Submitted:
02 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
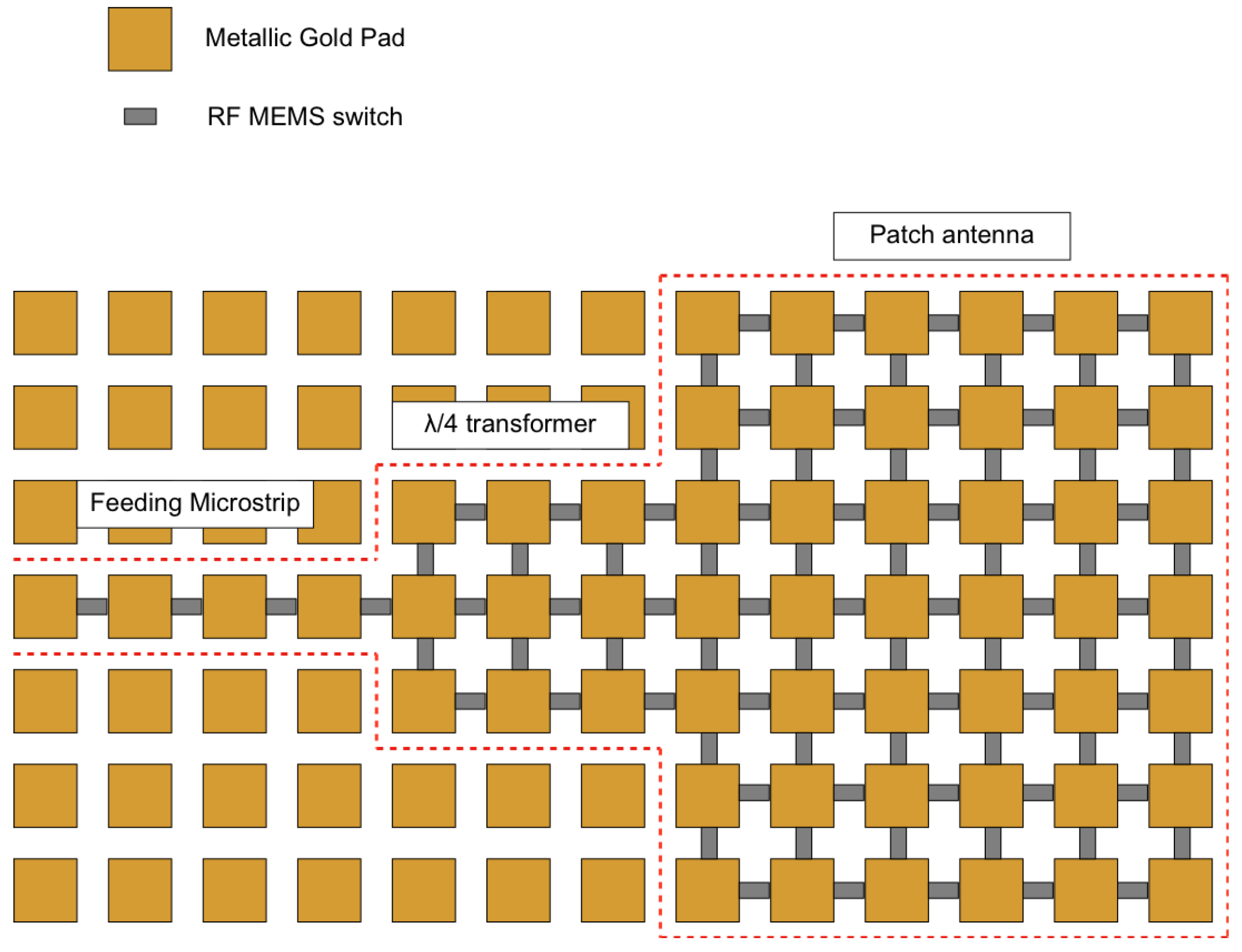
2. Reconfigurable Antenna Structure
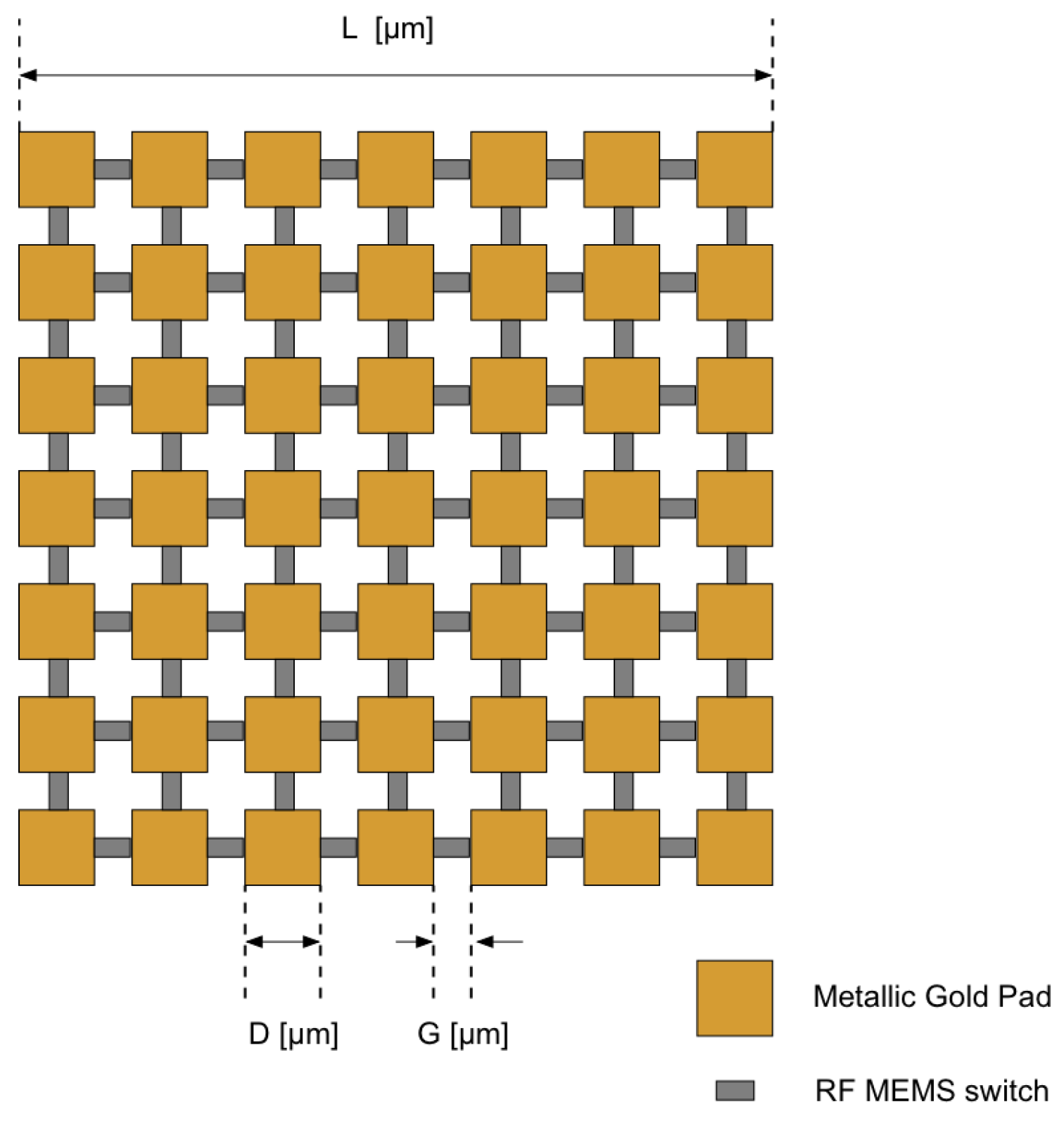
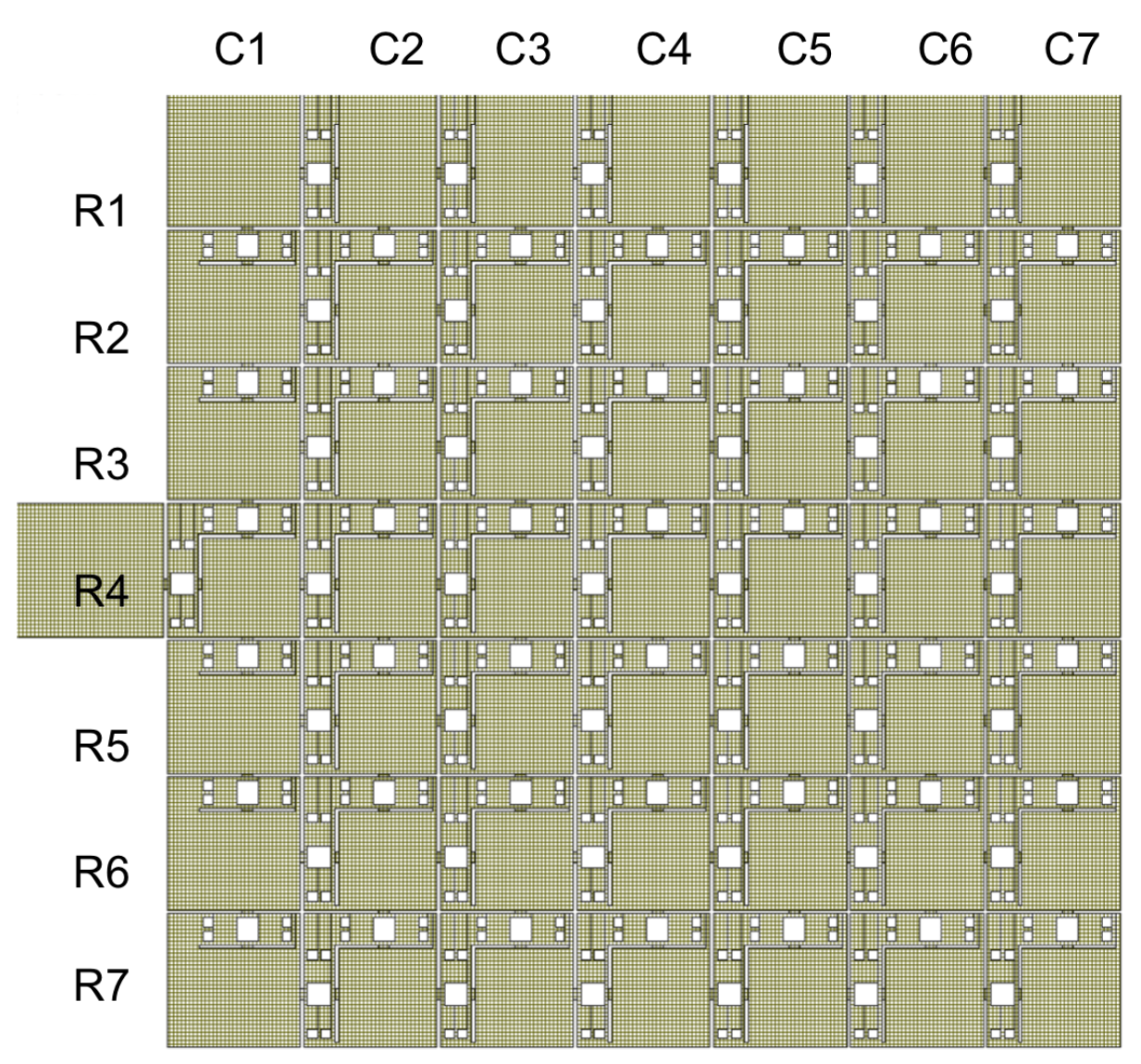
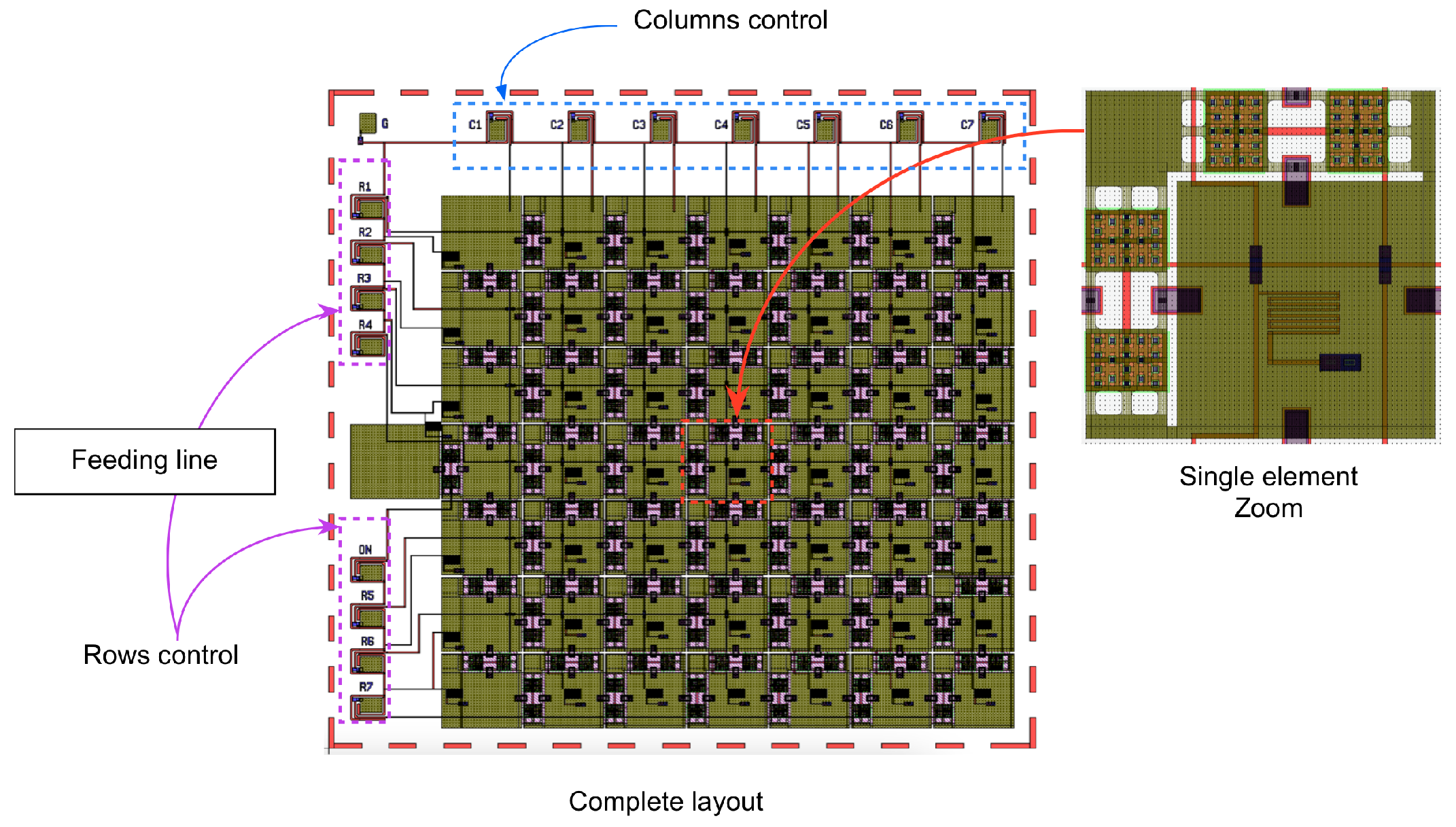
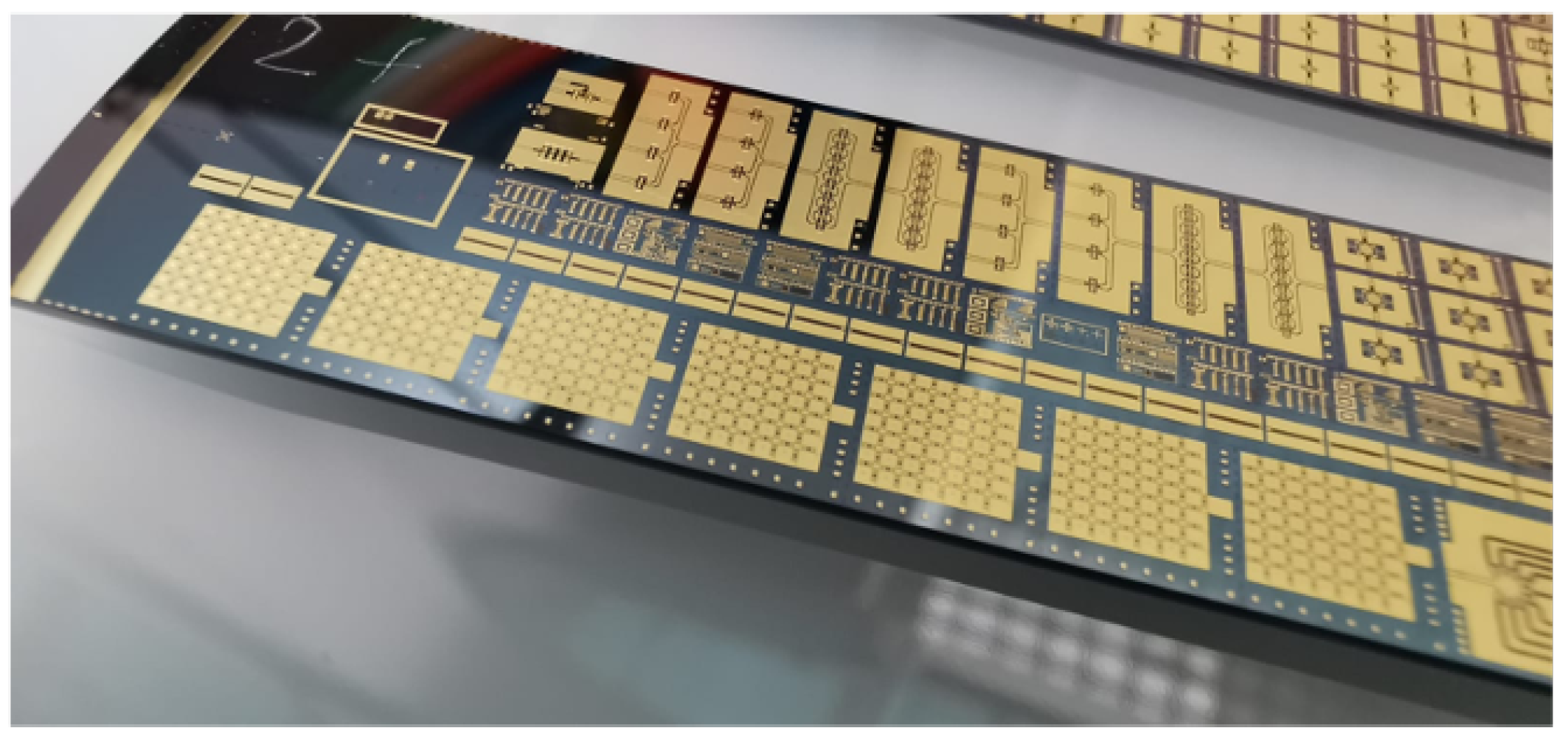
3. Development of a 7x7 Reconfigurable Matrix Structure Prototype
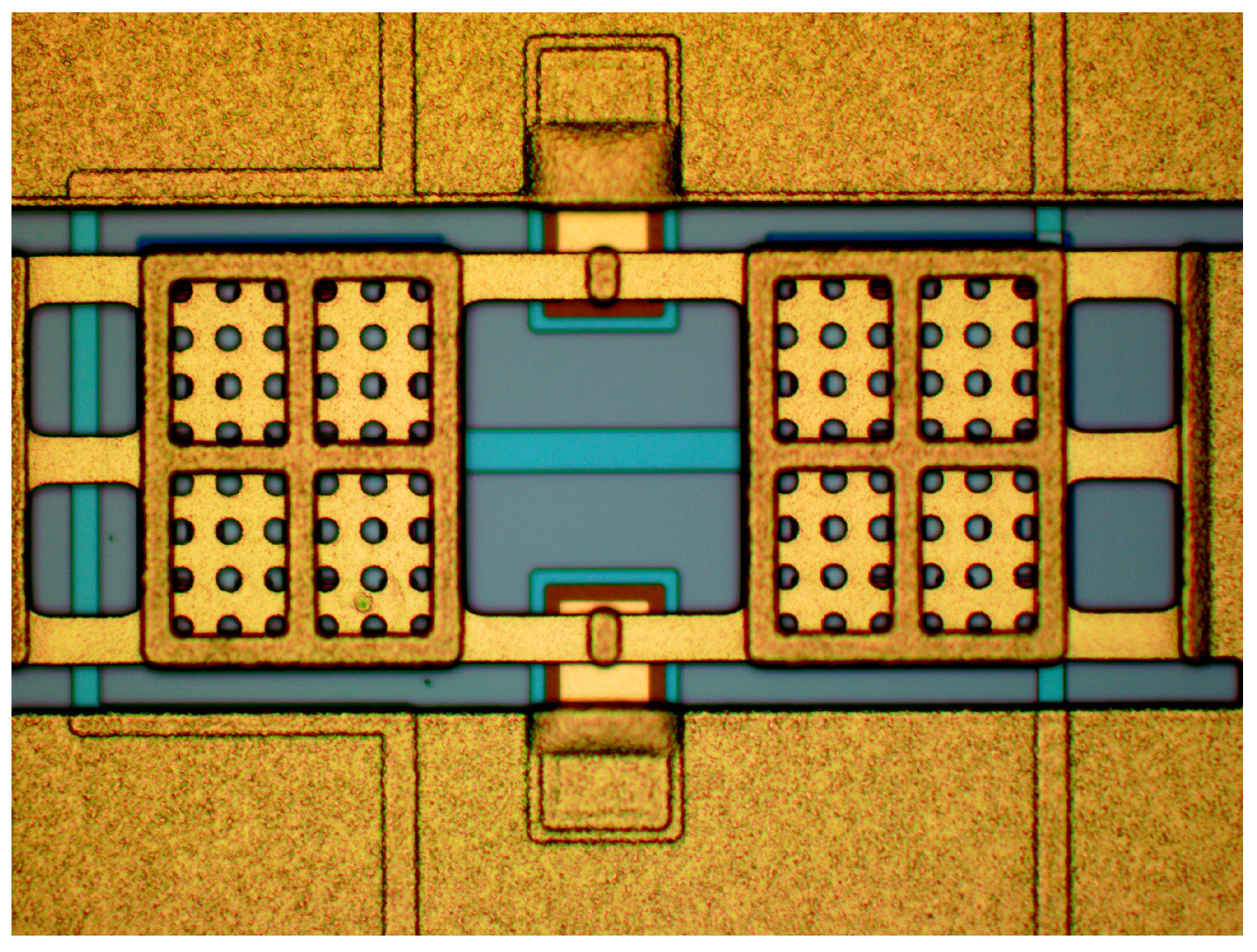
3.1. MEMs Switches Design
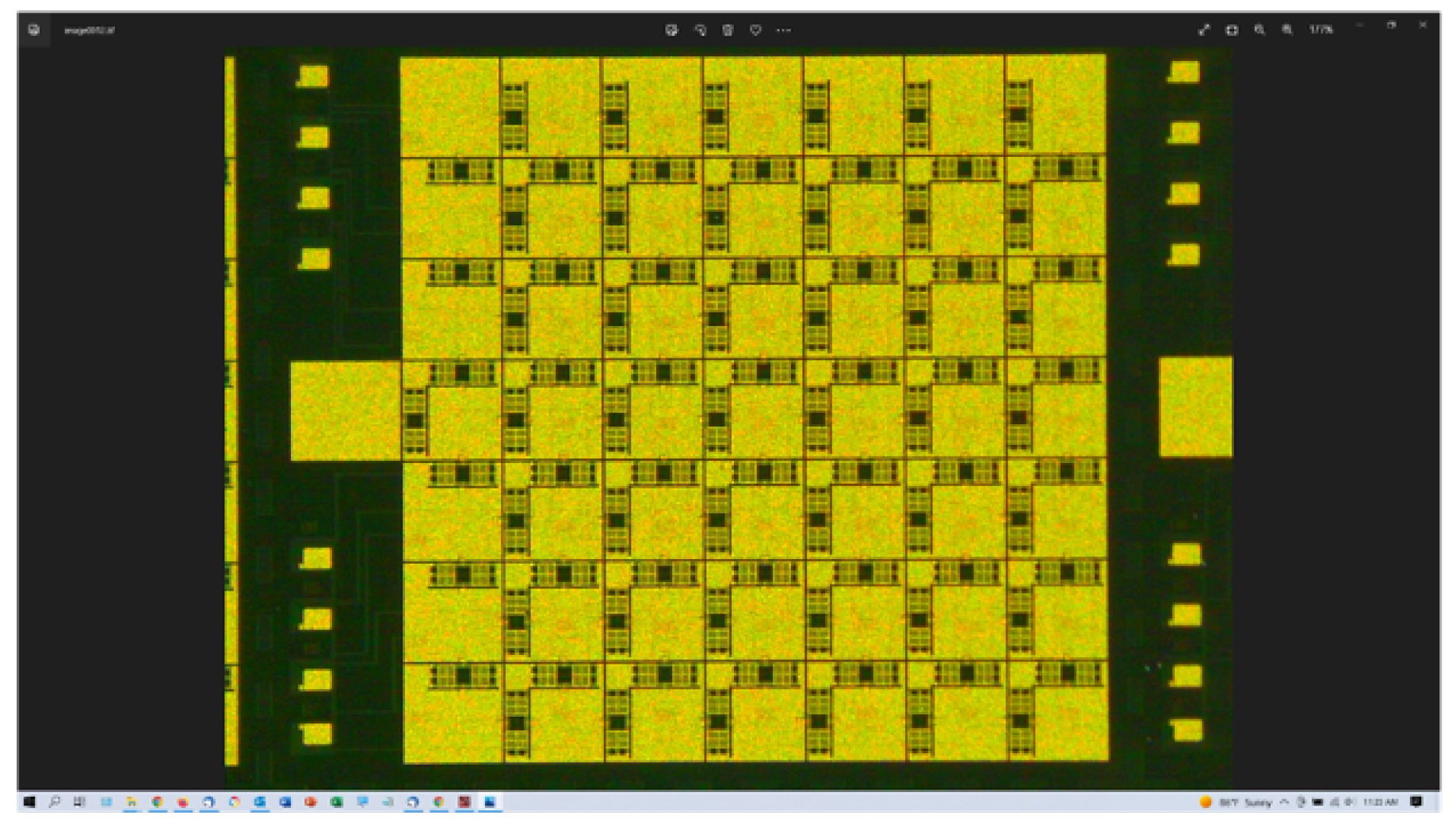
3.2. Matrix Prototype Description
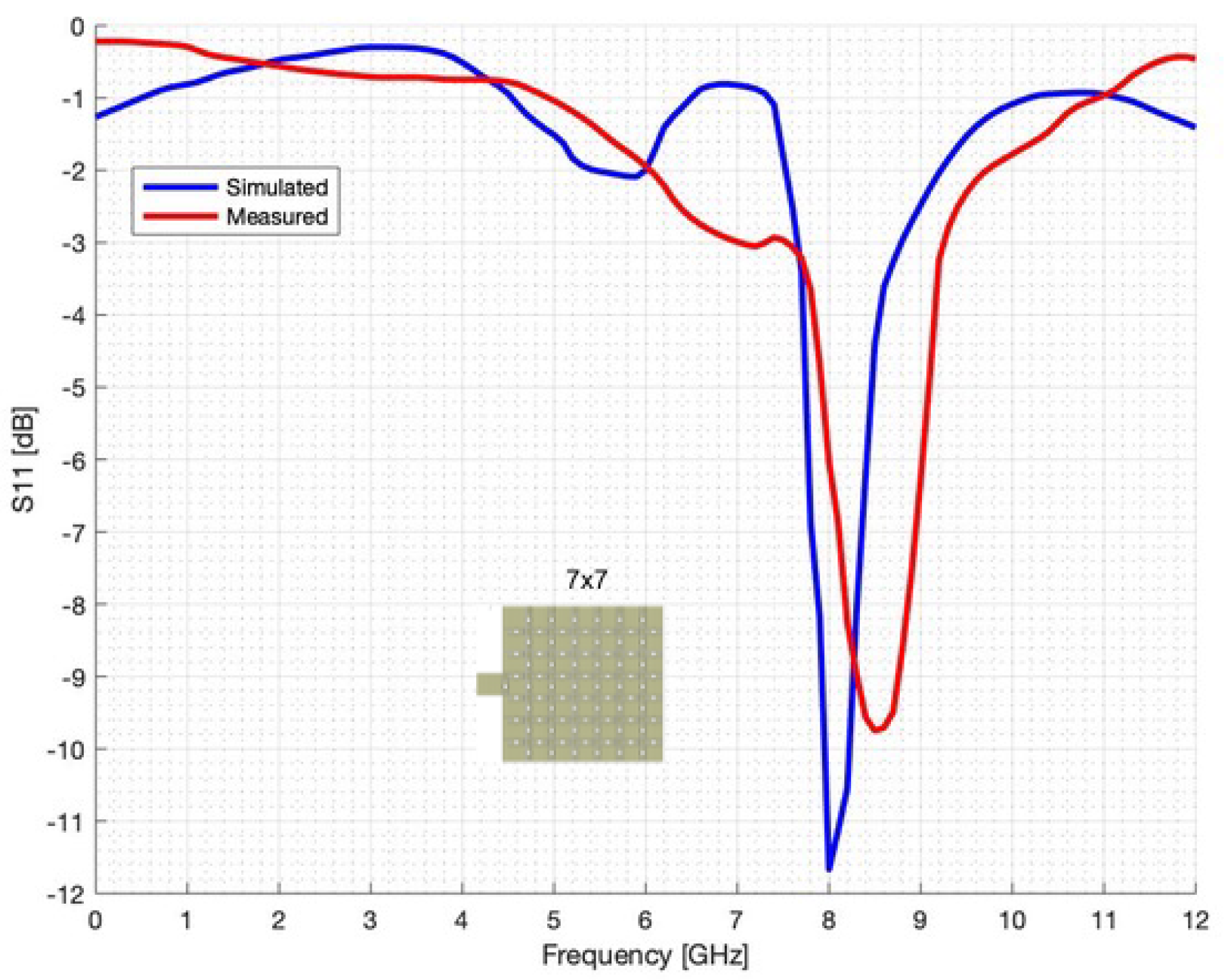
4. Numerical and Experimental Assessment
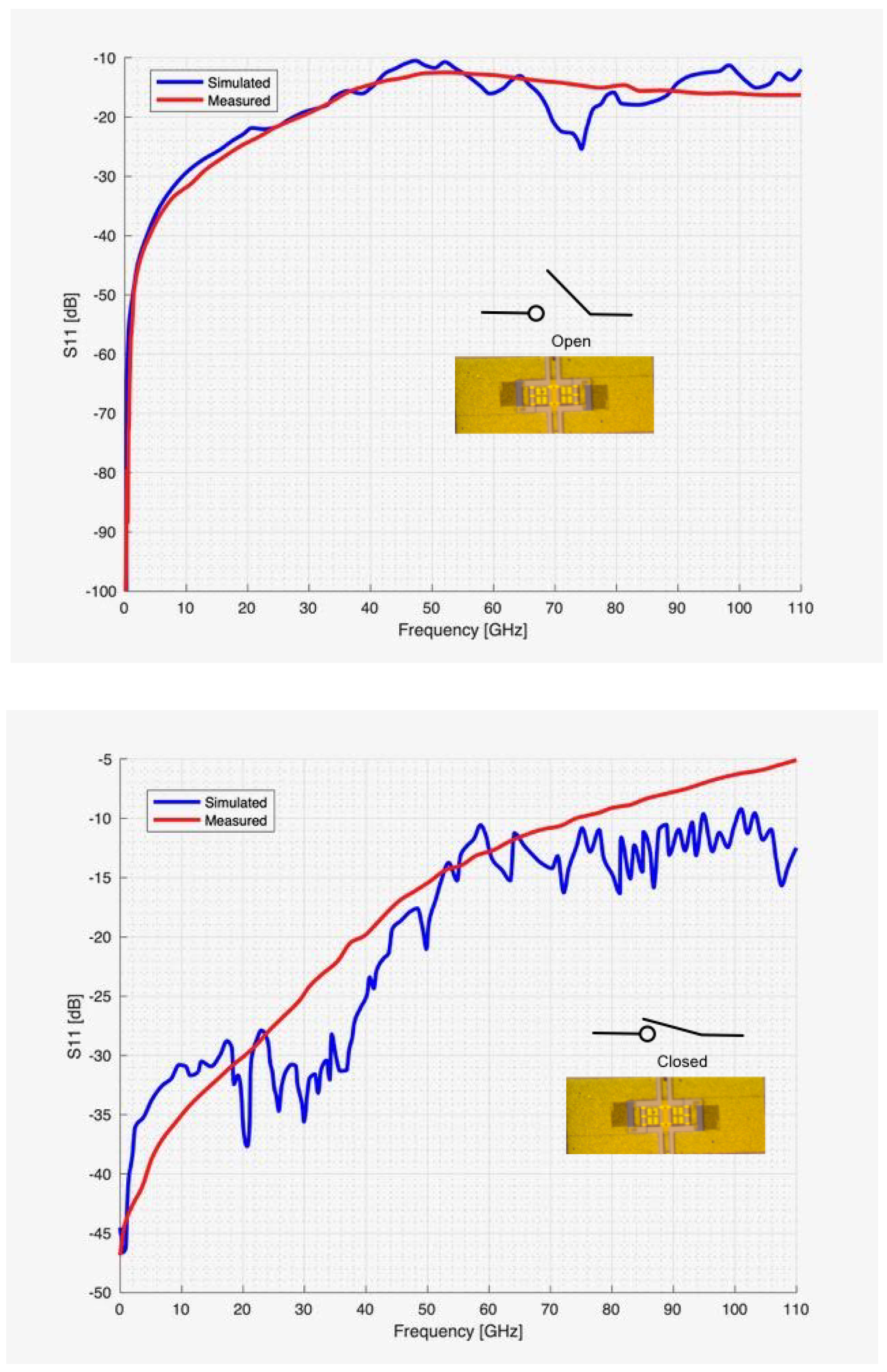
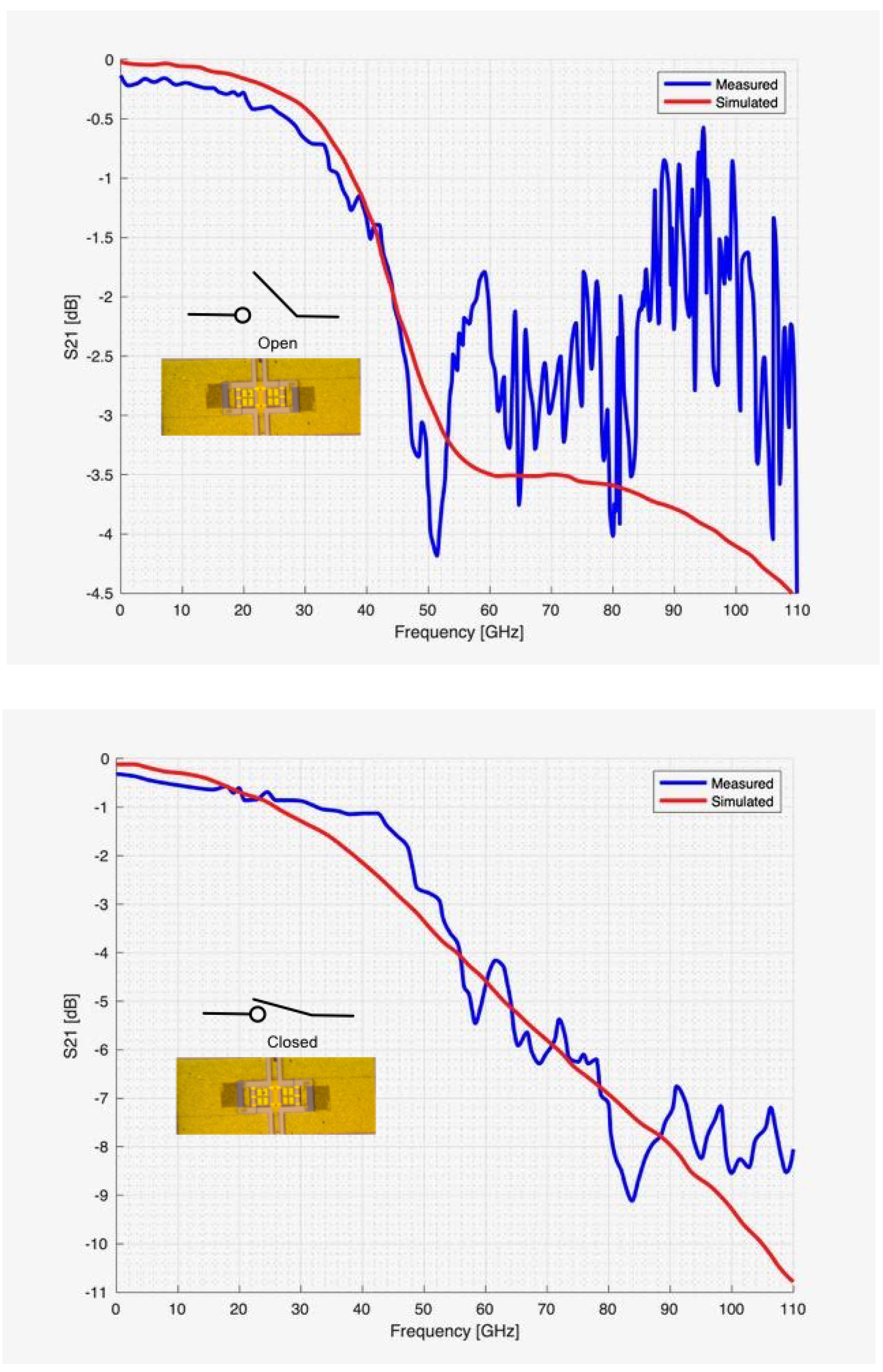
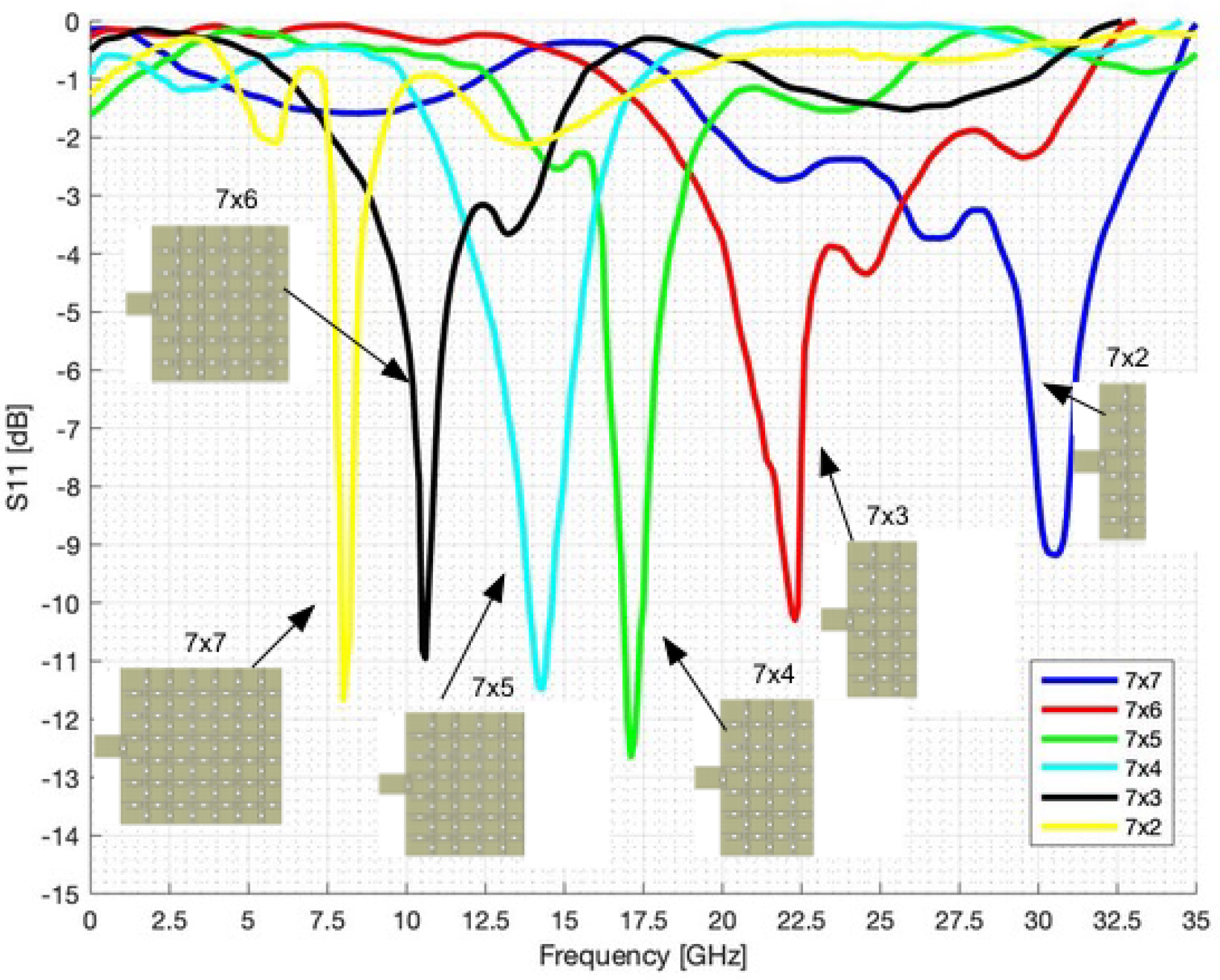
4.1. Numerical Assessment
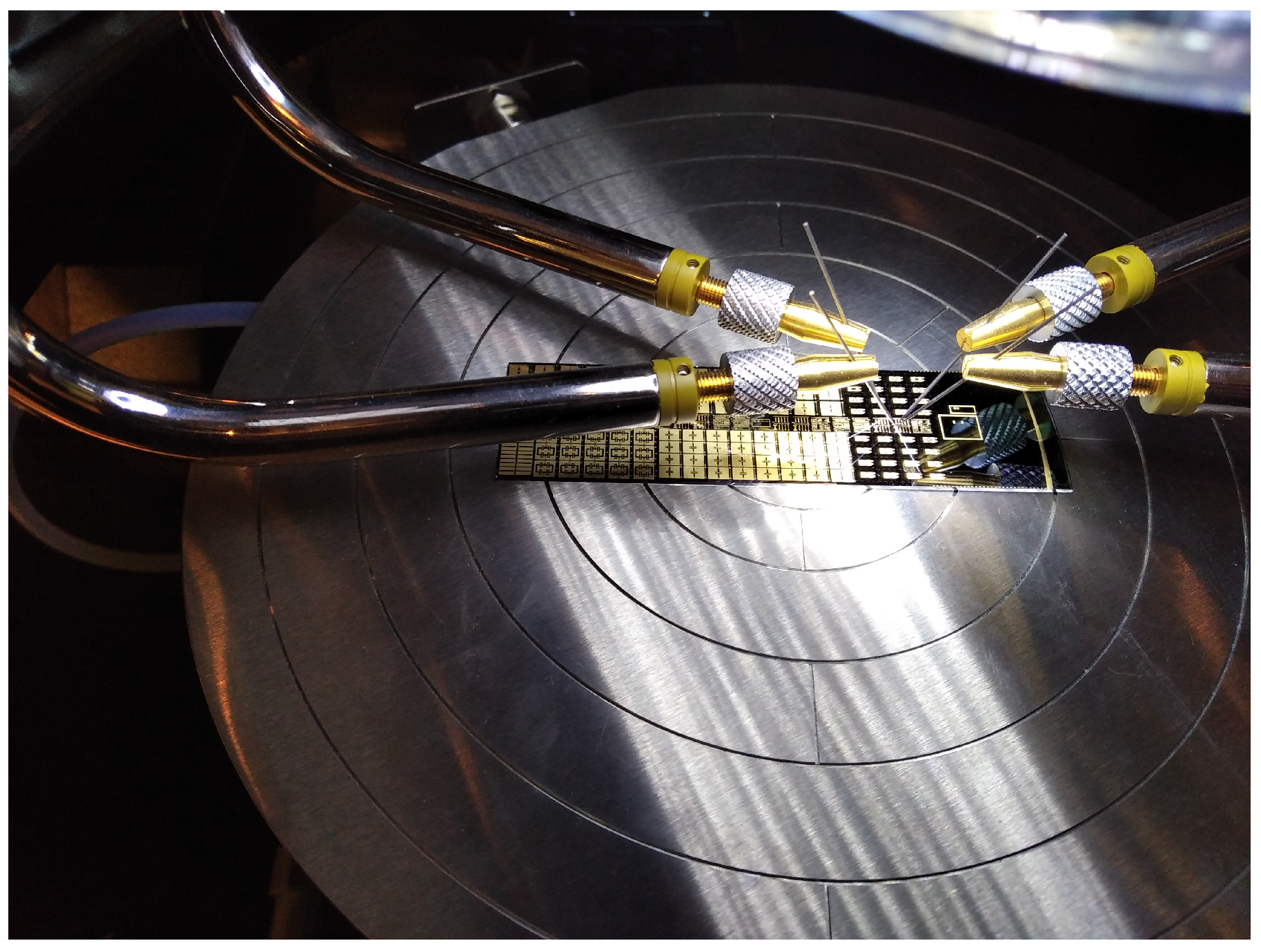
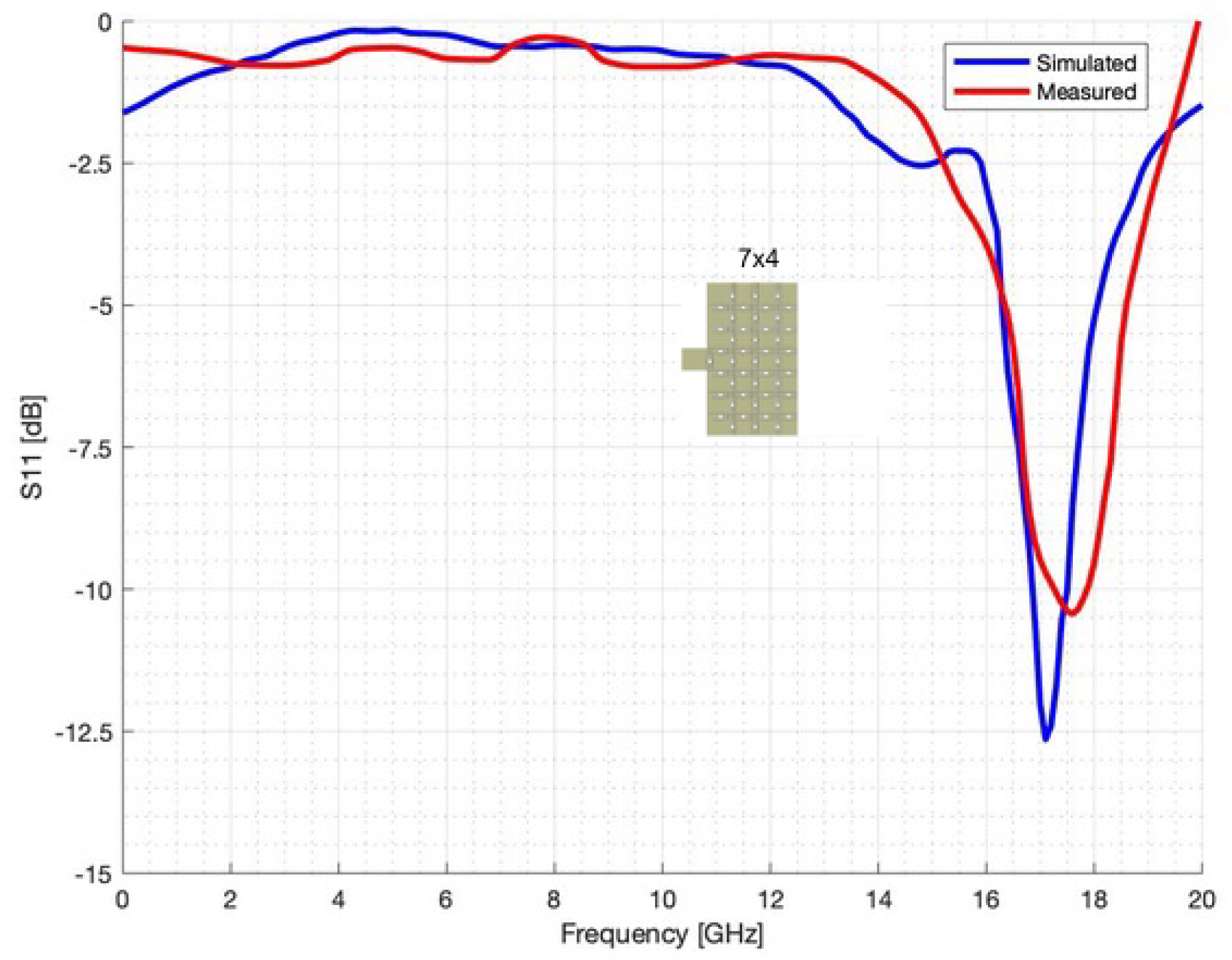
4.2. Experimental Assessment
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. Poulakis, “6G’s Metamaterials Solution: There’s plenty of bandwidth available if we use reconfigurable intelligent surfaces,” IEEE Spectr., vol. 59, no. 11, pp. 40–45, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. A. Balanis and P. I. Ioannides, Introduction to Smart Antennas. in Synthesis Lectures on Antennas. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2007. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Matin, Ed., Wideband, Multiband, and Smart Antenna Systems. in Signals and Communication Technology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Hansen, Phased array antennas, 2nd ed. in Wiley series in microwave and optical engineering. Hoboken, N.J: Wiley, 2009.
