Submitted:
30 August 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
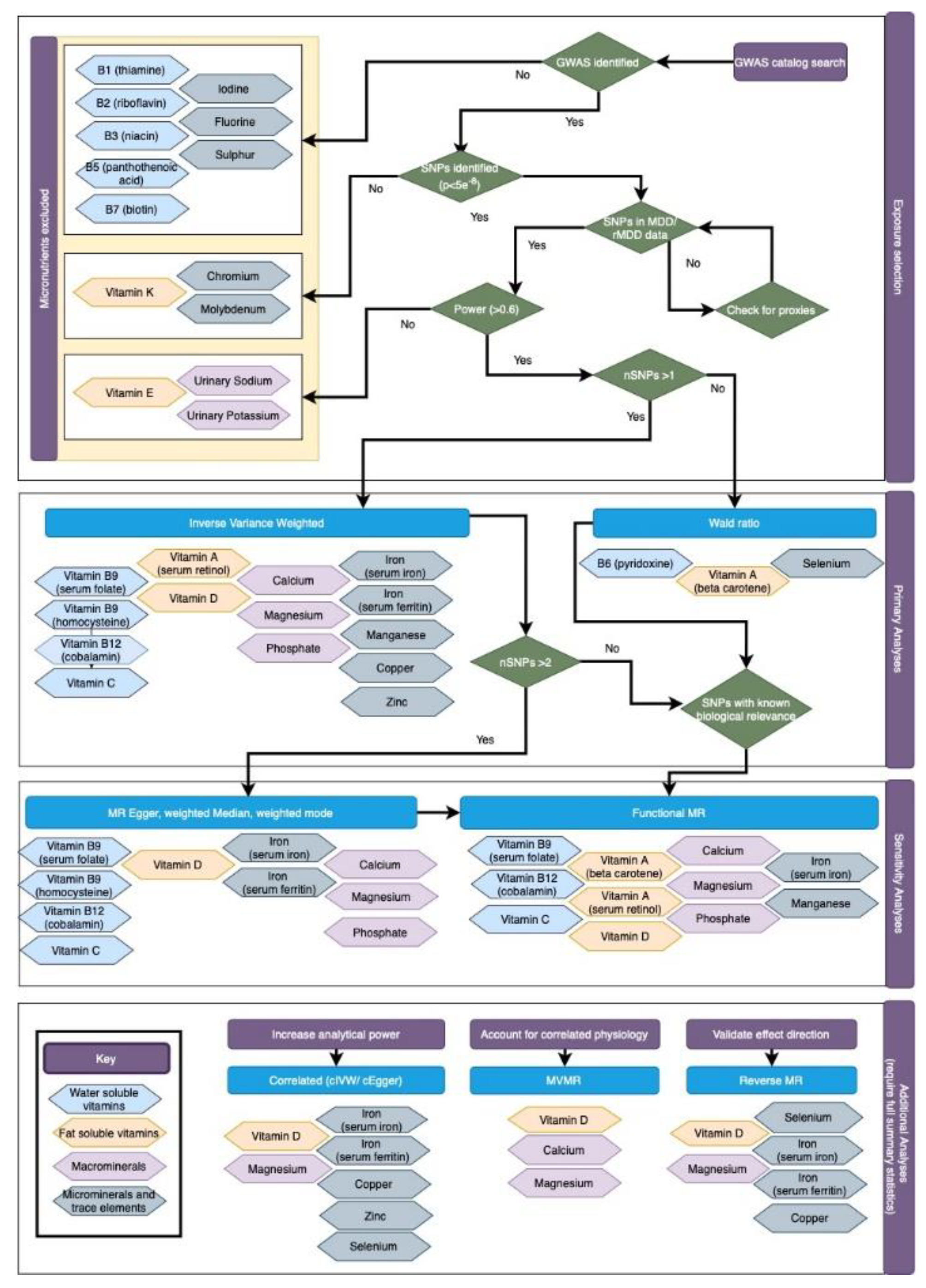
2.1. Data Sources
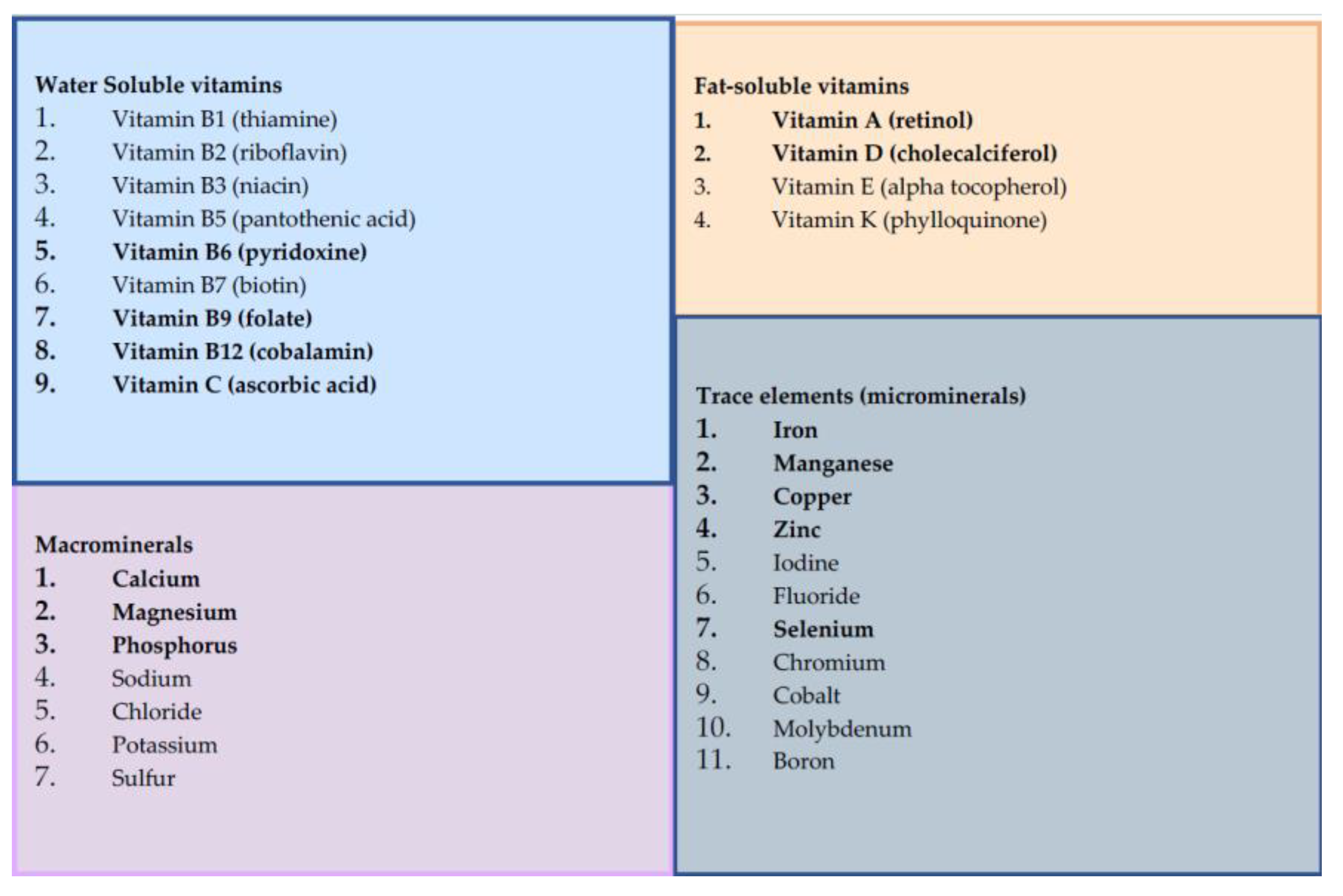
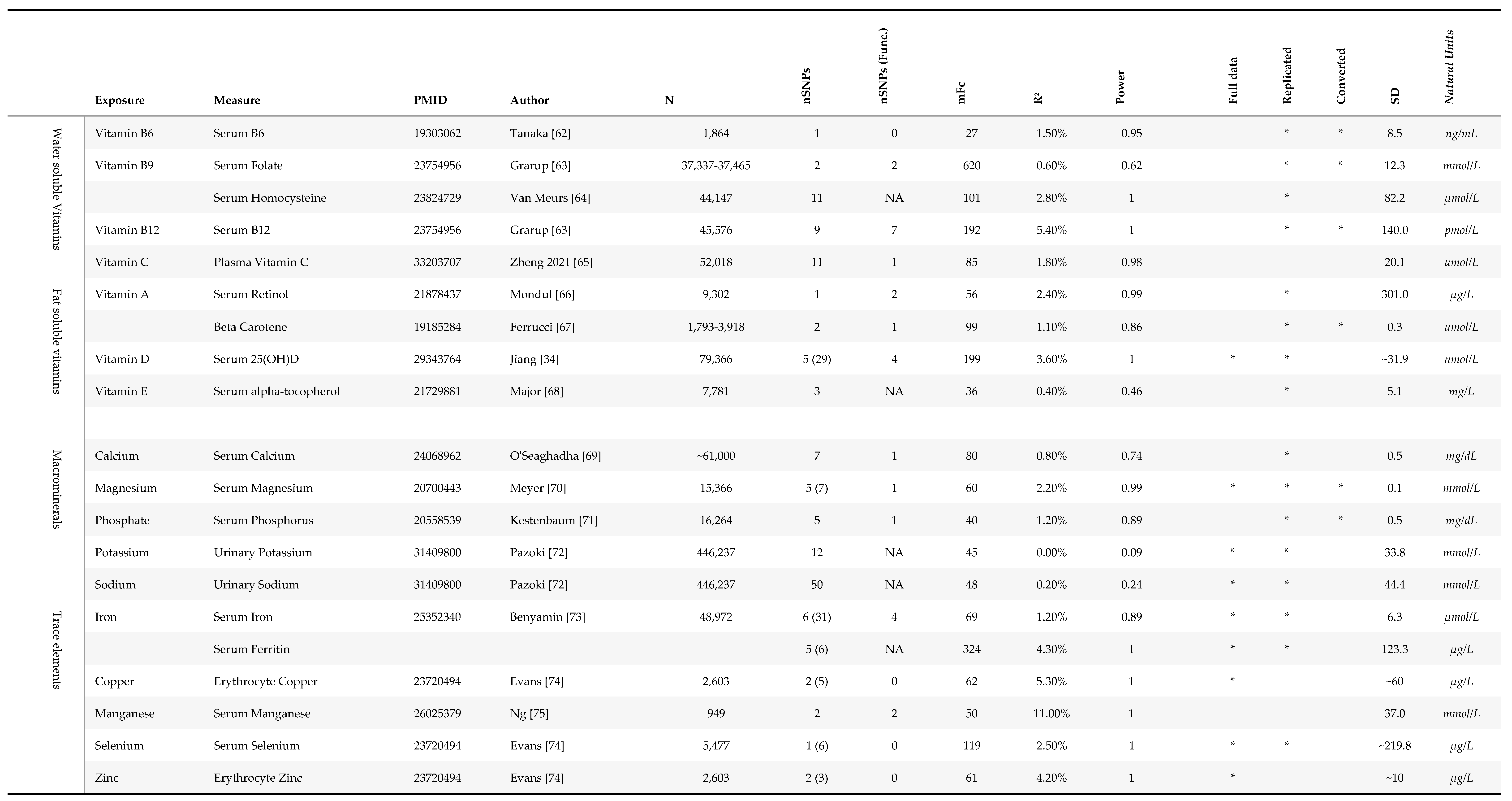
2.1.1. Micronutrient Exposures
2.1.2. Depression Data
2.2. Statistical Power
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Functional MR
2.3.2. Correlated MR
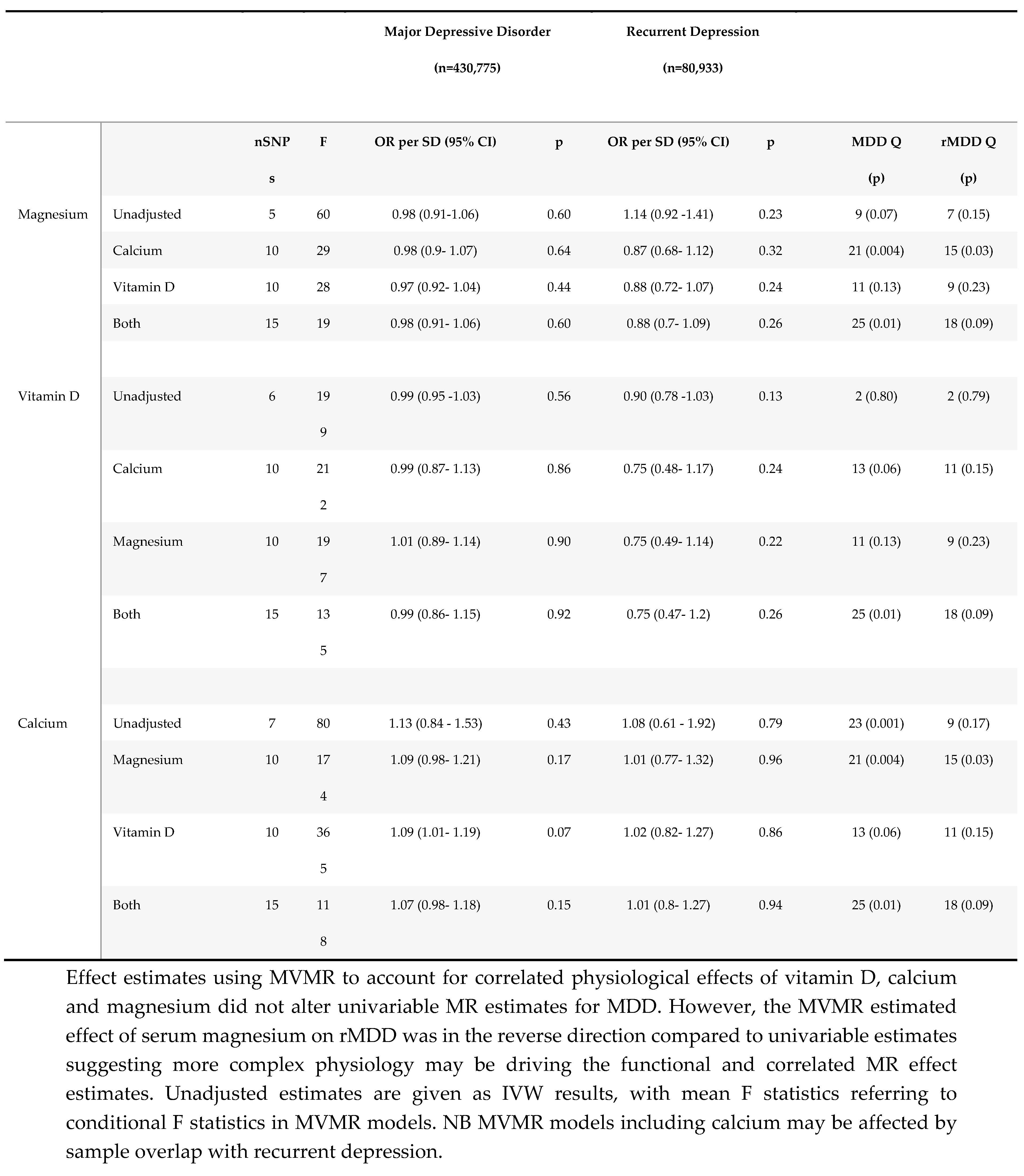
2.3.3. Multivariable MR
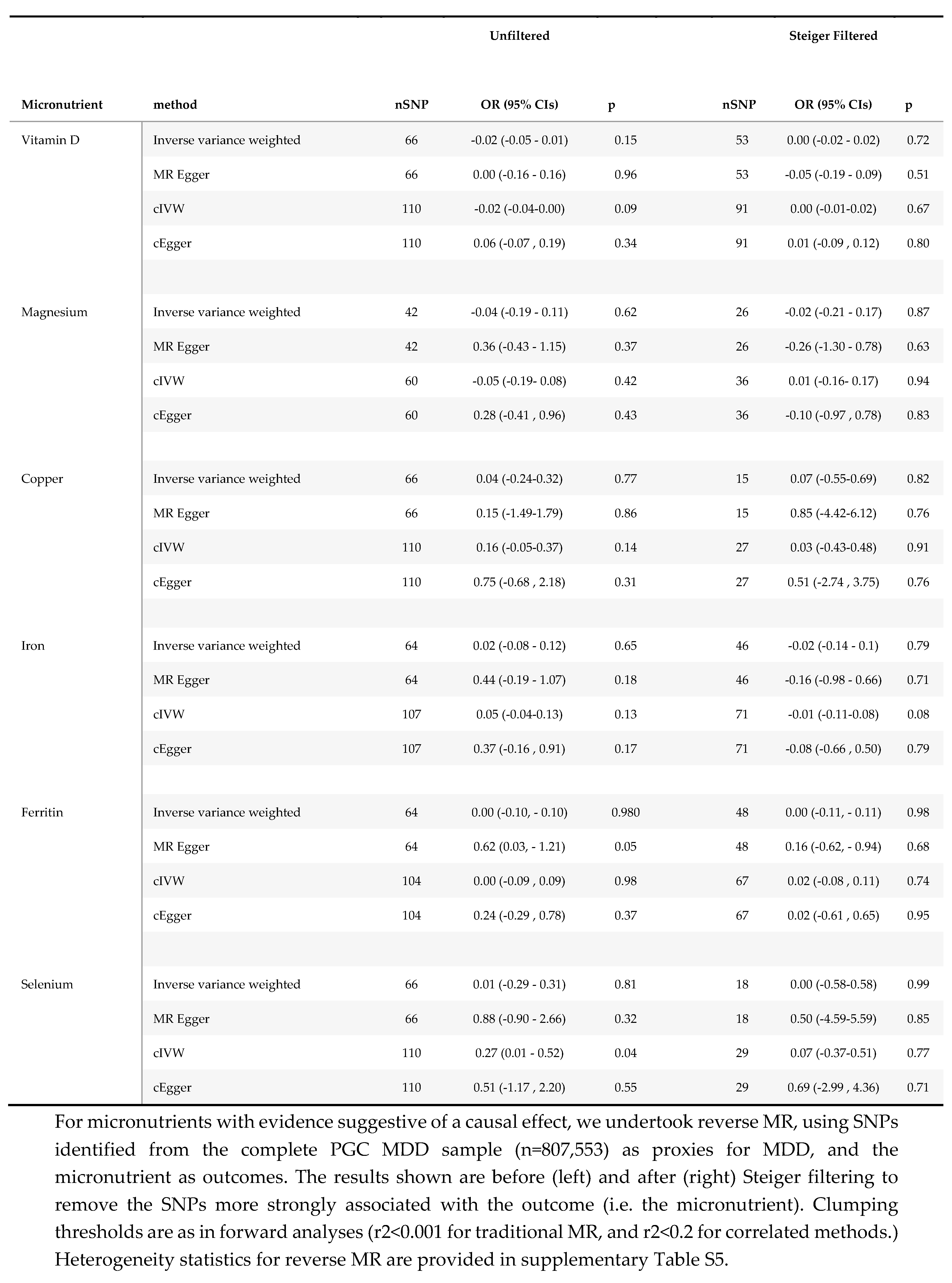
2.3.4. Reverse MR
Results
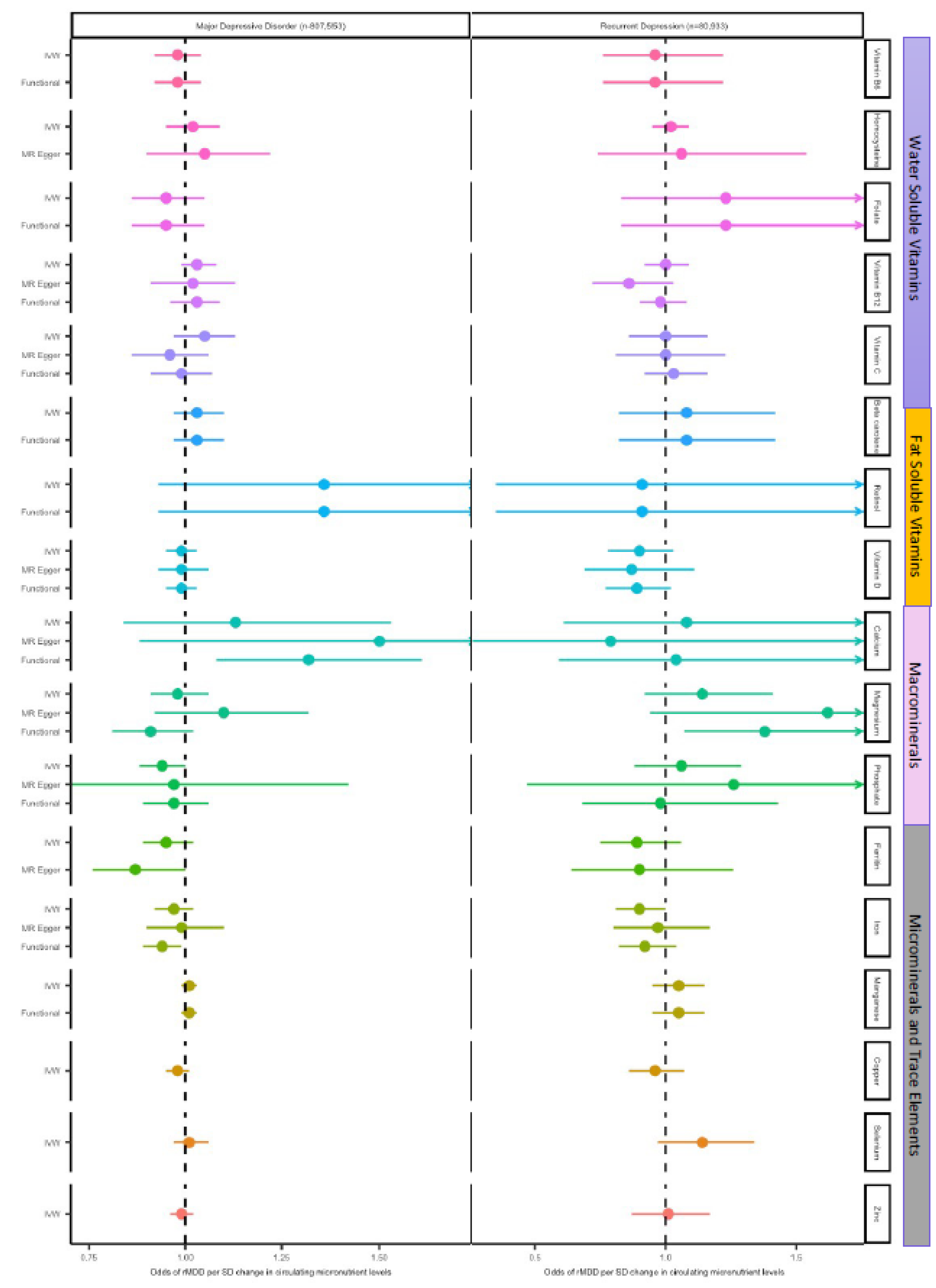
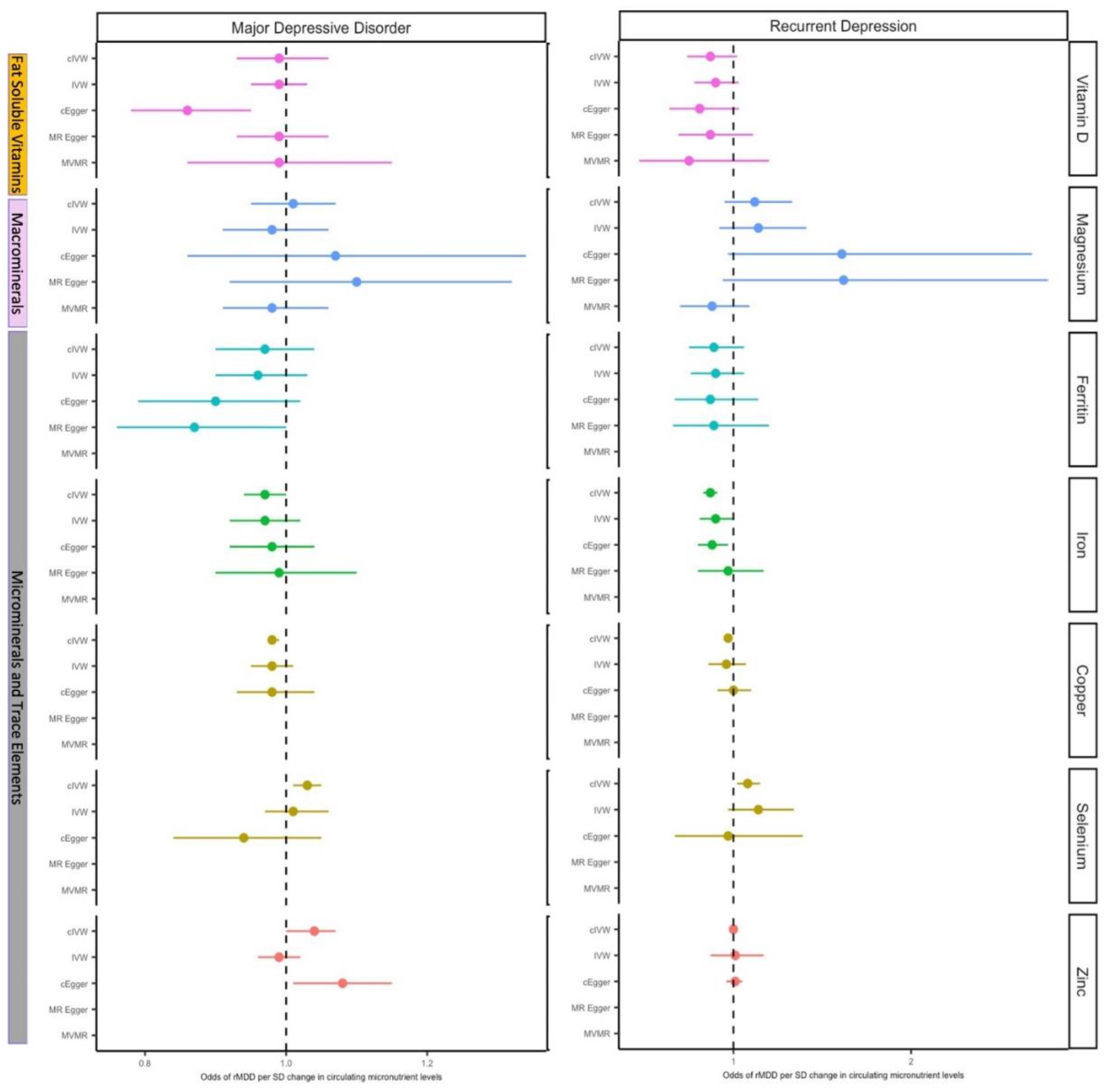
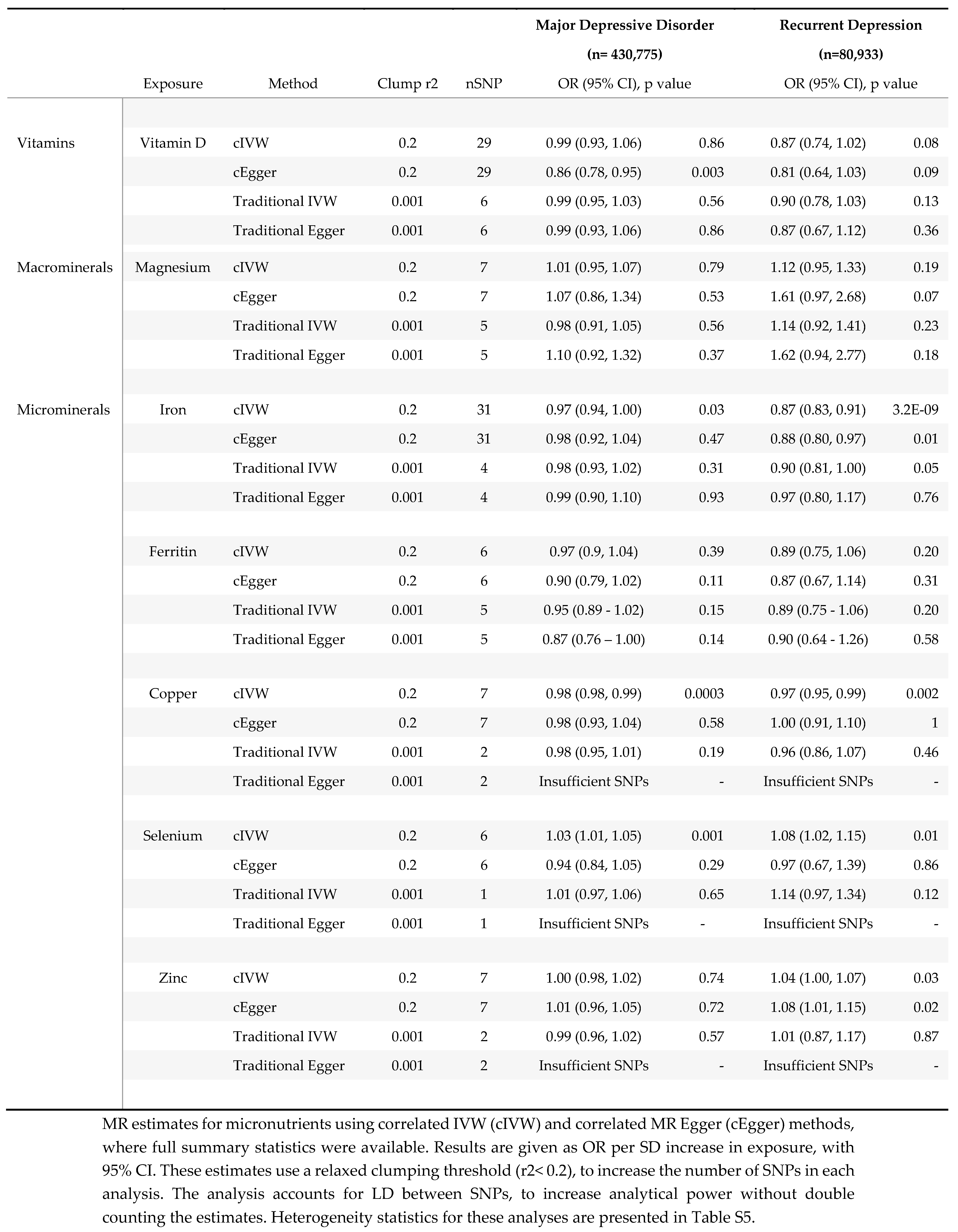
3.1. Effect of Micronutrients on Depressive Disorders
3.1.1. Vitamin D
3.1.2. Magnesium
3.1.3. Copper
3.1.4. Iron
3.1.5. Selenium
3.2. Effect of Major Depressive Disorder on Micronutrient Status
Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Data Availability*
Ethical Approval and Consent
Funding
References
