Submitted:
02 February 2025
Posted:
04 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This study presents the Bayesian-Optimized Attentive Neural Network (BOANN), a novel approach enhancing image classification performance by integrating Bayesian optimization with channel and spatial attention mechanisms. Traditional image classification struggles with the extensive data in today's big data era. Bayesian optimization has been integrated into neural networks in recent years to enhance model generalization, while channel and spatial attention mechanisms improve feature extraction capabilities. This paper introduces a model combining Bayesian optimization with these attention mechanisms to boost image classification performance. Bayesian optimization optimizes hyperparameter selection, accelerating model convergence and accuracy; the attention mechanisms augment feature extraction. Compared to traditional deep learning models, our model utilizes attention mechanisms for initial feature extraction, followed by a Bayesian-optimized neural network. On the CIFAR-100 dataset, our model outperforms classical models in metrics such as accuracy, loss, precision, recall, and F1 score, achieving an accuracy of 77.6%. These technologies have potential for broader application in image classification and other computer vision domains.
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
A. Bayesian Optimization
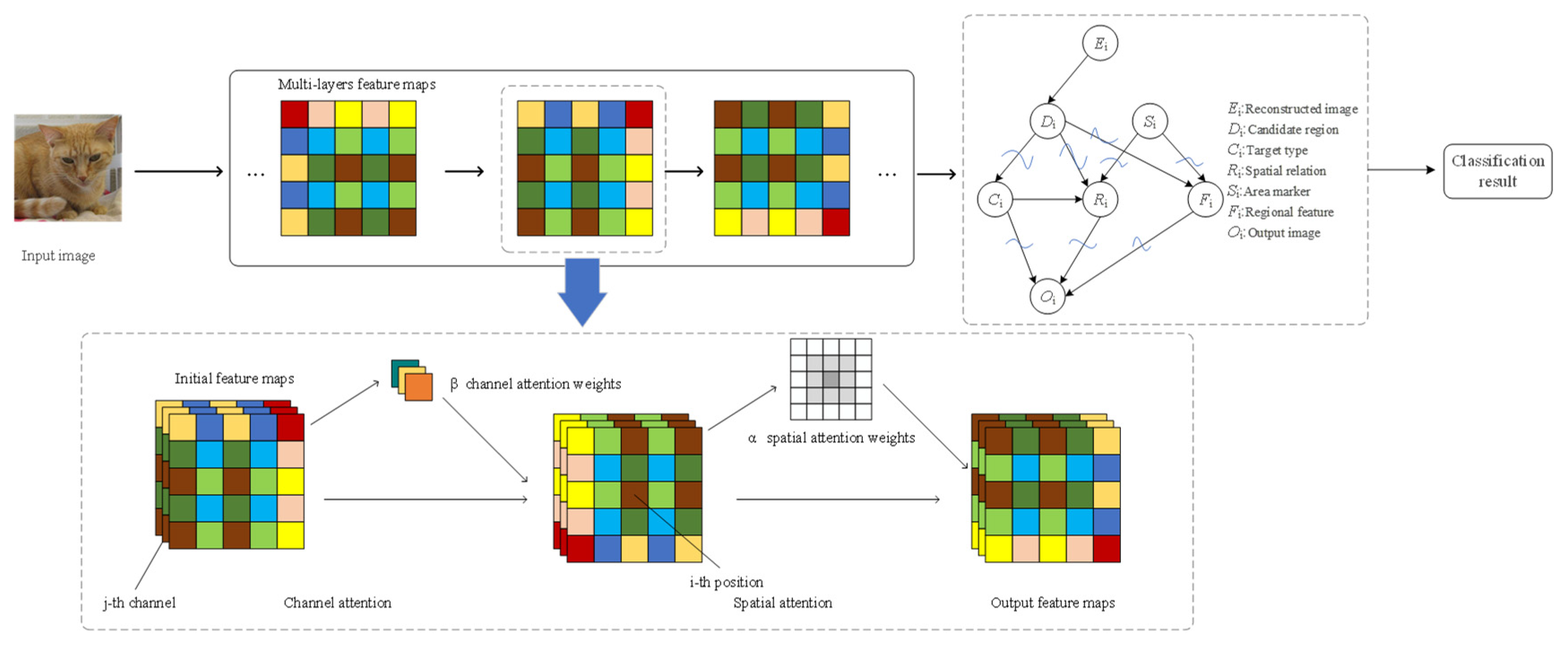
Experimental Results
A. Experimental Design
A. Model Performance Verification
A. Ablation Experiments
Conclusions
References
- Bhattacharyya, S. A brief survey of color image preprocessing and segmentation techniques[J]. Journal of Pattern Recognition Research, 2011, 1(1): 120-129.
