Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
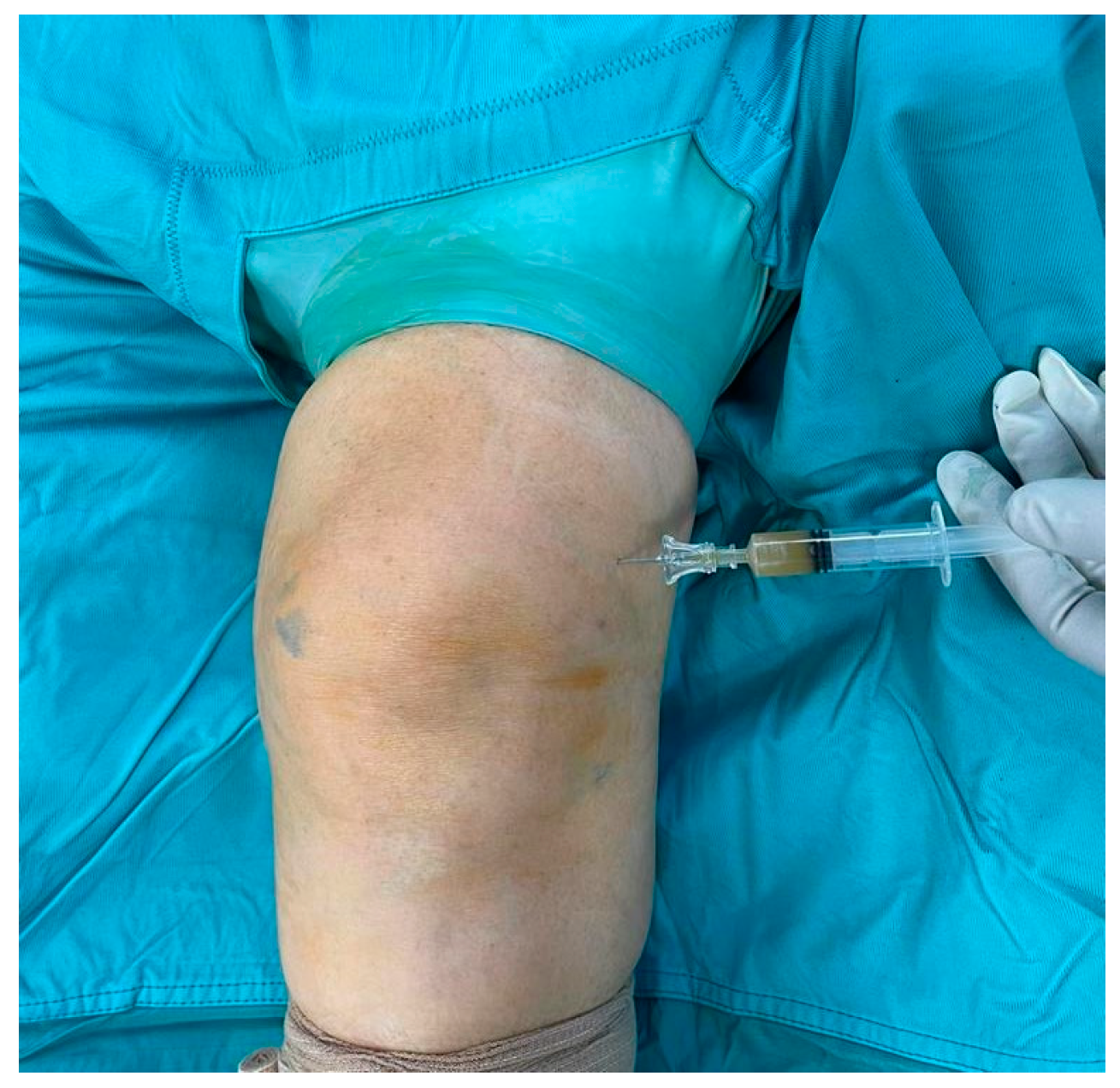
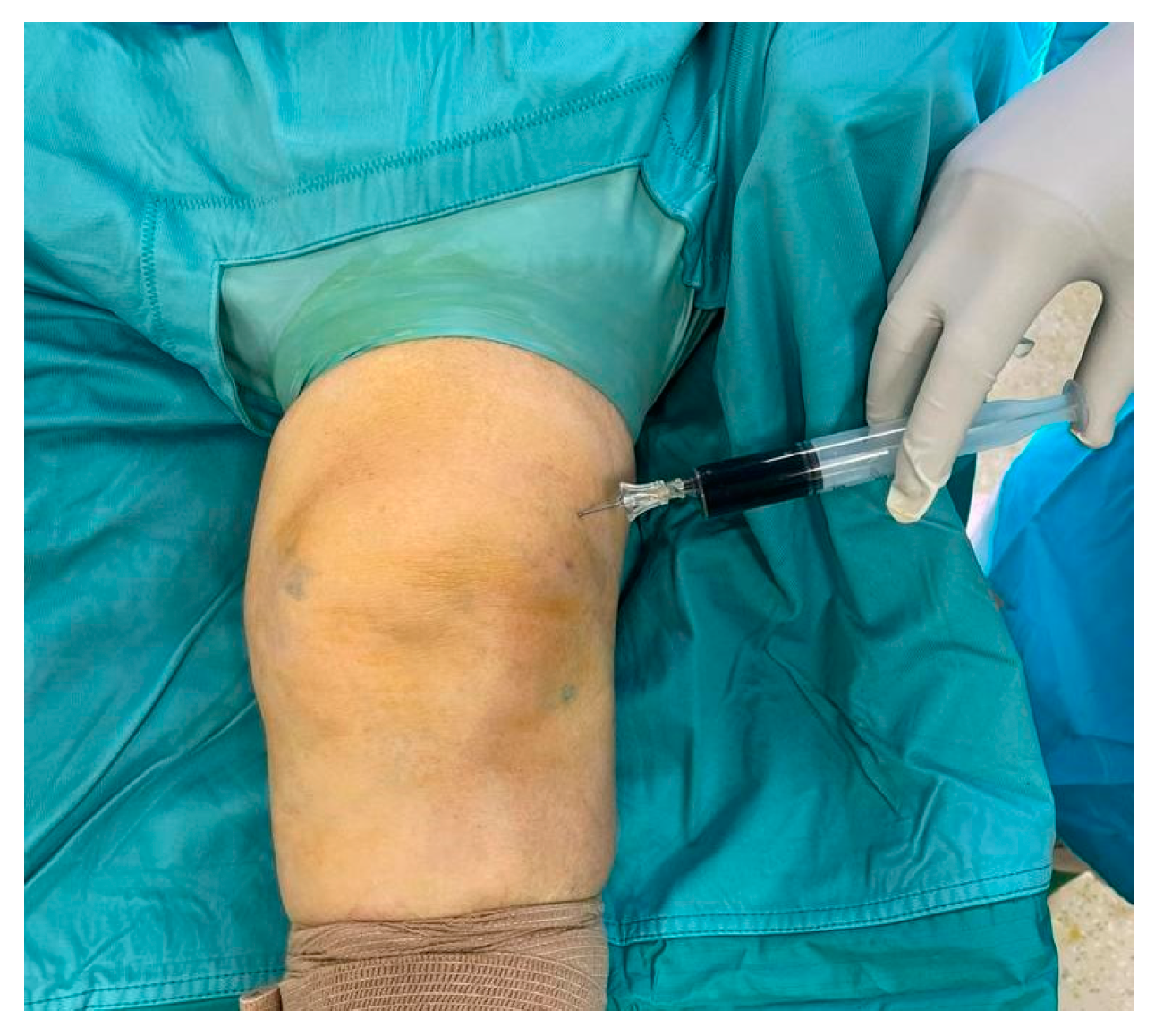
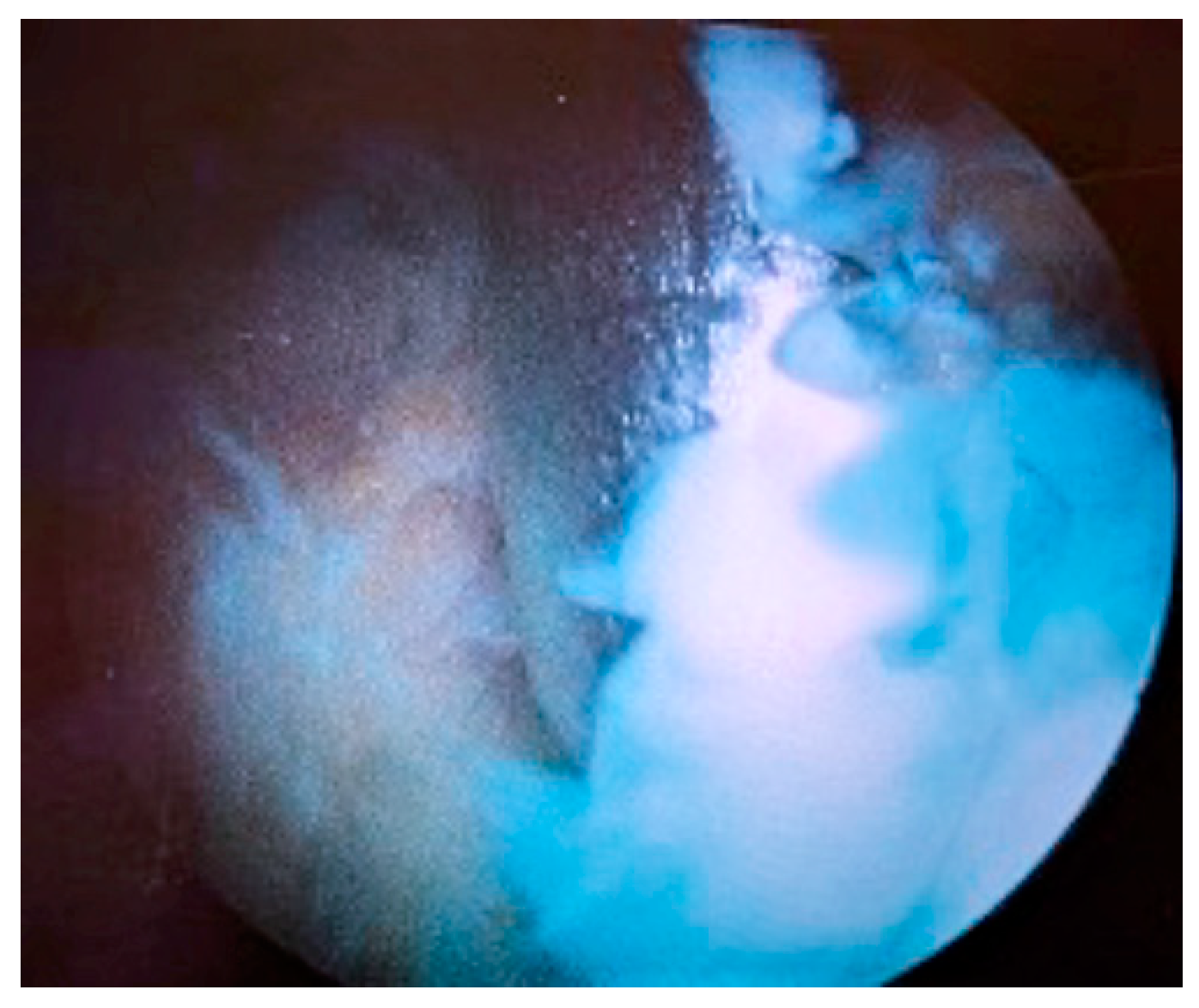
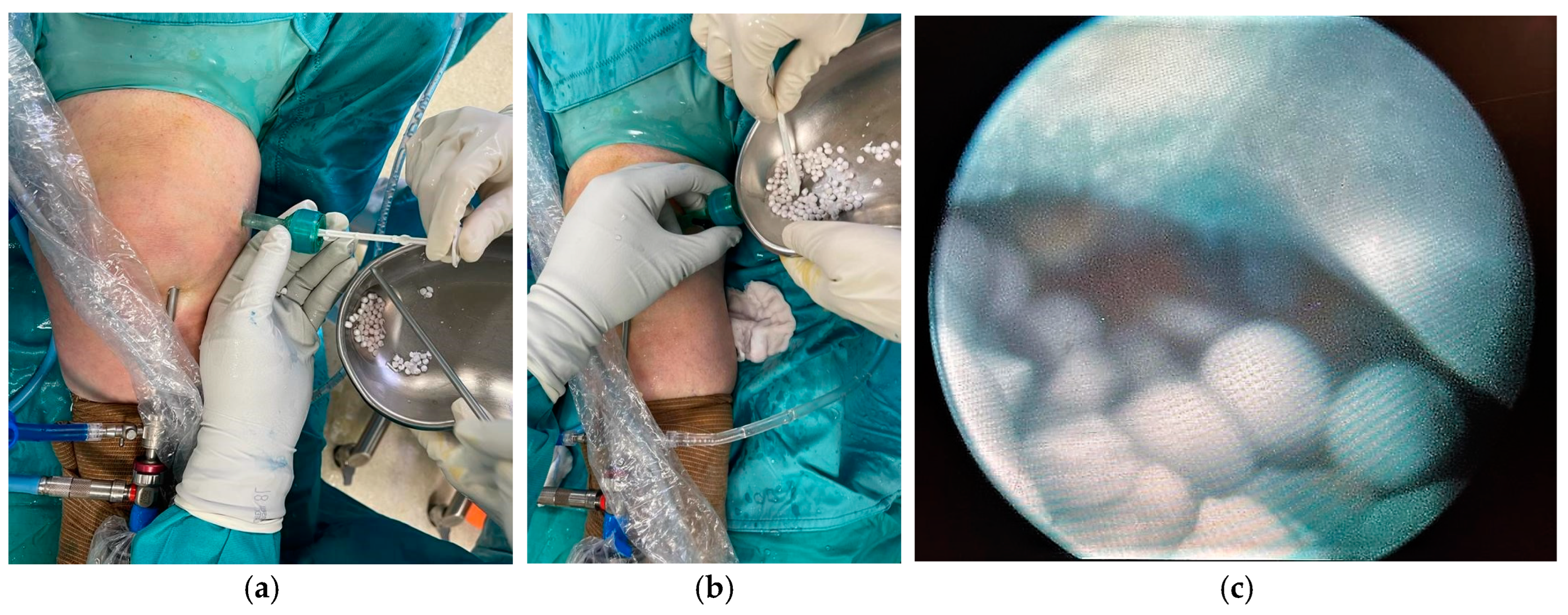
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Z.; Deng, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Similar Efficacy of Arthroscopy and Arthrotomy in Infection Eradication in the Treatment of Septic Knee : A Systematic Review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Surgery 2022, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franco, C.; Artiaco, S.; De