- S. Applebaum, “Adaptive arrays,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 585–598, Sep. 1976. [CrossRef]
- Shiann-Jeng Yu and Ju-Hong Lee, “Adaptive array beamforming based on an efficient technique,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 44, no. 8, pp. 1094–1101, Aug. 1996. [CrossRef]
- F. J. Ares-Pena, J. A. Rodriguez-Gonzalez, E. Villanueva-Lopez, and S. R. Rengarajan, “Genetic algorithms in the design and optimization of antenna array patterns,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 506–510, Mar. 1999. [CrossRef]
- A. Massa, M. Donelli, F. G. B. DeNatale, S. Caorsi, and A. Lommi, “Planar Antenna Array Control With Genetic Algorithms and Adaptive Array Theory,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 2919–2924, Nov. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. H. Son, S. Y. Eom, S. I. Jeon, and W. Hwang, “Automatic Phase Correction of Phased Array Antennas by a Genetic Algorithm,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 56, no. 8, pp. 2751–2754, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- M. Donelli, R. Azaro, F. G. B. DeNatale, and A. Massa, “An Innovative Computational Approach Based on a Particle Swarm Strategy for Adaptive Phased-Arrays Control,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 888–898, Mar. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Donelli, A. Martini, and A. Massa, “A Hybrid Approach Based on PSO and Hadamard Difference Sets for the Synthesis of Square Thinned Arrays,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 2491–2495, Aug. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. Behera, A. B. Sahoo, H. Pradhan, and B. B. Mangaraj, “Performance comparison of PSO optimized mutually coupled linear array antenna with Yagi-Uda antenna,” in 2013 IEEE CONFERENCE ON INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES, Thuckalay, Tamil Nadu, India: IEEE, Apr. 2013, pp. 718–723. [CrossRef]
