Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
04 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
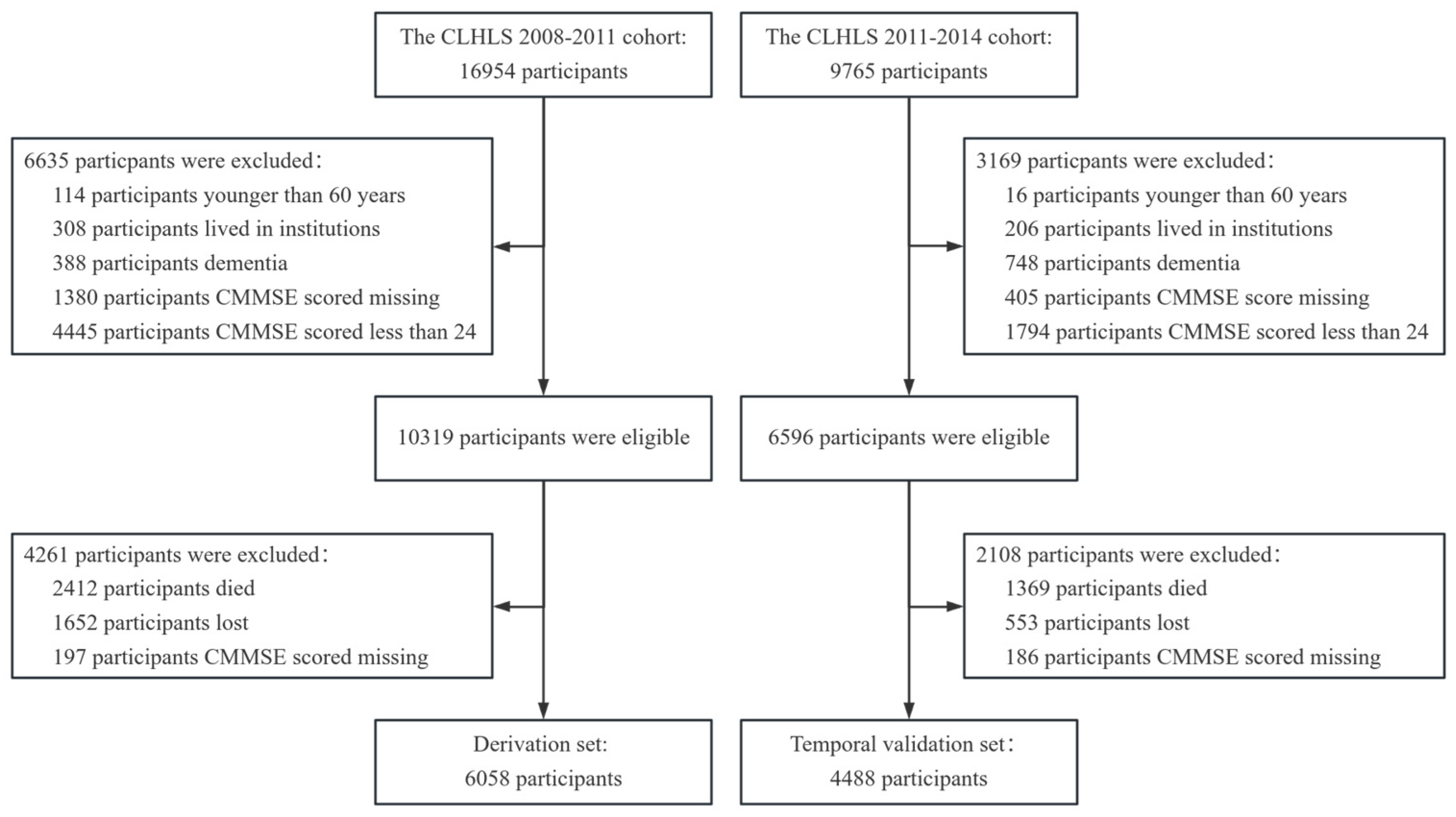
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Design and participants
2.3. Assessment of MCI
2.4. Definition of candidate variables
2.5. Sample size
2.6. Missing value
2.7. Statistical analysis
2.8. Model development and validation
3. Results
3.1. Participants
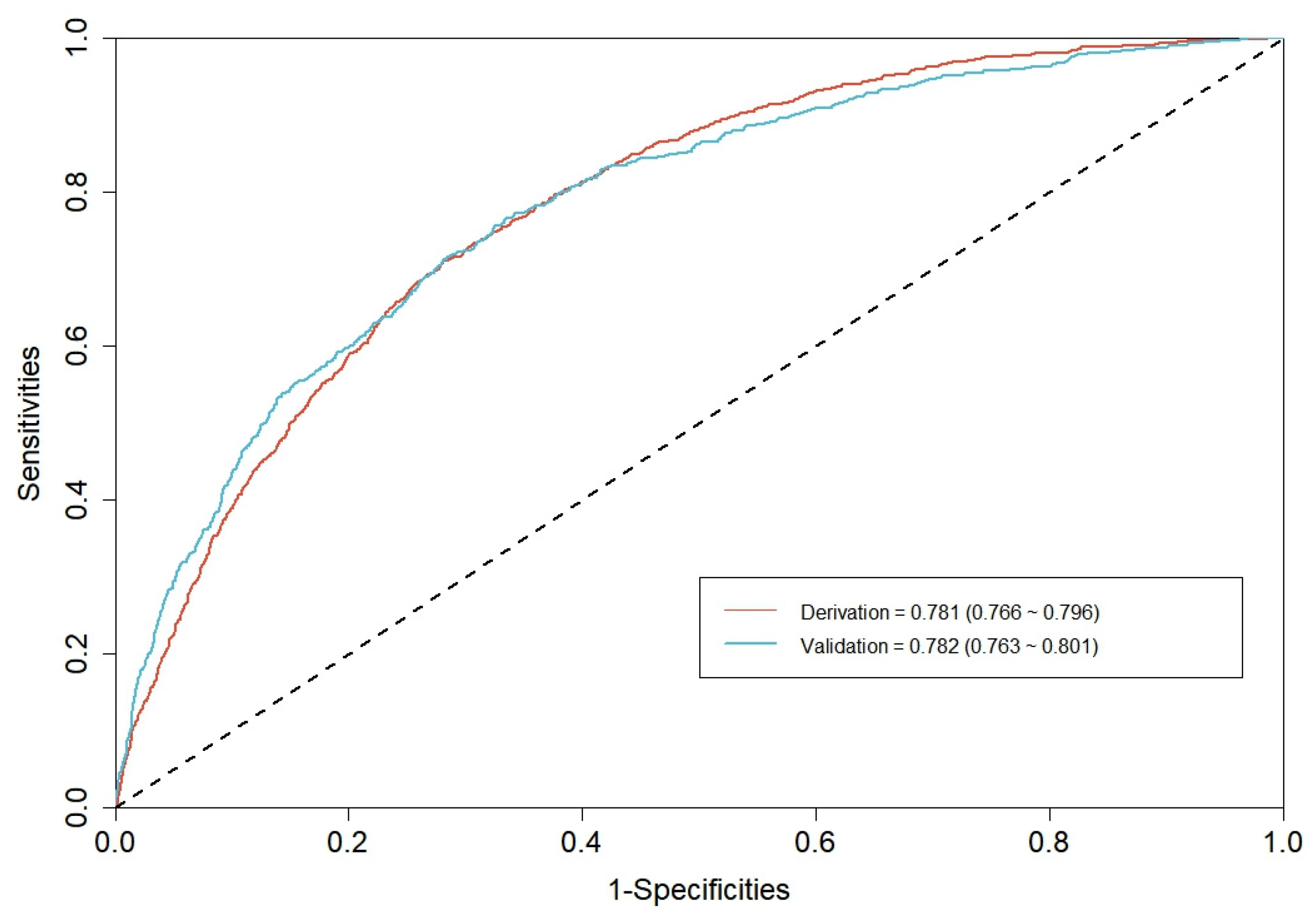
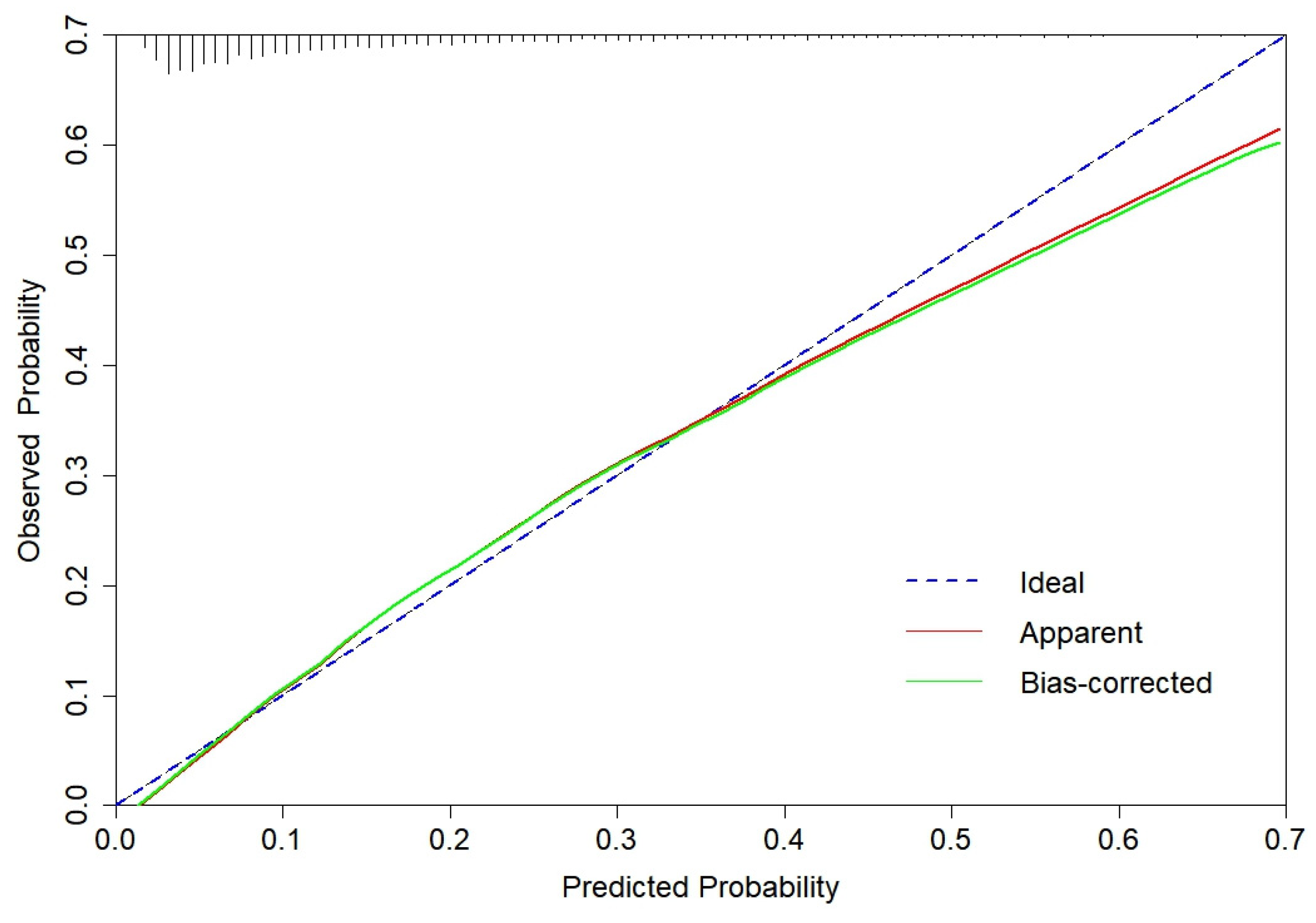
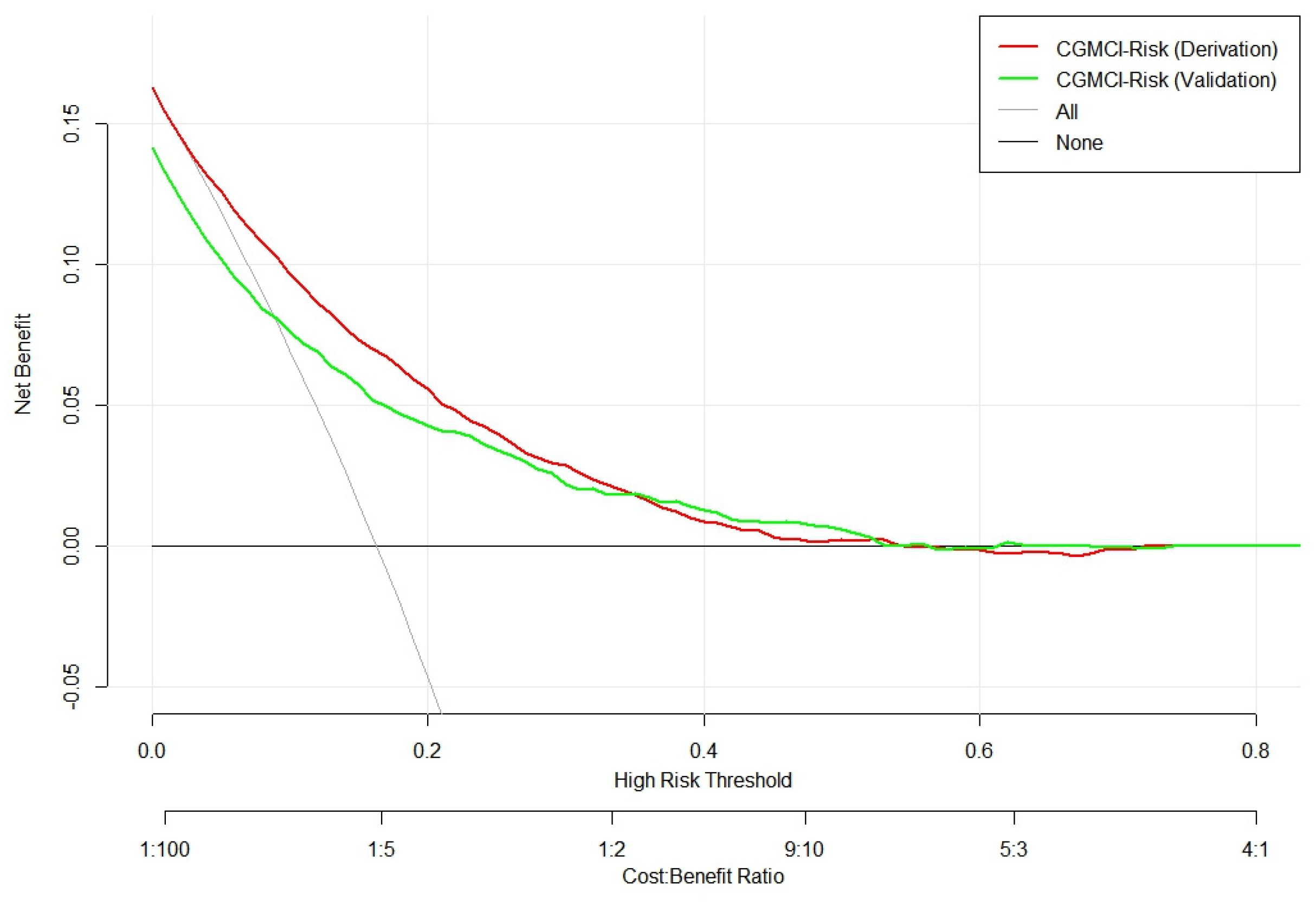
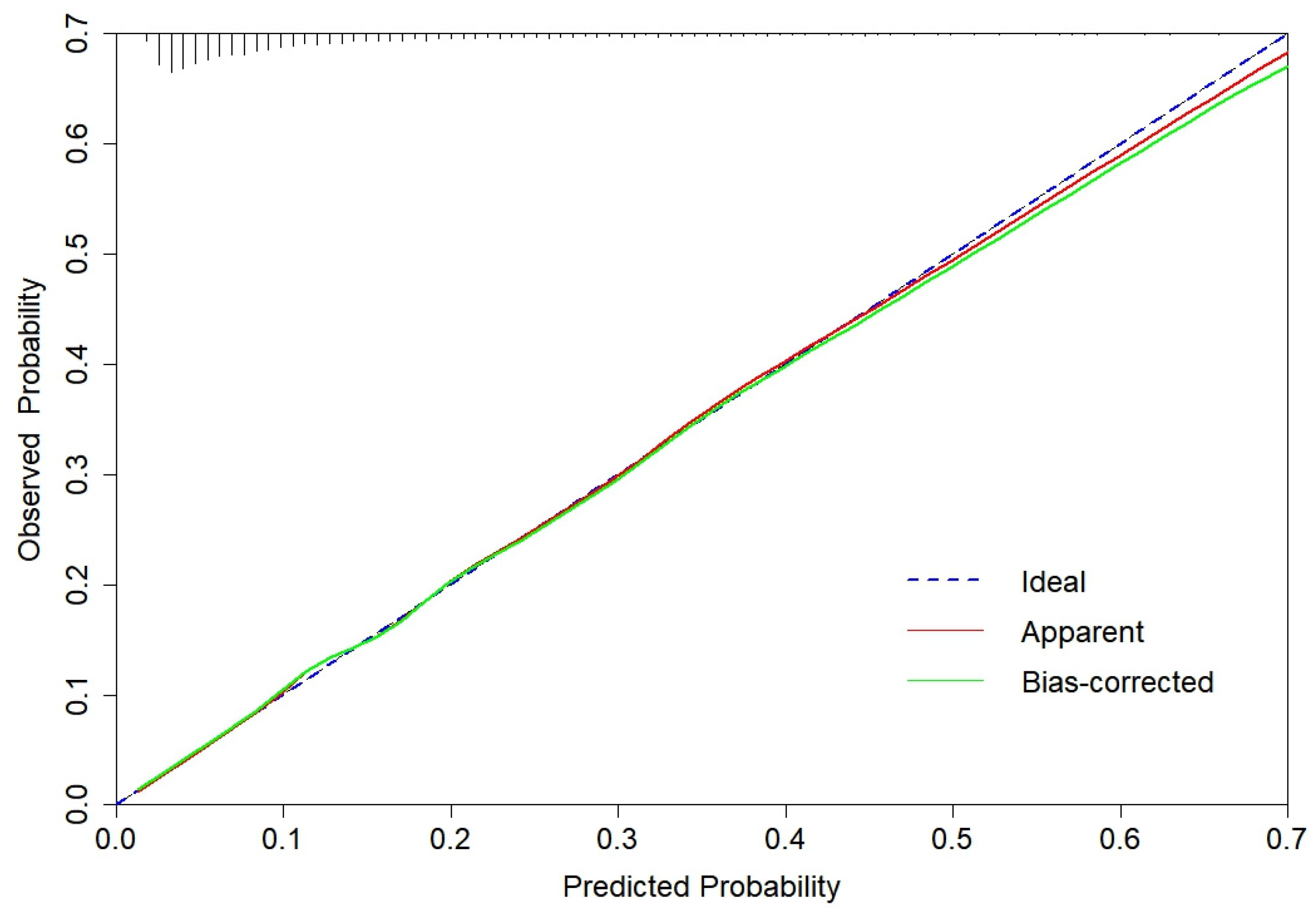
3.2. CGMCI-Risk development and validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajji, T.K. Transcranial Magnetic and Electrical Stimulation in Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics 2019, 106, 776-780. [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, T.; Dong, Y.; Han, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Grande, G.; Laukka, E.J.; Du, Y.; Qiu, C. Mild cognitive impairment among rural-dwelling older adults in China: A community-based study. Alzheimers Dement 2023, 19, 56-66. [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Chen, P.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Z.; Cheung, T.; Jackson, T.; Sha, S.; Xiang, Y.T. Worldwide prevalence of mild cognitive impairment among community dwellers aged 50 years and older: a meta-analysis and systematic review of epidemiology studies. Age and ageing 2022, 51, afac173. [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Du, Y.; Chu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jiao, H.; Song, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, M.; Wei, C.; Tang, Y.; Fang, B.; Guo, D.; Wang, F.; Zhou, A.; Chu, C.; Zuo, X.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Shi, S.; Yang, H.; Zhou, C.; Liao, Z.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Kan, M.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qin, W.; Jia, J.; COAST Group. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e661-e671. [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Reisberg, B.; Zaudig, M.; Petersen, R.C.; Ritchie, K.; Broich, K.; Belleville, S.; Brodaty, H.; Bennett, D.; Chertkow, H.; Cummings, J.L.; de Leon, M.; Feldman, H.; Ganguli, M.; Hampel, H.; Scheltens, P.; Tierney, M.C.; Whitehouse, P.; Winblad, B.; International Psychogeriatric Association Expert Conference on mild cognitive impairment. Mild cognitive impairment. Lancet 2006, 367, 1262-1270. [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Schneider, J.A.; Evans, D.A.; Beckett, L.A.