Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
27 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
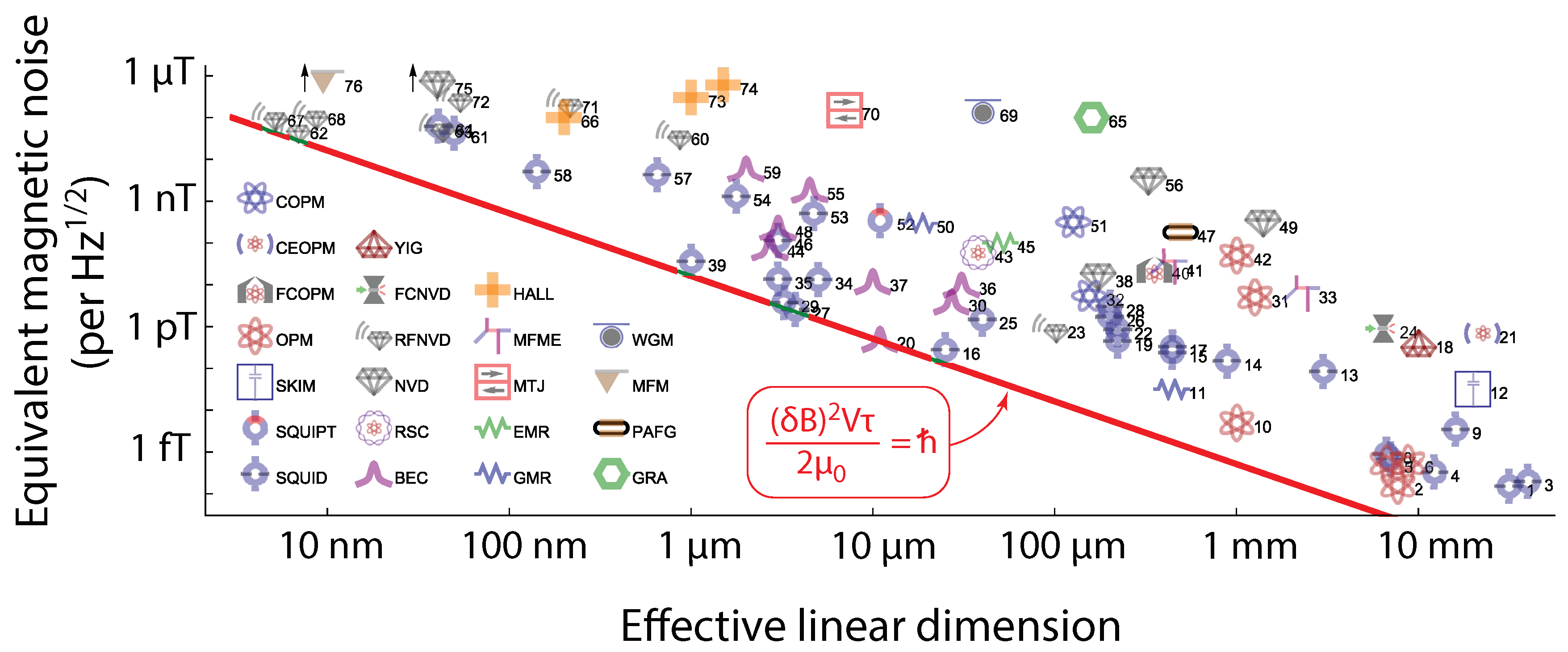
2. Introductory Comments about the Energy Resolution Limit
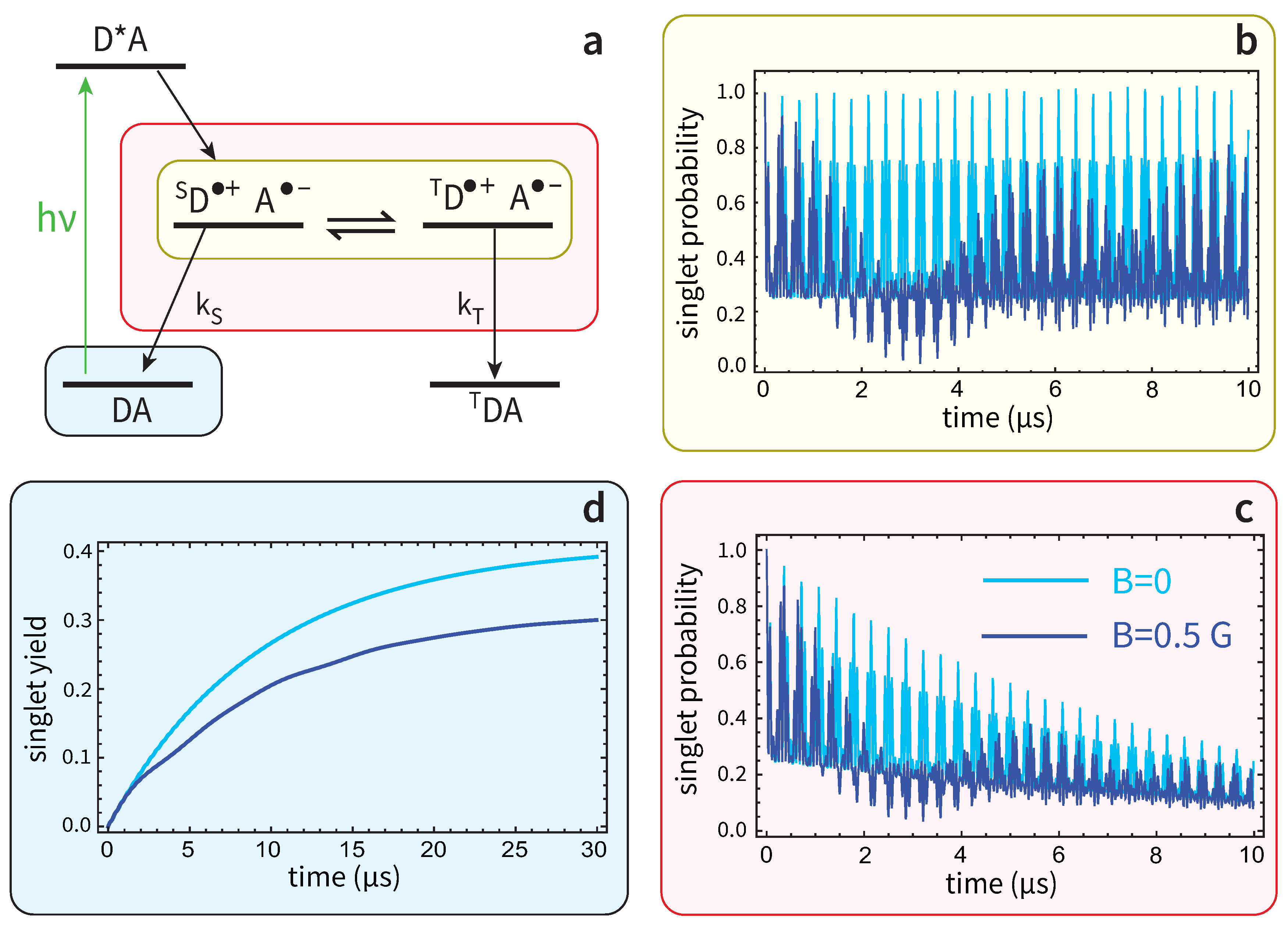
3. Radical-Pair Mechanism
3.1. Energy Resolution of Synthesized Radical-Pairs Probed with Laser Spectroscopy
3.2. What Is In Vivo?
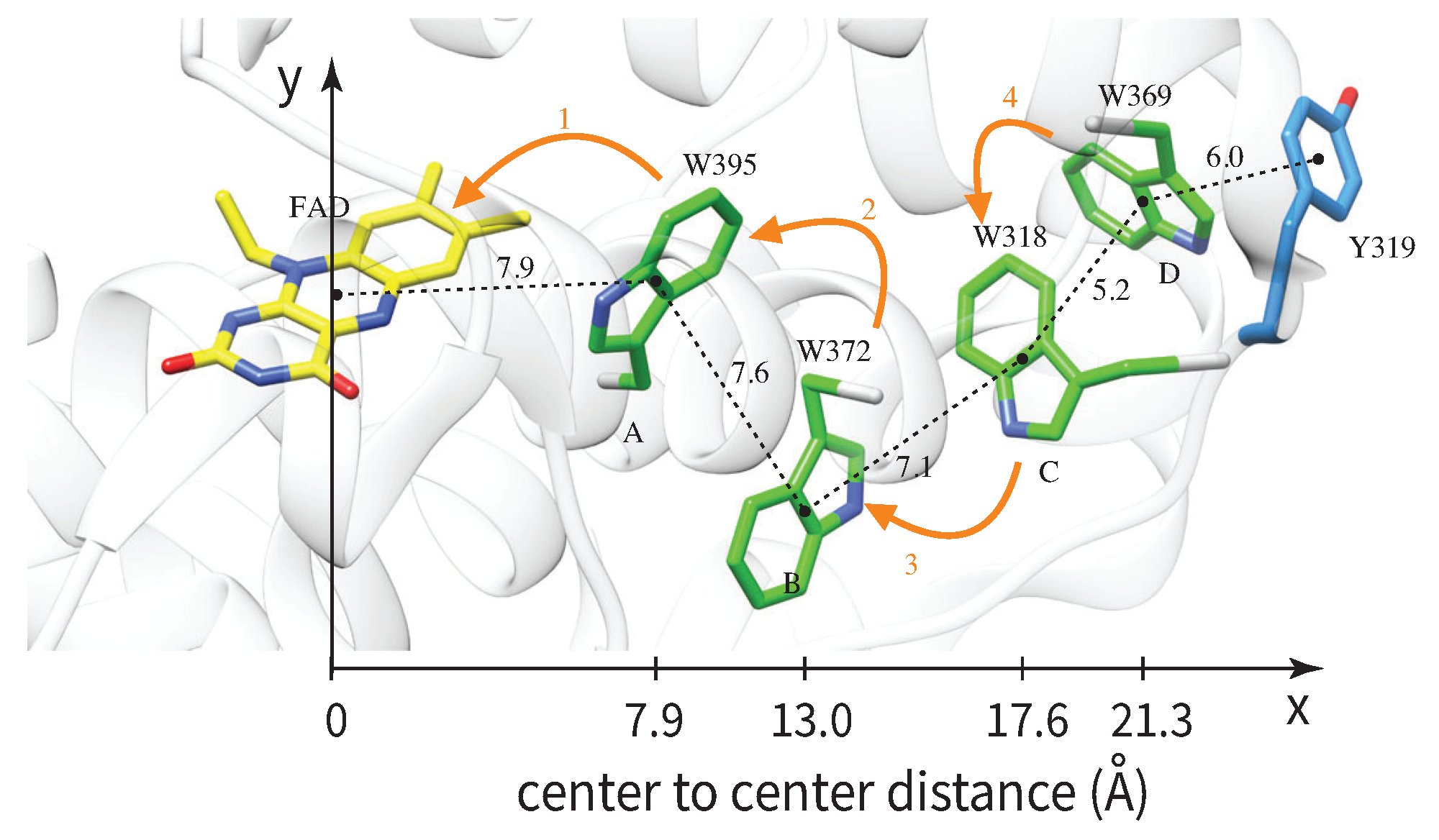
3.3. Energy Resolution In Vivo: Cryptochrome
3.4. Comment on the Sensor Volume
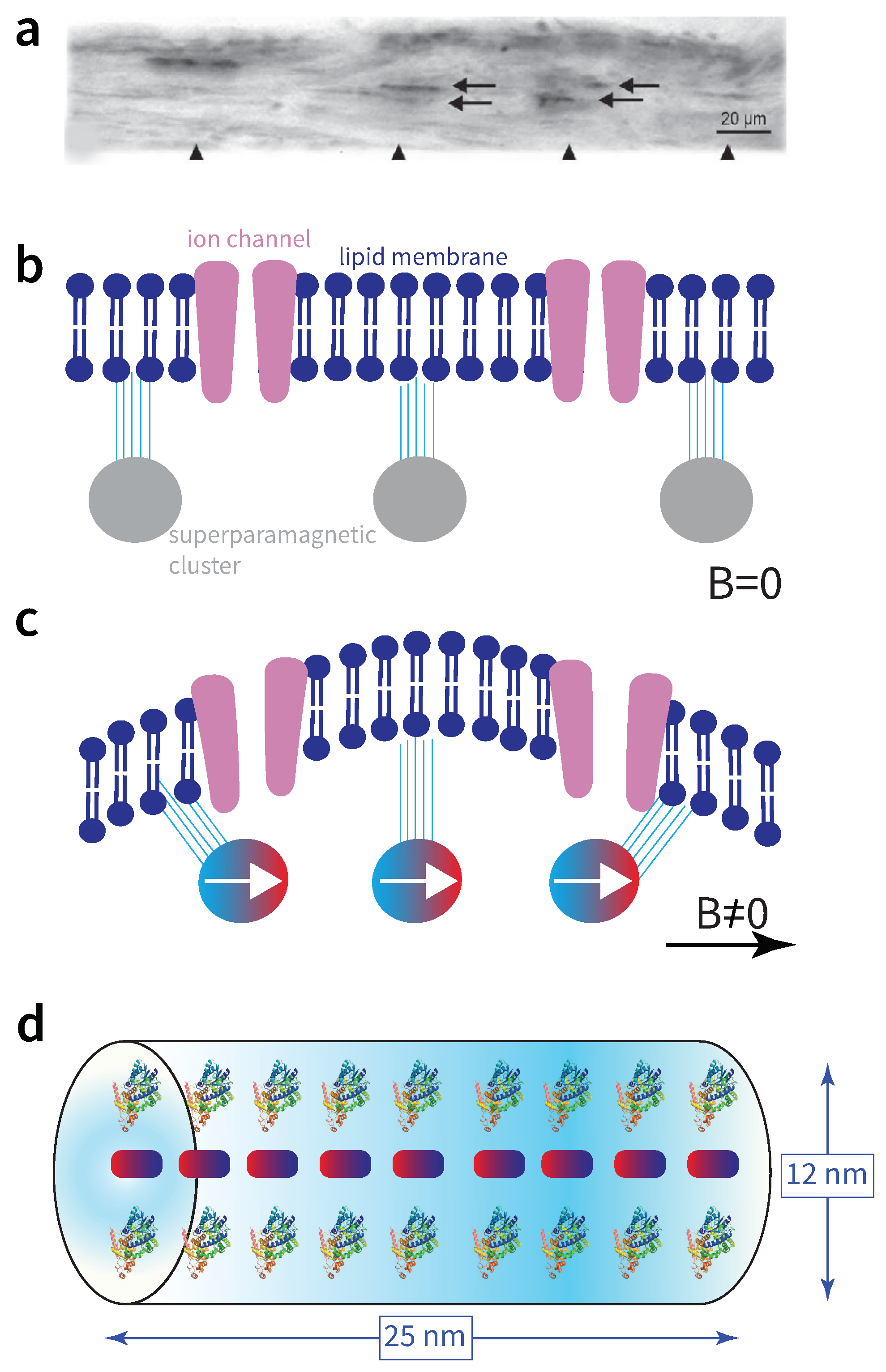
4. Magnetite Mechanism
5. MagR
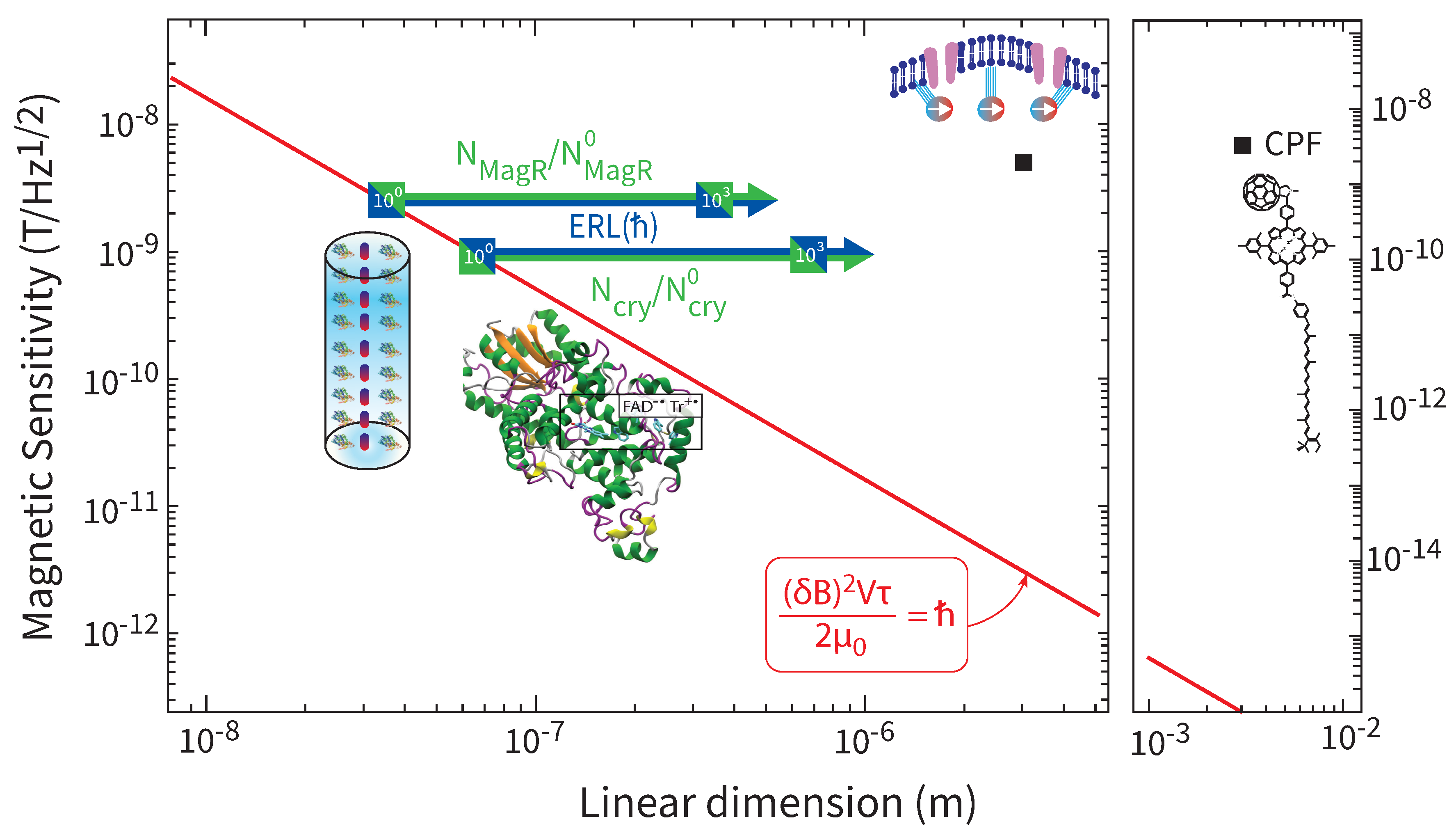
6. Global ER MAP for biological magnetoreception
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Keeton, W.T. Magnets interfere with pigeon homing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmijn, A.J. Biophysics of geomagnetic field detection. IEEE Trans. Magnetics 1981, 17, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.; Lohmann, K.J. The physics and neurobiology of magnetoreception. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltschko, W.; Wiltschko, R. Magnetic orientation and magnetoreception in birds and other animals. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2005, 191, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, S.; Lohmann, K. J. Magnetoreception in animals. Phys. Today 2008, 61, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritsen, H. Long-distance navigation and magnetoreception in migratory animals. Nature 2018, 558, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Jarocha, L. E.; Zollitsch, T.; Konowalczyk, M.; Henbest, K. B.; Richert, S.; Golesworthy, M. J.; Schmidt, J.; Déjean, V.; Sowood, D. J. C.; et