Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Granular material is one of the most common in nature. Recently, there has been a significant amount of interest in the granular materials, such as powders or sand. It is challenging to describe the motion of such kind of macroscopic size matter, because it behaves like solid, fluid or gas. Size division, pattern formation, avalanches, packing and convection - these are just a few examples from a wide range of observed phenomena that occur during the motion process of granular matter. Most of these processes are based by flow and no wonder that much effort has been devoted to obtain a hydrodynamic description in which granular materials are treated as a continuous medium. During the research of vertically shaken granular medium motion in an opened container it was found that experimental and numerical results are explained by hydrodynamic theory. This paper investigates the motion of a granular matter for a shallow, vertically shaken bed. We assume the Leidenfrost state as initial and the matter resembles a fluid heated up from below.A one-dimensional isothermal and a non-isothermal problem of granular material motion,simulatedby a hydrodynamic model are considered, and the material is assumed to be a continuous medium. The local temporal solvability of isothermal and non-isothermal initial boundary-value problem in Sobolev’s spaces is proved. This work presents a numerical study of the one-dimensional model of granular medium flow. The feature of this model is consideration of the Navier-Stokes equations accounting an interpolation form of VanderWaals constitutive equation for pressure. A finite-difference approximation for numerical solution is proposed.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Microscopic models and molecular dynamics simulations;