- S. I. M. Sheikh et al., “Analog/Digital Ferrite Phase Shifter for Phased Array Antennas,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 9, pp. 319–321. 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Herd and M. D. Conway, “The Evolution to Modern Phased Array Architectures,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 104, no. 3, pp. 519–529, Mar. 2016. [CrossRef]
- B. T. Perry et al., “Low cost phased array radar for applications in engineering education,” in 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Waltham, MA, USA: IEEE, Oct. 2013, pp. 416–420. [CrossRef]
- K. Gyoda and T. Ohira, “Design of electronically steerable passive array radiator (ESPAR) antennas,” in IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium. Transmitting Waves of Progress to the Next Millennium. 2000 Digest. Held in conjunction with: USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting (Cat. No.00CH37118), Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2000, pp. 922–925. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Migliore, D. Pinchera, and F. Schettino, “A simple and robust adaptive parasitic antenna,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 53, no. 10, pp. 3262–3272, Oct. 2005. [CrossRef]
- P. Rocca, M. Donelli, G. Oliveri, F. Viani, and A. Massa, “Reconfigurable sum–difference pattern by means of parasitic elements for forward-looking monopulse radar,” IET Radar, Sonar & amp; Navigation, vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 747–754, Aug. 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Raman, P. Mohanan, N. Timmons, and J. Morrison, “Microstrip-Fed Pattern- and Polarization- Reconfigurable Compact Truncated Monopole Antenna,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 12, pp. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Z. Qu, J. R. Kelly, Z. Wang, S. Alkaraki, and Y. Gao, “A Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna With Switchable Liquid-Metal Ground Plane,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 1045–1049, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, V. Manohar, and Y. Rahmat-Samii, “K-Band Circularly Polarized Beam Steerable Reflectarray Enabling Internet of Space: Conceptualization and Validation,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 70, no. 8, pp. 6703–6717, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Huang, M. Shirazi, and X. Gong, “A New Arraying Technique for Band-Switchable and Polarization-Reconfigurable Antenna Arrays With Wide Bandwidth,” IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag., vol. 3, pp. 1025–1040, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Carrasco, M. Barba, and J. A. Encinar, “X-Band Reflectarray Antenna With Switching-Beam Using PIN Diodes and Gathered Elements,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 5700–5708, Dec. 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. Wahab and J. Xu, “U-slot Circular Patch Antenna for WLAN Application,” TELKOMNIKA, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 323–328, May 2015. [CrossRef]
