Submitted:
11 September 2024
Posted:
12 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Motivation and Contributions
- In order to maximize the secrecy communication rate, we propose an efficient method of allocating active relay elements by repeatedly varying a number of parameters, including power levels, user positions, and relay numbers. It ensures optimal performance in a variety of contexts by taking into account several effects, including path loss and channel uncertainty, to adapt to changing channel conditions. Furthermore, the Jaya algorithm’s population-based search mechanism facilitates varied solution space exploration, raising the possibility of obtaining optimal configurations and removing the difficulties associated with local optima that are frequently encountered in conventional optimization techniques. Therefore, the proposed method is compared with the state-of-the-art schemes.
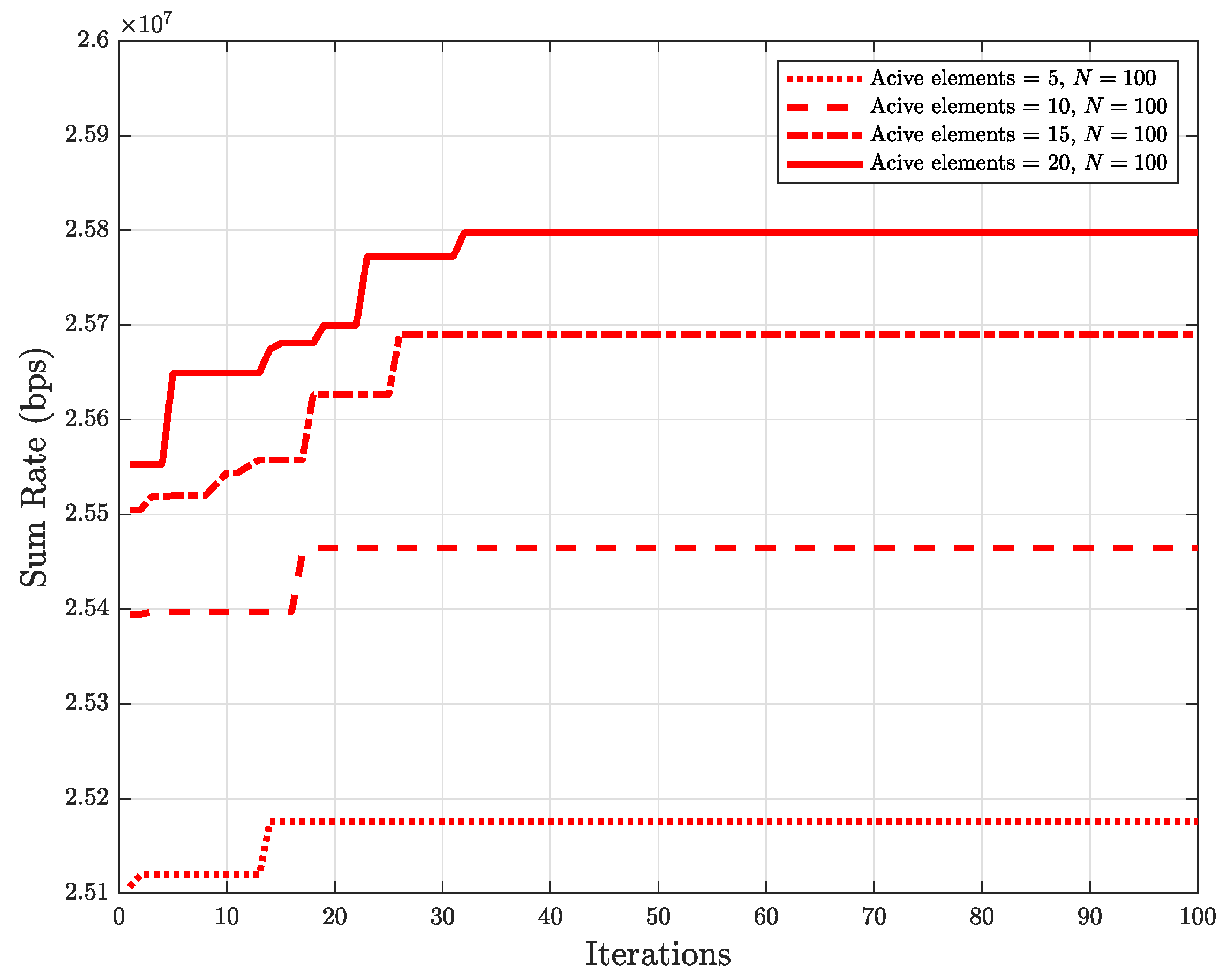
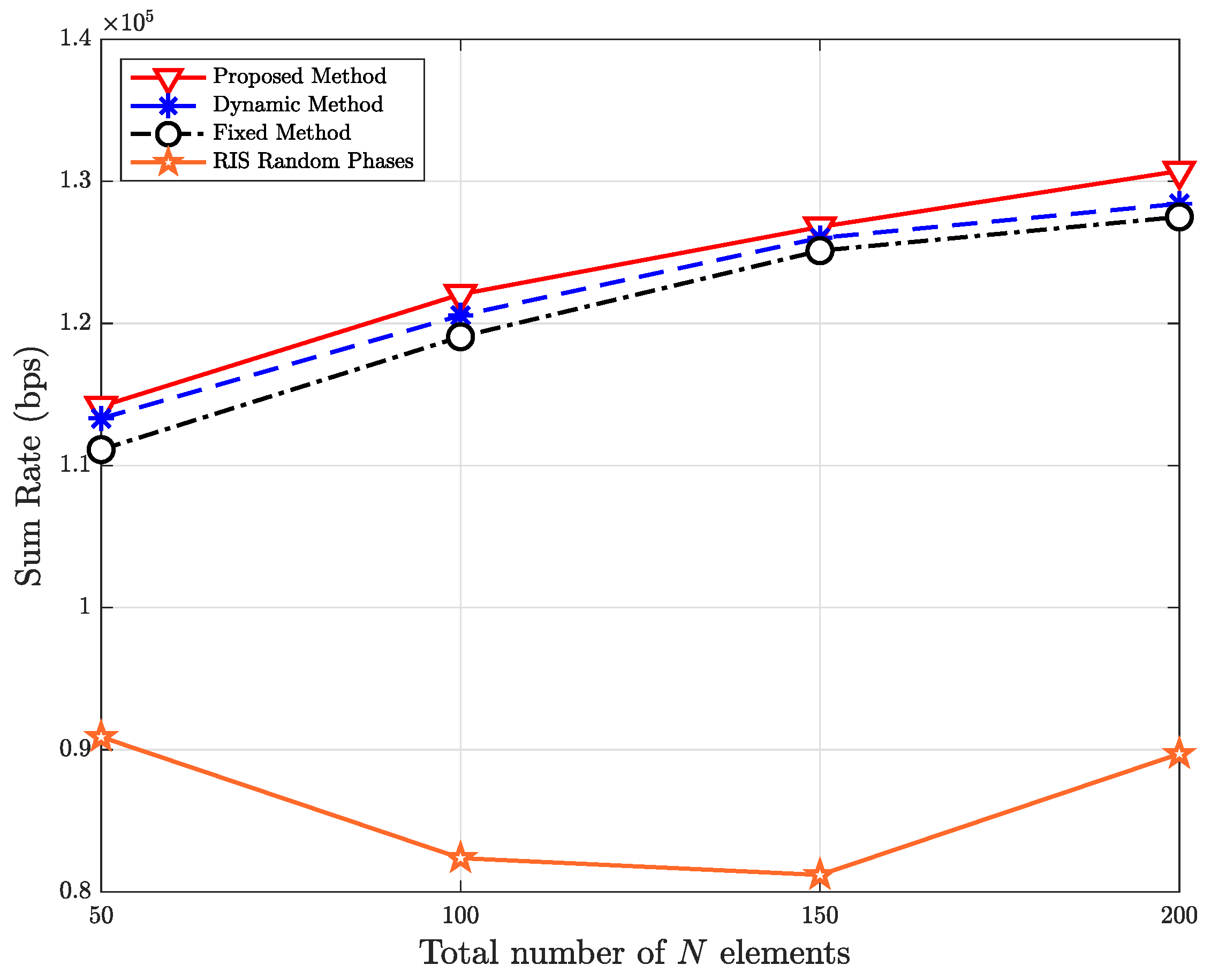
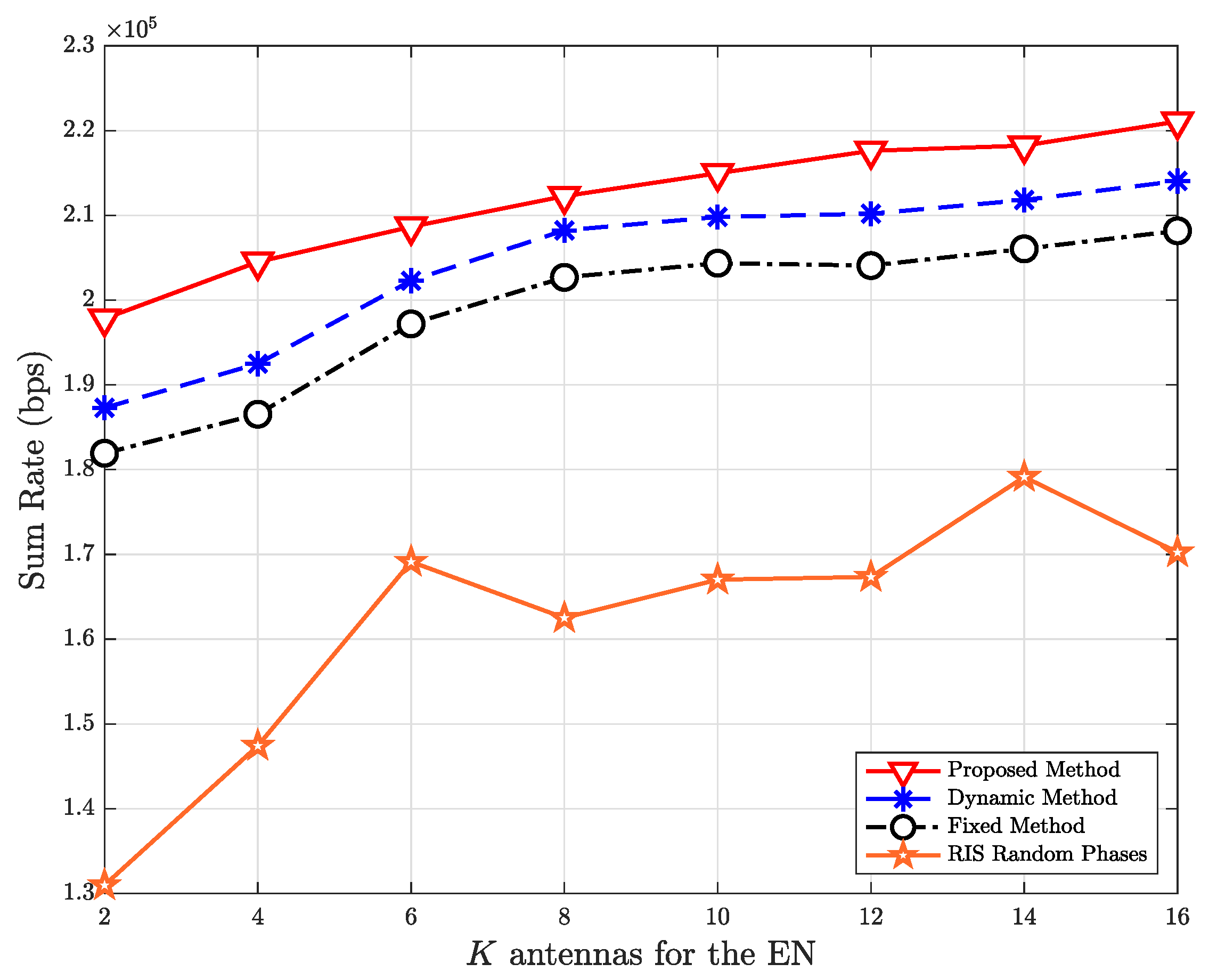
- The proposed method’s effectiveness in obtaining the best aspects active elements of HR-RIS under an extensive variety of scenarios is demonstrated by the simulation results. In particular, the number of RIS elements in the RIS, the number of antennas equipped with the edge node (EN), the user’s various locations, and the eavesdropper’s various locations are all investigated in terms of sum rate.
1.3. Paper Organization
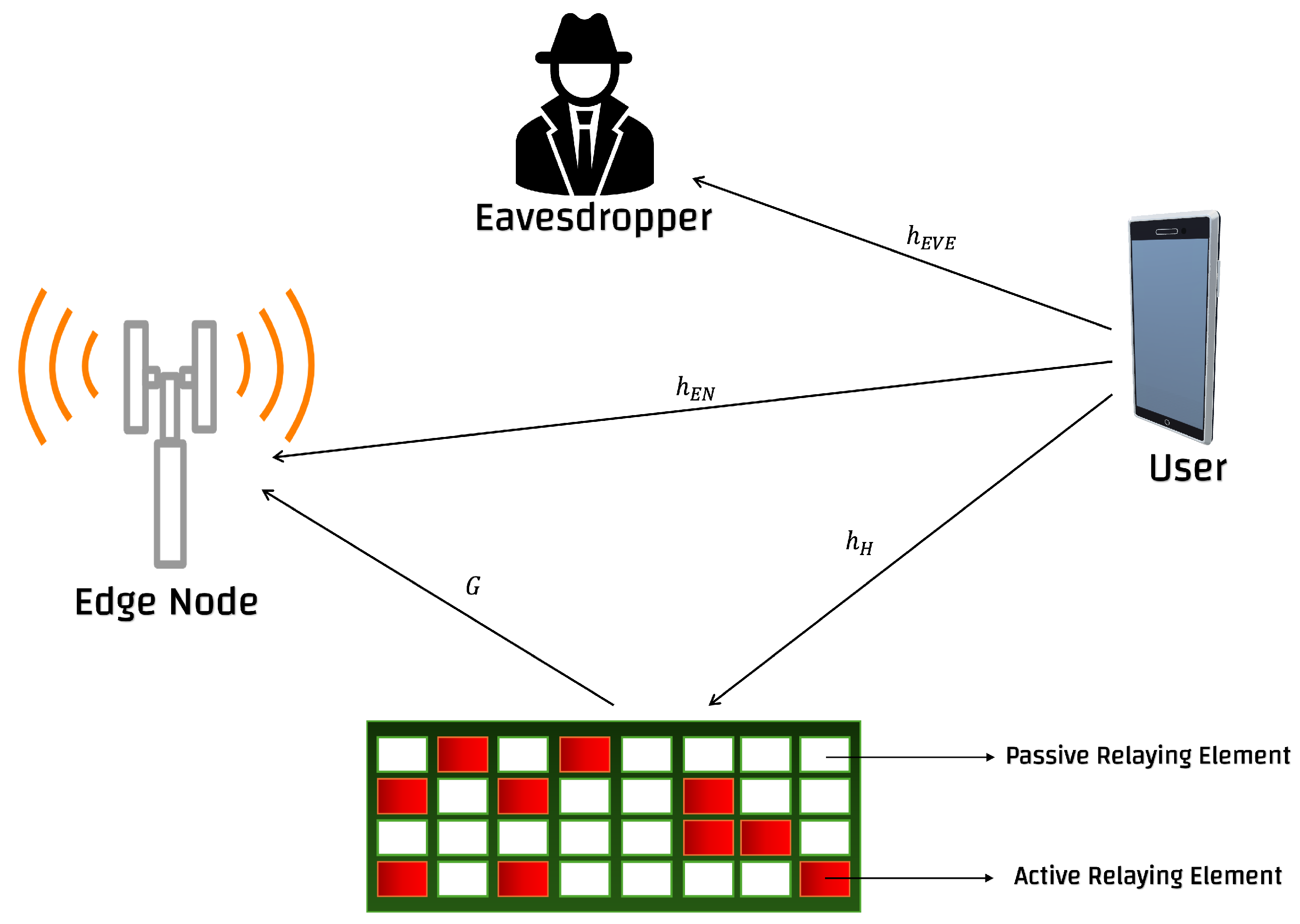
2. System Model
2.1. HR-RIS Architecture
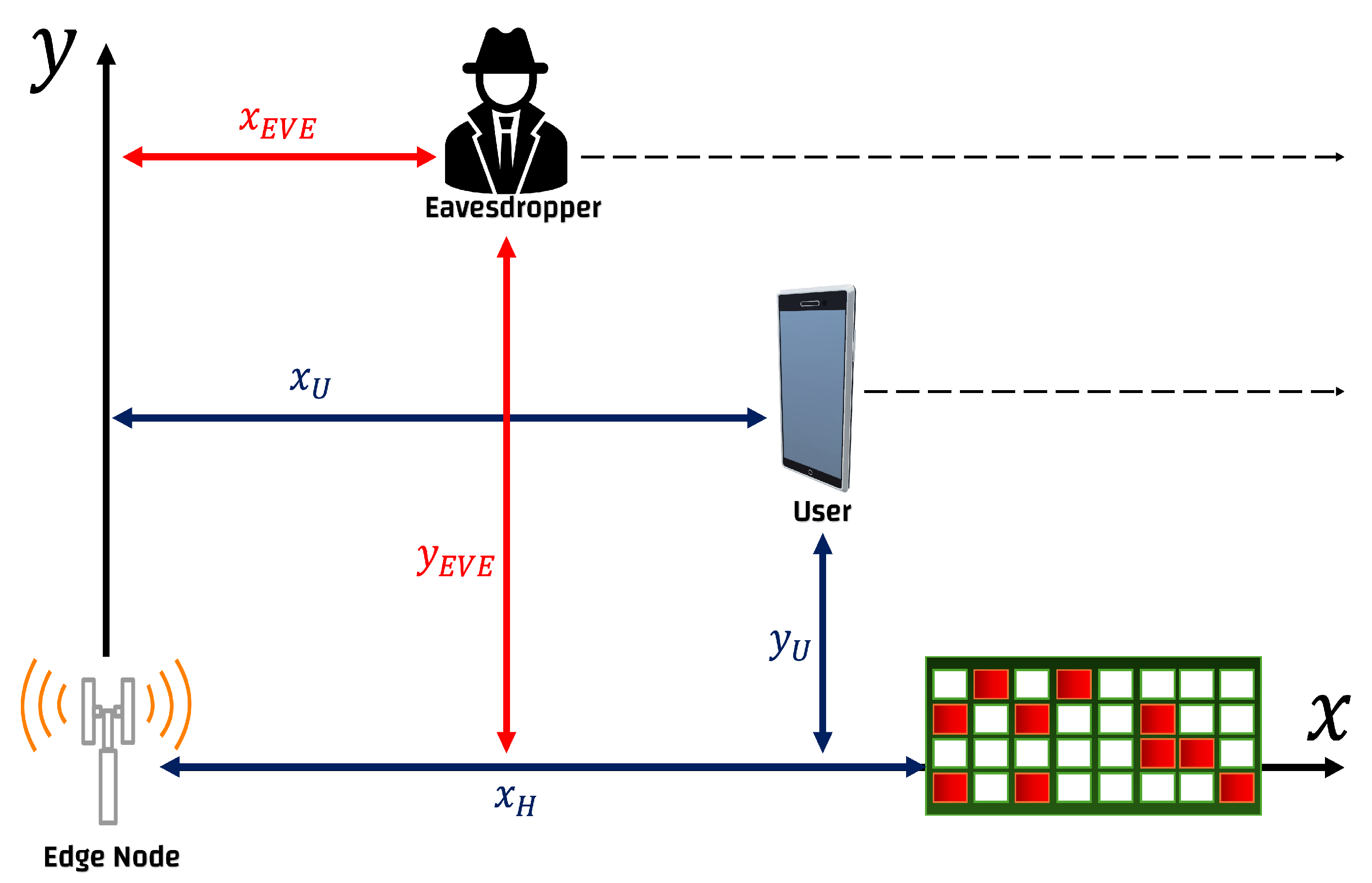
2.2. Channel Model
3. Problem Formulation
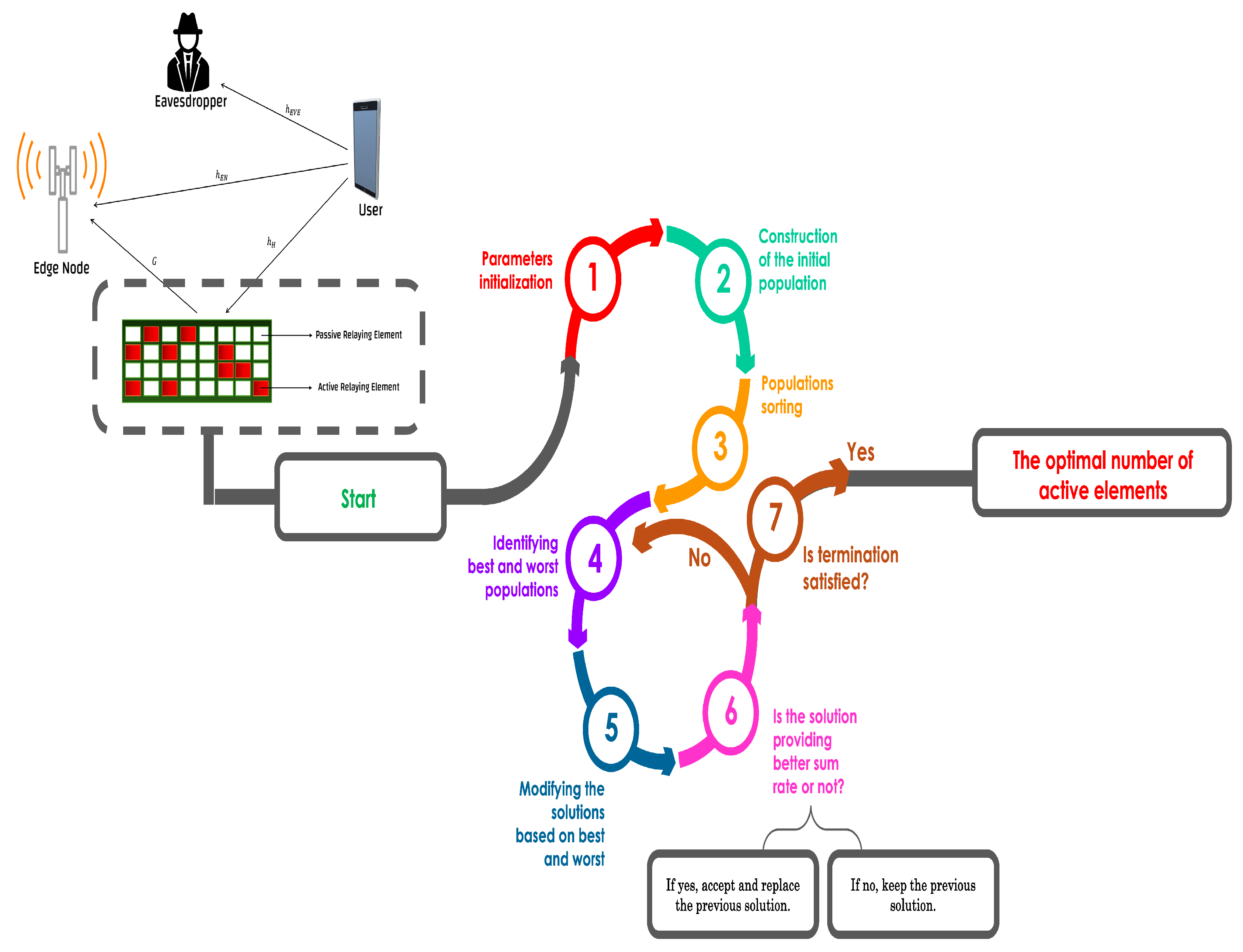
4. Proposed Solution
4.1. Background of Jaya Optimization Approach
4.2. Proposed Jaya Optimization Procedures
4.2.1. Parameters Initialization
4.2.2. Building up the Initial Populations for Jaya Approach
