Submitted:
24 September 2024
Posted:
25 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
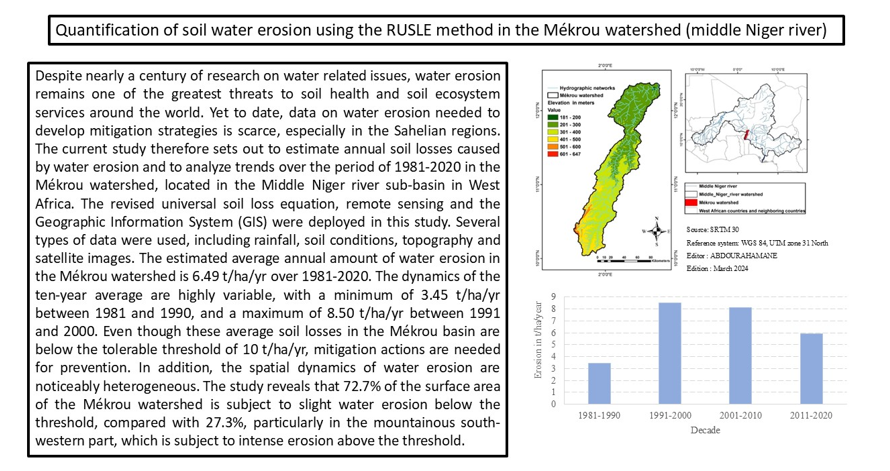
2. Presentation of the Mékrou River Watershed
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data and Tools Used
3.2. Data Analysis Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Main Morphometric and Soil Characteristics
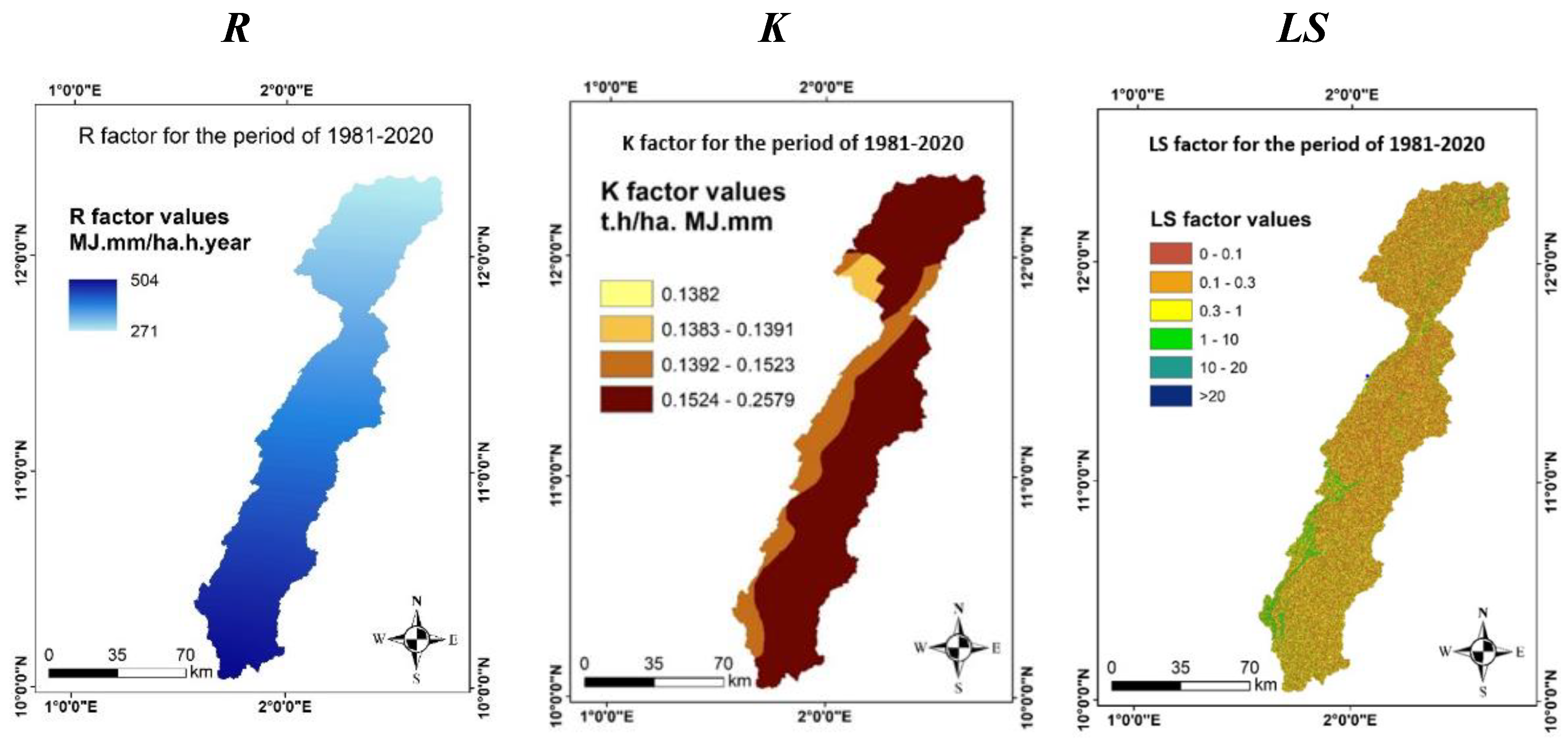
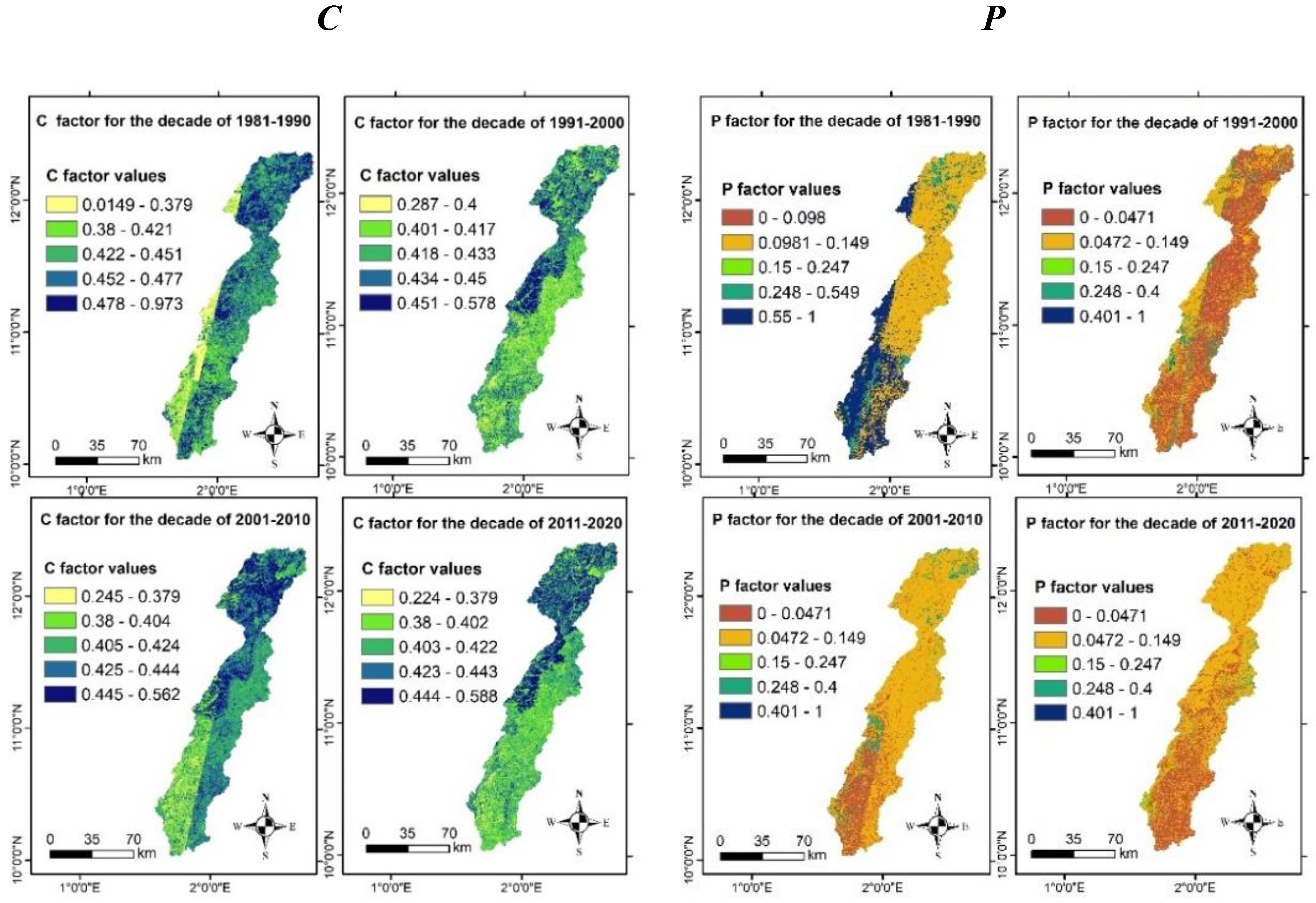
4.2. Estimates of Water Erosion Components in the Watershed
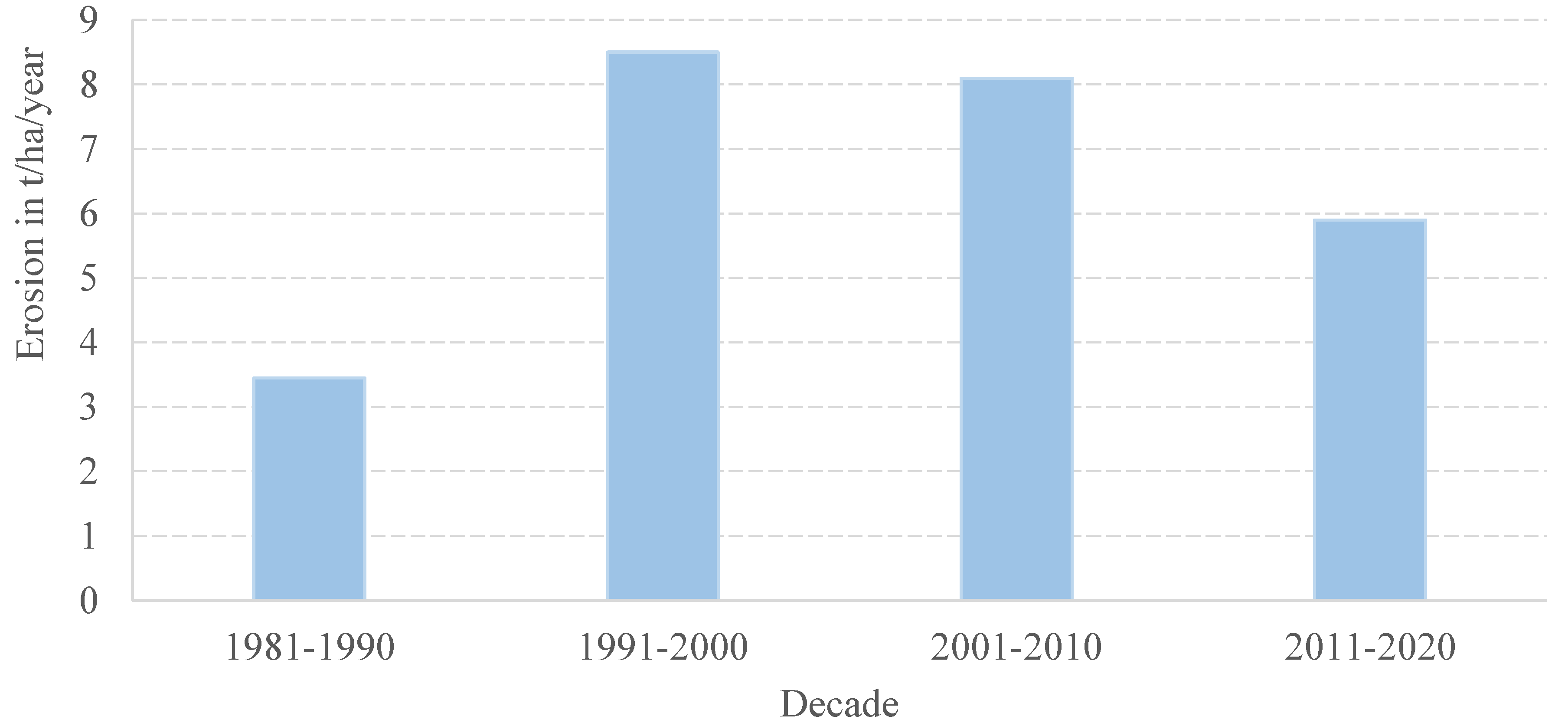
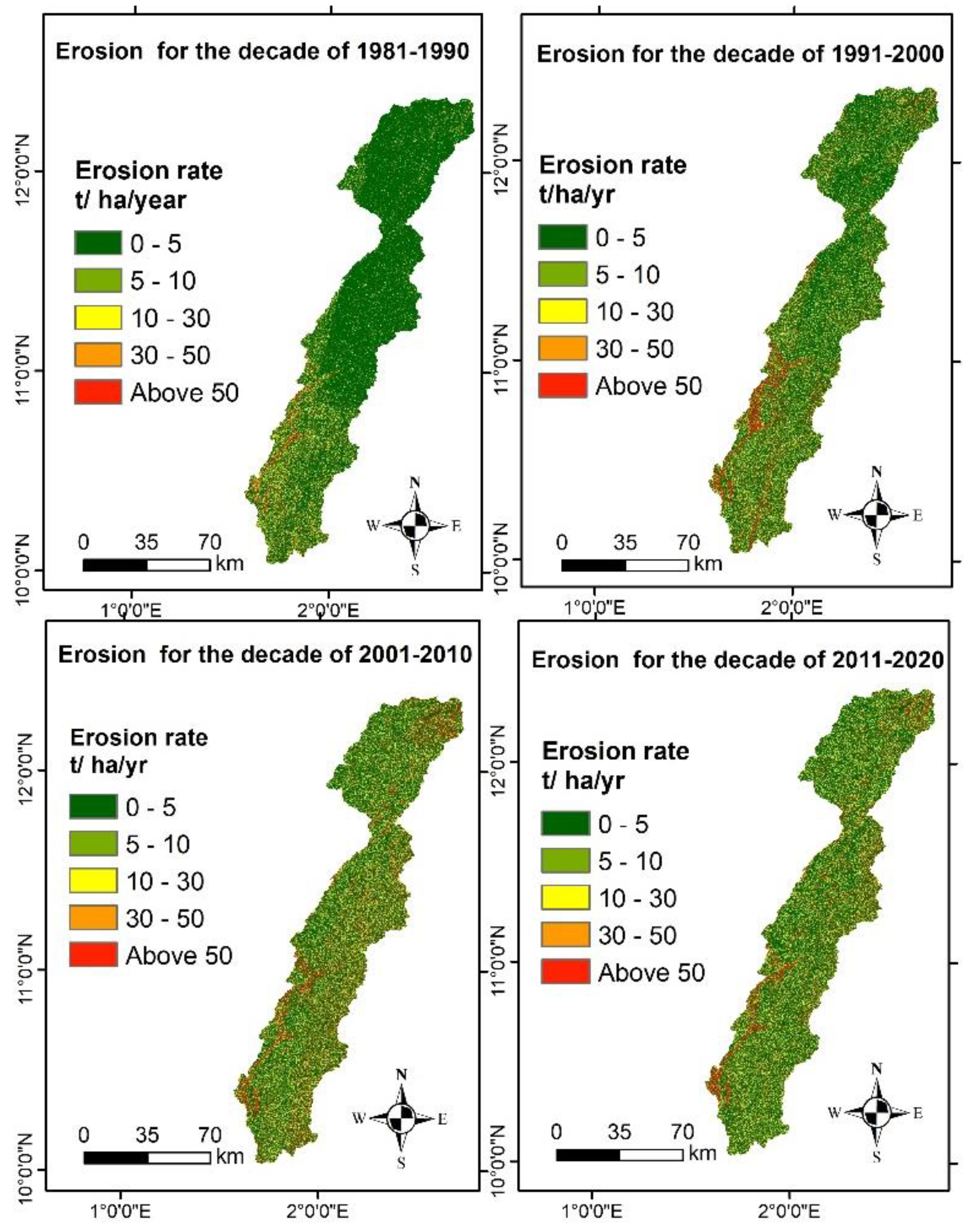
4.3. Estimated Soil Losses Due to Water Erosion in the Mékrou Watershed