- Berger, M.M.; Shenkin, A.; Schweinlin, A.; Amrein, K.; Augsburger, M.; Biesalski, H.-K.; Bischoff, S.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Gundogan, K.; Lepp, H.-L.; et al. ESPEN micronutrient guideline. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1357–1424. [CrossRef]
- Valsta, L.M.; Tapanainen, H.; Kortetmäki, T.; Sares-Jäske, L.; Paalanen, L.; Kaartinen, N.E.; Haario, P.; Kaljonen, M. Disparities in Nutritional Adequacy of Diets between Different Socioeconomic Groups of Finnish Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1347. [CrossRef]
- Rippin, H.L.; Hutchinson, J.; Jewell, J.; Breda, J.J.; Cade, J.E. Child and adolescent nutrient intakes from current national dietary surveys of European populations. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 32, 38–69. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan BJ, Field CJ, Crawford SG, Simpson JSA. Vitamins, minerals, and mood. Psychol Bull. 2007;133(5):747-60.
- Fulgoni VL, 3rd, Gaine PC, Scott MO, Ricciuto L, DiFrancesco L. Micronutrient Dilution and Added Sugars Intake in U.S. Adults: Examining This Association Using NHANES 2009-2014. Nutrients. 2020;12(4).
- Al-Hamzawi, A.; Alonso, J.; Bruffaerts, R.; de Almeida, J.M.C.; Chardoul, S.; Chiu, W.T.; Degenhardt, L.; Demler, O.V.; Ferry, F.; Gureje, O.; et al. Age of onset and cumulative risk of mental disorders: a cross-national analysis of population surveys from 29 countries. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 668–681. [CrossRef]
- Rubio-López, N.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M.; Pico, Y.; Livianos-Aldana, L.; Llopis-González, A. Nutrient Intake and Depression Symptoms in Spanish Children: The ANIVA Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2016, 13, 352. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lv, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D. Dietary magnesium and calcium intake and risk of depression in the general population: A meta-analysis. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2016, 51, 219–229. [CrossRef]