Matteo, V.; Bistolfi, A.; Balato, G.; Vallefuoco, S.; Massè, A.; Rosa, D. The Eradication Rate of Infection in Septic Knee Arthritis According to the Gächter Classification: A Systematic Review. Orthopedic Reviews 2022, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, C.; Félix, O.; Cavazos, V.; Blázquez, J.; Gregorio, S.; Villarreal, V. Comparison of Open Arthrotomy versus Arthroscopic Surgery for the Treatment of Septic Arthritis in Adults : A Systematic Review and Meta - Analysis. Int Orthop 2021, 45, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darraj, H.; Hakami, K.M.; Zogel, B.; Maghrabi, R.; Khired, Z. Septic Arthritis of the Knee in Children. Cureus 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larghi, M.M.; Grassi, M.; Placenza, E.; Faugno, L.; Cerveri, P.; Manzotti, A. Septic Arthritis Following Joint Injections : A 17 Years Retrospective Study in an Academic General Hospital. Acta Bio Medica: Atenei Parmensis 2021, 92, e2021308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.J. Septic Arthritis of Native Joints. Infect Dis Clin N Am 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubost, J.J.; Couderc, M.; Tatar, Z.; Tournadre, A.; Lopez, J.; Mathieu, S.; Soubrier, M. Three-Decade Trends in the Distribution of Organisms Causing Septic Arthritis in Native Joints: Single-Center Study of 374 Cases. Joint Bone Spine 2014, 81, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.; Zhou, A.; Abbas, H.; Azeem, H.; Matija, T. Risk Factors for Septic Arthritis and Multiple Arthroscopic Washouts : Minimum 2 - Year Follow - up at a Major Trauma Centre. Clin Rheumatol 2022, 41, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momodu, I.I.; Savaliya, V. Septic Arthritis. StatPearls 2023.