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Barnes, L.L.; Fox, J.H.; Bach, J. Natural history of mild cognitive impairment in older persons. Neurology 2002, 59, 198-205. [CrossRef]
- Mapstone, M.; Steffenella, T.M.; Duffy, C.J. A visuospatial variant of mild cognitive impairment: getting lost between aging and AD. Neurology 2003, 60, 802-808. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Rong, M.; Long, X.; Lian, S.; Fang, Y. Trajectories of cognitive decline in different domains prior to AD onset in persons with mild cognitive impairment. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2024, 122, 105375. [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia: a clinical perspective. Mayo Clinic proceedings 2014, 89, 1452-1459. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Han, T.; Liu, E. Changes in Cognitive Function and Risk Factors for Cognitive Impairment of the Elderly in China: 2005-2014. International journal of environmental research and public health 2019, 16, 2847. [CrossRef]
- Kilander, L.; Nyman, H.; Boberg, M.; Lithell, H. Cognitive function, vascular risk factors and education. A cross-sectional study based on a cohort of 70-year-old men. Journal of internal medicine 1997, 242, 313-321. [CrossRef]
- Beker, N.; Ganz, A.; Hulsman, M.; Klausch, T.; Schmand, B.A.; Scheltens, P.; Sikkes, S.A.M.; Holstege, H. Association of Cognitive Function Trajectories in Centenarians with Postmortem Neuropathology, Physical Health, and Other Risk Factors for Cognitive Decline. JAMA network open 2021, 4, e2031654. [CrossRef]
- Spiers, N.A.; Matthews, R.J.; Jagger, C.; Matthews, F.E.; Boult, C.; Robinson, T.G.; Brayne, C. Diseases and impairments as risk factors for onset of disability in the older population in England and Wales: findings from the Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences 2005, 60, 248-254. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yeom, H. Threshold effects of body mass index on cognitive function and heterogeneity by sex and cardiovascular risk factors. Frontiers in public health 2022, 10, 897691. [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Wurster, I.; Lerche, S.; Roeben, B.; Machetanz, G.; Sünkel, U.; von Thaler, A.K.; Eschweiler, G.; Fallgatter, A.J.; Maetzler, W.; Berg, D.; Brockmann, K. Orthostatic hypotension as a risk factor for longitudinal deterioration of cognitive function in the elderly. European journal of neurology 2020, 27, 160-167. [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Hao, J.; Wang, N. Visual impairment as a risk factor of cognitive function impairment A six-year cohort study. European journal of ophthalmology 2023, 33, 2146-2153. [CrossRef]
- AAn, Y.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, S.A.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.M.; Lee, T.K.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.D. Association of Hearing Loss with Anatomical and Functional Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. JAMA otolaryngology-head & neck surgery 2023, 149, 571-578. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jin, X.; Yan, J.; Jin, Y.; Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, W.; Zheng, P. Comparison of prevalence and associated risk factors of cognitive function status among elderly between nursing homes and common communities of China: A STROBE-compliant observational study. Medicine 2019, 98, e18248. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Hong, H.; Joo, M.; Kang, H. A Non-Randomized Combined Program of Walking and Low-Load Resistance Exercise Improves Cognitive Function and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Community-Dwelling Elderly Women. Healthcare (Basel) 2022, 10, 2106. [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, C.; Apostolopoulou, K.; Hornemann, S.; Efthymiou, A.; Machann, J.; Schmidt, S.; Primessnig, U.; Bergmann, M.M.; Grune, T.; Gerbracht, C.; Herber, K.; Pohrt, A.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Spranger, J.; Mai, K. Long-term effects of a food pattern on cardiovascular risk factors and age-related changes of muscular and cognitive function. Medicine 2020, 99, e22381. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Liang, J.; Matthews, A.K.; Barnes, L.L. Trajectories of Multiple Behavioral Risk Factors and Their Associations with Cognitive Function Trajectories Among Older African Americans and White Americans. Journal of aging and health 2021, 33, 674-684. [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Huang, L.; Lin, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Xiao, Q. Sex steroid and cognitive function among community-dwelling older men with or without vascular risk factors: a cross-sectional study. BMC geriatrics 2024, 24, 147. [CrossRef]
