Research | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [96] | 2018 | Modeling and maximizing influence diffusion in social networks for viral marketing | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [97] | 2018 | The interactive mobile social media advertising: An imminent approach to advertise tourism products and services? | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [98] | 2017 | The Social Media Use Integration Scale: Toward Reliability and Validity | High | Low | High | Low | Neutral |
| [99] | 2017 | Social media usage and firm performance: the mediating role of social capital | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [100] | 2017 | Using Social Media at National Meetings in Hematology—Optimal Use, Tips, Strategies, and Limitations | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [101] | 2017 | Succeeding on Social Media: Exploring Communication Strategies for Wine Marketing | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [102] | 2017 | Using online platforms to engage employees in unionism. The case of IBM | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [103] | 2017 | Integrating social media within an integrated marketing communication decision-making framework | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [104] | 2016 | Factors shaping attitudes towards UK bank brands: An exploratory analysis of social media data | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [105] | 2016 | Social network ad allocation and optimization: a geometric mapping-based approach | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [106] | 2022 | Utilization of Social Media and Its Impact on Marketing Performance: A Case Study of SMEs in Indonesia | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [107] | 2023 | Effective Social Media Marketing Strategies for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Indonesia | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [108] | 2021 | Exploring and Evaluating Success Factors of Social Media Marketing Strategy: A Multi-Dimensional-Multi-Criteria Framework | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [109] | 2021 | Integrating Social Media and Traditional Modes of Customer Interaction for New B2B Service Development | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [110] | 2021 | Mapping social media analytics for small business: A case study of business analytics | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [111] | 2024 | Exploring and Evaluating Success Factors of Social Media Marketing Strategy: A Multi-Dimensional-Multi-Criteria Framework | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [112] | 2022 | Thriving in a Shifting Landscape: Role of social media in Support of Business Strategy | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [113] | 2023 | Effectiveness of B2B Social Media Marketing: The Effect of Message Source and Message Content on Social Media Engagement | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [114] | 2024 | The Impact of Social Media Marketing on Brand Awareness, Brand Engagement, and Purchase Intention in Emerging Economies | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [115] | 2023 | Marketing Strategies on Social Media Platforms | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [116] | 2020 | Utilization and Effectiveness of Social Media Message Strategy: How B2B Brands Differ from B2C Brands | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| [117] | 2020 | Digital Engagement Strategies and Tactics in Social Media Marketing | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [118] | 2018 | Adoption Strategies of social media in B2B Firms: A Multiple Case Study Approach | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [119] | 2016 | Social Media Brand Building Strategies in B2B Companies | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| [120] | 2023 | Can Salespeople Use Social Media to Enhance Brand Awareness and Sales Performance? The Role of Manager Empowerment and Creativity | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Key Findings and Strategic Implications for Business Leaders
5. Decision-Making Framework for Implementation
6. Best Practices for Successful Implementation
7. Proposed Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Performance
9. Proposed Industry-Specific Frameworks for Study Topic
10. Real-Case Studies and How They Relate to Proposed Systematic Review
| Case Study | Industry | Social Media Strategy | Key Features | Strategic Outcomes | Relation to Systematic Review Findings | Ref. |
| Nike’s #JustDoIt Campaign | Retail | Engaging social media campaign leveraging user-generated content and influencer partnerships. | 1. Use of influencer marketing. 2. Encouragement of user-generated content with #JustDoIt hashtag. |
Significant increase in brand awareness and customer engagement through community-driven content. | The review highlights the importance of consistent engagement and user-generated content for boosting brand visibility. | [129] |
| Mayo Clinic’s Health Information Videos | Healthcare | Educational social media strategy focused on providing informative videos on health topics across platforms. | 1. Educational videos on common health concerns. 2. Patient engagement through Q&A sessions on social media. |
Improved patient trust and higher engagement through reliable, educational content. | The review discusses the need for informative and relevant content that builds trust in sectors such as healthcare. | [130] |
| Chase Bank’s Financial Literacy Initiative | Finance | Social media campaign focused on educating customers about personal finance and investment strategies. | 1. Creation of educational content tailored to different financial topics. 2. Personalized advice through social platforms. |
Increased customer retention and improved lead generation through educational content and direct interaction with clients. | The review highlights the role of educational content in building long-term relationships and enhancing customer trust. | [131] |
| Airbnb’s Experiential Marketing | Hospitality | Content-driven campaign focusing on sharing unique travel experiences and user stories on Instagram and YouTube. | 1. Storytelling through user-generated content. 2. Promotion of unique travel experiences in video format. |
Higher booking rates and brand loyalty through authentic storytelling and customer engagement. | The systematic review emphasizes the role of storytelling and user-generated content in enhancing customer engagement in hospitality. | [132] |
| John Deere’s Agricultural Network | Agriculture | Social media platform for farmers to share insights and agricultural best practices, leveraging user engagement for growth. | 1. Community-driven engagement platform. 2. Focus on promoting sustainable farming techniques. |
Increased brand loyalty and community growth through active user participation and sustainability messaging. | The review highlights the importance of community-driven engagement and sustainability-focused messaging in industries like agriculture. | [133] |
| Harvard University’s Virtual Classrooms | Education | Leveraging social media for promoting virtual classes and educational webinars, targeting both students and parents. | 1. Use of Facebook Live and Instagram to promote virtual classes. 2. Engaging webinars and Q&A sessions. |
Increased student engagement and enrollment through social media promotion of virtual learning opportunities. | The review discusses the role of educational content and real-time engagement in improving student enrollment and retention. | [134] |
| GE’s Industrial Internet Initiative | Manufacturing | Use of LinkedIn and YouTube to showcase innovations in manufacturing and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). | 1. Thought leadership through technical content. 2. Showcasing product innovations and case studies. |
Expanded B2B relationships and increased market visibility through content showcasing industry expertise. | The review highlights the role of technical content and thought leadership in building industry relationships and enhancing visibility in manufacturing. | [135] |
11. Proposed Roadmap for SMEs businesses and Policy Recommendations
| SME Industry | Strategic Actions | Technology and Tools | Content Strategy | Customer Engagement Approach | Policy Recommendations | Challenges | Opportunities | Expected Outcomes | Ties to Systematic Review Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | - Omnichannel marketing across social platforms (Instagram, Facebook, TikTok). - Leverage influencer partnerships to drive product visibility. - Integrate e-commerce with social media platforms. |
- CRM systems for customer data integration. - AI-powered chatbots for real-time customer interaction. |
- Focus on product storytelling and user-generated content. - Utilize Instagram Stories and Facebook Live for product launches. |
- Personalized messaging through targeted ads. - Host live Q&A sessions and virtual product demonstrations. |
- Tax incentives for digital marketing investments. - Policies promoting e-commerce growth. |
- High competition in digital space. - Managing customer data and privacy regulations. |
- Enhanced customer loyalty through personalized experiences. - Direct sales growth from integrated e-commerce and social platforms. |
- Increased sales revenue. - Improved customer retention. - Greater brand awareness and engagement. |
- Aligns with the review’s focus on engagement techniques and the importance of platform selection for SMEs to drive audience reach. |
| Healthcare | - Implement telehealth services with social media integration. - Use social media for patient education campaigns. - Collaborate with health influencers for awareness drives. |
- Video conferencing tools (e.g., Zoom) integrated with social media. - AI-based health monitoring apps linked with social media. |
- Educational content like health tips, live Q&A with doctors. - Create health awareness campaigns using Instagram and YouTube. |
- Use real-time social media platforms to answer patient inquiries. - Engage in community-building via health forums on Facebook. |
- Develop digital health regulations for telemedicine. - Guidelines for data security and patient privacy in social media use. |
- Ensuring patient data confidentiality. - Regulatory restrictions on social media marketing for healthcare services. |
- Better patient engagement and education. - Expansion of telemedicine services to underserved regions. |
- Increased patient satisfaction and retention. - Improved public health outcomes through outreach. |
- Tied to the systematic review’s emphasis on audience engagement, particularly in sectors with sensitive customer data like healthcare. |
| Manufacturing | - B2B digital marketing via LinkedIn for supplier engagement. - Use social media for product demos and industry updates. |
- ERP and CRM systems integrated with social media for real-time supplier updates. | - Share industry trends, innovation, and case studies through LinkedIn articles. - Run webinars for product training and tech adoption. |
- Build relationships with industry partners through LinkedIn and industry-specific forums. | - Government grants for tech adoption in manufacturing. - Policies encouraging digital transformation in industrial sectors. |
- High costs of transitioning traditional operations to digital. | - Operational efficiency through tech adoption. - Global visibility for B2B marketing and networking. |
- Higher supply chain efficiency. - Increased global market reach. - Enhanced brand reputation in industry sectors. |
- Reflects the review’s emphasis on sector-specific social media strategies, particularly for high-tech industries requiring professional networking. |
| Education | - Use live streaming platforms (YouTube, Facebook) for virtual classes. - Promote educational programs via social media. - Create partnerships with educational influencers. |
