Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The Gini Index
3. The nth Gini Index
- The nth Gini index exists for any non-negative random variable with . This property is of major significance because if X is an income distribution with , then the nth Gini index can always be calculated even if some of its conventional moments do not exist.
- .
- for all (from Proposition 3.1 and inequality (3)).
- for any , that is, the nth Gini index is not affected by ratio-scale changes of the X variable.
- if is a non-negative random variable (translation-scale changes). Therefore, transforming X into with diminishes the nth Gini index.
- , that is, the nth Gini index is the covariance between X and a transformation of X.
- The sequence is non-increasing and . (straightforward from Proposition 3.2).
3.1. The Extended Gini Index, the Lorenz Family and the -Gini Index
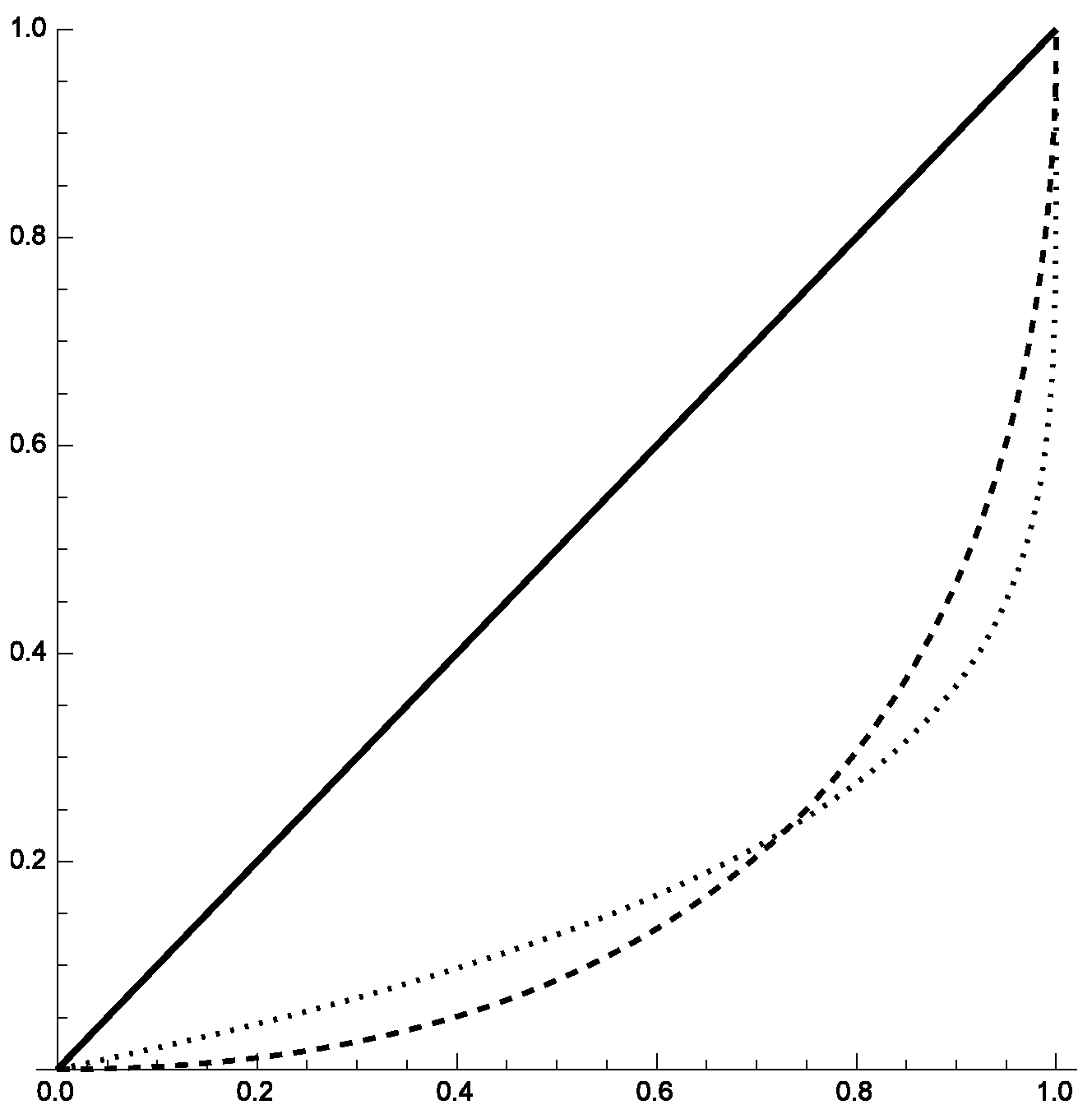
3.2. The nth Gini Index in Terms of the Lorenz Curve
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gini, C. Sulla misura della concentrazione e della variabilità dei caratteri. Atti del Reale Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti 1914, 73, 1203–1248. Reprinted in: C. Gini, (2005). On the measurement of concentration and variability of characters. Metron - International Journal of Statistics 63, 3-38.
