Submitted:
06 September 2024
Posted:
07 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
Introduction:
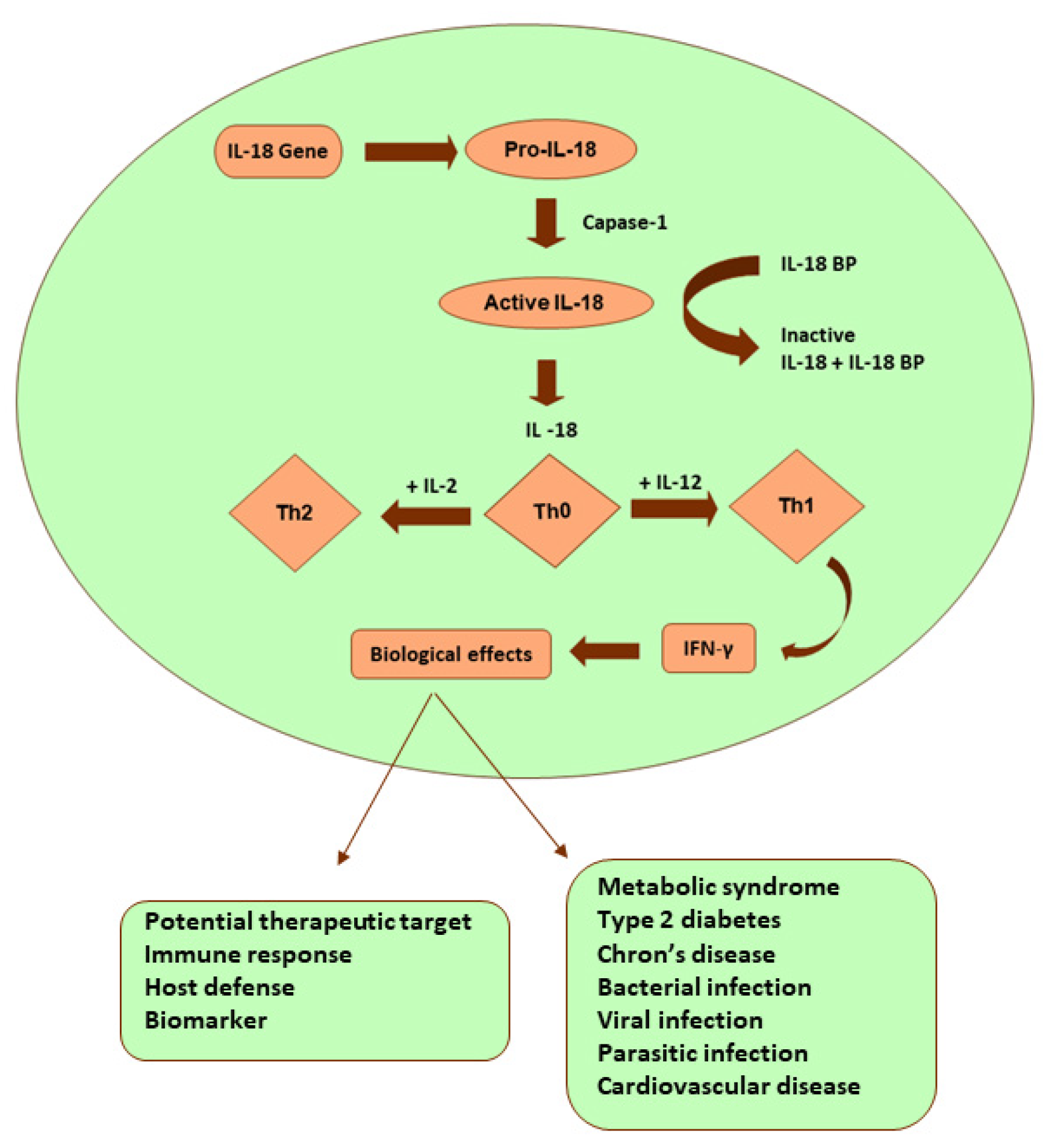
Interleukin -18 (IL-18):
Genetic Polymorphisms of IL-18
IL-18 Polymorphisms and Infectious Diseases
Parasitic Infections
Malaria
Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL)
Chagas Disease
Intestinal Amebiasis
Viral Infections
HIV Infection:
HBV Infection:
HCV Infection:
Dengue:
Bacterial Infections
Tuberculosis (TB):
H. pylori Infections:
Fungal Infections
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM):
Summary
Future Direction:
Acknowledgments
References
- K. Nakanishi, T. Yoshimoto, H. Tsutsui, H. Okamura, Interleukin-18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses, Annu Rev Immunol. 19 (2001) 423–474. https://doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.423. [CrossRef]
- J.E. Sims, D.E. Smith, The IL-1 family: regulators of immunity, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10 (2010) 89–102 https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2691.
