Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MSW Management in Ghana
3.1.1. Population and Waste Generation
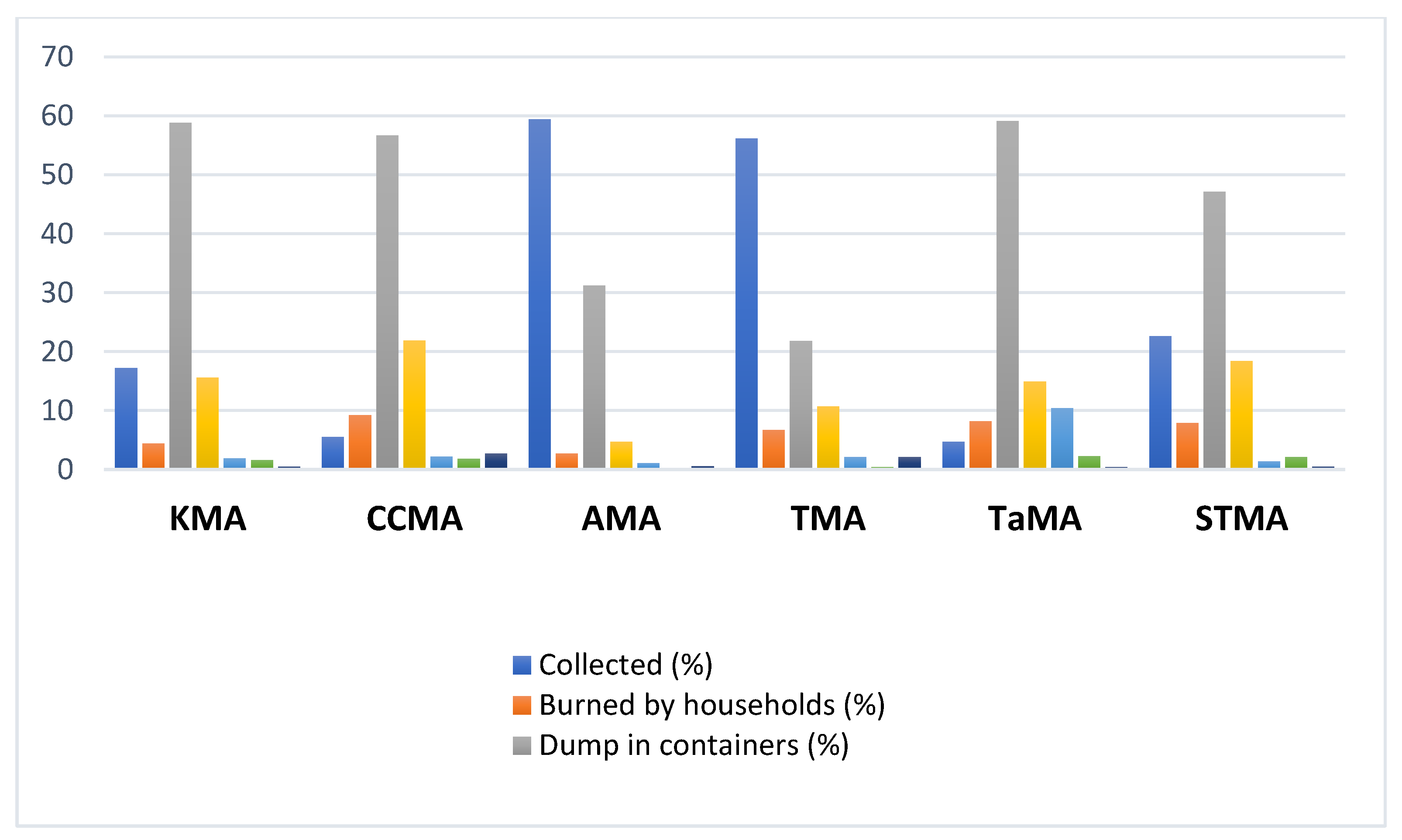
3.2. MSW Management in Ghana’s Metropolitan Assemblies
3.1.3. Waste Typology
3.2. Proximate Analysis of MSW from Ghana
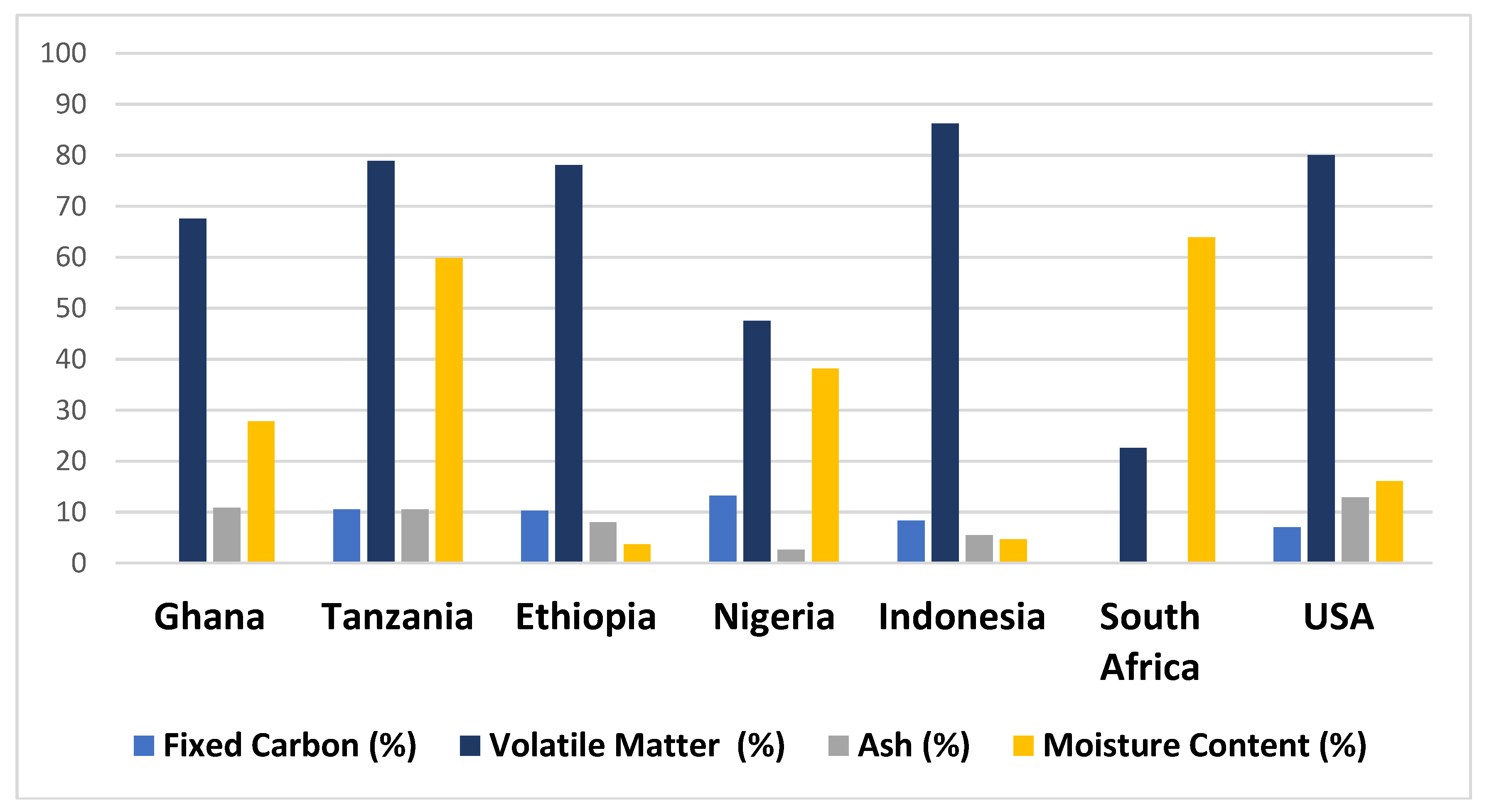
3.2.1. Proximate Composition of MSW- Ghana vs Other Countries
3.3. Ultimate Analysis of MSW from Ghana
| Region | H (%) | N (%) | C (%) | S (%) | O (%) | C/N ratio | Reference |
| Ashanti Ashanti Ashanti |
6.01 | 1.49 | 41.90 | 0.10 | 50.5 | 28.12 | [13] |
| 5.53 | 1.70 | 45.20 | 0.55 | 47.02 | 26.59 | [76] | |
| 24.8 | 1.4 | 43 | 0.4 | - | 30.71 | [46] | |
| Greater Accra | 5.62 | 1.20 | 38.66 | 0.14 | 26.17 | 32.22 | [90] |
| Greater Accra | 6.1 | 1.5 | 36.4 | 0.1 | 29.6 | 24.27 | [92] |
| Greater Accra & Ashanti | 9.33 | 0.62 | 63.7 | 0.11 | - | 102.7 | [79] |
3.3.1. Ultimate Analysis of MSW Ghana vs Other Countries
| Country | H (%) | N (%) | C (%) | S (%) | O (%) | C/N ratio | Reference |
| Ghana | 6.01 | 1.49 | 41.9 | 0.1 | 50.5 | 28.1 | [13] |
| South Africa | 6 | 2 | 45.32 | 0 | - | 22.7 | [86] |
| Nigeria | 6.98 | 1.56 | 50.09 | 1.23 | 30.15 | 30.1 | [91] |
| Tanzania | 5.29 | 2.36 | 54.8 | 0.3 | 34.6 | 23.2 | [83] |
| Ethiopia | 5.40 | 0.07 | 43.17 | 0.007 | 51.26 | 616.7 | [84] |
3.4. Calorific Value / Heating Value of MSW from Ghanaian Cities
| Region | Waste type | Calorific Value (MJ/kg) | Reference |