- Tarleton EK, Littenberg B. Magnesium Intake and Depression in Adults. J Am Board Fam Med. 2015;28(2):249-56.
- Jacka, F.N.; Maes, M.; Pasco, J.A.; Williams, L.J.; Berk, M. Nutrient intakes and the common mental disorders in women. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 79–85. [CrossRef]
- Winther G, Nielsen TW, Wegener G. Magnesium deficiency induces anxiety- and depression-like behavior and metabolic dysfunction in C57Bl/6J mice. Int J Neuropsychoph. 2012;15:198-9.
- Fu, L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yu, Z.; Xu, D.-X. Vitamin D deficiency impairs neurobehavioral development in male mice. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 333–339. [CrossRef]
- Depciuch, J.; Sowa-Kućma, M.; Nowak, G.; Szewczyk, B.; Doboszewska, U.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. The role of zinc deficiency-induced changes in the phospholipid-protein balance of blood serum in animal depression model by Raman, FTIR and UV–vis spectroscopy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 549–558. [CrossRef]
- Lang, U.E.; Beglinger, C.; Schweinfurth, N.; Walter, M.; Borgwardt, S. Nutritional Aspects of Depression. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1029–1043. [CrossRef]
- Sarris, J. Clinical use of nutraceuticals in the adjunctive treatment of depression in mood disorders. Australas. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 369–372. [CrossRef]
- Bot M, Brouwer IA, Roca M, Kohls E, Penninx B, Watkins E, et al. Effect of Multinutrient Supplementation and Food-Related Behavioral Activation Therapy on Prevention of Major Depressive Disorder Among Overweight or Obese Adults With Subsyndromal Depressive Symptoms: The MooDFOOD Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2019;321(9):858-68.
- Okereke OI, Reynolds CF, 3rd, Mischoulon D, Chang G, Vyas CM, Cook NR, et al. Effect of Long-term Vitamin D3 Supplementation vs Placebo on Risk of Depression or Clinically Relevant Depressive Symptoms and on Change in Mood Scores: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2020;324(5):471-80.
- Zheng, J.; Baird, D.; Borges, M.-C.; Bowden, J.; Hemani, G.; Haycock, P.; Evans, D.M.; Smith, G.D. Recent Developments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Curr. Epidemiology Rep. 2017, 4, 330–345. [CrossRef]
- Carnegie, R.; Zheng, J.; Sallis, H.M.; Jones, H.J.; Wade, K.H.; Evans, J.; Zammit, S.; Munafò, M.R.; Martin, R.M. Mendelian randomisation for nutritional psychiatry. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 7, 208–216. [CrossRef]
- Wesolowska K, Elovainio M, Hintsa T, Jokela M, Lehtimaki T, Raitakari OT, et al. Type-2 diabetes and depressive symptoms: Results of applying a Mendelian randomization in the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Psychother Psychosom. 2015;1):77.