- Youngje Sung, “Investigation Into the Polarization of Asymmetrical- Feed Triangular Microstrip Antennas and its Application to Reconfigurable Antennas,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 1039–1046, Apr. 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. Rebeiz et al., “Tuning in to RF MEMS,” IEEE Microwave, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 55–72, Oct. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Nishamol, V. P. Sarin, D. Tony, C. K. Aanandan, P. Mohanan, and K. Vasudevan, “An Electronically Reconfigurable Microstrip Antenna With Switchable Slots for Polarization Diversity,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 59, no. 9, pp. 3424–3427, Sep. 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. W. Lee and Y. Sung, “Compact Frequency Reconfigurable Antenna for LTE/WWAN Mobile Handset Applications,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 63, no. 10, pp. 4572–4577, Oct. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Chao Sun, Huili Zheng, Lingfei Zhang, and Ying Liu, “A Compact Frequency-Reconfigurable Patch Antenna for Beidou (COMPASS) Navigation System,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 13, pp. 967–970. 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. Sanchez-Escuderos, M. Ferrando-Bataller, M. Baquero-Escudero, and J. I. Herranz, “Reconfigurable Slot-Array Antenna With RF-MEMS,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 10, pp. 721–725. 2011. [CrossRef]
- T. Debogovic and J. Perruisseau-Carrier, “Low Loss MEMS-Reconfigurable 1-Bit Reflectarray Cell With Dual-Linear Polarization,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 62, no. 10, pp. 5055–5060, Oct. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Wenquan Cao, Bangning Zhang, Aijun Liu, Tongbin Yu, Daosheng Guo, and Kegang Pan, “A Reconfigurable Microstrip Antenna With Radiation Pattern Selectivity and Polarization Diversity,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 11, pp. 453–456. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Shirazi, J. Huang, T. Li, and X. Gong, “A Switchable-Frequency Slot-Ring Antenna Element for Designing a Reconfigurable Array,” Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 229–233, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. F. Macedo, D. Guedes, L. F. M. Vieira, M. A. M. Vieira, and M. Nogueira, “Programmable Networks—From Software-Defined Radio to Software-Defined Networking,” IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 1102–1125, 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Kaiser, "The potential of MEMS components for re-configurable RF interfaces in mobile communication terminals," in Proc. ESSCIRC. Villach Austria, 2001, pp. 25-28.
- G. M. Rebeiz, RF-MEMS: Theory Design, and Technology, 1st ed. Hoboken, NJ USA: Wiley, 2003 pp. 1-512.
- A. Ocera, P. Farinelli, P. Mezzanotte, R. Sorrentino, B. Margesin, and F. Giacomozzi, “A Novel MEMS-Tunable Hairpin Line Filter on Silicon Substrate,” in 2006 European Microwave Conference, Manchester, UK, Sep. 2006, pp. 803–806. [CrossRef]
- Ker Chia Lee, Hieng Tiong Su, and M. K. Haldar, “Performance of a configurable microstrip filter using triple mode resonator and RF-MEMS switches,” in 2010 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Applied Electromagnetics (APACE), Port Dickson, Nov. 