- J.E. Sims, M.j. Nicklin, J.F. Bazan, J.L. Barton, S.J. Busfield, J.E. Ford, A new nomenclature for IL-1-family genes, Trends Immunol. 22 (2001) 536–537. https://doi:10.1016/S1471-4906(01)02040-3. [CrossRef]
- K. Yasuda, K. Nakanishi, H. Tsutsui, Interleukin-18 in health and disease, Int J Mol Sci. 20 (2019) 649–701. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2691.
- M.C. Park, Y.B. Park, S.K. Lee, Elevated interleukin-18 levels correlated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus, Clin Rheumatol 23 (2004) 225-229. https://doi: 10.1007/s10067-004-0867-x. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Thomas, B.M. Huuskes, C.G. Sobey, G.R. Drummond, A. Vinh, The IL-18/ IL-18R1 signalling axis: Diagnostic and therapeutic potential in hypertension and chronic kidney disease, Pharmacol Ther. 239 (2022) 108191. https://doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108191. [CrossRef]
- F. Nicoletti, R. Di Marco, K. Mangano, F. Patti, E. Reggio, A. Nicoletti, Increased serum levels of interleukin-18 in patients with multiple sclerosis, J. Neurol. 57 (2001) 342–344. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.57.2.342. [CrossRef]
- T. Nakahashi, M.K. Ellingson, P. Wong, B. Israelow, C. Lucas, J. Klein, Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes, Nature. 588 (2020) 315–320. https://doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2700-3. [CrossRef]
- T.S. Rodrigues, K.S.G. de Sa, A.Y. Ishimoto, A. Becerra, S. Oliveira, L. Almeida, Inflammasomes are activated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and are associated with COVID-19 severity in patients. J Exp Med. 218 (2021) e20201707. https://doi: 10.1084/jem.20201707. [CrossRef]
- S. Lob, B. Ochmann, Z. Ma, T. Vilsmaier, C. Kuhn, E. Schmoeckel, The role of interleukin-18 in recurrent early pregnancy loss, J Reprod Immunol. 148 (2021) 103432. https://doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2021.103432. [CrossRef]
- S.K. Sedimbi, T. Hagglof, M.C. Karlsson, IL-18 in inflammatory and autoimmune disease, Cell Mol Life Sci 70 (2013) 4795–4808. https://doi: 10.1007/ s00018-013-1425-y. [CrossRef]
- K. Kobayashi, N. Nakata, M. Kai, T. Kasama, Y. Hanyuda, Y. Hatano, Decreased Expression of Cytokines That Induce Type 1 Helper T Cell/Interferon-γ Responses in Genetically Susceptible Mice Infected with Mycobacterium avium, J. Clin. immunol. 85 (1997) 112-116. https://doi.org/10.1006/clin.1997.4421. [CrossRef]
- R. Zhu, S. Mao, W. Shi, L. Wu, J. Zhang, A prediction study of IL-18 and IFN-γ in glucocorticoid treatment response in infants and young children with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia, Transl Pediatr. 11(2022) 738-747. https://doi.org/10.21037/tp-22-139. [CrossRef]
- K. Ohkusu, T. Yoshimoto, K. Takeda, T. Ogura, S. Kashiwamura, Y. Iwakura, S. Akira, H. Okamura, K. Nakanishi, Potentiality of Interleukin-18 as a Useful Reagent for Treatment and Prevention of Leishmania major Infection, Infect Immun. 68 (2000) 2449-2456. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.68.5.2449-2456.2000. [CrossRef]
- N. Fujioka, R. Akazawa, K. Ohashi, M. Fujii, M. Ikeda, M. Kurimot, Interleukin-18 Protects Mice against Acute Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Infection. J Virol 73 (1999) 2401-2409.https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.73.3.2401-2409.1999. [CrossRef]
- S. Ushio, M. Namba, T. Okura, K. Hattori, Y. Nukada, K. Akita K, Cloning of the cDNA for human IFN-gamma-inducing factor, expression in escherichia coli, and studies on the biologic activities of the protein, J Immunol. 156 (1996) 4274–4279. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.156.11.4274. [CrossRef]