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) integrated with social media platforms. - Cloud-based collaboration tools. |
- Promote virtual events, webinars, and educational workshops. - Engage students through interactive quizzes and polls on Instagram and Facebook. |
- Regular feedback collection via social media to improve learning experiences. - Create community groups for collaborative learning. |
- Government funding for digital literacy programs. - Support for remote learning technologies. |
- Digital divide in underserved areas. - Difficulty in ensuring student engagement in virtual settings. |
- Expanded access to educational resources. - Global student outreach through social media. |
- Increased enrollment and student engagement. - Better learning outcomes through online collaboration. |
- The review’s findings on targeted content and platform-specific engagement align with the education sector’s use of interactive media for learning. |
| Finance | - Develop thought leadership content via LinkedIn articles and Twitter discussions. - Use social media for financial literacy campaigns. - Run secure financial services ads on Facebook and Instagram. |
- Secure online banking apps integrated with social media for seamless engagement. | - Create educational content focused on personal finance tips. - Engage in thought leadership by hosting webinars on finance trends. |
- Leverage customer reviews and testimonials to build trust in financial services. - Encourage user-generated content for promoting financial success stories. |
- Cybersecurity policies for online banking. - Regulations for digital marketing in finance. |
- Maintaining trust and compliance with security regulations. | - Establish financial thought leadership. - Build customer trust and loyalty. |
- Higher customer retention through trust-based engagement. - Increased financial product adoption. |
- Reflects the review’s focus on trust-building and thought leadership as essential for customer engagement in industries like finance. |
| Hospitality | - Use Instagram and Facebook for tourism promotion. - Engage with travelers through visual content and influencer partnerships. - Leverage online reviews for reputation management. |
- Online booking platforms integrated with social media reviews. - AI chatbots for real-time booking queries. |
- Leverage user-generated content (UGC) from customers to promote destinations. - Run paid ads targeting travel enthusiasts on Instagram. |
- Use real-time feedback from customers to improve service. - Run personalized travel offers and packages via social media. |
- Policies to boost digital infrastructure in tourism. - Support for digital marketing in tourism through tax breaks. |
- Managing negative reviews and online reputation. - Highly competitive market. |
- Increased direct bookings via social media channels. - Enhanced international tourism marketing. |
- Higher customer retention through personalized experiences. - Increased brand loyalty via social engagement. |
- The review’s findings on engagement techniques and platform-specific strategies align with hospitality SMEs’ need for visual content and influencer marketing to boost customer engagement. |
| Agriculture | - Promote sustainable farming practices via social media platforms. - Use social media for supply chain transparency and consumer education. |
- IoT integration for real-time monitoring of agricultural processes. - Drones and automated tools for showcasing smart farming practices. |
- Post videos and updates on sustainable farming techniques and product quality. - Highlight success stories of local farmers using Facebook and LinkedIn. |
- Engage customers and stakeholders by offering insights into the farm-to-table journey. - Build online communities focused on sustainable agriculture. |
- Government incentives for rural connectivity and digital literacy programs in agriculture. - Policies promoting IoT adoption in rural farming. |
- Limited access to digital tools in rural areas. - High costs associated with IoT and tech adoption. |
- Enhanced market visibility for smallholder farmers. - Improved consumer trust through transparency. |
- Increased market share for sustainably produced goods. - Greater supply chain efficiency through real-time monitoring. |
- Reflects the review’s emphasis on sector-specific customization and how digital tools and engagement techniques are vital for industries like agriculture to enhance transparency and consumer trust. |
| Technology | - Use Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube for product launches and tech innovations. - Leverage social media for industry thought leadership. |
- AI-driven CRM systems to track customer behavior. - Data analytics platforms integrated with social media for real-time insights. |
- Publish technical content, how-to guides, and live demonstrations. - Host live Q&A sessions with developers or engineers to engage with tech enthusiasts. |
- Encourage user feedback through social media polls and forums. - Use LinkedIn for B2B networking and partnership development. |
- Policies supporting tech innovation and R&D tax incentives. - Government support for STEM education to fuel the tech talent pipeline. |
- Rapidly changing technologies and customer expectations. - Difficulty in retaining tech-savvy customers. |
- Establish industry thought leadership. - Build trust through open-source contributions and transparent practices. |
- Increased market penetration for new technologies. - Enhanced customer loyalty through continuous engagement and support. |
- Tied to the review’s findings on content quality, thought leadership, and audience engagement in tech-focused SMEs. |
| Creative Industries | - Use Instagram, Pinterest, and TikTok for showcasing creative work (design, fashion, art). - Leverage collaborations with influencers and brand ambassadors. |
- Design tools integrated with social media platforms (e.g., Adobe Creative Cloud, Canva). - Social commerce platforms for direct selling. |
- Focus on visual storytelling, portfolios, and behind-the-scenes content. - Use Instagram Stories and TikTok challenges to engage followers. |
- Run interactive contests and campaigns for user-generated content (UGC). - Collaborate with influencers to increase brand reach and authenticity. |
- Intellectual property protection policies for digital content creators. - Government support for creative digital entrepreneurship. |
- Saturation of social media platforms with creative content. - Difficulty in standing out and monetizing creative work. |
- Increased brand visibility through influencer collaborations. - Direct sales growth via social commerce platforms. |
- Expanded market reach through viral campaigns and collaborations. - Improved customer loyalty and brand affinity. |
- Aligns with the review’s focus on content relevance, engagement techniques, and platform selection, particularly for visual-heavy industries like design and fashion. |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silalahi, R.V.; Tiffanny; Panjaitan, A. “Brand awareness building through social media (Facebook and Instagram) (Case study: GianTree startup),” in AIP Conference Proceedings, 2023, vol. 2485, p. 080028.
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Ismagilova, E.; Hughes, D.L.; Carlson, J.; Filieri, R.; Jacobson, J.; Jain, V.; Karjaluoto, H.; Kefi, H.; Krishen, A.S.; et al. Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 59, 102168. [CrossRef]
- Rosário, A.T.; Dias, J.C. Marketing Strategies on Social Media Platforms. Int. J. E-Business Res. 2023, 19, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, R. The Role and Importance of Social Media Marketing in Brand Building. Ir. Interdiscip. J. Sci. Res. 2023, 07, 01–09. [CrossRef]
- Smith, Thomas & Johnson, Emma & Davis, Charles & Rusdi, Alip. (2024). Social Media Marketing is an Effective Strategy for Increasing Brand Awareness, Customer Loyalty, and Sales Keywords: Effects of social media marketing, Impact of social media on brand awareness, and Social media’s role in customer loyalty. Journal of Social Media Marketing. Vol 5. 61-78.
- O’Brien, C. (2022). How to Develop a Social Media Strategy That Drives Brand Awareness & ROI | Blog | Online Digital Marketing Courses. [online] Digital Marketing Institute. Available at: https://digitalmarketinginstitute.com/blog/social-media-strategy.
- Paquette, Holly, “Social Medi\.
- a as a Marketing Tool: A Literature Review” (2013). Major Papers by TMD Master of Science Students. Paper 2. https://digitalcommons.uri.edu/tmd_major_papers/2.
- Appel, G.; Grewal, L.; Hadi, R.; Stephen, A.T. The future of social media in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 79–95. [CrossRef]
- Jamil, K.; Dunnan, L.; Gul, R.F.; Shehzad, M.U.; Gillani, S.H.M.; Awan, F.H. Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Influencing Customer Intentions: A Perspective of a New Emerging Era. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 808525. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qasim, H. Does E-Brand experience matter in the consumer market? Explaining the impact of social media marketing activities on consumer-based brand equity and love. J. Consum. Behav. 2021, 20, 1065–1077. [CrossRef]
- Jamil, K.; Dunnan, L.; Gul, R.F.; Shehzad, M.U.; Gillani, S.H.M.; Awan, F.H. Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Influencing Customer Intentions: A Perspective of a New Emerging Era. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 808525. [CrossRef]
- Kenan, J. (2023). How to Build Your Social Media Marketing Strategy. [online] Sprout Social. Available at: https://sproutsocial.com/insights/social-media-marketing-strategy/.
- C. Newberry, “How to create a social media marketing strategy [template],” Social Media Marketing & Management Dashboard, 17-Jul-2024. [Online]. Available: https://blog.hootsuite.com/how-to-create-a-social-media-marketing-plan/.
- J. Kenan, “Social media marketing: What it is and how to build your strategy,” Sprout Social, 20-Sep-2023. [Online]. Available: https://sproutsocial.com/insights/social-media-marketing-strategy/.
- Digital Marketing Institute, “How to create the ultimate social media strategy that drives brand awareness & ROI,” Digital Marketing Institute, 20-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://digitalmarketinginstitute.com/blog/social-media-strategy. [Accessed: 12-Aug-2024].
- M. Saleem, S. A. Khan, I. R. Al Shamsi, and H. Magd, “Digital marketing through social media best practices: A case study of HEIs in the GCC region,” in Advances in Marketing, Customer Relationship Management, and E-Services, Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2023, pp. 17–30.
- Americaneagle.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.americaneagle.com/insights/blog/post/a-beginners-introduction-to-social-media-marketing. [Accessed: 12-Aug-2024].
- R., Rijitha. (2021). THE IMPACT OF SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING ON CONSUMER PURCHASE INTENTION. 223.
- Olsen, R.K.; Tenenboim, O.; Hess, K.; Westlund, O.; Lindén, C.-G.; Broersma, M. Platform paradoxes and public service media legitimacy: a cross-national study. Information, Commun. Soc. 2024, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Chan, F. (2022). A Study of Social Media Influencers and Impact on Consumer Buying Behaviour in the United Kingdom. International Journal of Business & Management Studies, [online] 03(7), pp.2694–1449. Available at: https://ijbms.net/assets/files/1659111546.pdf.
- Maryville University (2020). The Evolution of Social media: How Did It Begin and Where Could It Go next? [online] Maryville Online. Available at: https://online.maryville.edu/blog/evolution-social-media/.
- Oyza, Icha & Agwu, Edwin. (2015). Effectiveness of Social Media Networks as a Strategic Tool for Organizational Marketing Management. The Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce. 01. 10.4172/1204-5357.S2-006.