- Gini, C. Measurement of inequality of incomes. The Economic Journal 1921, 31, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsu, Ö.; Morton, A. Inequity averse optimization in operational research. European Journal of Operational Research 2015, 173, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, G.; Gigliarano, C. The Gini concentration index: a review of the inference literature. Journal of Economic Surveys 2016, 31, 1130–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.C.; Chang, Y.T. Income inequality, distributive unfairness, and support for democracy: evidence from East Asia and Latin America. Democratization 2019, 26, 1475–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, G. , Gini Coefficient. In In: P. Atkinson, S. Delamont, A. Cernat, J.W. Sakshaug, and R.A. Williams; SAGE Research Methods Foundations, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A. Inequality; Harvard University Press, 2015.
- Liu, Y.; Gastwirth, J. On the capacity of the Gini index to represent income distributions. METRON 2020, 78, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. How has the Literature on Gini’s Index Evolved in the Past 80 Years? Economics working paper, Dalhousie University, Canada, 2004.
- Farris, F. The Gini Index and Measures of Inequality. American Mathematical Monthly 2010, 117, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliazar, I. Harnessing inequality. Physics Reports 2016, 649, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliazar, I. A tour of inequality. Annals of Physics 2018, 389, 306–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliazar, I.; Giorgi, G. From Gini to Bonferroni to Tsallis: an inequality-indices trek. METRON 2020, 78, 119–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.; Sengupta, P.E. Gini Inequality Index: Methods and Applications; Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.; Bongiovanni, R. Use of Lorenz curves and Gini coefficients to assess yield inequality within paddocks. Field Crops Research 2004, 90, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, E. Demographic dynamics and kinship in anthropological populations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005, 102, 2248–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, R.; Bergh, S.; Nair, P. A New Approach to Galaxy Morphology: I. Analysis of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Early Data Release. The Astrophysical Journal 2003, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A.; Banerjee, P.; De, D.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, P. MedGini: Gini index based sustainable health monitoring system using dew computing. Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices 2022, 16, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernot, P.; Savin, A. Using the Gini coefficient to characterize the shape of computational chemistry error distributions. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts 2021, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasisi, B.; Perry, S.; Ilan, Y.; Wolfowicz, M. Concentrated and Close to Home: The Spatial Clustering and Distance Decay of Lone Terrorist Vehicular Attacks. Journal of Quantitative Criminology 2020, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittebolle, L.; Marzorati, M.; Clement, L.; Balloi, A.; Daffonchio, D.; Heylen, K.; De Vos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Initial community evenness favours functionality under selective stress. Nature 2009, 458, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, S. Ecology: Gini in the bottle. Nature 2009, 458, 579–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.; Chow, F.; Chau, H. Study of the Wealth Inequality in the Minority Game. Physical review. E, Statistical, nonlinear, and soft matter physics 2004, 70, 066110. [CrossRef]
- Beaugrand, G.; Edwards, M.; Legendre, L. Marine biodiversity, ecosystem functioning, and carbon cycles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107, 10120–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbel, Y.; Fialkoff, C.; Kerner, A.; Kerner, M. Do Population Density, Socio-Economic Ranking and Gini Index of Cities Influence Infection Rates from Coronavirus? Israel as a case Study. The Annals of regional science 2020, 68, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cima, E.; Uribe Opazo, M.; Bombacini, M.; Rocha, W.; Pagliosa Carvalho Guedes, L. Spatial Analysis: A Socioeconomic View on the Incidence of the New Coronavirus in Paraná-Brazil. Stats 2022, 5, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazuka, N.; ichi Inoue, J. Fluctuations in time intervals of financial data from the view point of the Gini index. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2007, 383, 49–53. Econophysics Colloquium 2006 and Third Bonzenfreies Colloquium. [CrossRef]