4.2.3. Evaluation Process
4.2.4. Updating
5. Simulation Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, L. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Systems: A Review. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 20, 3902–3919. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Towards Smart Wireless Communication Environments: An Overview of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 59, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; et al. Physical Layer Security with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface: A New Paradigm in Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 1389–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; et al. Securing Wireless Communication with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: Strategies and Applications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; et al. Rethinking Wireless Communication: Towards Secure and Energy-Efficient Systems with Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; et al. Physical Layer Security in Wireless Networks with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 71127–71139. [Google Scholar]
- Kammoun, A.; et al. Secrecy Analysis of RIS-Assisted Caching Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 5901–5916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; et al. Machine Learning for Secrecy Communications with Flat and Adaptive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 2452–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach for Secure Wireless Communications using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3334–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo, M.; et al. Economic Feasibility and Efficiency of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Wireless Communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Basar, E. Transmit Designs for Energy-Efficient and Secure Deployments of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC); 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; et al. Secrecy Rate Maximization for Hybrid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Wireless Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 3296–3315. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; et al. Multi-Objective Optimization for Secrecy Communication with Hybrid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 6000–6015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; et al. Secrecy Communications with Active and Passive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Under Imperfect Channel State Information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; et al. Energy-Efficient and Secure Hybrid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Systems: An Alternating Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 4323–4336. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.; et al. Game Theory-Based Active Elements Optimization in HR-RIS for Secrecy Communication. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 34567–34578. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; et al. Cost-Effective Secrecy Communication via Hybrid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 789–802. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.V. Jaya: A New Optimization Algorithm. Adv. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network: Joint active and passive beamforming design. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Commun. Conf. 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Vu, Q.-D.; Lee, K.; Juntti, M. Hybrid Relay-Reflecting Intelligent Surface-Assisted Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 6228–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, K.-H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Dinh, T.Q.; Hoang, T.-M.; Juntti, M. Low-Latency and Secure Computation Offloading Assisted by Hybrid Relay-Reflecting Intelligent Surface. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; 2021; pp. 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, R. Capacity Characterization for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided MIMO Communication. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Saad, W.; Debbah, M.; Hong, C.S. Asymptotic Optimality of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: Passive Beamforming and Achievable Rate. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC); 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khandaker, M.R.A.; Masouros, C.; Wong, K.-K. Constructive Interference Based Secure Precoding: A New Dimension in Physical Layer Security. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 2256–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jin, R.; Dai, H. Physical-Layer Assisted Secure Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 4054–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitar, R.A.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; et al. An Intensive and Comprehensive Overview of JAYA Algorithm, Its Versions and Applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 763–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
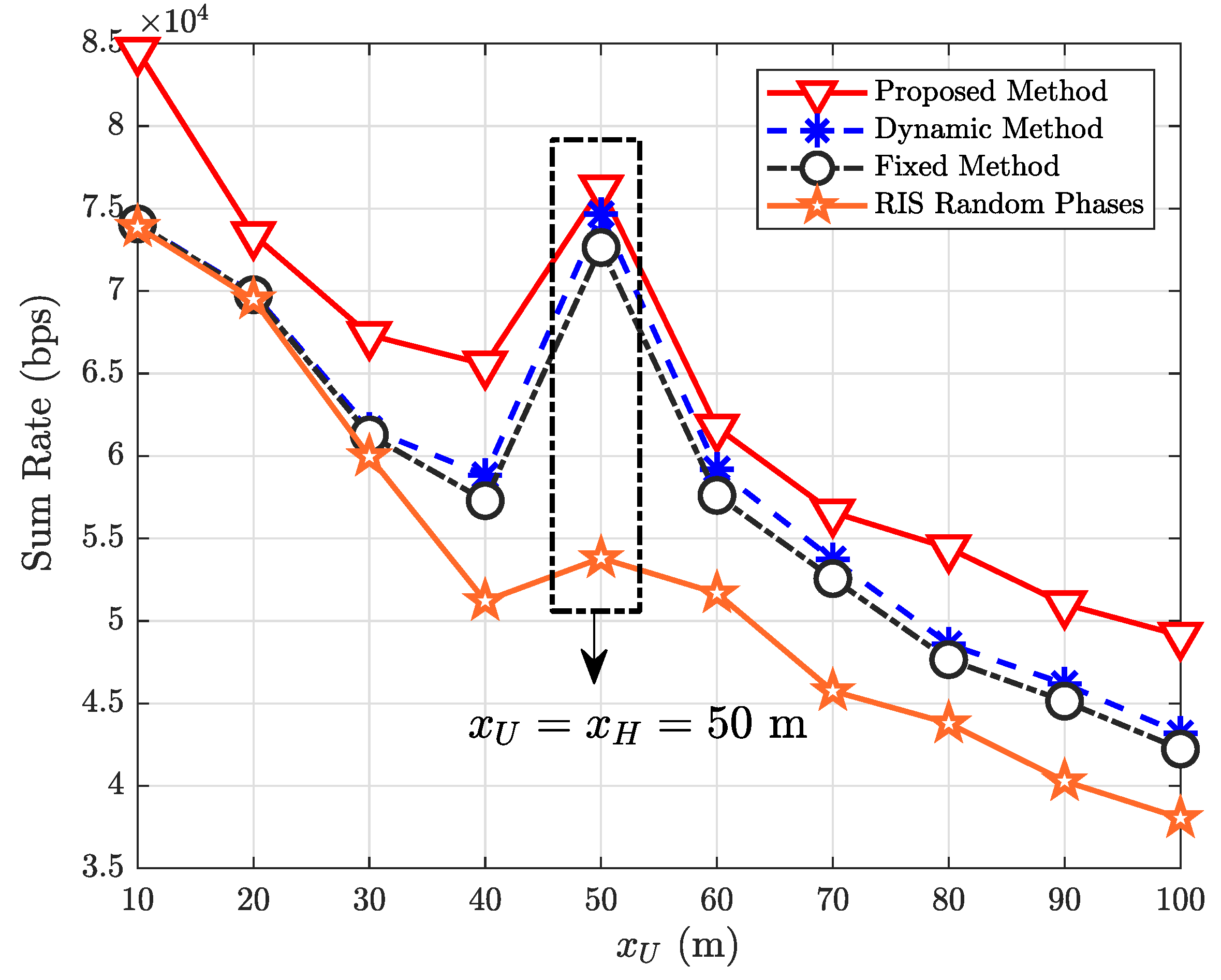
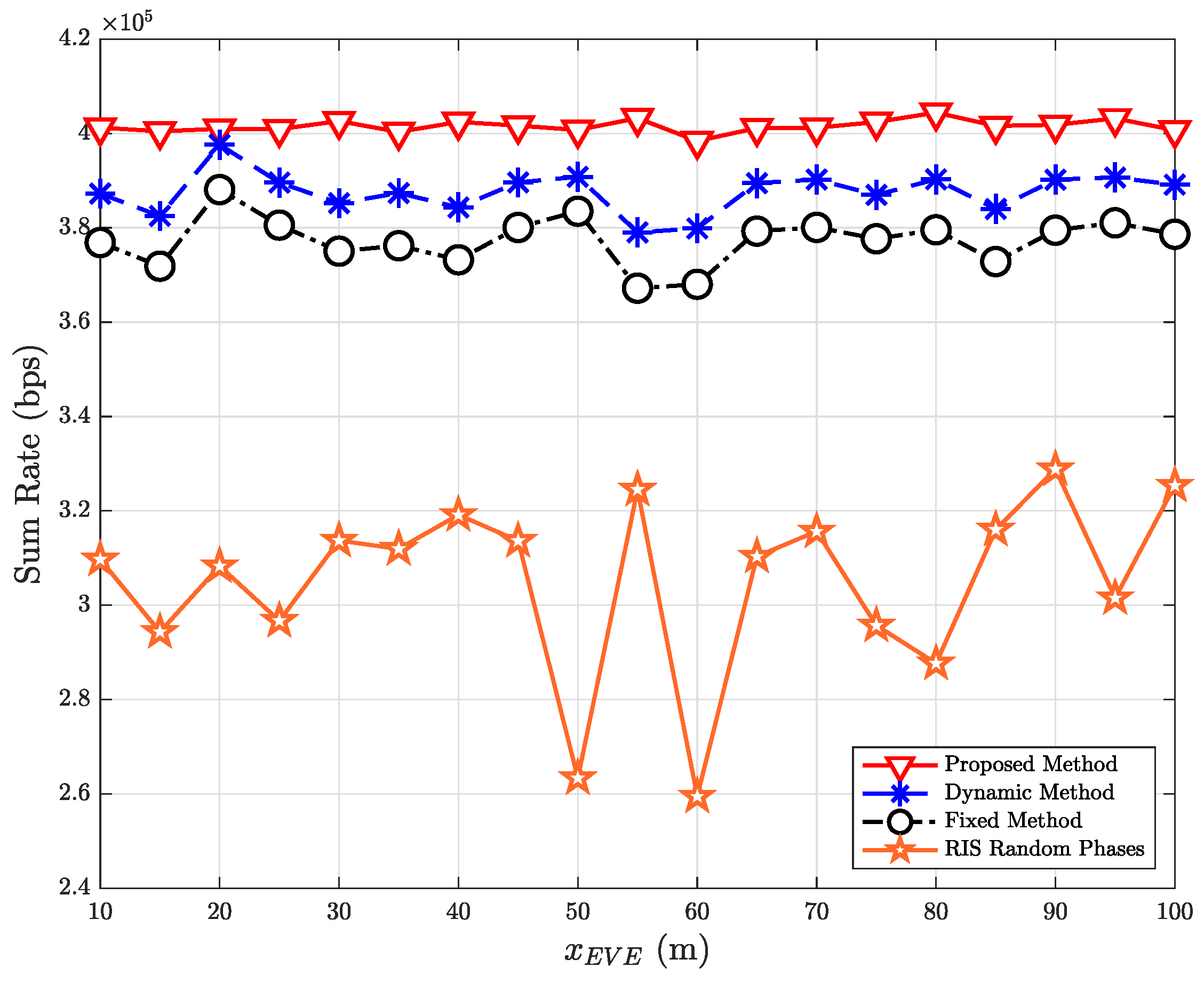
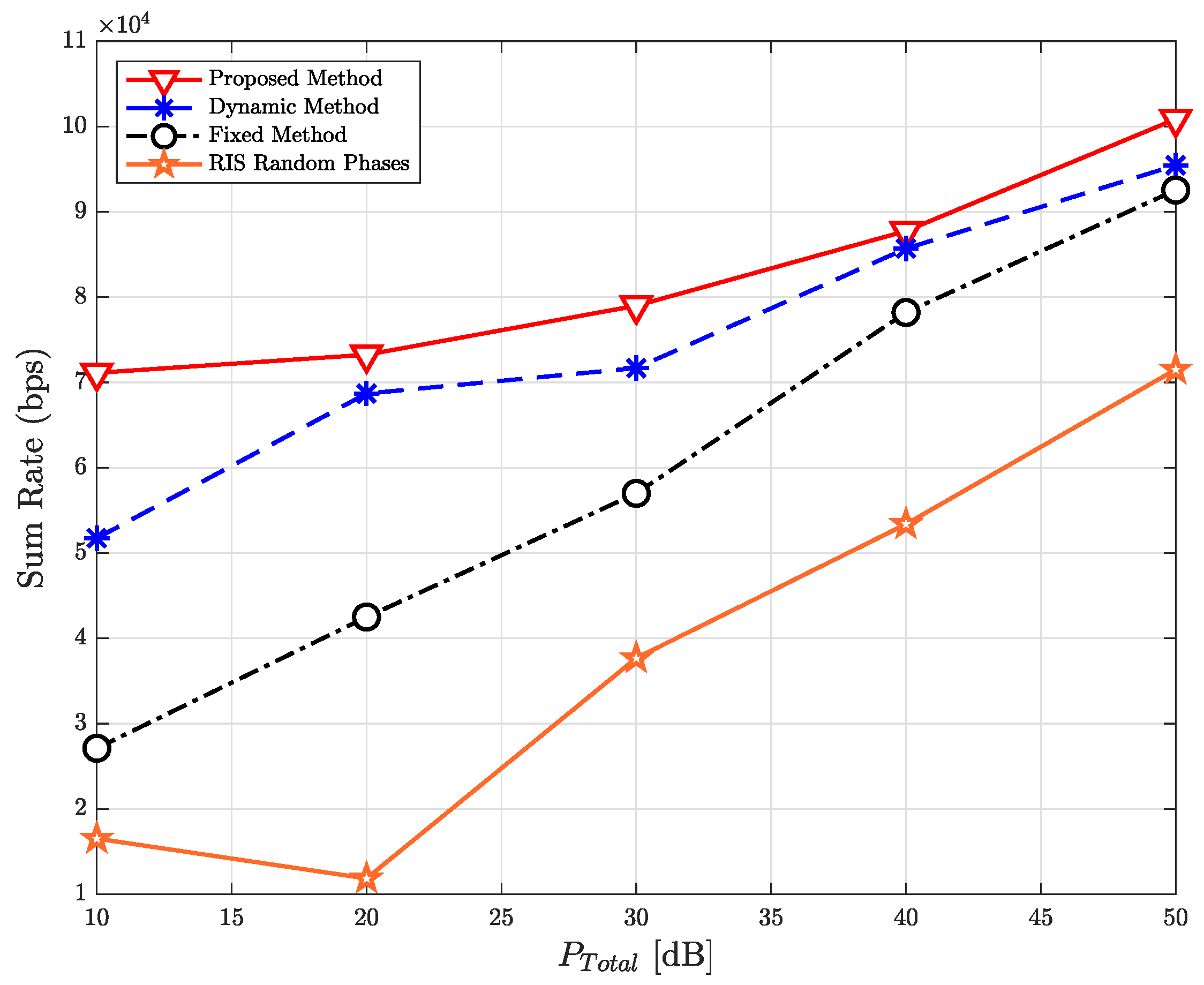
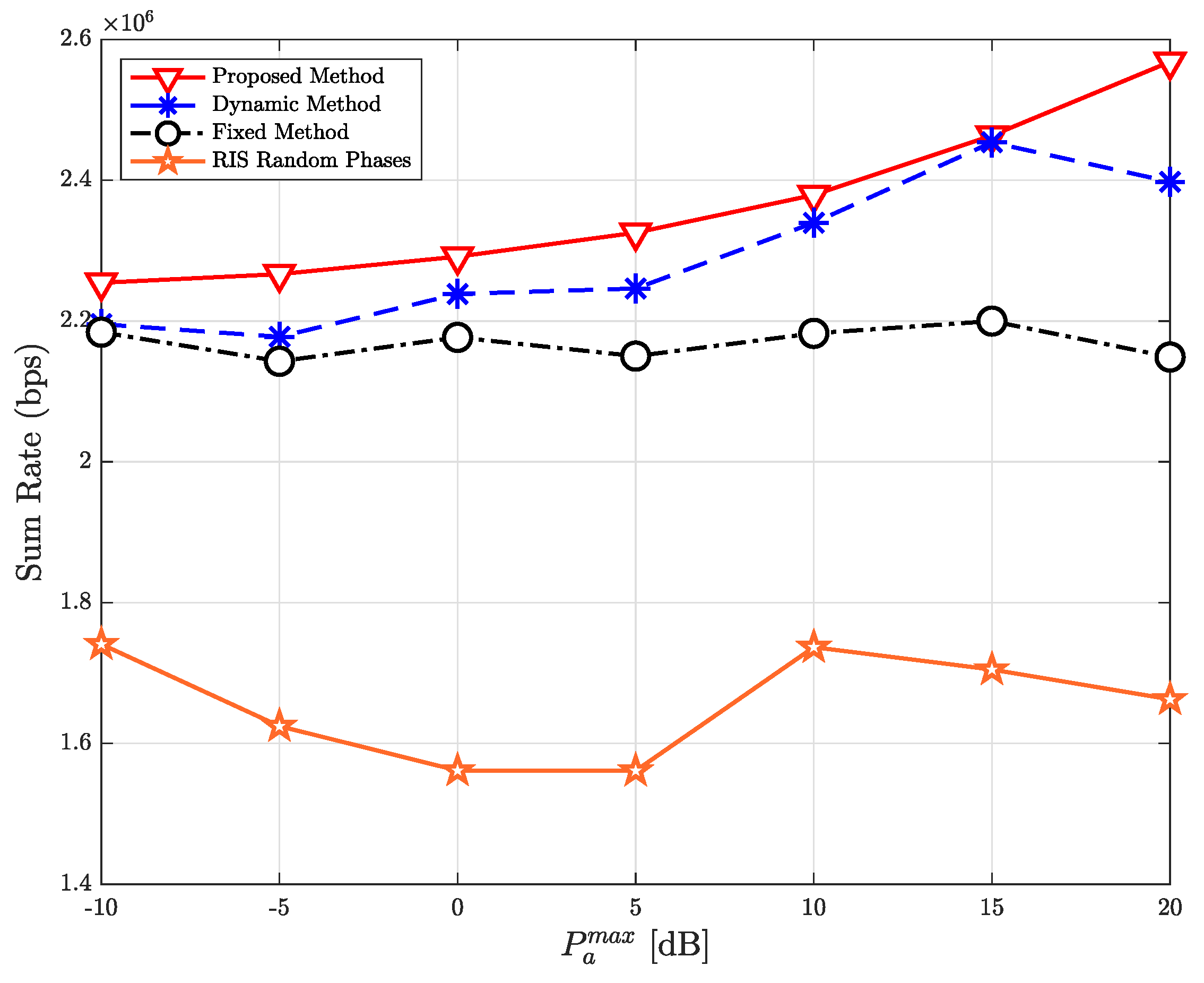

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Upper bound of the estimation error () | 0.1 |
| Bandwidth (B) | 1 MHz |
| The path loss at () | -30 dBm |
| -80 dBm | |
| m | |
| Power components: | dBm, and dBm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