- Noma, T.; Kayo, G.; Kabayama, M.; Gondo, Y.; Yasumoto, S.; Masui, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Akasaka, H.; Takami, Y.; Takeya, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikebe, K.; Arai, Y.; Ishizaki, T.; Rakugi, H.; Kamide, K. Lower cognitive function as a risk factor for anemia among older Japanese women from the longitudinal observation in the SONIC study. Geriatrics & gerontology international 2023, 23, 334-340. [CrossRef]
- Ferri, F.; Deschênes, S.S.; Power, N.; Schmitz, N. Association between depressive symptoms, metabolic risk factors, and cognitive function: cross-sectional results from a community study in Quebec, Canada. Aging & mental health 2021, 25, 2003-2010. [CrossRef]
- Gui, W.; Qiu, C.; Shao, Q.; Li, J. Associations of Vascular Risk Factors, APOE and TOMM40 Polymorphisms with Cognitive Function in Dementia-Free Chinese Older Adults: A Community-Based Study. Frontiers in psychiatry 2021, 12, 617773. [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.; Royston, P.; Vergouwe, Y.; Grobbee, D.E.; Altman, D.G. Prognosis and prognostic research: what, why, and how? BMJ 2009, 338, b375. [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, R.; Dong, C.; Gu, Z.; Gao, J. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting mild cognitive impairment in middle-aged and elderly people. Asian journal of psychiatry 2022, 75, 103224. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, W.; Lu, L.; Li, H.; Ding, J.; Sheng, S.; Liu, M.; Yuan, J. Developing and validating a nomogram for cognitive impairment in the older people based on the NHANES. Frontiers in neuroscience 2023, 17, 1195570. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yu, J.; Jiang, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Teng, J.; Jiao, H. A risk prediction model based on machine learning for early cognitive impairment in hypertension: Development and validation study. Frontiers in public health 2023, 11, 1143019. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, H. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for mild cognitive impairment in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Geriatric Nursing 2024, 58, 119-126. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ding, M.; Cui, M.; Fang, M.; Gong, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Q. Development and validation of a clinical model (DREAM-LDL) for post-stroke cognitive impairment at 6 months. Aging 2021, 13, 21628-21641. [CrossRef]