- Sazuka, N.; Inoue, J.i.; Scalas, E. The distribution of first-passage times and durations in FOREX and future markets. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2009, 388, 2839–2853. [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Sui, H.; Feng, W.; Sun, K.; Xu, C.; Han, Q. Detecting building façade damage from oblique aerial images using local symmetry feature and the Gini Index. Remote Sensing Letters 2017, 8, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechthaler, B.; Pauly, C.; Mücklich, F. Objective homogeneity quantification of a periodic surface using the Gini coefficient. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 14516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, P. Gini Coefficient: A New Way To Express Selectivity of Kinase Inhibitors against a Family of Kinases †. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2007, 50, 5773–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagan, S.; Wright Muelas, M.; Day, P.; Lundberg, E.; Kell, D. GeneGini: Assessment via the Gini Coefficient of Reference “Housekeeping” Genes and Diverse Human Transporter Expression Profiles. Cell Systems 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.; Dye, C.; Etard, J.F.; Smith, T.; Charlwood, J.; Garnett, G.; Hagan, P.; Hii, J.; Ndhlovu, P.; Quinnell, R.; Watts, C.; Chandiwana, S.; Anderson, R. Heterogeneities in the transmission of infectious agents: Implications for the design of control programs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1997, 94, 338–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindfuss, R.; Walsh, S.; Turner, B.; Fox, J.; Mishra, V. Developing a Science of Land Change: Challenges and Methodological Issues. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2004, 101, 13976–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörcher, D.; Graham, D. The Gini index of demand imbalances in public transport. Transportation 2021, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliazar, I.; Sokolov, I. Measuring statistical evenness: A panoramic overview. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2012, 391, 1323–1353. [CrossRef]
- Kokko, H.; Mackenzie, A.; Reynolds, J.; Lindström, J.; Sutherland, W. Measures of Inequality Are Not Equal. The American naturalist 1999, 154, 358–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, V.; Gherman, T.; Paliza, J. The Gini Index: A Modern Measure of Inequality; Palgrave Macmillan, Cham., 2022; pp. 55–84. [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. Economics and Information Theory; North-Holland Publishing Company, 1967.
- Dalton, H. Measurement of the Inequality of Income. Economic Journal 1920, 30, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, P.D. Measures of Inequality. American Sociological Review 1978, 43, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanescu, S. About the Accuracy of Gini Index for Measuring the Poverty. Romanian Journal of Economic Forecasting 2011, 43, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Pyatt, G. On the intepretation and disaggragation of Gini coefficient. Economic Journal 1976, 86, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Osberg, L. The social welfare implications, decomposability, and geometry of the Sen family of poverty indices. Canadian Journal of Economics 2002, 35, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osberg, L. On the Limitations of Some Current Usages of the Gini Index. Review of Income and Wealth 2017, 63, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T. Measuring and Analyzing Class Inequality with the Gini Index Informed by Model-Based Clustering. Sociological Methodology 2006, 36, 201 – 224. [CrossRef]
- Furman, E.; Kye, Y.; Su, J. Computing the Gini index: A note. Economics Letters 2019, 185, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, L.; Verme, P. Individual Diversity and the Gini Decomposition. Social Indicators Research 2015, 121, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliazar, I.I.; Sokolov, I.M. Gini characterization of extreme-value statistics. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2010, 389, 4462–4472. [CrossRef]
- Eliazar, I. Beautiful Gini. METRON 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetta1972. Sulla concentrazione delle distribuzioni doppie. In Atti della XXVII Riunione Scientifica della Società Italiana di Statistica, vol. II, Palermo 1972, pp. 127–150.