- Missionmediau.org. (2024). Foundations of Digital Engagement Strategies – Media training–Mission Media U. [online] https://www.missionmediau.org/foundations-of-digital-engagement-strategies/?gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAjwufq2BhAmEiwAnZqw8pHSjPj2kp94bsI4b5NmbgZEnKiJnv2ZZwkMfYSaIfY-apiEsnjMkhoCklQQAvD_Bw.
- Balaji, M.; Behl, A.; Jain, K.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Giannakis, M.; Shankar, A.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Effectiveness of B2B social media marketing: The effect of message source and message content on social media engagement. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2023, 113, 243–257. [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S. (n.d.). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING STRATEGIES AMONG MICROBREWERIES: A PERCEPTUAL ANALYSIS. [online] Available at: https://etd.cput.ac.za/bitstream/20.500.11838/3030/1/Goodwin_Sandi_209038853.pdf.
- Lawler, B. (2023). Does Social Media Marketing Improve Business Performance? |. [online] DSM | Digital School of Marketing. Available at: https://digitalschoolofmarketing.co.za/social-media-marketing-blog/does-social-media-marketing-improve-business-performance/.
- Barnhart, B. (2020). Social media and healthcare: how to prioritize what patients need. [online] Sprout Social. Available at: https://sproutsocial.com/insights/social-media-in-healthcare/.
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Ismagilova, E.; Hughes, D.L.; Carlson, J.; Filieri, R.; Jacobson, J.; Jain, V.; Karjaluoto, H.; Kefi, H.; Krishen, A.S.; et al. Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 59, 102168. [CrossRef]
- In-mind.org. (2018). Selfie-Esteem: The Relationship Between Body Dissatisfaction and Social Media in Adolescent and Young Women | Magazine issue 1/2018 - Issue 35 | In-Mind. [online] Available at: https://in-mind.org/article/selfie-esteem-the-relationship-between-body-dissatisfaction-and-social-media-in-adolescent?gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAjwufq2BhAmEiwAnZqw8ii7bJKqwGd3SwNJx_58clCGtt3p6sTizh1UVBDewXdJoiIGhW2bOxoCJSUQAvD_BwE.
- Feedipedia.org. (2020). Statista, 2020. Statista Inc., The Statistics Portal | Feedipedia. [online] Available at: https://www.feedipedia.org/node/26557.
- Parashar, “Social media challenges encountered by business ventures,” in Innovation, Technology, and Knowledge Management, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023, pp. 171–183.
- M. M. Hasan, F. Akter, I. Zahan Safia, A. Hossain Meraj, and M. Hasan, “Effective Digital Marketing Approaches for E-commerce Platforms,” in 2022 11th International Conference on Software and Computer Applications, 2022.
- Olson, E.M.; Olson, K.M.; Czaplewski, A.J.; Key, T.M. Business strategy and the management of digital marketing. Bus. Horizons 2021, 64, 285–293. [CrossRef]
- K. Shalender, “Building effective social media strategy: Case-based learning and recommendations,” in Digital Entertainment, Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2021, pp. 233–244.
- Arumugam, Vidhya. (2023). A STUDY ON THE IMPACT OF SOCIAL MEDIA ON MARKETING A BRAND. 10. 327.
- M. O. Opresnik, “Effective online advertising strategy,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 418–424.
- J. Lee, Business hack: The wealth dragon way to build a successful business in the digital age. Wiley, 2018.
- Inderscience Publishers - linking academia, business and industry through research,” Inderscience.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.inderscience.com/offers.php?id=79037. [Accessed: 12-Aug-2024].
- B. Ogbuji and A. Papazafeiropoulou, “Social media strategies for companies: A comprehensive framework,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016, pp. 3–14.
- Adisa, D. (2023). Everything you need to know about social media algorithms. [online] Sprout Social. Available at: https://sproutsocial.com/insights/social-media-algorithms/.
- Social Media Strategy Guide.” Available: https://blog.hootsuite.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Social-Media-Strategy-Guide.pdf.
- Chaffey, D. (2024). Global Social Media Research Summary 2024. [online] Smart Insights. Available at: https://www.smartinsights.com/social-media-marketing/social-media-strategy/new-global-social-media-research/.
- Hojnik, B.B.; Huđek, I. Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in the Digital Age: Understanding Characteristics and Essential Demands. Information 2023, 14, 606. [CrossRef]
- J. Kenan, “How to Build Your Social Media Marketing Strategy,” Sprout Social, Sep. 20, 2023. https://sproutsocial.com/insights/social-media-marketing-strategy/.
- Naim and S. K. Kautish, Eds., Building a brand image through electronic customer relationship management. Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2024.
- scribbr, “Types of Bias in Research,” Scribbr, 2022. https://www.scribbr.com/category/research-bias/.
- Biases Archive - Catalog of Bias,” Catalog of Bias, 2019. https://catalogofbias.org/biases/.
- Tsiu, S.; Ngobeni, M.; Mathabela, L.; Thango, B. Applications and Competitive Advantages of Data Mining and Business Intelligence in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090940. [CrossRef]
- Key Elements of Effective Social Media Marketing,” SCU, Nov. 04, 2023. https://onlinedegrees.scu.edu/media/blog/key-elements-of-effective-social-media-marketing.
- E. Han, “Setting Business Goals & Objectives: 4 Considerations | HBS Online,” Business Insights Blog, Oct. 31, 2023. https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/business-goals-and-objectives#:~:text=Setting%20business%20goals%20and%20objectives.
- Fan, Z.; Cheng, W.; Chen, G.; Huang, R. Meta-Analysis in Educational Technology Research: A Content Analysis. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Austin, TX, USA, 2016, pp. 460-462. [CrossRef]
- von Hippel, P.T. The heterogeneity statistic I2 can be biased in small meta-analyses. BMC Med Res. Methodol. 2015, 15, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Page et al., “PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews,” BMJ, vol. 372, p. n160, 2021.
- Research guides: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: Assess certainty,” 2020.
- Sadoyu, S.; Tanni, K.A.; Punrum, N.; Paengtrai, S.; Kategaew, W.; Promchit, N.; Lai, N.M.; Thakkinstian, A.; Ngorsuraches, S.; Bangpan, M.; et al. Methodological approaches for assessing certainty of the evidence in umbrella reviews: A scoping review. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0269009. [CrossRef]
- Kolaski, K.; Logan, L.R.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Guidance to best tools and practices for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, A.; Mokhothu, K.; Tshikhotho, M.; Thango, B. Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090882. [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, S.; Liu, H.; Raddats, C. Strategic use of social media within business-to-business (B2B) marketing: A systematic literature review. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2021, 97, 35–58. [CrossRef]
- H. Alves, C. Fernandes, and M. Raposo, “Social media marketing: A literature review and implications: Implications of social media marketing,” Psychol. Mark., vol. 33, no. 12, pp. 1029–1038, 2016.
- Borhan-Eddine, A.; Fee, L.Y.; Adnan, Z.H.; Nor, M.W.M. The Impact of Political Efficacy, Discussion, and Expression Through Social Media on Youth Political Participation: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2020, 10, 11–22. [CrossRef]
- B. Lal, E. Ismagilova, Y. K. Dwivedi, and S. Kwayu, “Return on investment in social media marketing: Literature review and suggestions for future research,” in Digital and Social Media Marketing, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 3–17.
- Ibrahim, B. Social Media Marketing Activities and Brand Loyalty: A Meta-Analysis Examination. J. Promot. Manag. 2021, 28, 60–90. [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Ismagilova, E.; Rana, N.P.; Raman, R. Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 25, 971–993. [CrossRef]
- Rowley, J.; Keegan, B.J. An overview of systematic literature reviews in social media marketing. J. Inf. Sci. 2019, 46, 725–738. [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274703542_SOCIAL_MEDIA_MARKETING_SMM_STRATEGIES_FOR_SMALL_TO_MEDIUM_ENTERPRISES_SMES. [Accessed: 19-Sep-2024].
- Bekoglu, F.B.; Onaylı, C. Strategic Approach in Social Media Marketing and a Study on Successful Facebook Cases. Eur. Sci. J. ESJ 2016, 12. [CrossRef]
- Y. K. Dwivedi, E. Ismagilova, N. P. Rana, and V. Weerakkody, “Use of social media by b2b companies: Systematic literature review and suggestions for future research,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019, pp. 345–355.
- Emmanuel, B.; Zhao, S.; Egala, S.B.; Mammet, Y.; Godson, K. Social Media and Its Connection to Business Performance—A Literature Review. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2022, 12, 877–893. [CrossRef]
- The relationship between social media marketing and SMEs performance in Nigeria: A systemic literature review. .
- Dissanayake, D.M.R.; Siriwardana, A.; Ismail, N. Social Media Marketing and Customer Engagement: A Review on Concepts and Empirical Contributions. Kelaniya J. Manag. 2019, 8, 71–85. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Aljarah, A.; Ababneh, B. Do Social Media Marketing Activities Enhance Consumer Perception of Brands? A Meta-Analytic Examination. J. Promot. Manag. 2020, 26, 544–568. [CrossRef]
- A. Alalwan, N. P. Rana, R. Algharabat, and A. Tarhini, “A systematic review of extant literature in social media in the marketing perspective,” in Social Media: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016, pp. 79–89.