- M. Tomura, S. Maruo, J. Mu, X.Y. Zhou, H.J. Ahn, T. Hamaoka, Differential capacities of CD4+, CD8+, and CD4-CD8- T cell subsets to express IL-18 receptor and produce IFN-gamma in response to IL-18. J Immunol 160(1998): 3759–65. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.160.8.3759. [CrossRef]
- G. Kaplanski, Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol Rev 281(2018):13853 https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12616. [CrossRef]
- [19] T. Yoshimoto, K. Takeda, T. Tanaka, K. Ohkusu, S. Kashiwamura, H. Okamura, IL-12 up-regulates IL-18 receptor expression on T cells, Th1 cells, and b cells: synergism with IL-18 for IFN-gamma production. J Immunol 161(1998):3400–7. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.161.7.3400. [CrossRef]
- K. Hoshino, H. Tsutsui, T. Kawai, K. Takeda, K. Nakanishi, Y. Takeda, Cutting edge: generation of IL-18 receptor-deficient mice: evidence for IL-1 receptor-related protein as an essential IL-18 binding receptor. J Immunol (1999) 162(9):5041–4. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.162.9.5041. [CrossRef]
- V. Giedraitis, B. He, W.X. Huang, J. Hillert, Cloning and mutation analysis of the human IL-18 promoter: a possible role of polymorphisms in expression regulation, J. Neuroimmunol. 112 (2001) 146-152, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-5728(00)00407-0. [CrossRef]
- S. Higa, T. Hiran, M. Mayumi, M. Hiraoka, Y. Ohshima, M. Nambu, E. Yamaguchi, N. Hizawa, N. Kondo, E. Matsui, Y. Katada, Association between interleukin-18 gene polymorphism 105A/C and asthma. Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 33 (2003) 1097-1102, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01739.x. [CrossRef]
- S.R. Thompson, and S.E. Humphries, Interleukin-18 genetics and inflammatory disease susceptibility, Genes & Immunity. 8 (2007) 91-99, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364366. [CrossRef]
- J. Arimitsu, T. Hirano, S. Higa, M. Kawai, T. Naka, A. Ogata, Y. Shima, M. Fujimoto, T. Yamadori, K. Hagiwara, T. Ohgawara, IL-18 gene polymorphisms affect IL-18 production capability by monocytes, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 342 (2006) 1413-1416, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.096. [CrossRef]
- A.U. AlRuwaisan, M.R. Al-Anazi, M.I. Shafeai, F.H. Rudiny, A.M. Motaen, S.M. Bin Dajem, H. Alothaid, K. Morsy, S. Alkahtani, A.A. Al-Qahtani, Associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms in Il-18 gene with plasmodium falciparum-associated malaria, J. Inflamm. Res. 14 (2021) 3587-3619, https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S314638. [CrossRef]
- D. Torre, M. Giola, F. Speranza, A. Matteelli, C. Basilico, and G. Biondi, Serum levels of interleukin-18 in patients with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria, Eur. Cytokine Netw. 12 (2001) 361-364.
- L. Malaguarnera, S. Pignatelli, M. Musumeci, J. Simporè, and S. Musumeci, Plasma levels of interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Parasite immunology, 24(2002) 489-492, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3024.2002.00485.x. [CrossRef]
- R.P. Singh, S.I. Kashiwamura, P. Rao, H. Okamura, A. Mukherjee, V.S. Chauhan. The role of IL-18 in blood-stage immunity against murine malaria Plasmodium yoelii 265 and Plasmodium berghei ANKA. The Journal of Immunology. 168 (2002) 4674-81.