- Momota, Y.; Bun, S.; Hirano, J.; Kamiya, K.; Ueda, R.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Takahata, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tezuka, T.; Kubota, M.; Seki, M.; Shikimoto, R.; Mimura, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Tabuchi, H.; Jinzaki, M.; Ito, D.; Mimura, M. Amyloid-β prediction machine learning model using source-based morphometry across neurocognitive disorders. Scientific reports 2024, 14, 7633. [CrossRef]
- Pase, M.P.; Beiser, A.S.; Himali, J.J.; Satizabal, C.L.; Aparicio, H.J.; DeCarli, C.; Chêne, G.; Dufouil, C.; Seshadri, S. Assessment of Plasma Total Tau Level as a Predictive Biomarker for Dementia and Related Endophenotypes. JAMA neurology 2019, 76, 598-606. [CrossRef]
- Betrouni, N.; Jiang, J.; Duering, M.; Georgakis, M.K.; Oestreich, L.; Sachdev, P.S.; O'Sullivan, M.; Wright, P.; Lo, J.W.; Bordet, R.; Stroke and Cognition (STROKOG) Collaboration. Texture Features of Magnetic Resonance Images Predict Poststroke Cognitive Impairment: Validation in a Multicenter Study. Stroke 2022, 53, 3446-3454. [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Huang, M.; Xu, W. Mitochondria-Related Candidate Genes and Diagnostic Model to Predict Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Journal of Alzheimer's disease 2024, 99, S299-S315. [CrossRef]
- Center for Healthy Aging and Development Studies. Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity and Happy Family Study (CLHLS-HF). Available online: https://opendata.pku.edu.cn/dataverse/CHADS (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): the TRIPOD statement. BMJ 2015, 350, g7594. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhen, Z.; Gu, D. Self-Rated Health, Interviewer-Rated Health, and Their Predictive Powers on Mortality in Old Age. The journals of gerontology. Series B, Psychological sciences and social sciences 2016, 71, 538-550. [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, T.J.; Mallin, R.; Still, C.N. Recognition of cognitive impairment in primary care outpatients. Southern medical journal 1983, 76, 1264-1265, 1270. [CrossRef]