- Pascucci, F.; Ancillai, C.; Cardinali, S. Exploring antecedents of social media usage in B2B: a systematic review. Manag. Res. Rev. 2018, 41, 629–656. [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Roy, S.K.; Lees-Marshment, J.; Dey, B.L.; Muhammad, S.S.; Kumar, S. Political social media marketing: a systematic literature review and agenda for future research. Electron. Commer. Res. 2023, 1–36. [CrossRef]
- Kgakatsi, M.; Galeboe, O.; Molelekwa, K.; Thango, B. The Impact of Big Data on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090985. [CrossRef]
- Liadeli, G.; Sotgiu, F.; Verlegh, P.W. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Brands’ Owned Social Media on Social Media Engagement and Sales. J. Mark. 2022, 87, 406–427. [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.J.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Mahdiraji, H.A. Exploring and evaluating success factors of social media marketing strategy: a multi-dimensional-multi-criteria framework. Foresight 2021, 23, 655–678. [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.H.; Jeyaraj, A. Alignment of business and social media strategies: insights from a text mining analysis. J. Bus. Anal. 2018, 1, 117–134. [CrossRef]
- M. T. Nuseir, G. A. El Refae, A. Aljumah, M. Alshurideh, S. Urabi, and B. A. Kurdi, “Digital marketing strategies and the impact on customer experience: A systematic review,” in Studies in Computational Intelligence, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023, pp. 21–44.
- Mokhtar, Noor Fadhiha & Rosufila, Zuha & Abu Hasan, Zuha & Masa Halim, Masa Halim & Halim, Abdul, “The social media and marketing strategies: how it impacts the small and medium sized enterprises business performance,” ResearchGate, 2017. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322488201_The_Social_Media_and_Marketing_Strategies_How_it_Impacts_the_Small-and_Medium-sized_Enterprises’_Business_Performance. [Accessed: 19-Sep-2024].
- Garg, M.; Bakshi, A. Exploring the impact of beauty vloggers’ credible attributes, parasocial interaction, and trust on consumer purchase intention in influencer marketing. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Semenda, O.; Sokolova, Y.; Korovina, O.; Bratko, O.; Polishchuk, I. Using Social Media Analysis to Improve E-commerce Marketing Strategies. Int. Rev. Manag. Mark. 2024, 14, 61–71. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Cao, G.; Weerawardena, J. Strategic use of social media in new product development in B2B firms: The role of absorptive capacity. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2024, 120, 132–145. [CrossRef]
- K. Nam, H. Kim, S. Kang, and H.-J. Kim, “The BTS ARMY on Twitter flocks together: How transnational fandom on social media build a viable system,” Telemat. Inform., vol. 91, no. 102143, p. 102143, 2024.
- The impact of digital marketing, social media, and digital transformation on the development of digital leadership abilities and the enhancement of employee performance: A case study of the. Amman Stock Exchange.
- Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, P.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Deveci, M.; Mardani, A. An integrated CRITIC-EDAS approach for assessing enterprise crisis management effectiveness based on Weibo. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2024, 32. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Hou, R.; Wang, S.; Omar, N.A.B. Social media, relationship marketing and corporate ESG performance. Finance Res. Lett. 2024, 63. [CrossRef]
- Çera, G.; Ndou, V. The role of innovation and social media in explaining corporate social responsibility–business sustainability nexus in entrepreneurial SMEs. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024, ahead-of-p. [CrossRef]
- Candellone, E.; Aleta, A.; de Arruda, H.F.; Meijaard, E.; Moreno, Y. Characteristics of the vegetable oil debate in social-media and its implications for sustainability. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Molete, O. B.; Mokhele, S. E.; Ntombela, S. D.; Thango, B. A. The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091024. [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, J. Exploring the social and spatial role of social media for community entrepreneurship. Entrep. Reg. Dev. 2023, 36, 1054–1070. [CrossRef]
- Rini, L.; Schouteten, J.J.; Faber, I.; Frøst, M.B.; A Perez-Cueto, F.J.; De Steur, H. Social media and food consumer behavior: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 143. [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdallah, G.; Barzani, R.; Dandis, A.O.; Eid, M.A.H. Social media marketing strategy: The impact of firm generated content on customer based brand equity in retail industry. J. Mark. Commun. 2024, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Rathi, N.; Jain, P. Impact of meme marketing on consumer purchase intention: Examining the mediating role of consumer engagement. Innov. Mark. 2023, 20, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Mothapo, M.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Tracking and Measuring Social Media Activity: Key Metrics for SME Strategic Success – A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091757. [CrossRef]
- Pedriza, S.B. Sources, Channels and Strategies of Disinformation in the 2020 US Election: Social Networks, Traditional Media and Political Candidates. Journal. Media 2021, 2, 605–624. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Han, M.; Cai, Z. Survey on data analysis in social media: A practical application aspect. Big Data Min. Anal. 2020, 3, 259–279. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liang, Q.; Mahto, R.V.; Deng, W.; Zhang, S.X. Entrepreneurial entry: The role of social media. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 161, 120337–120337. [CrossRef]
- Ngcobo, K.; Bhengu, S.; Mudau, A.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Enterprise Data Management: Types, Sources, and Real-Time Applications to Enhance Business Performance - A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091913. [CrossRef]
- P. Jitngernmadan and P. Boonmee, “Research trends of online marketing in social media research,” in 2018 International Conference on Information Technology (InCIT), 2018.
- Wang, W.; Street, W.N. Modeling and maximizing influence diffusion in social networks for viral marketing. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2018, 3, 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.W.-H.; Lee, V.-H.; Hew, J.-J.; Ooi, K.-B.; Wong, L.-W. The interactive mobile social media advertising: An imminent approach to advertise tourism products and services?. Telematics Informatics 2018, 35, 2270–2288. [CrossRef]
- Mohlala, T. T.; Mehlwana, L. L.; Nekhavhambe, U. P.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Strategic Innovation in HRIS and AI for Enhancing Workforce Productivity in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091996. [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, S.; Kumar, V.; Rahman, Z. Social media usage and firm performance: the mediating role of social capital. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2017, 7, 51–51:14. [CrossRef]
- C. Logan, “Using social media at national meetings in hematology-optimal use, tips, strategies, and limitations,” Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep., vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 605–610, 2017.
- Dolan, R.; Goodman, S. Succeeding on social media: Exploring communication strategies for wine marketing. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2017, 33, 23–30. [CrossRef]
- R. D. Maiorescu, “Using online platforms to engage employees in unionism. The case of IBM,” Public Relat. Rev., vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 963–968, 2017.
- Valos, M.J.; Maplestone, V.L.; Polonsky, M.J.; Ewing, M. Integrating social media within an integrated marketing communication decision-making framework. J. Mark. Manag. 2017, 33, 1522–1558. [CrossRef]
- Mogaji, E.; Farinloye, T.; Aririguzoh, S. Factors shaping attitudes towards UK bank brands: An exploratory analysis of social media data. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2016, 3. [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Miao, H.; Baras, J.S.; Hajiaghayi, M. Social network ad allocation and optimization: a geometric mapping-based approach. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2016, 6, 110. [CrossRef]
- Chabalala, K.; Boyana, S.; Kolisi, L.; Thango, B. A.; Matshaka, L. Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Advantage in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100020. [CrossRef]
- Effective Social Media Marketing Strategies for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Indonesia.
- Alam, I.(. Integrating Social Media and Traditional Modes of Customer Interaction for New B2B Service Development. J. Business-to-Business Mark. 2021, 28, 321–345. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Mapping social media analytics for small business: A case study of business analytics. Int. J. Fash. Des. Technol. Educ. 2021, 14, 218–231. [CrossRef]
- Tourani, N. Thriving in a shifting landscape: Role of social media in support of business strategy. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2022, 27, 276–281. [CrossRef]
- Balaji, M.; Behl, A.; Jain, K.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Giannakis, M.; Shankar, A.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Effectiveness of B2B social media marketing: The effect of message source and message content on social media engagement. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2023, 113, 243–257. [CrossRef]
- The Impact of Social Media Marketing on Brand Awareness, Brand Engagement, and Purchase Intention in Emerging Economies.
- Rosário, A.T.; Dias, J.C. Marketing Strategies on Social Media Platforms. Int. J. E-Business Res. 2023, 19, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, M. Utilization and effectiveness of social media message strategy: how B2B brands differ from B2C brands. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2020, 35, 721–740. [CrossRef]
- Drummond, C.; O'Toole, T.; McGrath, H. Digital engagement strategies and tactics in social media marketing. Eur. J. Mark. 2020, 54, 1247–1280. [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, M.; Sutton-Brady, C.; Søilen, K.S.; Ulfvengren, P. Adoption strategies of social media in B2B firms: a multiple case study approach. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2018, 33, 730–743. [CrossRef]
- Cawsey, T.; Rowley, J. Social media brand building strategies in B2B companies. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2016, 34, 754–776. [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Itani, O.S.; Rostami, A. Can salespeople use social media to enhance brand awareness and sales performance? The role of manager empowerment and creativity. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2023, 38, 1738–1753. [CrossRef]
- J. Ogilvie, R. Agnihotri, A. Rapp, and K. Trainor, “Social media technology use and salesperson performance: A two study examination of the role of salesperson behaviors, characteristics, and training,” Ind. Mark. Manag., vol. 75, pp. 55–65, 2018.
- Guardian sport, “Nike’s ‘Dream Crazy’ advert starring Colin Kaepernick wins Emmy,” the Guardian, Sep. 16, 2019. Available: https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2019/sep/16/nikes-dream-crazy-advert-starring-colin-kaepernick-wins-emmy.
- Extole, “Glossier marketing: How the beauty brand used word-of-mouth to shake up the industry | Extole,” Extole, Nov. 08, 2022. Available: https://www.extole.com/blog/glossier-marketing-how-the-beauty-brand-used-word-of-mouth-to-shake-up-the-industry/.