- Khandaker, G.; Zuber, V.; Rees, J.M.; Carvalho, L.; Mason, A.; Foley, C.; Gkatzionis, A.; Jones, P.; Burgess, S. Shared mechanisms between coronary heart disease and depression: findings from a large UK general population-based cohort.. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Møllehave, L.T.; Skaaby, T.; Simonsen, K.S.; Thuesen, B.H.; Mortensen, E.L.; Sandholt, C.H.; Pedersen, O.; Grarup, N.; Hansen, T.; Linneberg, A. Association studies of genetic scores of serum vitamin B12 and folate levels with symptoms of depression and anxiety in two danish population studies. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1054–1060. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.-Y. Mineral Nutrition and the Risk of Chronic Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 378. [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, K.; Melhus, H.; Larsson, S.C. Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations and Major Depression: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1987. [CrossRef]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Peyrot, W.J.; Nivard, M.G.; Mbarek, H.; Boomsma, D.I.; Penninx, B.W. A role for vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids in major depression? An exploration using genomics. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, A.; Lumsden, A.; Hyppönen, E. Relationship between Serum 25(OH)D and Depression: Causal Evidence from a Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2020, 13, 109. [CrossRef]
- Libuda, L.; Laabs, B.-H.; Ludwig, C.; Bühlmeier, J.; Antel, J.; Hinney, A.; Naaresh, R.; Föcker, M.; Hebebrand, J.; König, I.R.; et al. Vitamin D and the Risk of Depression: A Causal Relationship? Findings from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1085. [CrossRef]
- Revez, J.A.; Lin, T.; Qiao, Z.; Xue, A.; Holtz, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zeng, J.; Wang, H.; Sidorenko, J.; Kemper, K.E.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 143 loci associated with 25 hydroxyvitamin D concentration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, N.; Dimou, N.; Gill, D.; Tzoulaki, I.; Murphy, N.; Riboli, E.; Lewis, S.J.; Martin, R.M.; Gunter, M.J.; Tsilidis, K.K. Genetically predicted circulating concentrations of micronutrients and risk of breast cancer: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 148, 646–653. [CrossRef]
- Tsilidis, K.K.; Papadimitriou, N.; Dimou, N.; Gill, D.; Lewis, S.J.; Martin, R.M.; Murphy, N.; Markozannes, G.; Zuber, V.; Cross, A.J.; et al. Genetically predicted circulating concentrations of micronutrients and risk of colorectal cancer among individuals of European descent: a Mendelian randomization study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1490–1502. [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Han, C.; Tian, D.; Guo, N.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Genetically Predicted Circulating Concentrations of Micronutrients and Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 811699. [CrossRef]
- Daniel, N.; Bouras, E.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Hughes, D.J. Genetically Predicted Circulating Concentrations of Micronutrients and COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 842315. [CrossRef]
- A Lawlor, D. Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges. Leuk. Res. 2016, 45, 908–915. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; O'Reilly, P.F.; Aschard, H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Richards, J.B.; Dupuis, J.; Ingelsson, E.; Karasik, D.; Pilz, S.; Berry, D.; et al. Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 260. [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.-K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [CrossRef]
- Coleman JRI, Gaspar HA, Bryois J, Breen G. The genetics of the mood disorder spectrum: genome-wide association analyses of over 185,000 cases and 439,000 controls. Biol Psychiat.
- Timpson, N.J.; Forouhi, N.G.; Brion, M.-J.; Harbord, R.M.; Cook, D.G.; Johnson, P.; McConnachie, A.; Morris, R.W.; Rodriguez, S.; Luan, J.; et al. Genetic variation at the SLC23A1 locus is associated with circulating concentrations of l-ascorbic acid (vitamin C): evidence from 5 independent studies with >15,000 participants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 375–382. [CrossRef]
- Team} RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2018.
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7. [CrossRef]
- Yavorska, O.; Burgess, S. MendelianRandomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis: Springer-Verlag New York; 2016.
- Arakawa, K.; Kono, N.; Yamada, Y.; Mori, H.; Tomita, M. KEGG-based pathway visualization tool for complex omics data.. 2005, 5, 419–23.
- Burgess, S.; Dudbridge, F.; Thompson, S.G. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat. Med. 2015, 35, 1880–1906. [CrossRef]
- Bate, T.; Martin, R.M.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Haycock, P.C. Investigating the association between genetically proxied circulating levels of immune checkpoint proteins and cancer survival: protocol for a Mendelian randomisation analysis. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e075981. [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Freitag, D.F.; Khan, H.; Gorman, D.N.; Thompson, S.G. Using Multivariable Mendelian Randomization to Disentangle the Causal Effects of Lipid Fractions. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e108891–e108891. [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Spiller, W.; Bowden, J. Testing and correcting for weak and pleiotropic instruments in two-sample multivariable Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5434–5452. [CrossRef]
- Allgrove J. Physiology of Calcium, Phosphate, Magnesium and Vitamin D. Endocr Dev. 2015;28:7-32.