al. Magnetic sensitivity of cryptochrome 4 from a migratory songbird. Nature 2021, 594, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. R. Bellinger, J. Wei, U. Hartmann, H. Cadiou, M. Winklhofer, and M. A. Banks, Conservation of magnetite biomineralization genes in all domains of life and implications for magnetic sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2108655119. [CrossRef]
- Xie, C. Searching for unity in diversity of animal magnetoreception: from biology to quantum mechanics and back. Innov 2022, 3, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, K. J. Magnetic-field perception. Nature 2010, 464, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. Wiltschko and R. Wiltschko, Magnetic orientation in birds. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 29. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- H. Mouritsen and T. Ritz, Magnetoreception and its use in bird navigation. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 406. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D. A. Kishkinev and N. S. Chernetsov, Magnetoreception systems in birds: a review of current research. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2015, 5, 46. [CrossRef]
- R. Wiltschko, M. Ahmad, C. Nießner, D. Gehring, and W. Wiltschko, Light-dependent magnetoreception in birds: the crucial step occurs in the dark. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20151010. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. Wiltschko and W. Wiltschko, Magnetoreception in birds. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190295. [CrossRef]
- J. B. Phillips and O. Sayeed, Wavelength-dependent effects of light on magnetic compass orientation in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Comp. Physiol. 1993, 172, 303. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Gegear, A. Casselman, S. Waddell, and S. M. Reppert, Cryptochrome mediates light-dependent magnetosensitivity in Drosophila. Nature 2008, 454, 1014. [CrossRef]
- D. H. Dommer, P. J. Gazzolo, M. S. Painter, J. B. Phillips, Magnetic compass orientation by larval Drosophila melanogaster. J. Insect Phys. 2008, 54, 719. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J.-E. Bae, S. Bang, S. Min, S.-H. Lee, S.-H. Kwon, Y. Lee, Y.-H. Lee, J. Chung and K.-S. Chae, Positive geotactic behaviors induced by geomagnetic field in Drosophila. Molec. Brain 2016, 9, 55. [CrossRef]
- I.-T. Oh, H.-J. Kwon, S.-C. Kim, H.-J. Kim, K. J. Lohmann, and K.-S. Chae, Behavioral evidence for geomagnetic imprinting and transgenerational inheritance in fruit flies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1216. [CrossRef]
- A. Bradlaugh, A. L. Munro, A. R. Jones, and R. A. Baines, Exploiting the fruitfly, Drosophila melanogaster, to identify the molecular basis of cryptochrome-dependent magnetosensitivity. Quantum Rep. 2021, 3, 127. [CrossRef]
- A. A. Bradlaugh, G. Fedele, A. L. Munro, C. N. Hansen, J. M. Hares, S. Patel, C. P. Kyriacou, A. R. Jones, E. Rosato, R. A. Baines, Essential elements of radical pair magnetosensitivity in Drosophila. Nature 2023, 615, 111.