| Ashanti | Mixed | 15.7 | [46] |
| Ashanti | Mixed | 14.79 | [76] |
| Ashanti & Greater Accra | RDF | 30.24 - 31.59 | [79] |
| Greater Accra | Mixed | 16.84 | [95] |
| Eastern | Mixed | 14.96 - 21.46 | [78] |
3.4.1. Calorific Value of Ghana and Other Countries
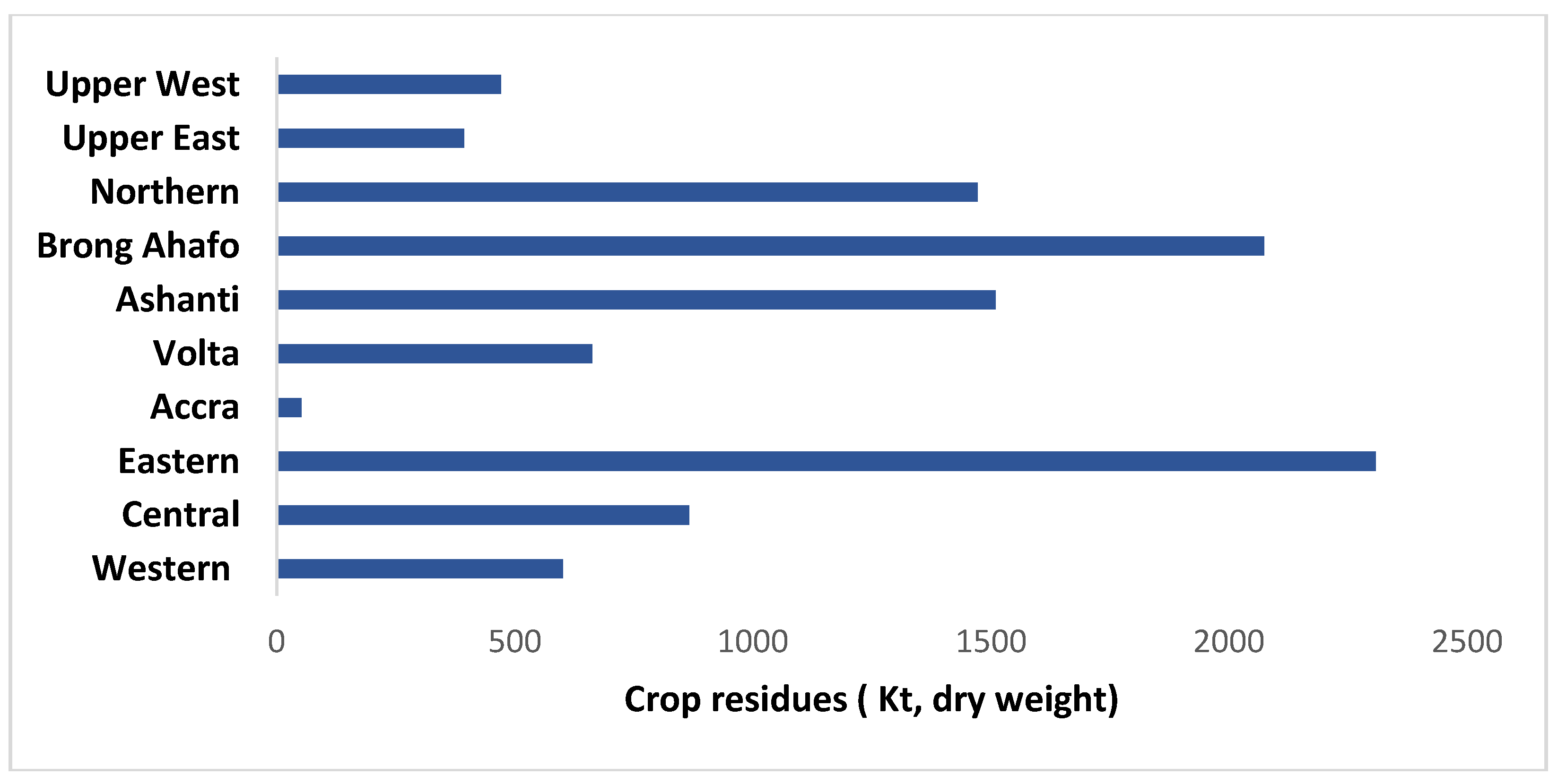
3.5. Bioenergy Potential of MSW in Ghana
| City | Food waste quantity (Kt) | Biogas (mm3) | Biomethane (mm3) | Electricity (GWh) | Diesel displaced (ml) |
| Accra | 245.32 | 190 | 143.83 | 59.34 | 17.92 |
| Kumasi | 339.35 | 262.83 | 198.96 | 82.09 | 24.79 |
| Tamale | 28.75 | 22.27 | 16.86 | 6.95 | 2.10 |
| Secondi -Takoradi | 89.94 | 69.66 | 52.73 | 21.76 | 6.57 |
| Total | 703.36 | 452.83 | 412.38 | 170.14 | 51.38 |
3.6. Implications to Ghana’s Energy Demands
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- X. Li, F. Lü, N. Liao, H. Zhang, N. Yang, and P. He, “Greenhouse gas emissions of municipal solid waste in Shanghai over the past 30 years: Dependent on the dynamic waste characteristics and treatment technologies,” Resour. Conserv. Recycl., vol. 201, 2024. [CrossRef]
- E. Kosior and I. Crescenzi, “Solutions to the plastic waste problem on land and in the oceans,” Plast. Waste Recycl. Environ. Impact, Soc. Issues, Prev. Solut., pp. 415–446, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Fletcher et al., “Policy Options to Eliminate Additional Marine Plastic Litter by 2050 Under the G20 Osaka Blue Ocean Vision,” An Int. Resour. Panel Think Piece, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Kaza, L. C. Yao, P. Bhada-Tata, and F. Van Woerden, “What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050,” What a Waste 2.0 A Glob. Snapshot Solid Waste Manag. to 2050, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. D. Simkin, K. C. Seto, R. I. McDonald, and W. Jetz, “Biodiversity impacts and conservation implications of urban land expansion projected to 2050,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 119, no. 12, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A.H. Khan et al., “Municipal solid waste generation and the current state of waste-to-energy potential: State of art review,” Energy Convers. Manag., vol. 267, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Murwendah, Inayati, H. Rosdiana, and L. Filberto Sardjono, “The challenges of providing safe sanitation as a public good in DKI Jakarta,” E3S Web Conf., vol. 211, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. V. Vassilev, D. Baxter, L. K. Andersen, and C. G. Vassileva, “An overview of the chemical composition of biomass,” Fuel, vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 913–933, 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Wahba and F. Ghesquiere, “Bridging the Gap in Solid Waste Management: governance requirements for results,” Bridg. Gap Solid Waste Manag., 2021, [Online]. Available: http://elibrary.worldbank.org/doi/book/10.1596/35703.