- Barber, N.; Taylor, C. Equity benefits of smaller wine regions and lifestyle segmentation. J. Brand Manag. 2011, 19, 158–175. [CrossRef]
- Van Dijck, J. The Culture of Connectivity: A Critical History of Social Media. Oxford University Press. Available online: https://global.oup.com/academic/product/the-culture-of-connectivity-9780199970773.
- Drew, J.M. Cold, warm, warmer, hot! Locating financial literacy hot spots. J. Financial Serv. Mark. 2013, 18, 220–226. [CrossRef]
- Hamari, J., & Koivisto, J. Why Do People Use Airbnb? Exploring Guest Engagement with Storytelling. Journal of Service Research, 19(3), 284–299. Available online: . [CrossRef]
- Lieb, R. Content Marketing: Think Like a Publisher – How to Use Content to Market Online and in Social Media. Que Publishing. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Content-Marketing-Think-Like-Publisher/dp/0789748372.
- Selwyn, N. Social Media in Higher Education. EDUCAUSE Review, 47(6), 36–46. Available online: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2012/11/social-media-in-higher-education.
- Westerman, G., Bonnet, D., & McAfee, A. Leading Digital: Turning Technology into Business Transformation. Harvard Business Review Press.
- Available online: https://hbr.org/product/leading-digital-turning-technology-into-business-transformation/2066E-KND-ENG.
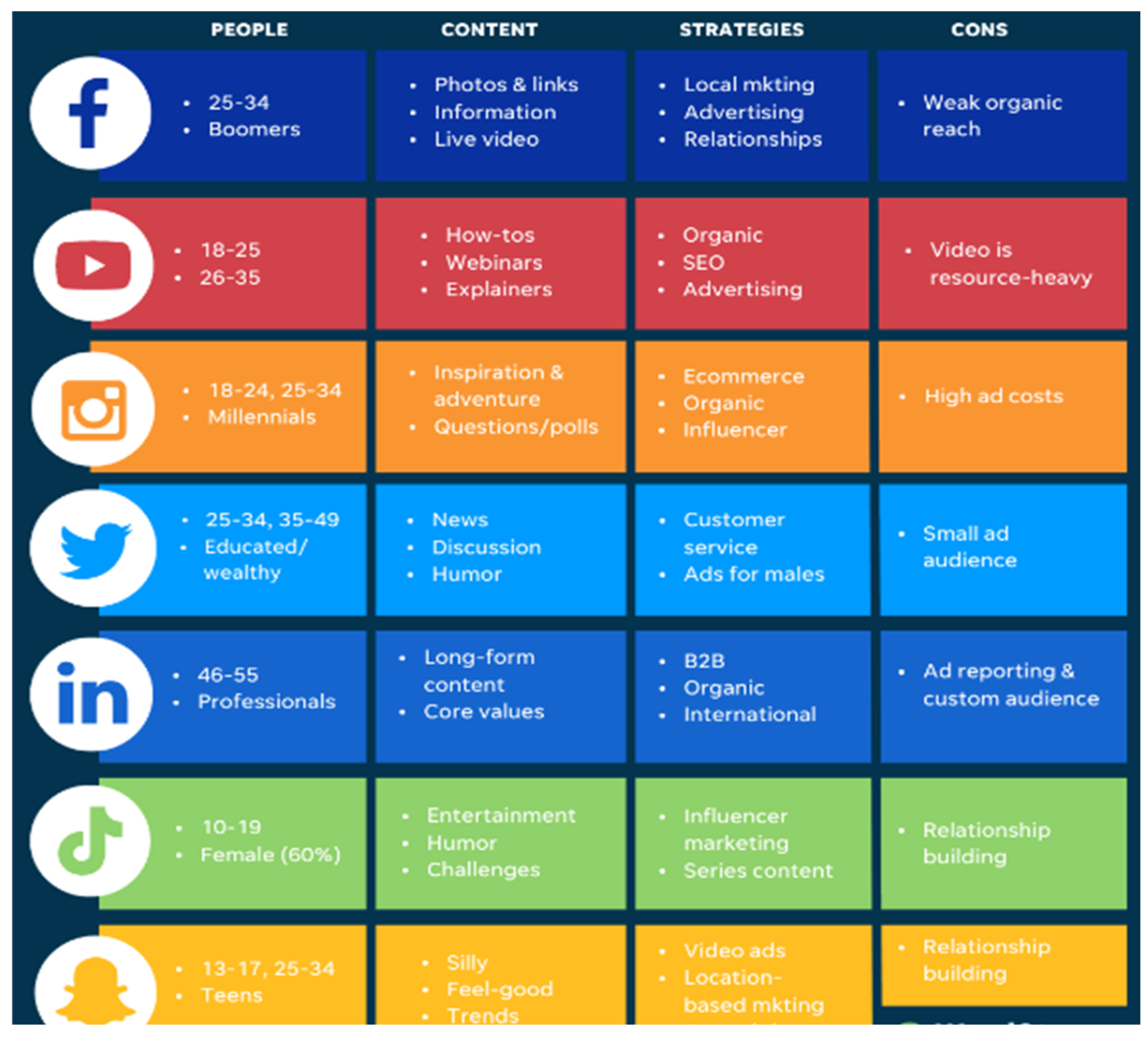


| Industry | Focus Area | Platform Priority | Strategy Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Privacy, regulatory content | LinkedIn, Facebook | Focus on informative content and compliance |
| Retail |
Brand storytelling, visuals |
Instagram, TikTok | Showcase products through engaging, visual posts |
| Finance | Authority, professionalism | LinkedIn, Twitter |
Build expertise, share insights and news |
| Legal Services | Expertise, regulatory focus | LinkedIn, Facebook | Position as experts, focus on trust and regulation |
| Hospitality | Experience-driven marketing | Instagram, Facebook | Highlight customer experience, visuals, and reviews |
| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | 5 | 2024 | Offers a platform for linking academia, business, and industry through research, providing insights on social media’s role in various sectors. | Promotes interdisciplinary research and collaboration, enriching the understanding of social media strategies. | May not focus specifically on practical applications for businesses. |
| [1] | 0 | 2023 | Explores brand awareness through social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram, focusing on a startup case study. | Highlights practical applications of social media for brand building | Limited to a specific case study, and may not generalize to all businesses. |
| [5] | 13 | 2023 | Discusses best practices for digital marketing via social media in higher education institutions in the GCC region. | Provides insights into effective strategies tailored for educational contexts. | Focuses on a niche sector, which may limit broader applicability. |
| [6] | 0 | 2023 | Examines challenges faced by businesses in leveraging social media effectively. | Identifies common pitfalls and obstacles, aiding businesses in strategy development. | Lacks specific solutions to the challenges discussed. |
| [8] | 0 | 2022 | Analyzes effective digital marketing approaches specifically for e-commerce platforms. | Offers targeted strategies for a rapidly growing sector. | May overlook traditional businesses not engaged in e-commerce. |
| [9] | 65 | 2021 | Investigates the relationship between business strategy and digital marketing management. | Connects overall business strategy with marketing efforts, emphasizing alignment. | Theoretical focus may not provide actionable insights for practitioners. |
| [10] | 8 | 2021 | Provides case-based learning and recommendations for building effective social media strategies. | Practical recommendations based on real-world examples enhance learning. | Case-based approach may not cover all potential scenarios. |
| [11] | 1 | 2020 | Discusses effective online advertising strategies within the realm of digital marketing. | Offers insights into online advertising, a key component of social media marketing. | May not address organic social media strategies adequately. |
| [12] | 0 | 2018 | Focuses on building successful businesses in the digital age, including social media strategies. | Comprehensive overview of digital business strategies, including social media. | The general+ approach may lack depth in specific social media tactics. |
| [13] | 5 | 2016 | Presents a comprehensive framework for social media strategies tailored for companies. | Provides a structured approach, enhancing strategic planning. | Framework may require adaptation for different business contexts. |
| Proposed Systematic Review | Consolidates existing research on social media strategies, focusing on their effectiveness in business marketing and branding. Identifies key factors for success and provides a framework for future studies | Offers a comprehensive analysis, covering multiple industries and demographics. Provides actionable insights and best practices for businesses to enhance their social media strategies. | |||
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | Articles must focus on Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business | Articles unassociated on Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business |
| Research Framework | Articles must have a research framework or technique for Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business | Articles must not have a research framework or technique for Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business |
| Language | Language must be written in English | Articles published in any other languages |
| Publication period | Articles must be published between the period of 2014 and 2024 | Articles must not be published between the period of 2014 and 2024 |
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Search Plan | Strategy to gather relevant papers through a range of sources. |
| Primary Sources | Specific search terms and keywords based on major themes and questions of the study. |
| Search Terms/Keywords | strategy*, enterprise*, company*, social media, impact, success, framework. |
| Boolean Operators | AND, OR, NOT used to combine search terms. |
| Purpose of Operators | To systematically combine terms and exclude irrelevant studies. |
| Filters and Limits | Applied to improve accuracy and ensure relevance to constructing successful social media strategies. |
| Element | Details | Importance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Objectives | Identify and define the business’s goals: brand awareness, traffic, lead generation, or customer engagement. | Essential for guiding strategy direction. | |
| Target Audience | Understand audience preferences, behaviors, and frequently used platforms for tailored content. | Crucial for effective content targeting. | |
| Content Strategy | Consistent posting with engaging and relevant content is crucial. | The core element of a successful strategy. | |
| Use of Analytics | Regularly monitor performance metrics to adjust strategies in real-time and meet objectives. | Enables real-time adjustments and improvements. | |
| Audience Engagement | Regularly monitor performance metrics to adjust strategies in real-time and meet objectives. | Builds community and enhances brand image. | |
| Additional Strategies | Collaborate with influencers and use targeted ads to amplify reach and effectiveness. | Expand reach and enhance campaign impact. |
| Study ID | Random Sequence Generation (Selection Bias) | Allocation Concealment (Selection Bias) | Blinding of Participants and Personnel (Performance Bias) | Blinding of Outcome Assessment (Detection Bias) | Incomplete Outcome Data (Attrition Bias) | Selective Reporting (Reporting Bias) | Other Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Unclear | Low |
| 2 | High | Unclear | Moderate | Low | Low | Unclear | Low |
| 3 | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low |
| 4 | Unclear | High | Moderate | High | Low | Unclear | High |
| 5 | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Low | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Focus Area | Findings | Strategic Implications | Opportunities | Challenges | Relevance to Systematic Review | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome (by Industry) |
| Content Strategy & Quality | Tailored content that aligns with the business’s brand and customer needs increases engagement, trust, and long-term customer loyalty. | SMEs must invest in creating personalized, high-quality content that speaks to their target audience. Content consistency is key for maintaining relevance in the digital space. | Opportunity to increase brand loyalty and retention by creating content that resonates deeply with customers and reflects the brand’s authenticity. | Developing consistent, high-quality content can be time-consuming and may require additional resources for SMEs with limited budgets. | Content strategy is a core element discussed in the review as one of the most significant drivers of social media success for SMEs. | Focus on customer personalization and consistent brand messaging. |
Retail: Enhance brand engagement, customer loyalty. Healthcare: Patient engagement through educational content. Manufacturing: Showcase innovation and sustainability. |
| Platform Selection | Different platforms serve different business purposes (e.g., Facebook for community engagement, LinkedIn for B2B, Instagram for visual branding). | Choose social media platforms that align with business goals and target audiences. SMEs should avoid spreading too thin across too many platforms, focusing on a few key ones to maximize engagement and reach. | Expanding reach through strategic use of each platform’s unique strengths (e.g., Instagram for visuals, LinkedIn for B2B connections). | Managing multiple platforms can become overwhelming without a dedicated team or strategy, leading to poor performance and inconsistency. | Platform selection is one of the systematic review’s critical areas, emphasizing that the right platform choice can significantly boost business success. | Maximize engagement through platform relevance and targeting. |
Retail: Instagram for product displays. Finance: LinkedIn for B2B relationships. Hospitality: Use of visual platforms for customer engagement. |
| Engagement Techniques | Regular interaction with customers (responding to comments, messages, creating polls) increases customer retention and brand advocacy. | Active customer engagement is necessary for creating a sense of community. SMEs should focus on real-time interaction, whether through comments, direct messages, or social media stories. | Greater engagement leads to increased brand loyalty, customer satisfaction, and word-of-mouth promotion. | Staying consistently active on social media can be resource-intensive, especially for small teams. | Engagement techniques are central to the review, highlighting their direct impact on long-term customer retention and satisfaction. | Direct customer interaction to boost retention and loyalty. |
