Submitted:
01 September 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Laboratory and Clinical Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Clinical, Biochemical, and Immunological Parameters in OA and OA+T2DM
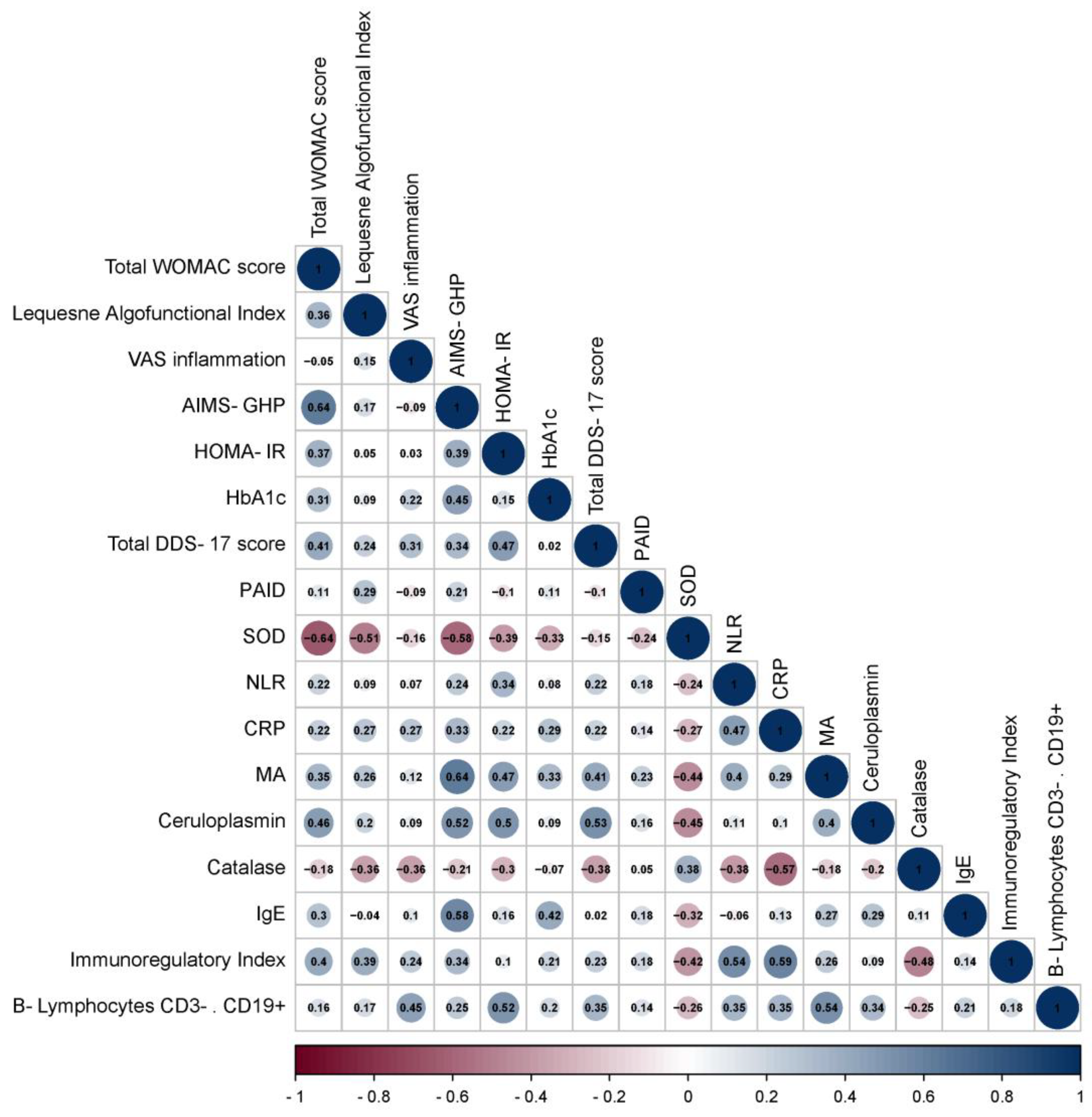
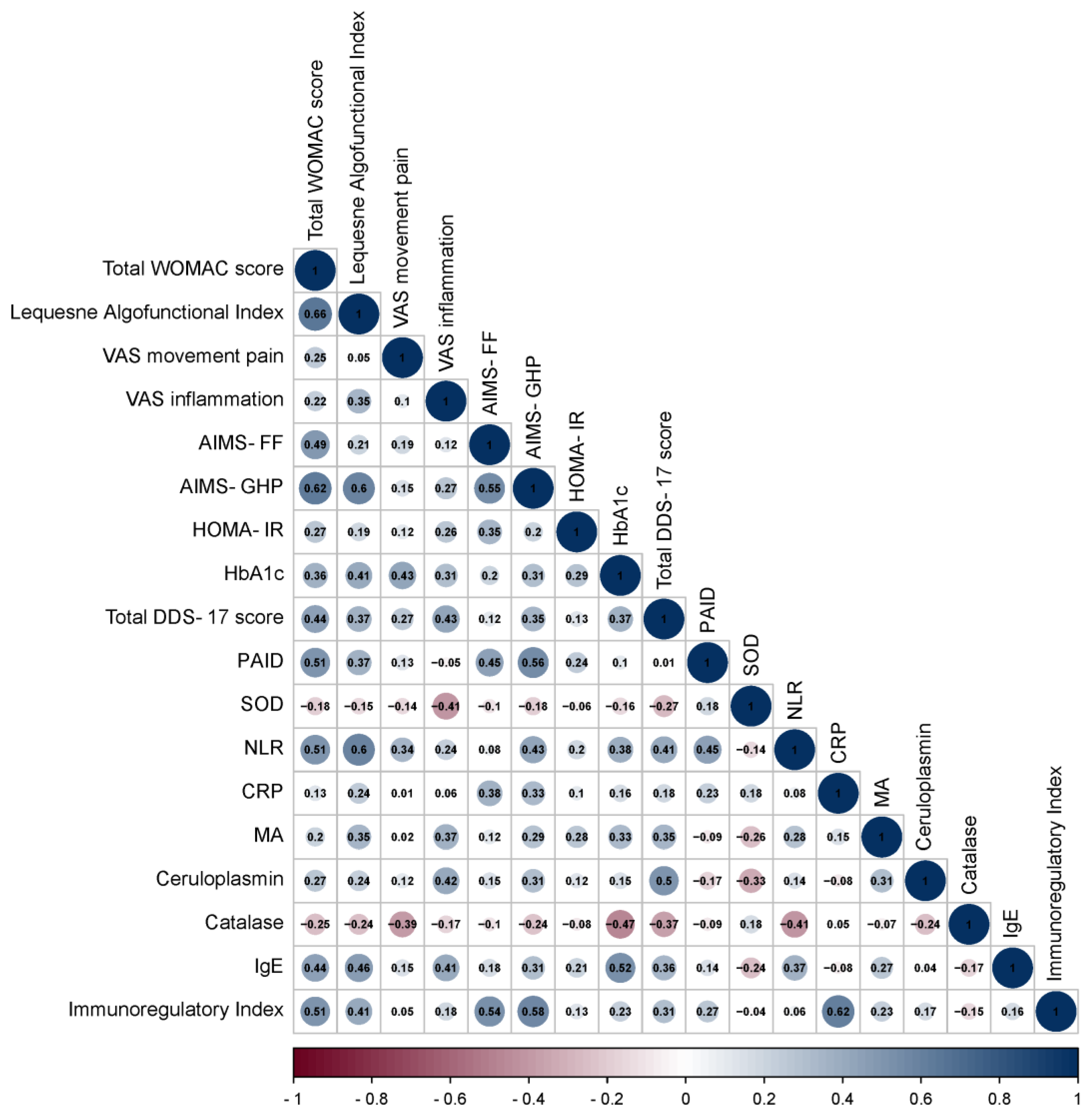
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Data in Patients with OA and OA+T2DM
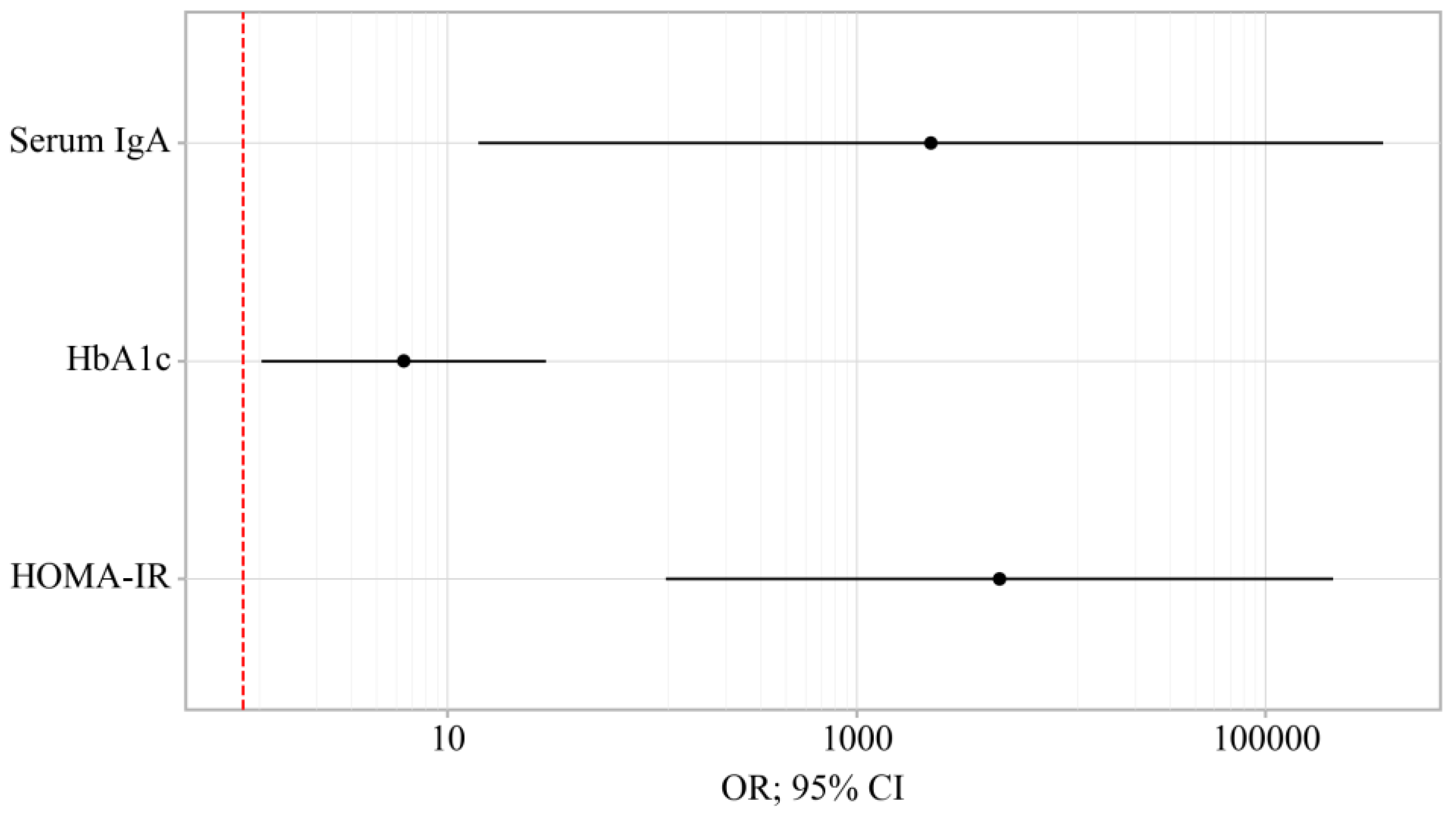
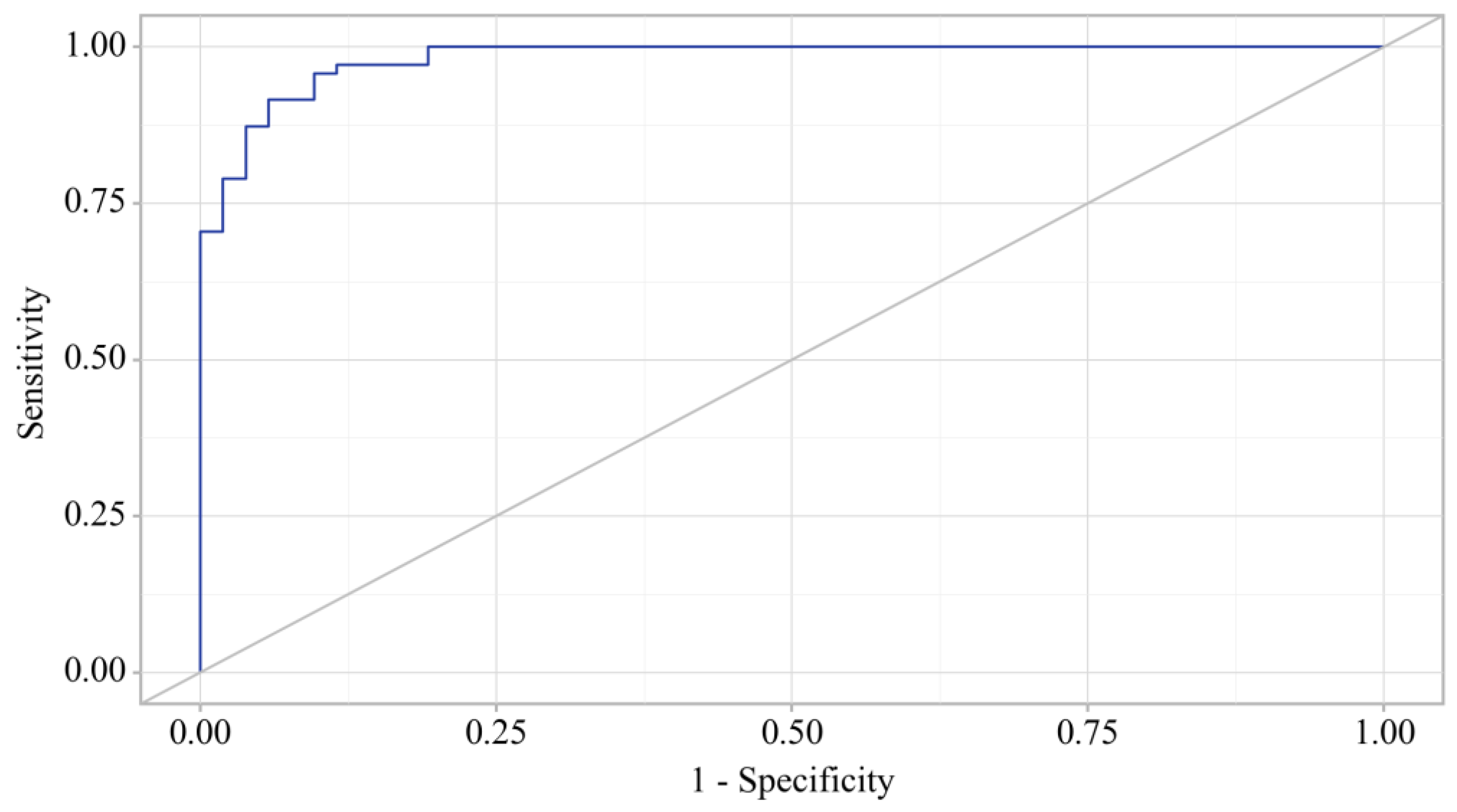
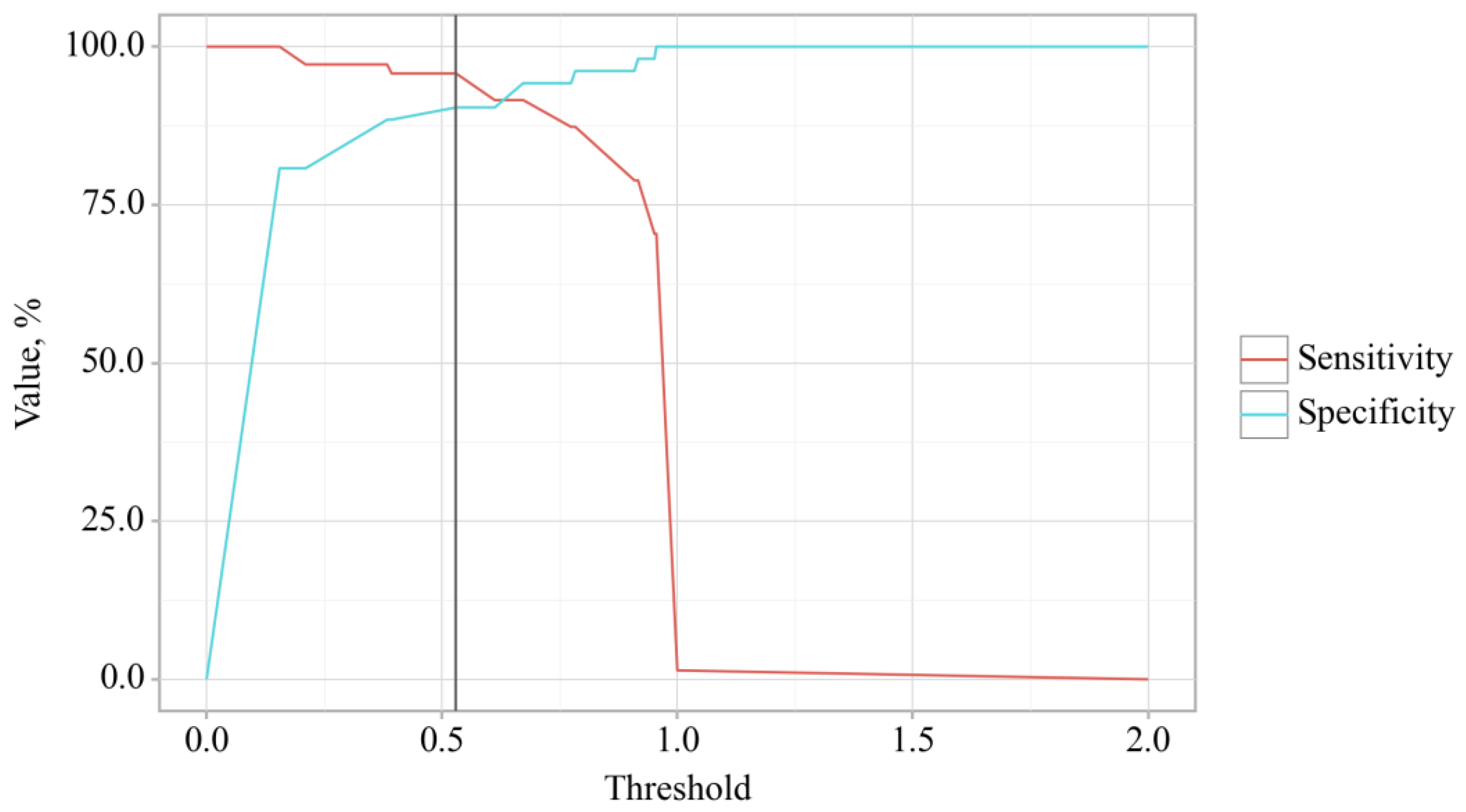
3.3. Binary Logistic Regression of Data in Patients with OA and OA+T2DM
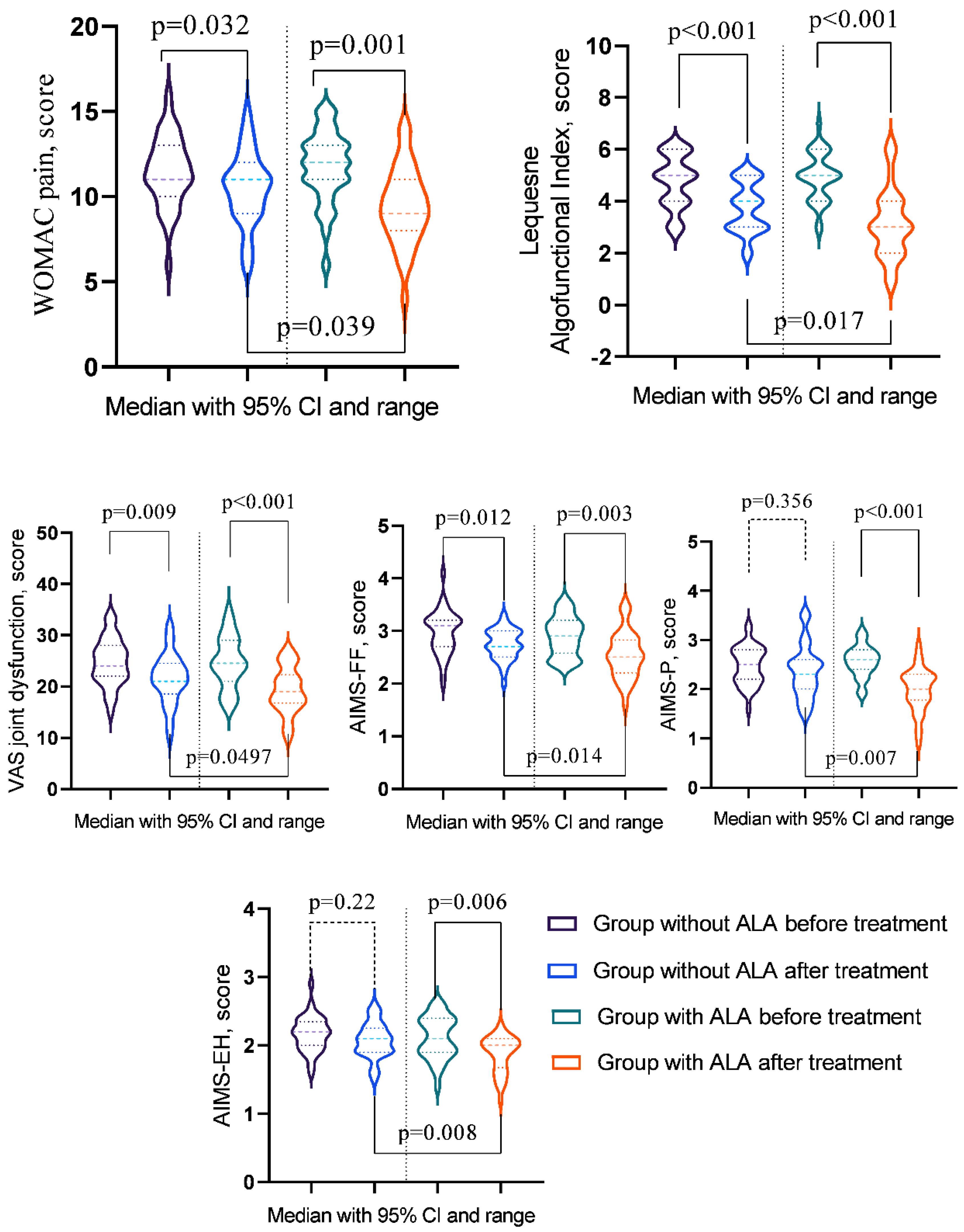
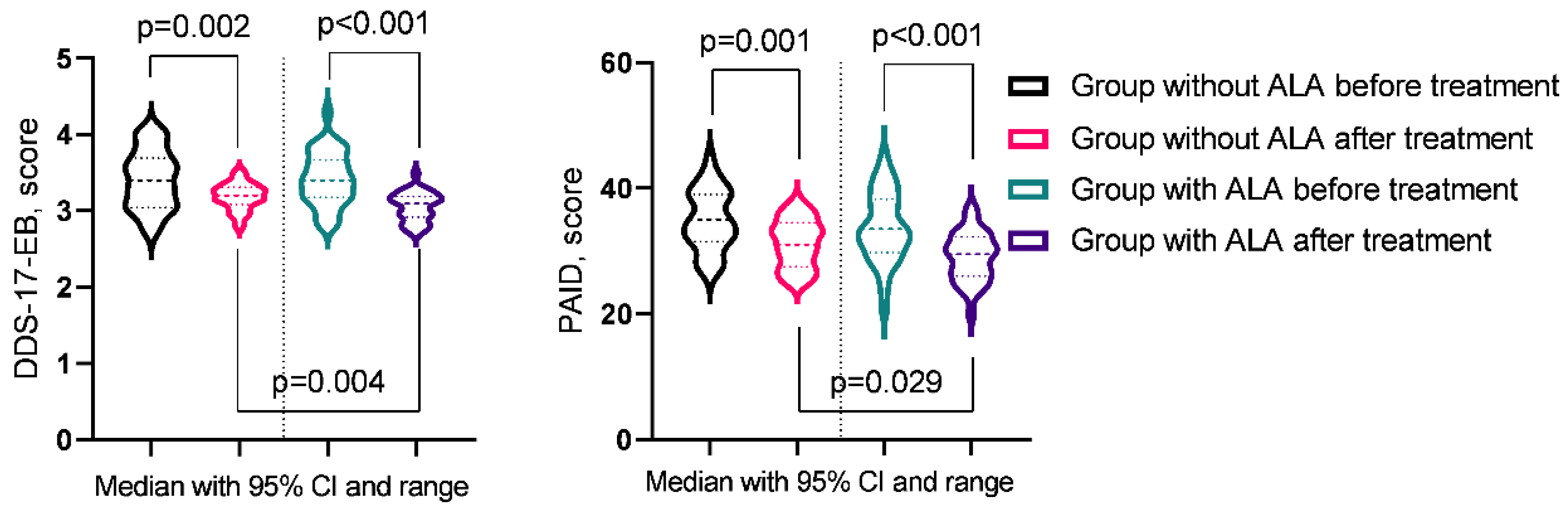
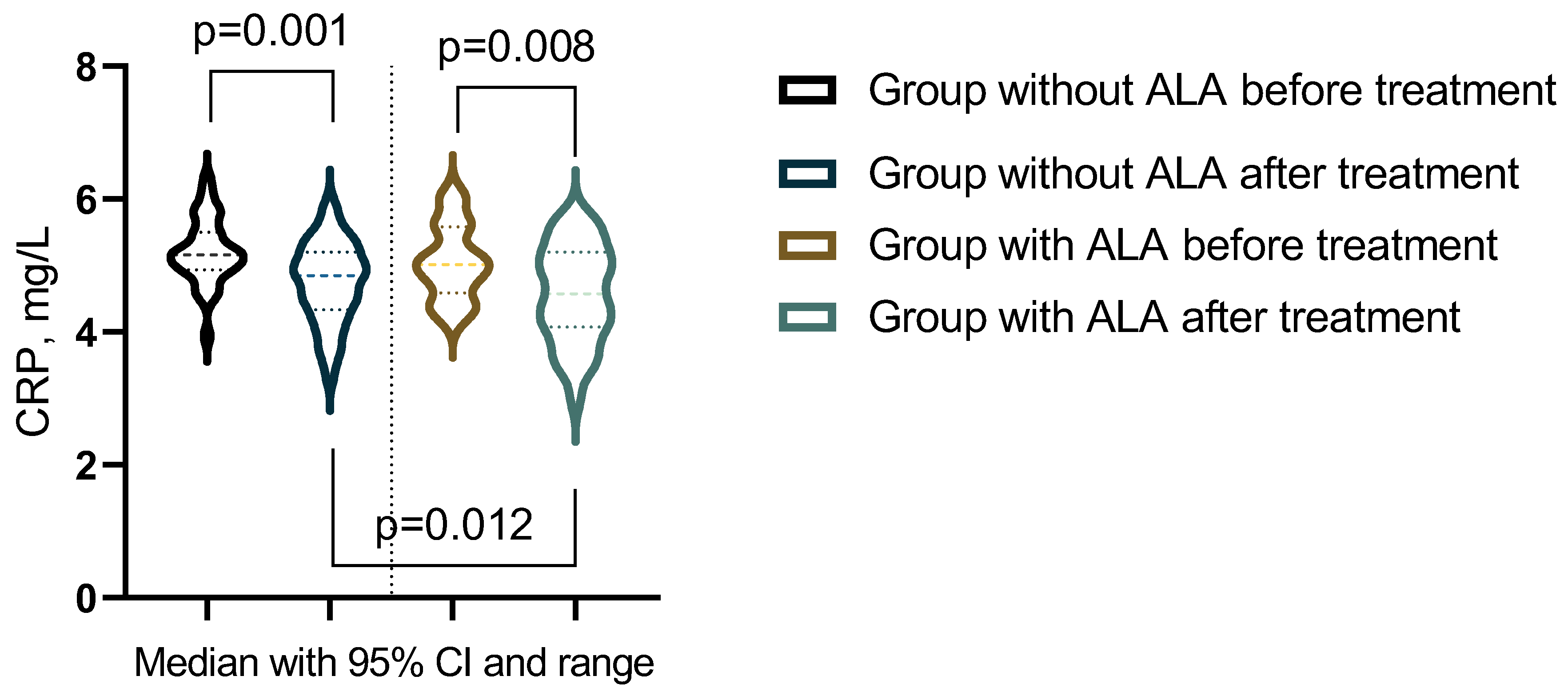
3.4. Сomparative Analysis of Treatment Outcomes in Patients with OA and T2DM With and Without ALA Supplementation
4. Discussion
6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oo, W. M. Prospects of Disease-Modifying Osteoarthritis Drugs. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America 2024, 50, 483–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabitska I, B. L. Different consequences of the treatment of osteoarthritis in gastrointestinal comorbidity with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Family Medicine & Primary Care Review 2021, 23, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Liu, L.; Feng, H.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H. Therapeutics of osteoarthritis and pharmacological mechanisms: A focus on RANK/RANKL signaling. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2023, 167, 115646. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, P.; Zeng, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zong, K.; Han, B.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y. The role of targeting glucose metabolism in chondrocytes in the pathogenesis and therapeutic mechanisms of osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Frontiers in endocrinology 2024, 15, 1319827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawl, M.; Geetha, T.; Burnett, D.; Babu, J. R. Omega-3 Supplementation and Its Effects on Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, W. W.; Kean, C. A.; Kean, W. F.; Rainsford, K. D. Osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Singh, S.; Kamath, S.; Shah, U.; Patel, S.; Kherajani, K.; Gupta, A.; Shaw, P.; Unnithan, V.; Kaithathara, S.; Gharde, P. Interplay Between Diabetes Mellitus and the Occurrence of Osteoarthritis and Associated Conditions in Women of Menopausal Age. Cureus 2024, 16, e58502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M. G.; Gordin, D.; Fu, J.; Park, K.; Li, Q.; King, G. L. Protective Factors and the Pathogenesis of Complications in Diabetes. Endocrine reviews 2024, 45, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gangwar, R.; Zargar, A. A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A. Prevalence of Diabetes in India: A Review of IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition. Current diabetes reviews 2024, 20, e130423215752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Xu, B. T.; Wan, S. R.; Ma, X. M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Z. The