- Statistical mechanics kinetic theory;
- Phenomenological model and continuum models.
2. Setting up the problem and formulation of the main result
3. Local solvability of the isothermal problem
4. Local solvability of the non-isothermal problem
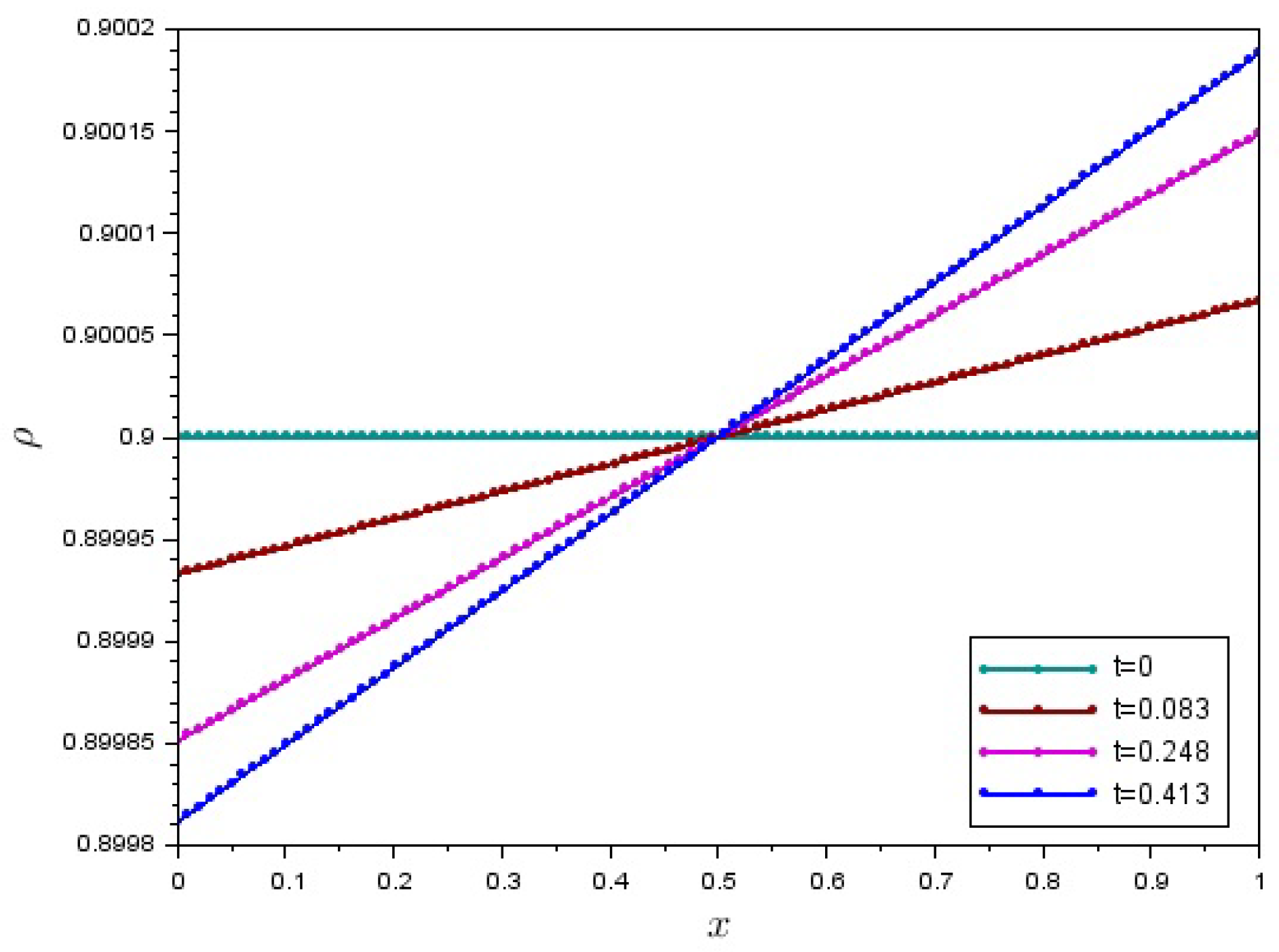
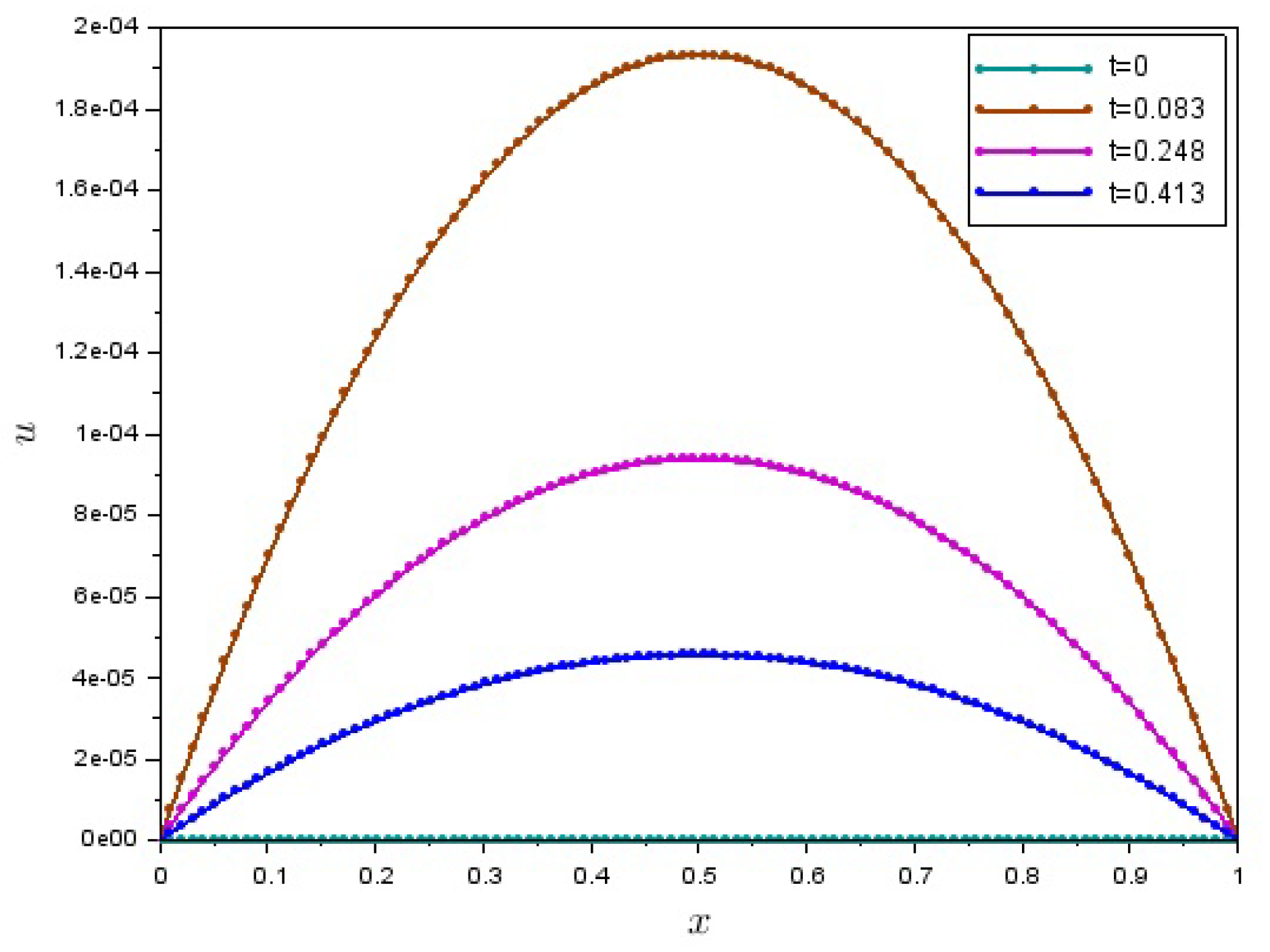
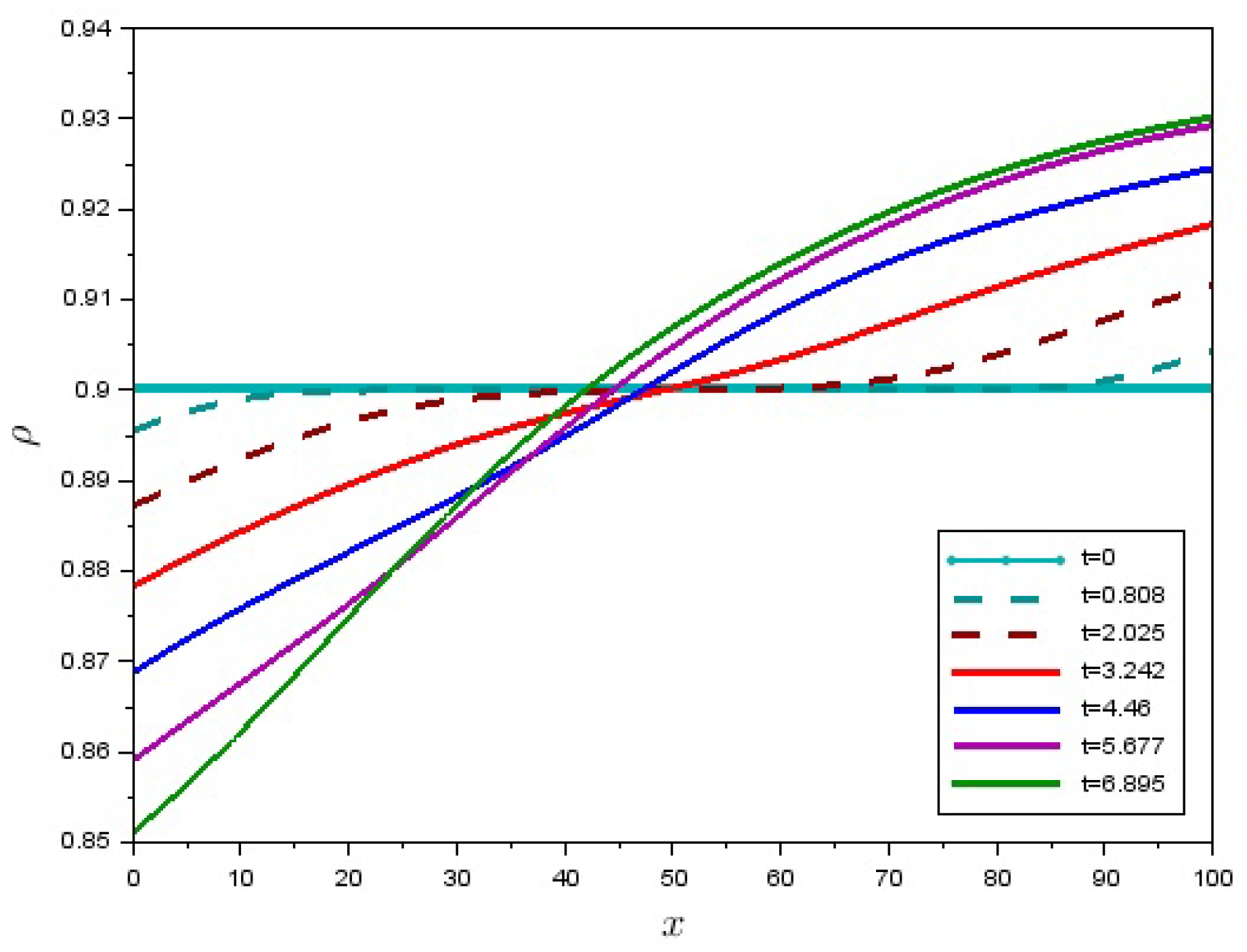
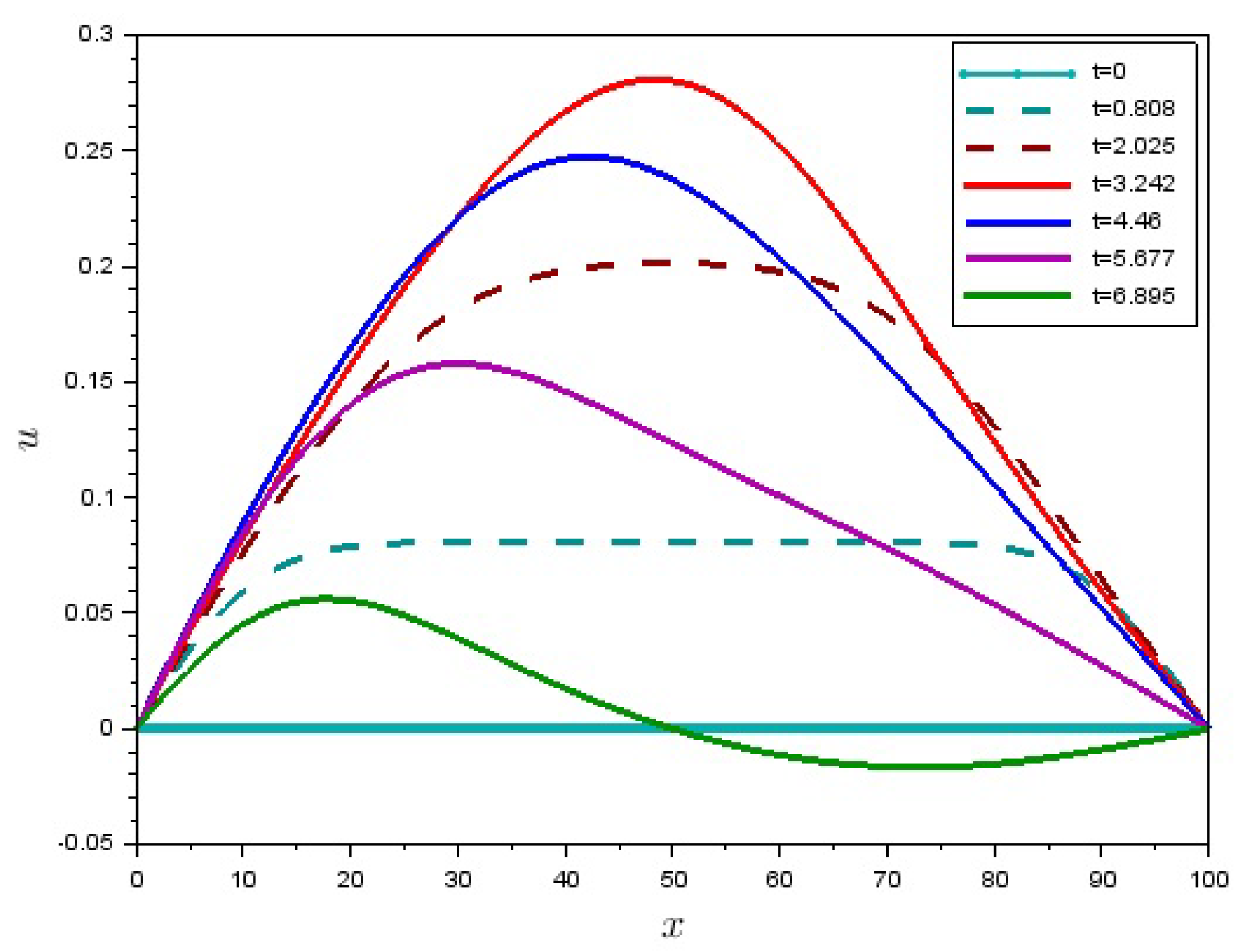
5. Numerical Solution of a Boundary-Value Problem for One-Dimensional Motion of a Granular Matter
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Vaisberg, L.A.; Demidov, I.V.; Ivanov, K.S. Mechanics of granular media under vibration action: the methods of description and mathematical modeling. Obogashchenie rud 2015, 4, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Revuzhenko, A.F. Mechanics of granular media: Some basic problems and applications. Journal of Mining Science 2014, 5, 5–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobryakov, A.P.; Revuzhenko, A.F. Experimental Determination of Deviation from Coaxilaity of Stress and Strain Tensors in Granular Media. Journal of Mining Science 2014, 4, 4–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobryakov, A.P.; Revuzhenko, A.F. Effect of Gas Flow on Dilatancy and Stress State in Granular Material. Journal of Mining Science 2018, 3, 3–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobryakov, A.P.; Klishin, S.V.; Revuzhenko, A.F. Stress