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- B.P. Ganasri and H. Ramesh, “Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS - A case study of Nethravathi Basin,” Geosci. Front., vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 953–961, 2016. [CrossRef]
- D.J.A.M. Ostovari, D.S. Ghorbani, H.A. Bashrami, M. Naderi, “Soil loss prediction by an integrated system using RUSLE, GIS and remote sensing in semi-arid regionle,” Geoderma Reg., vol. 1111, 2017, [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2017.06.003. [CrossRef]
- M. Schauer, “THE E CONOMICS OF The Economics of Land Degradation in Africa Benefits of Action Outweigh the Costs A complementary report to the ELD Initiative,” p. 151 pages, 2015, [Online]. Available: isbn: 978?92-808?6064-1%5CnThis ELD report was published with the support of the partner organisations of the ELD Initiative and Deutsche Gesellschaft fu? r Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH on behalf of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Coop.
- M.C. Singh, K. Sur, N. Al-Ansari, P.K. Arya, V. K. Verma, and A. Malik, “GIS integrated RUSLE model-based soil loss estimation and watershed prioritization for land and water conservation aspects,” Front. Environ. Sci., vol. 11, no. March, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Balasubramani, M. Veena, K. Kumaraswamy, and V. Saravanabavan, “Estimation of soil erosion in a semi-arid watershed of Tamil Nadu (India) using revised universal soil loss equation (rusle) model through GIS,” Model. Earth Syst. Environ., vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 1–17, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Butt, A. Waqas, and R. Mahmood, “The Combined Effect of Vegetation and Soil Erosion in the Water Resource Management,” Water Resour. Manag., vol. 24, no. 13, pp. 3701–3714, 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. Kayet, K. Pathak, A. Chakrabarty, and S. Sahoo, “Evaluation of soil loss estimation using the RUSLE model and SCS-CN method in hillslope mining areas,” Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 31–42, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Van der Oost, J. Beyer, and N. P. E. Vermeulen, “Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review,” Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 57–149, 2003. [CrossRef]
- J. Y. Marchal, “Vingt ans de lutte antiérosive au nord du Burkina Faso,” Cah. d’ORSTOM, série pédologie, vol. XXII, no. 2, pp. 173–180, 1986.
- E. Roose, “Gestion conservatoire des eaux et de la fertilité des sols dans les paysages soudano-sahéliens d’Afrique occidentale : Stratégies anciennes et nouvelles,” Séminaire "Gestion des eaux, des sols des plantes, p. 17, 1987.