role of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovascular diabetology 2023, 22, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, M.; Moustaki, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Vryonidou, A.; Paschou, S. A. Early onset type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update. Endocrine 2024, 85, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemlyak, O. S.; Babinets, L. S.; Halabitska, I. M. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXICOSIS AND INFLAMMATION IN DEEPENING THE PANCREATIC FUNCTIONAL INSUFFICIENCY IN CHRONIC PANCREATITIS IN COMBINATION WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES. Polski merkuriusz lekarski : organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego 2023, 51, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Arce, N. D.; Hum, N. R.; Loots, G. G. Interactions Between Diabetes Mellitus and Osteoarthritis: From Animal Studies to Clinical Data. JBMR plus 2022, 6, e10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; Bellamkonda, A.; Gousy, N.; Deb Roy, P. The Association Between Diabetes Mellitus and Osteoarthritis: Does Diabetes Mellitus Play a Role in the Severity of Pain in Osteoarthritis? Cureus 2022, 14, e21449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, R.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z. α-Lipoic acid improves mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics by enhancing antioxidant and inhibiting Wnt/Ca(2+) pathway to relieve fluoride-induced hepatotoxic injury. Chemico-biological interactions 2023, 385, 110719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capece, U.; Moffa, S.; Improta, I.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Nista, E. C.; Cefalo, C. M. A.; Cinti, F.; Pontecorvi, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Giaccari, A.; Mezza, T. Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Glucose Metabolism: A Comprehensive Update on Biochemical and Therapeutic Features. Nutrients 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosis-Nobelos, P.; Papagiouvannis, G.; Tziona, P.; Rekka, E. A. Lipoic acid. Kinetics and pluripotent biological properties and derivatives. Molecular biology reports 2021, 48, 6539–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S.; Richard, C.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of α-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Molecular nutrition & food research 2013, 57, 114–25. [Google Scholar]
- Halabitska, I. M.; Babinets, L. S.; Vysotskyi, V. I. POSSIBILITIES OF METABOLIC AND FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS CORRECTION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS WITH COMPLEX COMORBIDITY. Wiadomosci lekarskie (Warsaw, Poland : 1960) 2022, 75, 645–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Fu, Z.; Liu, M. Chondroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Free radical research 2016, 50, 767–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frondoza, C. G.; Fortuno, L. V.; Grzanna, M. W.; Ownby, S. L.; Au, A. Y.; Rashmir-Raven, A. M. α-Lipoic