- A.S. Mustafa, E.A. Elbishbishi, R. Agarwal, and U.C. Chaturvedi, Elevated levels of interleukin-13 and IL-18 in patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever, FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 30 (2001) 229-233, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2001.tb01575.x. [CrossRef]
- D. Kumar, P. Tiwary, J. Chakravarty, S. Sundar, Association of interleukin-18 gene polymorphism with susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in endemic area of Bihar, an Indian population, Sci. World J. 1 (2014) 852104, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/852104. [CrossRef]
- Moravej, M. Rasouli, S. Asaei, M. Kalani, and Y. Mansoori, Association of interleukin-18 gene variants with susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in Iranian population, Mol. Biol. Rep. 40 (2013) 4009-4014, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2479-x. [CrossRef]
- E. Ahmadpour, A. Bazmani, M.H. Kohansal, A. Kazemi, Z. Babaloo, IL-18 gene polymorphism in patients with visceral leishmaniasis in East Azarbaijan, Iran, J. Parasit. Dis. 40 (2016) 981–985, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0619-z. [CrossRef]
- M. Strauss, M. Acosta-Herrera, A. Alcaraz, D. Casares-Marfil, P. Bosch-Nicolau, M.S. Lo Presti, I. Molina, C.I. González, C.I., Chagas Genetics CYTED Network and J. Martín, Association of IL18 genetic polymorphisms with Chagas disease in Latin American populations, PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 13 (2019) e0007859, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0007859. [CrossRef]
- L.G. Nogueira, A.F. Frade, B.M. Ianni, L. Laugier, C.W. Pissetti, S. Cabantous, M. Baron, G. Lima Peixoto, A. de Melo Borges, E. Donadi and J.A. Marin-Neto, Functional IL18 polymorphism and susceptibility to Chronic Chagas Disease, Cytokine. 73 (2015) 79-83, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.01.037. [CrossRef]
- Gomes dos Santos, E.H. Watanabe, D.T. Ferreira, J. Oliveira, É.S. Nakanishi, C.S. Oliveira, E. Bocchi, C.T.G. Novaes, F. Cruz, N.B. Carvalho, P.K. Sato, A specific IL6 polymorphic genotype modulates the risk of Trypanosoma cruzi parasitemia while IL18, IL17A, and IL1B variant profiles and HIV infection protect against cardiomyopathy in Chagas disease, Front. immunol. 11 (2020) 521409, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.521409. [CrossRef]
- A.K. Al-Sultany, K.A.H. Al-Morshidy, Single nucleotide polymorphism of IL-18 gene and resistin gene in children infection with Entamoeba histolytica, Med. j. Babylon. 20 (2023) 697-704, https://doi.org/10.4103/MJBL.MJBL_70_23. [CrossRef]
- Deeks SG, Overbaugh J, Phillips A, Buchbinder S. HIV infection. Nature reviews Disease primers. 2015 Oct 1;1(1):1-22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.35. [CrossRef]
- R.C. Sobti, V.L. Sharma, A.M. Abitew, N. Berhane, S.A. Mahdi, M. Askari, V.S. Kuttiat, V.S. and A. Wanchu, The -137G/C polymorphism of interleukin 18 promoter and risk of HIV-1 infection and its progression to AIDS, Acta virologica. 55 (2011) 353, https://doi.org/10.4149/av_2011_04_353. [CrossRef]
- G.M. Al-Khateeb, M.S. Sater, R.R. Finan, F.E. Mustafa, A.S. Al-Busaidi, M.A. Al-Sulaiti, W.Y. Almawi, Analysis of interleukin-18 promoter polymorphisms and changes in interleukin-18 serum levels underscores the involvement of interleukin-18 in recurrent spontaneous miscarriage, Fertil. Steril. 96 (2011) 921-926, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.06.079. [CrossRef]
- H. Jiang, F. Cao, H. Cao H, Q. Rao, Y. Yang, Associations of human leukocyte antigen and interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms with viral load in patients with hepatitis B infection, Medicine. 97 (2018) 11249, http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011249. [CrossRef]
- P.A. Zhang, J.M. Wu, Y. Li and X.S. Yang, X.S, Relationship of interleukin-18 gene promoter polymorphisms with chronic hepatitis B in Chinese Han population. Chin. J. Genet. 22 (2005) 528-532. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.73.3.2401-2409.1999. [CrossRef]