- Belessiotis-Richards, C.; Livingston, G.; Marston, L.; Mukadam, N. A cross-sectional study of potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia and cognitive function in India: A secondary analysis of 10/66, LASI, and SAGE data. International journal of geriatric psychiatry 2021, 37, 5661. [CrossRef]
- Dale, W.; Kotwal, A.A.; Shega, J.W.; Schumm, L.P.; Kern, D.W.; Pinto, J.M.; Pudelek, K.M.; Waite, L.J.; McClintock, M.K. Cognitive Function and its Risk Factors Among Older US Adults Living at Home. Alzheimer disease and associated disorders 2018, 32, 207-213. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.W.; Yen, H.K.; Lin, Y.P.; Lai, C.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Groot, O.Q.; Janssen, S.J.; Schwab, J.H.; Hsu, F.M.; Lin, W.H. Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients with Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Ensor, J.; Snell, K.I.E.; Harrell, F.E.Jr.; Martin, G.P.; Reitsma, J.B.; Moons, K.G.M.; Collins, G.; van Smeden, M. Calculating the sample size required for developing a clinical prediction model. BMJ 2020, 368, m441. [CrossRef]
- Andridge, R.R.; Little, R.J.A. A Review of Hot Deck Imputation for Survey Non-response. International statistical review 2010, 78, 40-64. [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. Journal of thoracic oncology 2010, 5, 1315-1316. [CrossRef]
- Van Calster, B.; McLernon, D.J.; van Smeden, M.; Wynants, L.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Topic Group ‘Evaluating diagnostic tests and prediction models’ of the STRATOS initiative. Calibration: the Achilles heel of predictive analytics. BMC medicine 2019, 17, 230. [CrossRef]
- Van Calster, B.; Wynants, L.; Verbeek, J.F.M.; Verbakel, J.Y.; Christodoulou, E.; Vickers, A.J.; Roobol, M.J.; Steyerberg, E.W. Reporting and Interpreting Decision Curve Analysis: A Guide for Investigators. European urology 2018, 74, 796-804. [CrossRef]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Cook, N.R.; Gerds, T.; Gonen, M.; Obuchowski, N.; Pencina, M.J.; Kattan, M.W. Assessing the performance of prediction models: a framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 128-138. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.; Saville, B.R.; Lewis, R.J. Decision curve analysis. JAMA 2015, 313, 409-410. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, J.; Ma, C.; Chen, K.; Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Z. Accelerating Structural Degeneration in Temporal Regions and Their Effects on Cognition in Aging of MCI Patients. Cerebral cortex 2020, 30, 326-338. [CrossRef]
