Submitted:
15 September 2024
Posted:
16 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Text Emotion Recognition
2.2. Speech Emotion Recognition
2.3. Multimodal Emotion Recognition Using Text and Speech Data
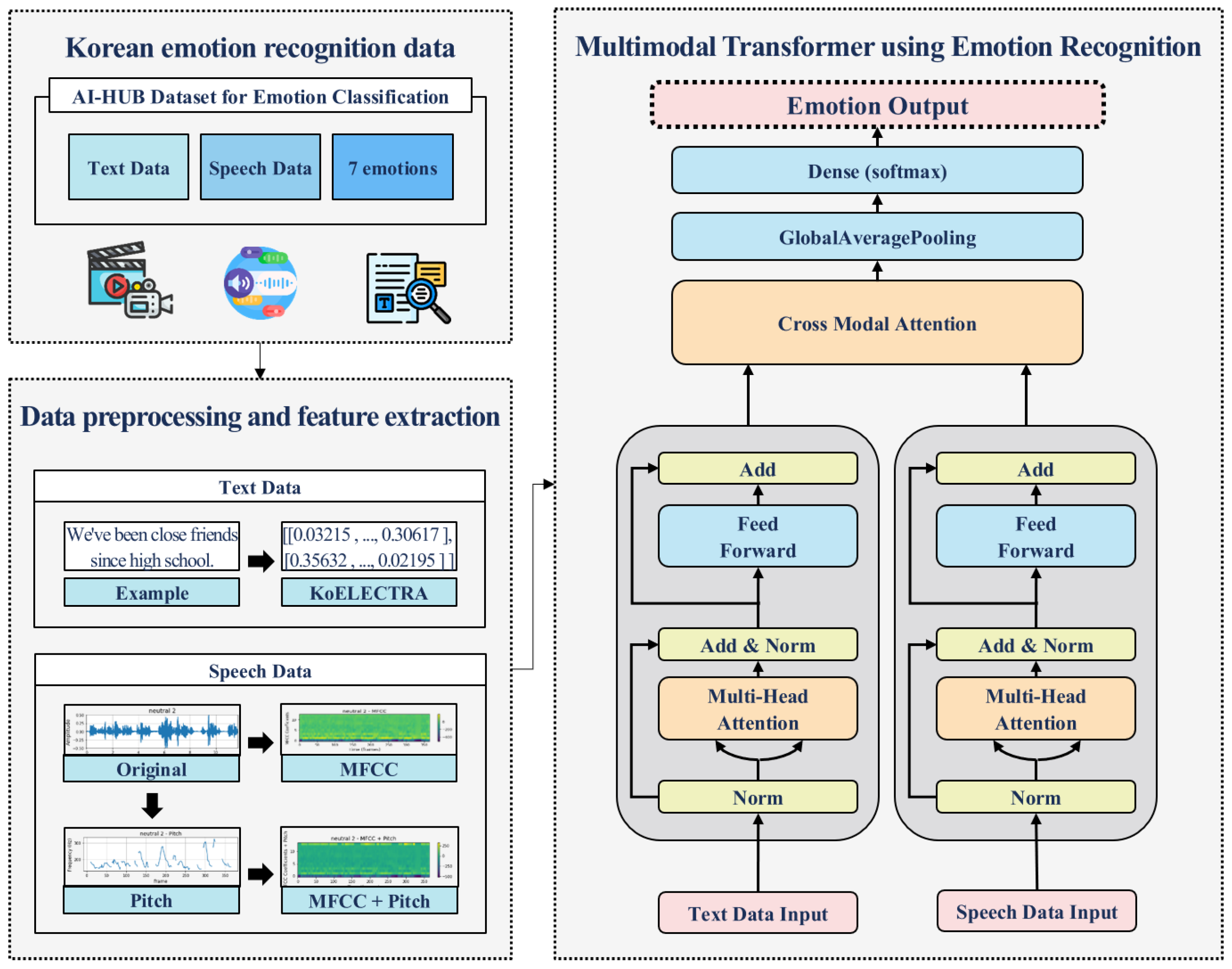
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Overall Process
3.2. Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
3.2.1. KoELECTRA, Which Takes Korean Characteristics into Account
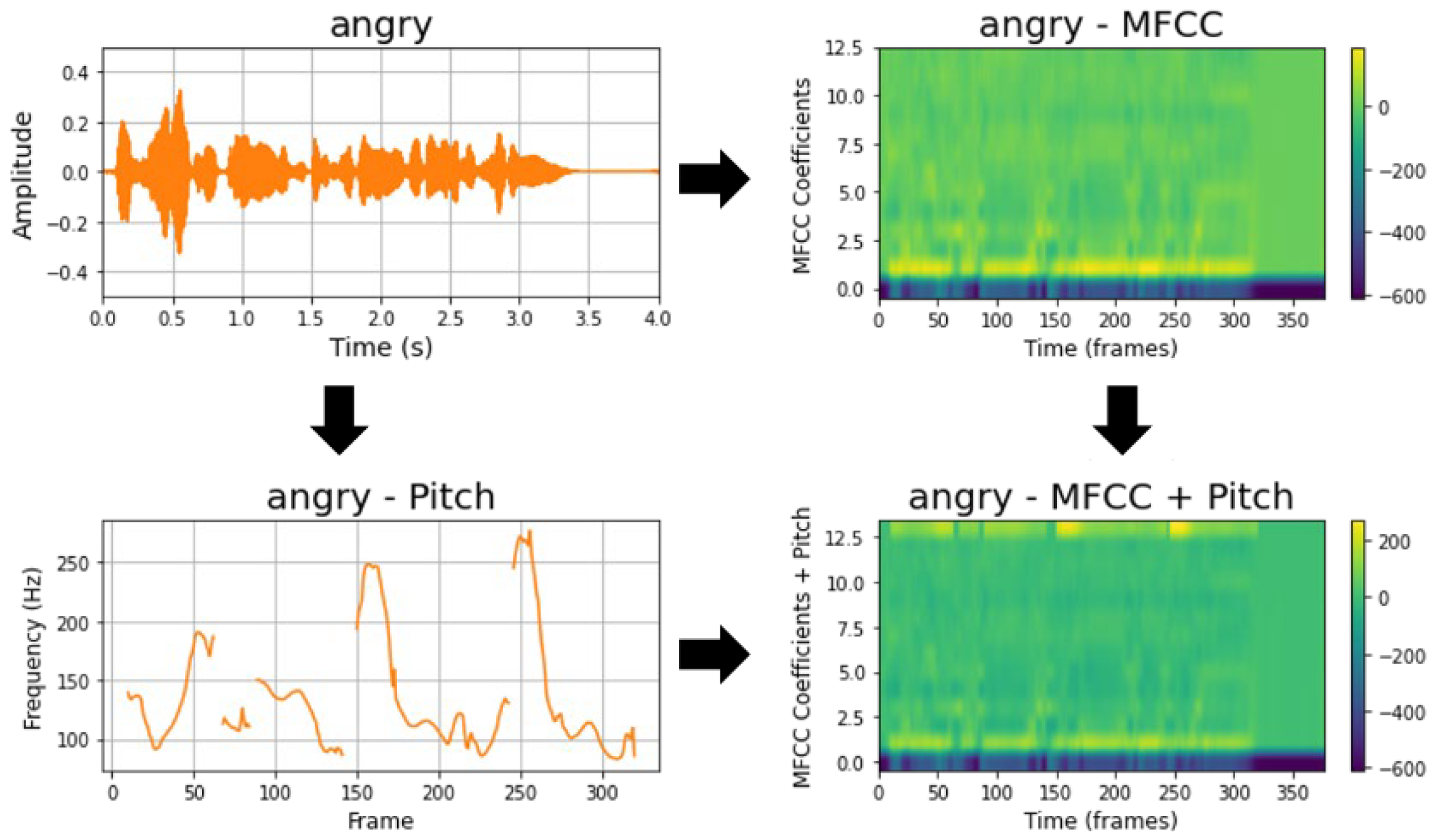