State of Conical Granular Pile. Journal of Mining Science 2019, 6, 6–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klishin, S.V.; Revuzhenko, A.F. Numerical analysis of plastic behavior of granular media exposed to deformation under broken path loading. Journal of Mining Science 2015, 5, 5–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klishin, S.V.; Revuzhenko, A.F. A class of vortex flows in granular medium. Journal of Mining Science 2015, 6, 6–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, E.I.; Medvedev, A.E.; Shabalin, I.I.; Lavrikov, S.V.; Revuzhenko, A.F. Modeling of the differential rotation effect in complex loading of granular media. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics 2009, 4, 4–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.T.; Savage, S.B. A theory for the rapid flow of identical, smooth, nearly elastic, spherical particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, Vol. 130, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haff, P.K. Grain flow as a fluid-mechanical phenomenon. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, Vol. 134, 401–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.; Richman, M. Boundary conditions for plane flows of smooth nearly elastic circular discs. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, Vol. 171, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.S. Rapid granular flows. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1990, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, H.M.; Nagel, S.R.; Behringer, R.P. Granular solids, liquids, and gases. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1996, 4, 4–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, H.M.; Behringer, R.P.; Nagel, S.R. The physics of granular materials. Phys. Today. 1996, Vol. 49, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, N.; Goldhirsch, I. Hydrodynamic equations for rapid flows of smooth inelastic spheres to Burnett order. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, Vol. 361, 41–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brey, J.J.; Dufty, J.W.; Kim, C.S.; Santos, A. Hydrodynamics for granular flow at low density. Phys. Rev. E. 1998, 4, 4–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadanoff, L.P. Built upon sand: theoretical ideas inspired by granular flows. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 1, 1–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, I. Rapid granular flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2003, 1, 1–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, I.; Noskowicz, S.; Bar-Lev, O. Nearly smooth granular gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, H.; Kadanoff, L.P. Breakdown of hydrodynamics in a one-dimensional system of inelastic particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, N.; Goldhirsch, I. Hydrodynamics of a one-dimensional granular medium. Phys. Fluids 1995, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, J. Sand, Powders and Grains: An Introduction to the Physics of Granular Materials. Springer. New-YorkPhys 1999, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranson, I.S.; Tsimring, L.S. Patterns