- Delmon, Essentials of an Effective Public-Private Partnerships Initiative:an essential guide for policy makers. Cambridge university press., 2017.
- M. Oteng-Ababio, “The quest for efficient waste management architecture in Ghana,” F. Actions Sci. Rep., vol. 2020, no. Special Issue 22, pp. 24–29, 2020.
- E. Volsuuri, E. Owusu-Sekyere, and A. Z. Imoro, “Rethinking solid waste governance in Ghana,” Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 12, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. Amponsem et al., “Electricity generation from biogas as resource recovery potential from solid waste composition in a mixed-income municipality,” Clean. Waste Syst., vol. 4, no. December 2022, p. 100067, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Miezah et al., “Municipal Solid Waste Management in a Low-Income Economy Through Biogas and Bioethanol Production,” Waste and Biomass Valorization, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 115–127, 2017. [CrossRef]
- B. Amponsem et al., “Electricity generation from biogas as resource recovery potential from solid waste composition in a mixed-income municipality,” Clean. Waste Syst., vol. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Lehmann, “Conceptualizing the Urban Nexus Framework for a Circular Economy: Linking Energy, Water, Food, and Waste (EWFW) in Southeast-Asian cities,” Urban Energy Transit. Renew. Strateg. Cities Reg., pp. 371–398, 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Anokye et al., “A systematic review of the impacts of open burning and open dumping of waste in Ghana : A way forward for sustainable waste management,” Clean. Waste Syst., vol. 8, no. June, p. 100152, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. Takase, M. Aboah, and R. Kipkoech, “A review on renewable energy potentials and energy usage statistics in Ghana,” Fuel Commun., vol. 11, no. April, p. 100065, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Abalo, P. Peprah, J. Nyonyo, R. Ampomah-sarpong, and W. Agyemang-duah, “A Review of the Triple Gains of Waste and the Way Forward for Ghana,” vol. 2018, 2018.
- C. Gangwar, A. Chauhan, A. Kumar, A. Singh, A. Tripathi, and R. Choudhari, “Assessment of air pollution caused by illegal e-waste burning to evaluate the human health risk,” Environ. Int., 2019.
- V. I. Seshie, K. Obiri-Danso, and K. Miezah, “Municipal Solid Waste Characterisation and Quantification as a measure towards Effective Waste Management in the Takoradi Sub-Metro, Ghana,” Ghana Min. J., vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 86–98, 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. D. Azasi, F. Offei, F. Kemausuor, and L. Akpalu, “Bioenergy from crop residues: A regional analysis for heat and electricity applications in Ghana,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 140, no. August, p. 105640, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Miezah, K. Obiri-danso, Z. Kádár, B. Fei-baffoe, and M. Y. Mensah, “Municipal solid waste characterization and quantification as a measure towards effective waste management in Ghana,” Waste Manag., vol. 46, pp. 15–27, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Y. W. Lee and J. Chung, “Bioproduction of hydrogen from food waste by pilot-scale combined hydrogen/methane fermentation,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, vol. 35, no. 21, pp. 11746–11755, 2010. [CrossRef]
- C. C. Chong, Y. W. Cheng, K. H. Ng, D. V. N. Vo, M. K. Lam, and J. W. Lim, “Bio-hydrogen production from steam reforming of liquid biomass wastes and biomass-derived oxygenates: A review,” Fuel, vol. 311, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Kumar and S. R. Samadder, “A review on technological options of waste to energy for effective management of municipal solid waste,” Waste Manag., vol. 69, pp. 407–422, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. P. Singh and A. Sarkar, “Waste management: Challenges, threats and opportunities,” Waste Manag. Challenges, Threat. Oppor., pp. 1–271, 2015.
- B. Aboagye, S. Gyamfi, E. A. Ofosu, and S. Djordjevic, “Status of renewable energy resources for electricity supply in Ghana,” Sci. African, vol. 11, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Takase, M. Aboah, and R. Kipkoech, “A review on renewable energy potentials and energy usage statistics in Ghana,” Fuel Commun., vol. 11, no. March, p. 100065, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. K. Debrah and D. G. Vidal, “Innovative Use of Plastic for a Clean and Sustainable Environmental Management : Learning Cases from,” pp. 1–11, 2021.