- Hajarizadeh, B., Grebely, J. & Dore, G. Epidemiology and natural history of HCV infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10, 553–562 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.107. [CrossRef]
- Manns, M., Buti, M., Gane, E. et al. Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3, 17006 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.6. [CrossRef]
- K. Kiyosawa, E. Tanaka, Hepatitis C Virus in the Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Perspect. Med. Virol. 6 (2002) 31–42, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-7069(02)06064-0. [CrossRef]
- F.V. Chisari, Unscrambling Hepatitis C Virus–Host Interactions, Nature. 436 (2005) 930–932, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04076. [CrossRef]
- S. Farid, L. Rashid, S. Swelam, The Role of Interleukin-18 Promoter Polymorphisms (-607 C/A and 137 G/C) in Determining HCV Clearance or Persistence, Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 50 (2018) 141-149, https://doi.org/10.21608/ejhm.2018.16083. [CrossRef]
- E.M. Said, M.S. Soliman, H.I. Shousha, M.S. Rashed, A.A. Elazm, R.Z. Aamer, M.H. Kamel and F.M. Abdelsalam, Interleukin-18 and its gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) influence chronic hepatitis C progression, J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 12 (2018) 257-264. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.9813. [CrossRef]
- P. An, C.L. Thio, G.D. Kirk, S. Donfield, J.J. Goedert, C.A. Winkler, Regulatory polymorphisms in the interleukin-18 promoter are associated with hepatitis C virus clearance, J. Infect. Dis. 198 (2008) 1159-1165, https://doi.org/10.1086/592047. [CrossRef]
- M. Yue, J.J. Wang, L. Feng, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Wang, X.Z. Deng, K. Xu and J. Zhang, J, Association of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms with the outcomes of hepatitis C virus infection in high-risk Chinese Han population, Immunol. Lett. 154 (2013) 54-60, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2013.08.007. [CrossRef]
- N. Hirankarn, C. Manonom, P. Tangkijvanich, Y. Poovorawan, Association of interleukin-18 gene polymorphism (− 607A/A genotype) with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B virus infection, Tissue Antigens. 70 (2007) 160-163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0039.2007.00865.x. [CrossRef]
- H.K. Lau, M.J. Hsieh, S.F. Yang, H.L. Wang, W.H. Kuo, H.L. Lee, and C.B. Yeh, Association between interleukin-18 polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence and clinical progression, Int. J. Med. Sci. Public Health. 13 (2016) 556, https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.15853. [CrossRef]
- J. Bao, Y. Lu, Y. Deng, C. Rong, Y. Liu, X. Huang, L. Song, S. Li, X. Qin, Association between IL-18 polymorphisms, serum levels, and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population: a retrospective case–control study, Cancer. Cell. Int. 15 (2015) 1-8, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-015-0223-z. [CrossRef]
- S.D.C. Ferreira, S.G.F. Chachá, F.F. Souza, A.C. Teixeira, R. de Carvalho Santana, N.H.S. Deghaide, S. Rodrigues, Marano, L.A., Mendes-Junior, C.T., Zucoloto, S. and Donadi, E.A, IL-18, TNF, and IFN-γ alleles and genotypes are associated with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B infection and severity of liver injury, J. Med. Virol. 87 (2015) 1689-1696. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.24225. [CrossRef]
- N. Li, Y.F. Gao, T.C. Zhang, P. Chen, X. Li, F. Su, Relationship between interleukin 18 polymorphisms and susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B virus infection, World J Hepatol. 4 (2012) 105, https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i3.105. [CrossRef]
- YS. Kim, JY. Cheong, SW. Cho, KM. Lee, JC. Hwang, B. Oh, K. Kimm, JA. Lee, BL. Park, HS. Cheong, HD. Shin, JH. Kim, A functional SNP of the interleukin-18 gene is associated with the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus-infected patients, J. Dig. Dis. Sci. 54 (2009) 2722–2728, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-009-0970-6. [CrossRef]