Acid Potentiates the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables in Chondrocyte Cultures. Cartilage 2018, 9, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabha, M.; Hochberg, M. C. Non-surgical management of hip and knee osteoarthritis; comparison of ACR/AF and OARSI 2019 and VA/DoD 2020 guidelines. Osteoarthritis and cartilage open 2022, 4, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, P. H.; Gao, H. X.; Close, K. L. American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2017. Journal of diabetes 2017, 9, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, R.; Valizadeh, L.; Negahban, H.; Karimi, M.; Goharpey, S.; Shahali, S. The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis, Lequesne Algofunctional index, Arthritis Impact Measurement Scale-short form, and Visual Analogue Scale in patients with knee osteoarthritis: responsiveness and minimal clinically important differences. Disability and rehabilitation 2023, 45, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y. T.; Wu, J. S. The Visual Analogue Scale for Rating, Ranking and Paired-Comparison (VAS-RRP): A new technique for psychological measurement. Behavior research methods 2018, 50, 1694–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gignac, M. A.; Cao, X.; McAlpine, J.; Badley, E. M. Measures of disability: Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales 2 (AIMS2), Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales 2-Short Form (AIMS2-SF), The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Long-Term Disability (LTD) Questionnaire, EQ-5D, World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule II (WHODASII), Late-Life Function and Disability Instrument (LLFDI), and Late-Life Function and Disability Instrument-Abbreviated Version (LLFDI-Abbreviated). Arthritis care & research 2011, 63 Suppl 11, S308-24. [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky, W. H.; Fisher, L.; Earles, J.; Dudl, R. J.; Lees, J.; Mullan, J.; Jackson, R. A. Assessing psychosocial distress in diabetes: development of the diabetes distress scale. Diabetes care 2005, 28, 626–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed Ahmed, H. A.; Mohamed, S. F.; Mostafa, M.; Elotla, S. F.; Shah, A.; Shah, J.; Fouad, A. M. Psychometric evaluation of the Arabic version of the 5-item Problem Areas in Diabetes (AR-PAID-5) scale. BMC primary care 2022, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Cooper, C.; Reginster, J. Y.; Hochberg, M.; Branco, J.; Bruyère, O.; Chapurlat, R.; Al-Daghri, N.; Dennison, E.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Kaux, J. F.; Maheu, E.; Rizzoli, R.; Roth, R.; Rovati, L. C.; Uebelhart, D.; Vlaskovska, M.; Scheen, A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism 2019, 49, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courties, A.; Sellam, J. Osteoarthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: What are the links? Diabetes research and clinical practice 2016, 122, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, A. L.; Hartley, A.; Katsoula, G.; Smith, G. D.; Morris, A. P.; Zeggini, E. Genetic underpinning of the comorbidity between type 2 diabetes and osteoarthritis. American journal of human genetics 2023, 110, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Mrosewski, I.; Silawal, S.; Schulze-Tanzil, G. The interrelation of osteoarthritis and diabetes mellitus: considering the potential role of interleukin-10 and in vitro models for further analysis. Inflammation research : official journal of the European Histamine Research Society... [et al.] 2018, 67, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitner, A.; Wildemann, B. Diabetes - osteoarthritis and joint pain. Bone & joint research 2021, 10, 307–309. [Google Scholar]
- Motta, F.; Barone, E.; Sica, A.; Selmi, C. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology 2023, 64, 222–238. [Google Scholar]
- Burbank, K. M.; Stevenson, J. H.; Czarnecki, G. R.; Dorfman, J. Chronic shoulder pain: part I. Evaluation and diagnosis. American family physician 2008, 77, 453–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colletti, A.; Cicero, A. F. G. Nutraceutical Approach to Chronic Osteoarthritis: From Molecular Research to Clinical Evidence. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, Y. B.; Wang, X. T.; Zhuang, J. P.; Zhou, C. L. Proline-Serine-Threonine Phosphatase-Interacting Protein 2 Alleviates Diabetes Mellitus-Osteoarthritis in Rats through Attenuating Synovial Inflammation and Cartilage Injury. Orthopaedic surgery 2021, 13, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, H. A.; Alzamil, N. M.; Al-Ani, B.; Haidara, M. A.; Kamar, S. S.; Dawood, A. F. Suppression of knee joint osteoarthritis induced secondary to type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats by resveratrol: role of glycated haemoglobin and hyperlipidaemia and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Archives of physiology and biochemistry 2022, 128, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Karimi, E.; Rezaie, P.; Ferns, G. A. Treatment with GLP1 receptor agonists reduce serum CRP concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of diabetes and its complications 2017, 31, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, M. C.; Fernandez, M. L. Inflammation and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes & metabolism 2012, 38, 183–91. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, A. V.; Lane, N. E., Bone and Joint Complications in Diabetes. In Diabetes in America, Cowie, C. C.; Casagrande, S. S.; Menke, A.; Cissell, M. A.; Eberhardt, M. S.; Meigs, J. B.; Gregg, E. W.; Knowler, W. C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Becker, D. J.; Brancati, F. L.; Boyko, E. J.; Herman, W. H.; Howard, B. V.; Narayan, K. M. V.; Rewers, M.; Fradkin, J. E., Eds. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US): Bethesda (MD) Schwartz received speaker honorarium and travel support to attend a conference from Chugai Pharmaceutical, served on an advisory panel for Janssen Pharmaceuticals and for Amgen, and received research support from Hologic., 2018. Rewers, M.