2010, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- F. Gentili, L. Pelliccia, F. Cacciamani, P. Farinelli, and R. Sorrentino, “RF -MEMS bandwidth-reconfigurable hairpin filters,” in 2012 Asia Pacific Microwave Conference Proceedings, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, Dec. 2012, pp. 735–737. [CrossRef]
- R. R. Mansour, “RF-MEMS for space applications,” in 2005 International Conference on MEMS,NANO and Smart Systems, Banff, AB, Canada, 2005, pp. 191–192. [CrossRef]
- J. Iannacci et al., “RF-MEMS for 5G mobile communications: A basic attenuator module demonstrated up to 50 GHz,” in 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, USA, Oct. 2016, pp. 1–3. [CrossRef]
- J. Iannacci, A. Faes, F. Mastri, D. Masotti, V. Rizzoli, “A MEMS-Based Wide-Band Multi- State Power Attenuator for Radio Frequency and Microwave Applications,” Proc. of TechConnect World, NSTI-Nanotech 2010, pp. 328-331, Jun. 2010.
- J. Iannacci, D. Masotti, T. Kuenzig, M. Niessner, “A reconfigurable impedance matching network entirely manufactured in RF- MEMS technology, ” Proc. of SPIE, vol. 8066, pp. 1-12, Apr. 2011.
- J. Iannacci, M. Huhn, C. Tschoban, H. Potter, “RF-MEMS Technology for 5G: Series and Shunt Attenuator Modules Demonstrated up to 110 GHz,” IEEE EDL, vol. 37, no. 10, pp. 1336-1339, Oct. 2016.
- J. Iannacci, M. Huhn, C. Tschoban, H. Potter, “RF-MEMS Technology for future (5G) mobile and high frequency applications: reconfigurable 8-bit power attenuator tested up to 110 GHz” IEEE EDL, vol. 37, no. 12, pp. 1646-1649, Dec. 2016.
- M. Donelli, M. Manekiya, and J. Iannacci, “Broadband MST sensor probes based on a SP3T MEMS switch,” in 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, Jul. 2019, pp. 649–650. [CrossRef]