3.2.2. Combining MFCC and Pitch While Considering the Characteristics of the Korean Language
3.3. Multimodal Transformer for Emotion Recognition
| Algorithm 1. Pseudocode of Multimodal Transformer Model for Emotion Recognition |
|
Input: Text Features , Speech Features Output: Emotion Classification // Initialize speech and text transformers // Feature Extraction and Input // Cross Modal Attention // Global Average Pooling and Final Output |
4. Experiments and Assessment
4.1. Data Set
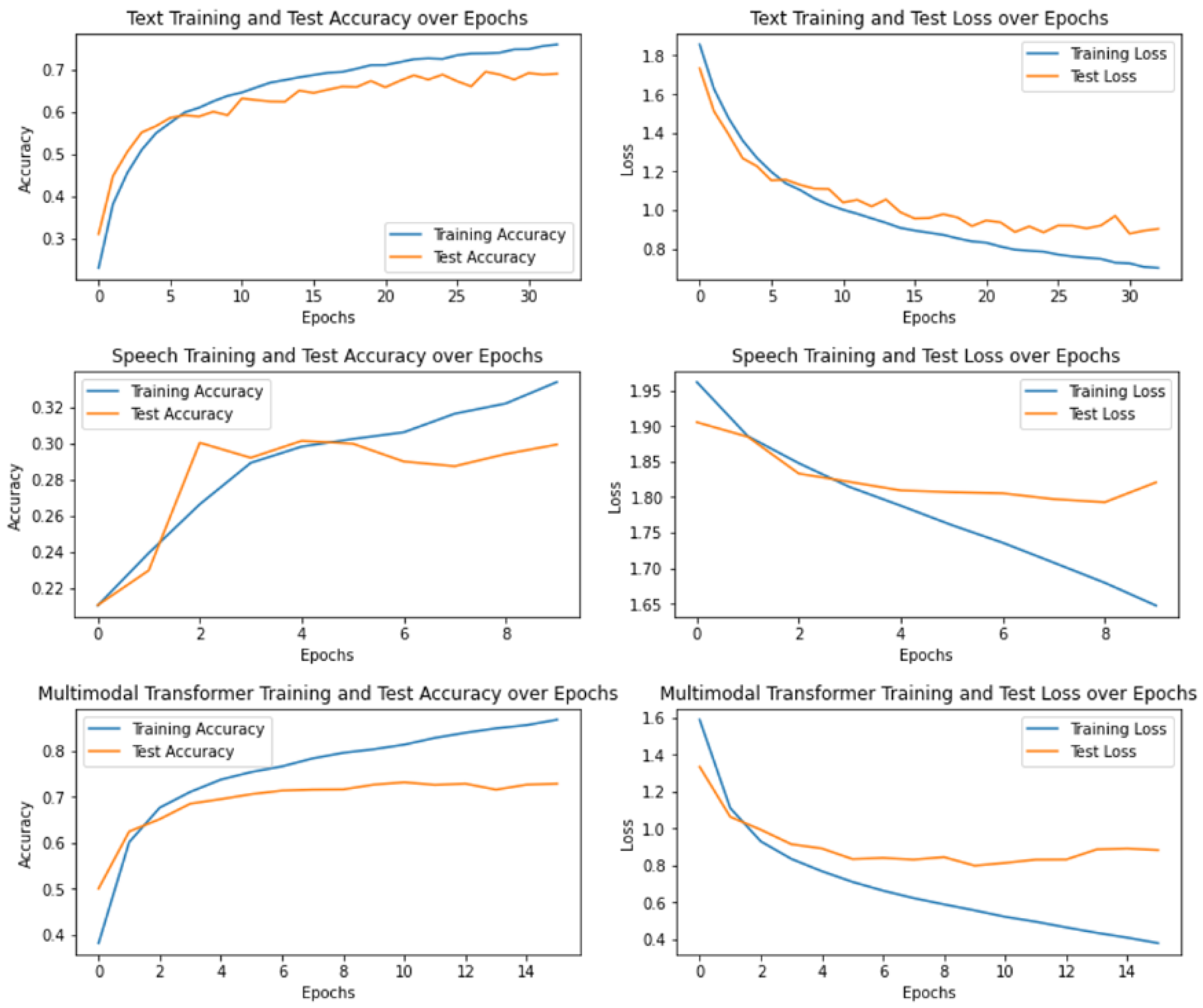
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusion
References
- Xie, Z.; Guan, L. Multimodal information fusion of audiovisual emotion recognition using novel information theoretic tools. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), San Jose, CA, USA, 15–19 July 2013; IEEE, 2013; pp. 1–6.
- Kalateh, S.; Estrada-Jimenez, L.A.; Pulikottil, T.; Hojjati, S.N.; Barata, J. The human role in Human-centric Industry. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2022), Brussels, Belgium, 17–20 October 2022; IEEE, 2022.