- M. Bassetto, T. Reichl, D. Kobylkov, D. R. Kattnig, M. Winklhofer, P. J. Hore, and H. Mouritsen, No evidence for magnetic field effects on the behaviour of Drosophila. Nature 2023, 620, 595.
- S. M. Reppert, Magnetic field effects on behaviour in Drosophila. Nature 2024, 629, E1. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Reppert, R. J. Gegear, and C. Merlin, Navigational mechanisms of migrating monarch butterflies. Trends Neurosc. 2010, 33, 399. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P. A. Guerra, R. J. Gegear, and S. M. Reppert, A magnetic compass aids monarch butterfly migration. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4164. [CrossRef]
- G. Wan, A. N. Hayden, S. E.Liams, and C. Merlin, Cryptochrome 1 mediates light-dependent inclination magnetosensing in monarch butterflies. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 771. [CrossRef]
- V. Courtillotl, G. Hulot, M. Alexandrescu, J.-L. le Mouël, and J. L. Kirschvink, Sensitivity and evolution of sea-turtle magnetoreception: observations, modelling and constraints from geomagnetic secular variation. Terra Nova 1997, 9, 203. [CrossRef]
- K. J. Lohmann, Sea turtles: navigating with magnetism. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R102. [CrossRef]
- W. P. Irwin and K. J. Lohmann, Disruption of magnetic orientation in hatchling loggerhead sea turtles by pulsed magnetic fields. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2005, 191, 475. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Anderson, T. M. Clegg, L. V. M. V. Q. Véras, and K. N. Holland, Insight into shark magnetic field perception from empirical observations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11042. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- B. A. Keller, N. F. Putman, R. D. Grubbs, D. S. Portnoy, and T. P. Murphy, Map-like use of Earth’s magnetic field in sharks. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 2881. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. G. Meyer, K. N. Holland, and Y. P. Papastamatiou, Sharks can detect changes in the geomagnetic field. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 2, 129. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. Nishi, G. Kawamura, and K. Matsumoto, Magnetic sense in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica, as determined by conditioning and electrocardiography. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 2965. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. M. F. Durif, H. I. Browman, J. B. Phillips, A. B. Skiftesvik, L. A. Vøllestad, and H. H. Stockhausen, Magnetic compass orientation in the European eel. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59212.
- A. Cresci, C. B. Paris, C. M. F. Durif, S. Shema, R. M. Bjelland, A. B. Skiftesvik, and H. I. Browman, Glass eels (Anguilla anguilla) have a magnetic compass linked to the tidal cycle. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602007. [CrossRef]
- M. Baltazar-Soares, C. Eizaguirre, Animal navigation: the eel’s magnetic guide to the Gulf stream. Current Biology 2017, 27, R604. [CrossRef]
- A. Cresci, C. M. Durif, C. B. Paris, S. D. Shema, A. B. Skiftesvik, and H. I. Browman, Glass eels (Anguilla anguilla) imprint the magnetic direction of tidal currents from their juvenile estuaries. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 366. [CrossRef]
- T. P. Quinn, Evidence for celestial and magnetic compass orientation in lake migrating sockeye salmon fry. J. Comp. Physiol. 1980, 137, 243. [CrossRef]
- N. F. Putman, Inherited magnetic maps in salmon and the role of geomagnetic change. Integr. Compar. Biol. 2015, 55, 396. [CrossRef]
- L. C. Naisbett-Jones, N. F. Putman, M. M. Scanlan, D. L. G. Noakes, and K. J. Lohmann, Magnetoreception in fishes: the effect of magnetic pulses on orientation of juvenile Pacific salmon. J. Exp. Biology 2020, 223, jeb222091.
- K. Schulten, C. E. Swenberg, and A. Weller, A biomagnetic sensory mechanism based on magnetic field modulated coherent electron spin motion. Z. Phys. Chem. 1978, 111, 1. [CrossRef]
- C. B. Grissom, Magnetic field effects in biology: A survey of possible mechanisms with emphasis on radical-pair recombination. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 3. [CrossRef]
- T. Ritz, S. Adem, and K. Schulten, A model for photoreceptor-based magnetoreception in birds. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 707. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P. J. Hore and H. Mouritsen, The radical-pair mechanism of magnetoreception. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2016, 45, 299. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- H. G. Hiscock, S. Worster, D. R. Kattnig, C. Steers, Y, Jina, D. E. Manolopoulos, H. Mouritsen, and P. J. Hore, The quantum needle of the avian magnetic compass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4634.
- S. Mann, N. H. C. Sparks, M. M. Walker, and J. L. Kirschvink, Ultrastructure, morphology and organization of biogenic magnetite from sockeye salmon, Oncorhynchus nerka: implications for magnetoreception. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 140, 35.
- J. L. Kirschvink, M. M. Walker, and C. E. Diebel, Magnetite-based magnetoreception. Curr. Op. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 462. [CrossRef]
- Winklhofer, M. Magnetite-based magnetoreception in higher organisms. In Microbiol. Monogr., D. Schüler, Magnetoreception and magnetosomes in bacteria; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- G. Fleissner, B. Stahl, P. Thalau, G. Falkenberg, and G. Fleissner, A novel concept of Fe-mineral-based magnetoreception: histological and physicochemical data from the upper beak of homing pigeons. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 631. [CrossRef]
- H. Cadiou and P. A. McNaughton, Avian magnetite-based magnetoreception: a physiologist’s perspective. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S193.
- Kalmijn, A. J. Electric and Magnetic Field Detection in Elasmobranch Fishes. Science 1982, 218, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- B. Rosenblum, R. L. Jungerman, and L. Longfellow, Limits to induction-based magnetoreception. In Magnetite biomineralization and magnetoreception in organisms; Kirschvink, J.L., Jones, D.S., MacFadden, B.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- T. C. A. Molteno and W. L. Kennedy, Navigation by induction-based magnetoreception in elasmobranch fishes. J. Biophys. 2009, 2009, 380976.
- S. Nimpf, G. C. Nordmann, D. Kagerbauer, E. P. Malkemper, L. Landler, A. Papadaki-Anastasopoulou, L. Ushakova, A. Wenninger-Weinzierl, M. Novatchkova, P. Vincent, T. Lendl, M. Colombini, M. J. Mason, and D. A. Keays, A putative mechanism for magnetoreception by electromagnetic induction in the pigeon inner ear. Current Biology 2019, 29, 4052.