- P. Borrelli, D.A. Robinson, L. R. Fleischer, E. Lugato, C. Ballabio, C. Alewell, K. Meusburger, S. Modugno, B Schütt, V. Ferro, V. Bagarello, K.V. Oost, L. Montanarella , P. Panagos, “An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion,” Nat. Commun., vol. 8, no. 1, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Salifou, G. Abdelali, A.T. Amadou, “Water erosion in south-western Niger: impacts of natural and anthropogenic factors on soil losses,” Géomorphologie Reli. Process. Environ., vol. 28-, 2022, [Online]. Available:. https://doi.org/10.4000/geomorphologie.16744. [CrossRef]
- L. Descroix, I. Mamadou, M. Malam-Abdou, A. Bachir, I. B. Moussa, L. B. Eric, S. Y. Kadidiatou, “État des lieux et proposition de restauration des sols sur le Bassin versant de Tondi Kiboro (Niger),” Lutte antiérosive, no. September 2016, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Mamadou, “ La dynamique accélérée des Koris de la région de Niamey et ses conséquences sur l’ensablement du fleuve Niger,” 2012.
- GWP, “Note politique Projet transfrontalier de la Mékrou gestion concertée du cours d ’ eau de la Mékrou pour s outenir une croissance économique verte et réduire la pauvreté au Bénin,” 2015.
- JRC, “Projet Mékrou,” 2017.
- K.G. Renard, G.R. Foster, G.A Weesies, D McCool, D.C. Yoder, Predicting soil erosion by water : A guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). US Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No.703USDA, USDA, Washington DC. 1997.
- Y. Farhan and S. Nawaiseh, “Spatial assessment of soil erosion risk using RUSLE and GIS techniques,” Environ. Earth Sci., vol. 74, no. 6, pp. 4649–4669, 2015. [CrossRef]
- E. Roose, Vingt Années En Petites Parcelles Expkri Esures. 1977.
- W.H. Wischmeier and D.D. Smith, “Predicting rainfall erosion losses,” Agric. Handb. no. 537, no. 537, pp. 285–291, 1978.
- T. Gashaw, T. Tulu, and M. Argaw, “Erosion risk assessment for prioritization of conservation measures in Geleda watershed, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia,” Environ. Syst. Res., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–15, 2018. [CrossRef]
- 22. R. Benavidez, J. Bethanna, M. Deborah, and N. Kevin, “A-review-of-the-Revised-Universal-Soil-Loss-Equation-RUSLE-With-a-view-to-increasing-its-global-applicability-and-improving-soil-loss-estimates Hydrology-and-Earth-System-SciencesOpen-Access,” Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., no. 1995, pp. 6059–6086, 2018.
- J. R. Kiniry, D. J. Major, R. C. Izaurralde, J. R. Williams, P. W. Gassman, M. Morrison, R. Z. Bergentine, R. P. Zentner, “EPIC model parameters for cereal, oilseed, and forage crops in the northern Great Plains region,” Can. J. Plant Sci., vol. 75, no. 3, pp. 679–688, 1995. [CrossRef]
- T.G. Pham, J. Degener, and M. Kappas, “Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam,” Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 99–110, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A.Y. Yesuph and A.B. Dagnew, “Soil erosion mapping and severity analysis based on RUSLE model and local perception in the Beshillo Catchment of the Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia,” Environ. Syst. Res., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–22, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Moore and J. P. Wilson, “Length-slope factors for the revised universal soil loss equation: simplified method of estimation,” J. Soil Water Conserv., vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 423–428, 1992.
- V. L. Durigon, D. F. Carvalho, M. A. H. Antunes, P. T. S. Oliveira, and M. M. Fernandes, “NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed,” Int. J. Remote Sens., vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 441–453, 2014. [CrossRef]
- C.B. Colman., K.M.P. Garcia, R.B. Pereira, E.A. Shinma, F.E. Lima, A.O Gomes, P. T. S. Oliveira, “Different approaches to estimate the sediment yield in a tropical watershed,” Rev. Bras. Recur. Hidricos, vol. 23, no. October, 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Tian, Z. Zhu, Q. Yue, H. Yi, Z. Zhang, H. Fanghua, G. Wenzhao, C. Lin,.