- Bahreini, K.; Nadolski, R.; Westera, W. Towards multimodal emotion recognition in e-learning environments. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2016, 24, 590–605. [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K.R.; Johnstone, T.; Klasmeyer, G. Vocal expression of emotion. In Handbook of Affective Sciences; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 433–456.
- Bharti, S.K.; Varadhaganapathy, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Shukla, P.K.; Bouye, M.; Hingaa, S.K.; Mahmoud, A. Text-Based Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Approach. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2645381. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.-P. A BiLSTM–Transformer and 2D CNN Architecture for Emotion Recognition from Speech. Electronics 2023, 12, 4034. [CrossRef]
- Park, H. Enhancement of Multimodal Emotion Recognition Classification Model through Weighted Average Ensemble of KoBART and CNN Models. Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers, 2023, pp. 2157-2159.
- Kim, Y.-J.; Roh, K.; Chae, D. Feature-based Emotion Recognition Model Using Multimodal Data. Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers 2023, 2157–2159.
- Kim, Y.; Roh, K.; Chae, D. Feature-based Emotion Recognition Model Using Multimodal Data. Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers 2023, 6, 2169–2171.
- Mutinda, J.; Mwangi, W.; Okeyo, G. Sentiment Analysis of Text Reviews Using Lexicon-Enhanced Bert Embedding (LeBERT) Model with Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1445. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, H. Weibo Text Sentiment Analysis Based on BERT and Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10774. [CrossRef]
- Reggiswarashari, F.; Sihwi, S.W. Speech emotion recognition using 2D-convolutional neural network. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 12, 6594–6601. [CrossRef]