- S. Qin, H. Yin, C. Yang, Y. Dou, Z. Liu, P. Zhang, H. Yu, Y. Huang, J. Feng, J. Hao, J. Hao, L. Deng, X. Yan, X. Dong, Z. Zhao, T. Jiang, H.-W. Wang, S.-J. Luo, and C. Xie, A magnetic protein biocompass. Nature Mater. 2016, 15, 217.
- D. I. Gordon and R. E. Brown, Recent advances in fluxgate magnetometry. IEEE Trans. Magn. MAG 1972, 8, 76. [CrossRef]
- P. Ripka, Review of fluxgate sensors. Sens. Actuators A 1992, 33, 129. [CrossRef]
- P. Ripka and M. Janošek, Advances in Magnetic Field Sensors. IEEE Sensors J. 2010, 10, 1108. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Dowling and G. J. Milburn, Quantum technology: the second quantum revolution. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2003, 361, 1655. [CrossRef]
- I. H. Deutsch, Harnessing the power of the second quantum revolution. PRX Quantum 2020, 1, 020101. [CrossRef]
- C. L. Degen, F. Reinhard, and P. Cappellaro, Quantum sensing. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 035002.
- Clarke, J. SQUID fundamentals, in W. H. Dordrecht, SQUlD Sensors: Fundamentals, Fabrication and Applications; (Kluwer Academic Press, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- R. L. Fagaly, SQUID instruments and applications. Rev. Sci. Instr. 2006, 77, 101101.
- M. Schmelz, V. Zakosarenko, T. Schönau, S. Anders, S. Linzen,R. Stolz, and H.-G. Meyer, Nearly quantum limited nanoSQUIDs based on cross-type Nb/AlOx/Nb junctions. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2017, 30, 014001. [CrossRef]
- I. K. Kominis, T. W. Kornack, J. C. Allred, and M. V. Romalis, A subfemtotesla multichannel atomic magnetometer. Nature 2003, 422, 596. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A. Fabricant, I. Novikova, and G. Bison, How to build a magnetometer with thermal atomic vapor: a tutorial. New J. Phys. 2023, 25, 025001. [CrossRef]
- G. Balasubramanian, I. Y. Chan, R. Kolesov, M. Al-Hmoud, J. Tisler, C. Shin, C. Kim, A. Wojcik, P. R. Hemmer, A. Krueger, T. Hanke, A. Leitenstorfer, R. Bratschitsch, F. Jelezko, and J. Wrachtrup, Nanoscale imaging magnetometry with diamond spins under ambient conditions. Nature 2008, 455, 648.
- J. M. Taylor, P. Cappellaro, L. Childress, L. Jiang, D. Budker, P. R. Hemmer, A. Yacoby, R. Walsworth, and M. D. Lukin, High-sensitivity diamond magnetometer with nanoscale resolution. Nature Phys. 2008, 4, 810.
- H. Zheng, Z. Sun, G. Chatzidrosos, C. Zhang, K. Nakamura, H. Sumiya, T. Ohshima, J. Isoya, J. Wrachtrup, A. Wickenbrock, and D. Budker, Microwave-free vector magnetometry with nitrogen-vacancy centers along a single axis in diamond. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 13, 044023. [CrossRef]
- M. Vengalattore, J. M. Higbie, S. R. Leslie, J. Guzman, L. E. Sadler, and D. M. Stamper-Kurn, High-resolution magnetometry with a spinor bose-einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 200801. [CrossRef]
- P. Gomez, F. Martin, C. Mazzinghi, D. B. Orenes, S. Palacios, and M. W. Mitchell, Bose-Einstein condensate comagnetometer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 170401.
- K. Gietka, F. Mivehvar and T. Busch, Cavity-enhanced magnetometer with a spinor Bose–Einstein condensate. New J. Phys. 2021, 23, 043020. [CrossRef]
- M. Hämäläinen, R. Hari, R. J. Ilmoniemi, J. Knuutila, and O. V. Lounasmaa, Magnetoencephalography - theory, instrumentation, and applications to noninvasive studies of the working human brain. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1993, 65, 413. [CrossRef]
- H. Xia, A. B.-A. Baranga, D. Hoffman, and M. V. Romalis, Magnetoencephalography with an atomic magnetometer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 211104. [CrossRef]
- E. J. Pratt, M. Ledbetter, R. Jiménez-Martínez, B. Shapiro, A. Solon, G. Z. Iwata, S. Garber, J. Gormley, D. Decker, D. Delgadillo, et al. Alford, Kernel Flux: a whole-head 432-magnetometer optically-pumped magnetoencephalography (OP-MEG) system for brain activity imaging during natural human experiences. Proc. SPIE 2021, 11700, 1170032.
- T. M. Tierney, N. Holmes, S. Mellor, J. D. López, G. Roberts, R. M. Hill, E. Boto, J. Leggett, V. Shah, M. J. Brookes, R. Bowtell, G. R. Barnes, Optically pumped magnetometers: From quantum origins to multi-channel magnetoencephalography. NeuroImage 2019, 199, 598.
- R. Zhang, W. Xiao, Y. Ding, Y. Feng, X. Peng, L. Shen, C. Sun, T. Wu, Y. Wu, Y. Yang, Z. Zheng, X. Zhang, J. Chen, and H. Guo, Recording brain activities in unshielded Earth’s field with optically pumped atomic magnetometers. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba8792. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- G. Bison, R. Wynands, and A. Weis, A laser-pumped magnetometer for the mapping of human cardiomagnetic fields. Appl. Phys. B 2003, 76, 325. [CrossRef]
- J. Kim, I. Savukov, and S. Newman, Magnetocardiography with a 16-channel fiber-coupled single-cell Rb optically pumped magnetometer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 143702. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Romalis and H. B. Dang, Atomic magnetometers for materials characterization. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 258. [CrossRef]
- F. Fabre, A. Finco, A. Purbawati, A. Hadj-Azzem, N. Rougemaille, J. Coraux, I. Philip, and V. Jacques, Characterization of room-temperature in-plane magnetization in thin flakes of CrTe 2 with a single-spin magnetometer. Phys. Rev. Materials 2021, 5, 034008. [CrossRef]
- N. Aslam, H. Zhou, E. K. Urbach, M. J. Turner, R. L. Walsworth, M. D. Lukin, and H. Park, Quantum sensors for biomedical applications. Nature Rev. Phys. 2023, 5, 157.