- Qu, Z. A.; Ma, X. J.; Huang, S. B.; Hao, X. R.; Li, D. M.; Feng, K. Y.; Wang, W. M. SIRT2 inhibits oxidative stress and inflammatory response in diabetic osteoarthritis. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences 2020, 24, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Bargues, C.; Alique, M.; Barrús-Ortiz, M. T.; Borrás, C.; Rodrigues-Díez, R. Special Issue "Oxidative Stress in Aging and Associated Chronic Diseases". Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadella, H.; Bloom, A. W.; Demory Beckler, M.; Kesselman, M. M. The Overlap of Diabetes and Osteoarthritis in American Populations. Cureus 2023, 15, e38287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courties, A.; Sellam, J.; Berenbaum, F. Metabolic syndrome-associated osteoarthritis. Current opinion in rheumatology 2017, 29, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, S. J. P.; Venkatesan, V.; Ghosh, S.; Kotikalapudi, N. Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Osteoarthritis-An Updated Review. Current obesity reports 2023, 12, 308–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, T.; Sun, D.; Liang, Z.; Li, Y.; Heianza, Y.; Qi, L. Glucosamine Use, Inflammation, and Genetic Susceptibility, and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Study in UK Biobank. Diabetes care 2020, 43, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; González-Gay, M.; Lago, F.; Karppinen, J.; Tervonen, O.; Mobasheri, A.; Gualillo, O. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nature reviews. Rheumatology 2022, 18, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, A. The F/B ratio as a biomarker for inflammation in COVID-19 and T2D: Impact of metformin. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2023, 163, 114892. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, F.; Cai, G. Osteoarthritis and risk of type 2 diabetes: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Journal of diabetes 2023, 15, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanick, J. I.; Apovian, C.; Brethauer, S.; Garvey, W. T.; Joffe, A. M.; Kim, J.; Kushner, R. F.; Lindquist, R.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Seger, J.; Urman, R. D.; Adams, S.; Cleek, J. B.; Correa, R.; Figaro, M. K.; Flanders, K.; Grams, J.; Hurley, D. L.; Kothari, S.; Seger, M. V.; Still, C. D. CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE PERIOPERATIVE NUTRITION, METABOLIC, AND NONSURGICAL SUPPORT OF PATIENTS UNDERGOING BARIATRIC PROCEDURES - 2019 UPDATE: COSPONSORED BY AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS/AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY, THE OBESITY SOCIETY, AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR METABOLIC & BARIATRIC SURGERY, OBESITY MEDICINE ASSOCIATION, AND AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ANESTHESIOLOGISTS - EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Endocrine practice : official journal of the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists 2019, 25, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nature reviews. Endocrinology 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repchuk, Y.; Sydorchuk, L. P.; Sydorchuk, A. R.; Fedonyuk, L. Y.; Kamyshnyi, O.; Korovenkova, O.; Plehutsa, I. M.; Dzhuryak, V. S.; Myshkovskii, Y. M.; Iftoda, O. M.; Sydorchuk, R. I. Linkage of blood pressure, obesity and diabetes mellitus with angiotensinogen gene (AGT 704T>C/rs699) polymorphism in hypertensive patients. Bratislavske lekarske listy 2021, 122, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyshna, II; Pavlovych, L. B.; Maslyanko, V. A.; Kamyshnyi, A. M. Analysis of the transcriptional activity of genes of neuropeptides and their receptors in the blood of patients with thyroid pathology. Journal of medicine and life 2021, 14, 243–249. [CrossRef]
- Yerevanian, A.; Soukas, A. A. Metformin: Mechanisms in Human Obesity and Weight Loss. Current obesity reports 2019, 8, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshnyi, O.; Matskevych, V.; Lenchuk, T.; Strilbytska, O.; Storey, K.; Lushchak, O. Metformin to decrease COVID-19 severity and mortality: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2021, 144, 112230. [Google Scholar]
- Triggle, C. R.; Mohammed, I.; Bshesh, K.; Marei, I.; Ye, K.; Ding, H.; MacDonald, R.; Hollenberg, M. D.; Hill, M. A. Metformin: Is it a drug for all reasons and diseases? Metabolism: clinical and experimental 2022, 133, 155223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Kobyliak, N.; Kamyshnyi, A. Gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A culture-based method. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2023, 13, 1142578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Kamyshnyi, A. Gene expression of protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 1 (PRKAA1), solute carrier family 2 member 1 (SLC2A1) and mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) in metformin-treated type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19: impact on inflammation markers. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Metformin Alters mRNA Expression of FOXP3, RORC, and TBX21 and Modulates Gut Microbiota in COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Viruses 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlo, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Kamyshnyi, A. Effects of metformin on the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Molecular metabolism 2023, 77, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMoia, T. E.; Shulman, G. I. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin Action. Endocrine reviews 2021, 42, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A. S.; Gubbi, S.; Barzilai, N. Benefits of Metformin in Attenuating the Hallmarks of Aging. Cell metabolism 2020, 32, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R. J. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. The Journal of biological chemistry 2018, 293, 7522–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; Martins, N.; Cho, W. C.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Insights on the Use of α-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Pellegrini, M. V.; Gupta, V. Alpha-Lipoic Acid. In StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing.
- Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Mark Pellegrini declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Vikas Gupta declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies., 2024.