- Lee, H.-S.; Chao, H.-H.; Huang, W.-T.; Chen, S.C.-C.; Yang, H.-Y. Psychiatric disorders risk in patients with iron deficiency anemia and association with iron supplementation medications: a nationwide database analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Su, T.-P.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hsu, J.-W.; Huang, K.-L.; Chang, W.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; Bai, Y.-M. Association between psychiatric disorders and iron deficiency anemia among children and adolescents: a nationwide population-based study. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 161–161. [CrossRef]
- Erikson, K.M.; Jones, B.C.; Hess, E.J.; Zhang, Q.; Beard, J.L. Iron deficiency decreases dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 69, 409–418. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Nyholt, D.R. Gene-based analyses reveal novel genetic overlap and allelic heterogeneity across five major psychiatric disorders. Hum. Genet. 2016, 136, 263–274. [CrossRef]
- Tarleton, E.K.; Kennedy, A.G.; Rose, G.L.; Crocker, A.; Littenberg, B. The Association between Serum Magnesium Levels and Depression in an Adult Primary Care Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1475. [CrossRef]
- Tarleton, E.K.; Littenberg, B.; MacLean, C.D.; Kennedy, A.G.; Daley, C. Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0180067–e0180067. [CrossRef]
- Sanders, G.T.; Huijgen, H.J.; Sanders, R. Magnesium in Disease: a Review with Special Emphasis on the Serum Ionized Magnesium. cclm 1999, 37, 1011–1033. [CrossRef]
- Himmerich, H.; Patsalos, O.; Lichtblau, N.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Dalton, B. Cytokine Research in Depression: Principles, Challenges, and Open Questions. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 30. [CrossRef]
- Schlingmann, K.P.; Weber, S.; Peters, M.; Niemann Nejsum, L.; Vitzthum, H.; Klingel, K.; Kratz, M.; Haddad, E.; Ristoff, E.; Dinour, D.; et al. Hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia is caused by mutations in TRPM6, a new member of the TRPM gene family. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 166–170. [CrossRef]
- Yarmolinsky, J.; Bonilla, C.; Haycock, P.C.; Langdon, R.J.Q.; A Lotta, L.; Langenberg, C.; Relton, C.L.; Lewis, S.J.; Evans, D.M.; PRACTICAL Consortium; et al. Circulating Selenium and Prostate Cancer Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1035–1038. [CrossRef]
- Lippman SM, Klein EA, Goodman PJ, Lucia MS, Thompson IM, Ford LG, et al. Effect of Selenium and Vitamin E on Risk of Prostate Cancer and Other Cancers The Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial ( SELECT). Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 2009;301(1):39-51.
- Madsen, E.; Gitlin, J.D. Copper and Iron Disorders of the Brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 317–337. [CrossRef]
- McLeod, M.N.; Golden, R.N. Chromium treatment of depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000, 3, 311–314. [CrossRef]
- Tonge, W.L. Nicotinic acid in the treatment of depression. Ann. Intern. Med. 1953, 38, 551–553. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka T, Scheet P, Giusti B, Bandinelli S, Piras MG, Usala G, et al. Genome-wide association study of vitamin B6, vitamin B12, folate, and homocysteine blood concentrations. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84(4):477-82.
- Grarup, N.; Sulem, P.; Sandholt, C.H.; Thorleifsson, G.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Bjarnason, H.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Magnusson, O.T.; Sparsø, T.; et al. Genetic Architecture of Vitamin B12 and Folate Levels Uncovered Applying Deeply Sequenced Large Datasets. PLOS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003530. [CrossRef]
- Van Meurs, J.B.; Pare, G.; Schwartz, S.M.; Hazra, A.; Tanaka, T.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Cotlarciuc, I.; Yuan, X.; Mälarstig, A.; Bandinelli, S.; et al. Common genetic loci influencing plasma homocysteine concentrations and their effect on risk of coronary artery disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 668–676. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-S.; Luan, J.; Sofianopoulou, E.; Imamura, F.; Stewart, I.D.; Day, F.R.; Pietzner, M.; Wheeler, E.; Lotta, L.A.; Gundersen, T.E.; et al. Plasma Vitamin C and Type 2 Diabetes: Genome-Wide Association Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis in European Populations. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, 98–106. [CrossRef]
- Mondul, A.M.; Yu, K.; Wheeler, W.; Zhang, H.; Weinstein, S.J.; Major, J.M.; Cornelis, M.C.; Männistö, S.; Hazra, A.; Hsing, A.W.; et al. Genome-wide association study of circulating retinol levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4724–4731. [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci L, Perry JR, Matteini A, Perola M, Tanaka T, Silander K, et al. Common variation in the beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase 1 gene affects circulating levels of carotenoids: a genome-wide association study. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84(2):123-33.
- Major, J.M.; Yu, K.; Wheeler, W.; Zhang, H.; Cornelis, M.C.; Wright, M.E.; Yeager, M.; Snyder, K.; Weinstein, S.J.; Mondul, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants associated with circulating vitamin E levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3876–3883. [CrossRef]
- O'Seaghdha, C.M.; Wu, H.; Yang, Q.; Kapur, K.; Guessous, I.; Zuber, A.M.; Köttgen, A.; Stoudmann, C.; Teumer, A.; Kutalik, Z.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies Identifies Six New Loci for Serum Calcium Concentrations. PLOS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003796. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.E.; Verwoert, G.C.; Hwang, S.-J.; Glazer, N.L.; Smith, A.V.; van Rooij, F.J.A.; Ehret, G.B.; Boerwinkle, E.; Felix, J.F.; Leak, T.S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Serum Magnesium, Potassium, and Sodium Concentrations Identify Six Loci Influencing Serum Magnesium Levels. PLOS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001045. [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B.; Glazer, N.L.; Köttgen, A.; Felix, J.F.; Hwang, S.-J.; Liu, Y.; Lohman, K.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Hausman, D.B.; Petersen, A.-K.; et al. Common Genetic Variants Associate with Serum Phosphorus Concentration. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1223–1232. [CrossRef]
- Pazoki, R.; Evangelou, E.; Mosen-Ansorena, D.; Pinto, R.C.; Karaman, I.; Blakeley, P.; Gill, D.; Zuber, V.; Elliott, P.; Tzoulaki, I.; et al. GWAS for urinary sodium and potassium excretion highlights pathways shared with cardiovascular traits. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Benyamin, B.; Esko, T.; Ried, J.S.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Traglia, M.; Gögele, M.; Anderson, D.; Broer, L.; Podmore, C.; et al. Novel loci affecting iron homeostasis and their effects in individuals at risk for hemochromatosis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Zhu, G.; Dy, V.; Heath, A.C.; Madden, P.A.F.; Kemp, J.P.; McMahon, G.; St Pourcain, B.; Timpson, N.J.; Golding, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies loci affecting blood copper, selenium and zinc. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3998–4006. [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Lind, P.M.; Lindgren, C.; Ingelsson, E.; Mahajan, A.; Morris, A.; Lind, L. Genome-wide association study of toxic metals and trace elements reveals novel associations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4739–4745. [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