- J.Y. Cheong, S.W. Cho, B. Oh, K. Kimm, K.M. Lee, S.J. Shin, J.A. Lee, B.L. Park, H.S. Cheong, H.D. Shin, and B.Y. Cho, Association of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms with hepatitis B virus clearance, Dig. Dis. Sci. 55 (2010) 1113-1119, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-009-0819-z. [CrossRef]
- Zhu R, Mao S, Shi W, Wu L, Zhang J. A prediction study of IL-18 and IFN-γ in glucocorticoid treatment response in infants and young children with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Transl Pediatr. 2022 May;11(5):738-747. https://doi.org/10.21037/tp-22-139. [CrossRef]
- Z.J. Dai, X.H. Liu, M. Wang, Y. Guo, W. Zhu, X. Li, S. Lin, T. Tian, K. Liu, Y. Zheng, P. Xu, IL-18 polymorphisms contribute to hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility in Chinese population: a case-control study, Oncotarget, 8 (2017) 81350. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18531. [CrossRef]
- H.T. Pohan, S. Suhendro, R. Bur, A. Matondang, S. Djauzi, K. Inada and S. Endo, Interleukin-18 levels in adult dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever, Med. J. Indones. 13 (2004) 86-9, https://doi.org/10.13181/mji.v13i2.136. [CrossRef]
- L.B. Zhen, Y.P. Sun, Y.Y. Chen, L.S. Yin, IL-18 polymorphisms and tuberculosis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Afr. Health Sci., 19(2019)1311-1320. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v19i1.2. [CrossRef]
- C. He, L. Liu, Associations of polymorphisms in IL-6 and IL-18 with tuberculosis: evidence from a meta-analysis, Microb. Pathog. 139 (2020) 103823, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103823. [CrossRef]
- B. Zhang, L. Xiao, Q. Qiu, L. Miao, S. Yan and S. Zhou, Association between IL-18, IFN-γ and TB susceptibility: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann. Palliat. Med. 10 (2021) 108780886-108710886, https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-21-2582. [CrossRef]
- M. Han, J. Yue, Y.Y. Lian, Y.L. Zhao, H.X. Wang, L.R. Liu, Relationship between single nucleotide polymorphism of interleukin-18 and susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in the Chinese Han population, Microbiol. Immunol. 55 (2011) 388-393, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2011.00332.x. [CrossRef]
- Pacifico L, Anania C, Osborn JF, Ferraro F, Chiesa C. Consequences of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. World J Gastroenterol. 2010 16(41):5181-94. https://doi.org/ 10.3748/wjg.v16.i41.5181. [CrossRef]
- Rezaeifar, E. Eskandari-Nasab, M. Moghadampour, E. Kharazi-Nejad, S.S.A. Hasani, A. Asadi-Saghandi, M. Hadadi-Fishani, A. Sepanjnia, and B. Sadeghi-Kalani, The association of interleukin-18 promoter polymorphisms and serum levels with duodenal ulcer, and their correlations with bacterial CagA and VacA virulence factors, Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 45 (2013) 584-592, https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2013.794301. [CrossRef]
- D.S. Myung, W.S. Lee, Y.L. Park, N. Kim, H.H. Oh, M.Y. Kim, C.Y. Oak, C.Y. Chung, H.C. Park, J.S. Kim, and S.B. Cho. Association between interleukin-18 gene polymorphism and Helicobacter pylori infection in the Korean population, Scientific reports, 5 (2015) 11535. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11535. [CrossRef]
- P.K. Sato, F.D. Busser, F.M.D.C. Carvalho, A. Gomes dos Santos, A. Sadahiro, C.L. Diogo, A.S.G. Kono, M.L. Moretti, O.D.C. Luiz and M.A. Shikanai-Yasuda, Polymorphism in the Promoter Region of the IL18 Gene and the Association with Severity on Paracoccidioidomycosis, Front. immunol. 11 (2020) 542210, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.542210. [CrossRef]
- S.B. Anyona, P. Kempaiah, E. Raballah, C. Ouma, T. Were, G.C. Davenport, S.N. Konah, J.M. Vulule, J.B. Hittner, C.W. Gichuki, J.M. Ong’echa. Functional promoter haplotypes of interleukin-18 condition susceptibility to severe malarial anemia and childhood mortality. Infect. Immun, 79(2011), 4923-4932. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.05601-11. [CrossRef]
- S.I. Oyedeji, H.O. Awobode, and J.F. Kun, Interleukin-18 Gene Promoter Polymorphisms in Children with Uncomplicated Malaria in Lafia, North-central Nigeria, FJPAS, 6 (2021) 10-19.