Retail: Polls, contests for customer loyalty. Healthcare: Health tips and patient Q&A sessions. Agriculture: Interaction with local consumers and suppliers. |
| Targeted Advertising | Paid advertising on platforms like Facebook and Instagram can drive quick results, especially when ads are personalized based on customer behavior. | SMEs should explore targeted ads to reach specific customer segments, driving conversions and enhancing brand visibility. A/B testing for different ad formats and content is recommended for continuous improvement. | Ability to directly reach high-potential customers, increasing conversion rates and promoting specific offers or products. | Advertising budgets may limit the reach for smaller SMEs, and improperly targeted ads can result in poor ROI and wasted resources. | The review emphasizes the power of targeted advertising, noting its effectiveness when well-aligned with customer preferences and business objectives. | Customer segmentation and behavior-based targeting. |
Retail: Product-specific promotions. Finance: Targeted financial services ads. Education: Advertising online courses and virtual classes. |
| Influencer Partnerships | Collaborating with influencers can significantly enhance brand visibility, especially for SMEs looking to build a larger audience quickly. | SMEs should consider partnering with micro or macro-influencers whose audience matches their target market. Such partnerships can increase credibility and expand the brand’s reach rapidly. | Influencer marketing offers the opportunity to tap into new markets and enhance trust in the brand, especially through authentic collaborations. | Finding the right influencer fit is crucial, and managing the relationship can be time-consuming, especially if expectations are not aligned. | Influencer partnerships are noted in the review as an effective strategy for expanding audience reach and increasing trust in the brand. | Leverage social proof and audience alignment through influencer collaboration. |
Retail: Product endorsements by local influencers. Hospitality: Travel bloggers promoting tourism services. Education: Partner with influencers for course enrollments. |
| Analytics & Data Use | Regular monitoring of social media analytics (e.g., engagement rates, conversion metrics) allows businesses to adjust strategies in real-time to optimize performance. | SMEs should use analytics tools (e.g., Facebook Insights, Google Analytics) to track the success of their social media efforts and make data-driven decisions that optimize engagement, reach, and ROI. | Access to real-time data allows SMEs to quickly adapt their strategies to what is working, improving engagement and campaign performance over time. | Many SMEs struggle with understanding and interpreting analytics, often leading to missed opportunities for optimization. | The review underscores the importance of data analytics in creating effective social media strategies that drive measurable results. | Real-time data-driven decisions for optimizing social media strategy. |
Retail: Adjust product promotions based on customer behavior. Finance: Measure success of educational campaigns. Healthcare: Track patient engagement and health outcomes. |
| Brand Awareness & Growth | Effective use of social media strategies, particularly content relevance and engagement, leads to increased brand awareness and market expansion. | Build a strong social media presence through relevant content and continuous engagement to drive brand awareness. SMEs can leverage paid and organic strategies for faster growth and reach. | SMEs have the opportunity to grow their brand visibility significantly by leveraging both organic reach and paid strategies. | Growing brand awareness takes time, and the impact of social media can be inconsistent without a clear, long-term strategy. | The systematic review highlights brand awareness as a critical outcome of social media strategy, particularly for SMEs seeking to expand their market. | Increased brand visibility through continuous, relevant engagement. |
Retail: Build a recognizable brand in new markets. Manufacturing: Use social media for thought leadership. Hospitality: Increase global visibility for local businesses. |
| Customer Retention | Consistent engagement and value-driven content directly contribute to increased customer retention rates. | Focus on long-term customer relationships through meaningful interactions and regular value-added content to increase retention and loyalty. | Higher retention rates translate into higher customer lifetime value (CLV) and reduced marketing costs for customer acquisition. | Failure to maintain a regular engagement strategy may lead to reduced customer loyalty and increased churn rates. | Customer retention is a significant point in the review, stressing the value of consistency and relevance in social media interactions. | Long-term engagement and content relevance to boost retention. |
Retail: Loyalty programs, frequent buyer incentives. Finance: Personalized offers for existing customers. Education: Consistent student engagement for retention. |
| Sustainability & Scalability | Implementing scalable social media strategies allows SMEs to grow their online presence gradually without overwhelming resources. | Develop a social media plan that scales with business growth, focusing on manageable goals and gradually increasing reach and engagement as resources permit. | Scalable strategies allow for sustainable growth over time, reducing the risk of overburdening small teams while maintaining social media activity. | Scaling social media efforts can be challenging without a clear roadmap or sufficient resources, leading to overextension. | The review supports the idea that sustainable, scalable strategies help SMEs grow their presence while balancing resources effectively. | Strategic scalability to balance growth with resource constraints. |
Manufacturing: Use scalable B2B marketing. Retail: Gradually expand into new geographic markets. Agriculture: Increase engagement with consumers and local networks. |
| Security & Data Privacy | The shift to digital platforms and data collection via social media necessitates stringent data privacy measures to build customer trust. | Ensure compliance with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR) and implement strong security practices to protect customer data. Transparency with customers about how their data is used builds trust and ensures legal compliance. | Transparency around data usage and strong privacy policies can build consumer trust, essential for long-term customer relationships. | The evolving nature of data privacy regulations can be difficult for SMEs to navigate without dedicated resources. | Data privacy is an emerging theme in the review, especially as SMEs collect more customer data via social media, underscoring the importance of compliance. | Compliance with privacy regulations and strong data protection practices. |
Finance: Ensure compliance with financial data protection laws. Healthcare: Protect patient data via secure protocols. Education: Secure student information and privacy. |
| Step | Description | Strategic Implications | Challenges | Opportunities | SME Categories | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome (by Industry) | Ties to Proposed Study |
| Needs Assessment | Analyzing business requirements, target audience, and current social media presence to identify gaps and opportunities. | Aligns social media strategy with business objectives for improved customer engagement and marketing outcomes. | SMEs may struggle to correctly identify relevant needs without the necessary expertise or data analysis capabilities. | Custom-tailored social media efforts that align with unique business needs, leading to better ROI. | Retail, Healthcare, Education, Manufacturing | Customer engagement, audience segmentation, and business alignment. |
Retail: Increased customer retention. Healthcare: Enhanced patient education and outreach. Finance: Better lead generation. |
Identifying gaps in current strategies is crucial for SMEs to build effective social media plans, as highlighted in the systematic review. |
| Feasibility Study | Evaluating technical and financial viability of social media tools, platforms, and integration with business operations. | Ensures chosen platforms and strategies align with operational capacity and financial constraints. | Limited resources can make it difficult for SMEs to choose between multiple platforms and tools. | Assess low-cost or free tools with strong engagement potential, such as Facebook or Instagram. | Retail, Finance, Agriculture | Budget constraints, operational scalability, and platform compatibility. |
Retail: Efficient platform selection for customer engagement. Agriculture: Cost-effective outreach in rural areas. Finance: Optimized for secure transactions. |
The study highlights that resource allocation is critical for SMEs to maximize social media investments and long-term growth. |
| Strategic Planning | Developing a strategic plan outlining key steps, resource allocation, timelines, and stakeholder involvement. | Ensures all elements of social media strategy, including content development and platform management, are executed efficiently. | Small teams or lack of dedicated social media managers may hinder timely execution. | Develop comprehensive but flexible strategies to adapt to changing trends or customer feedback. | Retail, Education, Manufacturing | Clear role assignments, phased rollouts, and stakeholder communication. |
Healthcare: Structured patient engagement strategies. Retail: Timely product promotions. Education: Resource allocation for student outreach. |
Strategic planning aligns with the systematic review’s findings on the importance of a well-defined social media strategy to enhance business success. |
| Platform Selection | Identifying the best social media platforms based on target audience demographics, industry standards, and engagement potential. | Optimizes resource allocation by focusing on platforms most likely to yield high engagement and conversion rates. | Choosing the wrong platform can waste resources and lead to lower engagement. | Focus on niche platforms that align with business objectives, such as LinkedIn for B2B or Instagram for visual marketing. | Retail, Education, Healthcare, Agriculture | Audience demographics, platform relevance, and competitive analysis. |
Retail: Leverage Instagram for customer engagement. Healthcare: LinkedIn for professional networking. Agriculture: Community outreach on Facebook. |
The study stresses the need for platform-specific strategies, identifying platform selection as a crucial factor for success in social media marketing. |
| Implementation & Resource Allocation | Executing the social media plan by allocating resources for content creation, community management, and engagement activities. | Ensures that social media strategies are implemented efficiently with adequate staffing and technology support. | Limited budgets or personnel may restrict the ability to fully implement strategies. | Gradual scaling of social media activities can help SMEs manage resources effectively. | Retail, Healthcare, Manufacturing | Adequate staffing, content creation, and community management. |