- 30. “Soil erosion assessment by RUSLE with improved P factor and its validation: Case study on mountainous and hilly areas of Hubei Province, China,” Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res., vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 433–444, 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Afouda, Water and crops in central and southern Benin: study of the variability of water balances in their relationship with the rural environment of the African savannah, New regime. 1990.
- P. Komla, “RENVERSEMENT DE LA TENDANCE A LA DEGRADATION DES TERRES ET DES EAUX DANS LE BASSIN BENINOIS DU FLEUVE NIGER,” 2001.
- H. Diawara, T. Berthe, S. Bengaly, E.V. Gaidukova, K. Sangare, S. Diarra, “Impact of climate change on the water balance of the Sankarani river basin in West Africa” Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. Vol-6, Issue-6; Nov-Dec, vol. 1878, no. November, pp. 119–126, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Masson, “Soil Erosion by Water in a Mediterranean Climate. Experimental Determination of Eroded Volumes at Field Level.,” Houille Blanche, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 673–678, 1972. [CrossRef]
- K. Khemiri and S. Jebari, “Évaluation de l’érosion hydrique dans des bassins versants de la zone semi-aride tunisienne avec les modèles RUSLE et MUSLE couplés à un Système d’information géographique,” Cah. Agric., vol. 30, p. 7, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Yameogo, Y.S.C. Some, A. Sirima, and D.E.C. DA, “Occupation des terres et érosion des sols dans le bassin versant supérieur de la Sissili, Burkina Faso,” Afrique Sci., vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 43–56, 2020.
- T.M. Akplo, F. K. Alladassi, P. Houngnandan, A. Saidou, M. Benmansour, and H.A. Azontonde, “Mapping the risk of soil erosion using RUSLE, GIS and remote sensing: A case study of Zou watershed in central Benin,” J. Agri. Sci, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 281–290, 2020, [Online]. Available: www.techagro.org.
- B.U. Dike, O.P. Alakwem, and H.U. Nwoke, “Potential Soil Loss Rates in Urualla , Nigeria using Rusle Potential Soil Loss Rates in Urualla Nigeria using Rusle,” vol. 18, no. January, pp. 2–8, 2018.