- P.Ssejjuuko, M. Donelli, and J. Iannacci, "Exploiting RF-MEMS Switches for pattern reconfigurable parasitic antennas," 2021 Springer International Conference on Micro/Nanoelectronics Systems Tracks of MNDCS-2021, Assam, India, 2021, Jan. 29-31.
- E. Hammerstad and O. Jensen, “Accurate Models for Microstrip Computer-Aided Design,” in MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Washington, DC,USA, 1980, vol. 80, pp. 407–409. [CrossRef]
- J. Iannacci, Practical Guide to RF-MEMS, 1st ed. Wiley, 2013. [CrossRef]
- V. Mulloni, F. Giacomozzi, and B. Margesin, “Controlling stress and stress gradient during the release process in gold suspended micro-structures,” Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, vol. 162, no. 1, pp. 93–99, Jul. 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Mollah and N. C. Karmakar, “RF-MEMS switches: paradigms of microwave switching,” in APMC 2001. 2001 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (Cat. No.01TH8577), Taipei, Taiwan: IEEE, 2001, pp. 1024–1027. [CrossRef]
| Rows | Coloumns | Thickness | Impedance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 430 | 54.75 |
| 2 | 7 | 1030 | 35.82 |
| 3 | 7 | 1630 | 25.42 |
| 4 | 7 | 2230 | 18.21 |
| 5 | 7 | 2830 | 12.68 |
| 6 | 7 | 3430 | 10.34 |
| Thickness | Simulated | Measured | Error % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 430 | 54.75 | 60.22 | 10.0 |
| 1030 | 35.82 | 38.68 | 8.0 |
| 1630 | 25.42 | 28.21 | 11.0 |
| 2230 | 18.21 | 19.81 | 8.8 |
| 2830 | 12.68 | 14.01 | 10.5 |
| 3430 | 10.34 | 11.30 | 9.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