- K. Miezah, K. Obiri-Danso, Z. Kádár, B. Fei-Baffoe, and M. Y. Mensah, “Municipal solid waste characterization and quantification as a measure towards effective waste management in Ghana,” Waste Manag., vol. 46, pp. 15–27, 2015. [CrossRef]
- P. A. Seglah et al., “Utilization of food waste for hydrogen-based power generation: Evidence from four cities in Ghana,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 3, p. e14373, 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Asamoah-Okyere, “Characterization and composting of solid waste generated in the Aburi Township,” 2011.
- P. A. Bowan and M. T. Tierobaar, “Characteristics And Management Of Solid Waste In Ghanaian Markets-A Study Of WA Municipality,” Civ. Environ. Res., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 114–119, 2014.
- Ghana Statistical Service, “Municipal solid waste characterization and quantification as a measure towards effective waste management in Ghana,” 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.statsghana.gov.gh/.
- N. Konadu-Agyeman, “Accra fishermen now landing ‘big catches’ of plastics.” Accessed: May 28, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.graphic.com.gh/features/features/accra-fishermen-now-landing-big-catches-of-plastics.html.
- V. I. Seshie, K. Miezah, and O.- Danso, “Municipal Solid Waste Characterisation and Quantification as a measure towards Effective Waste Management in the Takoradi,” no. 2, 2020.
- Energy Commission, “National Energy Statistics 2009-2018,” 2019.
- G. S. Service, “Ghana 2021 Population and Housng Census,” 2021.
- S. K. Annim, “Ghana 2021 Population and Housing Census,” Rev. Bras. Linguística Apl., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1689–1699, 2021.
- P. Gyimah, S. Mariwah, K. B. Antwi, and K. Ansah-Mensah, “Households’ solid waste separation practices in the Cape Coast Metropolitan area,” GeoJournal, vol. 86, no. 2, pp. 567–583, 2021.
- E. Yeboah-Assiamah, K. Asamoah, and T. A. Kyeremeh, “Decades of public-private partnership in solid waste management: a literature analysis of key lessons drawn from Ghana and India. Management of Environmental Quality,” An Int. J., vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 78-93., 2017.
- Plastic Foundation Revolution, “End-of-phase report,” 2013. [Online]. Available: https://www.revocean.org/wp content/uploads/2020/10/PRF-End-of-Phase-Report.pdf.
- Japan International Corporation Agency, “The Study on the Comprehensive Urban Development Plan for Greater Kumasi- Supporting Document,” 2013, [Online]. Available: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/1000014018_01.pdf.
- N. B. Douti, S. K. Abanyie, and S. Ampofo, “Solid waste management challenges in urban areas of Ghana: A case study of Bawku Municipality,” Int. J. Geosci., vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 494–513, 2017.
- G. Addae et al., “Market waste composition analysis and resource recovery potential in Kumasi , Ghana,” J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., vol. 71, no. 12, pp. 1529–1544, 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. L. Tihin, K. H. Mo, C. C. Onn, H. C. Ong, Y. H. Taufiq-Yap, and H. V. Lee, “Overview of municipal solid wastes-derived refuse-derived fuels for cement co-processing,” Alexandria Eng. J., vol. 84, no. October, pp. 153–174, 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Safo-adu and N. Owusu-adzorah, “Solid waste characterisation and recycling potential_ A study in secondary schools in Kumasi Metropolis, Ghana,” Clean. Waste Syst., vol. 4, no. September 2022, p. 100065, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Singh, Rajeev, P. Singh, A. S. F. Araujo, M. Hakimi Ibrahim, and O. Sulaiman, “Management of urban solid waste: Vermicomposting a sustainable option,” Resour. Conserv. Recycl., vol. 55, no. 7, pp. 719–729, 2011. [CrossRef]
- V. D. Azasi, F. Offei, F. Kemausuor, and L. Akpalu, “Bioenergy from crop residues: A regional analysis for heat and electricity applications in Ghana,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 140, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. I. Abdel-shafy and M. S. M. Mansour, “Solid waste issue : Sources , composition , disposal , recycling , and valorization,” Egypt. J. Pet., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 1275–1290, 2018. [CrossRef]
- O. A. Adeleke, S. A. Akinlabi, T. C. Jen, and I. Dunmade, “An overview of factors affecting the rate of generation and Physical Composition of Municipal Solid Waste,”.
- V. D. Azasi, F. Offei, F. Kemausuor, and L. Akpalu, “Bioenergy from crop residues: A regional analysis for heat and electricity applications in Ghana,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 140, no. July 2019, p. 105640, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mensah, “Waste management practices of small hotels in Accra: An application of the waste management hierarchy model,” J. Glob. Bus. Insights, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 33–46, 2020.
- F. B. Osei and A. Stein, “Spatio-temporal analysis of small-area intestinal parasites infections in Ghana,” Sci. Rep., vol. 7, no. 1, p. 12217, 2017.
- D. S. Madara, S. S. Namango, and C. Wetaka, “Consumer-perception on polyethylene-shopping-bags,” J. Environ. Earth Sci., vol. 11, pp. 12–36, 6AD.