- Hazra, S.K.; Shubham, M.; Kaushal, C.; Prabhakar, N. Emotion recognition of human speech using deep learning method and MFCC features. Radioelectron. Comput. Syst. 2022, 4, 161-172. [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Majumder, N.; Hazarika, D.; Cambria, E.; Gelbukh, A.; Hussain, A. Multimodal Sentiment Analysis: Addressing Key Issues and Setting Up the Baselines. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2018, 33, 17–25. [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.; Chen, M.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Tensor Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.07250.

| Original Text (in Korean) |
Embedding Vector | Vector Size |
|---|---|---|
| 어, 청소 니가 대신 해 줘! | [‘[CLS]’, ‘어’, ‘,’, ‘청소’, ‘니’, ‘##가’, ‘대신’, ‘해’, ‘줘’, ‘!’, ‘[SEP]’, ‘[PAD]’, ..., , ‘[PAD]’] |
(73, 768) |
| 둘 다 하기 싫어서 화내 | [‘[CLS]’, ‘둘’, ‘다’, ‘하’, ‘##기’, ‘싫’, ‘##어’, ‘##서’, ‘화’, ‘##내’, ‘.’, ‘[SEP]’, ‘[PAD]’, ..., , ‘[PAD]’] |
(73, 768) |
| 처음 학원에서 만났다가 서로 좋아해서 사귀게 되었지 |
[‘[CLS]’, ‘처음’, ‘학원’, ‘##에’, ‘##서’, ‘만났’, ‘##다가’, ‘서로’, ‘좋’, ‘##아’, ‘##해서’, ‘사귀’, ‘##게’, ‘되’, ‘##었’, ‘##지’, ‘.’, ‘[SEP]’, ‘[PAD]’, ..., , ‘[PAD]’] | (73, 768) |
| 룸메이트와 너무 자주 싸우게 돼 | [‘[CLS]’, ‘룸’, ‘##메이트’, ‘##와’, ‘너무’, ‘자주’, ‘싸우’, ‘##게’, ‘돼’, ‘.’, ‘[SEP]’, ‘[PAD]’, ..., , ‘[PAD]’] |
(73, 768) |
| 부모님한테 아직 말 안했는데 말하기가 두려워 |
[‘[CLS]’, ‘부모’, ‘##님’, ‘##한’, ‘##테’, ‘아직’, ‘말’, ‘안’, ‘##했’, ‘##는데’, ‘말’, ‘##하’, ‘##기’, ‘##가’, ‘두려워’, ‘.’, ‘[SEP]’, ‘[PAD]’, ..., , ‘[PAD]’] |
(73, 768) |
| Emotion | Collected Data | Final Data Used |
|---|---|---|
| Angry | 7,126 | 3,412 |
| Disgust | 2,265 | 2,265 |
| Fear | 2,534 | 2,534 |
| Happiness | 3,412 | 3,412 |
| Neutral | 5,611 | 3,412 |
| Sadness | 15,074 | 3,412 |
| Surprise | 866 | 866 |
| Total | 36,888 | 19,313 |
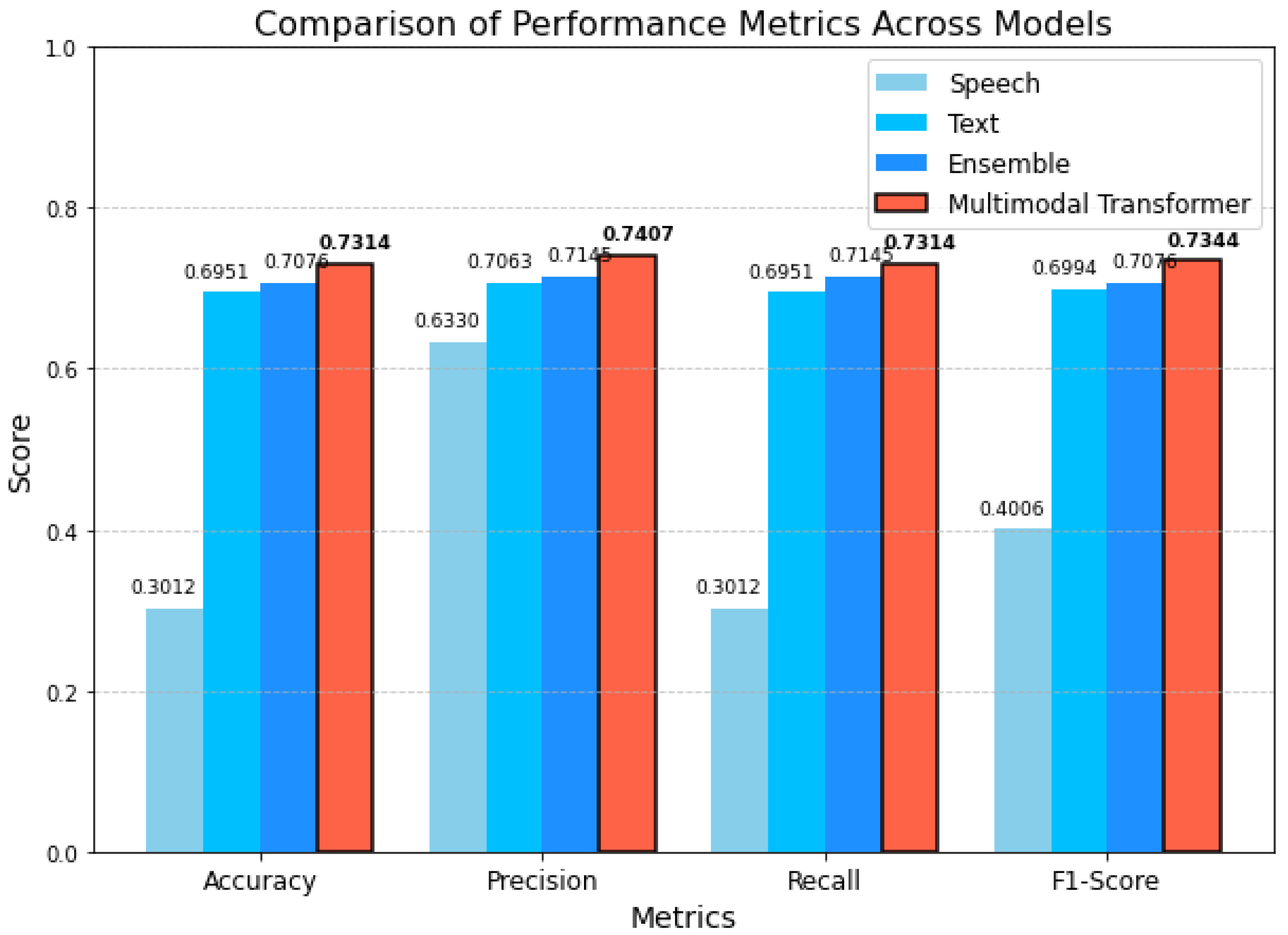
| Division | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Text Data : KoELECTRA | 0.6994 | 0.6951 |
| Speech Data : MFCC + Pitch | 0.4005 | 0.3012 |
| Balanced Ensemble | 0.7098 | 0.7075 |
| Multimodal Transformer | 0.7344 | 0.7313 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