- VK. Karra, PK. Gumma, SJ. Chowdhury, R. Ruttala, SK. Polipalli, A. Chakravarti, P. Kar, IL-18 polymorphisms in hepatitis B virus related liver disease, Cytokine. 73 (2015) 277-282, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.015. [CrossRef]
- K. Manohar, P.V. Suneetha, N.T. Sukriti, Pati, A.C. Gupta, S. Hissar, P. Sakhuja, P. and S.K.Sarin, Association of IL-18 promoter polymorphism with liver disease severity in HCV-infected patients, Hepatol. Int. 3 (2009) 371-377, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-009-9127-0. [CrossRef]
- N. Bouzgarrou, E. Hassen, E. Schvoerer, F. Stoll-Keller, O. Bahri, S. Gabbouj, I. Cheikh, N. Maamouri, N. Mammi, H. Saffar, A. Trabelsi, Association of interleukin-18 polymorphisms and plasma level with the outcome of chronic HCV infection, J. Med. Virol. 80 (2008) 607-614, https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.21079. [CrossRef]
- M. Harishankar, P. Selvaraj, DN. Rajeswari, SP. Anand, PR. Narayanan, Promoter polymorphism of IL-18 gene in pulmonary tuberculosis in South Indian population, Int. J. Immunogenet. 34 (2007) 317-320, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-313X.2007.00714.x. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhou, N. Ouyang, Q.H. Li, S.H. Luo, Q. He, S. Lei, H. and Q. Liu, The-137G/C single nucleotide polymorphism in IL-18 gene promoter contributes to tuberculosis susceptibility in Chinese Han population, Infect. Genet. Evol. 36 (2015) 76-380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2015.10.014. [CrossRef]
- M. Ponnana, R. Sivangala, L. Joshi, V. Valluri and S. Gaddam, IL-6 and IL-18 cytokine gene variants of pulmonary tuberculosis patients with co-morbid diabetes mellitus and their household contacts in Hyderabad, Gene. 627 (2017) 298-306, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.046. [CrossRef]
- Urazova, E.G. Churina, R.R. Hasanova, V.V. Novitskiy and V.S.Poletika, Association between polymorphisms of cytokine genes and secretion of IL-12p70, IL-18, and IL-27 by dendritic cells in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, Tuberculosis. 115 (2019) 56-62, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2019.02.003. [CrossRef]

| Infections | Population | SNPs | Location | Clinical impact | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visceral Leishmaniasis | Iranian 118 patients 156 controls |
rs1946519 (-656 G/T) rs187238 (-137 G/C) |
Promoter region | G allele at the position −656, a protective allele against VL. | [31]. |
| rs549908 (+105A/C) | Codon region | ||||
| Visceral Leishmaniasis | Indian 204 patients 267 controls |
rs1946519 (-656 G/T) rs187238 (-137 G/C) |
Promoter region | T allele at position−656, a protective against VL. | [30]. |
| rs549908 (+105A/C) | Codon region | ||||
| Visceral Leishmaniasis |
Iranian (East Azarbaijan) 91 patients, 185 controls |
rs1946518 (-607A/C) rs187238 (-137G/C) |
Promoter region | No significant association |
[32]. |
| Malaria | Saudi Arabian 250 patients 200 controls |
rs574429 (G to C) rs544354 (G to C) |
Promoter region | Increased susceptibility to P. falciparum infection and related parasitemia | [25]. |
| Severe malarial anemia (SMA) | Western Kenyan 123 patients 400 controls |
rs1946518 (-607C/A) rs187238 (-137G/C) |
Promoter region | −137G/−607C (GC) haplotype associated with increased susceptibility to SMA. −137C/−607C (CC) significantly associated with childhood mortality |
[68]. |
| Uncomplicated Malaria |