- Lambrecht and S. Asare, “The complexity of local tenure systems: A smallholders’ perspective on tenure in Ghana,” Land use policy, vol. 58, pp. 251–263, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Durogbitan, “Evaluation of impact of solid wastes and its potential as a source of renewable energy: A case study from Minna and its environs, Nigeria,” Acta Sci Agric, vol. 3, pp. 145–152, 2019.
- A. Amponsem et al., “Electricity generation from biogas as resource recovery potential from solid waste composition in a mixed-income municipality,” Clean. Waste Syst., vol. 4, no. September 2022, p. 100067, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Darmey, J., Ahiekpor, J. C., Achaw, O. W., Narra, S., & Mensah, “Bioenergy: Physicochemical Properties and Energy Potential of Selected Wastes in Kumasi, Ghana,” in In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Advances in “Chemical, Biological and Environmental Sciences,” 2023.
- S. Sukarni, “Exploring the potential of municipal solid waste (MSW) as solid fuel for energy generation: Case study in the Malang City, Indonesia,” in In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1778, No. 1), AIP Publishing, 2016.
- P. R. Bhat, H. N. Chanakya, and N. H. Ravindranath, “Biomass conversion technologies: a case for decentralized energy plantation.,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 355–369, 2001.
- IPCC, “IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories.” Accessed: Sep. 13, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/.
- S. Sukarni, “Exploring the Potential of Municipal Solid Waste ( MSW ) as,” 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. Liu, Y. Liao, S. Guo, X. Ma, C. Zeng, and J. Wu, “No Thermal behavior and kinetics of municipal solid waste during pyrolysis and combustion process,” Appl. Therm. Eng., vol. 98, pp. 400–408, 2016.
- P. Basu, Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction;: Practical Design and Theory. Academic Press, 2013.
- T. Chae, J. S., Kim, S. W., & In Ohm, “Combustion characteristics of solid refuse fuels from different waste sources,” J. Renew. Mater., vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 789–799, 2020.
- S. Mata-Alvarez, J., Dosta, J., Romero-Güiza, M. S., Fonoll, X., Peces, M., & Astals, “A critical review on anaerobic co-digestion achievements between 2010 and 2013,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 32, pp. 412–427, 2014.
- N. B. D. Thi, G. Kumar, and C. Y. Lin, “An overview of food waste management in developing countries: current status and future perspective,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 157, pp. 220–229, 2016.
- L. Chen, M. de Haro Marti, A. Moore, and C. Falen, “The composting process.,” Dairy Manure Compost Prod. Use Idahole, vol. 2, pp. 513–532, 2011.
- M. S. Ayilara, O. S. Olanrewaju, O. O. Babalola, and O. Odeyemi, “Waste Management through Composting : Challenges and Potentials Waste Management through Composting : Challenges”.
- M. S. Korai, R. B. Mahar, and M. A. Uqaili, “The feasibility of municipal solid waste for energy generation and its existing management practices in Pakistan,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 72, pp. 338–353, 2017.
- Y. B. Yang, V. N. Sharifi, and J. Swithenbank, “Numerical simulation of municipal solid waste incineration in a moving-grate furnace and the effect of waste moisture content,” Prog. Comput. Fluid Dyn. an Int. J., vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 261–273, 2007.
- N. B. Klinghoffer and M. J. Castaldi, “Waste to Energy Conversion Technology,” Waste to Energy Convers. Technol., pp. 1–234, 2013. [CrossRef]
- D. Carboo and J. N. Fobil, “Physico-chemical analysis of municipal solid waste (MSW) in the Accra metropolis,” West African J. Appl. Ecol., vol. 1, 7AD.
- Darmey, J. C. Ahiekpor, O. Achaw, S. Narra, and I. Mensah, “Bioenergy : Physicochemical Properties and Energy Potential of Selected Wastes in Kumasi- Ghana,” pp. 4–8, 2023.
- P. H. Brunner, “Waste to energy – key element for sustainable waste management,” vol. 37, no. March, pp. 3–12, 2015.
- R. Kuleape, S. J. Cobbina, S. B. Dampare, A. B. Duwiejuah, E. E. Amoako, and W. Asare, “Assessment of the energy recovery potentials of solid waste generated in Akosombo,” African J. Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 297–305, 2014.
- Sarquah et al., “Characterization of Municipal Solid Waste and Assessment of Its Potential for Refuse- Derived Fuel ( RDF) Its Potential for Refuse-Derived Fuel ( RDF ) Valorization”.
- S. A. Anaglate, S. Rahmaputro, and C. Ruiz, “Comparison between Landfill Gas and Waste Incineration for Power Generation in Accra, Ghana,” vol. 2, no. 1998.
- G. Situmorang, Y. A., Zhao, Z., Yoshida, A., Abudula, A., & Guan, “Small-scale biomass gasification systems for power generation (< 200 kW class):A review,” Renew. Sustain. energy Rev., vol. 177, p. 109486, 2020.
- J. Tumuluru, J. S., Yancey, N. A., & Kane, “Pilot-scale grinding and briquetting studies on variable moisture content municipal solid waste bales–Impact on physical properties, chemical composition, and calorific value,” Waste Manag., vol. 125, pp. 316–327, 2021.