- B. Bao, Y. Hua, R. Wang, and D. Li, Quantum-based magnetic field sensors for biosensing. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2023, 6, 2200146. [CrossRef]
- M. W. Mitchell and S. P. Alvarez, Colloquium: Quantum limits to the energy resolution of magnetic field sensors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 021001. [CrossRef]
- M. Meister, Physical limits to magnetogenetics. eLife 2016, 5, e17210. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. F. Huelga and M. B. Plenio, Vibrations, quanta and biology. Contemp. Phys. 2013, 54, 181. [CrossRef]
- I. K. Kominis, Quantum Zeno effect explains magnetic-sensitive radical-ion-pair reactions. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 056115. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. Cai, G. G. Guerreschi, and H. J. Briegel, Quantum control and entanglement in a chemical compass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 220502. [CrossRef]
- I. K. Kominis, Magnetic sensitivity and entanglement dynamics of the chemical compass. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 542, 143. [CrossRef]
- C. Y. Cai, Q. Ai, H. T. Quan, and C. P. Sun, Sensitive chemical compass assisted by quantum criticality. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 022315. [CrossRef]
- J. Cai and M. B. Plenio, Chemical compass model for avian magnetoreception as a quantum coherent device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 230503. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, G. P. Berman, and S. Kais, Sensitivity and entanglement in the avian chemical compass. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 042707. [CrossRef]
- V. S. Poonia, K. Kondabagil, D. Saha, and S. Ganguly, Functional window of the avian compass. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 052417. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K. M. Vitalis and I. K. Kominis, Quantum-limited biochemical magnetometers designed using the Fisher information and quantum reaction control. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 032129. [CrossRef]
- M. Tolunay, I. Liepuoniute, M. Vyushkova, and B. A. Jones. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 15115.
- A. Streltsov, G. Adesso, and M. B. Plenio, Colloquium: Quantum coherence as a resource. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 041003. [CrossRef]
- M. B. Plenio and S. Virmani, An introduction to entanglement measures. Quant. Inf. Comput. 2007, 7, 1.
- I. K. Kominis, Quantum relative entropy shows singlet-triplet coherence is a resource in the radical-pair mechanism of biological magnetic sensing. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 023206. [CrossRef]
- Kominis, I.K. Physiological search for quantum biological sensing effects based on the Wigner-Yanase connection between coherence and uncertainty. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2023, 2300292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Hou, D. Wang, K. Xiao, H. Zhang, S. Zheng, P. Li, Y. Tian, and L. Jiang, Magnetic gated biomimetic artificial nanochannels for controllable ion transportation inspired by homing pigeon. Small 2018, 14, 1703369. [CrossRef]
- Yei Hwan Jung, Byeonghak Park, Jong Uk Kim, and Tae-il Kim, Bioinspired electronics for artificial sensory systems. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803637.
- Xue, T. Hu, Z. Guo, C. Yang, Z. Wang, S. Qin, P. Yang, C. Xie, J. Xu, N. Li, Y. Shen, H. Jiang, D. Deng, N.Gu, and J. Sun, A novel biomimetic magnetosensor based on magneto-optically involved conformational variation of MagR/Cry4 complex. Adv. Electron. Mater. 1901168, 2020.
- Kominis, I.K. Quantum thermodynamic derivation of the energy resolution limit in magnetometry. arXiv arXiv:2405.14687.
- A. Vinante, C. Timberlake, D. Budker, D. F. Jackson Kimball, A. O. Sushkov, and H. Ulbricht, Surpassing the energy resolution limit with ferromagnetic torque sensors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 070801. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. P. Alvarez, P. Gomez, S. Coop, R. Zamora-Zamora, C. Mazzinghi, and M. W. Mitchell, Single-domain Bose condensate magnetometer achieves energy resolution per bandwidth below ℏ, Proc. Nat. Acad. USA 2022, 119, e2115339119. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- F. Ahrens, W. Ji, D. Budker, C. Timberlake, H. Ulbricht, and A. Vinante, Levitated ferromagnetic magnetometer with energy resolution well below ℏ. arXiv arXiv:2401:03774.
- I. K. Kominis, The radical-pair mechanism as a paradigm for the emerging science of quantum biology. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 29, 1530013. [CrossRef]
- R. E. Blankenship, T. J. Schaafsma, and W. W. Parson, Magnetic field effects on radical pair intermediates in bacterial photosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1977, 461, 297. [CrossRef]
- U. E. Steiner and T. Ulrich, Magnetic field effects in chemical kinetics and related phenomena. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 51. [CrossRef]
- C. R. Timmel, U. Till, B. Brocklehurst, K. A. Mclauchlan, and P. J. Hore, Effects of weak magnetic fields on free radical recombination reactions. Mol. Phys. 1998, 95, 71. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Lewis, T. P. Fay, D. E. Manolopoulos, C. Kerpal, S. Richert, and C. R. Timmel, On the low magnetic field effect in radical pair reactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 034103. [CrossRef]
- S. Y. Wong, P. Benjamin, and P. J. Hore, Magnetic field effects on radical pair reactions: estimation of B1/2 for flavin-tryptophan radical pairs in cryptochromes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 975. [CrossRef]
- T. Ritz, R. Wiltschko, P. J. Hore, C. T. Rodgers, K. Stapput, P. Thalau, C. R. Timmel, and W. Wiltschko, Magnetic compass of birds is based on a molecule with optimal directional sensitivity. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 3451. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- G. E. Katsoprinakis, A. T. Dellis, I. K. Kominis, Coherent triplet excitation suppresses the heading error of the avian compass. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 085016. [CrossRef]
- J. C. S. Lau, C. T. Rodgers, and P. J. Hore, Compass magnetoreception in birds arising from photo-induced radical pairs in rotationally disordered cryptochromes. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 3329. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Y. Zhang, Z. Hu, Y. Wang, and S. Kais, Quantum simulation of the radical pair dynamics of the avian compass. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 832. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. Ritz, P. Thalau, J. B. Phillips, R. Wiltschko, and W. Wiltschko, Resonance effects indicate a radical-pair mechanism for avian magnetic compass. Nature 2004, 429, 177. [CrossRef]
- N. Keary, T. Ruploh, J. Voss, P. Thalau, R. Wiltschko, W. Wiltschko, and H.-J. Bischof, Oscillating magnetic field disrupts magnetic orientation in Zebra finches, Taeniopygia guttata. Front. Zool. 2009, 6, 25. [CrossRef]
- S. Engels, N.-L. Schneider, N. Lefeldt, C. M. Hein, M. Zapka, A. Michalik, D. Elbers, A. Kittel, P. J. Hore, and H. Mouritsen, Anthropogenic electromagnetic noise disrupts magnetic compass orientation in a migratory bird. Nature 2014, 509, 353. [CrossRef]
- B. Leberecht, D. Kobylkov, T. Karwinkel, S. Döge, L. Burnus, S. Y. Wong, S. Apte, K. Haase, I. Musielak, R. Chetverikova, G. Dautaj, M. Bassetto, M. Winklhofer,P. J. Hore, and H. Mouritsen, Broadband 75–85 MHz radiofrequency fields disrupt magnetic compass orientation in night-migratory songbirds consistent with a flavin-based radical pair magnetoreceptor. J. Compar. Physiol. A 2022, 208, 97.
- C. L. Thompson, C. B. Rickman, S. J. Shaw, J. N. Ebright, U. Kelly, A. Sancar, and D. W. Rickman, Expression of the blue-light receptor cryptochrome in the human retina. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4515. [CrossRef]
- D. Heyers, M. Manns, H. Luksch, O. Güntürkün, and H. Mouritsen, A visual pathway links brain structures active during magnetic compass orientation in migratory birds. PLoS One 2007, 2, e937. [CrossRef]
- C. Nießner, S. Denzau, E. P. Malkemper, J. C. Gross, H. Burda, M. Winklhofer, and L. Peichl, Cryptochrome 1 in retinal cone photoreceptors suggests a novel functional role in mammals. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21848. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- H. Mouritsen, U. Janssen-Bienhold, M. Liedvogel, G. Feenders, J. Stalleicken, P. Dirks, and R. Weiler, Cryptochromes and neuronal-activity markers colocalize in the retina of migratory birds during magnetic orientation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14294. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Weaver, T. E. Vaughan, R. D. Astumian, Biological sensing of small field differences by magnetically sensitive chemical reactions. Nature 2000, 405, 707. [CrossRef]
- K. Maeda, K. B. Henbest, F. Cintolesi, I. Kuprov, C. T. Rodgers, P. A. Liddell, D. Gust, C. R. Timmel, and P. J. Hore, Chemical compass model of avian magnetoreception. Nature 2008, 453, 387.