- Zwierz, M.; Chabowski, A.; Sztolsztener, K. α-Lipoic acid - a promising agent for attenuating inflammation and preventing steatohepatitis in rats fed a high-fat diet. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 2023, 750, 109811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Houseiny, W.; Arisha, A. H.; Metwally, M. M. M.; Abdel-Warith, A. A.; Younis, E. M.; Davies, S. J.; Hassan, B. A.; Abd-Elhakim, Y. M. Alpha-lipoic acid suppresses gibberellic acid nephrotoxicity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) via modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, cytokine production, and apoptosis. Pesticide biochemistry and physiology 2023, 196, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; Du, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.; Qin, Y.; Meng, R.; Gan, L.; Zhang, J. Alpha-lipoic Acid Protects Against Chronic Alcohol Consumption-induced Cardiac Damage by the Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2-associated PINK/Parkin Pathway. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 2023, 82, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdullah Ali, M.; Naji Alhassani, A.; Kareem Hamad, B. Impacts of trelagliptin and remogliflozin alone and in combination with Alpha Lipoic Acid on cardiac function in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in rats. Cellular and molecular biology (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 2023, 69, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baicus, C.; Purcarea, A.; von Elm, E.; Delcea, C.; Furtunescu, F. L. Alpha-lipoic acid for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2024, 1, Cd012967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Q.; Ling, X.; Wang, H. J.; Chen, F. E. α-Lipoic acid chemistry: the past 70 years. RSC advances 2023, 13, 36346–36363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronan, J. E. Lipoic acid attachment to proteins: stimulating new developments. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews : MMBR 2024, 88, e0000524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihani, S. A. Role of Lipoic Acid in Testosterone Production in Males. The world journal of men's health 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhitano, L.; Distefano, A.; Amorini, A. M.; Orlando, L.; Giallongo, S.; Tibullo, D.; Lazzarino, G.; Nicolosi, A.; Alanazi, A. M.; Saoca, C.; Macaione, V.; Aguennouz, M.; Salomone, F.; Tropea, E.; Barbagallo, I. A.; Volti, G. L.; Lazzarino, G. (+)-Lipoic Acid Reduces Lipotoxicity and Regulates Mitochondrial Homeostasis and Energy Balance in an In Vitro Model of Liver Steatosis. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabin, E.; Dong, Y.; Roy, S.; Smirnova, J.; Smith, J. W.; Ralle, M.; Summers, K.; Yang, H.; Dev, S.; Wang, Y.; Devenney, B.; Cole, R. N.; Palumaa, P.; Lutsenko, S. α-lipoic acid ameliorates consequences of copper overload by up-regulating selenoproteins and decreasing redox misbalance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2023, 120, e2305961120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Donoso, M.; López-Chaparro, M.; Barahona-Vásquez, M.; Santana-Machuca, A.; Bruna-Mejias, A.; Nova-Baeza, P.; Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J. J. Effectiveness of alpha-lipoic acid in patients with neuropathic pain associated with type I and type II diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e35368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H. N.; Oh, T. J. Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatments for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetes & metabolism journal 2023, 47, 743–756. [Google Scholar]
- Gilron, I.; Robb, S.; Tu, D.; Holden, R. R.; Jackson, A. C.; Duggan, S.; Milev, R. Randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of a combination of alpha-lipoic acid and pregabalin for neuropathic pain: the PAIN-CARE trial. Pain 2024, 165, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genazzani, A. D.; Battipaglia, C.; Rusce, L.; Prampolini, G.; Aio, C.; Ricciardiello, F.; Foschi, M.; Sponzilli, A.; Semprini, E.; Petrillo, T. Alpha lipoic acid administration improved both peripheral sensitivity to insulin and liver clearance of insulin reducing potential risk of diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight/obese PCOS patients. Gynecological endocrinology : the official journal of the International Society of Gynecological Endocrinology 2024, 40, 2341701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| OA (n=52) | OA+T2DM (n=71) | pa-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 53.8% | 54.9% | p = 0.7521 |
| Female | 46.2% | 45.1% | |
| Age | 47 (37.75–52.25) | 48 (36–53.75) | p = 0.6143 |
| Duration of OA | 7 (5.5–9) | 8 (5.0–9.5) | p = 0.1157 |
| Group without ALA (n=37) | Group with ALA (n=34) | pa-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 56.8% | 52.9% | p = 0.3472 |
| Female | 46.2% | 47.1% | |
| Age | 47.5 (36.5–53) | 48 (35.75–54) | p = 0.7981 |
| Duration of OA | 7.5 (5.0–8.5) | 8 (5.25–9.75) | p = 0.2873 |
| Duration of T2DM | 6.5 (4.0-7.75) | 6 (4.25-8) | p = 0.5428 |
| OA (n=52) | OA+T2DM (n=71) | pa-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kellgren-Lawrence grade | 2 (2-2) | 2 (2-1) | pa = 0.469 |
| WOMAC pain | 11 (10-12) | 12 (11-13) | pa = 0.2091 |
| WOMAC stiffness | 4 (3-5) | 5 (4-5) | pa = 0.0003 |
| WOMAC physical function | 38 (36-40) | 40 (36-44) | pa = 0.0529 |
| Total WOMAC score | 54 (51-56) | 56 (53.0-60.5) | pa = 0.0043 |
| Lequesne Algofunctional Index | 5 (3.75-5) | 5 (4-6) | pa = 0.0117 |
| VAS rest pain | 32 (26.75-39) | 35 (32-39) | pa = 0.0371 |
| VAS movement pain | 52 (46-54.25) | 51 (48-55) | pa = 0.3074 |
| VAS inflammation | 30 (28-32.25) | 32 (28.5-36) | pa = 0.045 |
| VAS joint dysfunction | 23 (21-25) | 24 (22-28) | pa = 0.02 |
| AIMS-FF | 2.8 (2.3-3.2) | 3 (2.65-3.2) | pa = 0.0367 |
| AIMS-P | 2.5 (2.28-2.8) | 2.6 (2.2-2.8) | pa = 0.9283 |
| AIMS-SF | 1.9 (1.6-2.1) | 2 (1.8-2.2) | pa = 0.0045 |
| AIMS-EH | 2.15 (1.98-2.3) | 2.2 (1.9-2.4) | pa = 0.5849 |
| AIMS-GHP | 2.7 (2.4-2.9) | 2.9 (2.6-3.2) | pa = 0.0035 |
| OA (n=52) | OA+T2DM (n=71) | pa -value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood glucose, mmol/L | 4.2 (4.02-4.38) | 6.84 (6.51-7.63) | pa < 0.001 |
| C-peptide, ng/mL | 3 (2.51-3.55) | 4.54 (3.81-5.14) | pa < 0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.68 (2.47-2.83) | 3.46 (3.19-3.8) | pa < 0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.92 (5.38-6.33) | 6.72 (6.55-6.86) | pa < 0.001 |