- Vega-Rodriguez M, A. Feature extraction and image processing[J]. The Computer Journal, 2004, 47(2): 271-272.
- Perreault, S., & Hébert, P. (2007). Median filtering in constant time. IEEE transactions on image processing, 16(9), 2389-2394.
- Ślot, K., Kowalski, J., Napieralski, A., & Kacprzak, T. (1999). Analogue median/average image filter based on cellular neural network paradigm. Electronics Letters, 35(19), 1619-1620.
- Direkoglu C, Nixon M S. Image-based multiscale shape description using Gaussian filter[C]//2008 Sixth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics & Image Processing. IEEE, 2008: 673-678.
- Zhang, D., Liu, B., Sun, C., & Wang, X. (2011). Learning the Classifier Combination for Image Classification. J. Comput., 6(8), 1756-1763.
- Tao, Y., Jia, Y., Wang, N., & Wang, H. (2019, July). The fact: Taming latent factor models for explainability with factorization trees. In Proceedings of the 42nd international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval (pp. 295-304).
- Amato G, Falchi F. Local feature based image similarity functions for knn classification[C]//International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence. SCITEPRESS, 2011, 2: 157-166.
- Joachims, T. (1999). Making large-scale svm learning practical. advances in kernel methods-support vector learning. Available online: http://svmlight.joachims.org/.
- Xu, Y., Cai, Y., & Song, L. (2023). Latent fault detection and diagnosis for control rods drive mechanisms in nuclear power reactor based on GRU-AE. IEEE Sensors Journal, 23(6), 6018-6026.
- Zhang, J., Wang, X., Ren, W., Jiang, L., Wang, D., & Liu, K. (2024). RATT: AThought Structure for Coherent and Correct LLMReasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.02746.
- Lyu, W., Zheng, S., Ma, T., & Chen, C. (2022). A study of the attention abnormality in trojaned berts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.08305.
- Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., … & Rabinovich, A. (2015). Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1-9).
- Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
- Xu H, Yuan Y, Ma R, et al. Lithography hotspot detection through multi-scale feature fusion utilizing feature pyramid network and dense block[J]. Journal of Micro/Nanopatterning, Materials, and Metrology, 2024, 23(1): 013202-013202.
- He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 770-778.
- Dan, H. C., Yan, P., Tan, J., Zhou, Y., & Lu, B. (2024). Multiple distresses detection for Asphalt Pavement using improved you Only Look Once Algorithm based on convolutional neural network. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 25(1), 2308169.
- Tao, Y. (2023, August). Meta Learning Enabled Adversarial Defense. In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Sensors, Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICSECE) (pp. 1326-1330). IEEE.
- Yu, L., Cao, M., Cheung, J. C. K., & Dong, Y. (2024). Mechanisms of non-factual hallucinations in language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.18167.
- Grabner M, Grabner H, Bischof H. Fast approximated SIFT[C]//Computer Vision–ACCV 2006: 7th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Hyderabad, India, January 13-16, 2006. Proceedings, Part I 7. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006: 918-927.
- He L, Zou C, Zhao L, et al. An enhanced LBP feature based on facial expression recognition[C]//2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference. IEEE, 2006: 3300-3303.
- Déniz O, Bueno G, Salido J, et al. Face recognition using histograms of oriented gradients[J]. Pattern recognition letters, 2011, 32(12): 1598-1603.
- Guan, R., Li, Z., Tu, W., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Li, X.,… & Feng, R. (2024). Contrastive multi-view subspace clustering of hyperspectral images based on graph convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
- Guan, R., Li, Z., Li, X., & Tang, C. (2024, April). Pixel-superpixel contrastive learning and pseudo-label correction for hyperspectral image clustering. In ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6795-6799). IEEE.
- Xu, Y., Cai, Y. Z., & Song, L. (2023). Anomaly Detection for In-core Neutron Detectors Based on a Virtual Redundancy Model. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement.
- Li, Y., Yu, X., Liu, Y., Chen, H., & Liu, C. (2023, July). Uncertainty-Aware Bootstrap Learning for Joint Extraction on Distantly-Supervised Data. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers) (pp. 1349-1358).
- Li, C., Liu, X., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Yu, W., Shao, J., & Yuan, Y. (2024). GTP-4o: Modality-prompted Heterogeneous Graph Learning for Omni-modal Biomedical Representation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.05540.
- Zhou, Y., Geng, X., Shen, T., Long, G., & Jiang, D. (2022, April). Eventbert: A pre-trained model for event correlation reasoning. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022 (pp. 850-859).
- Lyu, W., Zheng, S., Pang, L., Ling, H., & Chen, C. (2023). Attention-enhancing backdoor attacks against bert-based models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.14480.
- Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Jiang, L., Gao, W., Wang, P., & Liu, K. (2024). TFWT: Tabular Feature Weighting with Transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.08403.
- Sun, D., Liang, Y., Yang, Y., Ma, Y., Zhan, Q., & Gao, E. (2024). Research on Optimization of Natural Language Processing Model Based on Multimodal Deep Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.08838.
- Liu, X., Dong, Z., & Zhang, P. (2024). Tackling data bias in music-avqa: Crafting a balanced dataset for unbiased question-answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (pp. 4478-4487).
- Zhang, Jingyu, et al. “Research on the Application of Computer Vision Based on Deep Learning in Autonomous Driving Technology.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.00490 (2024).
- Yin, Jianjian, et al. “Class Probability Space Regularization for semi-supervised semantic segmentation.” Computer Vision and Image Understanding (2024): 104146.
- Yin, Jianjian, et al. “Class-level multiple distributions representation are necessary for semantic segmentation.” International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2024.
- Yang, Qiming, et al. “Research on Improved U-net Based Remote Sensing Image Segmentation Algorithm.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.12672 (2024).
- Yukun, Song. “Deep Learning Applications in the Medical Image Recognition.” American Journal of Computer Science and Technology 9.1 (2019): 22-26.
- Weng, Yijie, and Jianhao Wu. “Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Enhance Data Security and Combat Cyber Attacks.” Journal of Artificial Intelligence General science (JAIGS) ISSN: 3006-4023 5.1 (2024): 392-399.
- Chen, Ke, et al. “Dynasmile: Video-based smile analysis software in orthodontics.” SoftwareX 29 (2025): 102004.
- Xu, Shengjie, et al. “Neural Architecture Sizing for Autonomous Systems.” 2024 ACM/IEEE 15th International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS). IEEE, 2024.
- Shangguan, Zhongkai, et al. “Neural process for black-box model optimization under bayesian framework.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.02487 (2021).
- Shang, Mingyang, et al. “V2F-Net: Explicit decomposition of occluded pedestrian detection.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.03106 (2021).
- Gong, Hao, and Mengdi Wang. “A duality approach for regret minimization in average-award ergodic markov decision processes.” Learning for Dynamics and Control. PMLR, 2020.
- Cheng, Qisen, Shuhui Qu, and Janghwan Lee. “72-3: Deep Learning Based Visual Defect Detection in Noisy and Imbalanced Data.” SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. Vol. 53. No. 1. 2022.
- Balakrishnan, Kaushik, et al. “6-4: Deep Learning for Classification of Repairable Defects in Display Panels Using Multi-Modal Data.” SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. Vol. 54. No. 1. 2023.
- Liu, Rui, et al. “Enhanced detection classification via clustering svm for various robot collaboration task.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.03026 (2024).
- Kang, Yixiao, et al. “6: Simultaneous Tracking, Tagging and Mapping for Augmented Reality.” SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. Vol. 52. 2021.
- Weng, Yijie. “Big data and machine learning in defence.” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology 16.2 (2024): 25-35.
- Ma, Danqing, et al. “Transformer-Based Classification Outcome Prediction for Multimodal Stroke Treatment.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.12634 (2024).
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
| AlexNet | 65.20% | 66.00% | 64.50% | 65.20% |
| GoogleNet | 70.80% | 71.50% | 69.80% | 70.60% |
| VGG16 | 68.30% | 68.90% | 67.40% | 68.10% |
| ResNet | 74.50% | 75.20% | 73.80% | 74.50% |
| BNNAM | 77.60% | 78.30% | 76.80% | 77.50% |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Training Time(h) | Inference Time(s/images) |
| Baseline Model | 74.50% | 75.20% | 73.80% | 74.50% | 5 | 0.05 |
| without Bayesian Optimization | 75.20% | 75.80% | 74.30% | 75.00% | 4.8 | 0.045 |
| without Channel Attention Mechanism | 76.00% | 76.50% | 75.20% | 75.80% | 4.6 | 0.04 |
| without Spatial Attention Mechanism | 75.50% | 76.00% | 74.70% | 75.30% | 4.7 | 0.042 |
| without All Attention | 75.00% | 75.60% | 74.20% | 74.90% | 4.8 | 0.032 |
| BNNAM | 77.60% | 78.30% | 76.80% | 77.50% | 5.1 | 0.041 |
| with multi-head Attention | 74.4% | 74.8% | 73.2% | 73.2% | 5.3 | 0.06 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
| Base Model | 75.00% | 73.00% | 72.00% | 72.50% |
| w Cross-Entropy | 76.00% | 74.00% | 73.00% | 73.50% |
| w KL Divergence | 75.00% | 73.00% | 72.00% | 72.50% |
| Proposed Model | 77.60% | 78.30% | 76.80% | 77.50% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