- C. Kerpal, S. Richert, J. G. Storey, S. Pillai, P. A. Liddell, D. Gust, S. R. Mackenzie, P. J. Hore, and C. R. Timmel, Chemical compass behaviour at microtesla magnetic fields strengthens the radical pair hypothesis of avian magnetoreception. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3707. [CrossRef]
- D. Budker and M. V. Romalis, Optical magnetometry. Nature Phys. 2007, 3, 227.
- S. G. Boxer, C. E. Chidsey, and M. G. Roelofs, Anisotropic magnetic interactions in the primary radical ion-pair of photosynthetic reaction centers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 4632. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- F. Cintolesi, T. Ritz, C.W.M. Kay, C.R. Timmel, and P.J. Hore, Anisotropic recombination of an immobilized photoinduced radical pair in a 50-μT magnetic field: a model avian photomagnetoreceptor. Chem. Phys. 2003, 294, 285.
- J. Luo, On the anisotropic weak magnetic field effect in radical-pair reactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 158, 234302. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ren, H. G. Hiscock, and P. J. Hore, Angular precision of radical pair compass magnetoreceptors. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 547. [CrossRef]
- A. V. Komolkin, P. A. V. Komolkin, P. Kupriyanov, A. Chudin, J. Bojarinova, K. Kavokin, and N. Chernetsov, Theoretically possible spatial accuracy of geomagnetic maps used by migrating animals. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20161002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K. J. Lohmann, K. M. Goforth, A. G. Mackiewicz, D. S. Lim, C. M. F. Lohmann, Magnetic maps in animal navigation. J. Compar. Physiol. A 2022, 208, 41.
- P. Semm and R. C. Beason, Responses to small magnetic variations by the trigeminal system of the bobolink. Brain Res. Bull. 1990, 25, 735. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K. J. Lohmann, N. F. Putman, S. Johnsen, and C. M. F. Lohmann, Animal magnetic sensitivity and magnetic displacement experiments. Commun. 2024, 7, 650.
- I. A. Solov’yov, T. Domratcheva, A. R. M. Shahi, and K. Schulten, Decrypting cryptochrome: revealing the molecular identity of the photoactivation reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18046. [CrossRef]
- K. Maeda, A. J. Robinson, K. B. Henbest, H. J. Hogben, T. Biskup, M. Ahmad, E. Schleicher, S. Weber, C. R. Timmel, and P. J. Hore, Magnetically sensitive light-induced reactions in cryptochrome are consistent with its proposed role as a magnetoreceptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4774. [CrossRef]
- I. A. Solov’yov, T. Domratcheva, and K. Schulten, Separation of photo-induced radical pair in cryptochrome to a functionally critical distance. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3845. [CrossRef]
- D. Nohr, S. Franz, R. Rodriguez, B. Paulus, L.-O. Essen, S. Weber, and E. Schleicher, Extended electron-transfer in animal cryptochromes mediated by a tetrad of aromatic amino acids. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 301. [CrossRef]
- A. K. Michael, J. L. Fribourgh, R. N. Van Gelder, and C. L. Partch, Animal cryptochromes: divergent roles in light perception, circadian timekeeping and beyond. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 128. [CrossRef]
- D. R. Kattnig, C. Nielsen, and I. A. Solov’yov, Molecular dynamics simulations disclose early stages of the photoactivation of cryptochrome 4. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 083018. [CrossRef]
- B. D. Zoltowski, Y. Chelliah, A. Wickramaratne, L. Jarocha, N. Karki, W. Xu, H. Mouritsen, P. J. Hore, R. E. Hibbs, C. B. Green, and J. S. Takahashi, Chemical and structural analysis of a photoactive vertebrate cryptochrome from pigeon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19449.
- T. Hochstoeger, T. Al Said, D. Maestre, F. Walter, A. Vilceanu, M. Pedron, T. D. Cushion, W. Snider, S. Nimpf, G. C.Nordmann, L. Landler, N. Edelman, L. Kruppa, G. Dürnberger, K. Mechtler, S. Schuechner, E. Ogris, E. P. Malkemper, S. Weber, E. Schleicher, and D. A. Keays, The biophysical, molecular, and anatomical landscape of pigeon CRY4: A candidate light-based quantal magnetosensor. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb9110.
- G. C. G. Parico and C. L. Partch, The tail of cryptochromes: an intrinsically disordered cog within the mammalian circadian clock. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 182. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. Y. Wong, Y. Wei, H. Mouritsen, I. A. Solov’yov, and P. J. Hore, Cryptochrome magnetoreception: four tryptophans could be better than three. J. R. Soc. Interface 2021, 18, 20210601. [CrossRef]
- S. Chandrasekaran, C. M. Schneps, R. Dunleavy, C. Lin, C. C. DeOliveira, A. Ganguly, and B. R. Crane, Tuning flavin environment to detect and control light-induced conformational switching in Drosophila cryptochrome. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 249. [CrossRef]
- A. Frederiksen, M. Aldag, I. A. Solov’yov, and Luca Gerhards, Activation of cryptochrome 4 from Atlantic herring. Biology 2024, 13, 262. [CrossRef]
- J. Deviers, F. Cailliez, A.de la Lande, and D. R. Kattnig, Avian cryptochrome 4 binds superoxide. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 26, 11. [CrossRef]
- F. Schuhmann, J. L. Ramsay, D. R. Kattnig, and I. A. Solov’yov, Structural rearrangements of pigeon cryptochrome 4 undergoing a complete redox cycle. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 3844. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- H. Wu, A. Scholten, A. Einwich, H. Mouritsen, K. -W. Koch, Protein-protein interaction of the putative magnetoreceptor cryptochrome 4 expressed in the avian retina. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7364. [CrossRef]
- A. Günther, A. Einwich, E. Sjulstok, R. Feederle, P. Bolte, K.-W. Koch, I. A. Solov’yov, and H. Mouritsen, Double-cone localization and seasonal expression pattern suggest a role in magnetoreception for European robin cryptochrome 4. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 211. [CrossRef]
- A. Pinzon-Rodriguez, S. Bensch, and R. Muheim, Expression patterns of cryptochrome genes in avian retina suggest involvement of Cry4 in light-dependent magnetoreception. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180058. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. Biskup, E. Schleicher, A. Okafuji, G. Link, K. Hitomi, E. D. Getzoff, and S. Weber, Direct observation of a photoinduced radical-pair intermediate in a cryptochrome DASH blue-light photoreceptor. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 404. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D. R. Kattnig, I. A. Solov’yov and P. J. Hore, Electron spin relaxation in cryptochrome-based magnetoreception. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 12443. [CrossRef]
- T. P. Fay, L. P. Lindoy, D. E. Manolopoulos, and P. J. Hore, How quantum is radical pair magnetoreception? Faraday Discuss. 2020, 221, 77. [CrossRef]
- S. Worster, D. R. Kattnig, and P. J. Hore, Spin relaxation of radicals in cryptochrome and its role in avian magnetoreception. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 145, 035104. [CrossRef]
- B. Lei, Rod-driven OFF pathway responses in the distal retina: dark-adapted flicker electroretinogram in mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43856. [CrossRef]
- O. Efimova and P. J. Hore, Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 156.