| DDS-17-EB | 1.2 (1.13-1.24) | 3.4 (3.15-3.66) | pa < 0.001 |
| DDS-17-PRD | 1.1 (1.04-1.17) | 4.07 (3.84-4.24) | pa < 0.001 |
| DDS-17-RRD | 1.13 (1.07-1.19) | 4.29 (4.0-4.5) | pa < 0.001 |
| DDS-17-ID | 1.22 (1.13-1.26) | 3.99 (3.69-4.35) | pa < 0.001 |
| Total DDS-17 score | 1.15 (1.13-1.19) | 3.91 (3.77-4.1) | pa < 0.001 |
| PAID | 6 (6-6) | 34 (31-39) | pa < 0.001 |
| OA (n=52) | OA+T2DM (n=71) | pb-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leukocytes, 109/L | 6.83 (6.19-7.37) | 7.07 (6.64-7.57) | pa = 0.0664 |
| Neutrophils, % | 53.5 (52-56.25) | 56 (52-61) | pa = 0.0332 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 21 (19-23.25) | 20 (19-22) | pa = 0.0343 |
| NLR | 2.55 (2.33-2.7) | 2.74 (2.54-3) | pa = 0.0003 |
| CRP, mg/L | 4.86 (4.46-5.53) | 5.1 (4.83-5.51) | pa = 0.0624 |
| Hydroxyproline, mg/L | 1.53 (1.36-1.67) | 1.61 (1.35-2.16) | pa = 0.066 |
| MA, µmol/L. | 4.61 (4.02-5.03) | 5.04 (4.54-5.42) | pa = 0.0008 |
| Ceruloplasmin, mg/L | 388.5 (368.2-408.5) | 399 (388.5-410.2) | pa = 0.0088 |
| Kallikrein, μg/L | 153.45 (145-158.4) | 156.8 (148.55-162.55) | pa = 0.0822 |
| SOD, U/mL | 53.02 (46.81-57.23) | 55.3 (50.6-60.7) | pa = 0.0711 |
| Catalase, U/mL | 16.74 (15.84-18.24) | 18.2 (16.35-20.95) | pa = 0.0051 |
| α1-Antitrypsin, g/L: | 1.69 (1.63-1.74) | 1.7 (1.58-1.81) | pa = 0.6375 |
| α2-Macroglobulin, g/L | 1.91 (1.86-1.99) | 1.89 (1.77-2.05) | pa = 0.3204 |
| OA (n=52) | OA+T2DM (n=71) | pb-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum IgA, g/L | 1.84 (1.73-1.97) | 1.93 (1.78-2.11) | pa = 0.0218 |
| IgM, g/L | 1.02 (0.9-1.11) | 1.05 (0.94-1.21) | pa = 0.1328 |
| IgG, g/L | 9.12 (8.49-9.66) | 9.08 (8.25-9.68) | pa = 0.6616 |
| IgE, IU/mL | 38.8 (37.18-39.59) | 40.4 (36.3-45.85) | pa = 0.0214 |
| T-Lymphocytes (CD3+, CD19-), % | 59.9 (56.78-62.75) | 60.6 (57.5-65.55) | pa = 0.0896 |
| T-Helpers (CD4+, CD8-), % | 42.55 (40.35-43.43) | 43.5 (40.8-47.4) | pa = 0.0795 |
| T-Cytotoxic Cells (CD4-, CD8+), % | 28 (25.48-30.65) | 27.7 (26.35-29.75) | pa = 0.7645 |
| Immunoregulatory Index | 1.5 (1.4-1.6) | 1.6 (1.41-1.72) | pa = 0.047 |
| Cytotoxic Cells (CD3+, CD56+), % | 4.7 (4.4-5.03) | 4.9 (4.3-5.45) | pa = 0.2383 |
| NK Cells (CD3-, CD56+), % | 9.5 (9.2-9.8) | 9.7 (8.8-10.65) | pa = 0.2447 |
| B-Lymphocytes (CD3-, CD19+), % | 9.75 (9.3-10.3) | 10.1 (9.6-10.8) | pa = 0.0709 |
| Monocytes/Macrophages (CD14), % | 8.1 (7.9-8.4) | 8.2 (7.5-8.85) | pa = 0.5743 |
| Predictors | Unadjusted | Adjusted | ||
| COR; 95% CI | p | AOR; 95% CI | p | |
| HOMA-IR | 2065.650; 121.146 – 35206.993 | < 0.001* | 4997.535; 116.980 – 213416.301 | < 0.001* |
| HbA1c | 14.986; 5.387 – 41.679 | < 0.001* | 6.120; 1.239 – 30.235 | 0.026* |
| Serum IgA | 9.210; 1.459 – 58.090 | 0.018* | 2306.762; 14.182 – 375119.530 | 0.003* |
| Group without ALA (n=37) | Group with ALA (n=34) | pbc-value | |||
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | ||
| Kellgren-Lawrence grade | 2 (1-2) | 2 (1-2) | 2 (1.25-2) | 2 (1-2) | pb = 0.7395 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.233 | pa = 0.484 | pc = 0.7298 | ||
| WOMAC pain | 11 (10-13) | 11 (9-12) | 12 (11-13) | 9 (8-11) | pb = 0.4518 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0321 | pa = 0.0014 | pc = 0.0390 | ||
| WOMAC stiffness | 5 (4-6) | 4 (4-5) | 5 (4-5) | 4 (3-4) | pb = 0.1993 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0010 | pa = 0.0055 | pc = 0.1937 | ||
| WOMAC physical function | 40 (35-44) | 37 (35-39) | 40 (36.25-43.75) | 36.5 (35-38.75) | pb = 0.7996 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.055 | pa = 0.0049 | pc = 0.9538 | ||
| Total WOMAC score | 56 (53-61) | 52 (48-53) | 56.5 (53.25-59.75) | 50 (47-53) | pb = 0.8853 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0028 | pa = < 0.001 | pc = 0.1876 | ||
| Lequesne Algofunctional Index |
5 (4-6) | 4 (3-5) | 5 (4-5.75) | 3 (2-4) | pb = 0.5299 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0006 | pa = < 0.001 | pc = 0.0172 | ||
| VAS rest pain | 37 (32-40) | 30 (27-34) | 34 (32-38) | 30.5 (28-34) | pb = 0.1541 |
| pac-value | pa < 0.001 | pa < 0.001 | pc = 0.751 | ||
| VAS movement pain | 52 (48-54) | 50 (43-53) | 50.5 (46.25-58.5) | 46.5 (39.5-50.75) | pb = 0.624 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0461 | pa = 0.0049 | pc = 0.0619 | ||
| VAS inflammation | 32 (28-34) | 27 (22-31) | 33 (29.25-37) | 26 (24-28.75) | pb = 0.3127 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0113 | pa < 0.001 | pc = 0.5757 | ||
| VAS joint dysfunction |
24 (22-28) | 21 (19-24) | 24.5 (21.25-28.75) | 19 (17-22) | pb = 0.9586 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0089 | pa = 0.0004 | pc = 0.0497 | ||
| AIMS-FF | 3.1 (2.7-3.2) | 2.7 (2.5-3) | 2.9 (2.6-3.18) | 2.5 (2.23-2.8) | pb = 0.3611 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0121 | pa = 0.0026 | pc = 0.0142 | ||
| AIMS-P | 2.5 (2.2-2.8) | 2.3 (2-2.6) | 2.6 (2.4-2.78) | 2 (1.8-2.3) | pb = 0.4018 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.3564 | pa < 0.001 | pc = 0.0073 | ||
| AIMS-SF | 2 (1.9-2.2) | 1.9 (1.7-2) | 2 (1.73-2.2) | 1.75 (1.6-1.9) | pb = 0.3663 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0241 | pa = 0.0146 | pc = 0.1003 | ||
| AIMS-EH | 2.2 (2-2.3) | 2.1 (1.9-2.2) | 2.1 (1.9-2.4) | 2 (1.7-2.1) | pb = 0.5388 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2196 | pa = 0.0055 | pc = 0.0083 | ||
| AIMS-GHP | 2.9 (2.6-3.1) | 2.7 (2.4-3) | 2.9 (2.7-3.28) | 2.6 (2.43-2.7) | pb = 0.3616 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0907 | pa = 0.0004 | pc = 0.2377 | ||
| Group without ALA (n=37) | Group with ALA (n=34) | pbc-value | |||
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | ||
| Fasting blood glucose, mmol/L | 6.87 (6.5-7.24) | 6.52 (6.17-6.8) | 6.8 (6.54-7.79) | 6.47 (5.8-6.99) | pb = 0,427 |
| pac-value | pa = 0,0271 | pa = 0,003 | pc = 0.881 | ||
| C-peptide, ng/mL | 4.49 (3.88-4.96) | 4.23 (3.78-4.92) | 4.55 (3.56-5.58) | 4.22 (3.88-4.79) | pb = 0,8674 |
| pac-value | pa = 0,4689 | pa = 0,1768 | pc = 0,8539 | ||
| HOMA-IR | 3.49 (3.19-3.75) | 3.4 (3.18-3.6) | 3.45 (3.2-3.83) | 3.35 (2.87-3.69) | pb = 0.8992 |
| pac-value | pa = 0,261 | pa = 0,093 | pc = 0,6452 | ||
| HbA1c, % | 6.7 (6.38-7.25) | 6.49 (6.34-6.96) | 6.73 (6.63-6.79) | 6.63 (6.41-6.94) | pb = 0.9449 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2642 | pa = 0.3308 | pc = 0.5805 | ||