and collective behavior in granular media: theoretical concepts. Rev. Mod. Phys., 2006, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshuis, P.; van der Weele, K.; Alam, M.; Gerner, H.J.; van der Hoef, M.; Kuipers, H.; Luding, S.; van der Meer, D.; Lohse, D. Buoyancy driven convection in vertically shaken granular matter: experiment, numerics, and theory. Granular Matter 2013, 15, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antontsev, S.N.; Kazhikhov, A.V.; Monakhov, V.N. Boundary Value Problems in Mechanics of Nonhomogenuous Fluids. Novosibirsk 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Kanel, Y.I. A model system of equations for the one-dimensional motion of a gas. Differentsial’nye Uravniniya 1968, 4, 721–734. [Google Scholar]
- Papin, A.A. The solvability in time of the system of one-dimensional motion of two mutually penetrating viscous incompressible liquids. Dinamika sploshnoi sredy 1999, 114, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Papin, A.A. Solvability of a system of equations of one-dimensional motion of two mutually penetrating viscous incompressible fluids “in the small” via initial data. Dinamika sploshnoi sredy 2000, 116, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Papin, A.A.; Akhmerova, I.G. Solvability of the system of equations of one-dimensional motion of a heat conducting two-phase mixture. Mathematical Notes 2010, 87, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papin, A.A.; Akhmerova, I.G. Solvability of the Boundary-Value Problem for Equations of One-Dimensional Motion of a Two-Phase Mixture. Mathematical Notes 2014, 96, 8–21. [Google Scholar]