- Adediji, A.M. Tukur, and K.A. Adepoju, “Assessment of Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in Katsina Area, Katsina State of Nigeria using Remote Sensing (RS) and Geographic Information System (GIS),” Off. Peer Rev. J. Babol Noshirvani Univ. Technol. BUT, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 255–264, 2010.
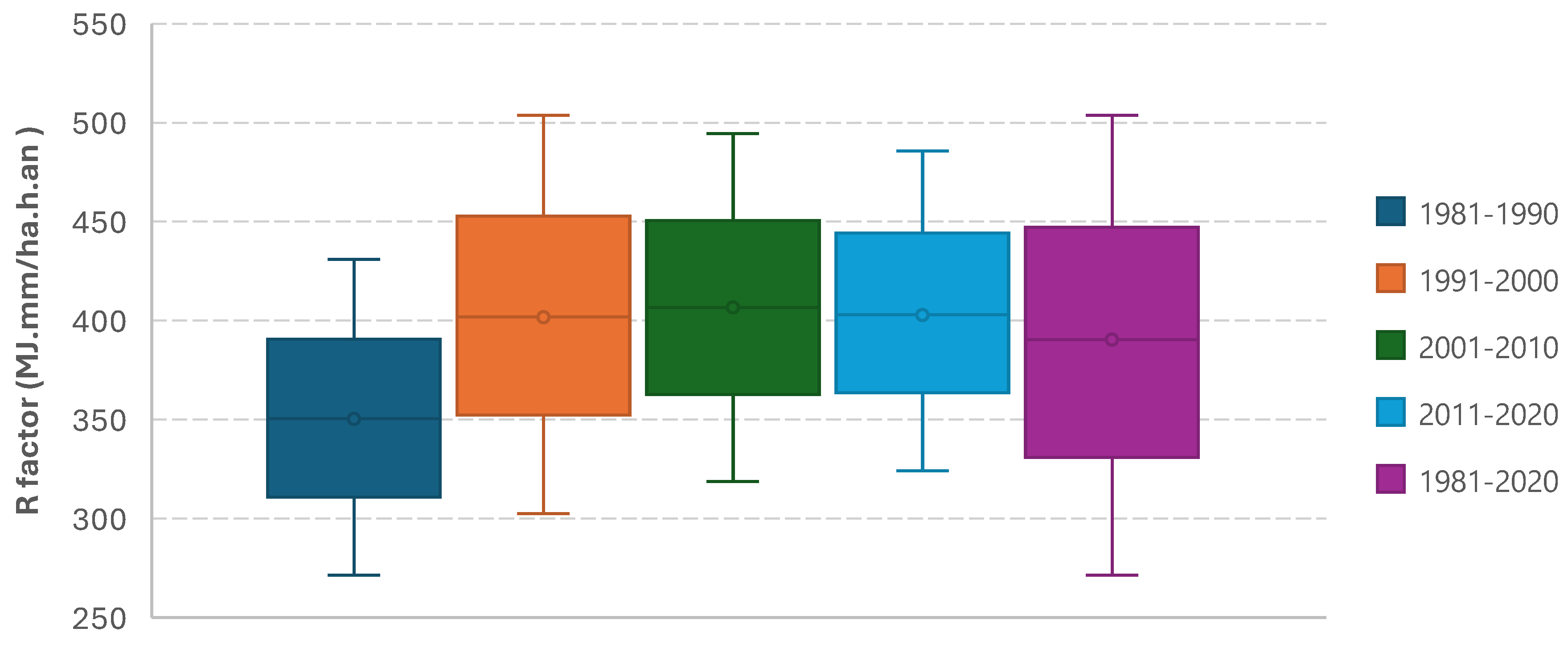
| Soil type | FAO code | Proportions in soil composition (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ms | msilt | mc | orgC | ||
| Eutric Gleysols | RE | 68.3 | 15.1 | 16.6 | 0.50 |
| Ferric Luvisols | LF | 74.6 | 09.6 | 15.8 | 0.26 |
| LITHOSOLS | I | 58.9 | 16.2 | 24.9 | 0.97 |
| Gleyic Luvisols | LG | 59.9 | 13.4 | 26.7 | 0.73 |
| Land use | Slope (%) | |||||||
| 0-5 | 5-10 | 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-50 | 50-100 | 0-100 | ||
| P factor | Agricultural land | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.70 | |
| Rangeland | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.75 | ||
| Bare soil | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1.00 | ||
| Forest | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.60 | ||
| Water | 0.00 | |||||||
| Urban land | 0.05 | |||||||
| Soil types | FAO code | K factor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| value in t.ha.h/ha.MJ.mm | Area in km² (% rate) | ||
| Ferric Luvisols | LF | 0.2579 | 6,655.2 (63.9) |
| Eutric Gleysols | RE | 0.1523 | 1,529.7 (14.7) |
| LITHOSOLS | I | 0.1394 | 1,921.3 (18.5) |
| Gleyic Luvisols | LG | 0.1382 | 298.1 (02.9) |
| Class (t/ha/yr) | wa (1981-2020) (km²) |
Occupancy rate of the watershed (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981-2020 | 1981-1990 | 1991-2000 | 2001-2010 | 2011-2020 | ||
| C1 : Very low (0-5) | 6,712.125 | 63.9 | 78.7 | 62.7 | 56.1 | 58.2 |
| C2 : Low (5-10) | 918.750 | 8.8 | 07.0 | 10.3 | 08.3 | 09.4 |
| C1 : Moderate (10-30) | 1,567.125 | 14.9 | 09.1 | 14.7 | 18.1 | 17.8 |
| C1 : High (30-50) | 525.000 | 5.0 | 02.4 | 04.5 | 07.0 | 06.1 |
| C1 : Very high (> 50) | 777.000 | 7.4 | 02.8 | 07.8 | 10.5 | 08.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