Retail: Improved content scheduling and management. Manufacturing: Building B2B relationships. Healthcare: Patient outreach through scheduled content. |
Proper resource allocation and management are emphasized as a key driver for social media success in SMEs, as discussed in the systematic review. |
| Monitoring & Adjustment | Tracking social media performance through analytics, adjusting strategies based on real-time data, and optimizing for better results. | Provides insights into what works and what doesn’t, allowing businesses to pivot and improve engagement. | SMEs may lack the tools or knowledge to interpret social media analytics effectively. | Real-time adjustments enable continuous optimization of social media efforts based on customer feedback and engagement metrics. | Retail, Finance, Healthcare, Agriculture | Data-driven decision-making, continuous performance improvement, and customer feedback integration. |
Retail: Adjust content for customer preferences. Healthcare: Modify patient outreach campaigns. Finance: Optimize ad campaigns for ROI. |
The systematic review outlines the importance of data-driven approaches, highlighting the need for ongoing monitoring and adjustments for SMEs. |
| Security & Data Privacy Compliance | Ensuring all social media activities comply with local and international data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR), protecting customer information. | Builds customer trust by ensuring their data is protected, which is particularly crucial for finance and healthcare industries. | Data privacy regulations can be complex and difficult to navigate for SMEs without dedicated legal or IT resources. | Compliance with data protection regulations can enhance customer trust and brand loyalty. | Finance, Healthcare, Retail | Legal compliance, customer trust, and secure data handling. |
Finance: Secure financial transactions. Healthcare: Protect patient information. Retail: Build customer trust with data privacy measures. |
Ensuring data privacy and security is critical for SMEs to maintain trust, as discussed in the systematic review’s emphasis on customer engagement. |
| Training & Capacity Building | Providing employees with training on social media tools, analytics, and customer engagement best practices to maximize ROI and engagement. | Ensures that employees can execute social media strategies effectively, leveraging tools and platforms to maximize engagement. | SMEs may not have the budget or time to invest in comprehensive training for employees. | Building in-house capacity reduces reliance on third-party services and improves long-term efficiency. | Retail, Healthcare, Education, Manufacturing | Employee skill development, social media management, and content creation. |
Retail: Training on customer engagement tactics. Healthcare: Staff education on patient outreach. Education: Social media as a student recruitment tool. |
Training and capacity building are key elements for long-term social media success, as highlighted in the systematic review’s focus on resource management. |
| Best Practice | Description | Strategic Implications | Challenges | Opportunities | SME Categories | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome (by Industry) | Ties to Proposed Study |
| Comprehensive Planning | Involve all stakeholders early in the process and ensure alignment of social media goals with business objectives, using project management tools. | Helps SMEs set clear goals and allocate resources efficiently, leading to better execution and outcomes. | SMEs may struggle to engage all stakeholders or lack clarity on long-term goals. | Clear, detailed planning ensures better resource allocation and helps manage timelines and expectations. | Retail, Healthcare, Manufacturing | Stakeholder alignment, resource management, and goal-setting. |
Retail: Improved brand awareness. Healthcare: Better patient outreach. Manufacturing: Enhanced B2B engagement. |
Clear, actionable planning is crucial for the success of social media strategies, as emphasized in the systematic review. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Regular communication with stakeholders through meetings, updates, and feedback mechanisms to keep them informed and involved throughout the process. | Ensures stakeholder buy-in and keeps the strategy aligned with business goals through continuous feedback. | Lack of stakeholder buy-in can hinder the effectiveness of social media strategies. | Strong engagement builds trust and ensures that the strategy remains aligned with evolving business needs. | Healthcare, Education, Retail | Continuous feedback, stakeholder communication, and alignment. |
Retail: Increased customer loyalty. Healthcare: Stronger patient communication. Education: Increased student outreach. |
The proposed study stresses the need for constant engagement with stakeholders to maintain the relevance and effectiveness of social media strategies. |
| Technology Assessment | Evaluate different social media tools and technologies through pilot tests and simulations to assess their scalability, performance, and security. | Allows SMEs to choose the most effective social media platforms and tools based on business size and industry-specific requirements. | SMEs may lack the resources or expertise to conduct thorough assessments of multiple platforms. | Piloting social media tools before full implementation can save time and resources, ensuring only effective technologies are used. | Retail, Finance, Agriculture | Technology scalability, performance analysis, and platform compatibility. |
Finance: Secure transactions. Retail: Higher engagement through optimized platforms. Agriculture: Better outreach in rural areas. |
The study highlights the importance of assessing technological capabilities to ensure alignment with business needs and goals. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stay updated with social media regulations, including data privacy laws like GDPR, and ensure compliance before deployment. | Reduces the risk of legal issues and builds customer trust by demonstrating responsible use of data and adherence to privacy regulations. | Compliance with data protection laws can be difficult for SMEs without dedicated legal resources. | Proper compliance enhances customer trust and reduces the risk of penalties or reputational damage. | Finance, Healthcare, Retail | Legal compliance, data privacy, and security. |
Healthcare: Compliance with patient privacy laws. Finance: Secure handling of financial data. Retail: Safe customer data handling. |
Regulatory compliance is a key driver in successful social media strategies, especially for industries dealing with sensitive information, as outlined in the review. |
| Security Measures | Implement strong security protocols, including encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to protect customer data and social media accounts. | Protects the integrity of social media platforms and customer data, ensuring business continuity and maintaining trust. | SMEs often overlook security, leaving them vulnerable to cyber-attacks or data breaches. | A strong security posture builds customer confidence and ensures uninterrupted social media operations. | Finance, Healthcare, Retail | Data protection, security measures, and customer trust. |
Finance: Secure online transactions. Healthcare: Protection of patient data. Retail: Secure handling of customer information. |
The proposed study highlights security as a critical component of social media strategies, especially for sensitive industries like finance and healthcare. |
| Continuous Monitoring and Improvement | Track social media performance through real-time analytics and continuously improve strategies based on user feedback and engagement metrics. | Ensures that social media strategies remain relevant, effective, and aligned with evolving business objectives and market conditions. | SMEs may lack access to advanced analytics tools or expertise to interpret data effectively. | Real-time monitoring enables SMEs to adjust strategies quickly, improving engagement and ROI. | Retail, Finance, Manufacturing, Healthcare | Real-time data analytics, performance tracking, and customer feedback integration. |
Retail: Improved engagement based on customer data. Manufacturing: Optimized supply chain communications. Healthcare: Better patient outreach based on feedback. |
The systematic review emphasizes the need for continuous improvement and real-time adjustment to keep social media strategies effective and relevant. |
| KPI | Description | Strategic Implications | Challenges | Opportunities | SME Categories | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome (by Industry) | Ties to Proposed Study |
| Engagement Rate | Measures the level of interaction with posts (likes, shares, comments) as a percentage of total followers or reach. | High engagement rates indicate that the content resonates with the audience and leads to stronger customer connections. | Engaging content creation can be resource-intensive, and low engagement can signal the need for strategic shifts. | High engagement can drive word-of-mouth marketing, leading to organic growth and customer loyalty. | Retail, Hospitality, Education | Content resonance, audience interaction, and customer loyalty. |
Retail: Increased product sales through higher customer interaction. Education: Greater student engagement. Hospitality: Increased bookings via social media. |
Engagement metrics are essential for measuring the effectiveness of customer-facing social media strategies, as shown in the review findings. |
| Reach/Impressions | Total number of unique users who have seen a social media post, showing potential audience size and visibility. | Higher reach indicates greater visibility and potential for brand awareness and audience expansion. | SMEs with limited budgets may struggle to increase reach without investing in paid advertisements. | Expanding reach improves brand visibility, which can translate into higher sales and customer acquisition. | Retail, Healthcare, Manufacturing | Brand awareness, audience expansion, and customer acquisition. |
Retail: Greater brand recognition. Healthcare: Improved patient awareness of services. Manufacturing: Expanded market presence. |
The review highlights that reach is a foundational metric in any social media strategy, helping businesses assess the impact of their content. |
| Conversion Rate | Percentage of users who take a desired action (e.g., sign-ups, purchases) after interacting with social media content. | High conversion rates suggest that social media campaigns are effective in driving business outcomes such as sales. | Low conversion rates can indicate a misalignment between the content and the target audience. | Improved conversions result in better ROI from social media investments. | Retail, Finance, Healthcare | Action-oriented outcomes, lead generation, and sales growth. |