- R. P. Blakemore, Magnetotactic bacteria. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1981, 36, 217.
- H. A. Lowenstam, Minerals formed by organisms. Science 1981, 211, 1126. [CrossRef]
- D. Faivre and D. Schüler, Magnetotactic bacteria and magnetosomes. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4875. [CrossRef]
- W. Lin, J. L. Kirschvink, G. A. Paterson, D. A. Bazylinski and Y. Pan, On the origin of microbial magnetoreception. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 472.
- C. L. Monteil and C. T. Lefevre, Magnetoreception in microorganisms. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 266. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. L. Gould, J. L. Kirschvink, and K. S. Deffeyes, Bees have magnetic remanence. Science 1978, 201, 1026. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C.-H. Liang, C.-L. Chuang, J.-A. Jiang, and E.-C. Yang, Magnetic sensing through the abdomen of the honey bee. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23657. [CrossRef]
- S. H. K. Eder, H. Cadiou, A. Muhamad, P. A. McNaughton, J. L. Kirschvink, and M. Winklhofer, Magnetic characterization of isolated candidate vertebrate magnetoreceptor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12022. [CrossRef]
- C. E. Diebel, R. Proksch, C. R. Green, P. Neilson, and M. M. Walker, Magnetite defines a vertebrate magnetoreceptor. Nature 2000, 406, 299. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Walker, C. E. Diebel, C. V. Haugh, P. M. Pankhurst, J. C. Montgomery, and C. R. Green, Structure and function of the vertebrate magnetic sense. Nature 1997, 390, 371.
- R. C. Beason and W. J. Brennan, Natural and induced magnetization in the bobolink, dolichonyx oryzivorus. J. Exp. Biol. 1986, 125, 49. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Kirschvink and J. L. Gould, Biogenic magnetite as a basis for magnetic field detection in animals. BioSystems 1981, 13, 181. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Kirschvink, Magnetite biomineralization and geomagnetic sensitivity in higher animals: an update and recommendations for future study. Bioelectromagnetics 1989, 10, 239. [CrossRef]
- S. Begall, H. Burda, and E. P. Malkemper, Magnetoreception in mammals. Adv. Stud. Behav. 2014, 46, 45.
- G. Fleissner, B. Stahl, P. Thalau, G. Falkenberg, and G. Fleissner, A novel concept of Fe-mineral-based magnetoreception: histological and physicochemical data from the upper beak of homing pigeons. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 631. [CrossRef]
- G. Falkenberg, G. Fleissner, K. Schuchardt, M. Kuehbacher, P. Thalau, H. Mouritsen, D. Heyers, G. Wellenreuther, G. Fleissner, Avian magnetoreception: elaborate iron mineral containing dendrites in the upper beak seem to be a common feature of birds. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9231. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D. Heyers, M. D. Heyers, M. Zapka, M. Hoffmeister, J. M. Wild and H. Mouritsen, Magnetic field changes activate the trigeminal brainstem complex in a migratory bird. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Wiltschko and W. Wiltschko, The magnetite-based receptors in the beak of birds and their role in avian navigation. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2013, 199, 89. [CrossRef]
- V. P. Shcherbakov and M. Winklhofer, The osmotic magnetometer: a new model for magnetite-based magnetoreceptors in animals. Eur. Biophys. J. 1999, 28, 380. [CrossRef]
- G. Fleissner, G. Fleissner, B. Stahl, and G. Falkenberg, Iron-mineral-based magnetoreception in birds: the stimulus conducting system. J. Ornithol. 2007, 148, S643. [CrossRef]
- I. A. Solov’yov and W. Greiner, Theoretical analysis of an iron mineral-based magnetoreceptor model in birds. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1493. [CrossRef]
- M. Winklhofer, and J. L. Kirschvink, A quantitative assessment of torque-transducer models for magnetoreception. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S273.
- A.F. Davila, G. A.F. Davila, G. Fleissner, M. Winklhofer, N. Petersen, A new model for a magnetoreceptor in homing pigeons based on interacting clusters of superparamagnetic magnetite. Phys. Chem. Earth 2003, 28, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Torbati, K. Mozaffari, L. Liu, and P. Sharma, Coupling of mechanical deformation and electromagnetic fields in biological cells. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2022, 94, 025003. [CrossRef]
- D. T. Grob, N. Wise, O. Oduwole, and S. Sheard, Magnetic susceptibility characterisation of superparamagnetic microspheres. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 452, 134. [CrossRef]
- J. Ashmore, Cochlear outer hair cell motility. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 173. [CrossRef]
- P. S. Langan, V. G. Vandavasi, W. Kopec, B. Sullivan, P. V. Afonne, K. L. Weiss, B. L. de Groot, and L. Coates, (2020), The structure of a potassium-selective ion channel reveals a hydrophobic gate regulating ion permeation. IUCrJ 2020, 7, 835. [CrossRef]
- V. Puerto-Belda, J. J. Ruz, C. Millá, A. Cano, M. L. Yubero, S. García, P. M. Kosaka, M. Calleja, and J. Tamayo, Measuring vibrational modes in living human cells. PRX Life 2024, 2, 013003.
- P. Jandačka, P. Alexa, J. Pištora, and J. Trojková, Hypothetical superparamagnetic magnetometer in a pigeon’s upper beak probably does not work. Eur. Phys. J. E 2013, 36, 40. [CrossRef]
- F. Curdt, K. Haase, L. Ziegenbalg, H. Greb, D. Heyers, and M. Winklhofer, Prussian blue technique is prone to yield false negative results in magnetoreception research. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8803. [CrossRef]
- Z. Guo, S. Xu, X. Chen, C. Wang, P. Yang, S. Qin, C. Zhao, F. Fei, X. Zhao, P.-H. Tan, J. Wang, and C. Xie, Modulation of MagR magnetic properties via iron–sulfur cluster binding. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23941.
- T. Tong, Y. Zhou, F. Fei, X. Zhou, Z. Guo, S. Wang, J. Zhang, P. Zhang, T. Cai, G. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, and C. Xie, The rational design of iron-sulfur cluster binding site for prolonged stability in magnetoreceptor MagR. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1051943. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhou, T. Tong, M. Wei, P. Zhang, F. Fei, X. Zhou, Z. Guo, J. Zhang, H. Xu, L. Zhang, S. Wang, J. Wang, T. Cai, X. Zhang, and C. Xie, Towards magnetism in pigeon MagR: iron- and iron-sulfur binding work indispensably and synergistically. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 142.
- J. Zhang, Y. Chang, P. Zhang, Y. Zhang, M. Wei, C. Han, S. Wang, H.-M. Lu, T. Cai, C. Xie, On the evolutionary trail of MagRs. Zool. Res. 2024, 45, 821.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