- Margaretten, M.E.; Kohlwes, J.; Moore, D.; Bent, S. Does This Adult Patient Have Septic Arthritis? JAMA 2007, 297, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.S.; Rao, A.; Manadan, A.M.; Block, J.A. Peripheral Bacterial Septic Arthritis: Review of Diagnosis and Management. J Clin Rheumatol 2017, 23, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, D.L.; Katzap, E.; Horowitz, S.; Barilla-LaBarca, M.-L. Approach to Septic Arthritis. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 84, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gamie, Z.; Karthikappallil, D.; Gamie, E.; Stamiris, S.; Kenanidis, E.; Tsiridis, E. Molecular Sequencing Technologies in the Diagnosis and Management of Prosthetic Joint Infections. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2022, 22, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullar, R.; Chisari, E.; Snyder, J.; Cooper, C.; Parvizi, J.; Sniffen, J. Next-Generation Sequencing Supports Targeted Antibiotic Treatment for Culture Negative Orthopedic Infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2023, 76, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjwani, T.; Wong, K.L.; Tan, S.H.S.; Liau, G.; Vaidya, N.; Krishna, L. Arthroscopic Debridement Has Lower Re-Operation Rates than Arthrotomy in the Treatment of Acute Septic Arthritis of the Knee: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of ISAKOS 2019, 4, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, G.; Kuster, M.S.; Kleinstück, F.; Gächter, A. Arthroscopic Management of Septic Arthritis: Stages of Infection and Results. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2000, 8, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaechter, A. Arthroscopic Lavage for Joint Infections. Orthopedics and Traumatology 1993, 2, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateschrang, A.; Albrecht, D.; Schröter, S.; Hirt, B.; Weise, K.; Dolderer, J.H. Septic Arthritis of the Knee: Presentation of a Novel