- A. Omari, B. Kichonge, G. John, K. Njau, and P. Mtui, “Potential of municipal solid waste, as renewable energy source: a case study of Arusha,Tanzania,” 2014.
- G. Gebreslassie, H. B. Gebreyesus, M. T. Gebretsadik, S. T. Bahta, and S. E. Birkie, “Characterization of Municipal Solid waste ’ s Potential for Power Generation at Mekelle City as a Waste Minimisation strategy Characterization of Municipal Solid waste ’s Potential for Power Generation at Mekelle City as a Waste Minimisation strategy,” vol. 7038, 2020. [CrossRef]
- O. A. Nwoke, W. I. Okonkwo, E. A. Echiegu, C. H. Okechukwu, and B. O. Ugwuishiwu, “Determination of the calorific value of municipal solid waste in enugu, nigeria and its potential for electricity generation,” vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 86–97, 2020.[86] F. Ayeleru, O. O., Okonta, F. N., & Ntuli, “Municipal solid waste generation and characterization in the City of Johannesburg: A pathway for the implementation of zero waste,” Waste Manag., vol. 79, pp. 87–97, 2018.
- S. V Vassilev, D. Baxter, L. K. Andersen, and C. G. Vassileva, “An overview of the chemical composition of biomass,” vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 913–933, 2010.
- W. Y. Deng, J. H. Yan, X. D. Li, F. Wang, S. Y. Lu, and K. F. Cen, “Measurement and simulation of the Effects of moisture content on microwave-assisted pyrolysis of municipal solid waste,” Chem. Eng. Sci., vol. 64, no. 2, pp. 4713–4720, 2009.
- A. Gil, J. A. Siles, A. Serrano, A. F. Chica, and M. A. Martín, “Effect of variation in the C/[N+P] ratio on anaerobic digestion,” Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 228–236, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Magrinho and V. Semiao, “Estimation of residual MSW heating value as a function of waste component recycling,” Waste Manag., vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 2675–2683, 2008.
- S. Adeboye, M. O. Idris, W. O. Adedeji, A. A. Adefajo, T. F. Oyewusi, and A. Adelekun, “Characterization and energy potential of municipal solid waste in Osogbo metropolis,” Clean. Waste Syst., vol. 2, no. May, p. 100020, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. (2012). Anaglate, S. A., Rahmaputro, S., Ruiz, C., & Rojas-Solórzano, “Comparison between landfill gas and waste incineration for power generation in Accra, Ghana,” Int. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. Res, vol. 3, pp. 1–7, 2012.
- R. M. Belgiorno, V., De Feo, G., Della Rocca, C., & Napoli, “Energy from gasification of solid wastes. Waste Management,” Waste Manag., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 1–15, 2003.
- S. R. Shukla and A. N. Vaidya, Municipal solid waste management and conversion technologies. In Waste Valorization. CRC Press, 2019.