- Yesavage, J.A.; O'Hara, R.; Kraemer, H.; Noda, A.; Taylor, J.L.; Ferris, S.; Gély-Nargeot, M.C.; Rosen, A.; Friedman, L.; Sheikh, J.; Derouesné, C. Modeling the prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Journal of psychiatric research 2002, 36, 281-286. [CrossRef]
- Au, B.; Dale-McGrath, S.; Tierney, M.C. Sex differences in the prevalence and incidence of mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Ageing research reviews 2017, 35, 176-199. [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Bian, L.; Ning, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Ping, P.; Fu, S. Positive associations between sex hormones, bone metabolism and cognitive impairment in Chinese oldest-old females. BMC psychiatry 2023, 23, 562. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Paranjpe, M.D.; Zhou, X.; Duy, P.Q.; Goyal, M.S.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Lu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y. Sex modulates the ApoE ε4 effect on brain tau deposition measured by (18)F-AV-1451 PET in individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4959-4970. [CrossRef]
- Raine, P.J.; Rao, H. Volume, density, and thickness brain abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment: an ALE meta-analysis controlling for age and education. Brain imaging and behavior 2022, 16, 2335-2352. [CrossRef]
- Rolstad, S.; Nordlund, A.; Eckerström, C.; Gustavsson, M.H.; Blennow, K.; Olesen, P.J.; Zetterberg, H.; Wallin, A. High education may offer protection against tauopathy in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Alzheimer's disease 2010, 21, 221-228. [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Katzman, R.; Losonczy, K.; Salive, M.; Wallace, R.; Berkman, L.; Taylor, J.; Fillenbaum, G.; Havlik, R. Association of education with incidence of cognitive impairment in three established populations for epidemiologic studies of the elderly. Journal of clinical epidemiology 1994, 47, 363-374. [CrossRef]
- Kiosses, D. N.; Alexopoulos, G.S. IADL functions, cognitive deficits, and severity of depression: a preliminary study. American journal of geriatric psychiatry 2005, 13, 244-249.