| DDS-17-EB | 3.4 (3.05-3.66) | 3.2 (3.11-3.29) | 3.4 (3.18-3.65) | 3.1 (2.94-3.19) | pb = 0.9266 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0022 | pa = 0.0001 | pc = 0.0035 | ||
| DDS-17-PRD | 4.07 (3.82-4.23) | 3.89 (3.51-4.11) | 4.11 (3.92-4.25) | 3.73 (3.42-4.02) | pb = 0.4439 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1843 | pa = 0.0022 | pc = 0.4406 | ||
| DDS-17-RRD | 4.3 (4.03-4.53) | 3.88 (3.69-4.18) | 4.25 (3.99-4.47) | 3.85 (3.72-3.98) | pb = 0.7385 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0036 | pa < 0.001 | pc = 0.4718 | ||
| DDS-17-ID | 3.93 (3.57-4.29) | 3.86 (3.41-4.2) | 4.02 (3.75-4.41) | 3.66 (3.3-3.96) | pb = 0.4007 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.3898 | pa = 0.0183 | pc = 0.4405 | ||
| Total DDS-17 score | 3.88 (3.76-4.1) | 3.71 (3.57-3.78) | 3.97 (3.77-4.09) | 3.55 (3.45-3.72) | pb = 0.9634 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.6635 | pa = 0.7301 | pc = 0.7596 | ||
| PAID | 35 (32-39) | 31 (28-34) | 33.5 (30.25-37.75) | 29.5 (26.25-31.75) | pb = 0.3837 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0012 | pa = 0.0002 | pc = 0.0293 | ||
| Group without ALA (n=37) | Group with ALA (n=34) | pbc-value | |||
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | ||
| Leukocytes, 109/L | 7.26 (6.64-7.63) | 7.04 (6.19-7.43) | 7.02 (6.63-7.29) | 6.55 (6.06-6.87) | pb = 0.2224 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1534 | pa = 0.0024 | pc = 0.0622 | ||
| Neutrophils, % | 56 (50-59) | 54 (50-56) | 57 (53-61,75) | 55 (50.25-61.75) | pb = 0.0889 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1366 | pa = 0.0054 | pc = 0.2517 | ||
| Lymphocytes, % | 19 (19-21) | 21 (19-22) | 20 (19-23.75) | 22 (20-24) | pb = 0.1237 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.3266 | pa = 0.1269 | pc = 0.0078 | ||
| NLR | 2.74 (2.55-2.94) | 2.52 (2.39-2.78) | 2.76 (2.54-3.08) | 2.42 (2.25-2.68) | pb = 0.4789 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0132 | pa = 0.0023 | pc = 0.0893 | ||
| CRP, mg/L | 5.16 (4.95-5.48) | 4.85 (4.38-5.2) | 5.02 (4.63-5.54) | 4.58 (4.11-5.16) | pb = 0,1286 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.001 | pa = 0.0078 | pc = 0,0119 | ||
| Hydroxyproline, mg/L | 1.61 (1.22-1.87) | 1.64 (1.32-1.8) | 1.64 (1.38-2.27) | 1.47 (1.12-2.04) | pb = 0.497 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.7571 | pa = 0.1324 | pc = 0.7472 | ||
| MA, µmol/L. | 5.04 (4.69-5.39) | 4.81 (4.32-5.42) | 5.04 (4.44-5.6) | 4.44 (3.93-5.05) | pb = 0.8449 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1056 | pa = 0.0031 | pc = 0.0546 | ||
| Ceruloplasmin, mg/L | 397.5 (387.1-410.5) | 390.2 (383.5-409.3) | 405 (391-408.4) | 388.1 (372.3-397.6) | pb = 0.5118 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1491 | pa = 0.0019 | pc = 0.1272 | ||
| Kallikrein, μg/L | 153.7 (148.2-162.4) | 152.1 (146.7-156.9) | 157.5 (150.4-162.5) | 152.2 (145-159.5) | pb = 0.5885 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2364 | pa = 0.1043 | pc = 0.7912 | ||
| SOD, U/mL | 57.5 (52.2-61.5) | 59.3 (55.5-63.3) | 54.75 (47.83-59.68) | 58.3 (53.7-63.58) | pb = 0.1837 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2189 | pa = 0.0033 | pc = 0.5229 | ||
| Catalase, U/mL | 18.3 (16.8-20.1) | 20.5 (18.43-23.26) | 17.7 (15.23-21.73) | 21.95 (20.45-23.98) | pb = 0.8314 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.0146 | pa = 0.0014 | pc = 0.1258 | ||
| α1-Antitrypsin, g/L | 1.7 (1.57-1.78) | 1.7 (1.51-1.76) | 1.71 (1.59-1.83) | 1.61 (1.45-1.79) | pb = 0.6083 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.7571 | pa = 0.1744 | pc = 0.4303 | ||
| α2-Macroglobulin, g/L | 1.88 (1.78-1.99) | 1.99 (1.79-2.09) | 1.9 (1.7-2.11) | 1.93 (1.84-2.12) | pb = 0.7956 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.245 | pa = 0.0889 | pc = 0.6827 | ||
| Group without ALA (n=37) | Group with ALA (n=34) | pbc-value | |||
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | ||
| Serum IgA, g/L | 1.93 (1.79-2.11) | 1.87 (1.69-2.08) | 1.92 (1.76-2.09) | 1.84 (1.56-2.04) | pb =0.9175 |
| pac-value | pa =0.02204 | pa = 0.0251 | pc = 0.3422 | ||
| IgM, g/L | 1.08 (1.02-1.21) | 0.99 (0.84-1.19) | 0.99 (0.89-1.2) | 0.99 (0.71-1.13) | pb = 0.0811 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2133 | pa = 0.1438 | pc = 0.4071 | ||
| IgG, g/L | 8.74 (8.26-9.41) | 8.81 (8.23-9.76) | 9.22 (8.19-9.74) | 8.59 (8.17-9.45) | pb = 0.4204 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.7399 | pa = 0.3303 | pc = 0.6786 | ||
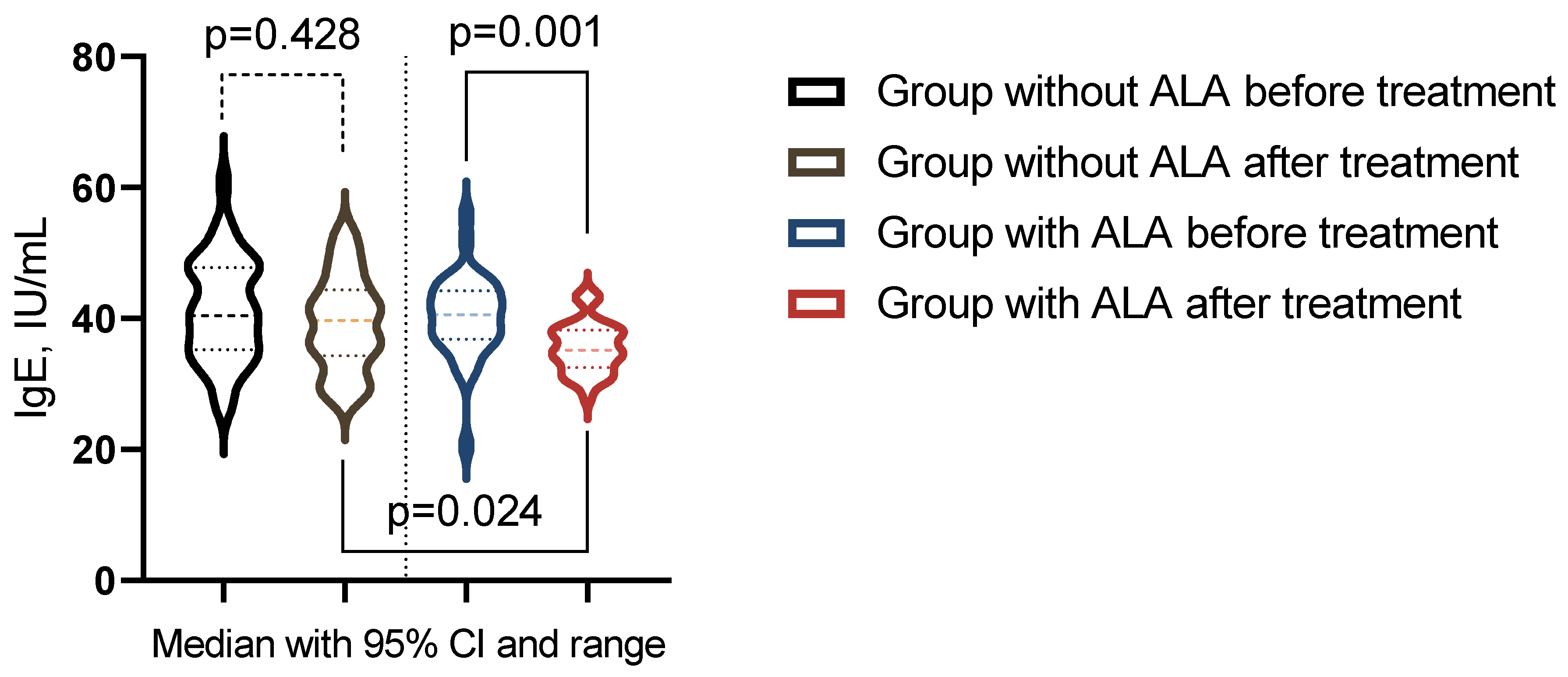
| IgE, IU/mL | 40.4 (35.4-47.6) | 39.7 (34.6-43.9) | 40.6 (36.93-44.15) | 35.15 (32.75-38.08) | pb = 0.704 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.4275 | pa = 0.0008 | pc = 0.0244 | ||
| T-Lymphocytes (CD3+, CD19-), % | 61 (56.6-65.4) | 57.2 (53.8-64.9) | 60 (57.58-66.03) | 58.6 (53.13-63.18) | pb = 0.7255 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1017 | pa = 0.099 | pc = 0.8001 | ||
| T-Helpers (CD4+, CD8-), % | 43.5 (41-46.9) | 42.6 (40.1-44.9) | 44.95 (40.28-47.85) | 40.45 (38.7-44.98) | pb = 0.872 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.4736 | pa = 0.0566 | pc = 0.2617 | ||
| T-Cytotoxic Cells (CD4-, CD8+), % | 28.2 (26.4-29.8) | 29.5 (26-30.8) | 27.45 (26.08-29.5) | 28.45 (27.1-32.25) | pb = 0.508 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.6838 | pa = 0.513 | pc = 0.2766 | ||
| Immunoregulatory Index | 1.61 (1.39-1.64) | 1.47 (1.4-1.67) | 1.59 (1.42-1.76) | 1.4 (1.27-1.55) | pb = 0.6247 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2677 | pa = 0.0125 | pc = 0.056 | ||
| Cytotoxic Cells (CD3+, CD56+), % | 4.8 (4.3-5.5) | 4.8 (4.4-5.2) | 4.9 (4.33-5.4) | 4.85 (4.3-5.1) | pb = 0.7294 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.5724 | pa = 0.6939 | pc = 0.7251 | ||
| NK Cells (CD3-, CD56+), % | 10.3 (9-10.8) | 9.5 (8.7-10.7) | 9.4 (8.73-10.55) | 9.15 (8.5-9.78) | pb = 0.2332 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.1996 | pa = 0.3879 | pc = 0.1389 | ||
| B-Lymphocytes (CD3-, CD19+), % | 10 (9.7-10.5) | 9.9 (9.3-10.7) | 10.2 (9.45-10.9) | 9.65 (8.03-10.45) | pb = 0.7427 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.8741 | pa = 0.0887 | pc = 0.1499 | ||
| Monocytes/Macrophages (CD14), % | 8.2 (7.5-9) | 8.1 (7.2-8.7) | 8.15 (7.55-8.58) | 7.65 (7.13-8.48) | pb = 0.5684 |
| pac-value | pa = 0.2233 | pa = 0.2814 | pc = 0.4403 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