- Robert, O. A., & Reiner, “The use of organic waste as an eco-efficient energy source in Ghana,” J. Environ. Prot. (Irvine,. Calif)., vol. 2012, 2012.
- S. Tumuluru, N. A. Yancey, and J. J. Kane, “Pilot-scale grinding and briquetting studies on variable moisture content municipal solid waste bales – Impact on physical properties, chemical composition, and calorific value,” Waste Manag., vol. 125, pp. 316–327, 2021. [CrossRef]

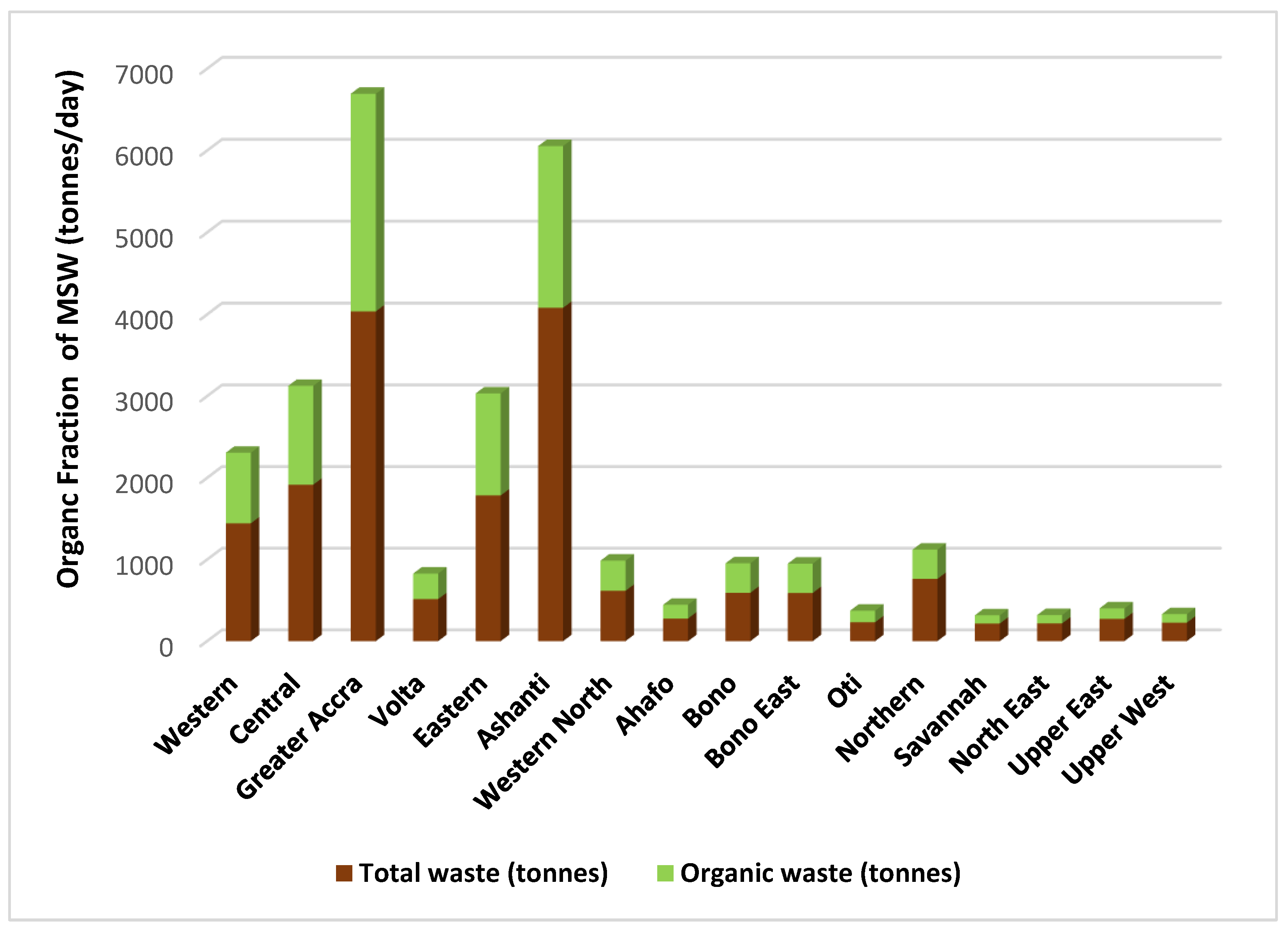
| Region | Population [40] | Waste (tonnes/day) | Percentage of waste (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western | 2060585 | 1442.41 | 8.1 | [21] |
| Central | 2859821 | 1916.08 | 10.8 | [31] |
| Greater Accra | 5455692 | 4037.21 | 22.7 | [31] |
| Volta | 1659040 | 514.30 | 2.9 | [31] |
| Eastern | 2925653 | 1784.65 | 10.0 | [33] |
| Ashanti | 5440463 | 4080.35 | 23.0 | [31] |
| Western North | 880921 | 616.64 | 3.5 | [21] |
| Ahafo | 564668 | 276.69 | 1.6 | [31] |
| Bono | 1208649 | 592.24 | 3.3 | [31] |
| Bono East | 1203400 | 589.67 | 3.3 | [31] |
| Oti | 747248 | 231.65 | 1.3 | [31] |
| Northern | 2310939 | 762.61 | 4.3 | [34] |
| Savannah | 653266 | 215.58 | 1.2 | [34] |
| North East | 658946 | 217.45 | 1.2 | [34] |
| Upper East | 1301226 | 273.26 | 1.5 | [34] |
| Upper West | 901502 | 225.38 | 1.3 | [34] |
| Total | 30832019 | 17776.16 | 100 |
| Municipality / Metropolis | Region | Organic (%) | Paper/ cardboard (%) | Plastic (%) | Metal (%) | Inert (%) | Textiles (%) | Glass (%) | Leather & rubber (%) | Others (%) | References |
| Accra | Greater Accra | 65.8 | 5.3 | 10.4 | 3.1 | 2.8 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 4.1 | [31] |
| Kumasi | Ashanti | 48.4 | 6.5 | 17.6 | 4.5 | 10.7 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 1.6 | 7.8 | [31] |
| Cape Coast | Central | 63.2 | 4.1 | 10.6 | 2.1 | 10.2 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 5.6 | [31] |
| Takoradi | Western | 60 | 7.1 | 11.5 | 2.4 | 8.0 | 29 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 5 | [37] |
| Tamale | Northern | 56 | 3.2 | 10.9 | 2.8 | 4.5 | 0.9 | 4.9 | 1.0 | 5.6 | [31] |
| Wa | Upper West | 47 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 29 | - | - | [34] |
| Aburi | Eastern | 70 | 6 | 16 | 3 | 5 | - | - | - | [33] |
| Region | Waste type | FC | VM (%) | Ash (%) | MC (%) | Reference |
| Ashanti Ashanti Ashanti |
CR | - | 57- 80.25 | 10.81 | 15.5 - 40.89 | [13] |
| Mixed | 17.59- 29.65 | 45-67.55 | 3.69 | 13.55- 21.57 | [76] | |
| Mixed | 80-87.4 | - | 71.8 - 80.6 | [46] | ||
| Eastern | Mixed | - | 6.24 - 6.47 | 36 - 58 | [78] | |
| Greater Accra & Ashanti |
RDF | - | - | - | 8.11-13.27 | [79] |
| Greater Accra | Mixed | - | - | - | 55 | [80] |
| Central | Mixed | - | - | 44.1 – 61.9 | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