- Lee, J.J.; Park, M.K.; Kim, N.; Kim, L.; Kim, G.S. Longitudinal Relationship Between Baseline Social Frailty and Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: 14-Year Follow-Up Results From the Korean Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2024, 25, 105124. [CrossRef]
- Al-Yawer, F.; Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; Wittich, W.; Mick, P.; Giroud, N.; Rehan, S.; Phillips, N.A. Sex-Specific Interactions Between Hearing and Memory in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: Findings From the COMPASS-ND Study. Ear and hearing 2023, 44, 751-767. [CrossRef]
- Loughrey, D.G.; Kelly, M.E.; Kelley, G.A.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A. Association of Age-Related Hearing Loss with Cognitive Function, Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA otolaryngology-head & neck surgery 2018, 144, 115-126. [CrossRef]
- Marito, P.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tamaki, K.; Sta Maria, M.T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Kusunoki, H.; Tsuji, S.; Wada, Y.; Ono, T.; Sawada, T.; Kishimoto, H.; Shinmura, K. The Association of Dietary Intake, Oral Health, and Blood Pressure in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1279. [CrossRef]
- Momose, T.; Nishikawa, J.; Watanabe, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Senda, M.; Kubota, K.; Sato, Y.; Funakoshi, M.; Minakuchi, S. Effect of mastication on regional cerebral blood flow in humans examined by positron-emission tomography with ¹⁵O-labelled water and magnetic resonance imaging. Archives of oral biology 1997, 42, 57-61. [CrossRef]
- Onozuka, M.; Fujita, M.; Watanabe, K.; Hirano, Y.; Niwa, M.; Nishiyama, K.; Saito, S. Mapping brain region activity during chewing: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of dental research 2002, 81, 743-746. [CrossRef]
- Kossioni, A.E. The Association of Poor Oral Health Parameters with Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Review Considering the Potential Implications for Cognitive Impairment. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1079. [CrossRef]
- Lexomboon, D.; Trulsson, M.; Wårdh, I.; Parker, M.G. Chewing ability and tooth loss: association with cognitive impairment in an elderly population study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2012, 60, 1951-1956. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, F.; Luo, Y. Relationship Between Physical Exercise and Cognitive Function Among Older Adults in China: Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study. JMIR public health and surveillance 2024, 10, e49790. [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Park, J. Effects of Changes in Physical Activity with Cognitive Decline in Korean Home-Dwelling Older Adults. Journal of multidisciplinary healthcare 2022, 15, 333-341. [CrossRef]
- Blume, G. R.; Royes, L.F.F. Peripheral to brain and hippocampus crosstalk induced by exercise mediates cognitive and structural hippocampal adaptations. Life sciences 2024, 352, 122799. [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.J.; Tschakovsky, M.E. Exercise and circulating BDNF: Mechanisms of release and implications for the design of exercise interventions. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism 2018, 43, 1095-1104. [CrossRef]
- Vedovelli, K.; Giacobbo, B.L.; Corrêa, M.S.; Wieck, A.; Argimon, I.I.L.; Bromberg, E. Multimodal physical activity increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and improves cognition in institutionalized older women. GeroScience 2017, 39, 407-417. [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Doi, T.; Lee, S.; Makizako, H. Reversible predictors of reversion from mild cognitive impairment to normal cognition: a 4-year longitudinal study. Alzheimer's research & therapy 2019, 11, 24. [CrossRef]
- Jarrott, S.E.; Gigliotti, C.M. Comparing Responses to Horticultural-Based and Traditional Activities in Dementia Care Programs. American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Other Dementias 2010, 25, 657-665. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.A.; Lee, A.Y.; Park, H.G.; Lee, W.L. Benefits of Gardening Activities for Cognitive Function According to Measurement of Brain Nerve Growth Factor Levels. International journal of environmental research and public health 2019, 16, 760. [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Yin, W.; Yuan, D. Association of home and community-based services and cognitive function of Chinese older adults: social participation as a mediator. BMC geriatrics 2023, 23, 691. [CrossRef]
- Major, L.; Simonsick, E.M.; Napolitano, M.A.; DiPietro, L. Domains of Sedentary Behavior and Cognitive Function: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study, 1999/2000 to 2006/2007. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences 2023, 78, 2035-2041. [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.S.; Chung, E. Television Viewing and Cognitive Dysfunction of Korean Older Adults. Healthcare (Basel) 2020, 8, 547. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Dementia Fact sheets on 15 March 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Gelosa, G.; Brooks, D.J. The prognostic value of amyloid imaging. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2012, 39, 1207-1219. [CrossRef]
- Patnode, C.D.; Perdue, L.A.; Rossom, R.C.; Rushkin, M.C.; Redmond, N.; Thomas, R.G.; Lin, J.S. Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2020, 323, 764-785. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