- Papin, A.A.; Akhmerova, I.G. Flow problem for the equations of motion of two interpenetrating viscous fluids. Sib.Math.J., Siberian branch of RAS, Novosibirsk 2004, 96, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Samarskiy, A.A.; Popov, Yu.P. Difference methods for solving gas dynamics problems. Nauka 1992, 424. [Google Scholar]
- Kovenya, V.M.; Slyunyaev, A.Yu. Splitting algorithms for solving Navier–Stokes equations. Computational Mathematic and Mathematical Physics, 2009, 4, 4–700. [Google Scholar]
- Kovenya, V.M.; Kuzmin, M.P.; Poltoratskiy, R.S. A predictor-corrector difference scheme for the numerical solution of the Navier-Stokes equations of a compressible heat-conducting gas. Vestnik NSU, Series: Mathematics, mechanics, informatics 2011, 11, 32–48. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, E.L.; Zhou, T.; Ben-Naim, E. Towards granular hydrodynamics in two-dimensions. Phys. Rev. E., 1997, 4, 4–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshuis, P.; van der Weele, K.; van der Meer, D.; Lohse, D. Granular Leidenfrost effect: experiment and theory of floating particle clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 258001-1–258001-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerson, B. , Pöschel, T., Bromberg, Y. Close-packed floating clusters: granular hydrodynamics beyond the freezing point? Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, P. Ordinary differential equations. Mir, 1970, Translation from English: Sabitova I.H., Egorova Yu. V.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