Irrigation-Suction System Tested in a Cadaver Study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2011, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.D.; Miller, S.; Plourde, A.; Shaw, D.L.; Wustrack, R.; Hansen, E.N. Methylene Blue-Guided Debridement as an Intraoperative Adjunct for the Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J Arthroplasty 2017, 32, 3718–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosala, A.; Ali, M. The Use of Calcium Sulphate Beads in Periprosthetic Joint Infection, a Systematic Review. J Bone Jt Infect 2020, 5, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereddy, P.; Nallamilli, S.R.; Gowda, V.P.; Kasha, S.; Godey, S.K.; Nallamilli, R.R.; Gprk, R.; Meda, V.G.R. The Use of Stimulan in Bone and Joint Infections. Bone Jt Open 2023, 4, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J. Combination Therapy with Vancomycin-Loaded Calcium Sulfate and Vancomycin-Loaded PMMA in the Treatment of Chronic Osteomyelitis. BMC musculoskeletal disorders 2016, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gächter, A. Der Gelenkinfekt. Inform Arzt 1985, 6, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.D.; Miller, S.; Plourde, A.; Shaw, D.L.; Wustrack, R.; Hansen, E.N. Methylene Blue–Guided Debridement as an Intraoperative Adjunct for the Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Journal of Arthroplasty 2017, 32, 3718–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanna, F.; Chen, F.; Risitano, S.; Vorhies, J.S.; Franceschini, M.; Giori, N.J.; Indelli, P.F. Debridement, Antibiotic Pearls, and Retention of the Implant (DAPRI): A Modified Technique for Implant Retention in Total Knee Arthroplasty PJI Treatment. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2019, 27, 2309499019874413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, H.W.; Engelbrecht, H. Depot effects of various antibiotics mixed with Palacos resins. Chirurg 1970, 41, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lun, D.; Li, S.; Li, N.; Mou, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Hu, Y. Limitations and Modifications in the Clinical Application of Calcium Sulfate. Front Surg 2024, 11, 1278421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steadman, W.; Chapman, P.R.; Schuetz, M.; Schmutz, B.; Trampuz, A.; Tetsworth, K. Local Antibiotic Delivery Options in Prosthetic Joint Infection. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosala, A.; Ali, M. The Use of Calcium Sulphate Beads in Periprosthetic Joint Infection, a Systematic Review. J Bone Jt Infect 2020, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ene, R.; Nica, M.; Ene, D.; Cursaru, A.; Cirstoiu, C. Review of Calcium-Sulphate-Based Ceramics and Synthetic Bone Substitutes Used for Antibiotic Delivery in PJI and Osteomyelitis Treatment. EFORT Open Rev 2021, 6, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, G.A.; Falk, D.P.; Fragomen, A.T.; Rozbruch, S.R. Calcium Sulfate in the Management of Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. Medicine 2022, 101, e31364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, A.I.; Okroj, K.T.; Rogers, T.; Della Valle, C.J.; Sporer, S.M. Systemic Absorption of Antibiotics From Antibiotic-Loaded Cement Spacers for the Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J Arthroplasty 2018, 33, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaratnam, V.; Roche, A.; Narayan, B.; Giotakis, N.; Mukhopadhaya, S.; Aniq, H.; Nayagam, S. Effectiveness of an Antibiotic-Impregnated Bioabsorbable Carrier for the Treatment of Chronic Intramedullary and Diffuse Osteomyelitis. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2023, 18, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, J.; Vander Voort, W.; Willey, M.; Sekar, P. A Case of Histoplasma Capsulatum Variety Capsulatum Septic Arthritis Successfully Treated with Surgery, Systemic Antifungals, and Local Amphotericin Cement Beads. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2018, 77, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowie, R.M.; Jennings, L.M. Third Body Damage and Wear in Arthroplasty Bearing Materials: A Review of Laboratory Methods. Biomaterials and biosystems 2021, 4, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowie, R.M.; Aiken, S.S.; Cooper, J.J.; Jennings, L.M. The Influence of a Calcium Sulphate Bone Void Filler on the Third-Body Damage and Polyethylene Wear of Total Knee Arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res 2019, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.M.; Carbone, S.; Aiken, S.; Cooper, J.J.; Jennings, L.M. Influence of Third-Body Particles Originating from Bone Void Fillers on the Wear of Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2016, 230, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudareva, M.; Kümin, M.; Vach, W.; Kaier, K.; Ferguson, J.; McNally, M.; Scarborough, M. Short or Long Antibiotic Regimes in Orthopaedics (SOLARIO): A Randomised Controlled Open-Label Non-Inferiority Trial of Duration of Systemic Antibiotics in Adults with Orthopaedic Infection Treated Operatively with Local Antibiotic Therapy. Trials 2019, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
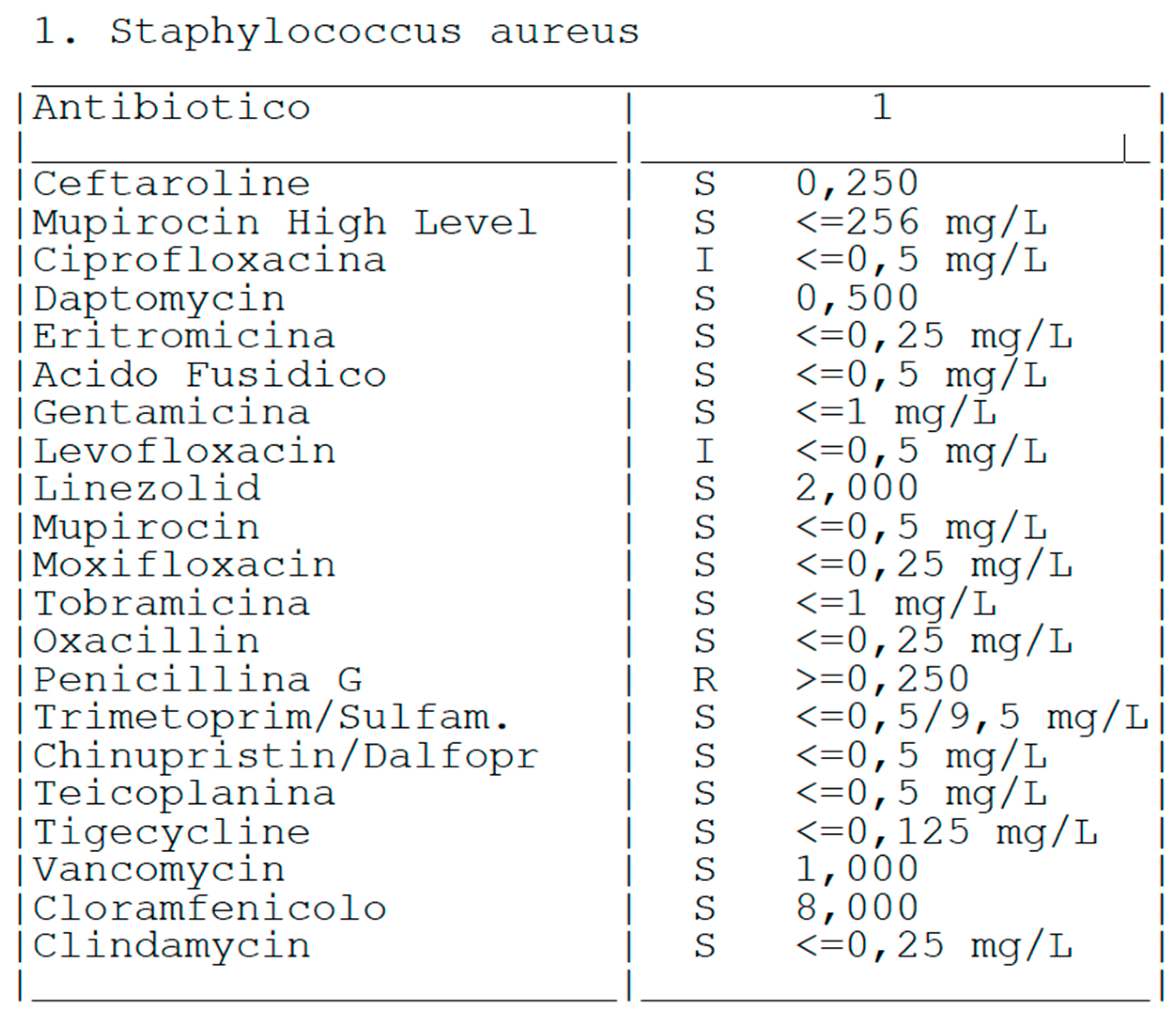
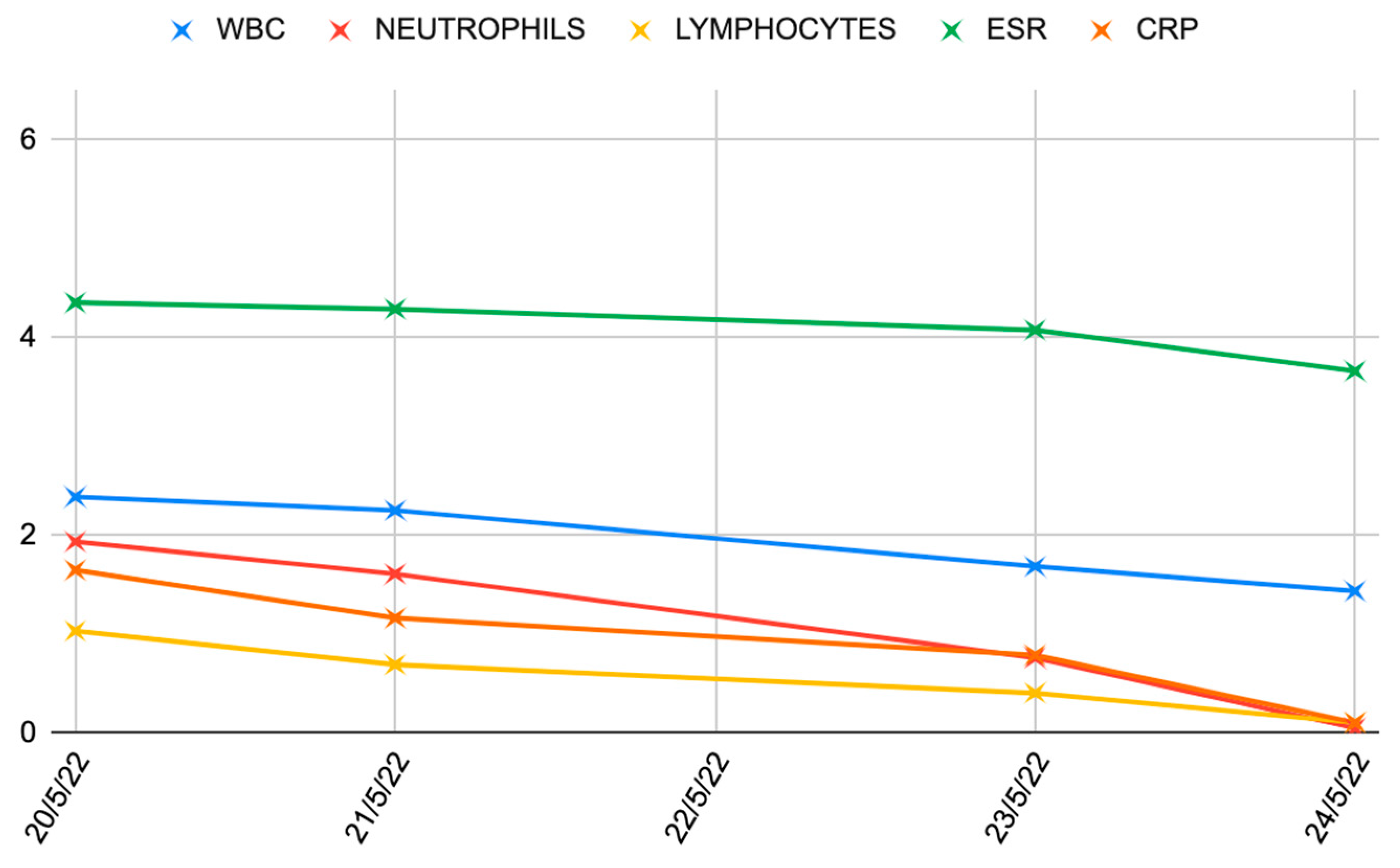

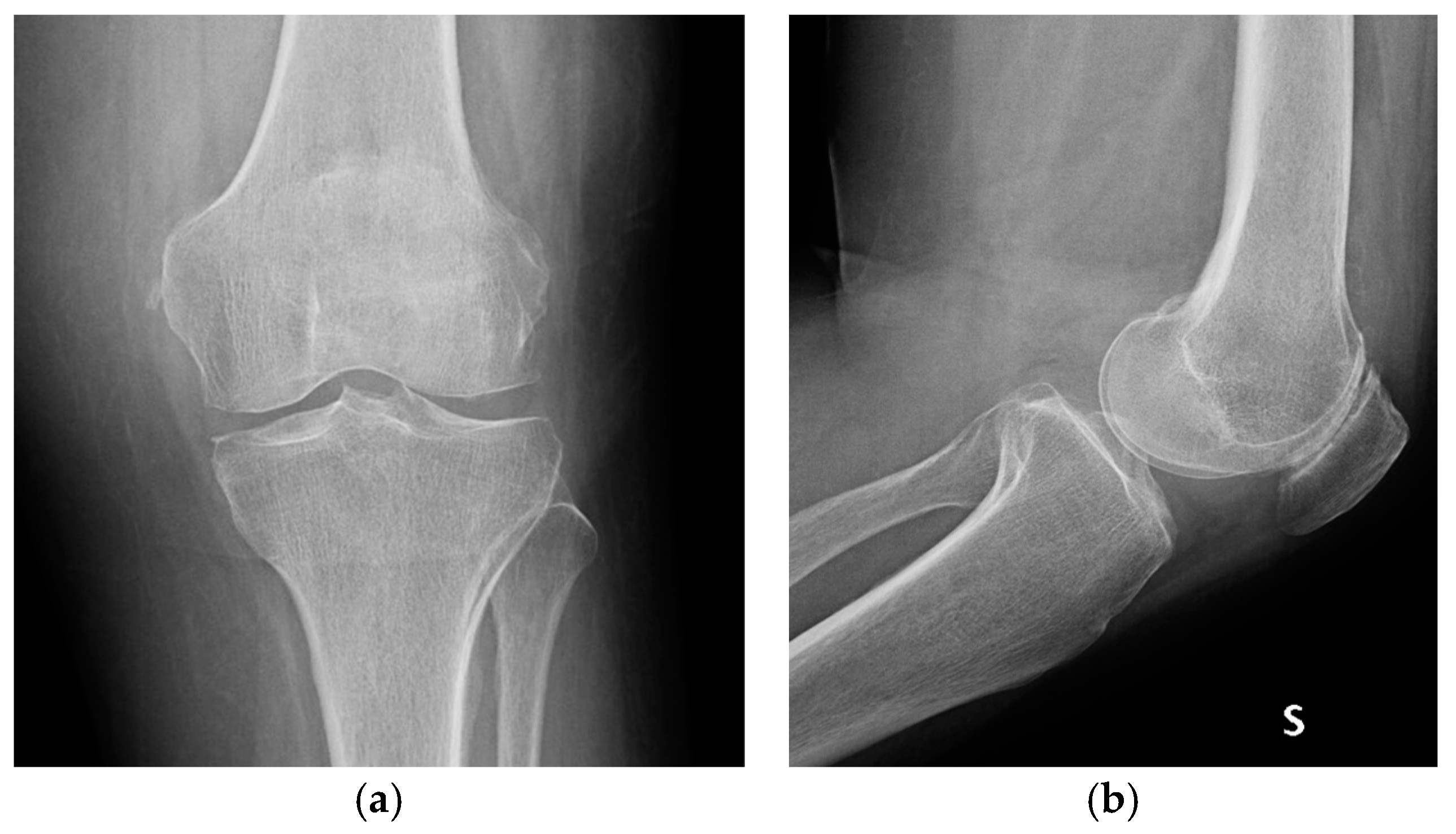
| Stage I | Opacity of fluid, redness of the synovial membrane, possible petechial bleeding, no radiological alterations |
| Stage II | Severe inflammation, fibrinous deposition, pus, no radiological alterations |
| Stage III | Thickening of the synovial membrane, compartment formation (“sponge-like” arthroscopic view, especially in the suprapatellar pouch), no radiological alterations |
| Stage IV | Aggressive pannus with infiltration of the cartilage, possibly undermining the cartilage, radiological signs of subchondral osteolysis, possible osseous erosions and cysts |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