Retail: Higher online sales. Finance: Increased client acquisitions. Healthcare: More patient bookings or consultations. |
Conversion metrics are central to determining the effectiveness of call-to-action (CTA) strategies, as emphasized in the study. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Measures the profitability of social media campaigns by comparing the cost of investment to the returns generated. | High ROI shows that social media strategies are generating profitable outcomes relative to the money spent. | Calculating social media ROI can be complex, especially for indirect benefits like brand awareness. | Strong ROI indicates a well-targeted and effective social media strategy that directly impacts the bottom line. | Retail, Finance, Manufacturing | Financial performance, cost efficiency, and profit margins. |
Retail: Increased profitability through optimized ad spend. Finance: Higher customer acquisition for lower costs. Manufacturing: Streamlined lead generation. |
The review underscores the importance of ROI as a key metric in assessing the financial viability of social media strategies for SMEs. |
| Customer Retention Rate | Percentage of customers retained over a specific period, showing how social media efforts contribute to loyalty. | High retention rates suggest that social media strategies are effective in keeping customers engaged and loyal. | Retaining customers through social media can be challenging without continuous engagement and fresh content. | High customer retention reduces churn and increases lifetime value, boosting long-term profitability. | Retail, Healthcare, Hospitality | Customer loyalty, engagement longevity, and lifetime value. |
Retail: Reduced customer churn. Healthcare: Higher patient retention. Hospitality: Repeat bookings and customer loyalty. |
Retention metrics are critical for businesses that rely on long-term customer relationships, as supported by the review’s findings. |
| Lead Generation | Number of potential customers gained through social media interactions who show interest in the company’s products. | High lead generation indicates that social media is being effectively used to attract new business opportunities. | Generating high-quality leads through social media can be difficult without a targeted approach. | Social media provides cost-effective ways to attract new leads and engage potential customers. | Finance, Real Estate, Manufacturing | New customer acquisition, pipeline growth, and business expansion. |
Finance: More qualified leads. Real Estate: Increased property inquiries. Manufacturing: Expanded B2B sales opportunities. |
Lead generation is a key outcome tied to social media strategies, as highlighted by the systematic review in driving customer acquisition. |
| Brand Awareness | Measures how familiar customers are with a brand, often gauged through surveys or social listening tools. | High brand awareness suggests that the business has a strong presence on social media and is well-known in its industry. | Brand awareness can be difficult to measure directly, and requires consistent social media presence. | Building brand awareness drives long-term business growth, market positioning, and customer trust. | Retail, Finance, Healthcare, Agriculture | Market positioning, customer trust, and visibility. |
Retail: Increased recognition of products. Finance: Trust in financial services. Agriculture: Awareness of sustainable farming practices. |
Brand awareness is foundational to establishing a market presence, as emphasized in the systematic review’s findings on social media success. |
| Audience Growth Rate | Percentage of new followers over time, showing the growth of social media presence and reach. | Audience growth indicates the potential for expanding influence and capturing a larger share of the target market. | Growth can stagnate without compelling content or effective outreach strategies. | Growing an audience increases the potential customer base and drives long-term business success. | Retail, Hospitality, Education | Market expansion, increased influence, and content outreach. |
Retail: Larger potential customer base. Hospitality: Greater guest outreach. Education: Expanded reach to prospective students. |
Audience growth is critical for scaling social media presence, which is crucial in the early stages of strategy implementation, as noted in the review. |
| Content Quality | Measures the relevance, originality, and engagement of social media content through user feedback and interaction. | High-quality content generates more engagement, builds trust, and enhances brand perception. | Creating consistently high-quality content can be challenging for SMEs with limited resources. | Effective content can significantly boost engagement, drive conversions, and enhance brand loyalty. | Retail, Healthcare, Hospitality | Engagement quality, brand perception, and customer interaction. |
Retail: Improved customer interaction. Healthcare: Stronger patient communication. Hospitality: Enhanced guest engagement. |
Content quality directly impacts engagement and brand perception, as discussed in the systematic review on social media strategies. |
| Sentiment Analysis | Measures customer emotions and attitudes towards a brand through social media comments and feedback. | Positive sentiment strengthens brand reputation and drives customer loyalty, while negative sentiment indicates areas for improvement. | Sentiment can be difficult to quantify and may not always reflect the full customer experience. | Sentiment analysis helps SMEs understand customer perceptions and tailor strategies to improve brand reputation. | Retail, Healthcare, Finance | Brand reputation, customer trust, and service improvement. |
Retail: Positive reviews and testimonials. Healthcare: Stronger patient relationships. Finance: Trust in financial advice. |
Understanding customer sentiment is crucial for maintaining a positive brand image, as outlined in the study’s findings on customer feedback. |
| Industry | Framework Focus | Key Features | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome (by Industry) | Ties to Proposed Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Customer engagement and brand awareness through multi-platform content distribution. | 1. Interactive content (videos, live streams). 2. Integration with e-commerce platforms for seamless purchasing. |
Engagement Quality - High-quality visual content to attract and retain customers. Content Optimization - Tailoring posts based on analytics to reach the right audience. |
Increased product sales through high engagement and seamless user experience. | The systematic review highlights the importance of tailored content and consistent engagement in driving customer conversions and sales growth. |
| Healthcare | Patient communication and trust-building through real-time, informative, and personalized content. | 1. Telehealth promotion through social media. 2. Educational content (health tips, expert videos). |
Trust & Transparency - Providing accurate and timely health information. Real-Time Communication: Engaging with patients via Q&A sessions and feedback mechanisms. |
Increased patient engagement and trust leading to more consultations and services booked online. | The review emphasizes the role of content relevance and trust-building in social media strategies, especially in health sectors. |
| Finance | Lead generation and customer retention through personalized content and secure, informative interactions. | 1. Content targeted at explaining complex financial services. 2. Customer support through social platforms. |
Financial Education: Simplifying complex financial services to attract leads. Customer Retention - Building long-term relationships through informative interactions. |
Increased client acquisition and retention through targeted financial education and personalized customer service. | The systematic review identifies lead generation and retention as critical for finance-related businesses leveraging social media strategies. |
| Hospitality | Customer experience enhancement through immersive, visual content and real-time engagement. | 1. Real-time booking integrations. 2. Customer testimonials and reviews shared across platforms. |
Customer Experience - Enhancing guest experience through virtual tours, real-time engagement, and user-generated content. | Increased bookings, improved brand perception, and higher customer satisfaction through direct engagement and real-time feedback. | The review shows how personalized, visual content contributes to improved customer satisfaction and engagement in the hospitality sector. |
| Education | Engagement with students and parents through educational content, virtual events, and interactive Q&A sessions. | 1. Live webinars and virtual classes shared on social platforms. 2. Student testimonials and success stories. |
Student Engagement - Promoting interactive learning environments and showcasing success stories. Virtual Learning - Providing accessible, real-time learning materials. |
Increased student enrollment and engagement through virtual content and live interactions. | The review stresses the need for interactive, engaging content in education to enhance enrollment and learner retention. |
| Manufacturing | B2B relationship-building through technical content and industry-related insights. | 1. Sharing case studies, white papers, and technical videos. 2. Showcasing innovations and product launches. |
Industry Expertise - Demonstrating thought leadership and industry innovation. B2B Networking - Using social platforms for partnerships and industry networking. |
Expanded industry partnerships and greater visibility through thought leadership and innovative product showcasing. | The review notes the importance of using social media for B2B networking and showcasing industry expertise in manufacturing sectors. |
| Agriculture | Community engagement and sustainability awareness through storytelling and visuals. | 1. Showcasing sustainable practices and technology in use. 2. Community-driven campaigns and storytelling. |
Sustainability - Promoting eco-friendly practices and community engagement. Visual Storytelling - Using images and videos to tell the brand’s sustainability story. |
Increased brand loyalty and awareness through the promotion of sustainability and responsible farming practices. | The review’s findings emphasize the role of storytelling and sustainability messaging in driving social media success in agriculture. |
| Real Estate | Client engagement and lead generation through virtual property tours and targeted ads. | 1. Virtual tours shared on social media. 2. Targeted advertising based on location and client demographics. |
Lead Generation - Using targeted ads to attract potential buyers. Customer Trust - Building trust through virtual, interactive tours of properties. |
Increased inquiries and property sales through engaging content and targeted advertising. | The systematic review highlights how targeted advertising and virtual engagement enhance client acquisition in the real estate industry. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