Nigerian 171 patients 166 controls |
rs1946518 (-607C/A) rs187238(-137G/C) |
Promoter region | No significant association |
[69]. |
| Chronic Chagas Disease |
Brazilian 849 patients 202 controls |
rs2043055 (A/G) | Promoter region |
No significant association |
[34]. |
| Intestinal amoebiasis |
Iraq 25 patients 25 controls |
rs1866694757(CC /CA) rs1946518(TT /TG) rs1946519(CC/AC) rs1215648807(AA /AC) |
Promoter region |
Increased susceptibility and associated with progression of E. histolytica infection |
[36]. |
| rs940255648 (GG /GC) rs1037707423 (CC /CT) rs1213044637 (GG /GA) rs1866697972 (GG /GT) rs1866698066 (GG /GT) rs1866698286 (AA /TT) |
Promoter region | Protection against progression of infection | |||
| HIV infection | Indian 500 patients 500 controls |
rs187238(-137G/C) | Promoter region |
Associated with the progression of HIV-1/AIDS | [38]. |
| HBV infection | Indian 271 patients 280 controls |
rs1946518(-607 A/C) rs187238(-137 C/G) |
Promoter region |
Allele A at position -607: a protective allele against HBV infection Allele C at position -137 is associated with increased susceptibility to HBV infections. |
[70]. |
| HBV infection | Chinese 376 patients 254 controls |
rs187238 (-137 G allele and GG genotype -137 G/C) |
Promotor region |
Protection against HBV infection |
[40]. |
| HBV infection | Chinese Han 231 patients 300 controls |
rs187238 (-137 G/C) rs1946518 (-607C/A) |
Promotor region | -137C allele protective against HBV infection -607AA genotype associated with increased susceptibility to HBV |
[41]. |
| HBV infection | Thailand 140 patients 140 controls |
rs1946518 (-607 A/A) |
Promotor region | Associated with progression of HBV infection. | [50]. |
| HBV infection | Korean 730 patients 320 controls |
rs1946519 (−667G>T) rs187238 (-148 G>C) |
Promotor region |
Associated with HBV clearance |
[56]. |
| rs360721 (+8925C>G) | Intron 1 | ||||
| rs549908 (+13925A>C) | Exon 4 | ||||
| HBV-related HCC* |
Chinese 153 Patients 165 controls |
rs1946518 (-607 C/A) rs187238 (-137 G/C) |
Promoter region | Protective allele against HBV-related HCC | [52]. |
| HCV infection |
Indian 204 Patients 350 controls |
rs1946518 (-607C/A) |
Promoter region | −607 position with A/A allele associated with protection against disease severity |
[71]. |
| HCV infection |
Tunisian 81 patients 82 controls |
rs187238 (-137G/C) | Promoter region | Associated with disease severity |
[72]. |
| Tuberculosis |
Indian 165 patients 173 controls |
rs1946518 (–607(C/A) rs187238 (–137G/A) |
Promoter region | No significant association |
[73]. |
| Tuberculosis | Chinese 407 patients 469 controls |
rs1946518 (–607(C/A) rs187238 (–137G/C) |
Promoter region | Increased susceptibility to tuberculosis | [74]. |
| Tuberculosis | Indian 505 patients 200 controls |
rs1946518 (–607(C/A) rs187238 (–137G/C) rs1800795 (-174G>C) |
Promoter region | AC genotype of IL-18 -607A>C increased susceptibility to PTB in the patients affected with co-morbid diabetes mellitus | [75]. |
| Tuberculosis | Russia 334 patients 183 Controls |
rs549908 (105C/A) | Promoter region | C allele and CC genotype of 105 A/C predisposes to the progression of disseminated TB |
[76]. |
| H-Pylori infection |
Korean 456 Patients 222 controls |
rs1946519 (−656 G/T) rs1946518 (−607 C/A) rs187238 (−137G/C) rs360718 (+113 T/G) rs360717 (+127 C/T) |
Promoter region |
−137G/C, 113T/G, +127C/T associated with protection against H. pylori infection | [66]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