- Taguchi, T. On the two-dimensional concentration surface and extensions of concentration coefficient and pareto distribution to the two dimensional. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics 1972-1973, part I (1972), vol. 24 355-381; part II (1972), vol. 24, 599-619; part III (1973), vol. 25, 215-237. .
- Koshevoy, G.; Mosler, K. Multivariate Gini Indices. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 1997, 60, 252–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, B.C. Inequality measures for multivariate distributions. Metron - International Journal of Statistics 2005, LXIII, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Grothe, O.; Kächele, F.; Schmid, F. A multivariate extension of the Lorenz curve based on copulas and a related multivariate Gini coefficient. The Journal of Economic Inequality 2022, 20, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietra, G. Delle relazioni tra gli indici di variabilità (Nota I). Atti del Reale Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere e Arti 1915, LXXIV, Part I, 775–792. Reprinted in: G. Pietra, (2014). On the relationships between variability indices (Note I). Metron - International Journal of Statistics 72, 5-16.
- Dorfman, R. A Formula for the Gini coefficient. Review of Economics and Statistics 1979, 61, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitzhaki, S.; Schechtman, E. The Properties of the Extended Gini Measures of Variability and Inequality. Technical report, Social Science Research Network, 2005. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=815564.
- Fishburn, P. Stochastic dominance and moments of distributions. Mathematics of Operations Research 1980, 5, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muliere, P.; Scarsini, M. A note on stochastic dominance and inequality measures. Journal of Economic Theory 1989, 49, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Abril, L.; Velasco, F.; Gavilan, J.M.; Sanchez-Reyes, L.M. The Similarity between the Square of the Coeficient of Variation and the Gini Index of a General Random Variable. Journal of Quantitative Methods for Economics and Business Administration 2010, 10, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, J.; Wolfson, M. Polarization and the Decline of the Middle Class in Canada and the U.S. The Journal of Economic Inequality 2010, 8, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.; Stuart, A. The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Vol. 1, Distribution Theory; Hafner Publishing Company, 1958.
- Yitzhaki, S. Stochastic Dominance, Mean Variance and Gini’s Mean Difference. American Economic Review 1982, 72, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yitzhaki, S.; Schechtman, E. The Gini methodology: A primer on a statistical methodology; Springer, New York, 2013.
- Lerman, R.; Yitzhaki, S. A Note on the Calculation and Interpretation of the Gini Index. Economics Letters 1984, 15, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcina, A.; Giorgi, G. Early Gini’s Contributions to Inequality Measurement and Statistical Inference. Electronic Journal for History of Probability and Statistics 2005, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yitzhaki, S. On a Extension of Gini inequality index. International Economic Review 1983, 24, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, S.; Kleiber, C. A characterization of income distributions in terms of generalized Gini coefficients. Social Choice and Welfare 2002, 19, 789–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kakwani, N. On a Class Poverty Measures. Econometrica 1980, 48, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, D.; Weymark, J. A Single Parameter Generalization of the Gini Indices of Inequality. Journal of Economic Theory 1980, 22, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaberge, R. Characterizations of Lorenz Curves and Income Distributions. Social Choice and Welfare 2000, 17, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A. On the measurement of inequality. Journal of Economic Theory 1970, 2, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | The inequality index is negative if is considered. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




